Students can download 10th Social Science Economics Chapter 2 Globalization and Trade Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Solutions Economics Chapter 2 Globalization and Trade
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Globalization and Trade Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Who is the head of the World Trade Organisation (WTO)?
(a) Ministerial conference
(b) Director General
(c) Deputy Director General
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Director General
Question 2.
How many countries were membership in WTO at present?
(a) 159
(b) 164
(c) 148
(d) 128
Answer:
(b) 164
Question 3.
Colonial advent in India:
(a) Portuguese, Dutch, English, Danish, French
(b) Dutch, English, Danish , French
(c) Portuguese , Danish, Dutch, French, English
(d) Danish, Portuguese, French, English, Dutch
Answer:
(a) Portuguese, Dutch, English, Danish, French
Question 4.
Who first came to India for trading purpose?
(a) Roman Empire
(b) Portuguese
(c) Dutch
(d) Danish
Answer:
(b) Portuguese
![]()
Question 5.
When did Portuguese colonize India?
(a) 1600 BC
(b) 1602 BC
(c) 1498 BC
(d) 1616 BC
Answer:
(c) 1498 BC
Question 6.
GATT’s first round held in
(a) Tokyo
(b) Uruguay
(c) Torquay
(d) Geneva
Answer:
(d) Geneva
Question 7.
India signed the Dunket proposal in:
(a) 1984
(b) 1976
(c) 1950
(d) 1994
Answer:
(d) 1994
Question 8.
Who granted the English “golden Fireman” in 1632?
(a) Jahangir
(b) Sultan of Golconda
(c) Akbar
(d) Aurangazeb
Answer:
(b) Sultan of Golconda
![]()
Question 9.
Foreign investment policy (FIR) announced in
(a) June 1991
(b) July 1991
(c) July-Aug-1991
(d) Aug 1991
Answer:
(c) July-Aug-1991
Question 10.
Indian government was introduced in …………. 1991.
(a) Globalization
(b) World Trade Organisation
(c) New Economic Policy
(d) none
Answer:
(c) New Economic Policy
II. Fill in the Blanks
- The Dutch captured Pondicherry in ………………
- A better economy Introduce rapid development of the ………………
- The East india Company built fortified factory in Madras which known as ………………
- WTO agreement came into force from ………………
- The term globalization Invented by ………………
- French East India company established second factory at ………………
Answer:
- 1693
- Capital market
- Fort St. George
- January 1, 1995
- Prof. Theodore Levitt
- Pondicherry
![]()
III. Choose the correct statement
Question 1.
(i) The East Indian Company especially to participate in the East Indian Spice Trade and later added cotton, silk, indigo.
(ii) Merchants cf the Dutch East India Company first established at Calicut
(iii) Nanadesis were a guild of traders at the time of Hoysala Empire
(a) (i) is correct
(b) (ii) and (iii) are correct
(c) (i) and (in) are correct
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct
Answer:
(a) (i) is correct
IV. Match the following
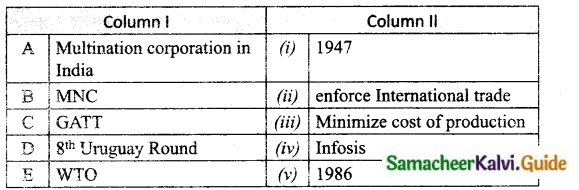
Answer:
A. (iv)
B. (iii)
C. (i)
D. (v)
E. (ii)
V. Give Short Answers
Question 1.
What is globalization?
Answer:
Globalization is the process of integrating various economies of the world without creating any barriers in the free flow of goods and services, technology, capital and even labour or human capital.
Question 2.
Write the types of globalization?
Answer:
The types of Globalization are:
- Economic Globalization: Countries integrating economically
- Social: Information and ideas integration socially all over the world.
- Political: Political co-operation between countries.
Question 3.
Write short note on Multinational corporation.
Answer:
Multinational corporation is a corporate organisation which owns or controls production of . goods or services in at least one country other than its home country. MNCs are also called Transnational corporation (TNG) or Multinational Enterprise (MNE). Most of the MNCs at present belong to the lour major exporting countries – USA. UK. France and Germany.
![]()
Question 4.
Short note: The Dutch in South India.
