TN State Board 12th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 21 The Sale of Goods Act, 1930
Question 1.
What is a contract of sale of goods?
Answer:
Contract of sale of goods is a contract whereby the seller transfers or agrees to transfer the property (ownership) of the goods to the buyer for a price. The term “ownership” is utmost importance in the sale of goods.
Question 2.
List down the essential elements of a contract of sale.
Answer:
- Two parties
- Transfer of property
- Goods
- Price
- Includes both “sale” and agreement to sell.
![]()
Question 3.
What is meant by goods?
Answer:
- The term goods mean every kind of movable property other than actionable claim and money.
- The term good includes shares, stocks growing crops, grass, things attached to the land.
- Goodwill, trademarks, copyrights, patent rights, etc., are also regarded as goods.
Question 4.
What is a Contingent Goods?
Answer:
Contingent goods are the goods, the acquisition of which by the seller depends upon a contingency. Contingent goods are a part of future goods.
Question 5.
What do you understand by warranty?
Answer:
Warranty represents a stipulation which is collateral to the main purpose of the contract. It is of secondary importance to the contract.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain the meaning of Agreement to sell.
Answer:
- The property (ownership or title) in the goods has to pass at a future time or after the fulfillment of certain conditions specified in the contract.
- Where the goods under the agreement to sell are destroyed the loss falls squarely on the seller as the ownership is still vested with the seller even though the possession of the goods is with the buyer.
- Where the buyer violates the contract the seller can repossess the goods from the former. He can sue for damages for violation of the contract.
- If the buyer becomes insolvent before the payment of the price, the seller can retain the goods if they are under his possession or even he can repossess the goods even if the possession of the goods is transferred to the buyer.
Question 7.
Discuss in detail about existing goods.
Answer:
- Existing goods are those owned or possessed by the seller at the time of contract of sale.
- Goods possessed even refer to sale by agents or pledgers.
- Existing goods may be either specific goods, ascertained goods, generic or unascertained goods.
![]()
Question 8.
Discuss the implied conditions and warranties in sale of goods contract.
Answer:
The term implied conditions means conditions which can be inferred from or guessed from the context of the contract. Following are the implied conditions.
(i) Conditions as to title:
In the case of sale, seller has a right to sell the goods. The buyer can assume that the seller has a right to sell the goods.
(ii) Conditions as to description:
In a contract of sale by description there is an implied condition that goods supplied should agree with the descriptions made by the seller.
(iii) Sale by sample:
Where goods are sold by showing samples by the seller.
Eg: Food grains. The bulk of goods supplied by the seller should be similar to the sample shown by the seller.
(iv) Conditions as to quality or fitness:
There is no implied condition as to the quality or fitness for any particular purpose of goods.
Question 9.
Discuss in detail the rights of an unpaid seller against the buyer personally.
Answer:
(i) Suit for price:
Where the ownership in the goods has passed to the buyer and the buyer refuses to pay for the goods, the seller can file case against the buyer for the price.
(ii) Suit for damages for non-acceptance:
Where the buyer wrongfully refuses to accept the goods, the seller can sue him for damages for non¬acceptance of the goods.
(iii) Suit for cancellation of the contract before the due date:
Where the buyer cancels the contract before the date of delivery, the seller may either treat the contract as continuing or wait till the due date or he can file a case against buyer immediately.
(iv) Suit for interest:
Where there is a specific agreement between buyer and seller regarding charging interest on the price, the seller can recover interest from the buyer from the due date of contract till the date of payment of purchase price.
![]()
Question 10.
Explain in detail the elements of Contract of sale.
Answer:
Following essential elements are necessary for a contract of sale.
(i) Two parties:
A contract of sale involves two parties the seller and the buyer. Both are the two different persons. If a person buys his own good there is no sale.
(ii) Transfer of property:
To constitute sale, the seller must transfer or agree to transfer the ownership in the good to the buyer. A mere transfer of possession does not amount to sale.
(iii) Goods:
The subject matter of contract of sale must be goods. The term “goods” includes every kind of movable property, stocks and shares, growing crops etc. Goodwill, trademarks, copyrights, patent rights etc, are all also regarded as goods.
(iv) Price:
The monetary consideration for the goods sold is called price. If goods are sold partly for goods and partly for money, the contract is one of sale.
(v) Includes both “sale” and agreement to sell:
The term contract of sale includes both sale and agreement to sell. If the property in goods is transferred immediately to the buyer, it is called a sale. If the transfer of property takes place at a future date or on fulfilment of certain conditions it is called an agreement to sell.
Question 11.
Distinguish between sale and agreement to sell.
Answer:
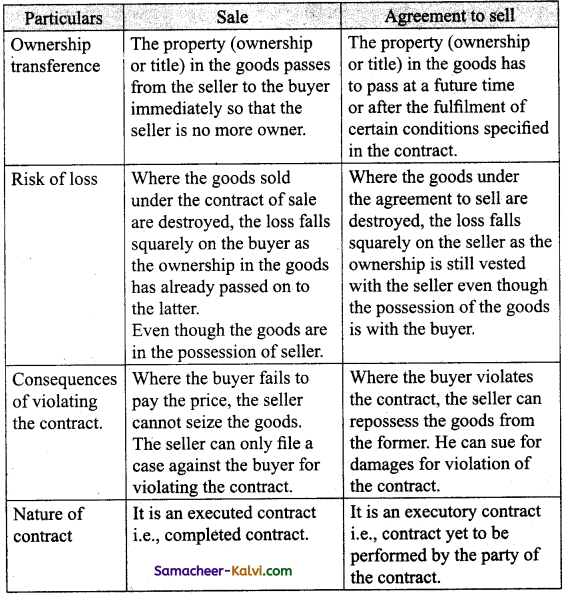
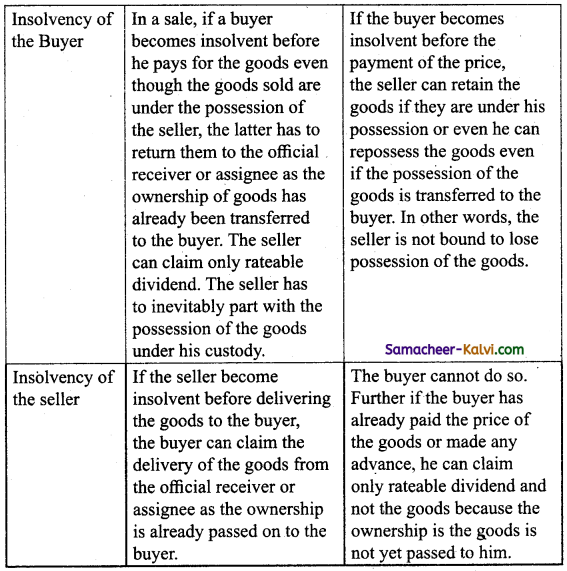
![]()
Question 12.
