TN State Board 11th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
Question 1.
Write the IUPAC names of the following:
(i) 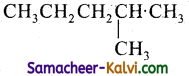
Answer:
2 – Methyl pentane
(ii) 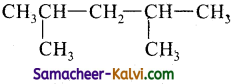
Answer:
2, 4- Dimethyl pentane
(iii) 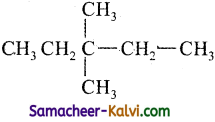
Answer:
3, 3 – Dimethyl pentane
(iv) 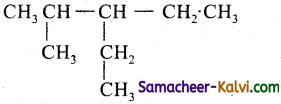
Answer:
3 – Ethyl – 2 – methylpentane
(v) 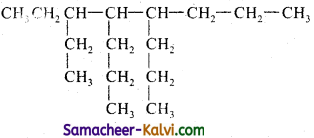
Answer:
3 – Ethyl – 4, 5 – dipropyl octane
(vi) 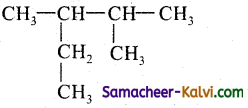
Answer:
2, 3 – Dimethylpentane
(vii) 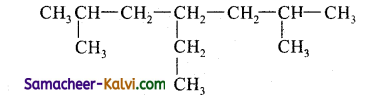
Answer:
4 – Ethyl – 2, 6 – Dimethylheptane
![]()
Question 2.
How will you prepare
(i) Propane from propene
(ii) Propane from propyne
(iii) Methane from sodium acetate
(iv) Propane from chloropropane
(v) Ethane from methyl bromide Give equations.
Answer:
(i)Propane from propene:
By hydrogenation
CH3CH = CH2 + H2 ![]() CH3CH2CH3
CH3CH2CH3
(ii) Propane from propyne:
By hydrogenation
CH3 C ≡ CH + 2H2 ![]() CH3CH2CH3 .
CH3CH2CH3 .
propyne-1
(iii)Methane from sodium acetate:
By decarboxylation i.e., heating sodium acetate with soda lime.
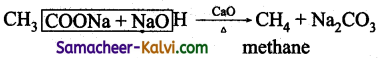
(iv) Propane from chloropropane:
By reduction using Zinc and HCl.
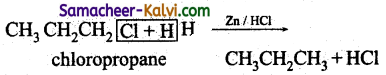
(v) Ethane from methyl bromide:
By Wurtz reaction.
CH3 Br + 2 Na + Br – CH3 ![]() Ch3 – CH3 (ethane) + 2 NaBr
Ch3 – CH3 (ethane) + 2 NaBr
![]()
Question 3.
How do you prepare ethane by Kolbe.’s electrolytic method?
Answer:
Electrolysis of a concentrated aqueous solution of either sodium or potassium salts
of acetic acid yields ethane at anode.
2 CH3COOK + 2H2O ![]() CH3 — CH3 + 2 CO2 + 2 KOH + H2
CH3 — CH3 + 2 CO2 + 2 KOH + H2
Question 4.
What are the reducing agents used in reduction of alkyl halides to alkanes?
Answer:
The hydrogen for reduction may be obtained by using any of the following reducing agents:
Zn + HCl, Zn + CH3COOH, Zn-Cu couple in ethanol, LiAlH4 etc…
Question 5.
How propane is prepared by Corey- House synthesis?
Answer:
An alkyl halide and lithium di alkyl cuprate are reacted to give higher alkane.
eg: 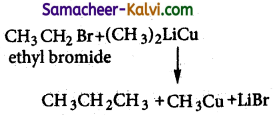
Question 6.
What are Grignard’reagents? blow do you prepare (i) ethane (ii) benzene from a suitable Grignard reagent?
Answer:
Halo alkanes reacts with magnesium in the presence of dry ethers to give alkyl magnesium halide which is known as Grignard reagents.
(i) Ethane is prepared from ethyl magnesium
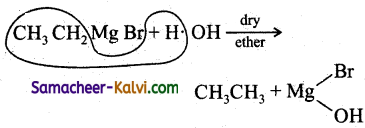
(ii) Benzene is prepared from phenyl magnesium bromide with water.
C6H5 Mg Br + H. OH ![]() C6H6 (benzene) + Mg(Br) . OH
C6H6 (benzene) + Mg(Br) . OH
![]()
Question 7.
The straight chain isomers have higher boiling point compared to branched chain isomers. Explain Why?
Answer:
The straight chain isomers have the most extended structure and larger surface area in comparison to branched chain isomers, which have compact structure. Thus the intermolecular forces are weaker in branched chain isomers. Hence they have lower boiling point Compared to straight chain isomers.
Question 8.
Whaf are conformers?
Answer:
The different arrangement of atoms or groups in space that result from the free rotation of carbon-carbon single bond axis are called conformations or conformational isomers or conformers.
Question 9.
Briefly outline conformation of ethane.
Answer:
(i) The free rotation about C — C bond in ethane results in infinite number of readily interconvertible three dimensional arrangements called conformers.
(ii) Of the various conformers possible, the skew form, eclipsed form and the staggered forms are important.
(iii) In the eclipsed conformation, the hydrogens of one carbon are directly bonded to the other. The repulsions between the atoms is maximum and it is the least stable conformer.
(iv) In the staggered conformation, the hydrogens of the both the atoms are few apart from each other. The repulsions
between them is minimum and it is the most stable conformer.
(v) Skew conformations are the infinite number of possible between the eclipsed and staggered conformations.
(vi) The stabilities of the various conformations are staggered > skew > eclipsed.
(vii) 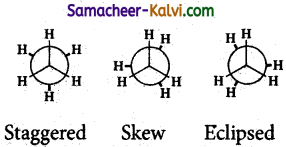
![]()
Question 10.
Give equations for (i) complete combustion and (ii) incomplete combustion of methane.
Answer:
(i) Complete combustion of methane gives CO2 and H2O.
CH4 (g) + 2 O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g) ∆H = – 890 kJ
(ii) Incomplete combustion of methane gives carbon monoxide and carbon.
CH4 + 3 O2 ![]() 2 CO + 4H2O
2 CO + 4H2O
CH4 + O2 → C + 2 H2O
Methane reacts with chlorine in the presence of light or when heated as follows:
CH4 + Cl2 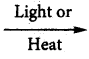 CH3Cl (methyl chloride) + HCl
CH3Cl (methyl chloride) + HCl
CH3Cl + Cl2  CH2Cl2 (methylene chloride) + HCl
CH2Cl2 (methylene chloride) + HCl
CHCl3 + Cl2  CCl4 (carbontetrachloride) + HCl
CCl4 (carbontetrachloride) + HCl
![]()
Question 11.
Explain free radical mechanism with a suitable example.
Answer:
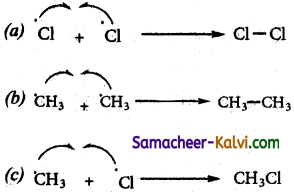
The mechanism involves three steps
(i) Initiation: (generation of free radical)
The chain is initiated by UV light leading to homolytic fission of chlorine molecules j into free radicals (chlorine atoms).
![]()
(ii) Propagation: It proceeds as follows,
(a) Chlorine free radical attacks the methane molecule and breaks the C – H bond resulting in the generation of methyl free radical.

(b) The methyl free radical thus obtained attacks the second molecule of chlorine to give chloromethane (CH3Cl) and a chlorine free radical as follows.

(c) Both step (a) and (b) are repeated several and this is known as propagation.
(iii) Termination:
The free radicals are destroyed during this step as follows.
![]()
Question 12.
Explain aromatisation with an example.
Answer:
The conversion of aliphatic compounds into aromatic compounds is known as aromatisation. Alkanes having 6 to 10 carbon atoms are converted to benzene or its homologous at high temperatures in the presence of a catalyst.
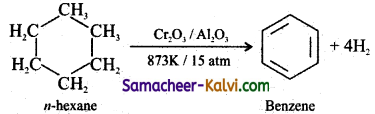
Question 13.
What is steam reforming process? Give an example.
Answer:
(i) Production of H2 gas from methane is known as steam reforming process.
(ii) Methane reacts with steam at 1273 K in the presence of Nickel and decomposes to form carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas.
CH4 (g) + H2O (g) ![]() CO (g) + 3 H2 (g)
CO (g) + 3 H2 (g)
![]()
Question 14.
Define pyrolysis. Explain with an example.
Answer:
Pyrolysis is defined as the thermal decomposi-tion of organic compound into smaller fragments in the absence of air through the application of heat.
In the absence of air, when alkane vapours are passed through red-hot metal it breaks down into simpler hydrocarbons.
(i) 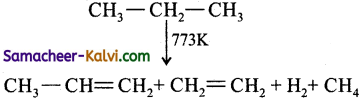
(ii) 2 CH3 — CH3 ![]() CH2 = CH2 + 2 CH4
CH2 = CH2 + 2 CH4
Question 15.
Explain isomerisation with an example.
Answer:
Isomerisation is a chemical process by which a compound is transformed into any its isomeric forms. Normal alkanes can be converted into branched alkanes in the presence of AlCl3 and HCl at 298 K.
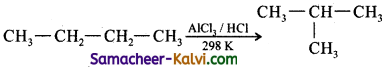
![]()
Question 16.
Mention the uses of alkanes.
Answer:
(i) Alkanes are used as fuels. Methane present in natural gas is used for home heating.
(ii) Mixtures of propane and butane(LPG) is used for domestic cooking purposes.
