Students can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Model Question Paper 1 English Medium Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamil Nadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Model Question Paper 1 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts
- You are to attempt all the questions in each part. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III, and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 14 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each.
These are to be answered by writing the correct answer along with the corresponding option code and the corresponding answer - Question numbers 15 to 28 in Part II are of two marks each. Any one question should be answered compulsorily.
- Question numbers 29 to 42 in Part III are of five marks each. Any one question should be answered compulsorily.
- Question numbers 43 to 44 in Part IV are of Eight marks each. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
Part – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer [14 × 1 = 14]
Question 1.
Which country after the World War I took to a policy of isolations?
(a) Britain
(b) France
(c) Germany
(d) USA
Answer:
(a) Britain
Question 2.
Name the president who made amendment to Monroe Doctrine to justify American intervention in the affairs of Latin America.
(a) Theodore Roosevelt
(b) Truman
(c) Eisenhower
(d) Woodrow Wilson
Answer:
(a) Theodore Roosevelt
![]()
Question 3.
Who became the Chairman of the PLO’s Executive Committee in 1969?
(a) 1975
(b) 1976
(c) 1973
(d) 1974
Answer:
(b) 1976
Question 4.
When did the Partition of Bengal come into effect?
(a) 19 June 1905
(b) 18 July 1906
(c) 19 August 1907
(d) 16 October 1905
Answer:
(d) 16 October 1905
Question 5.
On 8th January 1933 which day was observed ………………….
(a) Temple Entry Day
(b) Day of Deliverance
(c) Direct Action Day
(d) Independence Day
Answer:
(a) Temple Entry Day
Question 6.
Deccan Plateau covers an area of about …………………. sq. km.
(a) 8 lakhs
(b) 6 lakhs
(c) 5 lakhs
(d) 7 lakhs
Answer:
(d) 7 lakhs
Question 7.
…………………. is a line joining the places of equal rainfall.
(a) Isohyets
(b) Isobar
(c) Isotherm
(d) Latitudes
Answer:
(a) Isohyets
Question 8.
The state which leads in the production of coffee is ………………….
(a) West Bengal
(b) Karnataka
(c) Odisha
(d) Punjab
Answer:
(b) Karnataka
![]()
Question 9.
The district which has the largest forest cover in Tamil Nadu is ………………….
(a) Dharmapuri
(b) Vellore
(c) Dindugal
(d) Erode
Answer:
(a) Dharmapuri
Question 10.
…………………. Plains are formed by the older alluviums.
(a) Bhabar
(b) Tarai
(c) Bhangar
(d) Khadar
Answer:
(c) Bhangar
Question 11.
The Directive Principles can be classified into ………………….
(a) Liberal and Communist principles
(b) Socialist and Communist principles
(c) Liberal, Gandhian and Communist principles
(d) Socialist, Gandhian and Liberal principles
Answer:
(d) Socialist, Gandhian and Liberal principles
Question 12.
Non-Alliance means ………………….
(a) being neutral
(b) freedom to decide on issues independently
(e) demi I itari sat ion
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) freedom to decide on issues independently
Question 13.
Tamil Nadu Health System Projects has launched …………………. service at free of cost.
(a) 106 ambulance
(b) 108 ambulance
(c) 107 ambulance
(d) 105 ambulance
Answer:
(b) 108 ambulance
Question 14.
India economy is ………………….
(a) Developing Economy
(b) Emerging Economy
(c) Dual Economy
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
![]()
Part – II
Answer any 10 questions. Question No. 28 is compulsory. [10 × 2 = 20]
Question 15.
What was the impact of Swami Vivekananda’s activist ideology?
Answer:
- Vivekananda’s activist ideology related to the desire for political change among many ‘ western eductated young Bengalis.
- Many of the youths, who were involved in the militant nationalist struggle during the Swadeshi Movement, following the Partition of Bengal, were inspired by Vivekananda.
Question 16.
What are the objectives of IMF?
Answer:
The objectives of the IMF are to:
- Foster global monetary cooperation,
- Secure financial stability,
- Facilitate international trade,
- Promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and
- Reduce poverty around the world.
Question 17.
What was the bone of contention between the Company and Kattabomman?
Answer:
The company appointed its collectors to collect taxes from all the palayams. The collectors humiliated the Palayakkarars and adopted force to collect the taxes. This was the bone of contention between the English and Kattabomman.
Question 18.
Describe the Jallianwala Bagh Massacre.
