Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Guide Pdf Chapter 1 Metallurgy Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Solutions Chapter 1 Metallurgy
12th Chemistry Guide Metallurgy Text Book Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
1. Bauxite has the composition
a) Al2O3
b) Al2O3.nH2O
c) Fe2O3.2H2O
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Al2O3.nH2O
2. Roasting of sulphide ore gives the gas (A). (A) is a colorless gas. An aqueous solution of (A) is acidic. The gas (A) is
a) CO2
b) SO3
c) SO2
d)H2S
Answer:
c) SO2
3. Which one of the following reaction represents calcinations?
a) 2Zn + O2 → 2ZnO
b) 2ZnS + 3O2 → 2ZnO + 2SO2
c) MgCO3 → MgO + CO2
d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer:
c) MgCOa → MgO + CO2
![]()
4. The metal oxide which cannot be reduced to metal by carbon is
a) PbO
b) Al2O3
c) ZnO
d) FeO
Answer:
b) Al2O3
5. Which of the metal is extracted by Hall – Heroult process?
a) Al
b) Ni
c) Cu
d) Zn
Answer:
a) Al
6. Which of the following statements, about the advantage of roasting of sulphide ore before the reduction is not true?
a) ΔG°f of sulphide is greater than those for CS2 and H2S
b) ΔG°r is negative for roasting of sulphide ore to oxide
c) Roasting of the sulphide to its oxide is thermodynamically feasible.
d) Carbon and hydrogen are suitable reducing agents for metal sulphides.
Answer:
d) Carbon and hydrogen are suitable reducing agents for metal sulphides.
7. Match items in Column I – with the items of Column – II and assign the correct code.
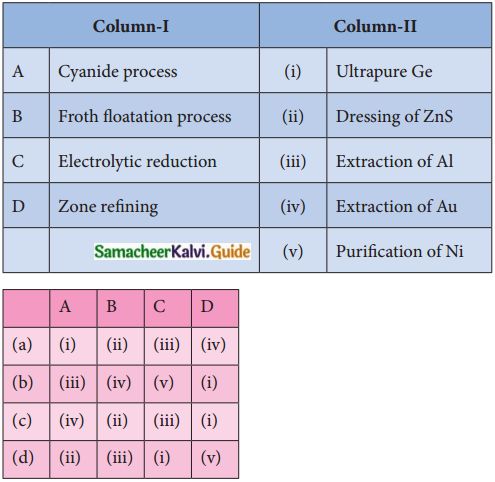
Answer:
c) (iv) (ii) (iii) (i)
8. Wolframite ore is separated from tinstone by the process of
a) Smelting
b) Calcination
c) Roasting
d) Electromagnetic separation
Answer:
d) Electromagnetic separation
![]()
9. Which one of the following is not feasible
a) Zn(S) + Cu2+(aq) → Cu(s) + Zn2+(aq)
b) Cu(S) + Zn2+(aq) → Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq)
c) Cu(S) + 2Ag+(aq) → Ag(s) + Cu2+(aq)
d) Fe(S) + Cu2+(aq) → Cu(s) + Fe2+(aq)
Answer:
b) Cu(S) + Zn2+(aq) → Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq)
10. Electrochemical process is used to extract
a) Iron
b) Lead
c) Sodium
d) Silver
Answer:
c) Sodium
11. Flux is a substance which is used to convert
a) Mineral’into silicate
b) Infusible impurities to soluble impurities
c) Soluble impurities to infusible impurities
d) All of these
Answer:
b) Infusible impurities to soluble impurities
12. Which one of the following ores is best concentrated by froth floatation method?
a) Magnetite
b) Heamatite
c) Galena
d) Cassiterite
Answer:
c) Galena
![]()
13. In the extraction of aluminium from alumina by electrolysis, cryolite is added to
a) Lower the melting point of alumina
b) Remove impurities from alumina
c) Decrease the electrical conductivity
d) Increase the rate of reduction
Answer:
a) Lower the melting point of alumina
14. Zinc is obtained from ZnO by
a) Carbon reduction
b) Reduction using silver
c) Electrochemical process
d) Acid leaching
Answer:
a) Carbon reduction
15. Extraction of gold and silver involves leaching with cyanide ion. silver is later recovered by (NEET – 2017)
a) Distillation
b) Zone refining
c) Displacement with zinc
d) liquation
Answer:
c) Displacement with zinc
16. Considering the Ellingham diagram, which of the following metals can be used to reduce alumina? (NEET – 2018)
a) Fe
b) Cu
c) Mg
d) Zn
Answer:
c) Mg
17. The following set of reactions are used in refining Zirconium
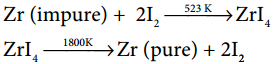
This method is known as
a) Liquation
b) Van Arkel process
c) Zone refining
d) Mond’s process
Answer:
b) Van Arkel process
![]()
18. Which of the following is used for concentrating ore in metallurgy?
a) Leaching
b) Roasting
c) Froth floatation
d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer:
d) Both (a) and (c)
19. The incorrect statement among the following is
a) Nickel is refined by Mond’s process
b) Titanium is refined by Van Arkel’s process
c) Zinc blende is concentrated by froth floatation
d) In the metallurgy of gold, the metal is leached with a dilute sodium chloride solution
Answer:
d) In the metallurgy of gold, the metal is leached with a dilute sodium chloride solution
20. In the electrolytic refining of copper, which one of the following is used as anode?
a) Pure copper
b) Impure copper
c) Carbon rod
d) Platinum electrode
Answer:
b) Impure copper
![]()
21. Which of the following plot gives Ellingham diagram
a) ΔS VsT
b) ΔG° VsT
c) ΔG° Vs1/T
d) ΔG° VsT²
Answer:
b) ΔG°VsT
22. In the Ellingham diagram, for the formation of carbon monoxide
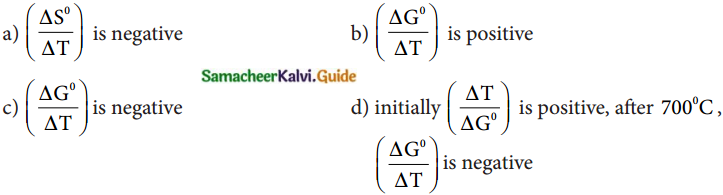
Answer:
c) \(\left(\frac{\Delta \mathrm{G}^{0}}{\Delta \mathrm{T}}\right)\) is negative
23. Which of the following reduction is not thermodynamically feasible?
a) Cr2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Cr
b) Al2O3 + 2Cr → Cr2O3 + 2Al
c) 3TiO2 + 4Al → 2Al2O3 + 3Ti
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Al2O3 + 2Cr → Cr2O3 + 2Al
24. Which of the following is not true with respect to the Ellingham diagram?
a) Free energy changes follow a straight line. The deviation occurs when there is a phase change.
b) The graph for the formation of CO2is a straight line almost parallel to the free energy axis.
c) Negative slope of CO shows that it becomes more stable with an increase in temperature.
d) Positive slope of metal oxides shows that their stabilities decrease with an increase in temperature.
Answer:
b) The graph for the formation of CO2 is a straight line almost parallel to the free energy axis.