(iii) Gasoline, is a complex mixture of several hydrocarbons used as a fuel for internal combustion engines.
(iv) Carbon black is used in the manufacture . of ink, printer ink and black pigments.
Question 17.
Write the IUPAC names of the following.
(i) CH3CH = CH2
(ii) CH3 — CH2 — CH = CH3
(iii) CH3 — CH = CH — CH3
(iv) 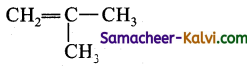
(v) 
Answer:
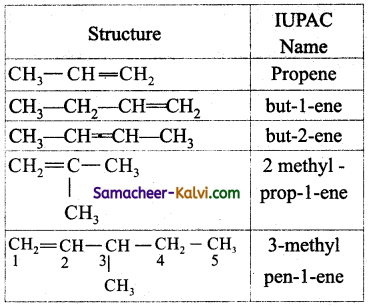
![]()
Question 18.
Write the structures and IUPAC names of different structural isomers of alkenes corresponding to C5H10.
Answer:
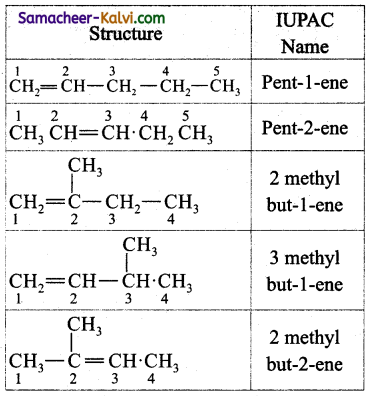
Question 19.
Explain geometrical isomerism with an example.
Answer:
(i) Geometrical isomerism arises due to restricted rotation across ![]() double bond.
double bond.
(ii) When similar groups lie on the same side of C = C double bond, it is known as ‘cis’ isomer.
(iii) When similar groups lie on the opposite side of C=C double bond, it is known as trans isomer.
eg: 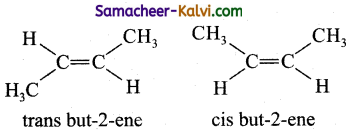
(iv) The melting point of a trans isomer is higher than that of its cis isomer.
(v) The solubility of a cis isomer is higher than that of its trans isomer in a given solvent.
(vi) cis isomer of an alkene is found to be more polar than its trans isomer.
(vii) The boiling point of the cis isomers are higher than those of their corresponding trans isomer.
![]()
Question 20.
What is dehydrohalogenation? Give an example.
Answer:
Removal of a hydrogen and halogen atom from adjacent carbon atom in an alkyl halide to form an alkene is known as dehydro halogenation.
eg: 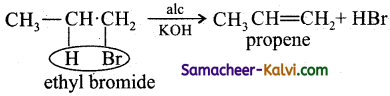
Question 21.
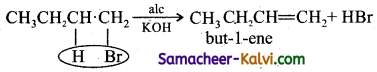
Give equations for the following reactions.
(i) 1 – bromo butane is treated with alcoholic potash.
Answer:
(ii) 1,2 di bromo propane.is heated with zinc and methyl alcohol.
Answer:

(iii) Potassium succinate is electrolysed using platinum electrodes.
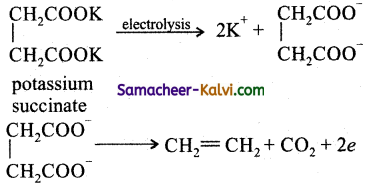
![]()
Question 22.
Starting from ethene, how will you prepare
(i) ethane
(ii) ethyl bromide
(iii) ethanol
(iv) formaldehyde
(v) poly ethylene. Give equations.
Answer:
(i) Ethene from ethane:
By treating ethene with hydrogen in the presence of nickel as catalyst.
CH2 = CH2 + H2 ![]() CH3 – CH3
CH3 – CH3
(ii) Ethyl bromide from ethene:
By treating ethene with HBr.
CH = CH + HBr → CH3CH2HBr (ethyl trioxide)
(iii) Ethanol from ethene:
By treating ethane with cold dilute sulphuric acid and hydrolysing the product formed.
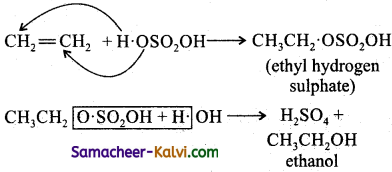
(iv) Formaldehyde from ethene: By treating ethene with ozone. The ozonide formed is decomposed by zinc and water.
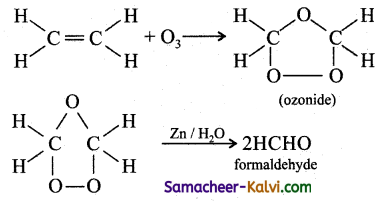
This reaction is known as ozonolysis.
(v) Polyethylene from ethene:
Ethene undergoes polymerisation when heated in a red hot tube at 873 K.
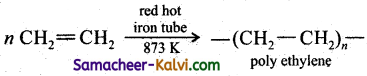
![]()
Question 23.
Complete the following equations:
(i) 
Answer:
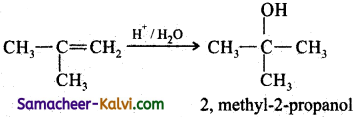
(ii) CH3CH = CH2 + HBr →
Answer:

(iii) CH3CH = CH.CH2 + HBr →
Answer:
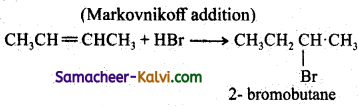
(iv) CH3CH = CH2 + HBr ![]()
Answer:
CH3 = CH2 + HBr ![]() CH3CH2CH2Br
CH3CH2CH2Br
(Anti – Markovnikoff’s addition)
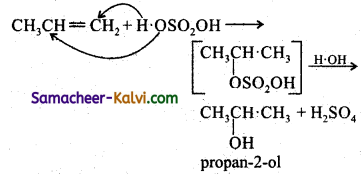
(v) CH3CH = CH2 + H2SO4 →
Answer:
Question 24.
Discuss the mechanism of addition of HBr to propene.
Answer:
Step – 1:
HBr → H+ + Br– (formation of electrophile)
Step – 2:
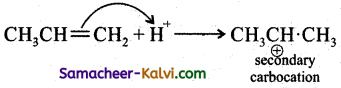
Step – 3:
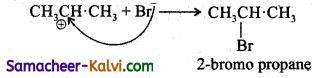
In Step 2 the pi electrons are attacked by the electrophile and form a more stable secondary earbocation, which is further attacked by Br to form the product.
![]()
Question 25.
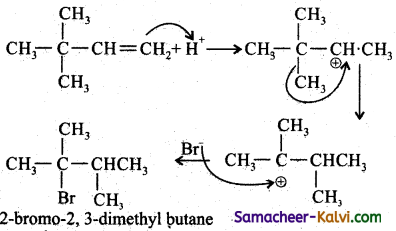
Addition of HBr to 3 – methyl – 1 – butene gives 2 – bromo – 2 – methyl butane as a major product. Explain Why?
Answer:
This is explained by the mechanism of the reaction.
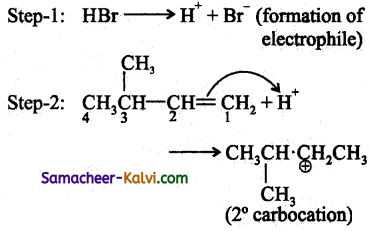
Since 2° carbocation is less stable than 3° carbocation, the hydrogen from the 3rd carbon atom migrates to the 2nd carbon atom with its bond pair of electrons. This is known as 1, 2 hydride shift.
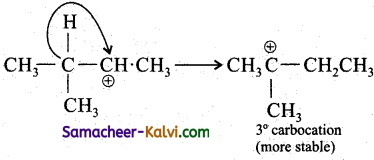
Step-3:
The Br attacks the tertiary carbon atom carrying the positive charge and forms the product.
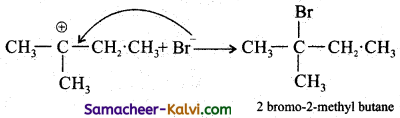
Question 26.
Predict the major product formed in the following reactions.
(i) CH3CH = CH2 + HBr →
Answer:
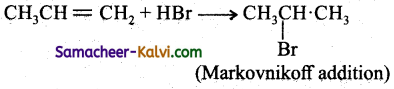
(ii) 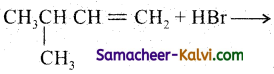
Answer:
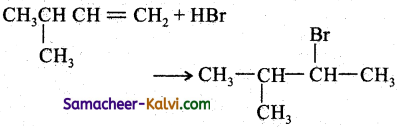
(iii) 
Answer:
Follow the same mechanism as (i).
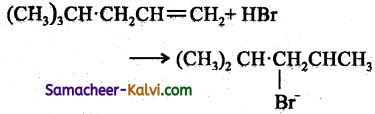
(iv) 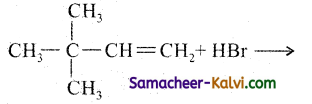
Answer:
![]()
Question 27.
Give the mechanism for the addition of HBr to propene in the presence of a peroxide.
Answer:
The addition of HBr to .propene in the presence of a peroxide occurs by a free radical mechanism. It consists of 3 steps.
