Students can download 10th Social Science Civics Chapter 4 India’s Foreign Policy Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Solutions Civics Chapter 4 India’s Foreign Policy
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science India’s Foreign Policy Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Which Minister plays a vital role in molding foreign policy of our country?
(a) Defense Minister
(b) Prime Minister
(c) External Affairs Minister
(d) Home Minister
Answer:
(c) External Affairs Minister
Question 2.
The Panchsheel Treaty has been signed between ……………..
(a) India and Nepal
(b) India and Pakistan
(c) India and China
(d) India and Sri Lanka
Answer:
(c) India and China
Question 3.
Which article of Indian constitution directs to adopt foreign policy?
(a) Article 50
(b) Article 51
(c) Article 52
(d) Article 53
Answer:
(b) Article 51
![]()
Question 4.
Apartheid is ………………
(a) An international association
(b) Energy diplomacy
(c) A policy of racial discrimination
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) A policy of racial discrimination
Question 5.
The Agreement signed by India and China in 1954 related to:
(a) Trade and Commerce
(b) Restoration of normal relations
(c) Cultural exchange programmes
(d) The Five Principles of Co existence
Answer:
(d) The Five Principles of Co existence
Question 6.
Which is not related to our foreign policy?
(a) World co-operation
(b) World peace
(c) Racial equality
(d) Colonialism
Answer:
(d) Colonialism
Question 7.
Which of the following country is not the founder member of NAM?
(a) Yugoslavia
(b) Indonesia
(c) Egypt
(d) Pakistan
Answer:
(d) Pakistan
![]()
Question 8.
Find the odd one ………….
(a) Social welfare
(b) Health care
(c) Diplomacy
(d) Domestic affairs
Answer:
(c) Diplomacy
Question 9.
Non-Alliance means:
(a) being neutral
(b) freedom to decide on issues independently
(c) demilitarisation
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(d) none of the above
Question 10.
Non-military issues are
(a) Energy security
(b) Water security
(c) Pandemics
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks
- India conducted its first nuclear test at ……………..
- At present our foreign policy acts as a means to generate …………….. for domestic growth and development.
- …………….. is the instrument for implementing foreign policy of a state.
- …………….. was India’s policy in the face of the bipolar order of the cold war.
- Our tradition and national ethos is to practice ……………..
Answer:
- Pokhran
- Inward Investment Business Technology
- Diplomacy
- Non – Alignment
- disarmament
III. Consider the following statement and tick the appropriate answer
Question 1.
Arrange the following in the correct chronological order and choose the correct answer from the code given below.
(i) Panchsheel
(ii) Nuclear test at Pokhran
(iii) Twenty-year Treaty
(iv) First Nuclear test
(a) (i), (iii), (iv), (ii)
(b) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(c) (i), (ii), (iv), (iii)
(d) (i), (iii), (ii), (iv)
Answer:
(a) (i), (iii), (iv), (ii)
Question 2.
Which of the following is not about NAM?
(i) The term Non-Alignment was coined by V. Krishna Menon.
(ii) It aimed to maintain national independence in foreign affairs by joining any military alliance.
(iii) At present it has 120 member countries.
(iv) It has transformed to an economical movement.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) only
(d) (iv) only
Answer:
(c) (ii) only
Question 3.
Write true or false against each of the statement.
(a) During Cold War India tried to form a third bloc of nations in the international affairs.
(b) The Ministry of Home Affairs is responsible for the conduct of the country’s foreign relations.
(c) The nuclear test at Pokhran was done under Subterranean Nuclear Explosions Project.
Answer:
(a) – True
(b) – False
(c) – True
Question 4.
Assertion(A): India aligned with Soviet Union by the Indo-Soviet treaty on 1971.
Reason(R): This began with a disastrous Indo -China war of 1962.
(a) A is correct and R explains A.
(b) A is correct and R does not explain A.
(c) A is correct and R is Wrong.
(d) Both A and R are wrong.
Answer:
(c) A is correct and R is Wrong.
![]()
Question 5.
Assertion(A): India has formal diplomatic relations with most of the nations. Reason(R): India is the World’s second most populous country.
(a) A is correct and R explains A
(b) A is correct and R does not explain A
(c) A is wrong and R is correct
(d) Both are wrong.