II. Answer the following questions
Question 1.
What is the difference between minerals and ores?
Answer:
Minerals:
- Minerals contain a low percentage of metal.
- Metal cannot be extracted easily from minerals.
- Clay Al2O3. SiO2. 2H2O is the mineral of aluminium.
Ores:
- Ores contain a large percentage of metal.
- Ores can be used for the extraction of metals on a large scale readily and economically.
- Bauxite Al2O3. 2H2O is the ore of aluminium.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the various steps involved in the extraction of pure metals from their ores?
Answer:
Steps involved in the extraction of pure metals from their ores are
- Concentration of the ore
- Extraction of the crude metal.
- Refining of the crude metal.
Question 3.
What is the role of Limestone in the extraction of iron from its oxide Fe2O3?
Answer:
- Limestone (CaO) is used as a flux in the extraction of iron from its oxide Fe2O3.
- Flux is a chemical substance that forms an easily fusible slag with gangue.
- Oxide of iron can be reduced by carbon monoxide as follows
Fe2O3(s) + 3CO(g) → 2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g) ↑ - In this extraction, a basic flux quick lime (or) lime (CaO) reacts with acidic gangue silica to form the slag calcium silicate.
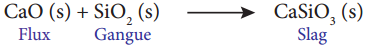
Question 4.
Which type of ores can be concentrated by froth floatation method? Give two examples for such ores.
Answer:
Sulphide ores can be concentrated by the froth floatation method.
e.g.,
- Copper pyrites (CuFeS2H2)
- Zinc blende (ZnS)
- Galena (PbS)
Question 5.
Describe a method for refining nickel Mond process for refining nickel: (PTA – 3)
Answer:
- Impure nickel is heated in a stream of carbon monoxide at around 350K. Nickel reacts with CO to form a highly volatile nickel tetracarbonyl. The solid impurities are left behind.
Ni(S) + 4CO(g) → Ni(Co)4(g) - On heating nickel tetra carbonyl around 460K, the complex decomposes to give a pure nickel.
Ni(CO)4(g) → Ni(S)+ 4CO(g)
Question 6.
Explain the zone refining process with an example. (PTA – 6 MARCH 2020)
Answer:
1. Zone Refining method is based on the principles of fractional crystallisation. When an impure metal is melted and allowed to solidify, the impurities will prefer to be in the molten region, i.e. impurities are more soluble in the melt than in the solid-state metal.
2. In this process, the impure metal is taken in the form of a rod. One end of the rod is heated using a mobile induction heater which results in the melting of the metal on that portion of the rod.
3. When the heater is slowly moved to the other end the pure metal crystallises while the impurities will move on to the adjacent molten zone formed due to the movement of the heater. As the heater moves further away, the molten zone containing impurities also moves along with it.
4. The process is repeated several times by moving the heater in the same direction again and again to achieve the desired purity level.
5. This process is carried out in an inert gas atmosphere to prevent the oxidation of metals.
6. Elements such as germanium (Ge), silicon (Si) and gallium (Ga) that are used as semiconductors are refined using this process.
![]()
Question 7.
Using the Ellingham diagram
(A) Predict the conditions under which
i) Aluminium might be expected to reduce magnesia.
ii) Magnesium could reduce alumina.
B) It is possible to reduce Fe2O3 by coke at a temperature around 1200K
Answer:
A) i) Ellingham diagram for the formation of Al2O3 and MgO intersects around 1600K. Above this temperature aluminium line lies below the magnesium line. Hence we can use aluminium to reduce magnesia above 1600K.
ii) In Ellingham diagram below 1600K magnesium line lies below aluminium line. Hence below 1600K magnesium can reduce alumina.
B) In Ellingham diagram above 1000K carbon line lies below the iron line. Hence it is possible to reduce Fe2O3 by coke at a temperature around 1200K.
Question 8.
Give the uses of zinc. (PTA – 4)
Answer:
- Metallic zinc is used in galvanisation to protect iron and steel structures from rusting and corrosion.
- Zinc is used to produce die – castings in the automobile, electrical and hardware industries.
- Zinc oxide is used in the manufacture of paints, rubber, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, plastics, inks, batteries, textiles and electrical equipment.
- Zinc sulphide is used in making luminous paints, fluorescent lights and x-ray screens.
- Brass an alloy of zinc which is highly resistant to corrosion is used in water valves and communication equipment.
Question 9.
Explain the electrometallurgy of aluminium.
Answer:
Hall – Heroult Process
Cathode: Iron tanked lined with carbon
Anode: Carbon blocks
Electrolyte: 20% solution of alumina obtained from bauxite + Molten Cryolite +10 % calcium chloride (lowers the melting point of the mixture)
Temperature: Above 1270K
Ionisation of Alumina Al2O3 → +2Al3+ + 3O2-
Reaction at cathode: Al3+ (melt) + 3e– → All
Reaction at anode : 2O2- (melt) → O2 (melt) + 4e–
Since carbon acts as anode the following reaction also takes place on it.
C(s) + O2 (melt) → CO + 2e–
C(s) + 2O2 (melt) → CO2 + 4e–
During electrolysis, anodes are slowly consumed due to the above two reactions. Pure aluminium is formed at the cathode and settles at the bottom.
Net electrolysis reaction is
4Al3+ (melt) + 6O2- (melt) + 3C(s) → 4Al(l) + 3CO2(g)
Question 10.
Explain the following terms with suitable examples, i) Gangue ii) Slag (PAT – 2)
Answer:
i) Gangue:
The non-metallic impurities, rocky materials and siliceous matter present in the ores are called gangue.
(eg): SiO2 is the gangue present in the iron ore Fe2O3.
ii) Slag:
Slag is a fusible chemical substance formed by the reaction of gangue with a flux.
![]()
Question 11.
Give the basic requirement for vapour phase refining.
Answer:
- The metal is treated with a suitable reagent to form a volatile compound.
- Then the volatile compound is decomposed to give the pure metal.
Question 12.
Describe the role of the following in the process mentioned.
i) Silica in the extraction of copper.
ii) Cryolite in the extraction of aluminium.
iii) Iodine in the refining of Zirconium.
iv) Sodium cyanide in froth floatation.
Answer:
i) In the extraction of copper silica acts as an acidic flux to remove FeO as slag FeSiO3.
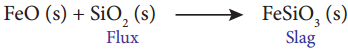
ii) As Al2O2 is a poor conductor cryolite improves the electrical conductivity.
In addition, crvolite serves as an added impurity and lowers the melting point of the electrolyte.
iii) First Iodine forms a Volatile tetraiodide with impure metal, which decomposes to give pure metal. Impure zirconium metal is heated in an evacuated vessel with iodine to form the volatile zirconium tetraiodide (Zrl4). The impurities are left behind, as they do not react with iodine.
Zr(S) + 2I2(S) → Zrl4(Vapour)
On passing volatile zirconium tetraiodide vapour over a tungsten filament, it is decomposed to give pure zirconium.