Answer:
Dutch East India company was formed in 1602. Dutch established factories at Masulipatnam, Pettapoli, Devanampattinam and with the help of King of Chandragiri Pulicut factory also. The commodities exported by the Dutch were Indigo, Saltpeter, Bengal raw silk. They captured Nagapatnam from Portuguese in 1659.
Question 5.
What are the reforms made to adopt globalization?
Answer:
The following reforms were made-to adapt globalization in India.
- Abolition of industrial licensing, except for a few industries.
- Reduction in the number of industries reserved for public sector.
- Fixation of a realistic exchange rate of rupee to exchange exports of Indian goods.
- Foreign exchange regulations were suitably amended.
- The Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) was reduced to increase lending by RBI.
Question 6.
What is fair trade?
Answer:
Fair trade is a way of doing business that ultimately aims to keep small farmers an active part of the world market and aims to empower consumer to make purchases that support their values.
Question 7.
Write any five principles of Fair Trade Practices.
Answer:
Five principles of Fair trade practices:
- Creating opportunities for economically disadvantaged producers.
- Transforming and accountability.
- Fair trading practices and payment of fair price.
- Ensuring no child labour and forced labour.
- Respect for the environment.
Question 8.
What is the main objective of WTO?
Answer:
The main objective of WTO (World Trade Organisation) is to enforce rules for International trade, to resolve trade disputes and to provide a forum for negotiating and monitoring trade.
Question 9.
Write short note on TRIPs and TRIMs.
Answer:
TRIPs – Trade Related aspects of Intellectual Property Rights – is an international legal agreement between all the member nations of the World Trade Organisation (WTO). It sets down minimum standards for the regulation by national Governments of many fonns of intellectual property as applied to nationals of other WTO member nations. TRIPs was negotiated at the end of the Uruguay Round of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) between 1989 and 1990 and is administered by the WTO.
TRIMS – Trade Related Investment Measures – The Uruguay Round Agreement on TRIMs referes to certain conditions or restrictions imposed by a Government in respect of foreign investment in the country in order to give adequate provisions for the home industries to develop.
![]()
Question 10.
Write the positive impact of Globalization.
Answer:
- A better economy introduces rapid development of the capital market
- Standard of living has increased
- Better trade, therefore more employment
- Introduction of new technologies
- New scientific research patterns .
- Increases GDP of a country
- Increase free flow of goods and
- Increase FDI – Foreign Direct Investment
VI. Brief Answer
Question 1.
Write briefly the history of Globalization.
Answer:
The term Globalization was introduced by Prof. Theodore Levitt. The history of Globalization can be explained in three stages namely
- Archaic globalization
- Proto Globalization
- Modem Globalization
Archaic Globalization: An early form of globalized economies and culture is known as Archaic Globalization existed during the Hellenistic Age. The trade links of the earlier days can be summarised as
- Between Sumerian and Indus Valley Civilisation
- Greek culture stretched from India to Spain
- Between Roman empire, Parthian empire and the Hans dynasty.
- The advent of Mongol empire greatly facilitated travel along the silk road.
These Pre-modem phases of global exchange are called Archaic Globalization.
Proto Globalization: It arose because of the rise of maritime European empires in the 16th and 17th Centuries, the Portuguese, Spanish, Dutch and British empires. In the 17th century, the British East India company is described as the first Multinational Company and the Dutch East India company were established.
Modern Globalization: It is witnessed between 19th and 20th century. In the 19th century – Global trade and capital investment. In the 20th century, higher share of trade in merchant production, Global trade in services, Rise in production and trade by MNCs and Technological changes. Agreements of trade contracts like the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) and World Trade Organisation (WTO). Technological changes lowered the cost of transport charges.
![]()
Question 2.
Briefly explain the evolution of MNC and its advantages and disadvantages.
Answer:
Multinational companies first started their activities in the extractive industries and controlled raw materials in the host countries during 1920s and then entered the manufacturing and service sectors after 1950s. Most of the MNCs at present belong to the four major exporting countries i.e., USA, UK, France and Germany. However, the largest is America. In 1971, the American Corporations held 52% of the total world stock of foreign direct inverstment. Great Britain held 14.5% followed by France 5% and Federal Republic of Germany 4.4% and Japan 2.7%.
Advantages of MNCs:
- MNCs produce the same quality of goods at lower cost and without transaction cost.
- They reduce prices and increase the purchasing power of consumers world wide.
- They are able to take advantage of tax variation.
- They spur job growth in the local economy.
