Students can download 10th Social Science Economics Chapter 3 Food Security and Nutrition Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Solutions Economics Chapter 3 Food Security and Nutrition
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Food Security and Nutrition Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
……………….. of food is physical availability of food stocks in desired quantities, which is a function of domestic production, changes in stocks and imports.
(a) Availability of food
(b) Access to food
(c) Absorption of food
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Availability of food
Question 2.
Buffer stock is the stock of food grains, namely wheat and rice, procured by the government through the ……………
(a) FCI
(b) Consumer Cooperatives
(c) ICICI
(d) IFCI
Answer:
(a) FCI
Question 3.
Which is correct?
(i) HYV-High Yielding Varieties
(ii) MSP-Minimum Support Price
(iii) PDS-Public Distribution System
(iv) FGi-Food Corporation of India
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) (iii) and (iv) are correct
(c) (ii) and (iii) are correct
(d) all are correct
Answer:
(d) all are correct
![]()
Question 4.
…………… extended assistance through its Public Law 480.
(a) United States of America
(b) India
(c) Singapore
(d) UK
Answer:
(a) United States of America
Question 5.
……………….. revolution was born in India paving way for self sufficiency in food grain production.
(a) Blue Revolution
(b) White Revolution
(c) Green Revolution
(d) Grey Revolution
Answer:
(c) Green Revolution
Question 6.
………….. is the only state in India to adopt universal PDS.
(a) Kerala
(b) Andhra Pradesh
(c) Tamil Nadu
(d) Karnataka
Answer:
(c) Tamil Nadu
Question 7.
……………….. is the process of providing or obtaining the food necessary for health and growth.
(a) Health
(b) Nutrition
(c) Sanitation
(d) Security
Answer:
(b) Nutrition
Question 8.
Tamil Nadu Integrated Nutrition Programme was started in …………..
(a) 1980
(b) 1975
(c) 1955
(d) 1985
Answer:
(a) 1980
Question 9.
……………….. status is one of the indicators of the overall well-being of population and human resources development.
(a) Health
(b) Nutritional
(c) Economic
(d) Wealth
Answer:
(a) Health
Question 10.
Tamil Nadu Health System Projects has launched ……….. service at free of cost.
(a) 106 ambulance
(b) 108 ambulance
(c) 107 ambulance
(d) 105 ambulance
Answer:
(b) 108 ambulance
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks
- ……………… foundation from USA introduced HYV in India.
- ……………… is an important indicator of nutrition deficiency.
- In the year ……………… National Food Security Act was passed by the Indian Parliament.
- ……………… play an important role in the supply of quality goods at reasonable rates to common people.
- ……………… is the value of currency expressed in terms of the amount of goods and services that one unit of money can buy.
Answers:
- Ford
- Underweight
- 2013
- Consumer co-operatives
- Purchasing Power
III. Match the following
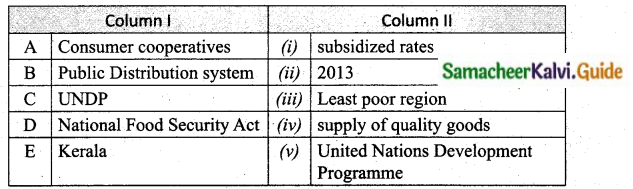
Answer:
A. (iv)
B. (i)
C. (v)
D. (ii)
E. (iii)
![]()
IV. Assertion and Reason
Question 1.
Assertion (A): Purchasing power increases, price decreases and vice versa.
Reason (R): The production of goods decline, the price of goods increases and then the purchasing power is affected.
(a) A is correct, R is false
(b) Both A and R are false statements
(c) A is correct but R is not a correct explanation
(d) A is correct, R is the correct explanation of A
Answer:
(d) A is correct, R is the correct explanation of A
V. Answer in Short
Question 1.
Define food security according to FAO.
Answer:
The United Nation’s Food and Agriculture Organisation defines food security as follows:
“Food security exists when all people, at all times, have physical, social and economic access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food which meets their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life.” (FAO, 2009)
Question 2.
what are the basic components of food and nutrition security?
Answer:
The hasic components of food and nutrition security are
- Availability of food
- Access to food
- Absorption of food
![]()
Question 3.
Explain ‘ship to mouth’ phenomenon.
Answer:
United States of America extended assistance through its Public Law 480 (PL 480) scheme to India during early 1960s. This situation was popularly known as ‘Ship to Mouth’ existence.
Question 4.
What is the role of FCl in Green Revolution?
