Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Guide Pdf Chapter 4 Electric Charge and Electric Current Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Solutions Chapter 4 Electric Charge and Electric Current
9th Science Guide Electric Charge and Electric Current Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
In current electricity, a positive charge refers to,
(a) presence of electron
(b) presence of proton
(c) absence of electron
(d) absence of proton
Answer:
(c) absence of electron
![]()
Question 2.
Rubbing of comb with hair
(a) creates electric charge
(b) transfers electric charge
(c) either (a) or (b)
(d) neither (a) nor (b)
Answer:
(b) transfers electric charge
Question 3.
Electric field lines ……………….. from positive charge and ……………………..in negative charge.
(a) start; start
(b) start; end
(c) start: end
(d) end; end
Answer:
(b) or (c) start, end
Question 4.
Potential near a charge is the measure of its……………to bring a positive charge at that point.
(a) force
(b) ability
(c) tendency
(d) work
Answer:
(d) work
![]()
Question 5.
Heating effect of current is called,
(a) Joule heating
(b) Coulomb heating
(c) Voltage heating
(d) Ampere heating
Answer:
(a) Joule heating
![]()
Question 6.
In an electrolyte, the current is due to the flow of
(a) electrons
(b) positive ions
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) neither (a) nor (b)
Answer:
(c) both (a) and (b)
Question 7.
Electroplating is an example of
(a) heating effects
(b) chemical effects
(c) flowing effects
(d) magnetic effect
Answer:
(b) chemical effect
![]()
Question 8.
Resistance of a wire depends on,
(a) temperature
(e) nature of material
(b) geometry
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
II. Match the following
| 1. Electric Charge | (a) ohm |
| 2. Potential difference | (b) ampere |
| 3. Electric field | (c) coulomb |
| 4. Resistance | (d) newton per coulomb |
| 5. Electric current | (e) volt |
Answer:
1 – c, 2 – e, 3 – d, 4 – a, 5 – b
III. State whether true or false. If false, correct the statement:
1. Electrically neutral means it is either zero or equal positive and negative charges.
Answer:
True.
2. Ammeter is connected in parallel in an electric circuit.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Ammeter is connected in series in an electric circuit.
3. The anode in the electrolyte is negative.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: The anode in the electrolyte is positive.
![]()
4. Current can produce the magnetic field.
Answer:
True.
IV. Fill in the blanks :
1. Electrons move from …………….. potential to …………….. potential.
Answer:
lower, higher
![]()
2. The direction opposite to the movement of electron is called …………….. current.
Answer:
conventional
3. The e.m.f of a cell is analogues to a pipeline.
Answer:
water pump
4. The domestic electricity in India is an ac with a frequency of Hz.
Answer:
50
![]()
V. Conceptual Questions:
Question 1.
A bird sitting on a high power electric line is still safe. How?
Answer:
Birds don’t get shocked when they sit on electrical wires because they are not good conductors of electricity. Electricity flowing through a single power line at 35,000 volts will continue along the path of least resistance and bypass birds because there is no difference in electrical potential.
Question 2.
Does a solar cell always maintain the potential across its terminals constant? Discuss.
Answer:
Solar cell delivers a constant current for any given illumination level, while the voltage is determined by the load resistance. Potential in a solar cell depends on the intensity of solar radiation. Since the intensity of solar radiation is not always constant, the potential across its terminal is also not constant.
![]()
Question 3.
Can electroplating be possible with the alternating current?
Answer:
Electroplating is a process where there is a continuous flow of ions for the deposition of copper, which is not possible in an Alternating current. Therefore, electroplating is possible with DC only, for the sake of perfectness and homogeneity of the electroplating.
![]()
VI. Answer the following:
Question 1.
On what factors does the electrostatic force between two charges depend?
Answer:
The electrostatic force between two charges depend on the following factors;
- value of charges on them,
- distance between them, and
- nature of medium between them.
Question 2.
What are the electric lines of force?
Answer:
The lines representing the electric field are called electric lines of force.
Question 3.
Define electric field.
Answer:
The electric lines of force are straight or curved paths along which a unit positive charge tends to move in the electric field.
![]()
Question 4.
Define electric current and give its unit.
Answer:
The electric current is defined as the rate of flow of electric charge through any section of a conductor.
Electric current I = Q/t
Its unit is Cs-1
Its SI unit: ampere (A).