Answer:
(a) A is correct and R explains A
Question 6.
Avoidance of military blocs was necessity for India after political freedom. Because India had to redeemed from:
(a) acute poverty
(b) illiteracy
(c) chaotic socio-economic conditions
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
IV. Match the following
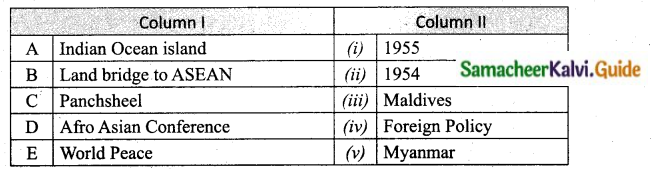
Answer:
A. (iii)
B. (v)
C. (ii)
D. (i)
E. (iv)
V. Give Short Answers
Question 1.
What is foreign policy?
Answer:
Foreign policy can be defined as a country’s policy that is conceived, designed and formulated to safeguard and promote her national interests in her external affairs, in the conduct of relationships with other countries, both bilaterally and multilaterally.
Question 2.
Explain India’s nuclear policy.
Answer:
- India’s nuclear policy is based on two themes:
- (a) No first use
- (b) Credible minimum deterrence.
- India has decided not to use nuclear power for offensive purposes.
Question 3.
Highlight the contribution by Nehru to India’s foreign policy.
Answer:
Nehru, India’s first Prime Minister, as opposed to the rivalry of the two superpowers (America and Russia). The aim of India’s foreign policy of that time was ‘world co-operation, world peace, end of colonial imperialism, racial equality and non-alignment’.
Question 4.
Differentiate: Domestic policy and Foreign policy.
Answer:
Domestic Policy:
- Domestic policy is the nation’s plan for dealing issues within its own nation.
- It includes laws focusing on domestic affairs, social welfare, health care, education, civil rights, economic issues and social issues.
Foreign Policy:
- Foreign policy is the nation’s plan for dealing with other nations.
- Trade, diplomacy, sanctions, defence, intelligence and global environments are the types of foreign policy.
Question 5.
List any four guiding principles of Panchsheel?
Answer:
Guiding principles of Panchsheel are:
- Mutual Respect for each other’s territorial integrity and sovereignty
- Mutual non-interference
- Equality and co-operation for mutual benefit
- Peaceful co-existence.
![]()
Question 6.
What was the reason for India to choose the path of Non-Alignment?
Answer:
- Nehru, India’s first Prime Minister was opposed to the rivalry of the two super powers (America and Russia) who were trying to extend their influence over the newly emerged nations of Asia and Africa.
- So he choose the path of Non – Alignment in the face of the bipolar order of the cold war and tried to form a third bloc of nations in international affairs.
Question 7.
In what ways are India’s global security concerns reflected?
Answer:
India’s global security concerns are reflected in its military modernisation, maritime security and nuclear policies.
Question 8.
List out the member countries of SAARC.
Answer:
The member countries are Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Maldives, Pakistan and Sri Lanka.
Question 9.
Name the architects of the Non-Aligned Movement.
Answer:
Jawaharlal Nehru of India, Tito of Yugoslavia, Nasser of Egypt, Sukarno of Indonesia, and Kwame Nkumarah of Ghana were the founding fathers of NAM.
Question 10.
Mention the main tools of foreign policy.
Answer:
The main tools of foreign policy are treaties and executive agreements, appointing ambassadors, foreign aid international trade and armed forces.
![]()
VI. Answer in detail
Question 1.
Write a detailed note on Non-alignment.
Answer:
- The team “Non – Alignment” was coined by V. Krishna Menon in his speech at the United Nationsin 1953.
- Non – Alignment has been regarded as the most important feature of India’s foreign policy.
- It aimed to maintain national independence in foreign affairs by not joining any military alliance.
- It was the largest political grouping of countries in a multilateral fora.
- The Non – Aligned Movement (NAM) was formed with a membership of 120 countries and 17 states as observers and 10 international organisations.
- It has transformed from a political movement to an economical movement.
The founding fathers of Non – Aligned Movement: Jawaharlal Nehru of India, Tito of Yugoslavia, Nasser of Egypt, Sukarno of Indonesia, and Kwame Nkumarah of Ghana were the founding fathers of NAM.