Disadvantages of MNCs:
- They have led to the downfall of smaller, local business.
- With more companies transferring offices and centering operations in other countries, jobs for the people living in developed countries are threatened.
- MNCs often invest in developing countries where they can take advantage of cheaper labour. Some MNCs prefer to put up branches in these parts of the world where there are no stringent policies in labour and where people need jobs because these MNCs can demand for cheaper labour and lesser healthcare benefits.
Question 3.
Explain the trade and traders in South India.
Answer:
- South India trade guilds were formed by merchants inorder to organise and expand their trading activities.
- South India trade was dominated by the Cholas and it w’as replaced by the Pallavas.
- Several trade guilds operated in medieval southern India such as the Gatrigas, Nakaras, Mummuridandas, Settis, Birudas, Gavaras etc.
- In the early trade, the Kalinga traders brought red coloured stone decorative objects for trade and also cotton textile to south east Asia.
- The discovery of a new all sea route from Europe to India via Cape of Good Hope by Vasco-do-Gama helped to flourish trade in India.
- India’s coastal and maritime trade was monopolized by the Europeans.
- Therefore it was due to the trading activities European companies came to India.
Question 4.
Write about the World Trade Organisation.
Answer:
The World Trade Organisation or WTO is the only global international organisation dealing with the rules of trade between nations. At its heart are the WTO agreements, negotiated and signed by the bulk of the world’s trending nations and satisfied in their Parliaments. The WTO began operations on January 1, 1995 after the completion of the Uruguay Round (1986-94) of Multi lateral trade negotiations.
WTO has six key objectives
- To set and enforce for international trade.
- To provide a forum for negotiating and monitoring further trade liberalisation.
- To resolve trade disputes.
- To increase the transparency of decision making.
- To corporate with other major international economic institutions involved in global economic management.
- To help developing countries benefit fully from the global trading system.
Question 5.
Write the challenges of Globalization.
Answer:
- Globalization means the integration of the home economy with the world Economy
- There is a general belief that the benefits of globalization extends to all countries. But that will not happen automatically.
- There is a constant fear the globalization leads to instability in the developing world.
- Due to globalization, the industrial world has increased global competition.
- This leads to race in low level, labour right and employment practices among the industrial world.
- It may led to global imbalance.
- It may result to activities like child labour, slavery.
- It may also affect health as consumers are tempted to use more attracti ve junk foods.
- It may affect environment .Because more of use and throw products and packed items may affect nature and our survival.
![]()
VII. Activity and Project
Question 2.
Students are collect the images regarded to the globalization and make the album, (south Indian trade and traders images, and silk route map, spice route map, and kalinga trade map, etc).
Answer:
Students should collect pictures of South Indian
(a) Traders and make it as an album: Student can access to google and search by typing” ancient South Indian Traders” images and collect the relevant information.
Silk route map: The silk route was an ancient network of trade routes that connected the East and the West connecting Asia, Europe and Africa. It was mainly used to transport silk.
Spice route map: Spice route is the name as spices were traded with a way of sea route. Spices such as cinnamon, ginger, pepper, turmeric etc. Traded between Asia, Europe and Africa.
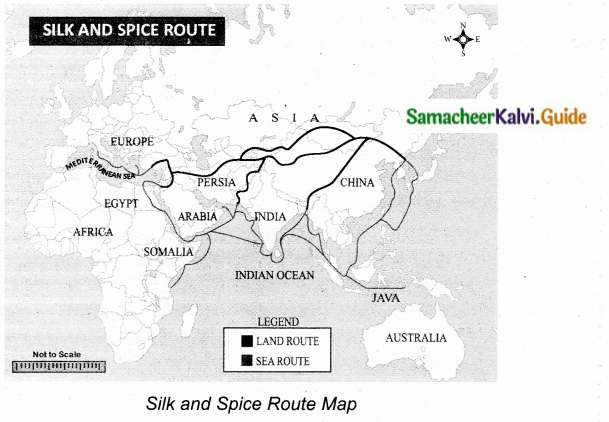
![]()
Kalinga route map: Trade routes of Kalinga sailors. They used to trade along their South West voyage along the East Coast of India. Their boats used to sail from Mahanadhi to Bali and right upto Nagapattinam in Cauvery delta. Also they sail along the East coast of Srilanka.