Question 5.
State Ohm’s law.
Answer:
Ohm’s law states that electric potential difference across two points in an electrical circuit is directly proportional to the current passing through it. That is V ~ I
The proportionality constant is the resistance (R) offered between the two points.
Hence, Ohm’s law is written as V = RI (or) V = IR
Where, V is the potential difference in volt (V), I is the current flow in ampere (A), R is the resistance in ohm (Ω)
Question 6.
Name any two appliances which work under the principle of heating effect of current.
Answer:
Electric heating appliances like an iron box, water heater, toaster, etc.
![]()
Question 7.
How are the home appliances connected in general, in series or parallel? Give reasons.
Answer:
The home appliances are connected in parallel. This is because, when the appliances are connected in parallel, each of them can be switched on and off independently. This is a feature that is essential in house wiring. Also, if the appliances were wired in series, the potential difference across each appliance would vary depending on the resistance of the appliance.
Question 8.
List the safety features whilehandling electricity.
Answer:
(i) Ground connection: The metal bodies of all the electrical appliances are to be connected to the ground by means of a third wire apart from the two wires used for electrical connection.
(ii) Trip switch: It is an electromechanical device which does not allow a current beyond a particular value by automatically switching off the connection.
(iii) Fuse: A fuse is another safety mechanism which works on the joule heating principle.
![]()
VII. Exercises:
Question 1.
Rubbing a comb on hair makes the comb get – 0.4C.
(a) Find which material has lost electron and which one gained it.
(b) Find how many electrons are transferred in this process.
Answer:
a. Comb gained electrons. Dry hair lost an electron
b. No. of electrons transferred = -0.4 C
1 coulomb = 6.25 × 1018 electron
– 0.4 C = 0.4 × 6.25 × 1018 electrons
= -2.5 × 1018 electrons
Question 2.
Calculate the amount of charge that would flow in 2 hours through an element of an electric bulb drawing a current of 2.5A.
Answer:
Current I = 2.5 A
time t = 2 hours = 2 × 3600 seconds
t = 7200 s
Amount of charge Q = I × t = 2.5 × 7200
Q = 18,000
![]()
Question 3.
The values of the current (I) flowing through a resistor for various potential differences V across the resistor are given below. What is the value of resistor?

[Hint: plot V-I graph and take slope]
Answer:
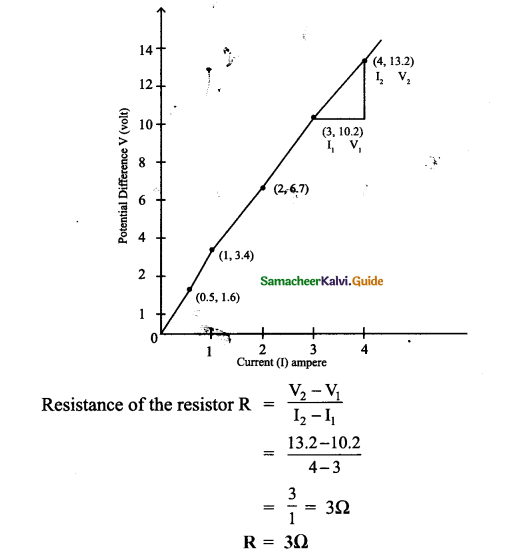
![]()
Intext Activities
ACTIVITY – 1
Take a condemned electronic circuit board in a TV remote or old mobile phone. Look at the electrical symbols used in the circuit. Find out the meaning of the symbols known to you.
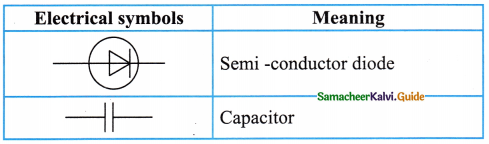
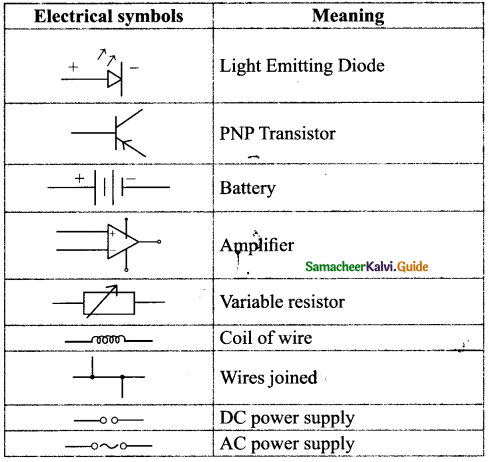
[End of the activity]
ACTIVITY – 2
Cut an arrow shaped strip from aluminium foil. Ensure that the head is a fine point. Keep the arrow shaped foil on a wooden board. Connect a thin pin to two lengths of wire. Connect the wires to the terminals of electric cell, may be of 9V. Press one pin onto the pointed tip and the other pin at a point about one or two mm away. Can you see that the tip of aluminum foil starts melting?