The Non – Alignment roots did not prevent India from entering into an alignment with the Soviet Union by the Indo – Soviet treaty of 1971 (20 – year pact of ‘peace, friendship and co operation’)
Then India embarked on a substantial programme of military modernisation. In 1974, India also conducted its first nuclear test at Pokhran under Subterranean Nuclear Explosion Project, in response to China’s nuclear test in 1964 at Lop Nor.
Question 2.
Discuss the core determinants of India’s foreign policy?
Answer:
Basic Determinants of a Foreign Policy:
- Geographical position and size of the territory
- Nation’s history, traditions and philosophical basis
- Natural resources
- The compulsion of economic development
- Political stability and structure of government
- The necessity of peace, disarmament and non-proliferation of nuclear weapons
- Military strength
- International milieu
![]()
Question 3.
Make a list on basic concepts followed by India to maintain friendly relations with its neighbours.
Answer:
Prioritising an integrated Neighbourhood first policy:
- India’s foreign policy has always regarded the concept of neighbourhood as one of widening concentric circles, around the central axis of historical and cultural commonalities.
- India gives political and diplomatic priority to her immediate neighbours and the Indian Ocean Island states such as Maldives.
- Greater connectivity and integration is provided so as to improve the free flow of goods, people, energy, capital and information.
Bridging diplomacy and development:
- One of the major objectives India’s foreign policy has been to leverage international partnership for India’s domestic development.
- This includes improving technological access, sourcing capital, gaining market access and securing natural resources.
A gradual transition from “Look East” to “Act East” Policy:
- South East Asia begins with North East India.
- Myanmar is our land bridge to the countries of the Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN).
- The purpose is to ensure a stable and multipolar balance of power in the Indo – Pacific and to become an integral part of Asia.
- This policy emphasises a more priductive role for ASEAN ans EAST Asian countries.
![]()
Economic development:
- Currently India’s political moves are being influenced by economic imperatives.
- Many nations are moving to forge better relationship with India.
- Accelerated, balanced and inclusive economic development to achieves this by ensuring peace and security, and by leveraging the nation’s international partnership.
India as a leading power:
- India is a member of the G20, the East Asia Summit and the BRICS coalition atestament to its status as a large country with a fast growing economy.
- India aspires for permanent membership of this UN Security Council.
- India now has an increasing range of interests, which are anchored in different parts of the world and which stem from a wide range of factors (energy, natural resources, investment, trade etc.,)
New challenges forced India to adjust to new realities. Even then, basic framework of its foreign policy remained more (or) less the same.
VII. Project and Activity
Question 1.
Identify any two aspects of India’s foreign policy that you would like to retain and to change if you were the decision maker.
Answer:
India’s Foreign Policy focus on the following:
- Preservation of national interest
- Achievement of world peace
- Disarmament
- Maintaining cordial relationship with other countries
- Anti – colonialism, Anti – Imperialism and Anti – Racism.
If I imagine myself as a decision maker of India’s foreign policy, I would like to retain the following two aspects of foreign policy.
- Maintaining world peace, Disarmament.
- Anti – colonialism, Anti – Imperialism and Anti – Racism.
The two aspects of foreign policy that I would like to change are:
- Fostering cordial relationship with other countries. We can maintain cordial relationship with all countries, but if they tries to attract us, we should be ready to defend ourselves.
- Equality in conducting International relations. We can maintain an equality in International relations along with the improvement in scientific economic aspects.
So, it can be enhancement in scientific and economic aspects in relation with other countries.
Note: The answer given is purely a sample answer, students should understand the answer, analyse, and think to give their personal views on the activity and submit to their teacher.
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science India’s Foreign Policy Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Which policy seeks to secure the best interest of the people? (territory and economy of the country).
(a) Panchsheel
(b) Imperialism
(c) Foreign Policy
(d) Non-co-operation
Answer:
(c) Foreign Policy
Question 2.
Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru’s five principles of peace are named as …………
(a) Swadesh
(b) New Deal
(c) Panchsheel
Answer:
(c) Panchsheel
Question 3.
An objective and goal oriented foreign policy has the potential to achieve:
(a) improved relation with other Nation.
(b) To accelerate growth
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(c) both (a) and (b)
Question 4.
