Students can download 10th Social Science History Chapter 3 World War II Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Solutions History Chapter 3 World War II
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science World War II Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
When did the Japanese formally sign of their surrender?
(a) 2 September, 1945
(b) 2 October, 1945
(c) 15 August, 1945
(d) 12 October, 1945
Answer:
(a) 2 September, 1945
Question 2.
Who initiated the formation of League of Nations?
(a) Roosevelt
(b) Chamberlain
(c) Woodrow Wilson
(d) Baldwin
Answer:
(a) Roosevelt
![]()
Question 3.
Where was the Japanese Navy defeated by the US Navy?
(a) Battle of Guadalcanal
(b) Battle of Midway
(c) Battle of Leningrad
(d) Battle of El Alamein
Answer:
(b) Battle of Midway
Question 4.
Where did the US drop its first atomic bomb?
(a) Kavashaki
(b) Innoshima
(c) Hiroshima
(d) Nagasaki
Answer:
(c) Hiroshima
Question 5.
Who were mainly persecuted by Hitler?
(a) Russians
(b) Arabs
(c) Turks
(d) Jews
Answer:
(d) Jews
Question 6.
Which Prime Minister of England who signed the Munich Pact with Germany?
(a) Chamberlain
(b) Winston Churchill
(c) Lloyd George
(d) Stanley Baldwin
Answer:
(a) Chamberlain
![]()
Question 7.
When was the Charter of the UN signed?
(a) June 26, 1942
(b) June 26, 1945
(c) January 1, 1942
(d) January 1, 1945
Answer:
(b) June 26, 1945
Question 8.
Where is the headquarters of the International Court of Justice located?
(a) New York
(b) Chicago
(c) London
(d) The Hague
Answer:
(d) The Hague
II. Fill in the blanks
- Hitler attacked ……………… which was a demilitarized zone.
- The alliance between Italy, Germany and Japan is known as ………………
- ……………… started the Lend-Lease programme.
- Britain Prime Minister ……………… resigned in 1940.
- Saluting the bravery of the ……………… Churchill said that “Never was so much owed by so many to so few”.
- ……………… is a device used to find out the enemy aircraft from a distance.
- The Universal Declaration of Human Rights set forth fundamental human rights in ……………… articles.
- After the World War II ……………… was voted into power in Great Britain.
Answers:
- Rhineland
- Rome – Berlin
- Roosevelt
- Chamberlain
- Royal Air force
- Radar
- 30
- Labour party
![]()
III. Choose the correct statement
Question 1.
(i) Banking was a major business activity among Jews.
(ii) Hitler persecuted the Jews.
(iii) In the concentration camps Jews were killed.
(iv) The United Nations has currently 129 member countries in it.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
(b) (i) and (Hi) are correct
(c) (iii) and (iv) are correct
(d) (i) is correct and (ii), (iii) and (iv) are wrong
Answer:
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct
Question 2.
Assertion (A): President Roosevelt realised that the United States had to change its policy of isolation.
Reason (R): He started a programme of Lend Lease in 1941.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) A is right but R is not the correct reason
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) R is right but it has no relevance to A
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct
![]()
IV. Match the Following

Answers:
A. (v)
B. (iv)
C. (i)
D. (ii)
E. (iii)
V. Answer the questions briefly
Question 1.
Mention the important clauses of the Treaty of Versailles relating to Germany.
Answer:
- Germany was forced to give up territories to the west, north and east of the German border.
- Germany had to be disarmed and was allowed to retain only a very restricted army, navy and air force.
- Germany was expected to pay huge military and civilian cost of the war to the allied nations (approx. $ 25 billion).
Question 2.
Who were the three prominent dictators of the post World War I?
Answer:
The three prominent dictators of the post-World War I were Mussolini (Italy), Hitler (Germany) and Franco (Spain).
Question 3.
How did Hitler get the support from the people of Germany?
Answer:
Hitler was able to sway away the emotions of the German people by his great speeches. He promised them that he will return back the glorious Germany. His racial superiority of the Germans as a pure Aryan race and a deep-rooted hatred for jews made him get the support of his people.
![]()
Question 4.
Describe the Pearl Harbour incident.
Answer:
Pearl Harbour incident took place in December 1941 when japan attacked American naval installations in Pearl Harbour, Hawaii, without warning to cripple America’s Pacific fleet. Many battle ships and numerous fighter planes were destroyed. The US declared war on Japan, with Britain and China. This brought together both the Asia Pacific and the European war into one common cause. Most importantly, it brought the United States with its enormous resources into the war as a part of the Allies.
Question 5.
What do you know of Beveridge Report?
Answer:
The Report that was published in the United Kingdom in 1942 to improve the general welfare of the people is called as Beveridge Report. It proposed that the government should provide citizens with adequate income, healthcare, education housing and employment to overcome poverty and disease thereby improve general welfare.
Question 6.
Name the Bretton Woods Twins.
Answer:
The World Bank and the International Monetary Fund.
Question 7.
What are the objectives of the IMF?
Answer:
- To foster global monetary co-operation
- To secure Financial Stability
- To facilitate International Trade
- To promote high employment and sustainable economic growth.
- To reduce poverty around the world.
![]()
VI. Answer the questions given under each caption
Question 1.