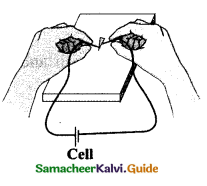
Aim :
To understand the heating effect of electric current.
Materials Required :
Aluminum strip, wooden board, bell pins, cell of 9 V.
Procedure :
Cut an arrow shaped strip from aluminum foil. Keep the arrow shaped foil on a wooden board. Connect a pin to two lengths of wire. Connect the wires to the terminals of electric cell of 9 V. Press one pin onto the pointed tip and another pin at a point about one or two mm away.
Observation :
The tip’of aluminum foil starts melting.
Conclusion :
It starts melting because the electrons while moving in the wire suffer resistance. Work is done to overcome the resistance which is converted into heat energy. This conversion of electrical energy into heating energy is called the heating effect of electric current.
![]()
ACTIVITY – 3
Take a beaker half filled with copper sulphate solution. Take a carbon rod from a used dry cell. Wind a wire on its upper end. Take a thick copper wire, clean it well and flatten it with a hammer. Immerse both the copper wire and carbon rod in the copper sulphate solution. Connect the carbon rod to the negative terminal of an electric cell and copper wire to the positive terminal of the cell. Also ensure that the copper and the carbon rod do not touch each other, but are close enough. Wait and watch. After some time you would find fine copper deposited over the carbon rod. This is called as electroplating. This is due to the chemical effect of the current.
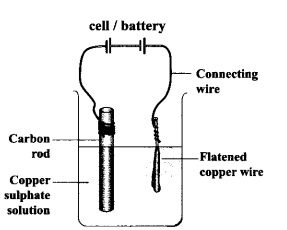
Aim:
Electroplating carbon rod with copper.
Materials Required:
Beaker, copper sulphate solution, carbon rod, thick copper wire and hammer.
Procedure :
- Take a beaker half filled with copper sulphate solution.
- Take a carbon rod and wind a wire on its upper end.
- Take a thick copper wire, clean it well and flatten it with a hammer.
- Immerse both the copper wire and carbon rod in the copper sulphate solution.
- Connect the carbon rod to the negative terminal of the cell and copper wire to the positive terminal of the cell.
- Ensure both the rods do not touch each other, but are close enough.
- Observe for some time.
Observation :
After some time, we would find fine copper deposited over the carbon rod.
Conclusion :
When the current passes through the copper sulphate solution, the copper ions migrate from the copper sulphate solution towards the cathode (-ve terminal). These copper ions get deposited on the carbon rod and form a coating of a fine layer on it.
This process of coating a metal over another metal by electrolysis is called electroplating. This is due to the chemical effect of electric current.
9th Science Guide Electric Charge and Electric Current Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
A current of 2A passing through the conductor produces 80 J of heat in 10 seconds. The resistance of the conductor is ……………..
(a) 0.5Ω
(b) 2Ω
(c) 4Ω
(d) 20Ω
Answer:
(b) 2Ω
Question 2.
The resistance of a straight conductor is independent of …………………..
(a) temperature
(b) material
(c) cross sectional area
(d) shape of cross section
Answer:
(d) shape of cross section
Question 3.
Two resistances R1 and R2 are connected is parallel. Their equivalent resistance is
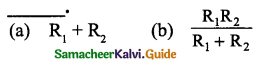
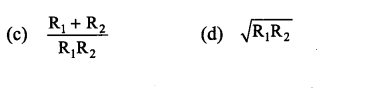
Answer:
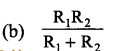
Question 4.
If in the circuit, power dissipation is 150 W, then R is ……………..
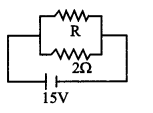
(a) 2Ω
(b) 6Ω
(c) 5Ω
(d) 4Ω
Answer:
(b) 6Ω
![]()
Question 5.