Answer:
The Food Corporation of India helped the State to procure the harvested grains at the beginning of the cropping season. The FCI built huge storage godowns and built buffer stocks of food grain during the harvest season to be distributed throughout the year.
Question 5.
What are the effects of Green Revolution?
Answer:
- It increase the production and cultivation
- It increase the productivity
- Changes in cropping system
- Industrial development
Question 6.
Write a note on Differential Universal PDS and Targeted PDS.
Answer:
- Under Universal Public Distribution System all the family ration card holders are entitled to the supplies from PDS.
- Under Targeted PDS, the beneficiaries are identified based on certain criteria and given their entitlements, leaving the others.
- Tamil Nadu is following Universal PDS.
Question 7.
Write a short note on purchasing power.
Answer:
Purchasing power is the value of a currency expressed in terms of the amount of goods or services that one unit of money can buy. Price increases purchasing power declines and vice versa.
Question 8.
What are the main reasons for the New Agricultural Policy?
Answer:
- To raise agricultural production and productivity.
- To remove export restrictions such as export duty, export ban and quota restriction on organic and processed agricultural products.
- All round development of the agriculture sector.
Question 9.
Write short note on multi-dimensional nature of poverty.
Answer:
Multi-dimensional poverty measures can be used to create a more comprehensive picture. They reveal who is poor, how they are poor and the range of disadvantages they experience. As well as providing a headline measure of poverty, multi-dimensional measures can be broken down to reveal the poverty level in different areas of a country, and among different subgroups of people.
![]()
Question 10.
Write some name of the nutrition programmes in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS), Mid-Day Meals Scheme, Reproductive and child Health Programmes (RHP) and National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) Puratchi Thalaivar MGR Nutritious Meal Programme (PTMGRNMP), Mid day meal programme.
VI. Answer in detail
Question 1.
Elucidate why the Green Revolution was born.
Answer:
- For a country’s overall development process food security of people is one of the key determining factor.
- After independence, even though India focused on Agriculture, industrialization was also given priority.
- But the problem of drought experienced in India forced her to be dependent on imports of food grains.
- Therefore India had to plead for food grains from richer countries at concessional rates.
- United states of America extended assistance through its Public Law 480 to India. This situation was popularly known as ship to mouth existence.
- An American Organisation Ford Foundation formulated a plan to increase food production in the country by introducing High Yielding varieties of wheat and rice.
- When the results was very good in India, the idea of Green Revolution also bom in India.
Question 2.
Explain Minimum Support Price.
Answer:
Minimum Support Price is a price fixed by an expert group for a particular crop by considering various costs involved in the cultivation of that crop. After announcing the MSP, the State will open procurement centres in places where these crops are widely grown. However, the farmers are free to sell in the open market if they get a better price for their crop produce. On the other hand, if the open market price is lower than the MSP, the farmers would get an assured price (the MSP) by selling their produce to the FCI. Thus, with the implementation of MSP farmers are certain about the price they would get at the end of the crop season. Further, farmers also get insulated against any price crash during the harvest season.
![]()
Question 3.
Elaborate the Public Distribution System.
Answer:
- Public Distribution system refers to the Ration Shops.
- The step taken by the Government to distribute food grains at subsidised rates is through this Public Distribution System.
- The nature, scope and functioning of PDS varies from State to State.
- There are two types of Public Distribution System.
- They are universal PDS and Targeted PDS.
- Under universal PDS, all the family ration card holders are entitled to the supplies from PDS.
- In the targeted PDS, the beneficiaries are identified based on certain criteria, leaving others.
- Tamil Nadu continues to have the universal system of PDS and supplies rice at free of cost to all card holders.
- Both the Union and the State Governments subsidised the supplies distributed through PDS.
- The National Food Security Act was passed by the Indian Parliament in 2013.
- According to this Act 50% of urban households and 75% of the rural households are known as priority households based on a set of criteria.
- They are supplied rice at ₹3 per kg, and wheat at ₹2 per kg, and millets at ₹1 per kg.
- The Government of Tamil Nadu has declared that SMART family cards in lieu of existing family cards.
Question 4.
What are the factors affecting the purchasing power and explain them.
Answer:
• Over population: The population growth rate in India is high as 1.7 per 1000. Large population leads to increasing demand, but supply was not equal to the demand. So, the normal price level will be going an higher. So it affect purchasing power, especially in rural population.