Battle of Stalingrad
(a) When did Germany attack Stalingrad?
Answer:
In August 1942, Germany attacked Stalingrad.
(b) What were the main manufactures of Stalingrad?
Answer:
The main manufactures of Stalingrad were armaments and tractors.
(c) What was the name of the plan formulated by Hitler to attack Stalingrad?
Answer:
Fall Blau or Operation Blue
(d) What is the significance of the Battle of Stalingrad?
Answer:
The people of Russia were grateful for Stalin’s conduct of the war. They regarded him as ‘a prodigy of patience, tenacity and vigilance, almost omnipresent, almost omniscient.
Question 2.
Japanese Aggression In South-east Asia
(a) Name the South-east Asian countries which fell to the Japanese.
Answer:
Guam, the Philippines, Hong Kong, Singapore, Malaya, the Dutch East Indies and the Burma all fell to the Japanese.
![]()
(b) Account for the setback of Allies in the Pacific region?
Answer:
The Allies had a setback in the Pacific region because of their inadequate preparation. The local people had to face the atrocities of the Japanese.
(c) What is the significance of Battle of Midway?
Answer:
The U.S. navy defeated the Japanese navy in the Battle of Midway. Thus, the battle is in favour of the Allies.
(d) What happened to the Indians living in Burma?
Answer:
The Indians living in Burma walked all the way to the Indian border facing many hardships. Many died of disease and exhaustion.
Question 3.
General Assembly and Security Council
(a) List the permanent member countries of the Security Council.
Answer:
The United States, Britain, France, Russia and China.
(b) What is the Holocaust?
Answer:
The word ‘holocaust’ is used to describe the genocide of nearly six million Jews by the Germans during the Second World War.
(c) Who was the Chairperson of the UN Commission on Human Rights?
Answer:
The widow of US President Franklin Roosevelt was the chairperson of the UN Commission on Human Rights.
(d) What is meant by veto?
Answer:
A veto is the power to unilaterally stop an official action, especially the enactment of legislation.
![]()
VII. Answer in detail
Question 1.
Attempt an essay on the rise and fall of Adolf Hitler.
Answer:
- Adolf Hitler Was the founder of the National Socialist party, generally known as the Nazi party.
- His great oratorical skill, his promise to bring back the glorious past of Germany, his support for the German race and hatred towards the Jews helped him to get people support.
- He came to power in 1933 and ruled Germany till 1945.
- He began to re-arm Germany and recruitment of new armed forces.
- The manufacture of armaments and machinery for the army, navy and air force with large spending from government resulted in the revival of the economic condition and helped to solve the unemployment problem in the economy.
- He followed aggressive policy and therefore in 1936, he invaded Rhine land, the demilitarized zone.
- His alliance with Italy and Japan became Rome-Berlin-Tokyo axis.
- He signed Munich pact stating Germany would not conquer any other territory, rather in 1939, he invaded Czechoslovakia.
- His attack on Poland resulted in the declaration of war by Britain and France against Germany.
- In 1941, German army invaded Russia. But the resistance of the German army and Russian winter defeated German army.
- When the allied forces fought back, Germany also retaliated. Finally, Hitler committed suicide in 1945.
- In 1945, allies occupied Berlin and Germany was divided as two sections after the war.
Question 2.
Analyse the effects of World War II.
Answer:
World War II was the most devastating war in history. It left a deep impact on the entire world. It changed the world in fundamental ways. Here are the effects of this War:
(i) The world got polarised into two main blocs led by superpowers, one led by the United States which followed anti-communist ideology, and the other by Soviet Russia which was essentially communist in nature. Europe was thus divided into two: Communist and non-communist.
(ii) The United States and the Soviet Union entered into a race to have more nuclear powered World War II 43 weapons. They built a large stockpile of such weapons. Meanwhile, Britain and France developed their own nuclear weapons.
(iii) Gradually there arose competition among countries. They began to devote large amount of resources in developing more and more powerful weapons with great destructive power, and defence spending skyrocketed in many countries.
(iv) It was realised that the League of Nations was ineffective and weak. So countries of the world decided not to repeat the mistake. Instead, many international agencies, in particular the United Nations, the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund came into existence providing a forum for countries large and small.
(v) Many other important social and economic changes also took place in the post-War world. Colonial powers were forced to give independence to former colonies in a process of decolonisation. India was the first country to get independence.
(vi) Women became the part of labour force in huge numbers. They became economically independent.
![]()
Question 3.
Assess the structure and activities of the UN.
Answer:
The charter of the United Nations was signed on June 26, 1945 by 51 nations. Now, the United Nations has 193 member states and each one has an equal vote in the UN.
Structure of UN:
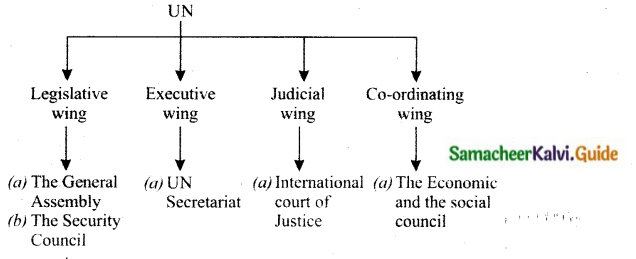
The General Assembly: Meets once in a year. Issues of interest and points of conflict are discussed in the Assembly.