(a) Initiation:
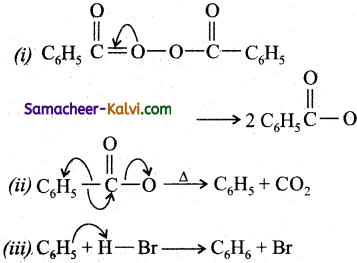
(b) Propagation:
During the first step, a bromine free radical adds to the double bond in such a way to give a more stable free radical. In the second step, the free radical thus produced abstracts a H from
(i) CH3 — CH = CH2 + Br → CH3CHCH2 Br 2° radical (more stable)
(ii) 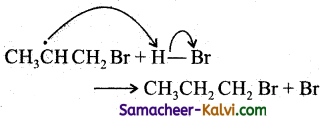
(c) Termination:
(i) 2 Br → Br2
(ii) 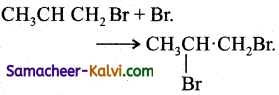
(iii) 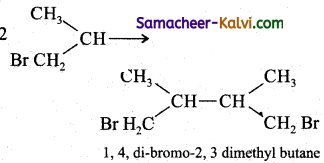
![]()
Question 28.
Peroxide effect is not observed with HCl or HI. Explain Why?
Answer:
This is due to the following reasons:
(i) H — Cl bond (103 k.cal/mol) is stronger than H — Br bond (87.5 k.cal/mol). HCl is not decomposed by the peroxide to a free radical.
(ii) H — I bond is weaker than H — Br or H — Cl bond and it can form iodine free radical readily, but the iodine free radicals readily combine together to form iodine molecules rather than attacking the double bond.
Question 29.
What is Baeyer’s reagent? How is it used to detect the presence of a multiple bond in alkenes/alkyne?
Answer:
(i) Cold, dilute alkaline potassium permanganate solution is known as Baeyer’s reagent.
(ii) When added to an alkene or alkyne the purple solution becomes dark green and then produces a dark brown precipitate. This indicates the presence of a double/ triple bond.
![]()
Question 30.
Complete the following equations:
(i) CH2 = CH2 + H2 ![]()
Answer:
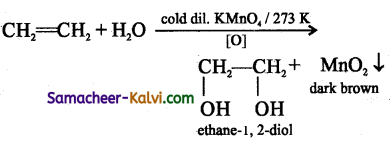
(ii) 
Answer:
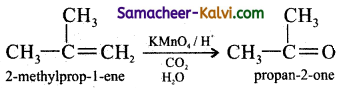
(iii) CH3CH = CH CH3 ![]()
Answer:
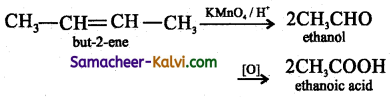
![]()
Question 31.
Explain the term ozonolysis with an example.
Answer:
Ozonolysis is a reaction between ozone and an alkene or an alkyne. In this reaction, ozone adds across the multiple bond to form an ozonide which decomposes to give one or more carbonyl compound, depending on the alkene/alkyne taken.
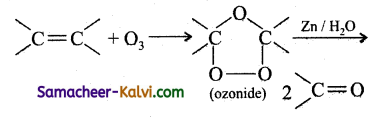
eg: 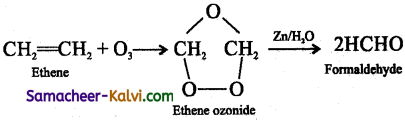
Question 32.
Predict the products of ozonolysis of the following compounds.
(i) CH3CH = CH2
(ii) 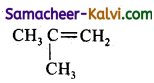
(iii) 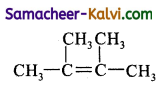
(iv) 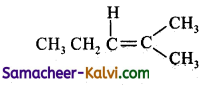
Answer:
To predict the product of ozonolysis draw a line across C = C, and add one oxygen atom on either side.
(i) 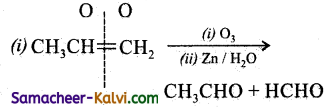
(ii) 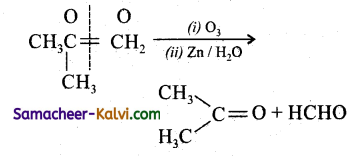
(iii) 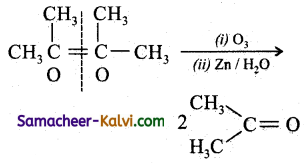
(iv) 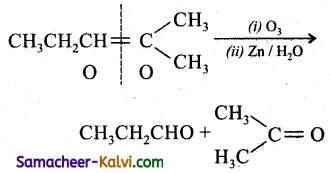
![]()
Question 33.
Explain the term polymerisation.
Answer:
Polymerisation is a process which involves the combination of several simple molecules (known as monomers) to form a giant molecule (known as polymer) under suitable experimental conditions.
eg: ethylene polymerises to polythene.
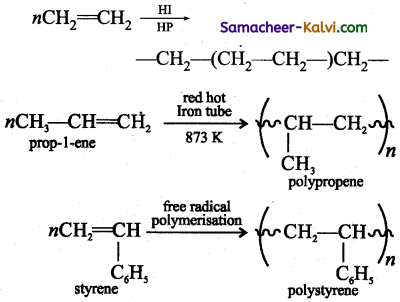
Question 34.
Mention the uses of the following:
(i) Polyethylene terephthalate (PET):
Answer:
Soft drinks bottles, jars, vegetable oil bottle.
(ii) High density polyethylene (HDPE):
Answer:
Milk, water and juice containers.
(iii) Polyvinyl chloride (PVC):
Answer:
Shampoo bottles, plastic pipes.
(iv) Low density polyethylene (LDPE):
Answer:
Sandwich bags, grocery bags.
(v) Polypropylene (PP):
Answer:
Straws, diaper, toys.
(vi) Polystyrene (PS):
Answer:
Disposable utensils, foam cups.
(vii) Multilayer plastics:
Answer:
Various flexible item.
![]()
Question 35.
Mention the uses of alkenes.
Answer:
(i) As a starting material in the synthesis of alcohol, plastics, liquors, detergents and fuels.
(ii) Used in the manufacture of floor tiles, shoes, synthetic fibres, rain coats, pipes etc.
Question 36.
Write the IUPAC name and carbon skeleton formula for
(i) CH3 — C ≡ CH
(ii) CH3 — CH2 C ≡ CH
(iii) CH3 C ≡ C CH3
(iv) 
Answer:
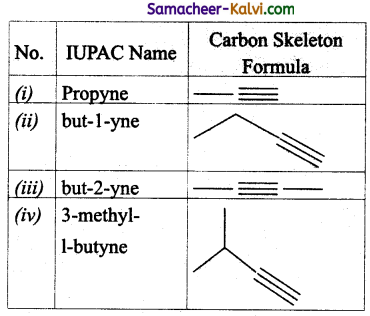
![]()
Question 37.
How will you prepare the following? Give equations:
(i) Acetylene from ethylene:
Answer:
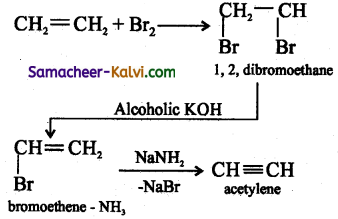
(ii) Prop – 1 – yne from 1, 2 dichloro propane:
Answer:
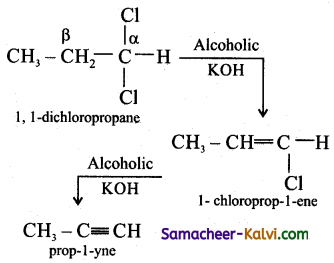
(iii) Acetylene from potassium succinate:
Answer:
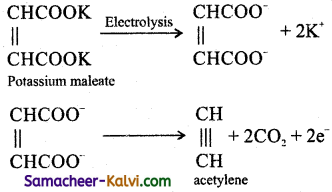
Question 38.
Briefly outline the acidic nature of alkynes.
Answer:
(i) An acidic substance should contain an ionisable hydrogen. Alkynes which contain a hydrogen atom (terminal alkyne) attached to an ‘sp’ hybridised atoms are acidic in nature, eg: Ethyne (CH ≡ CH), propyne (CH3C ≡ CH) etc. An ‘sp’ hybridised carbon is more electronegative than an sp2 or sp3 hybrid orbitals. Hence it pulls the electron pair towards itself resulting in the ionisation of alkane as follows:
HC ≡ CH → HC ≡ C– (acetylide ion) + H+
Hence, terminal alkynes are acidic.
(ii) Terminal alkynes undergo the following reactions which the non-terminal alkynes do not
(a) They produce a while precipitate on treatment with ammoniacal silver nitrate.
CH3CH2C (but-l-yne) ≡ CH + 2 AgNO3 + 2 NH4OH → CH3CH2C ≡ CAg (Silver butynide) ↓+ 2 NH4NO3 + 2H2O
(b) They produce a red precipitate on treatment with ammonical cuprous chloride.
2 CH3 – CH2 – C ≡ CH (but-l-yne) + Cu2Cl2 + 2 NH4OH → CH3 – CH2 – C ≡ C – Cu ↓(Copper butynide) + 2 NH4Cl + 2 H2O
![]()
Question 39.