Zrl4(Vapour) → Zrl(S) + 2I2(S)
iv) Sodium cyanide acts as a depressing agent in froth floatation process. It prevent other metal sulphides from coming to the froth.
eg: NaCN depresses the floatation property ZnS present in Galena (PbS) by forming a layer of Zinc complex Na2[Zn(CN)4] on the surface of Zinc sulphide.
![]()
Question 13.
Explain the principle of electrolytic refining with an example. (PTA – 5)
Answer:
- Crude metal is refined by electrolysis carried out in an electrolytic cell.
- Cathode: Thin strips of pure metal.
Anode: Impure metal to be refined.
Electrolyte: Aqueous solution of the salt of the metal with dilute acid. - As the current is passed, the metal of interest dissolves from the anode and passes into the electrolytic solution.
- At the same time, same amount of metal ions from the electrolytic solution will be deposited at the cathode.
- Less electro positive impurities in the anode settle down as anode mud.
- eg: Electrorefining of silver:
Cathode: Pure silver Anode: Impure silver rods.
Electrolyte: Acidified aqueous solution of silver nitrate. - On passing current the following reactions will take place.
Reaction at anode: Ag(s) → Ag+(aq) + e–
Reaction at cathode: Ag+(aq) + e– → Ag(s) - At anode silver atoms lose electrons and enter the solution. From the solution silver ions migrate towards the cathode. At cathode silver ions get discharged by gaining electrons and deposited on the cathode.
Question 14.
The selection of reducing agent depends on the thermodynamic factor: Explain with an example.
Answer:
- A suitable reducing agent is selected based on the thermodynamic considerations.
- For a spontaneous reaction AG should be negative.
- Thermodynamically, the reduction of metal oxide with a given reducing agent can occur if AG for the coupled reaction is negative.
- Hence the reducing agent is selected in such a way that it provides a large negative value for the coupled reaction.
- Ellingham diagram is used to predict thermodynamic feasibility of reduction of oxides of one metal by another metal.
- Any metal can reduce the oxides of other metals that are located above it in the diagram.
- Ellingham diagram for the formation of FeO and CO intersects around 1000K. Below this temperature the carbon line lies above the iron line.
- Hence FeO is more stable than CO and the reduction is not thermodynamically feasible.
- However above 1000K carbon line lies below the iron line. Hence at this condition, FeO is less stable than CO and the reduction is thermodynamically feasible. So coke can be used as a reducing agent above this temperature.
- Following free energy calculation also confirm that the reduction is thermo¬dynamically favoured.
- From theEllingham diagram at 1500K
2Fe(s) + O2(g) → 2FeO(g) = 350 KJmol-1 …………….. 1
2C(s) + 022(g) → 2CO(g) = 480 KJmol-1 ……………… 2
Reverse the reaction 1
2FeO(s) → 2Fe(s) + O2(g) = 350 KJmol-1 ……………… 3
Couple the reactions 2 and 3
2FeO(s) + 2C(s) → 2Fe(s)+ 2CO(g) = 130 KJmol-1 ……………… 4 - The standard tree energy change for the reduction of one mole of FeO is = \(\frac{\Delta \mathrm{G}_{3}}{2}\) = -65 KJmol-1
Question 15.
Give the limitations of Ellingham diagram.
Answer:
- Ellingham diagram is constructed based only on thermodynamic considerations.
- It gives information about the thermodynamic feasibility of a reaction.
- It does not tell anything about the rate of the reaction.
- Moreover, it does not: give an idea about the possibility of other reactions that might be taking place.
- The interpreparation of G is based on the assumption that the reactants are in equilibrium with the product which is not always true.
Question 16.
Write a short note on electrochemical principles of metallurgy.
Answer:
- Reduction of oxides of active metals such as sodium, potassium etc. by carbon is thermodynamically not feasible.
- Such metals are extracted from their ores by using electrochemical methods.
- In this method the metal salts are taken infused form or in solution form.
- The metal ion present can be reduced by treating the solution with a suitable reducing agent or by electrolysis.
- Gibbs free energy change for the electrolysis is ∆G° = nFE°
n = number of electrons involved in the reduction
F = Faraday = 96500 coulombs
E° = electrode potential of the redox couple. - If E° is positive, is negative and the reduction is spontaneous.
- Hence a redox reaction is planned in such a way that the e.mi of the net redox reaction is positive.
A more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its salt solution.
eg;Cu2+(aq) + Zn(s) → Cu(s) + Zn2+(aq) - Zinc is more reactive than copper and displaces copper from its salt solution.
III. Evaluate yourself
Question 1.
Write the equation for the extraction of silver by leaching with sodium cyanide and show that the leaching process is a redox reaction.
Answer:
Ag → Ag+ (O.N increases from 0 to +1, hence oxidation)
O2 OH– (O.N decreases from 0 to -2, hence reduction)
The leaching of silver is a redox reaction.
Question 2.
Magnesite (Magnesium carbonate) is calcined to obtain magnesia, which is used to make refractory bricks. Write the decomposition reaction
Answer:
MgCO3\(\underrightarrow { \triangle } \) MgO + CO2
![]()
Question 3.
Using the Ellingham diagram (fig 1.4) indicates the lowest temperature at which ZnO can be reduced to Zinc metal by carbon. Write the overall reduction reaction at this temperature
Answer:
Ellingham diagram for the formation of ZnO and CO intersects around 1200K Below this temperature, Carbon line lies above Zinc line. Hence ZnO is more stable than CO so the reduction is thermodynamically not feasible at this temperature range. However above 1200K carbon line lies below the zinc line, hence carbon can be used as a reducing agent above 1200K.
2Zn + O2 → 2ZnO ………………….. 1
2C + O2 → 2CO ………………….. 2
Reversing 1 and adding with equation 2
2ZnO → 2Zn + O2
2C + O2 → 2CO
2ZnO +2C → 2Zn + 2CO
Question 4.
Metallic Sodium is extracted by the electrolysis of brine (aq.NaCl). After electrolysis, the electrolytic solution becomes basic in nature. Write the possible electrode reactions.
Answer:
2NaCl(aq) → 2Na+(aq) + 2Cl(aq)
Anode: 2Cl(aq) → Cl2(g) + 2e
Cathode: 2H2O(l) + 2e → H2(g) + 2OH(aq)
Nothing happens to sodium ion but it is still important. Na+ ions are spectator ions and combine with OH– ions to form NaOH
Three products are H2, Cl2 and NaOH
Over all equation is
2NaCl(aq) + 2H2O → H2(g) + Cl2(g) + 2NaOH(aq)
Ionic equation is
2H2O(l) + 2Cl–(aq) + 2Na–(aq) → 2Na+(aq) + 2OH(aq) + H2(g) + Cl2(g)
(or)
2H2O(l) + 2Cl–(aq) → 2OH(aq) + H2(g) + Cl2(g)
12th Chemistry Guide Metallurgy Additional Questions and Answers
Part – II – Additional Questions one mark
I. Match the following
1.