The Security Council: Consist of five permanent members (USA, Britain, France, Russia, China) and ten non-permanent members (elected in rotation). Each permanent member has the right to veto (A right to reject a decision).
UN Secretariat: Headed by the Secretary by law General. He is elected by the General Assembly on the recommendations of the Security Council. He, with his cabinet and officials run the UN.
International Court of Justice: Headquarters at the Hague in Holland.
The Economic and the Social Council: Co-ordinates all the social and economic work of the U.N. Headed by economists like Gunnar Myrdal.
![]()
Activities of the UN:
- Human Rights, Refugees problem, climatic change, gender equality are the important issues taken over and deals with it. Earlier in 1960’s decolonisation was also a part of their activity.
- UN peace keeping force acted in many areas of conflict all over the World. Indian army has been a part of it.
- The preamble of the UN declares, its activities include human rights, equality of men and women.
VIII. Students Activity
Question 1.
A debate in the class on the success or failure of the UN in preserving World Peace.
Answer:
The students can take the following topics for debate and finally conclude, UN is successful as it has stopped the nations from bringing another war. Small to big clashes were/are handled by UN efficiently.
Argument for:
The topics of discussion for debate are:
- Solving International conflicts: Since 1945, UN peacekeepers have undertaken over 60 field missions and negotiated 172 peaceful settlements that ended Regional conflicts.
- Liberation from Colonial rule: Eighty nations and more than 750 million people have been freed from colonialism.
- Human Rights: Custodian for the protection of human rights, discrimination against women, Children’s rights, torture, missing persons etc. in many countries.
- Enhancing Human life: Specialised agencies of the UN engaged in enhancing all aspects of human life, including education, health, poverty reduction, climate change.
- Treaties: More than 560 multilateral treaties on human rights, refugees, disarmament.
Argument against:
Non-proliferation Treaty (NPT): Signed by 190 nations, all live superpowers owned nuclear weapons. Later, several countries North Korea, Israel, Pakistan, India developed nuclear weapons.
Veto Power: Veto power has limited its effectiveness at critical times.
War Criminals: The International criminal court has prosecuted several war criminals. But it has been criticised for prosecuting only African leaders. But Western powers too have committed war crimes.
Israel Attack: Israel attacked homes schools, U.N. shelters in Gaza killing 2,200 Palestinians. The U.N. Security Council has failed any action against Israel.
Conclusion: U.N. is imperfect but it is also indispensable. It is successful as, it is avoiding any other war.
![]()
Question 3.
Marking the Allies and Axis countries, as well as important battlefields of World War II in a world map.
Answer:

IX. Map Work
Question 1.
Mark the following on the world map.
1. Axis Power Countries
2. Allied Power Countries
3. Hiroshima, Nagasaki, Hawai Island, Moscow, San Fransico
Answer:
(2)

(3)
Timeline:

![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science World War II Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The financial cost of the II World War was ……………….. times higher than that of the I World War.
(a) one
(b) three
(c) five
(d) seven
Answer:
(c) five
Question 2.
The coal mines given to France were ………
(a) Jharia
(b) Saar
(c) Bokaro
Answer:
(b) Saar
Question 3.
“Money in wheelbarrows to buy bread” in the 1920’s. Which country referred to here.
(a) Italy
(b) Austria
(c) Germany
(d) Spain
Answer:
(c) Germany
![]()
Question 4.
The principles of war and conquests was glorified by ………
(a) Moderates
(b) Dictators
(c) Extremists
Answer:
(b) Dictators
Question 5.
Hitler broke the Munich pact by invading ……………….. in 1939.
(a) Manchuria
(b) Sudetenland
(c) Poland
(d) Czechoslovakia
Answer:
(d) Czechoslovakia
Question 6.
Hitler demanded the surrender of ………
(a) Danzig
(b) Jutland
(c) Estonia
Answer:
(a) Danzig
Question 7.
The attack of ……………….. by Germany was the final act which result in the initiation of II World War.
(a) Britain
(b) France
(c) Russia
(d) Poland
Answer:
(d) Poland
Question 8.
The British Prime Minister during the Second World War was ………
(a) Sir Winston Churchill
(b) Clement Atlee
(c) Lloyd George
Answer:
(a) Sir Winston Churchill
Question 9.
The tactic followed by Germany to overrun other countries was called as:
(a) Sea-borne invasion
(b) Blitzkrieg
(c) Dunkirk
(d) None
Answer:
(b) Blitzkrieg
Question 10.
In ………, Hitler invaded Russia.
(a) 1940
(b) 1941
(c) 1943
Answer:
(b) 1941
Question 11.
“We shall fight in the fields and in the streets” ……………….. but, we shall never surrender.”- said by
(a) Winston Churchill
(b) Napoleon Bonaparte
(c) George Washington
(d) Roosevelt.
Answer:
(a) Winston Churchill
![]()
Question 12.
……………….. used the device radar for detecting aircraft at a distance in World War II.
(a) Germany
(b) Japan
(c) Britain
(d) USA
Answer:
(c) Britain
Question 13.