Answer:
1. On 13 April 1919, a public meeting was organised at Jallianwala Bagh in Amritsar in defiance of the Rowlatt Act. As it happened to be Baisaki Day, thousands of villagers had gathered there to enjoy the day together.
2. General Reginald Dyer, on hearing the assemblage, surrounded the place with his troops and an armoured vehicle. He blocked the only entrance to the park and ordered his troops to fire without any warning.
3. The firing continued for ten minutes in which about 370 were killed and more than thousand injured. However, an unofficial estimates put the death toll at more than thousand. The Jallianwala Bagh massacre is a big scar on the British Indian history.
Question 19.
What is meant by ‘normal lapse rate’?
Answer:
Temperature decreases at the rate of 6.5°C for every 1000 metres of ascent. It is called normal lapse rate.
Question 20.
Define soil.
Answer:
Soil is the uppermost layer of the land surface, usually composed of minerals, organic matter, living organisms, air and water. Its formation is mainly related to the parent rock material, surface relief, climate and natural vegetation.
![]()
Question 21.
Mention the major areas of Jute production in India.
Answer:
West Bengal, Andhra pradesh, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Assam, Chattisgarh, Odisha are the major jute producing area.
Question 22.
What are the classical languages in India?
Answer:
There are six classical languages namely – Tamil, Sanskrit, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam and Odia.
Question 23.
Write a short note on Strategic partnership Agreement (SPA).
Answer:
Indo-Afghan relation was strengthened by the Strategic Partnership Agreement (SPA). SPA provides assistance to re-build Afghan’s infrastructure, institutions, agriculture, water, education, health and providing duty-free access to the Indian market.
Question 24.
What is Fair trade ?
Answer:
- Fair trade is an industrial arrangement designed to help producers in developing countries achieve better trading conditions.
- Fair trade is about better prices, decent working conditions and fair terms of trade for farmers and workers.
Question 25.
Name the sectors contribute to the GDP with example.
Answer:
Name of the sectors are :
- Primary sector
- Secondary sector and
- Tertiary sector.
Question 26.
Write any five principles of Fair Trade Practices.
Answer:
Five principles of Fair trade practices:
- Creating opportunities for economically disadvantaged producers.
- Transforming and accountability.
- Fair trading practices and payment of fair price.
- Ensuring no child labour and forced labour.
- Respect for the environment.
Question 27.
What is Entrepreneurship?
Answer:
Entrepreneurship is a process of an action of an entrepreneur who undertakes to establish his entreprise. It is the ability to create and build something.
Question 28.
During cyclone, how does the Meterological department warn the fishermen?
Answer:
1. During disturbed weather over the seas, the ports likely to be affected are warned by concerned ACWCs / CWCs by advising the port authorities through port warnings to hoist appropriate Storm Warning Signals. The Department also issue “Fleet forecast” for Indian Navy.
2. Coastal Bulletins for Indian coastal areas covering up to 75 km from the coast line and sea area bulletins for the sea areas beyond 75 km. The special warnings are issued for fishermen four times a day in normal weather and every three hourly in accordance with the four stage warning in case of disturbed weather.
3. The general public, the coastal residents and fishermen are warned through state government officials and broadcast of warnings through All India Radio and National Television telecast programmes in national and regional hook up. A sytem of warning dissemination for fishermen through World Space Digital Based radio receiver is being planned.
![]()
Part – III
Answer any 10 questions. Question No. 42 is compulsory. [10 × 5 = 50]
Question 26.
Fill in the blanks:
(i) Germany joined the NATO in ………………….
(ii) The plateau which his between the Nilgiris and Dharmapuri district is ………………….
(iii) At present our foreign policy acts as a means to generate ………………….for domestic growth
and development.
(iv) ………………….foundation from USA introduced HYV in India.
(v) Agriculture of Tamil Nadu constitutes ………………….economy.
Answers:
(i) 1955
(ii) Bharamahal
(iii) inward investment
(iv) FORD
(v) 21%
Question 30.
Match the following:

Answers:

Question 31.
Match the following:

Answers:

Question 32.
(a) Distinguish between
(i) Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats
(ii) Tropical Evergreen forest and Deciduous forest
Answer:
(a) (i) Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats:
Western Ghats :
- They run parallel to the western coast and form the western boundary of the Deccan Plateau
- They are continuous and can be crossed only through the passes like Pal Ghat, Thai Ghat, Bhor Ghat.
- The highest peak of this region is Anaimudi with a height of 2,659 m.
- These Ghats are higher and their average height is 900 – 1600 meters
- They face the rain bearing winds and cause orographic rainfall.