• Increasing prices of essential goods: Even though there has been a constant growth in the GDP and growth opportunities in the Indian economy, there have been steady increase in the prices of essential goods. The continuous rise in the prices erodes the purchasing power and adversely affect the poor people. During 2015-16 an average rate of 2% flood inflation, the prices of pulses rose by about 40%.
• Demand for goods: When demand for goods increases, the price of goods increases then the purchasing power is affected.
• Price of goods affect the value of currency: When the price increases the purchasing power decreases and finally the value of currency decreases and vice versa.
• Production and supply of goods: The production and supply of goods decline, the price of goods increases, then the purchasing power is affected.
• Poverty and inequality: There exists a huge economic disparity in the Indian economy. The proportion of income and assets owned by the top 10% of Indian goes on increasing. This has led to an increase in the poverty level in society. Generally purchasing power is affected by poverty and unequal distribution of wealth also.
Purchasing power affects every aspect of economics, from consumers buying goods to investors and stock prices to a country’s economic prosperity. As such, a country’s government institutes policies and regulations to protect a currency’s purchasing power and keep an economy healthy. One method to monitor purchasing power is through the Consumer Price Index.
Question 5.
Write briefly some of the important objectives of India’s agricultural policy.
Answer:
The New Agricultural Policy was announced by the Government of India in 2018. The main objectives of the policy are:
- Raising the productivity of inputs: Inputs for the growth of crops of such as HYV seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, irrigation projects should be improved.
- Raising value – added per hectare: The policy aims at increasing the value addition per hectare by raising the productivity in small and marginal holding instead of raising physical output in general.
- Protecting the interest of the poor farmers: The policy help the poor and marginal farmers by abolishing intermediaries, extended credit support and land reforms,
- Modernising Agriculture sector: Introduction of modem technology in agricultural operations and application of improved agricultural inputs like HYV seeds, fertilizers etc.
- Environmental Degradation: One of the objective of the agricultural policy is to check the environmental degradation of natural base.
- Removing bureaucracy: Bureaucratic obstacles on the farmers co-operative societies and self – help institutions is to be removed so that farmers can work freely.
Question 6.
Discuss about the Multi-dimentional Poverty Index India and Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Multi-dimensional Poverty Index 2018 report prepared by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative makes the following observations about India.
India has reduced its poverty rate drastically from 55% to 28% in 10 years, with 271 million people moving out of poverty between 2005-06 and 2015-16.
• India still had 364 million poor people in 2015-16, the largest for any country, although it is down from 635 million in 2005-06.
• Of the 364 million people who were MPI poor in 2015-16,156 million were children whereas in 2005-06 there were 292 million poor children in India. This represents a 47% decrease or 136 million fewer children growing up in multi-dimensional poverty.
• 80% of people belonging to ST were poor in 2005-06 and 50% of them were still poor in 2015-16.
• Bihar with more than half its population in poverty was the poorest state in 2015-16.
• The four poorest states Bihar, Jharkhand, Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh were still home to 196 million MPI poor people, which was over half of all the MPI poor people in India.
• Kerala, one of the least poor regions in 2006, reduced its MPI by around 92%.
Multi-dimensional Poverty Index 2018 Report in Tamil Nadu:
Over the last decades, Tamil Nadu has made a significant progress in poverty reduction. The districts in Tamil Nadu are classified into three categories, namely high-poverty districts (more than 40% of the population living below poverty line), moderately poor districts (30% to 40%) and low level poverty districts (below 30%).
After 1994, poverty has declined steadily in both rural and urban areas of Tamil Nadu and the state has a smaller share of India’s poor relative to its-population. After 2005, the poverty reduction in this state has been faster than in many other states in India. Tamil Nadu leads in the poverty alleviation programmes during 2014-2017. Government of India is implementing many policies and programmes to eradicate poverty.
These policies and programmes, if continued, will completely eradicate the poverty in the state. In future, Tamil Nadu can become a model of development in India.
Question 7.
Briefly explain the nutritional and health status of Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
- Nutrition plays a crucial role in human health and well being.
- Tamil Nadu has played a pioneering role in bringing about significant changes in the health and nutrition status.
- Children below six years of age, pregnant women, lactating mothers and adolescent girls are mainly taken care of.
- Tamil Nadu’s budget allocation for health and nutrition is the highest in the country.
- The performance of the Integrated Child Development Services, and the Puratchi Thalaivar MGR Nutritious Meal Programme (PTMGRNMP) are considered one of the best in the country.
- In Tamil Nadu, ICDs is being implemented through 54,439 child centres, that is 49,499 Anganwadi centres and 4,940 mini Anganwadi centres.