In September 1940, London was bombed mercilessly by German Air force. This action was called as:
(a) Spit fires
(b) Hurricanes
(c) Blitz
(d) Dunkirk
Answer:
(c) Blitz
Question 14.
Land lease programme of USA took place between the years:
(a) 1939 – 1945
(b) 1941 – 1945
(c) 1936 – 1940
(d) 1914 – 1918
Answer:
(b) 1941 – 1945
Question 15.
In the war between Germany and Russia in 1941, ……………….. was defeated.
(a) Germany
(b) Russia
(c) Britain
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Germany
Question 16.
Stalingrad I situated along the banks of the river:
(a) Miami
(b) Volga
(c) Hwang-Ho
(d) Marne
Answer:
(b) Volga
Question 17.
In the battle of Stalingrad, Germans used the code word ……………….. on Russia.
(a) Alamein
(b) Land lease
(c) Fall Blau
(d) Montegomary
Answer:
(c) Fall Blau
Question 18.
Mussolini was killed by a ……………….. partisan.
(a) Germany
(b) Italy
(c) Russia
(d) Britain
Answer:
(b) Italy
![]()
Question 19.
Mussolini was killed in:
(a) May 1945
(b) April 1944
(c) April 1945
(d) May 1946
Answer:
(c) April 1945
Question 20.
In 1945 ……………….. was divided into two sections.
(a) Germany
(b) Italy
(c) Bengal
(d) Russia
Answer:
(a) Germany
Question 21.
Japanese army indulged in the biggest slaughter in the place ……………….. in China.
(a) Manchuria
(b) Nanking
(c) Peking
(d) Shangai
Answer:
(b) Nanking
Question 22.
Japan announced surrendered to U.S on ……………….. 1945.
(a) 2nd September
(b) 15th August
(c) 3rd August
(d) 5th February
Answer:
(b) 15th August
Question 23.
The Security council has ……………….. members.
(a) 10
(b) 15
(c) 25
(d) 3
Answer:
(b) 15
Question 24.
At present, the United Nations has ……………….. member states.
(a) 196
(b) 195
(c) 194
(d) 193
Answer:
(d) 193
![]()
Question 25.
The World Bank is located at:
(a) Sweden
(b) New Zealand
(c) Washington
(d) New York
Answer:
(c) Washington
Question 26.
IMF has at present ……………….. member countries.
(a) 200
(b) 187
(c) 189
(d) 190
Answer:
(c) 189
Question 27.
IMF help the countries to solve their ……………….. position.
(a) debt
(b) Balance of payment
(c) Independency
(d) Trade
Answer:
(b) Balance of payment
Question 28.
The report published in 1942, in United Kingdom for the general welfare of the people was called as ……………….. report.
(a) Bretton Woods
(b) Beveridge
(c) Blitzkrieg
(d) Common wealth
Answer:
(b) Beveridge
Question 29.
……………….. party in Great Britain promised for a welfare state to the people.
(a) Communist party
(b) Democratic party
(c) Socialised party
(d) Labour party
Answer:
(d) Labour party
![]()
Question 30.
The benefits to the people can be achieved either through ……………….. transfers or free services.
(a) Cash
(b) Country
(c) State
(d) Regional
Answer:
(a) Cash
II. Fill in the blanks
- World War II began in ……………… and ended in ………………
- The Treaty of ……………… was signed at the end of World War I in 1919.
- The Germans offered to pay ……………… billion gold marks to the allies.
- The United States was faced with great depression after ………………
- The National Socialist party in Germany was generally known as ………………
- In 1938, Hitler signed the Munich pact with Prime Minister ………………
- In 1939, Hitler invaded ……………… as against his promise in Munich pact.
- Hitler showed hatred against ………………
- Hitler came to power in ……………… and ruled till ………………
- World War II was a ……………… war fought with tanks, submarines, bomber planes etc.
- Britain and France declared war on Germany in ………………
- In ………………, Italy and Japan joined the axis powers.
- In September 1940, London war bombed by Germans mercilessly. This action was known as ………………
- Blitzkrieg means ………………
- The name of the Britain navy was ………………
- The war between Britain and ……………… took place in Dunkirk in 1940.
- The fighter planes of the British Royal force was called as ……………… and ………………
- ……………… of America started the Land Lease programme.
- Caucasus was famous for its ……………… in Russia.
- Mussolini of Italy was killed by an ……………… partisan.
- The battle of ……………… was considered to be the Great patriotic war by the Russians.
- Italy surrendered to the allies in ………………
- The Allied forces under the command of ……………… invaded Normanday in France.
- Canton was called as ……………… in China.
- On December 1941, ……………… attacked American naval installations in Pearl Harbour.
- Guadalcanal is in the ……………… islands.
- USA dropped an atomic bomb on ……………… and ……………… cities of Japan.
- Japan announced their surrender on ………………
- Japan formally signed their surrender marking the end of the World War II was ………………
- ……………… and ……………… are the two super powers after the II World War.
- US and Soviet Russia entered into a race to have more ………………
- ………………, ………………, and ……………… came into existence after the II World War.
- ……………… started entering into labour force in huge number after World War II.
- In the process ofdecolonisation ……………… was the first country toget Independence.