| Ore | Formula |
| 1. Magnetite | a) ZnCO3 |
| 2. Cuprite | b) PbCO3 |
| 3. Calamine | c) Fe3O4 |
| 4. Cerrusite | d) SnO2 |
| 5. Cassiterite | e) Cu2O |
Answer:
| Ore | Formula |
| 1. Magnetite | c) Fe3O4 |
| 2. Cuprite | e) Cu2O |
| 3. Calamine | a) ZnCO3 |
| 4. Cerrusite | b) PbCO3 |
| 5. Cassiterite | d) SnO2 |
2.
| Ore of metal | Name |
| 1. Ore of copper | a) Diaspore |
| 2. Ore of aluminium | b) Chlorargyrite |
| 3. Ore of iron | c) Malachite |
| 4. Ore of lead | d) Limonite |
| 5. Ore of silver | e) Anglesite |
Answer:
| Ore of metal | Name |
| 1. Ore of copper | c) Malachite |
| 2. Ore of aluminium | a) Diaspore |
| 3. Ore of iron | d) Limonite |
| 4. Ore of lead | e) Anglesite |
| 5. Ore of silver | b) Chlorargyrite |
3.
| Concentration | Ore |
| Gravity separation | a) Pyrolusite |
| Froth floatation | b) Alumina |
| Cyanide leaching | c) Zinc blende |
| Alkali leaching | d) Tinstone |
| Magnetic separation | e) Gold |
Answer:
| Concentration | Ore |
| Gravity separation | d) Tinstone |
| Froth floatation | c) Zinc blende |
| Cyanide leaching | e) Gold |
| Alkali leaching | b) Alumina |
| Magnetic separation | a) Pyrolusite |
4.
| Purification | Metal |
| 1. Distillation | a) Silicon |
| 2. Liquation | b) Zinc |
| 3. Electrolytic refining | c) Nickel |
| 4. Zone refining | d) Tin |
| 5. Mond process | e) Silver |
Answer:
| Purification | Metal |
| 1. Distillation | b) Zinc |
| 2. Liquation | d) Tin |
| 3. Electrolytic refining | e) Silver |
| 4. Zone refining | a) Silicon |
| 5. Mond process | c) Nickel |
II. Fill in the blanks
1. The metal which shows high resistance to corrosion and used in the design of Chemical reactors is ___________ .
Answer:
Aluminium
2. ___________ are used for increasing the efficiency of the solar cells.
Answer:
Gold nanoparticles
3. The removal of gangue from ores is called as ___________ .
Answer:
Concentration of ores
4. ___________ is the process in which concentrated ore is strongly heated in the absence of air.
Answer:
Calcination
III. Find the odd man out.
1. a) Sphalerite b) Galena c) Azurite d) Iron pyrite
Answer:
c) Azurite. This is a basic carbonate ore others are sulphide ores.
2. a) Malachite b) Limonite c) Siderite d) Haematite
Answer:
a) Malachite. This is the ore of copper, others are ores of iron.
IV. Choose the incorrect pair.
1. a) Malachite, Azurite b) Ruby silver, Horn silver c) Zincite, Cuprite d) Anglesite, Cerrusite
Answer:
c) Zincite, Cuprite. They are ores of Zinc and copper
![]()
2. a) Kaolinite, Aluminium b) Stefinite, Silver c) Galena, Lead d) Prousitite, Tin
Answer:
d) Prousitite, Tin. Correct pair is prousitite, silver.
V. Choose the correct pair.
1. Choose the correct pair.
a) Cerrusite, Cassiterite b) Siderite, Limonite c) Anglesite, Zincite d) Azurite, Kaolinite
Answer:
b) Siderite, Limonite. Both are ores of irons.
2. a) Diaspore, Copper b) Galena, Tin c) Stefinite, Silver d) Malachite, Aluminium
Answer:
c) Stefinite, Silver. Stefinite is the ore of silver
VI. Assertion and Reason
1. Assertion (A): Tinstone ore is concentrated by magnetic separation.
Reason (R) : Wolframite impurities are magnetic
i) A and R are correct, R explains A.
ii) A is correct, R is wrong
iii) A is wrong, R is correct
iv) A and R are correct but R does not explain A.
Answer:
i) A and R are correct, R explains A. 2
2. Correct Assertion (A): Aluminium can be commercially extracted from china clay which is a profitable one
Reason (R): China clay is a mineral of aluminium.
i) A and R are correct, R explains A.
ii) A is correct, R is wrong
iii) A is wrong, R is correct
iv) A and R are correct but R does not explain A.
Answer:
iii) A is wrong, R is correct
Correct Assertion: Aluminium can be commercially extracted from bauxite which is a profitable ore
![]()
3. Assertion (A): Zinc blend can be concentrated by the froth floatation method.
Reason (R) : Metallic ore particles are preferentially wetted by water and settle at the bottom.
A and R are correct, R explains A.
A is correct, R is wrong A is wrong, R is correct A and R are correct but R does not explain A.
Answer:
ii) A is correct, R is wrong
Correct (R) : Metallic particles are preferentially wetted by oil and rise to the surface.
4. Assertion (A) : Cr2O3 is reduced into chromium by aluminothermic process.
Reason (R): Aluminium acts as the reducing agent.
i) A and R are correct, R explains A.
ii) A is correct, R is wrong
iii) A is wrong, R is correct
iv) A and R are correct but R does not explain A.
Answer:
i) A and R are correct, R explains A.
VII. Choose the correct statement
1. a) Metals having more chemical reactivity occur as native elements.
b) Removal of gangue from ores is called refining.
c) Tin stone ore is concentrated by gravity separation.
d) Silver glance is a carbonate ore.
Answer:
c) Tin stone ore is concentrated by gravity separation.
2. a) In froth floatation sodium ethyl xanthate acts as a collector.
b) In leaching the ore is converted into insoluble salt or complex and the gangue remains in the solution.
c) Ammonia leaching is suitable for gold and silver.
d) Bauxite ore is subjected to acid leaching.
Answer:
a) In froth floatation sodium ethyl xanthate acts as a collector.
![]()
3. a) Calcination is the process in which concentrated ore is strongly heated in the presence of air.
b) Flux is a chemical substance that forms an easily fusible slag with gangue.
c) In aluminothermic process the ignition mixture used is magnesium peroxide and barium.
d) Any metal can reduce the oxides of other metals that are located below it in Ellingham diagram.
Answer:
b) Flux is a chemical substance that forms an easily fusible slag with gangue.
4. a) In electrorefining pure metal is taken as anode and impure metal is taken as cathode.
b) Distillation is employed for high boiling nonvolatile metals.
c) Zone refining is based on the principle of fractional crystallisation.
d) Mond’s process is used for refining titanium.
Answer:
c) Zone refining is based on the principle of fractional crystallisation.