India is called by the name of ………..
(a) Superpower
(b) Terrorist
(c) A great peacemaker
Answer:
(c) A great peacemaker
![]()
Question 5.
Which Institute provides training for officers of Indian Foreign Services (IFS)?
(a) The Foreign Services Training Institute
(b) An international association
(c) Ministry of external affairs of India
(d) All the above
Answer:
(a) The Foreign Services Training Institute
Question 6.
China became a Republic in ………..
(a) 1945
(b) 1947
(c) 1949
Answer:
(c) 1949
Question 7.
………………… principles were incorporated in the Bandung Declaration.
(a) Non – Aligned Movement
(b) Panchsheel
(c) Trade and commerce
(d) Racial discrimination
Answer:
(b) Panchsheel
Question 8.
Bangladesh got freedom due to the efforts of ………….
(a) Nehru
(b) Indira Gandhi
(c) Gandhi
Answer:
(b) Indira Gandhi
Question 9.
What is the main aim of India’s foreign policy in the following?
(a) World co – operation
(b) World peace
(c) Racial equality
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question 10.
The term ‘Non-Alignment’ was coined by ………….
(a) V. Krishna Menon
(b) Abul Ashar
(c) Jinnah
Answer:
(a) V. Krishna Menon
Question 11.
Whose vote against Iran at the’lnternational Atomic Energy agency?
(a) China
(b) India
(c) Myanmar
(d) Egypt
Answer:
(b) India
Question 12.
The foremost task of india’s foreign policy:
(a) Domestic transformation
(b) Inward investment
(c) Business and technology
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
![]()
Question 13.
India’s global security concerns:
(a) Military modernisation
(b) Nuclear policies
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Question 14.
Mention the basic concepts of India’s Foreign Policy.
(a) Disarmament
(b) Colonisation
(c) Imperialism
(d) Racism
Answer:
(a) Disarmament
Question 15.
How many member countries in SAARC organisation?
(a) 5
(b) 8
(c) 10
(d) 12
Answer:
(b) 8
![]()
Question 16.
Which of the following country is a member of the SAARC?
(a) Myanmar
(b) Pakistan
(c) Egypt
(d) Indonesia
Answer:
(b) Pakistan
Question 17.
………………… policies aim to promote welfare economics and collective self-reliance among the countries (South Asia)
(a) SAARC
(b) Panchsheel
(c) Non – Alignment
(d) none
Answer:
(a) SAARC
Question 18.
………………… is the instrument for implementing the foreign policy of a state.
(a) Diplomacy
(b) Disarmament
(c) Racism
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Diplomacy
Question 19.
Who supported UN disarmament programme?
(a) Bangladesh
(b) Srilanka
(c) China
(d) India
Answer:
(d) India
Question 20.
………………… is the world’s second most populous country.
(a) China
(b) India
(c) Pakistan
(d) Srilanka
Answer:
(b) India
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks
- The Foreign Service Training Institute was established in ………………….
- The Afro – Asian conference held in ………………….
- …………………. has been regarded as the most important feature of India’s foreign policy.
- The founding father of NAM …………………. of India.
- The Non – Aligned Movement (NAM) was formed with a membership of …………………. countries and …………………. international organisation.
- India embarked on a substantial programme of ………………
- The ……………… is meant for mutual assistance among nations for peace and progress.
- The ……………… stance of India was supporting the cause of decolonisation.
- India supported UN ……………… programme.
- ……………… is an organisation of eight countries that are primarily located in ………………
- SAARC Disaster management centre was set up at ………………
- SAARC satellite is a proposed communication cum – meteorology satellite by ………………
- The SAARC policies aim to accelerate ……………… development in the region.
- ……………… is the nations plan for dealing with other nations.
- India aspires for permanent membership on the ………………
- ……………… forced India to adjust new realities.
- Indo – US civilian ……………… marks significant progress in India’s foreign policy.
- India provides ……………… with support as needed in the form of resources and training.
- Since ……………… global non – proliferation has been a dominant theme of India’s nuclear policy.
- Indian ……………… in 1974 and 1998 is only done for strategic purposes.