- There are 434 Child Development Blocks in which 385 in rural areas, 47 urban areas and 2 in tribal areas.
- The Government of Tamil Nadu’s policy for “A Malnutrition free Tamil Nadu” guides the State’s long term Multi – sectoral strategy for eliminating malnutrition,
- Amartya Sen, Noble prize winning Economist stated that he sees a political will and commitment in the state of Tamil Nadu to tackle these issues to achieve the status of a “Malnutrition” “Free state”.
![]()
VII. Activity and Projects
Question 1.
Visit nearby “Uzhavar Sandhai” and collect the information about the functions of market.
Answer:
Uzhavar Sandhai is a scheme of the Government of Tamil Nadu to promote direct contact between farmers and consumers in Tamil Nadu.
Functions of Uzhavar Sandhai:
- Uzhavar Sandhai also called as Farmer’s market was started at Madurai in 1999 to help the farmers to sell their produce at reasonable rate without the interference of the middlemen.
- Uzhavar Sandhai starts its functioning from early morning.
- It facilitates direct contact between farmers and the public.
- It provides fresh vegetables and fruits at reasonable price daily without any interference from the middlemen.
- Prices are listed down in the blackboards in every shop.
- It provides correct measurement to the consumers with the price lesser than the retail price in the market.
- It also acts as a technical training centre to the farmers.
- Some of the Uzhavar Sandhai’s also sell seeds and other inputs to the farmers.
- Farmers those who produce less can also sell in these farmer’s market and benefit themselves.
Question 2.
Collect information about health centre functioning nearby your location.
Answer:
Health centres provide continuous and comprehensive care to the patients. It helps in making the patients available with the social welfare and pubilc health services initiated by the Governing bodies.
Functions of Health Centre:
- Provision of medical care.
- Education about health.
- Prevention and control of locally epedemic diseases.
- Safe water supply and basic sanitation.
- Maternal – child health including family planning.
- Clinical Services.
- Aged and disability care.
- Child care.
- Overall Health Promotion.
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Food Security and Nutrition Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The minimum support price is the price announced by the Government at the ……………… of the cropping season.
(a) end
(b) beginning
(c) harvest
(d) none
Answer:
(b) beginning
Question 2.
………… The programme was implemented in selected districts where irrigation was assured.
(a) FCI
(b) HYV
(c) MSD
Answer:
(b) HYV
Question 3.
The nature, scope and functioning of the ……………… varies from State to State.
(a) FCI
(b) PDS
(c) IRDP
(d) None
Answer:
(b) PDS
Question 4.
Buffer stock scheme purpose is …………..
(a) To save food grains from pest attack
(b) To deliver food
(c) To stop price fluctuations
Answer:
(c) To stop price fluctuations
Question 5.
Around 94% of the fair – price shops are run by ……………… in Tamil Nadu.
(a) banks
(b) government
(c) co-operatives
(d) local heads
Answer:
(c) co-operatives
Question 6.
It has been proposed to open new fair price shops so that, no cardholder walks more than ……………… km.
(a) 4
(b) 3.5
(c) 2.5
(d) 1.5
Answer:
(d) 1.5
![]()
Question 7.
……………… is a method of monitoring purchasing power.
(a) Purchasing power parity
(b) Whole sale price Index
(c) Consumer price index
(d) Inflation
Answer:
(c) Consumer price index
Question 8.
In general, purchasing power is affected by :
(a) Poverty
(b) Unequal distribution of wealth
(c) Price of the goods
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question 9.
……………… is the largest economy in terms of PPP – GDP in 2019.
(a) USA
(b) China
(c) Japan
(d) India
Answer:
(b) China
Question 10.
……………… are the factors that constitute the Multi-Dimensional Poverty Index.
(a) Quality of work
(b) Health
(c) Education
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
![]()
Question 11.
……………… district tops in Multi-dimensional index in Tamil Nadu.
(a) Coimbatore
(b) Kancheepuram
(c) Ariyalur
(d) Virudunagar
Answer:
(b) Kancheepuram
Question 12.
The status of ……………… in urban and Rural areas are traced with the help of the National Family Health Survey.
(a) Poverty
(b) Health
(c) Nutrition
(d) All the above
Answer:
(c) Nutrition
Question 13.
……………… is considered to be one of the world’s largest programme of its kind for the holistic development of the child.
(a) ICDS
(b) RCH
(c) NRHM
(d) All the above
Answer:
(a) ICDS
Question 14.