VIII. Choose the incorrect statement
1. i) In cyanide leaching gold is converted into an insoluble cyanide complex.
ii) In ammonia leaching nickel forms a soluble complex.
iii) In alkali leaching aluminum forms an insoluble complex,
a) i & ii
b) i & iii
c) ii & iii
d) i, ii, iii
Answer:
D) i,ii & iii
2. i) In the Ellingham diagram for most of the metal oxide forming the slope is negative.
ii) Oxygen gas is consumed during the formation of metal oxides resulting in the increase of randomness.
iii) As temperature increases value for the formation of the metal oxide become more negative
a) i & ii
b) i & iii
c) ii & iii
d) i, ii, & iii
Answer:
c) ii & iii
3. i) The reduction of oxides of active metals such as sodium, potassium, etc. by carbon is thermodynamically feasible
ii) When a more reactive metal is added to the solution containing less reactive metal, the less reactive metal will go into the solution.
iii) Copper displaces zinc from zinc salt
solution.
a) i & ii
b) i & iii
c) ii & iii
d) i, ii, iii
Answer:
d) i, ii & iii
![]()
4. i) When an impure metal is melted and allowed to solidify, the impurities will prefer to be in the solid region.
ii) Zone refining is carried out in an inert gas atmosphere to prevent the reduction of metals.
iii) Elements such as germanium, silicon, and gallium are refined by zone refining.
a) i & ii
b) i & iii
c) ii & iii
d) i, ii, iii
Answer:
a) i & ii
IX. Choose the best answer.
1. Which of the following is not an oxide ore?
a) Cuprite
b) Siderite
c) Cassiterite
d) Zincite
Answer:
b) Siderite
2. Which of the following is an oxide ore?
a) Sphalerite
b) Calamine
c) Cassiterite
d) Stefinite
Answer:
c) Cassiterite
3. The process of converting hydrated alumina into anhydrous alumina is called
a) Roasting
b) Smelting
c) Auto-reduction
d) Calcination
Answer:
d) Calcination
4. Which of the following is a sulphide ore?
a) Pyrargyrite
b) Malachite
c) Limonite
d) Kaolinite
Answer:
a) Pyrargyrite
![]()
5. Which of the following is not a carbonate ore?
a) Siderite
b) Calamine
c) Cerrusite
d) Cassiterite
Answer:
d) Cassiterite
6. Which of the following is a carbonate ore?
a) Limonite
b) Siderite
c) Magnetite
d) Haematite
Answer:
b) Siderite
7. Which of the following is the ore of iron?
a) Limonite
b) Azurite
c) Stefinite
d) Cerrusite
Answer:
a) Limonite
8. Which of the following is not an ore of iron?
a) Haematite
b) Magnetite
c) Siderite
d) Anglesite
Answer:
d) Anglesite
9. Which of the following is an ore of silver?
a) Azurite
b) Prousitite
c) Cerrusite
d) Limonite
Answer:
b) Prousitite
10. Which of the following is a sulphate ore?
a) Galena
b) Zinc blende
c) Cerrusite
d) Anglesite
Answer:
d) Anglesite
11. Non-metallic impurities, rocky materials, and siliceous matter which are associated with ores are called as.
a) Slag
b) Flux
c) Gangue
d) residue
Answer:
c) Gangue
![]()
12. Gravity separation is suitable for
a) Oxide ore
b) Sulphide ore
c) Carbonate ore
d) Sulphate ore
Answer:
a) Oxide ore
13. Froth floatation is suitable for
a) Oxide ore
b) Sulphide ore
c) Carbonate ore
d) Sulphate ore
Answer:
b) Sulphide ore
14. In froth floatation, pine oil is used as a
a) Collector
b) depressing agent
c) Frothing agent
d) Flux
Answer:
c) Frothing agent
15. In froth floatation sodium ethyl Xanthate is used as a
a) Collector
b) depressing agent
c) frothing agent
d) Flux
Answer:
a) Collector
16. In froth floatation sodium cyanide is used as a
a) Collector
b) depressing agent
c) frothing agent
d) Flux
Answer:
b) depressing agent
17. The floatation property of the impurity ZnS present in galena is depressed by adding
a) Pure oil
b) Eucalyptus oil
c) Sodium cyanide
d) Sodium ethyl Xanthate
Answer:
c) Sodium cyanide
18. Which method of purification represented by the equation?
Ti(Impure) + 2I2 \(\underrightarrow { 550K } \) Til4 \(\underrightarrow { 1800K } \) Ti(pure) + 2I2
a) Cupellation
b) Zone refining
c) Van-Arkel method
d) Mond’s process
Answer:
c) Van-Arkel method
![]()
19. Concentration of gold ore is done by
a) Cyanide leaching
b) Ammonia leaching
c) Alkali leaching
d) Acid leaching
Answer:
a) Cyanide leaching
20. Ammonia leaching is done for the concentration of the ore of
a) Silver
b) Copper
c) Aluminium
d) Zinc
Answer:
b) Copper
21. During roasting sulphide ores are converted into their
a) Metals
b) Oxides
c) Carbonates
d) nitrates
Answer:
b) Oxides
22. During the calcination of carbonate ore the expelled gas is
a) Carbon monoxide
b) Carbon dioxide
c) Sulphur dioxide
d) Nitrogen dioxide
Answer:
b) Carbon dioxide
23. Sulphite ores of metals are usually concentrated by froth floatation process. Which one of the following sulphide ore offers an exception and is concentrated by chemical leaching.
a) Argentite
b) galena
c) Copper pyrites
d) Sphalerite
Answer:
a) Argentite
24. Cinnabar is converted into mercury by
a) Reduction by metal
b) Reduction by hydrogen
c) Reduction by carbon
d) Auto reduction
Answer:
d) Auto reduction
25. Thermodynamically the reduction of metal oxide with a given reducing agent can occur if the free energy change for the coupled reaction is
a) Positive
b) Negative
c) One
d) Zero
Answer:
b) Negative
26. For the reduction of metal oxide into metal a reducing agent is selected in such a way that for the coupled reaction it provides a
a) Large positive G value
b) Small positive G value
c) Large negative G value
d) Small negative G value
Answer:
c) Large negative G value
27. For the formation of various metal oxides Ellingham diagram is a graphical representation between
a) G° & S
b) G° & H
c) G° & T
d) H & S
Answer:
c) G° & T
28. In the Ellingham diagram, for most of the metal oxide formation the slope is
a) Positive
b) Negative
c) Zero
d) One
Answer:
a) Positive
29. Elements like Silicon and Germanium to be used as a semiconductor is purified by (PTA – 1)
a) heating under Vaccum
b) Van-Arkel method
c) Zone refining
d) Electrolysis
Answer:
c)Zone refining
30. If the e.m.f of the net redox reaction is positive, its G is
a) Positive
b) Negative
c) Zero
d) One
Answer:
b) Negative
31. Which of the following metal is refined by distillation?
a) Tin
b) Lead
c) Zinc
d) Bismuth
Answer:
c) Zinc
32. Which of the following is not refined by zone refining?
a) Germanium
b) Zirconium
c) Silicon
d) Gallium
Answer:
b) Zirconium
![]()
33. Which of the following is refined by the Mond process?
a) Silicon
b) Copper
c) Nickel
d) Zinc
Answer:
c) Nickel
34. Which of the following is defined by Van
Arkel method?
a) Gallium
b) Titanium
c) Germanium
d) Silicon
Answer:
b) Titanium
35. Which of the following metal is used in galvanization?
a) Copper
b) Aluminium
c) Zinc
d) Gold
Answer:
c) Zinc
36. Which is used in making luminous paints, fluorescent lights, and x-ray screens?
a) Brass
b) Zinc sulphide
c) Cast iron
d) Gold nanoparticles
Answer:
b) Zinc sulphide
37. Which is used for increasing the efficiency of solar cells?
a) Brass
b) Zinc sulphide
c) Cast iron
d) Gold nanoparticles
Answer:
d) Gold nanoparticles
38. Which is not refined by liquation?
a) Tin
b) Zinc
c) Lead
d) Bismuth
Answer:
b) Zinc. Zinc is refined by distillation.