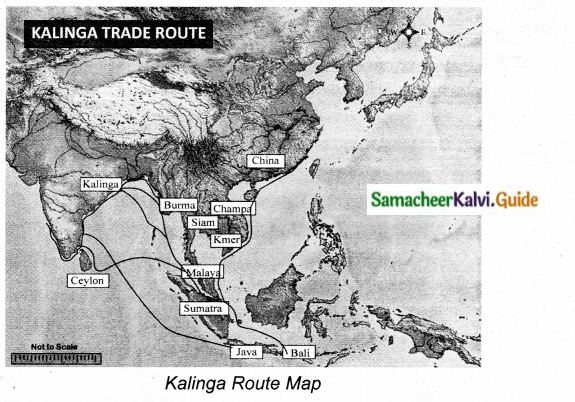
Question 3.
Students are collect the picture of various Multinational corporation companies in India and its products pictures.
Answer:
Students can collect the pictures of various Multinational corporation companies (list is given in the text book itself) and paste the pictures and make an album.
| Multinational corporation in India | Products |
| Microsoft Corporation India | Software products |
| IBM – International Business Machines Corporation | Business consulting, storage solutions. |
| Nestle | Food products |
| Proctor and Gamble (P & G) | Beauty care, Grooming, healthcare and house hold care |
| Citi group | Banking operations |
| Sony corporation | Electronic products and entertainment products. |
| Hewlett-Packar (hp) | Laptops, monitors, desktop and Printers |
| Coco-cola | Non-Alcoholic beverages |
| Pepsico | Snacks and beverages |
| Apple inc | Laptop, phone, software, online services. |
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Globalization and Trade Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The supporting pillars of NEP, 1991 of India is …………………
(a) LPG
(b) WTO
(c) IMF
(d) None
Answer:
(a) LPG
Question 2.
The Dames sold all their Indian settlements to ……………
(a) the British
(b) the French
(c) the Portuguese
(d) none
Answer:
(a) the British
Question 3.
The term ………………… refers to the integration of the domestic economy with the rest of the world.
(a) Privatisation
(b) Liberalisation
(c) Globalization
(d) World trade
Answer:
(c) Globalization
Question 4.
Which among the following was the largest MNC in India in 2018?
(a) Pepsi Company
(b) Tata Group
(c) Microsoft Corporation
(d) Sony Corporation
Answer:
(d) Sony Corporation
Question 5.
The term Globalization was introduced by …………………
(a) Simon Kuznets
(b) Theodore Levitt
(c) Marshall
(d) Adam Smith
Answer:
(b) Theodore Levitt
Question 6.
A company that owns or controls production in more than one nation is called ………………
(a) Foreign Company
(b) Multinational Company
(c) Local Company
Answer:
(b) Multinational Company
Question 7.
Archaic Globalization is the ………………… stage of Globalization.
(a) one
(b) two
(c) three
(d) four
Answer:
(a) one
![]()
Question 8.
Which one of the following is not an MNC?
(a) Reebok shoes
(b) SAIL
(c) Infosys
Answer:
(b) SAIL
Question 9.
Proto Globalization is the ………………… stage of Globalization.
(a) one
(b) two
(c) three
(d) four
Answer:
(b) two
Question 10.
WTO is dominated by countries like …………….
(a) US and UK
(b) China and France
(c) India and Japan
Answer:
(a) US and UK
Question 11.
The 17th century Globalization became ………………… business phenomenon.
(a) Government
(b) Private
(c) Domestic
(d) Foreign
Answer:
(b) Private
Question 12.
………………… is an example for a multinational trade agreement.
(a) GATT
(b) WTO
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) MNC
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Question 13.
South India trade ………………… were formed by merchants in order to organize and expand their trade activities.
(a) routes
(b) guilds
(c) organisation
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(b) guilds
![]()
Question 14.
The olden days Kalinga is the present day …………………
(a) Tamil Nadu
(b) Orissa
(c) M.P.
(d) Delhi
Answer:
(b) Orissa
Question 15.
Chettiars in Tamil Nadu are examples of early …………………
(a) people
(b) Traders
(c) nationalists
(d) Bankers
Answer:
(b) Traders
Question 16.
The arrival of Alvarez cabral in India in 1500 A.D. led to the establishment of trading station at …………………
(a) Cochin
(b) Calcutta
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
![]()
Question 17.
………………… was the headquarters of the Dutch in India.