The force between two parallel wires carrying currents has been used to define…………..
(a) ampere
(b) coulomb
(c) volt
(d) watt
Answer:
(a) ampere
Question 6.
Electric current passes through a metallic conductor due to the movement of ……………
(a) ions
(b) ampere
(c) electrons
(d) protons
Answer:
(c) electrons
Question 7.
What is the maximum resistance one can make with ten 1Ω resistors?
(a) 1Ω
(b) 2Ω
(c) 5Ω
(d) 10Ω
Answer:
(d) 10Ω
Question 8.
Two conductors of resistance 2 R and R are connected in series in a battery circuit. The ratio of heat developed In them is ……………………
(a) 2 : 1
(b) 1 : 2
(c) 1 : 3
(d) 1 : 4
Ans:
(a) 2 : 11
![]()
Question 9.
1 volt = …………..
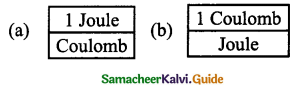
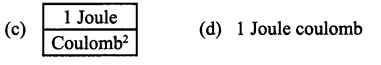
Answer:

Question 10.
The resistance of a conductor is R. If Its length is doubled, then its new resistance will be ……………….
(a) R
(b) 2R
(c) 4R
(d) 8R
Answer:
(C) 4R
![]()
Question 11.
The following is not a safety device.
(a) Fuse
(b) Trip switch
(c) Ground connection
(d) Wire
Answer:
(d) wirel
Question 12.
In India the frequency of alternating current is,
(a) 220 Hz
(b) 50 Hz
(c) 5 Hz
(d) 100 Hz
Answer:
(b) 50 Hz
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks:
1. The number of electrons constituting 1-coulomb charge is………………….
Answer:
6.25 × 1018
2. Resistors are connected in series if the resistance of the electric circuit is to be………………….
Answer:
increased
3. Electric fuse is a wire made up of a material having ………………….melting point.
Answer:
low
4. ………………….is the only non-metal that is a good conductor of electricity.
Answer:
Graphite
5. If the area of cross section of the conductor is doubled its resistance gets ………………….
Answer:
halved
![]()
6. A negative charge will move from …………………. to …………………. potential.
Answer:
lower, higher
7. ………………….is work done per unit charge.
Answer:
Potential difference
![]()
8. An electrochemical cell converts …………………. energy into …………………. energy.
Answer:
chemical, electrical
9. Three resistors are connected in series with a cell. If the current in each resistor is 1.5A, then the current through the cell will be ………………….. Answer:
1.5A
10. Three resistors are connected in parallel with a battery. If the current in each resistor is 2A, then the current through the battery will be …………………..
Answer:
6A
11. As electrons are revolving in the ………………….of an atom they can be easily removed from an atom and also added to it.
Answer:
orbits
![]()
12. If an electron is added in excess to an atom then the atom is ………………….charged.
Answer:
negatively
13. The excess of electrons make an object negative and ………………….of electrons make it positive.
Answer:
deficit
14. Electric charge is ………………….in nature.
Answer:
additive
15. Electric lines of force are ………………….lines.
Answer:
imaginary
![]()
16. For an isolated positive charge the electric lines of force are radial…………………. and for an isolated negative charge they are radial…………………..
Answer:
outwards, inwards
17. ………………….at a point is a measure of force acting on a unit positive charge placed at that point.
Answer:
Electric field
18. Electric potential is a measure of the ………………….on the unit positive charge to bring it to that point against all electrical forces.
Answer:
work done
![]()
19. The movement of positive charge is called as ………………….
Answer:
conventional current
20. The …………………. is the measure of opposition offered by the component to the flow of electric current through it.
Answer:
resistance
21. The process of conduction of electric current through solution is called………………….
Answer:
electrolysis
22. The device used to convert AC to DC is called………………….
Answer:
rectifier
23. Trip switch is a …………………. safety device.
Answer:
electro mechanical
![]()
III. True or False:
1. A fuse is used in an electric circuit to stop high current flowing through the circuit.
Answer:
True.
2. Rheostat is also known as fixed resistance.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Rheostat is also known as a variable resistance.
3. An ammeter is always placed in parallel with the circuit.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: An ammeter is always placed in series with the circuit.
4. The resistance of a dry human body is high.
Answer:
True.