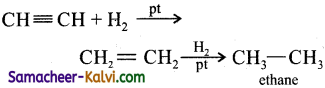
Give equation for the reaction of propyne with:
(i) H2 in the presence of Pt as catalyst:
Answer:
(ii) Bromine in carbon tetrachloride:
Answer:
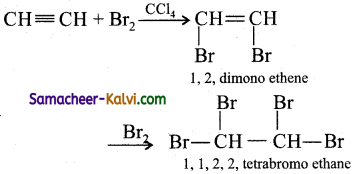
(iii) Hydrogen chloride:
Answer:
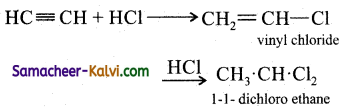
(iv) Mercuric sulphate and dilute sulphuric acid at 333 K:
Answer:
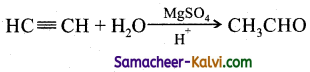
(v) Ozone followed by Zn / H2O:
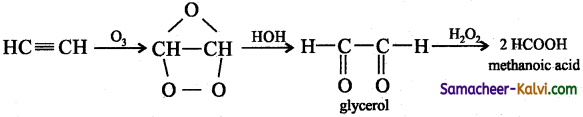
Answer:
![]()
Question 40.
Distinguish by means of a chemical test.
(i) but-l-ene and but-l-yne:
Answer:


(ii) butane and but-1 -ene:
Answer:

(iii) but-2-yne and but-1 -yne:
Answer:

Question 41.
Give equation for the reaction of propyne with:
(i) Br2
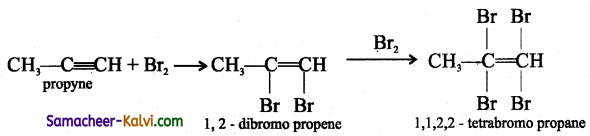
Answer:
(ii) HgSO4 / H2SO4:
Answer:
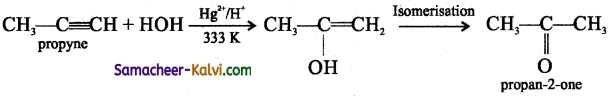
(iii) O3 / HOH:
Answer:
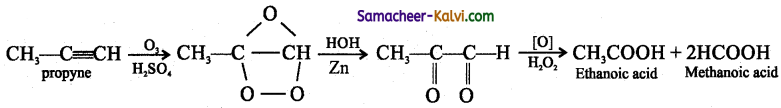
![]()
Question 42.
Give a brief account on polymerisation of alkynes.
Answer:
Acetylene undergoes polymerisation producing different pr&lucts under different conditions.
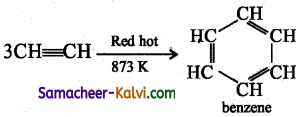
(i) Cyclic poIymerisation:
When acetylene is passed brouh a red hot metallic tube at 873 K, cyclic polyrnerisaiion occurs with the formation of beniene.
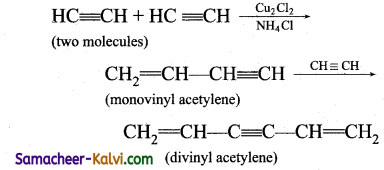
(ii) When acetylene is treated with cuprous chloride solution containing ammonium chloride, linear polymerisation occurs forming mono vinyl acetylene and divinyl acetelene.
Question 43.
Give two examples each for monocyclic and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Answer:
Monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons:
Benzene(C6H6) and toluene(C6H5 CH3)
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons:
Naphthalene (C6H5 – C6H5) and
Anthracene:
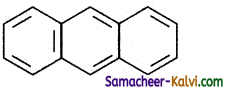
![]()
Question 44.
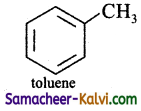
Write the structures of the following:
(i) Toluene
Answer:
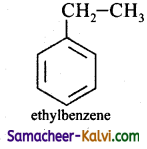
(ii) Ethyl benzene
Answer:
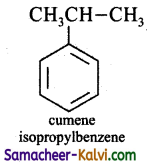
(iii) Isopropyl benzene
Answer:
(iv) o – xylene
Answer:
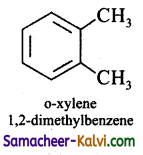
(v) m – xylene
Answer:
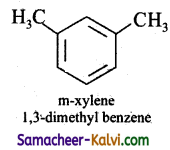
(vi) p – xylene
Answer:
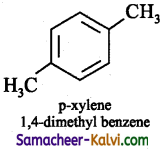
Question 45.
Mention the conditions for an organic compound to be classified as aromatic. [OR] Explain Huckel’s rule.
Answer:
Huckel proposed that aromaticity is a function of electronic structure. A compound may be aromatic, if it obeys the following rules:
(i) The molecule must be co – planar
(ii) Complete delocalization of n electron in the ring
(iii) Presence of (4n + 2)π electrons in the ring where n is an integer (n = 0,1,2….)
This is known as Huckel’s rule.
![]()
Question 46.
Predict the following compounds are aromatic or not.
(i) Benzene
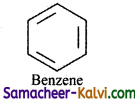
Answer:
(a) The benzene is a planar molecule.
(b) It has six delocalised π electrons.
(c) 4n + 2 = 6
4n = 6 – 2
4n = 4
n = 1
It obeys Huckel’s (4n + 2) π electron rule with n = 1.
Hence, benzene is aromatic.
(ii) Naphthalene
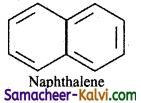
Answer:
(a) Naphthalene has a planar ring structure.
(b) It has 10 delocalised it electrons.
(c) 4n + 2 = 10
4n = 10 – 2
4n = 8
n = 8/4 = 2
Hence, naphthalene is aromatic.
(iii) Anthracene:
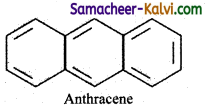
Answer:
It has a planar ring structure with 14 delocalised n electrons. Applying Huckel’s rule 4n + 2 = 14π electrons. n = 3 Hence it is an aromatic compound.
(iv) Cyclo penta diene:

Answer:
(a) It has planar structure.
(b) It has four π electron but the π electrons are not delocalised and hence it is not an aromatic compound.
(v) Cyclooctatetraene
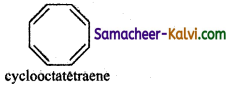
Answer:
Molecule is non-planar and hence it is not an aromatic compound.
(vi) Cyclopropenylcation
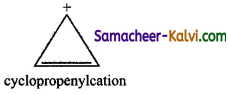
Answer:
(a) Cyclopropenylcation has planar structure.
(b) It has 2 delocalised π electron.
(c) 4n + 2 = 2
4n = 0
n = 0 (an integer) and hence it is aromatic compound.
![]()
Question 47.
Briefly explain the structure of benzene based on resonance.
Answer:
(i) On the basis of resonance, benzene is believed to be a resonance hybrid of the I and II are called Kekule structures and contribute more towards resonance hybrid than the rest of the structures.
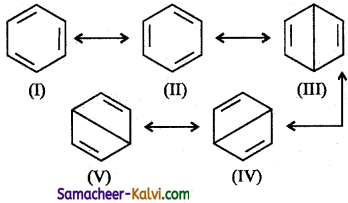
(ii) The two Kekule structures are equivalent and hence the stability of the resonance hybrid is high. Because of resonance, all the C — C bond lengths are equal which is intermediate to C = C and C — C bond lengths.
(iii) Resonance can occur only if the molecule is planar. Thus, benzene is a planar molecule, where all the six carbon and six hydrogen atoms lie in the same plane.
(iv) All the pi electrons are delocalised. This is represented by a circle inside the benzene ring. For convenience, Benzene is represented as
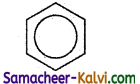
(Note: The resonance hybrid cannot be represented on paper.)
Question 48.
Briefly explain the molecular orbital structure of benzene.
Answer:
(i) All the six carbon atoms in benzene are ‘sp2‘ hybridised. The sp2 hybrid orbitals overlap with each other and with ‘s’ orbitals of the six hydrogen atoms forming C — C and C — H bonds.
(ii) Since, the bond results from the overlap of ‘sp2’ planar hybrid orbitals, all carbon and hydrogen atoms in benzene lie. in the same plane and all the bond angles are 120° as shown below:
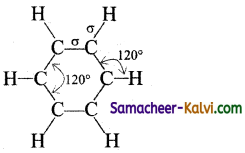
(iii) The unused ‘2p’ orbitals of each carbon atom which lie above and below the plane overlap laterally producing 3π molecular orbitals containing six electrons as shown in (a) and (b) below:
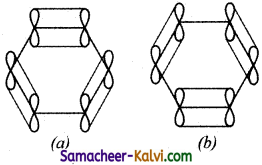
(iv) As the overlapping on both sides are equal, all the six ‘‘p’ orbitals unite to form a continues n molecular orbitals containing six electrons as shown below:
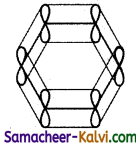
The formation of continuous molecular orbital suggests that all the six pi electrons are common to all the six carbon atom. The participation of pi electrons in more than one bond is called delocalisation of pi electrons.
(v) The molecular orbital picture of benzene explains all the known facts of about benzene, i.e., planarity of the molecule, bond angle, equal C — C bond lengths and stabilisation of the molecule.
![]()
Question 49.
How is benzene obtained from coal tar?
Answer:
Coal tar is a viscous liquid obtained by the pyrolysis of coal. During fractional distillation, coal tar is heated and distills away its volatile compounds namely benzene, toluene, xylene in the temperature range of 350 to 443 K. These vapours are collected at the upper part of the fractionating column.