Dr. Muthulakshmi Reddy Maternity Benefit Scheme gives financial assistance to poor pregnant women upto :
(a) ₹ 25,000
(b) ₹ 12,000
(c) ₹ 15,000
(d) ₹ 50,000
Answer:
(b) ₹ 12,000
Question 15.
Better medical care leads to ……………… population.
(a) stable
(b) healthy
(c) disease less
(d) growth of active
Answer:
(b) healthy
![]()
II. Match the following
Question 1.
Match the Column I with Column II.
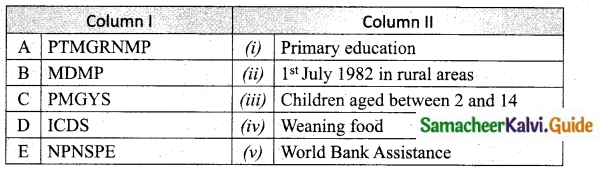
Answer:
A. (ii)
B. (iii)
C. (iv)
D. (v)
E. (i)
Question 2.
Match the Column I with Column II
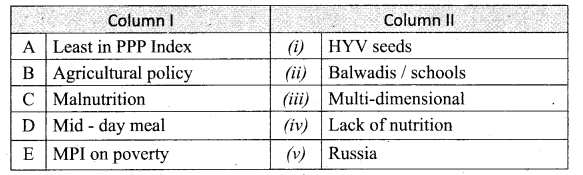
Answer:
A. (v)
B. (i)
C. (iv)
D. (ii)
E. (iii)
![]()
III. Choose the correct statement
Question 1.
(i) India has reduced the poverty rate drastically from 55% to 28 % in the past 10 years.
(ii) Multidimensional poverty index reveals who is poor, how they are poor, and the disadvantages they experience.
(iii) A substantial number of Indian women and children are underweight, anaemic and deficient in micro-nutrient.
(iv) Though India has achieved self – sufficiency in food production, yet to attain food security to all.
(a) (i), (iv) are correct
(b) (i), (ii), (iii) are correct
(c) (ii), (iii) are correct
(d) all are correct
Answer:
(d) all are correct
Question 2.
(i) Raising the productivity of inputs and modernising agricultural is one of the aim of PMGYS.
(ii) Amartya Sen is an leading nobel laureate in agricultural science.
(iii) Tamil Nadu Integrated Nutrition programme is assisted financially by the world bank.
(iv) The National Food Security Act was implemented in Tamil Nadu in 2016.
(a) (i), (ii), (iii) are correct
(b) only (iv) is correct
(c) (i), (iv) are wrong
(d) (iii), (iv) are correct
Answer:
(b) only (iv) is correct
![]()
IV. Assertion and Reason
Question 1.
Assertion (A): The New Agricultural policy was announced by the Government of India in 2018.
Reason (R): The Government decided to remove export restrictions on most organic and processed agricultural products.
(a) A is correct but R is not the correct explanation to A.
(b) A and R are wrong.
(c) A is correct and R is the correct explanation to A.
(d) A is wrong but R is correct.
Answer:
(c) A is correct and R is the correct explanation to A.
Question 2.
Assertion (A): Government of India is implementing many policies and programmes to eradicate poverty in India.
Reason (R): These policies if continued, Tamil Nadu can become a model of development in India in future.
(a) A is correct but R is not the correct explanation to A.
(b) A is wrong R is correct.
(c) A is correct but R is the correct explanation to A.
(d) A and R are wrong.
Answer:
(a) A is correct but R is not the correct explanation to A.
V. Answer in Short
Question 1.
Write about the National Food Security Act in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
On 1 November 2016, Tamil Nadu became the last state in the country to implement the National Food Security Act after holding out for three years. In a government order issued on 27 October, the state specified that while it was enforcing the law, it would be modifying its provisions.
Question 2.
Define Nutrition Security.
Answer:
According to eminent agricultural scientist M.S.Swaminathan, Nutrition security is, “Physical, Economic and social access to a balanced diet, safe drinking water, environmental hygiene, primary health care and primary education.
Question 3.
What is the purchasing power parity?
Answer:
• PPP is an economic theory that estimates the amount that needs to be adjusted to the price of an item, given exchange rates of the two countries, in order for the exchange to match each currency’s purchasing power.
• PPP can be used to compare countries income levels and other relevant economics data concerning the cost of living, or possible rates of inflation and deflation.
Question 4.
What does availability of food depend upon?
Answer:
The Availability of food depends upon the domestic production, changes in stocks and imports.
Question 5.