![]()
5. For current to flow, one needs art open circuit.
Answer:
Correct statement: For current to flow, one needs a closed circuit.
6. A comb rubbed with hair and brought near pieces of paper attracts them, because both comb and paper get similarly charged.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: A comb rubbed with hair and brought near pieces of paper attracts them, because both comb and paper get oppositely charged.
7. Overloading of electric circuits can lead to short-circuiting.
Answer:
True.
![]()
8. Electrons in outer orbits are called free electrons.
Answer:
True.
9. Electric fuse works on the Joule heating principle.
Answer:
True.
![]()
IV. Match the following:
I.
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Resistor | a) Galvanometer |
| 2. Connecting wire | b) Voltmeter |
| 3. Current in an electric circuit | c) Copper |
| 4. Potential difference | d) Constantan |
Answer:
1-d, 2-c, 3 -a, 4-b
II.
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Electric power | a) Volt |
| 2. Electrical energy | b) Coulomb |
| 3. Electric charge | c) Watt |
| c) Watt | d) Joule |
Answer:
1-c, 2-d, 3-c, 4-a
![]()
V. Assertion and Reason type questions :
Mark the correct choice as :
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Question 1.
Assertion (A): Electric current will not flow between two charged bodies when connected if their charges are the same.
Reason (R): Current is the rate of flow of charge.
Answer:
(d) Assertion is false but the reason is true
Reason: Current will not flow when two bodies are at the same potential. When their charges are the same, their potential may be different. Hence current may flow in this case.
![]()
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : A bird perches on a high power line and nothing happens to the bird.
Reason (R) : The level of the bird is very high from the ground.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false
Reason: Electric shock is due to the electric current flowing through a living body. When the bird perches on a single high power line, no current passes through its body. Because its body is at an equipotent surface (i.e.) there is no potential difference. While when a man touches the same line, standing bare foot on the ground the electrical circuit is completed through the ground. The hands of man are at high potential and his feet are at low potential. Hence the large amount of current flows through the body of the man and the person, therefore, gets a fatal shock.
VI. Answer in one word:
Question 1.
Name the force which acts between two point charges obey Newton’s third law.
Answer:
Electrostatic force.
Question 2.
What is the SI unit for the current?
Answer:
ampere (A).
![]()
Question 3.
Name the device which is used to measure the strength of the electric current in an electric circuit.
Answer:
Ammeter.
Question 4.
What is the rate at which charges flow past a point on a circuit?
Answer:
Current.
Question 5.
Name a device that helps to maintain a potential difference across conductors.
Answer:
Cell or battery.
Question 6.
What does the circuit symbol ![]() represent?
represent?
Answer:
Wire crossing without touching each other.
![]()
Question 7.
How many electrons accumulate to make 1C of electric charge?
Answer:
1C = 6.25 × 1018 electrons.
Question 8.
What is the charge of one electron?
Answer:
e= 1.6 × 10-19C.
Question 9.
What is the measure of the work done on the unit positive charge to bring it to that point against all electrical forces?
Answer:
Electric potential
Question 10.
How is a voltmeter connected in the circuit to measure the potential difference between two points?
Answer:
Parallel
![]()
VII. Subjective Problems:
Question 1.
Calculate the charge passing through a lamp in 2 minutes if the current is 3A.
Solution:
Current I = 3A
Time t = 2 minutes = 120seconds
Charge q = ?
q = I × t = 3 × 120
Charge q = 36.C
Question 2.
Calculate the current in a wire if a charge of 1500 coulomb flows through it in 5 minutes.
Solution:
Charge q = 1500 C
Time t = 5 minutes = 300 seconds
Current I =?
I = q/t = \(\frac{1500}{300}\)
Current I = 5A
![]()
Question 3.
A charge of 400C flows through a conductor for 13 minutes and 20 seconds. Find the magnitude of the current flowing through the conductor.
Answer:
Q = 400C
t = 13 min and 20s = 13 × 60 + 20
= 780 + 20
= 800s
Current I = \(\frac{Q}{t}=\frac{400}{800}=0.5 \mathrm{A}\)
Question 4.
1020 electrons, each having a charge of 1.6 x 10-19 C, flows in a circuit V is 0.1s. What is the current in ampere?