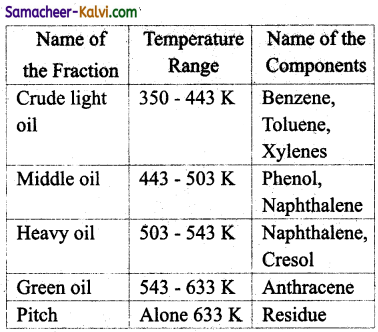
Question 50.
Give equations for the following reactions.
(i) Sodium benzoate is heated with soda lime.
Answer:

(ii) Phenol vapours are passed over zinc dust.
Answer:
C6H5OH + Zn → C6H6 + ZnO
(iii) Bromo benzene and iodo methane is heated with metallic sodium in the presence of ether.
Answer:
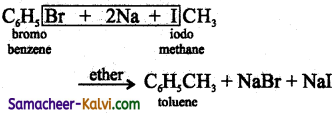
(iv) Benzene is treated with methyl chloride m the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride. .
Answer:

![]()
Question 51.
Identify the products in the following equations.
(i) 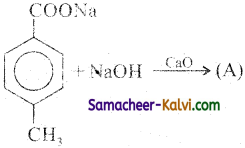
Answer:
A = 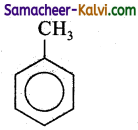
(ii) 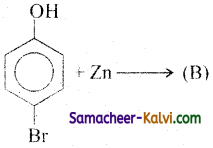
Answer:
B = 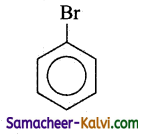
(iii) 
Answer:
C = 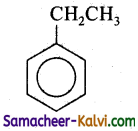
(iv) 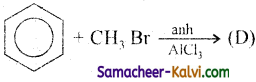
Answer:
D = 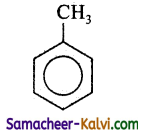
Question 52.
Explain the mechanism of chlorination of benzene.
Answer:
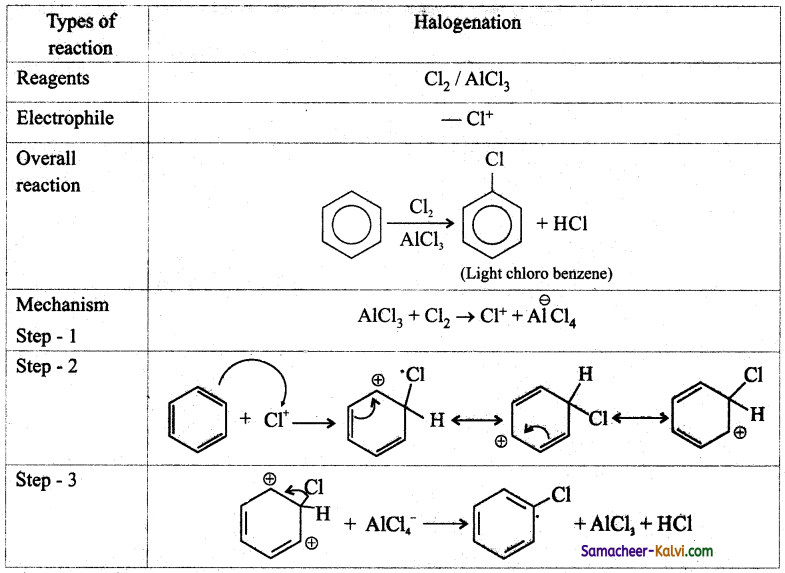
![]()
Question 53.
How do you get the following from benzene.
(i) cyclohexane
Answer:
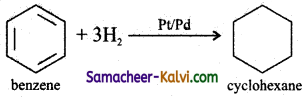
(ii) benzene hexachloride
Answer:
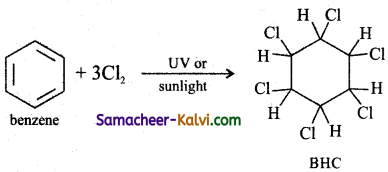
(iii) maleic anhydride
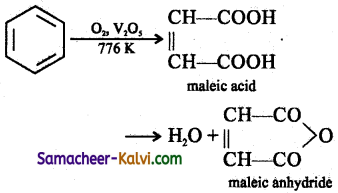
Answer:
(iv) 1, 4 cyclo hexane
Answer:
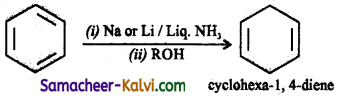
Question 54.
Give examples for Ortho and para directing groups.
Answer:
All the activating groups are ‘ortho-para’ directors.
eg: — OH, — NH2, — NHR, — NHCOCH3, — OCH2 — CH3 — C2H5 etc.
![]()
Question 55.
What are metadirecting groups? Give example.
Answer:
Generally all deactivating groups are meta-directors,
eg: — NO2, — CN, — CHO,— COR, — COOH, — COOR, — SO3H etc.
Question 56.
Phenol on bromination gives a mixture of ortho and para bromo phenol but not m-bromo phenol. Explain why?
Answer:
The actual structure of phenol is a resonance hybrid of the following structures.
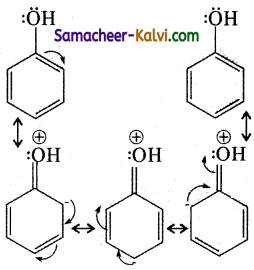
The ‘OH’ group in phenol is an ortho para orienting group. It activates the benzene orienting ring through its +M effect. As a result, the ortho and para position became electron rich compared to the meta position and the electrophile i.e., Br+ attacks the ortho and para positions. Hence bromination of benzene gives a mixture of ortho and para bromo phenols.
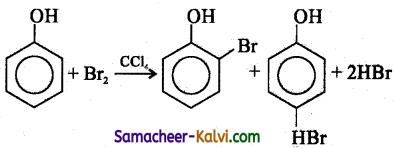
![]()
Question 57.
The halogen atom is halo benzene, has deactivate the benzene ring, yet ortho and para products are formed during electrophilic substitution reactions. Explain why?
Answer:
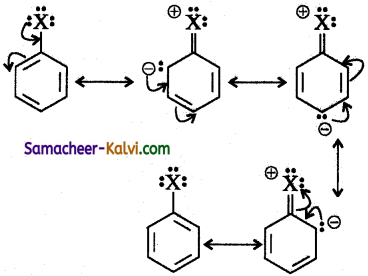
In aryl halides, the strong – I effect of the halogens (electron Withdrawing tendency) decreases the electron density of benzene ring, thereby deactivating for electrophilic attack.
However the presence of lone pair on halogens involved in the resonance with pi electrons of benzene ring, increases electron density at ortho and para position.
Thus the electrophile attacks the ortho and para position.
Question 58.
Explain how a meta directing group facilitate the meta substituents in benzene ring. [OR] “CHO” group in meta directing in electrophilic substitutions reaction. Explain why?
Answer:
Meta directing groups deactivate the benzene ring through their -M effect. As a results the electron density at ortho and para positions become electron deficient compared to the meta position. Or the meta position is relatively electron rich compared to ortho and para positions. Hence the electrophile attacks the meta position. For example the.aldehyde group (-CHO) is meta directing. The actual structure of benzaldehyde is a resonance hybrid of the following structures.
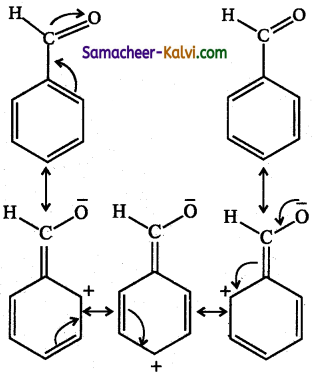
Because of -M effect, a positive charge is created at ortho and para position. This means the electron density at the meta position is relatively higher than ortho and para positions. Hence, meta directing groups favours meta substitution.
![]()
Question 59.
Write a short note on Carcinogenity and toxicity.
Answer:
Poly nuclear hydrocarbons are toxic and said to possess cancer producing (carcinogenic) property. These polynuclear hydrocarbons are produced by incomplete combustion of organic matter such as coal, petroleum, tobacco etc., They enter into the human body and undergo various biochemical reaction and finally damage DNA to cause cancer. Examples of polynuclear hydrocarbons having carcinogenic activity are 1, 2 benzanthracene, 1, 2, benzpyrene, 1, 2, 5, 6 dibenzanthracene.
Question 60.
Complete the following reactions:
(i) 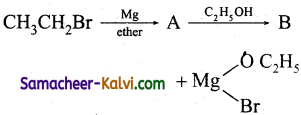
Answer:
A = CH3CH2MgBr; B = CH3CH3
(ii) 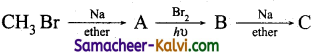
Answer:
A = CH3 – CH3; B = CH3 CH2Br;
C = CH3 CH2 CH2 CH3
(iii) 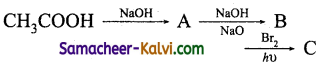
Answer:
A = CH3COONa; B = CH4; C = CH3Br
(iv) ![]()
Answer:
A = CH3COONa; B = CH3 – CH3
(v) CaC2 + H2O —> A + B .
Answer:
A = C2H2 ; B = Ca(OH)2
(vi) 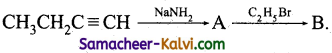
Answer:
A = CH3 CHO; B = (CH3)2CO
(vii) 
Answer:
A = CH3CH2 C = C.Na;
B = CH3CH2C = C. CH2 CH3
(viii) 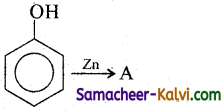
Answer:
A = C6H6
(ix) 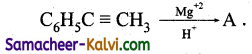
Answer:
A = C6H5CO CH2 CH3
![]()
Question 61.