Eastern Ghats :
- They run parallel to the eastern coast and form the eastern boundary of the Deccan Plateau
- These are more discontinuous and irregular.
- The highest peak of this region is Mahendragiri with a height of 1,051 m.
- These Ghats are lower than the western ghats with an average height of about 600 meters
- It is almost parallel to monsoon winds originating from the Bay of Bengal and does not cause much rainfall.
(ii) Tropical Evergreen forest and Deciduous forest:
Tropical Evergreen forest :
- These forests are located in regions of heavy rainfall more their 200 cm of rainfall.
- The trees in these forests are evergreen.
- These forest are very dense and composed of tall trees reaching up to the height of above 60 metres.
- The important trees of these forests are Rosewood, Ebony, Mahogany,and . Chinchona, Bamboo and Lianas.
Deciduous forest :
- These forests are located in regions of rainfall between 70-200 cm.
- The trees in the deciduous forests shed their leaves due to dryness during the spring and early summer.
- The tropical deciduous forests are commercially important as they yeild valuable timber and other forest products.
- The main trees of these forests are Teak, Sal, Sisam, Sandalwood, Wattle and Neem.
(b) Give reason: The great Indian desert is called Marusthali.
Answer:
The Thar desert, also known as the Great Indian desert is a large arid region in the north western part of the Indian Subcontinent that covers an area of 2,00,000 Km2 and forms a natural boundary between India and Pakistan.
Marusthali means sand-dune. It covered eastern portion of the Great Indian Thar Desert in Western Rajasthan. It extends over about 24,000 square miles north of the Luni River.
![]()
Question 33.
Estimate the role of Mao Tse tung in making China a communist country.
Answer:
1. Mao was greatly influenced by the ideas of Max and Lenin. He wanted to make China a communist country. So, he became active in the political activities of Hunan from the year 1912.
2. After the death of Sun Yat-Sen in 1925, The Kuomintang was organised under the leadership of Chang Kai-Shek. Being an avowed critic of communists, Chiang removed all the important position holders in the Communist Party including Mao Tse Tung to weaken the party. However, the communists continued to influence the workers and peasants the Kuomintang represented the interests of landlords and capitalists.
3. Mao had understood that the Kuomintang grip on the towns was too strong. So, he started organising the peasantry. When the relationships between Kuomintang and Communist Party broke, a few hundred Communist led by Mao retreated into the wild mountains on the border between the provinces of Kiangsi and Hunan. The Kuomintang could not penetrate the mountains.
4. Meanwhile, the campaign against the communists got distracted as Chiang Kai-Shek had to deal with the constant threat from Japan.
5. By 1933 Mao had gained full control of the Chinese Communist Party. In 1934, he set out on a long march with the help of about 100,000 communist army. He also got support of other communist armies.
6. By 1937, Mao had become the leader of over 10 million people. He organised workers and peasants councils in villages of Shensi and Kansu and finally got success in making China a communist country.
Question 34.
Describe the background for the formation of the Justice party and point out its contribution to the cause of social justice.
Answer:
1. It was the period of World War I. The British government thought to introduce representative institutions for Indians after the war. Fearing that such political reforms would further strengthen the political power of Brahmins, educated non-Brahmins decided to organise themselves politically.
2. So, in 1916, some prominent non-Brahmin leaders came together from South Indian Liberation Federation (SILF). It later came to be known as the Justice Party. It was a political party in the Madras Presidency of British India.
Contribution of the Justice Party to the cause-social justice:
- The Justice Party government widened education and employment opportunities for the majority of the population and created space for them in the political sphere.
- The Justices removed the legal hindrances restricting inter-caste marriages and broke the barriers that prevented Adi Dravidars from the use of public wells and tanks.
- In 1921, the Madras legislature under the Justice Party government was the first to approve participators of women in the electoral politics.
Question 35.
Explain the divisions of Northern Mountains and its importance to India.
Answer:
- The Himalayas geologically young and structurally fold mountains stretch over the northern borders of India.
- The Himalayas represent the loftiest and one of the most rugged mountain harries of the world.
- The mountain ranges run in a west-east direction from the India to the Brahmaputra.
- They form an arc, which covers a distance of about 2,400 km. Their width varies from 1,400 km in Kashmir to 150 km in Arunachal Pradesh.
Division of Himalayas:
1. Himadri or Inner Himalayas:
- The Northern most range is known as the Great or Inner Himalayas or the “Himadri”.
- It is the most continuous range consisting of the loftiest peaks with an average height of 6,000 metres.
