Students can download 10th Science Chapter 18 Heredity Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Solutions Chapter 18 Heredity
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Heredity Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
According to Mendel alleles have the following character:
(a) Pair of genes
(b) Responsible for character
(c) Production of gametes
(d) Recessive factors
Answer:
(b) Responsible for character
Question 2.
9 : 3 : 3 : 1 ratio is due to ______.
(a) Segregation
(b) Crossing over
(c) Independent assortment
(d) Recessiveness.
Answer:
(c) Independent assortment
![]()
Question 3.
The region of the chromosome where the spindle fibres get attached during cell division:
(a) Chromomere
(b) Centrosome
(c) Centromere
(d) Chromonema
Answer:
(c) Centromere
Question 4.
The centromere is found at the centre of the ______ chromosome.
(a) Telocentric
(b) Metacentric
(c) Sub – metacentric
(d) Acrocentric.
Answer:
(b) Metacentric
Question 5.
The units form the backbone of the DNA.
(a) 5 carbon sugar
(b) Phosphate
(c) Nitrogenous bases
(d) Sugar phosphate
Answer:
(d) Sugar phosphate
Question 6.
Okazaki fragments are joined together by ______.
(a) Helicase
(b) DNA polymerase
(c) RNA primer
(d) DNA ligase.
Answer:
(d) DNA ligase.
Question 7.
The number of chromosomes found in human beings are:
(a) 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of allosomes.
(b) 22 autosomes and 1 allosome
(c) 46 autosomes
(d) 46 pairs autosomes and 1 pair of allosomes.
Answer:
(a) 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of allosomes.
Question 8.
The loss of one or more chromosome in ploidy is called ______.
(a) Tetraploidy
(b) Aneuploidy
(c) Euploidy
(d) Polyploidy.
Answer:
(b) Aneuploidy
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks:
- The pairs of contrasting character (traits) of Mendel are called ……..
- Physical expression of a gene is called ………..
- The thin thread like structures found in the nucleus of each cell are called ……….
- DNA consists of two ……….. chains.
- An inheritable change in the amount or the structure of a gene or a chromosome is called ……….
Answer:
- alleles or allelomorphs
- Phenotype
- Chromosomes
- Polynucleotide chain
- Mutation
III. Identify whether the statement are True or False. Correct the false statement.
- A typical Mendelian dihybrid ratio of F2 generation is 3 : 1.
- A recessive factor is altered by the presence of a dominant factor.
- Each gamete has only one allele of a gene.
- Hybrid is an offspring from a cross between genetically different parent.
- Some of the chromosomes have an elongated knob-like appendages known as telomere.
- New nucleotides are added and new complementary strand of DNA is formed with the help of enzyme DNA polymerase.
- Down’s syndrome is the genetic condition with 45 chromosomes.
Answer:
- False – A typical Mendelian dihybrid ratio of F2 generation is 9 : 3 : 3 : 1
- True
- True
- True
- False – Some of the chromosomes have an elongated knob-like appendages known as satellite
- True
- True
IV. Match the following:
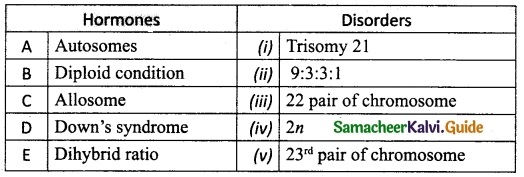
Answer:
A. (iii)
B. (iv)
C. (v)
D. (i)
E. (ii)
V. Answer in a sentence.
Question 1.
What is a cross in which inheritance of two pairs of contrasting characters are studied?
Answer:
Dihybrid cross is a cross in which inheritance of two pairs of contrasting characters.
Question 2.
Name the conditions when both the aisles are identical?
Answer:
Homozygous alleles.
Question 3.
A garden pea plant produces axial white flowers. Another of the same species produced terminal violet flowers. Identify the dominant trait.
Answer:
The dominant trait is axial white flower.
![]()
Question 4.
What is the name given to the segments of DNA, which are responsible for the inheritance of a particular character?
Answer:
Genes are the segments of DNA, which are responsible for the inheritance of a particular character.
Question 5.
Name the bond which binds the nucleotides in a DNA.
Answer:
Hydrogen bond binds the nucleotides in a DNA.
VI. Short Answer Questions.
Question 1.