Name the three-tier structure of consumer cooperative societies in India?
Answer:
- Primary consumer cooperative societies
- Central consumer cooperative stores.
- State-level consumer federation.
Question 6.
Write a note on National Food Security Act in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
The National Food Security Act was passed by the Indian Parliament in 2013. On Nov 1, 2016 Tamil Nadu became a last state in the country to implement the Act. On 27th October, the State specified that while enforcing the law, it would modify the provisions.
Question 7.
What is meant by Buffer stock?
Answer:
Buffer stock is the stock of food grains namely wheat and rice procured by the Government through the Food Corporation of India.
Question 8.
How does the Buffer stock scheme help the people?
Answer:
The Buffer stock helps to resolve the problem of shortage of food during adverse weather conditions or during the periods of calamity.
![]()
Question 9.
What is meant by Issue Price?
Answer:
Buffer stock is done to distribute food grains in the deficit areas and among the poorer strata of the society at a price lower than the market price also known as the Issue Price.
Question 10.
What are the three major dimensions of poverty?
Answer:
Health, Education and living standard are the major dimensions of poverty.
Question 11.
What is Padhumaiyar Kuzhu?
Answer:
Empowering adolescent girls and making them participate in the peer group services and activities as a group. This would enable them to gain confidence and became a catalyst of change.
Question 12.
What is PPP?
Answer:
PPP refers to the Purchasing Power Parity. It is an economic theory that estimates the amount that needs to be adjusted to the price of the item, given the exchange rate of the two countries.
Question 13.
What are the uses of PPP?
Answer:
PPP is used to compare countries income levels, and other relevant economic data concerning the cost of living, (or) possible rates of Inflation or deflation.
Question 14.
What is meant by Agricultural policy?
Answer:
Agricultural policy of a country is designed for increasing the agricultural production and productivity thereby raising the level of income and standard of living of the farmers within a particular period of time.
![]()
Question 15.
What are the ten indicators of Multi – Dimensional poverty index.
Answer:
- Nutrition and child mortality under health.
- Years of schooling and school attendance under education.
- Cooking fuel, sanitation, water, Electricity, floor, assets under living standards.
Question 16.
Write a note on The Chief Minister’s Comprehensive Health Insurance scheme.
Answer:
- It was launched in 2011 – 12.
- Aims to provide free medical and surgical treatment in Government and private hospital to any family whose annual income is less than ? 72,000
- To reach the goal of Universal Health Care to All.
Question 17.
When does Food security exists?
Answer:
Food security exists when all people, at all times, have physical, social, and economic access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food to meet dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life.
Question 18.
Write a note a Dr. Muthulakshmi Reddy Maternity Benefit Scheme.
Answer:
- Gives financial assistance upto ₹ 12,000 to poor pregnant women on nutritious diet in 3 instalments.
- This helps to avoid low birth weight of new bom babies.
- These women can avail ante – natal care delivering and immunising the baby bom on Government hospitals.
Question 19.
What was the aim of the National leprosy Eradication Programme?
Answer:
Its aim is to detect and to provide sustained regular treatment to all leprosy patients in the State.
Question 20.
Write the names of the four poorest states of India.
Answer:
Bihar, Jharkhand, Uttarpradesh and Madhyapradesh are the four states with more number of poor people live.
![]()
VI. Answer in Detail
Question 1.
Explain the role of consumer co-operation in food security of India.
Answer:
- Consumer co-operatives play an important role in the supply of quality goods at reasonable rates to common people.
- It has a three tier structure.
- They are Primary Consumer Co-operative Society, Central Consumer Co-operative Stores, State Level Consumer Federations.
- More than 50,000 village level societies are engaged in the distribution of consumer goods in rural areas.
- There are other benefits from consumer co-operatives such as Health Care, Insurance, Housing etc.,
- Consumer co-operatives play a very important role in Tamil Nadu can be well witnessed as to around 94% of fair price shops are being run by co-operatives.
![]()
Question 2.
Name and explain the two components of food security system in India:
Answer:
The two components of food security system in India are Buffer stock and Public distribution system.
(i) Buffer Stock:
It is the stock of food grains (wheat and rice) procured by the government through Food Corporation of India (FCI). It is used to distribute food grain in the deficit areas and among the poorer strata of society at a price lower than the market price. This , stock is also used during among natural calamity such as drought or earthquake.
(ii) Public Distribution System:
The food produced by the FCI is distributed through government-regulated ration shops among the poorer section of the society. This is called the Public Distribution System.