An alkene ‘A’ on ozonolysis gives a mixture of ethanal and pentan-3-one. Write the structure and IUPAC name of A.
Write the structures of the products of ozonolysis side by side with their oxygen atoms pointing towards each other. Remove the oxygen atom and join the two carbon atoms by a double bond.
Answer:
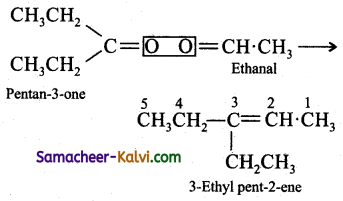
Question 62.
Bring out the following conversions:
(i) ethyl bromide to butane:
Answer:
CH3CH2Br ![]() CH3CH3
CH3CH3
(ii) benzoic acid to benzene:
Answer:
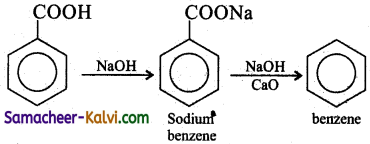
(iii) ethyl bromide to butane:
Answer:
CH3CH2Br ![]() CH3CH2CH2CH3
CH3CH2CH2CH3
(iv) propene to 2-bromoprppane:
Answer:
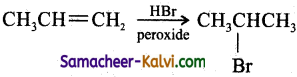
(v) ethyl bromide to ethylene glycol:
Answer:
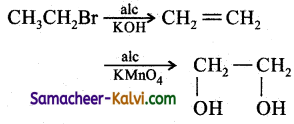
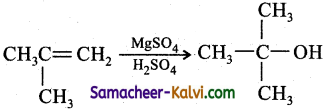
(vi) 2-methyl prop-l-ene to propan-2-ol:
Answer:
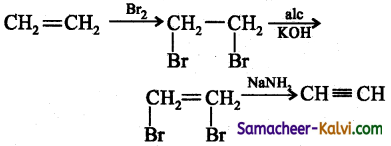
(vii) ethane to ethyne:
Answer:
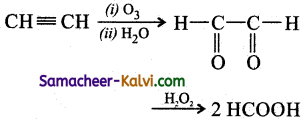
(viii) acetylene to methanoic acid.
Answer:
(ix) Toluene to o – bromo toluene.
Answer:
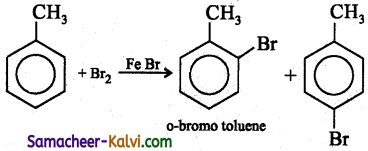
(x) benzene to m – dinitro benzene.
Answer:
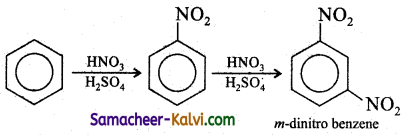
![]()
Question 63.
Bring out the following conversions:
(i) Benzene to o – dichloro benzene.
Answer:
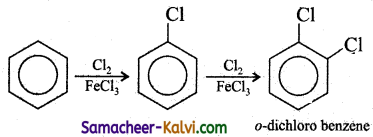
(ii) Benzene to o – nitro toulene.
Answer:
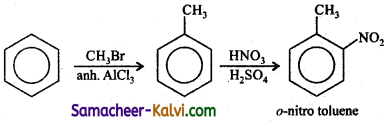
(iii) Benzene to m – nitro toulene.
Answer:
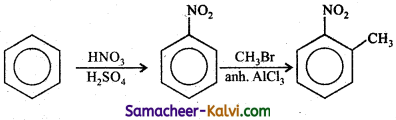
(iv) Benzene to p – nitro toulene.
Answer:
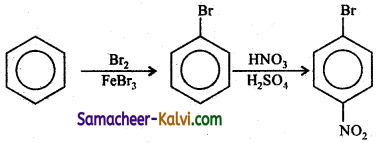
(v) Benzene to m – di nitro benzene.
Answer:
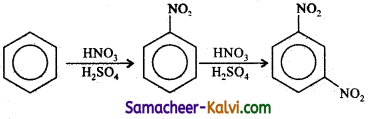
Choose the correct answer:
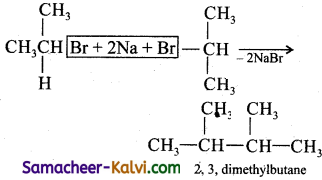
Question 1.
Isopropyl bromide on wurtz reaction gives:
(a) hexane
(b) propane
(c) 2, 3 dimethyl butane
(d) neohexane
Answer:
(c) 2, 3 dimethyl butane
Hint:
Question 2.
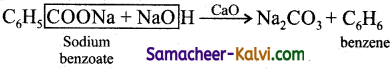
Heating a mixture of sodium benzoate with soda lime gives:
(a) benzene
(b) methane
(c) benzoic acid
(d) calcium benzoat
Answer:
(a) benzene
Hint:
![]()
Question 3.
Which of the following alkane has the lowest boiling point and highest melting point?
(a) w-pentane
(b) iso pentane
(c) neo pentane
(d) n-hexane
Answer:
(c) neo pentane
Hint:
Due to least surface area, neo pentane has the lowest boiling point, but due to high symmetry it has the highest melting point.
Question 4.
On mixing certain alkane with chlorine and irradiating it with ultraviolet light, one forms only one monochloro alkane. The alkane could be:
(a) neopentane
(b) propane
(c) pentane
(d) isopentane
Answer:
(a) neopentane
Hint:
Neopentane, has only one type carbon atoms attached to the carbon atom as
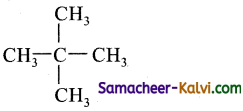
All hydrogen atoms are equivalent and hence it forms only one monochloro derivative.
![]()
Question 5.
Which one of the following exhibit geometrical ‘ isomerism?
(a) 1 – phenyl – 2 – butene
(b) 3 – phenyl – 1 – butene
(c) 2 – phenyl – 1 – butene
(d) 1, 1 diphenyl – 1 – propane
Answer:
(a) 1 – phenyl – 2 – butene
Hint:
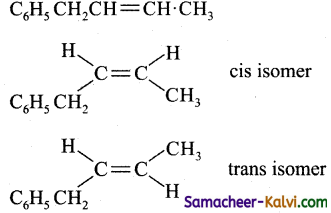
Question 6.
Give the IUPAC name of
(a) 3 – methyl-4-propyl-3-octene
(b) 4- butyl-3-methyl-3-heptene
(c) 2 – ethyl-3-propyl-2-heptene
(d) 2 – ethyl-2-propyl-2-heptene
Answer:
(a) 3 – methyl-4-propyl-3-octene
Hint:
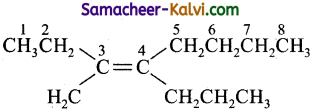
Question 7.
1-chlorobutane on reaction with alcoholic potash gives:
(a) 1 – Butene
(b) 1 – Butanol
(c) 2 – Butene
(d) 2 – Butanol
Answer:
(a) 1 – Butene
Hint:
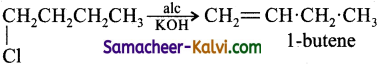
![]()
Question 8.
Butene – 1 – may be converted to butane on reaction with:
(a) Pd / H2
(b) Zn / HCl
(c) Sn / HCl
(d) Zn – Hg
Answer:
(a) Pd / H2
Hint:
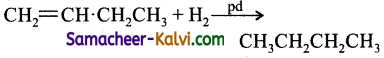
Question 9.
Which of the following gives an ozonolysis both aldehydes and ketones?
(a) (CH3)2C = CH CH3
(b) (CH3)2C = C.(CH3)2
(c) 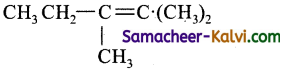
(d) 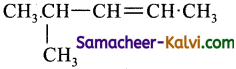
Answer:
(a) (CH3)2C = CH CH3
Hint:
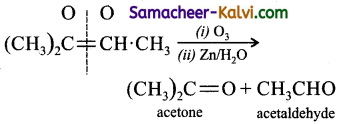
![]()
Question 10.
Identify the compounds A and B in the following reaction sequence.
![]()
(a) A is ethylene; B is acetaldehyde
(b) A is acetylene; B is propionaldehyde
(c) A is ethane; B is ethanol
(d) A is acetylene; B is acetaldehyde
Answer:
(d) A is acetylene; B is acetaldehyde
Hint:
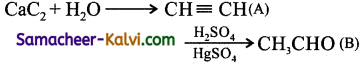
Question 11.
A gas decolourises alkaline KMnO4 but does not give a precipitate with AgNO3 is:
(a) CH4
(b) C2H4
(c) C2H2
(d) C2H6
Answer:
(b) C2H4
Hint:
Ethylene decolourises KMnO4but does not give a precipitate with AgNO3.
Question 12.
The ortho-para directing group among the following is:
(a) COOH
(b) CN
(c) COCH3
(d) NHCOCH3
Answer:
(d) NHCOCH3
![]()
Question 13.