Solution :
n = 1020 electrons
e = 1.6 × 10-19C
t = 0.1s
Charge q = ne
= 1020 × 1.6 × 10-19
= 16C
Current I = \(\frac{q}{t}=\frac{16}{0.1}=160 \mathrm{~A}\)
∴ Current = 160 A
![]()
VIII. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
a State Ohm’s law.
b. Draw a circuit diagram for the verification of ohm’s law. Also, plot graphically the variation of current with a potential difference.
Answer:
a. Ohm’s law states that the current passing through a conductor is directly proportional
to the potential difference a cross its ends, provided the physical conditions like temperature density etc. remain unchanged V ∝ I or V = IR.
b.
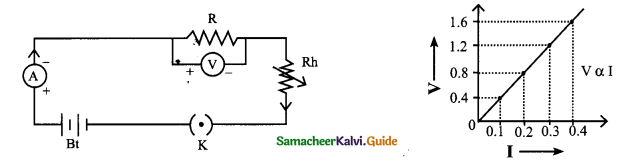
Question 2.
a. Why is series arrangement not used for domestic cricuits?
b. Explain why fuse wire is always connected in series arrangement.
c. Why are copper and aluminium wires useually employed for electricity transmission?
Answer:
a. Series arrangement is not used for domestic circuits because same current will flow through all the appliances. The equivalent resistance will get added and hence the current drawn by the circuit will be less.
b. Fuse wire is always connected in series in a circuit as it has to check the flow of current through the circuit and prevent the extra flow of current through it.
c. Fuse wire is always connected in series in a circuit as it has to check the flow of current through the circuit and prevent the extra flow of current through it.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the dangers of electricity and precautions to be taken while handling electricity.
Answer:
- Damaged insulation – Do not touch the bare wire, use safety gloves, and stand on an insulating stool or rubber slippers while handling electricity.
- Overheating of cables – use quality ISI certified cable wires for domestic wiring
- Overload of power sockets – do not connect too many electrical devices to a single electrical socket.
- Inappropriate use of electrical appliances – always uses the electrical appliances according to the power rating of the device like AC point, TV point, microwave oven point, etc.
- Environment with moisture and dampness – keep the place where there is electricity out of moisture and wetness as it will lead to leakage of electric current.
- Beyond the reach of children – the electrical sockets are to be kept away from the reach of little children who do not know the dangers of electricity.
Question 4.
Write the difference between resistance in series and in parallel.
Answer:
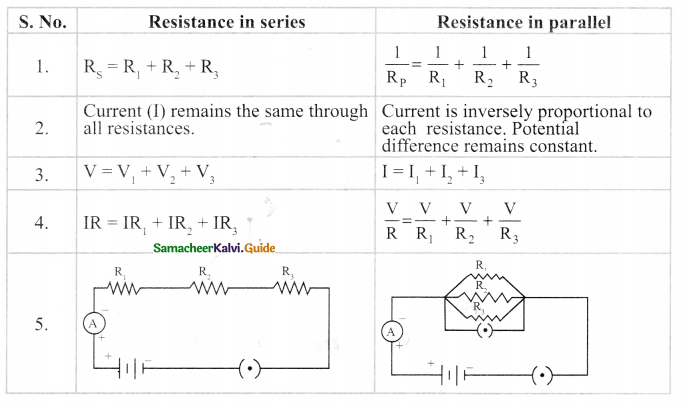
![]()
IX.
Question 1.
Distinguish e.m.f and potential difference.
Answer:
As both e.m.f and potential difference are measured in volt, they may appear the same. But they are not. The e.m.f refers to the voltage developed across the terminals of an electrical source when it does not produce current in the circuit. Potential difference refers to the voltage developed between any two points (even across electrical devices) in an electric circuit when there is current in the circuit.
Question 2.
Some common symbols in the electrical circuit.