Why did Mendel select pea plant for his experiments?
Answer:
- It is naturally self-pollinating and so is very easy to raise pure breeding individuals.
- It has a short life span as it is an annual and so it was possible to follow several generations.
- It is easy to cross-pollinate.
- It has deeply defined contrasting characters.
- The flowers are bisexual.
Question 2.
What do you understand by the term phenotype and genotype?
Answer:
- The external expression of a particular trait is known as the phenotype.
- The genetic expression of an organism is a genotype.
Question 3.
What are allosomes?
Answer:
Allosomes are chromosomes which are responsible for determining the sex of an individual. They are also called as sex chromosomes or hetero-chromosomes. There are two types of sex chromosomes, X and Y- chromosomes.
Question 4.
What are the Okazaki fragments?
Answer:
The short segments of DNA are called Okazaki fragments.
Question 5.
Why is euploidy considered to be advantageous to both plants and animals?
Answer:
Euploidy is the condition in which individual bears more than the usual number of diploid (2n) chromosome. It is used in plant breeding and horticulture. It has economic significance by the production of large sized flowers and fruits. It plays a significant role in the evolution of new species.
Question 6.
A pure tall plant (TT) is crossed with the pure dwarf plant (tt), what would be the F1 and F2 generations? Explain.
Answer:
In the F1 generation, all are tall plants. (Genotype all are Tt and phenotype all are tall).
In F2 generation, genotype three tall and one dwarf. [TT : Tt : tt = 1 : 2 : 1] phenotype.
Tall : dwarf 3 : 1 [TT : Tt : Tt : tt].
![]()
Question 7.
Explain the structure of a chromosome.
Answer:
The chromosomes are thin, long and thread like structures consisting of two identical strands called sister chromatids. They are held together by the centromere. Each chromatid is made up of spirally coiled thin structure called chromonema. The chromonema has number of bead-like structures along its length which are called chromomeres.
Question 8.
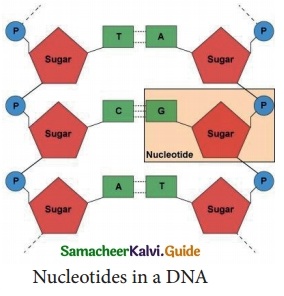
Label the parts of the DNA in the diagram given below. Explain the structure briefly.
Answer:
(i) DNA molecule consists of two polynucleotide chains.
(ii) These chains form a double helix structure with two strands which run anti-parallel to one another.
(iii) Nitrogenous bases in the centre are linked to sugar-phosphate units which form the backbone of the DNA.
(iv) Pairing between the nitrogenous bases is very specific and is always between purine and pyrimidine linked by hydrogen bonds.
VII. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain with an example of the inheritance of dihybrid cross. How is it different from a monohybrid cross?
Answer:
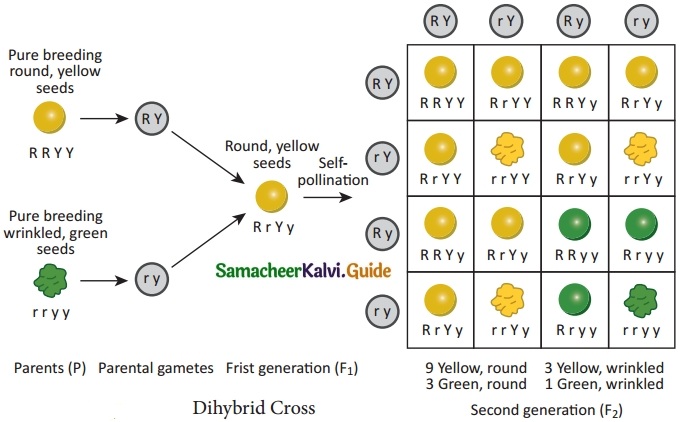
Dihybrid cross involves the inheritance of two pairs of contrasting characteristics (or contrasting traits) at the same time. The two pairs of contrasting characteristics chosen by Mendel were shape and color of seeds: round-yellow seeds and wrinkled-green seeds.
Mendel crossed pea plants having round-yellow seeds with pea plants having wrinkled-green seeds. Mendel made the following observations:
(i) Mendel first crossed pure breeding pea plants having round-yellow seeds with pure breeding pea plants having wrinkled-green seeds and found that only round-yellow seeds were produced in the first generation (F1). No wrinkled-green seeds were obtained in the F1 generation. From this it was concluded that round shape and yellow color of the seeds were dominant traits over the wrinkled shape and green color of the seeds.