- The word ……………… refers the genocide of Jews by the Germans during Second World War.
- A major outcome of the Holocaust was the creation of the State of ………………
- ……………… became the Homeland for Jews after II World War.
- The Un efforts to protect human rights at the global levei resulted in the UN commission on ………………
- The Un adopted the Human Rights Charter on ………………
- ……………… is observed globally as Human Rights Day.
- Britain and United States gave a joint declaration called as ……………… in 1941 that helped in the formation of UNO.
- ……………… were the axis powers of the II World War.
- The initial member States of the UN were ……………… nations.
- The Charter of the United Nations was signed on ………………
- Each member State in U.N.has ……………… vote.
- The UN functions almost like a ………………
- There are ………………, ………………, ………………, ……………… wing for the UN.
- Veto means ………………
- ……………… has veto power.
- ……………… permanent members are there in UN.
- WHO means ………………
- UNICEF means ………………
- FAO means ………………
- UNESCO expansion is ………………
- UNDP expansion is ………………
- The ……………… has been a port of peace keeping force of the UN in deployment to many parts of the World.
- The World Bank and the IMP are referred to as ………………
- The two main organs of the World Bank are ……………… and ………………
- IBRD expansion is ………………
- IDA expansion is ………………
- The IDA lends money to the ……………… for development activities.
- The loans sanctioned by IDA at low interest rates for development purposes are called as ………………
- Soft loans are given for ……………… years.
- The ……………… functions with private enterprises in developing countries.
- IFC expansion is ………………
- The World Bank is actively promoting the cause of improving the and eradicating the ………………
- The IMF was the brainchild of ……………… and ………………
- The initial member countries of IMF were ………………
- Its primary objective is to ensure ……………… and development across the World.
- The fund gives resources to countries facing ……………… problem.
- The number of member countries of IMF at present are ……………… countries.
- All the countries in the Western Europe are now ………………
- The ……………… in Great Britain after World War I promised to look at the people from the cradle to the grave.
- Legislations was enacted to provide comprehensive free health coverage to the citizens in Britain through ………………
- The monetary benefits after World War II by Labour party was ………………, ……………… etc.
Answers:
- 1939, 1945
- Versailles
- 100
- 1929
- Nazis
- Chamberlin
- Czechoslovakia
- Jews
- 1933, 1945
- modem
- 1939
- 1940
- Blitz
- Lightning strike
- Royal Navy
- France
- Spitfires, Hurricanes
- President Roosevelt
- Oil fields
- Italian
- Stalingrad
- 1943
- General Elsenhower
- Guangzhou
- Japan
- Solomon
- Hiroshima, Nagasaki
- 15th August 1945
- 2nd Sept 1945
- United States, Soviet Russia
- Nuclear weapons
- United Nations, World Bank, International Monetary Fund
- Women
- India
- Holocaust
- Israel
- Israel
- Human Rights
- 10th Dec 1948
- 10th Dec 1948
- Atlantic Charter
- Germany, Italy, Japan
- 51
- June 26, 1945
- One
- Government
- Executive, Judicial, Legislative, Co-ordinating
- The right to block major decisions
- Permanent members
- Five
- World Health Organisation
- United Nations Children’s Fund
- Food and Agricultural Organisation
- UN educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation
- United Nations Development programme
- Indian Army
- Bretton Woods Twins
- IBRD, IDA
- International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
- International Development Agency
- Government
- Soft loans
- 50
- IFC
- International Finance Corporation
- Environment, AIDS
- Hary Dexter, John Maynard Keynes
- 29
- Financial Stability
- Balance of payment
- 189
- Welfare states
- Labour party
- National Health Service
- Old age pension, Child care services
![]()
III. Choose the correct statement
Question 1.
(i) The axis powers of World War II were Germany, Italy and Japan.
(ii) Russia attacked the American naval base at Pearl Harbour in 1941.
(iii) The UN adopted the historic human rights charter on 10th December 1947.
(iv) The executive wing of the UN is the UN Secretariat.
(a) (i) (ii) are correct
(b) (i) (ii) (iii) are correct
(c) (i) (iv) are correct
(d) (ii) (iv) are wrong.
Answer:
(c) (i) (iv) are correct
Question 2.
(i) Reparations refers to the compensation exacted from a defeated nation by the victorious nation.
(ii) Slaughter is compulsory military service.
(iii) Japanese navy was defeated by the US Navy at the battle of mid way.
(iv) Progression taxation by taxing the higher income groups at relatively high rates.
(a) (ii) (iii) (iv) are correct
(b) (ii) (iv) are wrong
(c) (iii) (iv) are correct
(d) (iii) (iv) are wrong.
Answer:
(a) (ii) (iii) (iv) are correct
Question 3.
(i) The Security Council of the UNO has fifteen members.
(ii) The mass killing of Jews in Nazi was called holocaust
(iii) Battle of Ex Alamein was considered one of the greatest battles by Russia.
(iv) The Japanese navy defeated the US navy in the battle of Midway.
(a) (i) (ii) are correct
(b) (ii) (iv) are correct
(c) (i) (ii) (iii) are correct
(d) (i) (iv) are wrong
Answer:
(a) (i) (ii) are correct
![]()
Question 4.