Answers:
- 1986
- Indonesia
- Non – Alignment
- Jawaharlal Nehru
- 120, 10
- Military modernisation
- Non – Aligned Movement
- foreign policy
- disarmament
- SAARC, South Asia
- New Delhi
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
- Socio-cultural
- Foreign Policy
- UN Security Council
- New Challenges
- Nuclear deal
- neighbours
- Independence
- Nuclear Programme
![]()
III. Consider the following statement and tick the appropriate answer.
Question 1.
Which of the following is not about SAARC (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation)?
(i) SAARC is an economic and geopolitical organisation of eight countries that are primarily located in south Asia.
(ii) SAARC policies aim to promote welfare economics and to accelerate socio-cultural development in the region.
(iii) SAARC Disaster management centre was set up at Mumbai.
(iv) SAARC satellite is a proposed communication cum – meteorology satellite by (ISRO).
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (iii) only
(d) (iv) only
Answer:
(c) (iii) only
Question 2.
Assertion (A): The Ministry of External Affairs of India also known as Foreign Ministry comes under Government of India.
Reason (R): It is responsible for the conduct of foreign relations of India.
(a) A is correct and R explains A.
(b) A is correct and R does not explains A.
(c) A is correct and R is wrong.
(d) Both A and R are wrong.
Answer:
(a) A is correct and R explains A.
Question 3.
Assertion (A): During Cold, War India tried to form a third block of Nations in international affairs.
Reason (R); The aim of India’s foreign policy of that time was world cooperation world peace racial equality and non – alignment.
(a) A is correct and R explains A.
(b) A is correct and R does not explain A.
(c) A is correct and R is wrong.
(d) Both A and R are right.
Answer:
(a) A is correct and R explains A.
![]()
Question 4.
Which of the following is about NAM?
(i) Non – alignment has been regarded most important feature if India’s Foreign Policy.
(ii) NAM was formed with 180 member countries.
(iii) NAM is establishing economic cooperation among under developed countries.
(iv) It was the largest political groping countries in a multilateral fora.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i), (iii),(iv)
(c) (ii) only
(d) (ii),(iv)
Answer:
(b) (i), (iii),(iv)
Question 5.
Assertion (A): : Since Independence global Non – proliferation has been dominant theme of India’s nuclear policy.
Reason (R): So India’s supported U.N Disarmament programme.
(a) A is correct and R explains A.
(b) A is correct and R does not explains A.
(c) A is correct and R is wrong.
(d) Both A and R are right.
Answer:
(d) Both A and R are right.
IV. Match the following
Question 1.
Match the Column I with Column II.
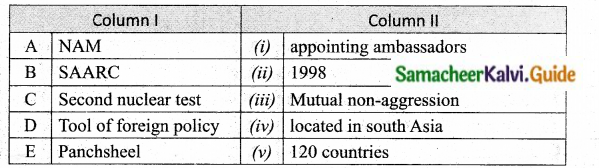
Answer:
A. (v)
B. (iv)
C. (ii)
D. (i)
E. (iii)
Question 2.
Match the Column I with Column ll.
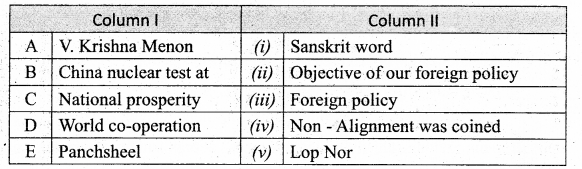
Answer:
A. (iv)
B. (v)
C. (ii)
D. (iii)
E. (i)
![]()
V. Give short answers
Question 1.
What is Diplomacy?
Answer:
Diplomacy is the instrument for implementing the foreign policy of a state.
Question 2.
What is meant by G – 20 global group of countries?
Answer:
G – 20 refers to the largest established and emerging economies of the world. India is also a member of G – 20 countries.
Question 3.
Write a note on the policy of Apartheid.
Answer:
- In South Africa the whites, did not give equal rights to the Native Africans.
- India raised this issue for the first time in the UN General Assembly in 1946.
- It was due to the constant moral support of India and the continuous struggle of Dr. Nelson Mandela, the policy of Apartheid was abolished in 1990.
Question 4.
List out the basic concept of India’s of foreign policy?
Answer:
- Preservation of National interest.
- Achievement of world peace.
- Disarmament
- Fostering cordial relationship with other countries.
- Solving conflicts by peaceful means.