(ii) When the hybrids of F1 generation pea plants having round-yellow seeds were cross-bred by self pollination, then four types of seeds having different combinations of shape and color were obtained in second generation or F2 generation. They were round yellow, round-green, wrinkled-yellow and wrinkled-green seeds.
The ratio of each phenotype (or appearance)of seeds in the F2 generation is 9 : 3 : 3 : 1. This is known as the Dihybrid ratio.
Monohybrid cross is a genetic cross that involves a single pair of gene or trait. In this parents differ by single trait. Eg: Height.
Dihybrid cross is a genetic cross that involves two pairs of genes, which are responsible for two trait. In this, parents have two different independent trait. Eg: flower colour, stem length.
Question 2.
How is the structure of DNA organised? What is the biological significance of DNA?
Answer:
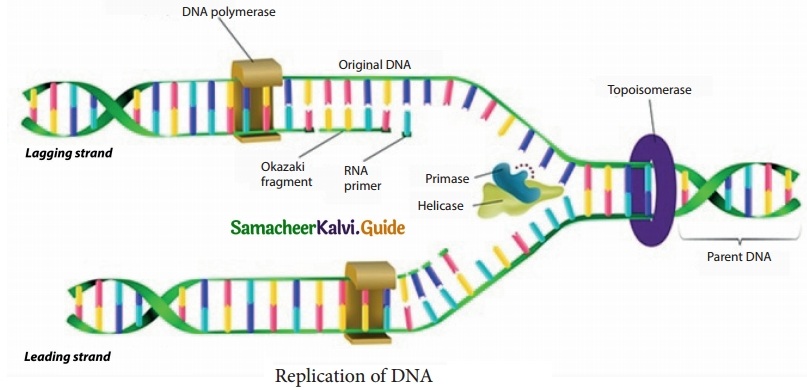
DNA is the genetic material of almost all the organisms. One of the active functions of DNA is to make its copies which are transmitted to the daughter cells. Replication is the process by which DNA makes exact copies of itself. Replication is the basis of like and takes place during the inter phase stage.
During replication of DNA, two complementary strand of DNA unwind and separate from one end in a zipper like fashion. The enzyme helicase unwinds the two strands of the DNA. The enzyme called topoisomerase separates the double helix above the replication fork and removes the twists formed during the unwinding process. For the synthesis of new DNA, two things are required. One is RNA primer and enzyme primase. The DNA polymerase moves along the newly formed RNA primer nucleotides, which leads to the elongation of DNA. In the other strand DNA is synthesized in small fragments called Okazaki fragments.
These fragments are linked by the enzyme called ligase. In the resulting DNA, one of the strand is parental and the other is the newer strands which is formed discontinuously.
Significance of DNA:
(i) It is responsible for the transmission of hereditary information from one generation to next generation.
(ii) It contains information required for the formation of proteins.
(iii) It controls the developmental process and life activities of an organism.
Question 3.
The sex of the new born child is a matter of chance and neither of the parents may be considered responsible for it. What would be the possible fusion of gametes to determine the sex of the child?
Answer:
Sex determination is a chance of probability as to which category of sperm fuses with the egg. If the egg (X) is fused by the X-bearing sperm an XX individual (female) is produced. If the egg (X) is fused by the Y-bearing sperm an XY individual (male) is produced. The sperm, produced by the father, determines the sex of the child. The mother is not responsible in determining the sex of the child.
Now let’s see how the chromosomes take part in this formation. Fertilization of the egg (22+X) with a sperm (22+X) will produce a female child (44+XX). while fertilization of the egg (22+X) with a sperm (22+Y) will give rise to a male child (44+XY).
![]()
VIII. Higher Order Thinking Skills: (HOTS)
Question 1.
Flowers of the garden pea are bisexual and self-pollinated. Therefore, it is difficult to perform hybridization experiment by crossing a particular pistil with the specific pollen grains. How Mendel made it possible in his monohybrid and dihybrid crosses?
Answer:
He worked on nearly 10,000 pea plants of 34 different varieties. He had chosen 7 pairs of contrasting characters. As the pea plants, are self-pollinating it is easy to raise pure breeding individuals. It is easy to cross-pollinate. It has contrasting characters. So Mendel made it possible in his monohybrid and dihybrid crosses.