(a) Portuguese
(b) Dutch
(c) Arabia
(d) Pulicut
Answer:
(d) Pulicut
Question 18.
The Sultan of Golconda granted the English the “Golden Fireman” in …………………
(a) 1634
(b) 1632
(c) 1631
(d) 1630
Answer:
(b) 1632
Question 19.
In 1639, English build a fortified factory in Madras which was known as …………………
(a) Fort Pulicut
(b) Fort St. George
(c) Fort Masulipatnam
(d) Fort Pettapoli
Answer:
(b) Fort St. George
Question 20.
The first French factory in India was established in ………………… by obtaining permission from the Sultan of Golconda.
(a) 1634
(b) 1668
(c) 1693
(d) 1642
Answer:
(b) 1668
Question 21.
Pondicherry was the headquarters of the
(a) British
(b) Spanish
(c) French
(d) Dutch
Answer:
(c) French
Question 22.
Initially Pondicherry was captured by the ………………… and later handed over to the French.
(a) British
(b) Dutch
(c) Spaniards
(d) Sultan of Golconda
Answer:
(b) Dutch
Question 23.
Pondicherry became the headquarters of the France in the year …………………
(a) 1664
(b) 1693
(c) 1700
(d) 1701
Answer:
(d) 1701
Question 24.
India signed the Dunkel draft in the year …………………
(a) 1664
(b) 1993
(c) 1994
(d) 1893
Answer:
(c) 1994
![]()
Question 25.
One of the reform made to adopt Globalization was …………………
(a) Abolition of Industrial licensing
(b) Reduction of Public Sector
(c) Foreign exchange regulations
(d) All the industries above
Answer:
(d) All the industries above
Question 26.
Multinational corporations are also called as …………………
(a) Transnational corporation
(b) Multi-national Enterprise
(c) MNCs
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question 27.
………………… country has the largest multinational companies in the world.
(a) USA
(b) UK
(c) France
(d) Germany
Answer:
(a) USA
Question 28.
Of the below given choices, find out, which is a multinational corporation.
(a) Tata Group
(b) Nettle
(c) IBM
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question 29.
GATT was established in …………………
(a) 1946
(b) 1945
(c) 1947
(d) 1948
Answer:
(c) 1947
Question 30.
Eighth round of GATT was known as ………………… Round.
(a) Tokyo
(b) Uruguay
(c) Torquay
(d) Geneva
Answer:
(b) Uruguay
Question 31.
………………… countries participated in the eighth round of GATT.
(a) 127
(b) 117
(c) 167
(d) 107
Answer:
(b) 117
Question 32.
The eighth round of Talks of GATT took place in the year …………………
(a) 1983
(b) 1984
(c) 1985
(d) 1986
Answer:
(d) 1986
![]()
Question 33.
Uruguay Round final Act was signed by the member nations in the year …………………
(a) 1986
(b) 1990
(c) 1992
(d) 1994
Answer:
(d) 1994
Question 34.
The Headquarters of WTO is in …………………
(a) Geneva
(b) Scotland
(c) America
(d) Holland
Answer:
(a) Geneva
Question 35.
G7 countries means ………………… countries of the world.
(a) Developed
(b) Developing
(c) Under developed
(d) Less developed
Answer:
(a) Developed
Question 36.
GATT was signed by ………………… countries in 1947.
(a) 22
(b) 23
(c) 21
(d) 117
Answer:
(b) 23
Question 37.
TRIPS include the following areas of …………………
(a) Trade Secrets
(b) Copy rights
(c) patents
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question 38.
Globalization increases GDP of a country by free flow of goods and also to increase …………………
(a) FDI
(b) GNP
(c) Technological improvement
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Question 39.
TRIMs refers to certain ………………… imposed by the government in respect of foreign investment of a country.
(a) Conditions
(b) Control
(c) Restrictions
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question 40.
………………… sometimes may lead to Child labour and slavery.
(a) Liberalisation
(b) Privatisation
(c) Globalization
(d) None
Answer:
(c) Globalization
![]()
II. Fill in the Blanks
- LPG is the supporting pillar of India’s ………………..
- means integration of the international market for goods and services.
- The term Globalization was introduced by Prof ………………..
- The History of Globalization can be studied under ……………….. stages.
- The first stage of the history of Globalization is called ……………….. Globalization.
- The third stage of the history of Globalization is called ……………….. Globalization.