39. Which is not refined by zone refining?
a) Silicon
b) Gallium
c) Zirconium
d) Germanium
Answer:
c) Zirconium. Zirconium is refined by Van Arkel method
X. Two Mark Questions
Question 1.
What is a mineral?
Answer:
A naturally occurring substance obtained by mining, which contains the metal in a free state or in the form of compounds like oxides, sulphides, etc; is called a mineral.
Question 2.
What is an ore?
Answer:
A mineral which contains high percentage of metal, from which it can be extracted conveniently and economically is called an ore.
![]()
Question 3.
What is a concentration of ores?
Answer:
The removal of non metallic impurities, rocky materials and siliceous matter (called as gangue) from the ores is known as concentration of ores.
Question 4.
What is leaching?
Answer:
The process of dissolving metal present in an ore in a suitable solvent to form a soluble metal salt or complex leaving the gangue undissolved is called leaching.
Question 5.
What is the reaction of Ammonia with Iron and copper salts? (PTA – 4)
Answer:
Ammonia reacts with metallic salts to give metal hydroxides (in case of Fe) or forming complexes (in case of Cu)
Fe3+ + 3NH+4 → Fe(OH)3 + 3NH+4
Cu2+ + 4NH3 → [Cu(NH3)4 ]2+
Tetra ammine copper (II) ion
Question 6.
What is acid leaching?
Answer:
- Sulphide ores ZnS, PbS can be leached with hot aqueous sulphuric acid.
- In this process, the insoluble sulphide is converted into soluble sulphate and elemental sulphur.
2ZnS(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) + O2(g) → 2ZnSO4(aq) + 2S(s) + 2H2O
Question 7.
What is the role of the depressing agent In the froth flotation process? (PTA – 1)
Answer:
When impurities such as ZnS is present in galena (PbS), sodium cyanide (NaCN) is added to depresses the flotation property of ZnS by forming a layer of zinc complex Na2[Zn(CN)4] on the surface of zinc sulphide.
![]()
Question 8.
In the extraction of metal, the ore is first converted into metal oxide before reduction into metal, why?
Answer:
- In the concentrated ore, the metal exists in a positive oxidation state and hence it is to be reduced to an elemental state.
- From the principles of thermodynamics, the reduction of oxide is easier compared to the reduction of other compounds of metal.
- Hence before reduction, the ore is first converted into metal oxide.
Question 9.
Write about roasting.
Answer:
- Roasting is applied for the conversion of sulphide ores into their oxides.
- Concentrated ore is oxidised by heating with excess of oxygen below the melting point of the metal in a suitable furnace.
2PbS + 3O2 → 2PbO+ 2SO2 ↑ - Roasting also removes impurities like aresenic, sulphur, phosphorous into their volatile oxides.
4As + 3O2 → 2AS2O3
Question 10.
Write about the extraction of metal by the process of reduction by carbon.
Answer:
- In this method oxide ore of the metal is mixed with coal (coke) and heated strongly in a blast furnace.
- This method can be applied to metals which do not form carbides with carbon at the reduction temperature.
ZnO(s) + C → Zn(s) + CO(g) ↑
Question 11.
Write about the extraction of metal by the process of reduction by hydrogen.
Answer:
- This method can be applied to the oxides of the metals (Fe, Pb, Cu) which are less electropositive than hydrogen.
Ag2O(s) + H2(g) 2Ag(s) + H2O(l) ↑ - Nickel oxide is reduced to nickel by a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide (water gas)
2NiO(s) + CO(g) + H2(g) → 2Ni(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) ↑
Question 12.
Write about the extraction of metal by the process of reduction by metal.
Answer:
- In this process a metal oxide is reduced to metal by some active metals, like sodium, potassium and calcium.
Rb2O3 + 3Mg → 2Rb + 3MgO
TiO2 + 2Mg → Ti + 2MgO
ThO2 + 2Ca \(\underrightarrow { 1260K } \) Th + 2CaO - Alumino thermite process is also an example of reduction by metal.
Question 13.
How Cr2O3 is reduced to Cr by Al powder? (PTA – 6)
Answer:
- In this method a metal oxide is reduced to metal by aluminium.
- It is an exothermic process where heat is liberated.
- Cr2O3 is mixed with aluminium powder in a fire clay crucible.
- Ignition mixture is magnesium and barium peroxide.
BBaO2 + Mg —> BaO + MgO - Temperature = 2400°C Heat liberated = 852KJmol-1 This heat helps the reduction of Cr2O3 by Al.
Cr2O3 + 2Al \(\underrightarrow { \triangle } \) 2Cr + Al2O3
Question 14.
What is auto reduction of metallic ores?
Answer:
- Simple roasting of some of the metallic ores give the crude metal.
- Use of reducing agent is not necessary.
- (eg) Cinnabar is roasted to give mercury.
HgS(s) + O2(g) → Hg(l) + SO2(g) ↑
Question 15.
What is the role of graphite rods in the electrometallurgy of Aluminium? (PTA – 1)
Answer:
Electrolysis is carried in an iron tank lined with carbon which acts as a cathode. The carbon blocks immersed in the electrolyte acts as a anode.
![]()
Question 16.
Write about the distillation process of refining a metal?
Answer:
In this method, impure metal is heated to evaporate and the vapours are condensed to get pure metal.
This method is used for low boiling volatile metals like zinc and mercury.
Question 17.
Write about the liquation process of refining a metal?
Answer:
- This method is used to remove the impurities with high melting points from metals having relatively low melting points,
(eg) Tin, lead, mercury, bismuth. - Crude metal is heated to form a fusible liquid and allowed to flow on a sloping surface.
- Impure metal is placed on the sloping hearth of a reverberatory furnace.
- Impure metal is heated just above the melting point of the metal in the absence of air.
- The molten pure metal flows down. Impurities are left behind.
- Molten metal is collected and solidified.
Question 18.
Write the applications or uses of copper.
Answer:
- Copper is the first metal used by humans and extended use of its alloy bronze resulted in a new era, ‘Bronze age’.
- Used for making coins and ornaments along with gold and other metals.
- Copper and its alloys are used for making wires, water pipes and other electrical parts.
Question 19.
Write the applications or uses of gold.
Answer:
- Gold is one of the expensive and precious metals.
- Used for coinage and has been used as standard for monetary systems in some countries.
- Extensively used in jewellery in its alloy form with copper.
- Used in electroplating to cover other metals with a thin layer of gold in watches, artificial limb joints, cheap jewelry, dental fillings and electrical connectors.
- Gold nanoparticles are used for increasing the efficiency of solar cells.