Question 2.
Pure-bred tall pea plants are first crossed with pure-bred dwarf pea plants. The pea plants obtained in F1 generation are then cross-bred to produce F2 generation of pea plants.
(a) What do the plants of F1 generation look like?
(b) What is the ratio of tall plants to dwarf plants in F2 generation?
(c) Which type of plants were missing in F1 generation but reappeared in F2 generation?
Answer:
(a) plants will be tall
(b) 3 : 1
(c) Tall heterozygous (Tt)
Question 3.
Kavitha gave birth to a female baby. Her family members say that she can give birth to only female babies because of her family history. Is the statement given by her family members true? Justify your answer.
Answer:
The statement given by her family members were not true. It is not hereditary or family history. The sex determination mainly depends on which category of sperm fuses with the egg. If the egg [X] is fused by the X – bearing sperm, an XX individual (female) is produced. If the egg [X] is fused by the Y – bearing sperm an XY individual (male) is produced.
IX. Value-Based Questions
Question 1.
Under which conditions does the law of independent assortment hold good and why?
Answer:
During meiosis, chromosomes assort randomly into gametes, such that the segregation of alleles of one gene is independent of alleles of another gene. This is stated in Mendel’s Second Law and is known as the law of independent assortment.
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Heredity Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
Exchange of genetic material take place in:
(a) vegetative reproduction
(b) asexual reproduction
(c) sexual reproduction
(d) budding
Answer:
(c) sexual reproduction
Question 2.
In human, the number of chromosomes in each cell is _______
(a) 22 pairs
(b) 21 pairs
(c) 23 pairs
(d) 20 pairs
Answer:
(c) 23 pairs
![]()
Question 3.
If a round green seeded pea plant (RRYY) is crossed with wrinkled, yellow seeded pea plant,(rrYY) the seeds produced in F1 generation are:
(a) round and yellow
(b) round and green
(c) wrinkled and green
(d) wrinkled and yellow
Answer:
(a) round and yellow
Question 4.
In the new complementary strand of DNA, in one strand, the daughter strand is synthesized, as a continuous strand called ______
(a) Lagging strand
(b) Parent strand
(c) RNA primer
(d) Leading strand
Answer:
(d) Leading strand
Question 5.
A zygote which has an X-chromosome inherited from the father will develop into a:
(a) boy
(b) girl
(c) x- chromosome does not determine the sex of a child
(d) either boy or girl
Answer:
(b) girl
Question 6.
In pea, a pure tall plant (TT) is crossed to a short plant (tt). The ratio of pure tall plants to short plants in F2 is:
(a) 1 : 3
(b) 3 : 1
(c) 1 : 1
(d) 2 : 1
Answer:
(b) 3 : 1
Question 7.
The number of pairs of sex chromosomes in the zygote of human is:
(a) one
(b) two
(c) three
(d) four
Answer:
(a) one
Question 8.
Pure breeding varieties are otherwise called as:
(a) dominant
(b) recessive
(c) wild type
(d) mixed type
Answer:
(c) wild type
Question 9.
The genotype of a character is influenced by factors called:
(a) chromosome
(b) nucleus
(c) cytoplasm
(d) genes
Answer:
(d) genes
Question 10.
Monosomy is represented by:
(a) 2n + 1
(b) 2n – 1
(c) 2n + 2
(d) 2n – 2
Answer:
(b) 2n – 1
![]()
Question 11.
The term chromosome was introduced by:
(a) Bridges
(b) Waldeyer
(c) Balboni
(d) Flemming
Answer:
(b) Waldeyer
Question 12.
Diagrammatic representation of Karyotype of a species is:
(a) Idiogram
(b) Albinism
(c) Karyo tyning
(d) Heredity
Answer:
(a) Idiogram
II. Fill in the blanks:
1. The Genotypic ratio of Monohybrid cross is ………….
2. ……… is a graphical representation to calculate the probability of all possible genotype of off spring in a genetic cross.
3. The gene is present at a specific position on the chromosome called ……….
4. The end of the chromosome is called ………
5. The chromosomes with satellites are called as ………..
6. ……… act as a aging clock in every cell.