- The Proto Globalization is the ……………….. stage of the history of Globalization.
- The Archaic Globalization existed during the ……………….. Age.
- The Dutch East India Company was founded in the year ………………..
- The expansion of GATT is ………………..
- The ……………….. is the expansion for WTO
- South Indian trade was dominated by the ……………….. and replaced by the ………………..
- Kalinga traders brought ……………….. coloured stone decorative objects for trade.
- India’s coastal and maritime trade was monopolized by the ………………..
- The Portuguese under the leadership of Vasco do Gama landed at Calicut in ………………..
- ……………….. was the early capital of Portuguese in India.
- The Sultan of Golconda granted the English the ……………….. in 1632.
- In 1639, English build a fortified factory in Madras which is known as ………………..
- ……………….. was the headquarters of Danes in India
- The first French factory was established in ………………..
- The first French factory was established with the permission from the Sultan of ………………..
- ……………….. was the headquarters of the French.
- Pondicherry became the headquarters of the French in the year ………………..
- Recently the Government of India has set up ……………….. to boost exports.
- India signed the Dunkel Draft in the year ………………..
- When India was in crisis in 1990’s India mortgaged 40 tons of gold to the Bank of ………………..
- The New Economic Policy was put forth in the year ………………..
- The ……………….. is a corporate organisation operates in many countries other than home country.
- Multinational Corporations are also called as ………………..
- Of the MNC ……………….. is the largest, holding a major share of the FDI
- India announced the Foreign Investment policy in the year ………………..
- The growth of MNC may lead to the downfall of smaller local ……………….. of the host country.
- The expansion of FCRA is ………………..
- GATT was signed in the year ………………..
- Initially, GATT was signed by ……………….. countries.
- In the seventh round of GATT ……………….. countries participated.
- GATT’s primary purpose was to increase International Trade by reducing ………………..
- The headquarters of GATT is in ………………..
- The Eighth round of GATT is called as ………………..
- The signing of GATT in 1994 paved the way for the setting up of ………………..
- Intellectual property right may be defined as ………………..
- The expansion of TRIPs is ………………..
- The expansion of TRIMs is ………………..
- One of the negative effect of ……………….. is that it may lead to slavery and Child labour.
- The Trade Secret is an agreement covered under ………………..
Answers:
- New Economic Policy
- Globalization
- Theodore Levitt
- Three
- Archaic
- Modem
- Second
- Hellenistic
- 1602
- General Agreement on Tariffs and
- World Trade Organisation
- Cholas, Pallavas
- Red
- Europeans
- 1498
- Cochin
- Golden Fireman
- Fort St.George
- Triangular
- 1668
- Golconda
- Pondicherry
- 1701
- Special Economic Zones
- 1994
- England
- 1991
- MNC
- Multinational Enterprise
- America
- 1991
- Business
- Foreign Contribution Regulation Act
- 1947
- 23
- 99
- various tariffs
- Geneva
- Uruguay Round
- WTO
- Information with a commercial value
- Trade Related Intellectual Property Rights
- Trade Related Investment Measures
- Globalization
- TRIPs
![]()
III. Choose the correct statement
Question 1.
(i) Globalization has led to environmental degradation.
(ii) GATT was signed by 73 countries in 1949
(iii) TRIPs and TRIMs are a part of WTO
(iv) It takes only a few hours to transport goods between continents today.
(a) (i), (iii), (iv) is correct
(b) (i), (ii), (iv) is correct
(c) (i), (ii) is correct
(d) (ii), (iv) is correct
Answer:
(a) (i), (iii), (iv) is correct
Question 2.
(i) Proto Globalization was characterized by the rise of maritime European Empires.
(ii) The pre-modern phase of global exchange are sometimes known as Proto Globalization.
(iii) The Kalinga traders brought Red coloured stone decorative objects for trade
(iv) The Danes formed an East India Company and arrive in India in 1616.
(a) (i), (iii), (iv) is correct
(b) (i), (ii), (iv) is correct
(c) (i), (ii), (iii)is correct
(d) (iii), (iv) is correct
Answer:
(a) (i), (iii), (iv) is correct
Question 3.
(i) The MNC first started their activities in controlling the industries of the host countries.
(ii) Indian Government mortgaged 40 tons of gold to the Bank of England prior to 1991.
(iii) To boost exports, recently, the Government of India announced Demonetisation and Goods and Services Tax.