(i) The World Bank and the IMF are referred to as the Bretton Woods Twins.
(ii) The post World War I led to the rise of dictatorship in Italy, Germany, and Spain.
(iii) The post World War II changed the world into two blocks as communist and non communist.
(iv) The Shakespeare’s play the Merchant of Venice clearlv depicts the dislike and distrust of Jews among the Nazi people.
(a) (i) (ii) are correct
(b) (i) (ii) (iii) are wrong
(c) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) are correct
(d) (iii) (iv) (ii) are wrong
Answer:
(c) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) are correct
Question 5.
(i) IMF lends money from its resources to countries facing balance of payment problem.
(ii) The Munich pact was signed between Germany and the Soviet Union.
(iii) Huge worthless money for bread often refers to the Britain’s severe inflation after II World War.
(iv) Franco of Spain was the only dictatorship that emerged after II World War.
(a) (i) (ii) are correct
(b) (i) (iii) (iv) are correct
(c) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) are wrong
(d) (i) (iv) are correct
Answer:
(a) (i) (ii) are correct
Question 6.
(i) Japanese extended their empire throughout South-east Asia.
(ii) Burma, Indonesia, Singapore, Malaya, Hong Kong, Philippines all fell to the Japanese.
(iii) Many Indians walked ail the way from Burma to the Indian border facing many sufferings.
(iv) Many Indians who stayed there suffered under the Japanese.
(a) (ii) (iv) are wrong
(b) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) are correct
(c) (iii) (i) are correct
(d) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) are wrong
Answer:
(b) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) are correct
![]()
Question 7.
(i) Hitler was killed by his countrymen in 1945
(ii) Mussolini committed suicide in April 1945
(iii) The United States declared war on Japan on December 1944.
(iv) In 1938, Japan invaded China and seized Beijing.
(a) (ii) (iv) are wrong
(b) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) are correct
(c) (i) (ii) are correct
(d) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) are wrong
Answer:
(d) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) are wrong
Question 8.
(i) In the year 1940, the British Prime Minister Chamberlain resigned.
(ii) The newly elected British Prime Minister next was Winston Churchill.
(iii) The end of World War II signalled a change in the world order and political configurations among the major powers.
(iv) The Treaty of Versailles ended the World War II.
(a) (i) (iv) are wrong
(b) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) are correct
(c) (i) (ii) (iii) are correct
(d) (i) (ii) (iv) are correct
Answer:
(c) (i) (ii) (iii) are correct
IV. Assertion and Reason
Question 1.
Assertion (A): World War I (1914-18) and World War II (1939-45) are only referred as World wars.
Reason (R): The high death of the civilians and the soldiers and the extended area of the conflicts.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) A is correct but R is not the correct reason
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) R is correct but A is wrong.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct
Question 2.
Assertion (A): The League remained an ineffectual international body. Reason (R): Along with the USA, as a non-member mainly Germany was determined to maintain a non-interventionist attitude.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) A is correct but R is not the correct reason
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) R is correct but A is wrong.
Answer:
(b) A is correct but R is not the correct reason
Question 3.
Assertion (A): Hitler invaded Austria and Czechoslovakia in 1938.
Reason (R): Hitler claimed all the German speaking people should be united into one nation.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) A is correct but R is not the correct reason
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) R is correct but A is not relevant to R.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct
Question 4.
Assertion (A): The mood in Britain was not in favour of starting another war after World War I.
Reason (R): Just as the United States they wanted to be concerned with the revival of the economy after great depression.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) A is correct but R is not the correct reason
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) R is correct but A is not relevant to A.
Answer:
(b) A is correct but R is not the correct reason
Question 5.
Assertion (A): Germany developed a fleet of sub-marines which caused havoc in the Atlantic Ocean.
Reason (R): Germany ensured themselves for a sea-borne invasion on allies.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) A is right but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) R is correct, which is not relevant to A.
Answer:
(b) A is right but R is not the correct explanation of A.
![]()
Question 6.
Assertion (A): The long term objective of Germany was to exploit Russia’s natural Resource oil.
Reason (R): German army invaded Russia.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) A is right but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) R is correct, which is not relevant to A.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct
Question 7.
Assertion (A): Germans tried to capture the city of Stalingrad in Russia. Reason (R): Stalingrad was the militarised zone of Russia.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) A is right, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) R is right, A is wrong.
Answer:
(b) A is right, but R is not the correct explanation of A
Question 8.
Assertion (A): Hitler committed suicide in April 1945.
Reason (R): The Allied forces in 1945, occupied parts of Berlin and began to attack Germany from the east.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) A is correct but R is not the correct explanation.
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) R is correct but A is not relevant to R.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct
Question 9.
Assertion (A): The United States declared war on Japan.
Reason (R): In 1931, the Japanese army invaded Manchuria and in 1937, invaded China and seized Beijing.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) A is correct but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) R is correct but R is not relevant to A.
Answer:
(b) A is correct but R is not the correct explanation of A
Question 10.
Assertion (A): U.S. dropped an atomic bomb on Hiroshima and another bomb was dropped on Nagasaki.
Reason (R): U.S. developed hatred over the development of two cities Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) A is correct, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) R is correct but it is the correct reason for A.