7. Nitrogen base + sugar = …………
8. The two strands of DNA open and separate at the point forming …………
9. Nullisomy is represented by ……….
10. The gametes produced by the organisms contain a single set of chromosomes is ……….
Answer:
1. 1 : 2 : 1
2. Punnet square
3. Locus
4. Telomere
5. Sat-chromosome
6. Telomeres
7. Nucleoside
8. Replication fork
9. 2n – 2
10. haploid (n)
III. Match the following:
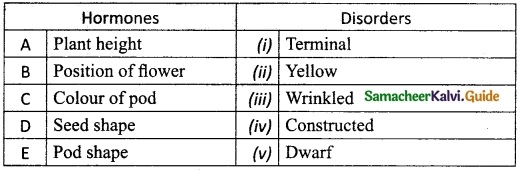
Answer:
A. (v)
B. (i)
C. (ii)
D. (iii)
E. (iv)
IV. State whether True or false, If false write the correct statement:
- The daughter strand synthesized in DNA is called logging strand.
- The centromere is found near the centre of the chromosome in sub metacentric.
- Primary construction in chromosome is called as nucleolar organizer.
- T.H. Morgan was awarded Nobel prize for determining the role of chromosome in heredity.
- Adenine links Thymine with three hydrogen bonds.
Answer:
- False – The daughter strand synthesized in DNA is called leading strand
- True
- False – Primary construction in chromosome is called as secondary construction.
- True
- False – Adenine links Thymine with two hydrogen bonds.
![]()
V. Answer in a word or sentence:
Question 1.
What is heredity?
Answer:
Heredity is transmission of characters from one generation to the next generation.
Question 2.
What is Alleles or Allelomorphs?
Answer:
The factors making up a pair of contrasting characters are called alleles or allelomorphs.
Question 3.
Define variation.
Answer:
Differences shown by the individuals of the same species and also by the offspring of the same parents.
Question 4.
What is Terminus?
Answer:
The replication fork of DNA, of the two sides, meet at a site called terminus.
Question 5.
Write the expanded form of DNA.
Answer:
Deoxyribo nucleic acid
Question 6.
What is the satellite?
Answer:
Some of the chromosomes have an elongated knob-like appendage at one end of the chromosome known as the satellite.
Question 7.
How many types of nitrogenous bases are present in DNA? Name them.
Answer:
There are two types of nitrogenous bases in DNA. They are purines (Adenine and Guanine) pyrimidines (Cytosine and Thymine).
Question 8.
Why is DNA called polynucleotide?
Answer:
DNA is a large molecule consisting of millions of nucleotides. Hence it is called as polynucleotide.
![]()
Question 9.
Name two purine nitrogenous bases found in a DNA molecule.
Answer:
Adenine and Guanine
Question 10.
What are the three chemically essential parts of nucleotides containing a DNA?
Answer:
Nitrogenous base, pentose sugar and phosphate.
Question 11.
What are autosomes?
Answer:
Autosomes are chromosomes that contain genes which determine the somatic characters.
Question 12.
How is the sex of a new born determines in humans?
Answer:
The sperm produced by the father determines the sex of the child.
Question 13.
Define genetics.
Answer:
The branch of biology that deals with the genes genetic variation and heredity of living organisms is called genetics.
Question 14.
Define mutation.
Answer:
Mutation is an inheritable sudden change in the genetic material (DNA) of an organism.
Question 15.
Name the types of chromosomes based on the position of centromere.
Answer:
Based on the position of centromere, the chromosomes are classified as Telocentric, Aerocentric, submeta centric and meta centric.
VI. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are chromosomes made up of?
Answer:
Chromosomes are made up of DNA, RNA, chromosomal proteins (histones and non-histones) and certain metallic ions. These proteins provide structural support to the chromosome.
Question 2.
What is the mechanism behind the expression of a particular trait? Explain.
Answer:
The factor for each character or trait remain independent and maintain their identity in the gametes. The factors are independent to each other and pass to the offspring through gametes.
![]()
Question 3.
If a pure tall pea plant is crossed with a pure dwarf plant, then in the first generation only tall plant appears.
(a) What happens to the traits of the dwarf plant?
(b) In the second generation, the dwarf trait reappears? Why?
Answer:
(a) The tall plant (dominant) mask the expression of the dwarf plant.
(b) When F1 hybrids are self crossed, the two entities separate and then unite independently forming tall and dwarf plant.
Question 4.
Explain the types of chromosome-based on function.