The number of structural isomers of C6H14 is:
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 6
Answer:
(d) 6
Hint:
n-hexane : CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3
2 – methyl pentane:
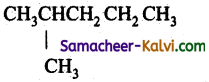
3 – methyl pentane:
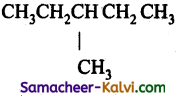
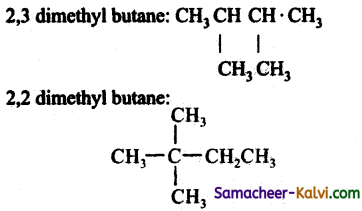
Question 14.
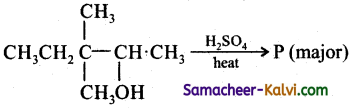
What is the major product ‘P’ in the above reaction?
(a) 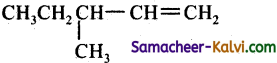
(b) 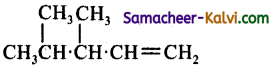
(c) 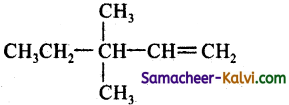
(d) 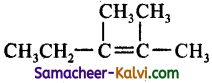
Answer:
(d) 
Hint:
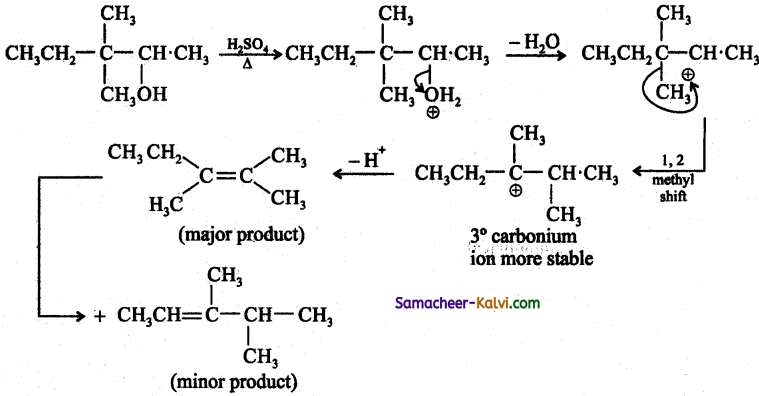
![]()
Question 15.
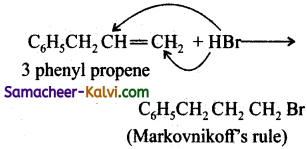
3 – phenyl propene on reaction with HBr gives as a major product:
(a)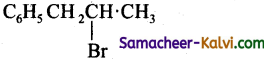
(b) 
(c) C6H5 CH2 CH2 CH2 Br
(d) 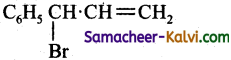
Answer:
(b) 
Hint:
Question 16.
CHCHCH = CH + HBr ![]() [X] (major) + [Y] (minor) [X] and [Y] respectively are:
[X] (major) + [Y] (minor) [X] and [Y] respectively are:
(a) BrCH2CH2CH = CH2 and C2H5CH(Br) . CH3
(b) C2H5 CH2 CH2 Br and – CH2 CH2 – CH = CH2
(c) C2H5 CH2 CH2 Br and C2H5 CH (Br) . CH3
(d) C2H5 CH (Br) . CH3 and C2H5 CH2 CH2 Br
Answer:
(c) C2H5 CH2 CH2 Br and C2H5 CH (Br) . CH3
Hint:
X is formed by the anti Markovnikoff’s addition. i.e., CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 Br (X) as the major product. C2H5 CH (Br). CH3 is fonned as a minor product.
![]()
Question 17.
Which of these will not react with acetylene?
(a) NaOH
(b)ammonical AgNO3
(c)Na
(d)HCl
Answer:
(a) NaOH
Hint:
HC ≡ CH + NaOH (weaker base) → HC ≡ CNa (Stroinger base) + H2O
A weaker base cannot displace a stronger base.
Question 18.
Predict the product (c) in the following reaction of butyne – 1
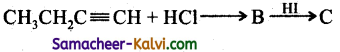
(a) 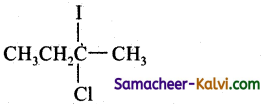
(b) 
(c) 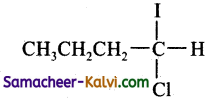
(d) 
Answer:
(a) 
Hint:
Addition of both HCl and HI occurs in accordance with Markovniff’s rule.
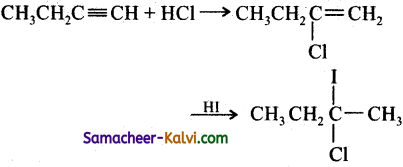
![]()
Question 19.
When 2 – butyne is treated with dilute H2SO4 / HgSO4, the product formed is:
(a) butanol – 1
(b) butanol – 2
(c) 2 – butanone
(d) butanal
Answer:
(c) 2 – butanone
Hint:
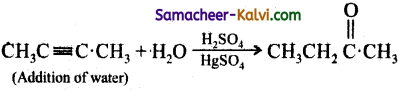
Question 20.
Which of the following reagents will be able to j distinguish between 1 -butyne and 2-butyne?
(a) NaNH2
(b) HCl
(c) O2
(d) Br2
Answer:
(a) NaNH2
Hint:
1 – Butyne being a terminal alkyne has an acidic hydrogen. Hence reacts with sodium in liquid ammonia (NaNH2) to evolve NH3 gas but 2 – butyne does not.
![]()
Question 21.
The molecular formula of diphenyl methane is C13H12. It is represented as
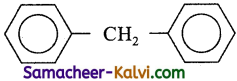
How many structural isomers are possible when one of the hydrogens are replaced by chlorine atom?
(a) 4
(b) 8
(c) 7
(d) 8
Answer:
(a) 4
Hint:
One hydrogen in CH2, ortho, meta and para hydrogens. Hence 4.
Question 22.
Which of the following compounds is not aromatic?
(a) 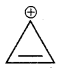
(b) 
(c) 
(d) 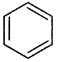
Answer:
(c) 
Hint:
Has a cyclic cloud of 2π electrons and hence aromatic, (b) and (c) have a cyclic cloud of six pi electrons and hence aromatic, (c) has 4π electrons and hence anti-aromatic.
![]()
Question 23.
The radical, 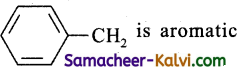 is aromatic because it has:
is aromatic because it has:
(a) seven ‘p’ orbitals and seven unpaired electrons
(b) six ‘p’ orbitals and seven unpaired electrons
(c) six ‘p’ orbitals and six unpaired electrons
(d) seven ‘p’ orbitals and six unpaired, electrons
Answer:
(c) six ‘p’ orbitals and six unpaired electrons
Hint:
six ‘p’ orbitals and six pi- electrons from a cyclic electron cloud containing 6π i.e.,(4n + 2) π electron which is responsible for aromatic character. The seventh electron as such has nothing to do with the aromatic character of benzyl radical.The enthalpy of hydrogenation of these compounds will be in the order of:
Question 24.
Given
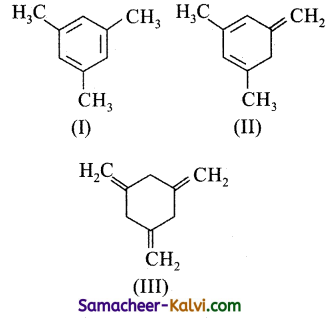
The enthalpy of hydrogenation of these compounds will be in the order of:
(a) II > III > I
(b) II > I > III
(c) I > II > III
(d) III > II > I
Answer:
(d) III > II > I
Hint:
The enthalpy of hydrogenation is inversely proportional to its stability.
i.e., Lower the stability, greater is its enthalpy of hydrogenation.
(I) is aromatic and hence most stable.
(II) is less stable than (I) because it is a cyclic conjugated diene.
(III) is least stable because it is neither aromatic nor a cyclic conjugated diene. Hence, the stability of alkenes decrease in the order I > II > III and the enthalpy of hydrogenation in the order III > II > I.
![]()
Question 25.
Among the following compounds, the one that is most reactive towards electrophilic nitration is: 2012)
(a) benzoic acid
(b) nitrobenzene
(c) toluene
(d) benzene
Answer:
(c) toluene
Hint:
Toluene has electron releasing methyl group while others have electron with -drawing groups. Hence toluene is most reactive among others towards electrophilic substitution reaction.
Question 26.
Find the major product in the following reaction:
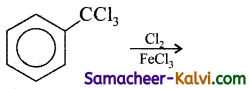
(a) 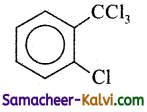
(b) 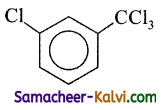
(c) 
(d) 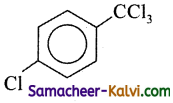
Answer:
(b) 
Hint:
– CCl3 is meta directing.
![]()
Assertion-Reason type Questions:
Question 27.
Assertion:
Boiling points of cis isomers are higher than those of trans isomers.
Reason:
Dipole moments of cis isomers are higher than these of trans isomers.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reasons are false.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Question 28.
Assertion:
Propene is more reactive thanethene towards electrophilic addition reactions.
Reason:
Hyper conjugation effect of the methyl group increases the electron density in the double bond.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reasons are false.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
![]()
Question 29.
Assertion:
The C – H bond in ethyne is shorter than C – H bond in ethane.
Reason:
The hydrogen atoms in ethyne are acidic.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reasons are false.
Answer:
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Hint:
The C – H bond in ethyne is sp2 hybridised and that in ethane sp3 hybridised. The sp2 hybridised carbon is more electronegative than sp3 hybridised carbon.
