Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Notes Chapter 6 Money Market
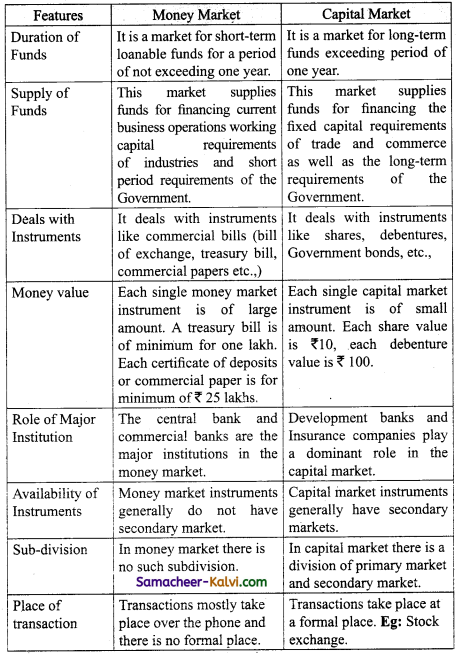
→ Money is a market for purely short term funds. It deals with financial assets and securities whose maturity period does not exceed one year.
→ Money market is the segment of financial markets where in financial instruments having maturities of less than one year are traded.
Eg: Treasury Bills, Commercial Bills, Certificate of Deposits, Government securities etc.,
Money market serves the following objectives:
→ Providing an equilibrium mechanism for ironing out short term surplus and deficits.
→ Providing a focal point for central bank intervention for influencing liquidity in the company.
→ Providing access in uses to users of short term money to meet their requirements at a reasonable price.
→ The main characteristics of money market short term funds or financial assets called near money. Assets which can be converted into cash with minimum transaction cost. Transaction take place through phone oral communication. It comprises of several submarkets each specializing in a particular type of financing Eg: call money market, bill market.
→ Commercial bank play a dominant role in this market. There are money participants in money market. It deals with money’instruments like treasury bills, commercial bills, commercial papers etc.
→ A market for the purchase and sale of treasury bills is known as a “Treasury bills market” treasury bills may be classified into three. They are:
- 91 days,
- 182 days,
- 364 days. Treasury Bills.
Certificate of deposit:
→ Certificate of deposit are short term deposit instruments issued by banks and financial institutions to raise large sums of money. Certificate of deposits are issued in the form of usance promissory notes.
→ A bill of exchange issued by a commercial organization to raise money for short term needs. These bills are of 30 days, 60 days and 90 days maturity.
→ A market where by the Government or gilt – edged securities can be bought and sold is called “Government Securities Market”.
→ Government securities are issued for the purposes of refunding the maturing securities, for advance refunding securities which have not yet matured and for cash financing that is raising fresh cash resources.
How to Invest Money in Money Market Funds?
Gathering information about Money Market Funds
Learn about money market
Understand the goal of money market funds
Learn the disadvantages of money market funds
Investing in Money Market Funds
Understand the different types of Money Market Funds
Understand the purpose of Money Market Funds Compare past yields
Buying and Tracking of Money Market Funds.
Information:
Money market is a market for purely short term funds. It deals with the financial assets and securities whose maturity period does not exceed one year.
Money value:
Treasury bill minimum for one lakh. Certificate deposits or commercial paper is for minimum of? 25 lakhs.
Participants:
Brokers bankers RBI and Government.
High liquidity in money market.
Number of instruments:
- Inter bank call money
- Short term deposits up to 3 months
- 91 days Treasury bill
- 182 days Treasury bill
- Commercial papers.
Regulator – Central bank is the regulator of money market.
→ High level of liquidity that they offer it is easy to make money market trade across currencies maturities, debt structure as well as credit risk which makes it ideal for institution seeking to borrow or invest the short term money market.
→ A money market fund is a kind of mutual fund that invest only in high liquid instruments such as cash, cash equivalent securities and high credit rating debt based securities with short term less than 13 months (maturity).
→ These funds offer high liquidity with a very low level of risk. The goal of money market to provide a reasonable access to users of short term funds to meet their requirement quickly, adequately and at reasonable cost.
→ A money market fund generates income taxable or tax free depending on its port folio but little capital appreciation.
If you earn money, which investment plan would you like?
- Mutual Funds,
- Shares,
- Debentures,
- Treasury Bill,
- Commercial Bill,
- Certificate of Deposit. Why? Give reasons
A mutual fund is a professionally managed investment fund that pools money from many investors to purchase securities.
A mutual fund is a type of financial vehicle made up of a pool of money collected form many investors to invest in securities such as stocks, bonds and money market instruments.
Reasons:
Earn higher returns, creating wealth over time, offer returns on your money over time, grow your money, and reach financial goals.