Answer:
Based on function, the chromosomes are classified into:
- Autosomes: Autosomes contain genes that determine the somatic (body) characters. Male and female have an equal number of autosomes.
- Allosomes: Allosomes are responsible for determining the sex of an individual. They are also called sex chromosomes or heterochromosomes. There are two types of sex chromosomes.
The human male has one X chromosome and one Y chromosome and human female have two X chromosomes.
VII. Long Question and Answer:
Question 1.
How are Mutation classified? Explain.
Answer:
Mutations are classified into two main types, namely chromosomal mutation and gene mutation.
Chromosomal mutation:
The sudden change in the structure or number of chromosomes is called a chromosomal mutation. This may result in
(i) Changes in the structure of chromosomes: Structural changes in the chromosomes usually occurs due to errors in cell division. Changes in the number and arrangement of genes take place as a result of deletion, duplication, inversion and translocation in chromosomes.
(ii) Changes in the number of chromosomes: They involve addition or deletion in the number of chromosomes present in a cell. This is called ploidy. There are two types of ploidy
(a) Euploidy (b) Aneuploidy.
Gene or point mutation: Gene mutation is the changes occurring in the nucleotide sequence of a gene. It involves substitution, deletion, insertion or inversion of a single or more than one nitrogenous base. Gene alteration results in abnormal protein formation in an organism.
Question 2.
What is a mutation? Explain the two types of mutation.
Answer:
The mutation is an inheritable sudden change in the genetic material (DNA) of an organism. Mutations are broadly classified into 1. Chromosomal mutation and 2. Gene mutation.
1. Chromosomal Mutation:
The sudden change in the structure or number of chromosomes is called chromosomal mutation. This result in
(a) Change in the structure of chromosomes: Structural changes occur due to errors in cell division. Changes in the number and arrangement of genes take place as a result of deletion, duplication, inversion and translocation in chromosomes.
(b) Changes in the number of chromosomes: They involve addition or deletion in the number of chromosomes present in a cell and is called ploidy. The two types of ploidy are:
(i) Euploidy: It is the condition, in which the individual bears more than the usual number. If an individual has three haploid sets of chromosomes, the condition is called triploidy [3n]. Triploid plants and animals are sterile. If an individual has four haploid sets of chromosomes, the condition is called tetraploidy [4n], Tetraploid plants often result in increased fruit and flower size.
(ii) Aneuploidy:
It is the loss or gain of one or more chromosomes in a set. It is of three types:
- Monosomy [2n – 1]
- Trisomy [2n + 1]
- Nullisomy [2n – 2]
(iii) Down’s syndrome:
It is one of the commonly known aneuploid condition, in man. It is a genetic condition, in which there is an extra copy of chromosome 21 (Trisomy 21). It is associated with mental retardation, delayed development, behavioural problems, weak muscle tone, vision and hearing disability are some of the conditions seen in children.
2. Gene or point mutation:
Gene mutation is the changes occurring in the nucleotide sequence of a gene. It involves substitution, deletion, insertion or inversion of a single or more than one nitrogenous base. Gene alteration results in abnormal protein formation.
Question 3.
Write a note on down’s syndrome.
Answer:
Down’s syndrome: This condition was first identified by a doctor named Langdon Down in 1866. It is a genetic condition in which there is an extra copy of chromosome 21 (Trisomy 21). It is associated with mental retardation, delayed development, behavioural problems, weak muscle tone, vision and hearing disability are some of the conditions seen in these children.
![]()
VIII. Higher Order Thinking Skills: (HOTS)
Question 1.
In a plant gene ‘A’ is responsible for tallness and its recessibe allele ‘a’ for dwarfness and ‘B’ is responsible for red colour to recessive allele ‘b’ for white flower colour. A tall and red flowered plant with genotype AaBb crossed with dwarf and red flowers (aaBb). What is the percentage of dwarf white flowered off spring of above cross?
Answer:
12.5 %
Question 2.
In a population of 1000 individuals 360 belong to genotype AA, 480 to Aa and the remaining 160 to aa. Based on this data, the frequency of allele A in the population is:
Answer:
0.6
Question 3.
A tall true breeding garden pea plant is crossed with dwarf true breeding garden Pea plant. When the F1 plants were selfed the resulting genotypes were in the ratio of:
Answer:
1 : 2 : 1 :: Tall homozygous; Tall heterozygous Dwarf.