(iv) The French failed in India and in 1845, they were forced to sell all their Indian settlements to the British.
(a) (i), (iii), (iv) is correct
(b) (i), (ii), (iv) is correct
(c) (i), (ii), (iii) is correct
(d) (i), (ii) is correct
Answer:
(d) (i), (ii) is correct
Question 4.
(i) The main reason for the growth of MNC is on the account of technological superiorities.
(ii) An MNC is able to take advantage of tax variation.
(iii) WTO provides a forum for negotiating and monitoring trade liberalisation.
(iv) The agreement of the final act of Uruguay Round was agreed by 104 member countries.
(a) (i),(ii),(iii) are correct
(b) (i),(ii),(iii) and (iv) are correct
(c) (i), (ii), (iii) are wrong
(d) (i) is correct
Answer:
(b) (i),(ii),(iii) and (iv) are correct
![]()
IV. Assertion and Reason
Question 1.
Assertion (A): After 1991, there was a spurt of foreign collaborations in India and increase flow of FDI-Foreign Direct Investment.
Reason (R): The liberalized Foreign Investment Policy (FIP) was announced in India in July-August 1991.
(a) A is correct and R is the correct explanation to A
(b) A is correct and R is not the correct explanation to A
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) A is wrong, but R is correct
Answer:
(a) A is correct and R is the correct explanation to A
Question 2.
Assertion (A); The introduction of MNC into a host country’s economy may lead to the downfall of small, local business.
Reason (R): Spurring job growth in the local economies.
(a) A is correct and R is the correct explanation to A
(b) A is correct and R is not the correct explanation to A
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) A is wrong, but R is correct
Answer:
(b) A is correct and R is not the correct explanation to A
Question 3.
Assertion (A): India’s coastal and maritime trade was monopolized by the Europeans.
Reason (R): Trade guilds were channels through which Indian Culture was exported to other lands.
(a) A is correct and R is the correct explanation to A.
(b) A is correct and R is not the correct explanation to A
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) A is wrong, but R is correct.
Answer:
(b) A is correct and R is not the correct explanation to A
![]()
V. Match the following
Question 1.
Match the Column I with Column II.
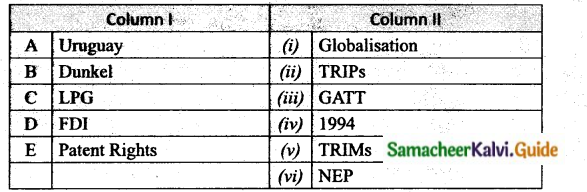
Answer:
A. (iii)
B. (iv)
C. (vi)
D. (i)
E. (ii)
Question 2.
Match the Column I with Column II.
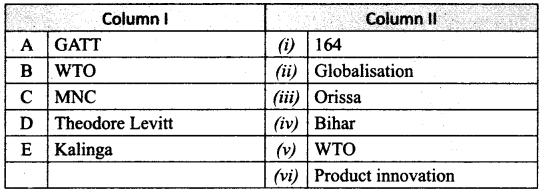
Answer:
A. (v)
B. (i)
C. (vi)
D. (ii)
E. (iii)
VI. Give Short answers
Question 1.
What is the Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010?
Answer”
The Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act or FCRA, 2010 has been enacted the Parliament to consolidate the law to regulate the acceptance and utilisation of Foreign contributions or foreign hospitality by certain individuals or associations or companies and to prohibit acceptance and utilisation of foreign contribution or foreign hospitality for any activities detrimental to national interest and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
Question 2.
How did India’s NEP emerged?
Answer:
When India was facing a down grading economic crisis situation, the government presented a budget in July 1991 for 1991-92 with a series of policy changes which underlined liberalization, privatization and globalization. This has come to be called as India’s New Economic policy.
Question 3.
What came to be known as India’s new economic policy? How was this policy strengthened?
Answer:
With the downgrading of India’s credit rating by some international agencies, these was heavy flight of capital out of India. The Government has to mortgage 40 tons of gold to the Bank of England. Under these circumstances, the Government for 1991-92 presented its budget in July 1991 with a series of policy changes which underlined globalization, liberalisation and privatisation. This has come to be called as India’s new economic policy.
Question 4.
Write a note on SEZ?
Answer:
SEZ means Special Economic Zones . Recently the Government of India has set up special Economic Zones in southern states of especially in Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka and Kerala with a view to boost exports. Few SEZ in Tamil Nadu are Nanguneri SEZ, Ennore SEZ, Coimbatore SEZ.