Answer:
(b) A is correct, but R is not the correct explanation of A
![]()
Question 11.
Assertion (A): The U.S. and the Soviet Union followed communist and non¬communist ideas.
Reason (R): Countries began to devote large amount of resources in developing dangerous weapons.
(a) Both A and R are correct
(b) A is correct, but not relevant to R
(c) Both A and R are wrong
(d) R is correct, but not relevant to A.
Answer:
(c) Both A and R are wrong
V. Match the Following
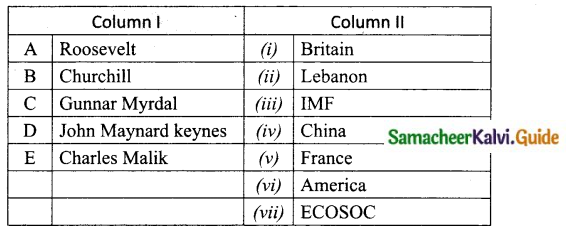
Question 1.
Match the Column I with Column II.
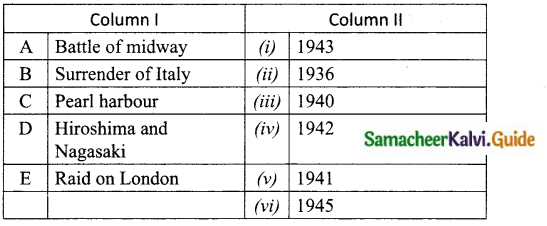
Answer:
A. (iv)
B. (i)
C. (v)
D. (vi)
E. (iii)
Question 2.
Match the Column I with Column II.
Answer:
A. (v)
B. (i)
C. (vi)
D. (iii)
E. (ii)
![]()
VI. Answer the questions briefly
Question 1.
What are soft loans?
Answer:
The loans that are sanctioned by the International Development Agency to the Governments for developmental activities are called as soft loans. They are given at very low rate of interest of 50 years.
Question 2.
Did Munich Pact bring peace for some time? How?
Answer:
- In September 1938, Hitler threatened Czechoslovakia.
- The British Prime Minister Neville chamberlain initiated talks and signed Munich pact,
- Hitler promised not to take any more Czech territory.
- Chamberlain believed that he had achieved “Peace for some time”. But within six months Hitler seized the remainder of Czechoslovakia. So Munich pact has brought peace only for some time.
Question 3.
What do you know about the World Bank?
Answer:
The World bank consists of two main organs namely The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) and the International Development Agency (IDA). Together they are called as the World Bank.
Question 4.
Why did America declare war on Japan?
Answer:
- The Japanese had attacked the American fleet stationed at Pearl Harbour on December 7, 1941.
- This disastrous attack forced the Americans to enter into the war.
- The very next day the USA declared war on Japan.
Question 5.
What are the axis powers and the ally powers of II World War?
Answer:
Germany, Italy, Japan – Axis powers.
Britain, France, Russia, USA – Ally powers.
Question 6.
Name the countries involved in World War II.
Answer:
- The allies countries were under the leadership of Britain. [Britain, France, Russia and U.S.A]
- The axis countries were under the leadership of Germany. [Germany, Italy and Japan]
Question 7.
What was the immediate cause of the II World War?
Answer:
The main and immediate cause of the II World War was the aggressive, military, dictatorship attitude of Germany, fast-developing Japan. Hitler’s attack on Poland in 1939, resulted in the declaration of the War by Britain and France.
![]()
Question 8.
Write a brief note on security council.
Answer:
- The council has five permanent members and ten non-permanent members.
- The five permanent members are the USA, UK, France, Russian Federation and China,
- The non-permanent members are elected by the General Assembly for two years term,
- The permanent members have the right to veto for any council decision.
- Its main responsibility is to maintain International peace and security.
Question 9.
What is ECOSOC? What are its organs?
Answer:
The Economic and Social Council, is the UN organ which is responsible for co-ordinating all the economic and social work of the United Nations. The Regional Economic commissions functioning for regional development across the various regions of the World are its organs. (Asia pacific, West Asia, Europe, Africa, Latin America).
Question 10.
Name some of the specialized agencies of the UNO.
Answer:
- The World Health Organisation [WHO]
- The United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organisation(UNESCO)
- The United Nation’s Children’s Fund (UNICEF)
- The International Labour Organisation (ILO)
- Food and Agricultural Organisation (FAO)
- International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD)
VII. Answer the questions given under each caption
Question 1.
Causes of the Second World War.
(a) Name the treaty signed by Japan, Italy and Germany.
Answer:
Italy – Germany – Japan signed the Rome – Berlin – Tokyo Axis treaty.
(b) Mention some of the ideologies that emerged after the First World War.
Answer:
Democracy, Communism, Fascism and Nazism.
(c) What was the policy followed by the statesmen of the major world powers?
Answer:
The statesmen of the major world powers followed the policy of appeasement.
(d) What did Hitler violate?
Answer:
He violated the Munich Pact.
![]()
Question 2.
Munich Pact
(a) Who concluded the Munich pact with Germany?
Answer:
In 1938, Prime Minister Chamberlain concluded the Munich pact with Germany.
(b) What did Hitler do in 1939?