- Used as catalyst.
Question 20.
Describe the underlying principle of froth floation process. (PTA – 3)
Answer:
This method is commonly used to concentrate sulphide ores such as galena (pbs) Zinc blende (Zns)
In this method, the metalic ore particles which are preferentially wetted by oil can be separated from gangue.
XI. Three Mark Questions
Question 1.
Write about gravity separation or hydraulic wash?
Answer:
- Ore with high specific gravity is separated from gangue with low specific gravity by simply washing with running water.
- The finely powdered ore is treated with rapidly flowing current of water.
- Lighter gangue particles are washed away by the running water.
- This method is used for concentrating native ore such as gold and oxide ores such as haematite, tinstone.
Question 2.
What is cyanide leaching?
Answer:
- Crushed ore of gold is leached with aerated dilute solution of sodium cyanide.
- Gold is converted into a soluble cyanide complex.
- The gangue alumino silicate remains insoluble.
4Au(s) + 8CN–(aq) + O2(g)+ 2H2O(l) → 4[Au(CN)2]–(aq) + 4OH–(aq) - Gold can be recovered by reacting the deoxygenated leached solution with Zinc. Gold is reduced to its elemental state (zero oxidation state.)
- This process is called cementation.
Zn(s) + 2[Au(CN)2]–(aq) → [Zn(CN)4]2-(aq) + 2Au(s)
Question 3.
Write about alkali leaching?
Answer:
- In this method, the ore is heated with aqueous alkali to form a soluble complex.
- Bauxite is heated with a solution of sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate at 470K – 520K and 35 atm to form soluble sodium meta aluminate.
- The impurities iron oxide and titanium oxide are left behind.
Al2O3(s) + 2NaOH(aq) + 3H2O(l) → 2Na [Al(OH)4](aq) - The hot solution is decanted, cooled and diluted.
- This solution is neutralised by passing CO2 gas to form a hydrated Al2O3 precipitate.
2Na[AZ(0H)4](aq)4CO2(g) → Al2O3.XH2O(s) + 2NaHCO3(aq) - The precipitate is filtered off and heated around 1670K to get pure Alumina Al2O3.
Question 4.
Write about magnetic separation.
Answer:
- This method is applicable to ferromagnetic ores.
- It is based on the difference in the magnetic properties of the ore and the impurities.
- Non-magnetic tin stone can be separated from the magnetic impurities wolframite.
- Similarly magnetic ores chromite, pyrolusite can be removed from non-magnetic siliceous impurities.
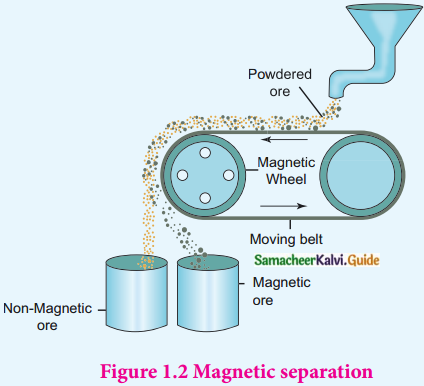
- Crushed ore is poured on to an electromagnetic separator with a belt moving over two rollers of which one is magnetic.
- The magnetic part of the ore is attracted towards the magnet and falls as a heap close to the magnetic region.
- The non-magnetic part falls away from it.
Question 5.
Write about calcination. (PTA – 4)
Answer:
- Calcination is the process in which the concentrated ore is strongly heated in the absence of air.
- During this process water of crystallisation present in the hydrated oxide escapes as moisture.
- Any organic matter present also get expelled leaving the ore porous.
- This method can also be carried out with a limited supply of air.
- During the calcination of carbonate ore, carbon dioxide is liberated.
PbCO3 \(\underrightarrow { \triangle } \) PbO + CO2 ↑
CaCO3 \(\underrightarrow { \triangle } \) CaO + CO2 ↑
Al2O3. 2H2O \(\underrightarrow { \triangle } \) Al2O3(s) + 2H2O(g) ↑
![]()
Question 6.
Write about smelting.
Answer:
- Smelting is a process in which the concentrated ore is mixed with a mixture of a flux and reducing agent in a smelting furnace.
- Flux is a chemical substance which forms an easily fusible slag with gangue.
- Carbon, carbon monoxide, and aluminium are used as reducing agents.
- Iron oxide can be reduced by carbon monoxide.
Fe2O3(s) + 3CO(g) → 2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g) ↑ - Silica gangue present m the ore is acidic, hence a basic flux lime combines with it forming slag calcium silicate.
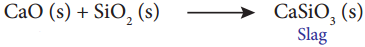
Question 7.
Write about the Ellingham diagram.
Answer:
- The graphical representation of the variation of the standard Gibbs free energy for the formation of various metal oxides with temperature is called the Ellingham diagram.
- Change in Gibbs free energy ∆G is given as ∆G = ∆H – T∆S
∆H = Enthalpy change T = Temperature in Kelvin S = Entropy change. - For an equilibrium, ∆G° can be calculated using the equilibrium constant by the equation.
∆G° = -RT In Kp - By treating the reduction of metal oxides as an equilibrium process Harold Ellingham used the above relationship to calculate ∆G° values at various temperatures.
- Fie Plotted T in the x-axis and ∆G° for the formation of metal oxides in the y axis.
- He obtained a straight line graph with ∆S as slope and ∆H as the y-intercept.
Question 8.
Write the observations from the Ellingham diagram.
Answer:
- For most of the metal oxide forming the slope is positive. This can be explained as follows. Oxygen gas is consumed during the formation of metal oxides resulting in the decrease of randomness. Hence ∆S becomes negative, T∆S is positive in the straight line equation.
- For the formation of carbon monoxide the graph is a straight line with a negative slope. In this case ∆S is positive because 2 moles of CO. gas is formed by consuming 1 mole of oxygen gas. This shows CO is more stable at higher temperature.
- As temperature increases ∆G for the formation of metal oxide becomes less negative and becomes zero at a particular temperature. Below this temperature is negative and the oxide is stable. Above this temperature ∆G is positive and the oxide is less stable. Metal oxides become less stable at higher temperature and their decomposition becomes easier.
- Due to phase transition (melting or evaporation) there is a sudden change in the slope at a particular temperature for some metal oxides like MgO, HgO.
Question 9.
Write about Van – Arkel method for refining zirconium/titanium?
Answer:
- This method is based on the thermal decomposition of metal compounds to metals.
(eg) Titanium and Zirconium. - Impure titanium is heated in an evacuated vessel with iodine at 550K to form volatile titanium tetraiodide.
- The impurities do not react with iodine.
Ti(s) + 2I2(s) → Til4(vapour) - Volatile titanium tetraiodide is passed over a tungsten filament at 1800K.
- Titanium tetraiodide is decomposed to pure titanium which is deposited over the filament.
- Iodine is reused. TiI4(vapour) → Ti(s) + 2I2(s)
Question 10.
Write the applications or uses of aluminium.
Answer:
- For making heat exchangers/ sinks.
- For making our day to day vessels.
- For making aluminium foils for packing, food items.