Answer:
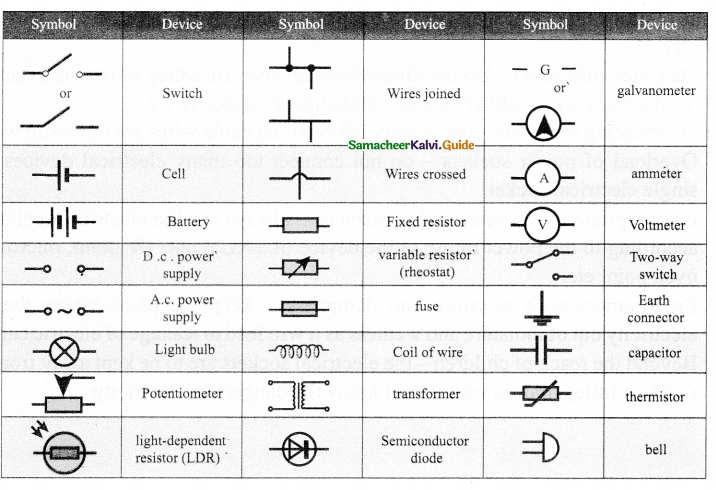
Question 3.
Write a note on direct current.
Answer:
- Current in electrical circuits is due to the motion of positive charge from higher potential to lower potential or electron from lower to higher electrical potential.
- Electrons move from negative terminal of the battery to positive of the battery. Battery is used to maintain a potential difference between the two ends of the wire.
- Battery is one of the sources for dc current. The dc is due to the unidirectional flow of electric charges. Some other sources of dc are solar cells, thermocouples etc. The graph depicting the direct current is shown in Figure.
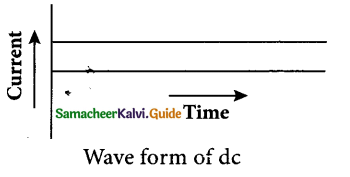
- Many electronic circuits use dc. Some examples of devices which work on dc are cell phones, radio, electric keyboard, electric vehicles etc.
![]()
Question 4.
Write a note on alternating current.
Answer:
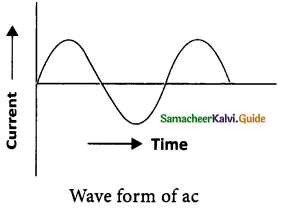
- If the direction of the current in a resistor or in any other element changes its direction alternately, the current is called an alternating current.
- The alternating current varies sinusoidally with time. This variation is characterised by a term called as frequency.
- Frequency is the number of complete cycle of variation, gone through by the ac in
one second. s - In ac, the electrons do not flow in one direction because the potential of the terminals vary between high and low alternately.
- Thus, the electrons move to and fro in the wire carrying alternating current. It is diagrammatically represented in Figure
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the advantages of Ac over Dc.
Answer:
- The voltage of ac can be varied easily using a device called transformer. The ac can be carried over long distances using step-up transformers.
- The loss of energy while distributing current in the form of ac is negligible. Direct current cannot be transmitted as such.
- The ac can be easily converted into dc and generating ac is easier than dc
- The ac can produce electromagnetic induction which is useful in several ways.
X. Define the following:
1. Electric force: The force existing between the charges is called an ‘electric force’.
2. Electric potential: Electric potential is a measure of the work done on the unit positive charge to bring it to that point against all electrical forces.
3. Conventional current and electron current: The movement of the positive charge is called as ‘conventional current’. The flow of electrons is termed as ‘electron current’.
4. Current: Current is the rate at which charges flow past a point on a circuit.
5. Electromotive force (e.m.f.): The e.m.f of an electrical energy source is one volt if one joule of work is done by the source to drive one coulomb of charge completely around the circuit.
6. One ohm: One ohm is the resistance of a component when the potential difference of one volt applied across the component drives a current of one ampere through it.
7. Fixed resistor: A fixed resistor has a resistance of a fixed value. Common types of fixed resistors include carbon film resistors and wire-wound resistors.
8. Variable resistor: A variable resistor has a resistance that can be varied. It is used to vary the amount of current flowing in a circuit.
9. Electrolysis and electrolyte: The process of conduction of electric current through solutions is called ‘electrolysis’. The solution through which the electricity passes is called ‘electrolyte’.
10. Synaptic signals: Extremely weak electric current is produced in the human body by the movement of charged particles. These are called synaptic signals. These signals are produced by the electrochemical process. They travel between the brain and the organs through the nervous system.
11. Magnetic effect of current: A wire or a conductor carrying current develops a magnetic field perpendicular to the direction of the flow of current. This is called the magnetic effect of current.
12. Frequency: Frequency is the number of the complete cycle of variations, gone through by the ac in one second.
13. Rectifier: The device used to convert ac to dc is called a rectifier.
14. Resistance: The measure of opposition offered by the component to the flow of electric current through it.
15. Resistors: The components used for providing resistance are called resistors.