- Equality in conducting international relations.
- Anti – colonialism anti – imperialism anti – racism.
Question 5.
Write short notes on Article-51.
Answer:
Lays down the Directive Principles of India’s foreign policy.
The state shall endeavour to
- Promote international peace and security
- Maintain just and honourable relations between nations.
- Foster respect for international law and international organisation.
- Encourage settlement of international disputes by arbitration.
![]()
Question 6.
What is the major objectives of India’s foreign policy?
Answer:
- one of the major objectives of India’s foreign policy has been to leverage international partnership for India’s domestic development.
- This include improving technological access source of capital, gaining market access and securing natural resources.
Question 7.
What are the elements in our eastern policy?
Answer:
The three big elements in our eastern policy are stronger emphasis on physical connectivity commercial and security related.
Question 8.
Non – Alignement defined by Nehru?
Answer:
“Broudly, non – alignment means not tying yourself off with military blocks. It means trying to view things, as far as possible, not form the military point of view, though that has to come in sometimes, but independently, and trying to maintain friendly relations with all countries”.
– Jawaharlal Nehru
Question 9.
Mention few basic determinants of a foreign policy.
Answer:
- Geographical position and size of territory.
- Nation’s history, traditions and philosophical basis.
- Natural resources
- Political stability and structure of Government.
Question 10.
What do you mean by NAM?
Answer:
NAM means Non – Aligned Movement.
- The NAM is meant for mutual assistance among nations for peace and progress.
- It aimed to maintain national independence in foreign affairs by not , jointing any military alliance.
![]()
VI. Answer in detail
Question 1.
Explain about the shifts in India’s foreign policy.
Answer:
The shifts in India’s policy manifested in various ways such as:
- Better relations with China – The look East policy (1992).
- The second nuclear test at Pokhran (1998) in Rajasthan.
- Defence procurement relationship with Israel.
- Energy diplomacy with Arab countries and Iran.
- Agreeing to US nuclear missile defence programme and
- India’s vote against Iran at the International Automatic Energy Agency.
Question 2.
Write a short note on SAARC.
Answer:
SAARC:
SAARC means, The South Asian Association for regional co-operation.
(i) India took the initiative to form SAARC to maintain peace in the regional level.
(ii) SAARC’s first meeting was held at Dacca in Bangladesh in Dec 7, 1985.
(iii) Ashan of Bangladesh was the first secretary-general of SAARC.
(iv) The member countries are Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, Afghanistan and Sri Lanka.
(v) On April 3, 2007 the SAARC’s annual summit was held in New Delhi. Afghan president Hamid Karzai attended this meeting Afghanistan become its 8th member.
(vi) 18th SAARC summit took place on 26th and 27th of November 2014 at Kathmandu the capital of Nepal.
(vii) The SAARC countries identified mutual co-operation in the following areas transportation postal service, tourism, shipping meteorology, health, agriculture rural reconstruction and telecommunication.
Question 3.
How India accelerated balanced and inclusive economic development?
Answer:
- India achieved economic development by ensuring peace and security.
- By leveraging the nations international partnership, to obtain all that is needed to fuel economic development.
- Economic development in the filed of markets, investment, fair global governance and a stable and fair environment conducive for growth.
- Currently’ India’s political moves are being influenced by economic imperatives.
- Many nations are moving to forge better relationship with India.
Question 4.
Explain about the principles of India’s foreign policy.
Answer:
Lays down directive principles of India’s foreign policy.
The state shall endeavour to
- Promote International Peace and Security.
- Maintain just and honourable relations between nations.
- Foster respect for International law and international organisation.
- Encourage settlement of International disputes by arbitration.
![]()
Question 5.
Write a short note on SAARC.
Answer:
SAARC – South Asian Association for Regional Co-operation.
- SAARC is an economic and geopolitical organisation of eight countries that are primarily located in South Asia.
- The SAARC policies aim to promote welfare economies, collective self – reliance and to accelerate socio – cultural development in the region.
- SAARC Disaster Management Center was set up at New Delhi.
- This centre working on various dimensions of disaster risk reduction and management,
- SAARC satellite is a proposed communication-cum-meteorology satellite by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) for the SAARC region.
- The member countries are Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Maldives, Pakistan, and SriLanka.