Answer:
In 1939, Hitler invaded Czechoslovakia breaking the munich pact that Germany would not attack any other country.
(c) Which act of Hitler made Britain and France declare war on Germany?
Answer:
His act of attack on Poland made Britain and France declare war on Germany.
(d) What were the weapons used in World War II?
Answer:
Heavy military equipment such as tanks, sub-marines, battleships, aircraft carriers, fighter planes and bomber planes.
Question 3.
Organs of the UNO
(a) Name the major organs of the UNO.
Answer:
- The General Assembly
- The Security Council
- The Economic and Social Council
- The Trusteeship Council
- The International Court of Justice
- The Secretariat
(b) Who was elected as the President of the UN General Assembly in 1953?
Answer:
Mrs. Vijaya Lakshmi Pandit
(c) What is the function of the Trusteeship Council?
Answer:
The Trusteeship Council looks after certain territories placed under the trusteeship of the UNO.
(d) How is the Secretary-General of the UNO appointed?
Answer:
The Secretary-General is appointed by the General Assembly on the advice of the Security Council.
![]()
Question 4.
Birth of Israel.
(a) What is meant by Holocaust?
Answer:
Holocaust refers to the mass killing of jews by the Germans during World War II.
(b) What was the major outcome of the Holocaust?
Answer:
The major outcome of the Holocaust was the creation of the State of Israel as a homeland for the Jews.
(c) What did the Israel occupy?
Answer:
The Israel has occupied large parts of Palestinian homelands.
(d) From whom does Israel get the support from?
Answer:
Israel get the vast support from the United States.
Question 5.
The United Nations
(a) Who took the first initiative for the formation of the United Nations?
Answer:
The United states and the Britain in 1941.
(b) Name the joint declaration they issued?
Answer:
The Atlantic Charter was the name of the joint declaration they issued.
(c) How many countries accepted the declaration at first?
Answer:
The declaration of the United Nations was accepted by 26 countries, on New years Day 1942.
(d) How many nations signed the charter? When?
Answer:
On June 26, 1945, 51 nations signed the charter.
![]()
Question 6.
International Monetary Fund (IMF)
(a) On whose idea the International Monetary Fund was initiated?
Answer:
Harry Dexter white and John Maynard Keynes ideas brought the emergence of IMF.
(b) When was it formally organised?
Answer:
It was formally organised in 1945 with 29 member countries (at present 189).
(c) What were the three main agendas of the IMF?
Answer:
- To promote International monetary co-operation.
- To expand International trade.
- To bring exchange stability.
(d) State the main reason of its funding?
Answer:
The IMF lends money from its resources to countries facing Balance of payment problems.
VIII. Answer in detail
Question 1.
What were the results of Second World War?
Answer:
- The destruction to life and property was on a much larger scale than the First World War.
- Over 50 millions lost their lives.
- It sounded the death knell to dictatorship in Germany and Italy.
- Germany was occupied by the Allied forces, and later it was divided into two parts.
- The West Germany was controlled by Britain, France and America and the East Germany by Russia.
- At the end of the war, Japan was occupied by American forces under General Mc. Arthur.
- The war weakened Britain and France.
- America and Russia emerged as super powers.
- The war did not end totalitarianism in Russia. A cold war started between Russia and America.
- The war quickened the phase of national movements in Asia and Africa.
- India, Burma, Egypt, Ceylon and Malaya won their freedom from Britain.
- Philippines got independence from America.
- Indo-china got independence from France.
- Indonesia got independence from the Dutch.
- The European countries gave up the policy of colonialism and imperialism.
- The United Nations Organisation was set up to maintain international peace and harmony. It works hard to maintain international co-operation and for the promotion of human welfare.
Question 2.
Write a note on international Monetary Fund (IMF).
Answer:
- International Monetary Fund was established in 1945 after the Bretton Woods conference in 1944 along with the World Bank.
- It is located in the Washington in United States.
- The idea of starting of IMF was given by Harry Dexter, White and John Maynard Keynes, a famous economist.
- The initial members of the IMF were 29. Now, there are 189 member countries with IMF,
- The main objectives of IMF include to foster global monetary co-operation, to secure financial stability, to facilitate trade, promote employment, to sustain economic growth and reduce poverty all over the world.
- The fund lends money to its member countries to correct their balance of payment position if they are unable to pay for their imports.
- The funding from IMF is not very easy as it strictly imposes restrictions on lending.
- It imposes the developing nations to tighten the budgets and reduce fiscal expenditure.
![]()
Question 3.
Write a note on the UN Commission of Human Rights.
Answer:
- Human Rights means the fundamental freedom for all human beings without any differences in race, sex, language and religion.
- The UN efforts to protect human rights on a global basis resulted in the formation of the UN commission on Human Rights.
- A committee was set up for its formation. It was headed by the wife of FDR of USA, after his death.
- The other members of the commission included Charles Malik from Lebanon, P.C.Chang from China, Rene Casin from France.
- The Commission set forth with 30 articles.
- The UN adopted this historic charter on 10th December 1948.
- This day, the 10th December is observed as Human Rights Day all over the World.
- According to the Franklin and Eleanor institute in New York, reports, from 1948 till now, nearly 90 National constitutions are part of this Human Rights Commission of UN.