- Alloys of aluminium with copper, manganese, magnesium, silicon are lightweight and strong hence used in design of aeroplanes and other forms of transport.
- Due to its high resistance to corrosion, it is used in the design of chemical reactors, medical equipments, refrigeration units and gas pipelines.
- It is a good electrical conductor and cheap, hence used in electrical overhead cables with a steel core for strength.
![]()
Question 11.
Write the applications or uses of iron.
Answer:
- Iron is one the most useful metals and its alloys are used everywhere including bridges, electricity pylons, bicycle chains, cutting tools and rifle barrels.
- Cast iron is used to make pipes, valves and pumps stoves etc.
- Magnets can be made of iron and its alloys and compounds.
- An important alloy of iron is stainless steel which is very resistant to corrosion.
- It is used in architecture, bearings, cutlery, surgical instruments and jewellery.
- Nickel steel is used for making cables, automobiles, and aeroplane parts.
- Chrome steels are used for manufacturing cutting tools and crushing machines.
Question 12.
Out of coke and CO, which is a better reducing agent for the reduction of ZnO? why? (PTA – 2)
Answer:
- Out of coke and CO, coke is a better reducing agent than CO for the reduction of ZnO.
- Reduction by carbon can be applied to zinc which does not form carbide with carbon at the reduction temperature.
ZnO(s) + C → Zn(s) + CO(g) ↑ - ZnO lies above CO in the Ellingham diagram meaning that CO is more stable than ZnO. Hence carbon can be used as a reducing agent for the reduction of ZnO. During reduction oxygen from ZnO combines with carbon used for reduction.
XII. Five Mark Questions
Question 1.
Explain the froth floatation method.
Answer:
- This is used to concentrate sulphide ores such as galena (PbS) Zinc blende (ZnS) etc.
- Metallic ore particles preferentially wetted by oil can be separated from gangue.
- Crushed ore is mixed with water and a frothing agent like pine oil or eucalyptus oil.
- A small amount of sodium ethyl xanthate is added as a collector.
- A froth is formed by blowing air through the mixture.
- The collector molecules attach to the ore particles and make them water repellent.
- As a result ore particles wetted by the oil rise to the surface along with the froth.
- The froth is skimmed off and dried to recover the concentrated ore.
- Gangue particles preferentially wetted by water settle at the bottom.
- If the sulphide ore contains other metal sulphides as impurities, they are selectively prevented from coming to the froth by using depressing agents like sodium cyanide, sodium carbonate, etc.
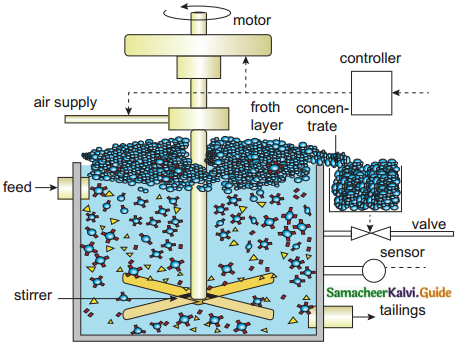
- Sodium cyanide depresses the floatation property of the impurity ZnS present in galena (PbS) by forming a layer of zinc complex Na2[Zn(CN)4] on the surface of ZnS.
Question 2.
How is copper extracted from its ore. (PTA – 5)
Answer:
- Principle ore: Copper pyrites.
- Concentration: Froth floatation Concentrated ore is heated in a reverberatory furnace with an acidic flux silica.
- The basic ferrous oxide formed reacts with silica to form the slag ferrous silicate.
- Mutually soluble metal sulphides Cu2S and FeS known as copper matte is formed.
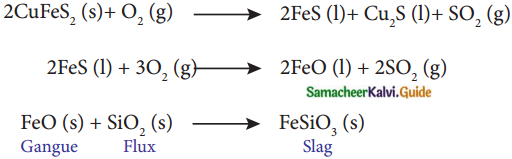
- Matte is removed from the slag and fed to the converting furnace.
- FeS present in the matte is first converted to FeO.
- FeO is removed as slag with silica.
- The remaining copper sulfide is oxidised to cuprous oxide.
- Cuprous oxide and copper sulphide react to form metallic copper. :
2Cu2S(l,s) + 3O2(g) 2Cu2O(l,s) + 2SO2(g)
2Cu2O(l) 6Cu(l) + SO2(g) - SO2 is liberated through molten copper and on solidification it has blistered appearance. This copper is called blister copper.
Electrorefining:
Cathode: Thin pure sheet of copper.
Anode: Impure Copper
Electrolyte: CuSO4 solution + dil H2SO4
On passing, current pure copper is deposited at the cathode.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the thermodynamic principle of metallurgy.
Answer:
- Extraction of metals can be carried out by using different reducing agents.
- Consider the reduction of a metal oxide Mx Oy
\(\frac{2}{Y}\) MxOy(s) → \(\frac{2}{Y}\)M(s) + O2(g) ……………….. 1 - Above reduction may be carried out with carbon.
- In this case the reducing agent carbon may be oxidised to CO or CO2
C + O2 → CO2(g) …………….. 2
2C + O2 → 2CO(g) ……………………… 3 - If carbon monoxide is used as a reducing agent, it is oxidised to CO2
2CO + O2 → 2CO2 ……………………… 4 - A suitable reducing agent is selected based on thermodynamic considerations.
- For a spontaneous reaction, the change in free energy ∆G should be negative.
- Thermodynamically the reduction of metal oxide [equation (1)] with a given reducing agent [equation 2,3, or 4] can occur if the free energy change for the coupled reaction [equation 1&2, 1&3 or 1&4] is negative.
- Hence the reducing agent which gives large negative ∆G value for the coupled reaction is selected.
Question 4.
Write the applications of Eliingham diagram.
Answer:
- Eliingham diagram helps us to select a suitable reducing agent and appropriate temperature range for reduction.
- Reduction of metal oxide to metal is considered as a competition between the element used for reduction and the metal to combine with oxygen.
- If metal oxide is more stable, oxygen remains with the metal.
- If oxide of the element used for reduction is more stable, oxygen from metal oxide combines with the element used for reduction.
- From Eliingham diagram the relative stablility of different metal oxides at a given temperature can be inferred.
- Eliingham diagram for the formation of Ag2O and HgO is at the upper part and their decomposition temperatures are 600 and 700K respectively. This shows that these oxides are unstable at moderate temperatures and will decompose on heating even in the absence of a reducing agent.
- Eliingham diagram is used to predict the thermodynamic feasibility of reduction of oxides of one metal by another metal.
- For example, in the Eliingham diagram, the line for the formation chromium oxide ties above that of aluminium, meaning that Al2O3 is more stable than Cr2O3. Hence aluminium can be used as a reducing agent for the reduction of chromic oxide.
- However, aluminium can not be used to reduce the oxides of magnesium and calcium since they occupy lower position than aluminium oxide in the Eliingham diagram.
- Any metal can reduce the oxides of other metals that are located above it in the diagram.
- Carbon line cuts across the lines of many metal oxides and hence it can reduce all these metal oxides at sufficently high temperature.