Classify goods under the Sale of Goods Act.
Answer:
(i) Existing goods:
Existing goods are those owned or possessed by the seller at the time of contract of sale. Goods possessed even refer to sale by agents or by pledgers. Existing goods may be either specific goods, ascertained goods and generic or unascertained goods.
(ii) Future goods:
These are goods which a seller does not possess at the time of contract of sale but which will be manufactured or produced or acquired by him after entering into the contract of sale agreement.
(iii) Contingent goods:
Contingent goods are the goods, the acquisition of which by the seller depends upon a contingency, (an event which may or may not happen) Contingent goods are a part of future goods.
Question 13.
Distinguish between Conditions and Warranty.
Answer:
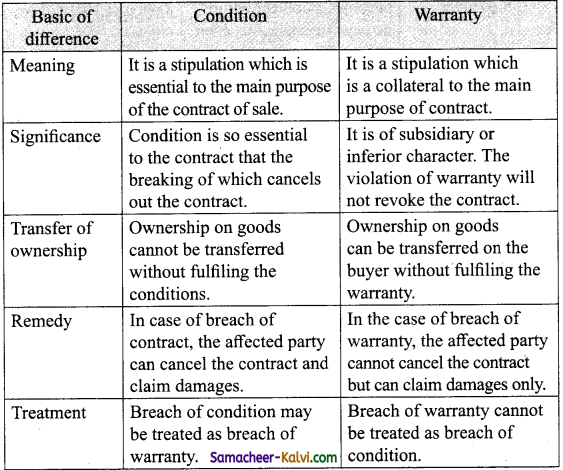
![]()
Question 14.
Discuss in detail the rights of an unpaid seller against the goods.
Answer:
Where the property in the goods has passed to the buyer.
(a) Right to lien:
An unpaid seller has a right to retain the goods till he receives the price. But to exercise this lien,
(i) He must be in possession of goods.
(ii) The goods must have been sold without any stipulation as to credit or where goods have been sold on credit the terms of credit must have expired.
Circumstances under which the rights of lien is lost:
(i) When he delivers the goods to a carrier or other bailee for the purpose of transmission to the buyer without reserving the right of disposal of the goods.
(ii) When the buyer or his agent lawfully obtain possession of them.
(iii) When the seller waives his right of lien.
(b) Right of stoppage in transit:
Goods must be neither with the seller nor with the buyer but should be in the hands of a carrier. Further the buyer must have become an unsolvant.
Termination of right to stoppage:
The right to stop the goods comes to an end.
(i) When the goods are delivered to the buyer or his agent.
(ii) When, on arrival of the goods at the appointed destination his agent, that he is holding the goods on his behalf.
Right to resale:
The unpaid seller can resell the goods.
(i) Where they are of a perishable in nature.
(ii) Where the seller has expressly reserved the right of resale in the contract itself.
![]()
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Sale of Goods Act was passed in the year:
(a) 1940
(b) 1997
(c) 1930
(d) 1960
Answer:
(c) 1930
Question 2.
Which of the below constitutes the essential element of contract of sale?
(a) Two parties
(b) Transfer of property
(c) Price
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 3.
Which of the below is not a good?
(a) Stocks
(b) Dividend due
(c) Crops
(d) water
Answer:
(b) Dividend due
![]()
Question 4.
In case of the sale, the _________ has the right to sell.
(a) Buyer
(b) Seller
(c) Hirer
(d) Consignee
Answer:
(b) Seller
Question 5.
The property in the goods means the:
(a) Possession of goods
(b) Custody of goods
(c) Ownership of goods
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(c) Ownership of goods
Question 6.
Specific goods denote goods identified upon the time of _______ of sale.
(a) Agreement
(b) Contract
(c) Order
(d) Obligation
Answer:
(b) Contract.
![]()
Question 7.
In which of the following types, the ownership is immediately transferred to buyer?
(a) When goods are ascertained
(b) When goods are appropriate
(c) Delivery to the carrier
(d) Sale or return basis
Answer:
(c) Delivery to the carrier
Question 8.
__________ is a stipulation which is collateral to main purpose of contract.
(a) Warranty
(b) Condition
(c) Right
(d) Agreement
Answer:
(a) Warranty
Question 9.
Unpaid seller can exercise his right of lien over the goods, where he is in possession of the goods as:
(a) Owner of goods
(b) Agent of buyer
(c) Bailee for buyer
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
![]()
Question 10.
The unpaid seller can exercise his right of stoppage of goods in transit where the buyer:
(a) Becomes insolvent
(b) Refuses to pay price
(c) Payment of price
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(a) Becomes insolvent