- It contains all the prominent Himalayan peaks.
- The core of this past of Himalayas is composed of granite.
- It is perennially snow bound, and a number of glaciers descend from this range.
2. Himachal or Lesser Himalayas:
- Below Himadri is the most rugged mountain system and is know as Himachal or lesser Himalaya.
- They range are mainly composed of highly compressed and altered rocks.
- The altitude varies between 3,700 and 4,500 metres and the average width is of 50 km.
- While the Pir Pangal range forms the longest and the most important range. The Dhaula Dhar and the Mahabharat ranges are also prominent ones.
- This range consists of the famous valley of Kashmir, the Kangra and Kullu valley in Himachal Pradesh.
- This region is well known for its hill stations.
3. Siwaliks:
The outermost range of the Himalayas is called the Siwaliks.
- They extend over a width of 10 – 50 km and have an altitude varying between 900 and 1100 metres.
- These range are composed of unconsolidated sediments brought down by rivers from the main Himalayan ranges located further north.
- These valleys are covered with thick gravel and alluvium.
- The longitudinal valley lying between lesser Himalayas and the Siwaliks are known as Duns. Dehra Dun, Kofli Dun and Pati Dun are some of the well-known Duns.
Importance of Himalayas:
- Himalayas blocks southwest monsoon winds and cause heavy rainfall to north India.
- It forms a natural barrier to the Sub-continent.
- It is the source for many perennial rivers like Indus, Ganges, Brahmaputra etc.
- The Northern Mountains are described as paradise of tourists due to its natural beauty.
- Many hill stations and pilgrim centres like Amarnath, Kedarnath, Badrinath and Vaishnavidevi temples situated here.
- It provides raw materials for many forest based industries.
- It prevents the cold winds blowing from the central Asia and protects India from severe cold.
- Himalayas renowned for the rich biodiversity.
![]()
Question 36.
Explain the factors responsible for the concentration of jute industries in the hooghly region.
Most of the Jute mills of India are centralised in “Hooghly Basin” of the West Bengal. The factors responsible for the concentration of Jute industry in Hooghly Basin region are:
- Ganga, Brahmaputra delta regions grow about 90% of India’s Jute and provides raw materials in jute mills.
- Coal for power is obtained from Raniganj coalfields.
- Hooghly River provides cheap water transport and soft water for washing, processing, retting and dyeing jute.
- Humid climate is favourable for spinning and weaving.
- Cheap labour is available from West Bengal, Bihar and Uttar Pradesh.
- Conductive port facility of Kolkata for export and import at Kolkata.
- In addition to West Bengal, Jute mills are also located in Andhra pradesh, Uttar pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha.
- India exports jute products to Australia, U.K, Thailand, U.S.A, Canada, Argentina, East Africa, New Zealand and Indonesia.
Question 37.
Mention the differences between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State Policy.
Answer:
Here are the differences between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State Policy.
S.No. Fundamental Rights Directive Principles of State Policy
- It was derived from the Constitution of the USA.
- These Rights cannot be taken away even by the Government.
- These Rights are enforceable by a Court of Law.
- These have legal sanctions.
- These rights strengthen political democracy in the country.
- These are natural rights.
Directive Principles of State Policy :
- It was drawn on the model of the Constitution of Ireland
- These are mere instructions to the Government.
- These are not enforceable in any court.
- These have moral and political sanctions.
- The implementation of these principles ensures social and economic democracy.
- These lead to protect human rights.
Question 38.
Elucidate why the Green Revolution was born.
Answer:
- The Green Revolution was bom in the country paving way for self-sufficiency in food grain production.
- Increased food grain production was made possible by an increase area cultivated with HYV of rice and wheat as also an increase in the yield of these major cereal crops.
- Area under food grains was a little more than 98 million hectares during early 1950s. The country was producing just 54 million tonnes of food grains then with an average yield of food grains of 547 kg per hectare.
- The food situation has steadily improved over a period of 65 years. Area under food grain ‘ cultivation has grown to 122 million hectares, with an increase of five-fold increase in
food grain production. - Yield of food grains has increased four-fold between the time of independence and at present.
Question 39.
Discuss the core determinants of India’s foreign policy?
Answer:
Basic Determinants of a Foreign Policy:
- Geographical position and size of territory
- Nation’s history, traditions and philosophical basis
- Natural resources
- The compulsion of economic development
- Political stability and structure of government ‘
- The necessity of peace, disarmament and non-proliferation of nuclear weapons
- Military strength
- International milieu
Question 40.