Question 30.
Assertion:
Benzene does not decolorise bromine water.
Reason:
Benzene contains three double bonds.
(a) Both assertion and reason are .true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reasons are false.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
Hint:
The correct reason is that the pi electrons of benzene are delocalised.
![]()
Question 31.
Assertion:
Friedel – Craft’s reaction is used to introduce an alkyl or allyl group into the benzene ring.
Reason:
Benzene is a solvent for the Friedel – Craft’s alkylation of bromo benzene.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
Hint:
Benzene is more reactive than bromobenzene. Hence, Friedel-Craft’s reaction will occur preferentially in benzene rather than bromo benzene and hence benzene cannot be used as a solvent in this reaction.
Question 32.
Which of the following will not show geometrical isomerism?
(a) 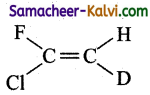
(b) 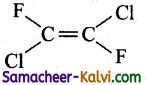
(c) 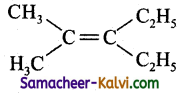
(d) 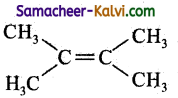
Answer:
(d) 
![]()
Question 33.
Pick out the alkanes which differs from the other members of the group.
(a) 2, 2, dimethyl propane
(b) pentane
(c) 3, methyl butane
(d) 2, 2, dimethyl butane
Answer:
(d) 2, 2, dimethyl butane
Hint:
(a), (b), (c) are all isomers but ‘d’ is not.
Question 34.
Methane can be converted into ethane by the following reactions:
(a) chlorination followed by the reaction with alcoholic KOH.
(b) Chlorination followed by the reaction with aq. KOH.
(c) Chlorination followed by wurtz reaction.
(d) Chlorination followed by decarboxylation.
Answer:
(c) Chlorination followed by wurtz reaction.
Hint:
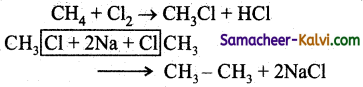
![]()
Question 35.
Which of the following pairs of alkynes contain only acidic hydrogen atoms?
(a) CH ≡ CH and CH3 C . CH3
(b) CH3 C ≡ CH and CH ≡ CH
(c) CH3C = C . CH3 and CH3CH2C = C CH3
(d) CH2 = CH2 and CH ≡ CH.
Answer:
(b) CH3 C ≡ CH and CH ≡ CH
Question 36.
Among the following, the pair of alkynes which show position isomerism is:
(a) But – 1 – yne and But – 2 – yne
(b) Pent – 1 – yne and 3 methyl but – 1 – yne
(c) But – 1 – yne and But – 3 – diene
(d) Propyne and Cyclopropene.
Answer:
(a) But – 1 – yne and But – 2 – yne
Hint:
CH3CH2C = CH and CH3C ≡ C . CH3 are position isomers.
 are chain isomers.
are chain isomers.
CH3CH2 C ≡ CH and CH2 = CH — CH = CH2 are functional isomers.
CH3C ≡ CH and ![]() are ring chain isomers.
are ring chain isomers.
![]()
Question 37.
Assertion:
Melting point of neopentane is higher than that of n – pentane but the boiling point of n – pentane is higher than that of neopentane.
Reason:
Melting point depends upon packing of molecules in the crystal lattice while boiling point depends upon the surface area of the molecule.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
(a) If both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Question 38.
Assertion:
The C — H bond in ethyne is shorter than C — H bonds in ethene.
Reason:
Carbon atoms in ethene is sp hybridised while it is sp2 hybridised in ethyne.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
Hint:
Correct reason: carbon atom in ethene is sp2 hybridised while it is sp in ethyne.
![]()
Question 39.
Assertion :
Acetylene on treating with NaNH2 gives sodium acetylide and ammonia.
Reason : sp hybridised carbon atoms | of acetylene are considerably
electronegative.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
(b) If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Hint:
Correct reason: Acetylene is a stronger acid than ammonia.
Question 40.
Assertion:
Friedel crafts reaction is used to introduce an alkyl or alyl group in benzene nucleus.
Reason:
Benzene is a software for the Friedel-crafts alkylation of bromo benzene. (AIIMS – 2008)
(a) If both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
Hint:
Correct reason: Since benzene is more reactive than bromobenzene Friedel – crafts reaction occur preferential in benzene, rathar than in bromobenzene and hence benzene cannot be used as a solvent in this reaction.
![]()
Question 41.
Assertion:
The reaction of conc.HNO3 and conc.H2SO4 on nitrobenzene gives m-dinitrobenzene.
Reason:
The nitro group in benzene ring decreases the electron density in the benzene ring.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
(b) If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Hint:
Correct reason:
The nitro group in nitro benzene decreases the electron density at ortho and para positions. Hence the meta position in relatively high in electron density, i.e., NO2 group is theta directing.
Question 42.
Choose the correct statements from the following sentences.
Presence of a nitro group in a benzene ring.
(a) Deactivates the ring towards electrophilic substitution reaction.
(b) Activates the ring towards electrophilic Substitution reactions.
(c) Renders the ring basic.
(d) Deactivates the ring toward nucleophilic substitution ring.
Answer:
(a) Deactivates the ring towards electrophilic substitution reaction.
![]()
Question 43.
Identify the incorrect statement with regard to the structure of benzene.
(a) Benzene is a planar molecule.
(b) All C — C bonds in benzene have equal bond length due to resonance.
(c) Benzene exhibits resonance.
(d) Benzene contains three double bonds and three single bonds.
Answer:
(d) Benzene contains three double bonds and three single bonds.
Hint:
Benzene has delocalised pi electrons.
Question 44.
Which of the following reactions does not produce methane as a product?
(a) Decarboxylation of sodium acetate
(b) Electrolysis of potassium acetate
(c) Reduction of methyl bromide with zinc and hydrochloric acid.
(d) Hydrolysis of aluminium carbide.
Answer:
(b) Electrolysis of potassium acetate
Hint:
Electrolysis of CH3COOK produces ethane.
![]()
Question 45.
Choose the correct statement with regard to the boiling points of alkenes.
(a) The boiling point of straight chain alkane decreases regularly with their molecular mass.
(b) The branched chain alkane has a higher boiling point than the corresponding n – alkane.
(c) The boiling point of 2, 2, dimethyl propane is lower than these of 2 – methyl butane.
(d) The increase in boiling point of alkanes is
Answer:
(c) The boiling point of 2, 2, dimethyl propane is lower than these of 2 – methyl butane.
Hint:
Among isomeric alkanes, the branched chain isomer has a lower boiling point than the corresponding n-alkane. This is because, with branching the shape of the molecule tends to approach that of a sphere. Hence, surface area j of branched chain isomer decreases and so, magnitude of vanderwaals forces decrease.
As a result ion energy is required to break the force of attraction. 2, 2, dimethyl propane with two branches has a lower boiling point than that of 2-methyl butane which has one branch chain.
Question 46.
Choose the incorrect state with respect to electrophilic substitution reactions of benzene.
(a) In the bromination of benzene, a Lewis acid is used to generate the electrophile.
(b) In the nitration reactions, the electrophile is NO2+ (nitronium ion).
(c) In sulphonation reactions, the electrophile, SO3 is produced by the reaction.
2 H2SO4 ⇌ SO3 + HSO4– + H3O+
(d) The pi electrons of the benzene ring are tightly held and acts as a source for nucleophiles.
Answer:
(d) The pi electrons of the benzene ring are tightly held and acts as a source for nucleophiles.
Hint:
The pi electrons of the benzene ring are loosely held and easily available for electrophilic attack.
![]()
Question 47.
Match the entities of column I with appropriate entities of column II
Column I Column II
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Formation of methane by heating sodium ethanoate with soda lime | (A) Dehydration |
| (ii) Formation of ethene by distilling ethane with cone H<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>4</sub> | (B) Hydration |
| (iii) Formation of propan-2-ol by heating propene with conc. H<sub>2</sub>SO<sub>4</sub> | (C) Polymerisation |
| (iv) Formation of polythene from ethene | (D) Decarboxylation |
due to increase in molecular mass.
(a) (i) – (D), (ii) – (A), (iii) – (B), (iv) – (C)
(b) (i) – (A), (ii) – (C), (iii) – (D), (iv) – (B)
(c) (i) – (B ),(ii) – (D), (iii) – (A), (iv) – (C)
(d) (i) – (C), (ii) – (D), (iii) – (A), (iv) – (B)
Answer:
(i) – (D), (ii) – (A), (iii) – (B), (iv) – (C)
![]()
Question 48.
Match the entities of column I with appropriate entities of column II
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) n-Butane and 2-methyl propane | (A) position isomers |
| (ii) But – 1 – ene and But – 2 – ene | (B) geometrical isomers |
| (iii) cis butene and trans butene | (C) functional isomers |
| (iv) Ethyl alcohol and dimethyl ether | (D) chain isomers |
(a) (i) – (D), (ii) – (A), (iii) – (B), (iv) – (C)
(b) (i) – (A), (ii) – (C), (iii) – (D), (iv) – (B)
(c) (i) – (B), (ii) – (A), (iii) – (D), (iv) – (C)
(d) (i) – (D), (ii) – (B), (iii) – (C), (iv)- (A)
Answer:
(a) (i) – (D), (ii) – (A), (iii) – (B), (iv) – (C)