Question 5.
How are producers beneficiaries of fair trade?
Answer:
For producers fair trade is unique in offering four important benefits.
- Stable prices that cover the costs of sustainable production.
- Market access That enables buyers to trade with producers who would otherwise be excluded from market.
- Partnerships (producers are involved) in decisions that affect their future.
![]()
Question 6.
Write any type of subsidies the WTO offers to its member countries?
Answer:
- Tax concessions such as exemptions , credits (or) deferrals.
- Cash subsidies such as the grants.
Question 7.
What was the idea behind developing SEZ in India?
Answer:
To attract foreign companies to invest in India.
VII. Brief Answer
Question 1.
What is fair trade? Who are the beneficiaries of fair trade practices? How?
Answer:
Fair trade is an industrial arrangement designed to help producers in developing countries achieve better trading conditions. Fair trade is about better prices, decent working conditions and fair terms of trade for fanners and workers.
With fair trade, everyone is the beneficiary. Take examples of consumers, traders and producers.
(i) Consumers – Fair trade relationship provide the basis for connecting producers with consumer and for informing consumers of the need for social justice and the opportunities for change. Consumer support enables fair trade organisation to be advocates and campaigners for wider reform of international trading rules, to achieve the ultimate goal of a just and equitable global trading system. Shoppers can buy products in line with their values and principles. They can choose from an ever growing range of great products.
(ii) Traders / Companies – Since its launch in 2002, the fair trade mark has become the most widely, recognised social and development label in the world. Fair trade offers companies a credible way to ensure that their trade has a positive impact for the people at the end of the chain.
(iii) Producers – For producers fair trade is unique in offering important benefits:
(a) stable prices that cover the costs of sustainable production,
(b) market access that enables buyers to trade with producers who would otherwise be excluded from market,
(c) partnership
(d) empowerment of farmers and workers.
Question 2.
Write a note on the beneficiaries of Fair Trade practices.
Answer:
Fair Trade is about better prices, decent working conditions and fair terms of trade for farmers and workers.
Beneficiaries of Fair Trade practices:
Consumers:
- Consumers are the main beneficiaries.
- This is because they can advocate and compare for wide reform of International trading rules.
- They can choose from growing range of great products.
- Consumers support producers by buying fair trade labelled products who are struggling to improve their lives.
Traders (or) companies:
- Fair Trade offer companies a credible way to ensure that they have a positive impact.
- Launched in 2002, Fair Trade mark has become the most widely, recognized social and development label in the world.
Producers:
- It gives the farmers / producers a kind of empowerment.
- Stable prices cover the cost of sustainable production.
- Buyers easily access the market and trade with producers, which in turn boost production.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the factors that multinational companies take into account before setting up a factory in different countries?
Answer:
Before setting up a company or a factory, an MNC takes into account the following things:
(i) Availability of cheap labour and other resources:
MNC’s setup offices and factories for production in various regions of the world, where cheap labour and other resources are available in order to earn greater profit.
(ii) Partnership with local companies:
MNC’s setup partnership with local companies, by a closely competing with local companies or buying local companies for supply. As a result, production in these widely dispersed locations gets interlinked.
(iii) Favourable Government Policy:
If the Government Policies are favourable, it helps MNC’s. For example: Flexibility of labour laws will reduce cost of production. MNC’s are able to hire worker on casual and contractual wages for a short period instead of a regular basis. This reduces the cost of labour for the company and increases its margin of profit.
Question 4.
What are the reasons for the growth of MNC?
Answer:
Expansion of Market: For a large size firm, when its activities expand more and more , it goes beyond their country’s boundary and move to other countries market.
Marketing superiorities:
- A MNC enjoys market reputation easily .
- It faces loss difficulty in selling the products .
- It can adopt very effective advertisement tactics.
- All these help in their sales promotion.
High level of financial resources:
- A MNC has high level of financial resources which helps them in high level of fund utilisation.
- Easy access to external capital market.
- Can raise more International resources to improve their production at any cost.
Advancement in Technology:
- The High level of technology of the MNCs attract them to participate in Industrial development.
- It helps them to offer products at a low price.
Product Innovation:
- They can develop new products.
- New Designs of existing products.
- Designs that help the new generations to apply their knowledge.