Describe the powers and functions of the High Court.
Answer:
The powers and functions of the High Court:
- The High Court enjoys original jurisdiction in matters of admiralty, probate, matrimonial and contempt of court.
- It hears appeals in both civil and criminal cases against the decisions of the subordinate courts and can review their judgments.
- It can issue writs such as habeas corpus, mandamus, prohibition, quo warranto and certiorari not only for the enforcement of the Fundamental Rights but also for other purposes.
- It has the power of supervision over all courts and tribunals functioning in its territorial jurisdiction (except military courts or tribunals).
- It controls and supervises the working of the lower courts and maintains records of its proceedings and decisions.
Question 41.
Draw a time line for the following:
Write any five important events between 1828-1875
Answer:

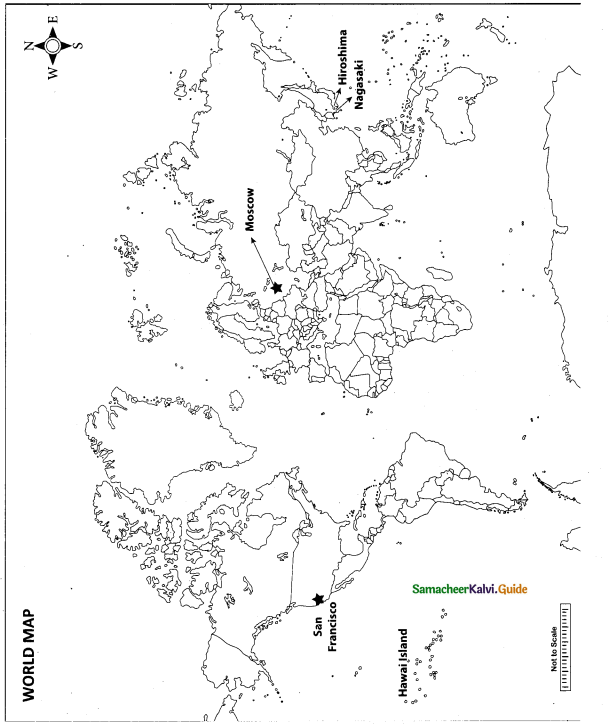
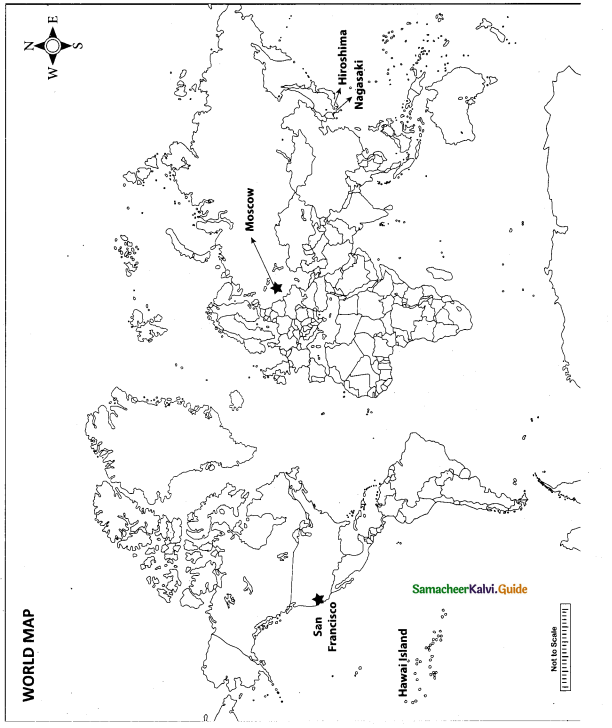
Question 42.
Mark the following places on the world map.
(i) San Fransico
(ii) Hawai Island
(iii) Hiroshima
(iv) Moscow
(v) Nagasaki
Answer:
![]()
Part – IV
Answer both questions. [2 × 8 = 16]
Question 43.
(a) Imperialism
(i) What do you know of monopoly capitalism?
(ii) How did Japan emerge as an imperial power?
(iii) Why did the industrial countries need colonies in the nineteenth century?
(iv) What were the contrasts capitalism produced?
Answer:
(a) Imperialism
(i) Monopoly capitalism is a capitalist system typified by tread monopolies in the hands of a few people. After 1870, the capitalism of free competition (based on the principle of free trade without any control or regulation by the state) became the capitalism of monopolies.
(ii) Japan took to Western education and machinery with a modem army and navy had emerged as an advanced industrialised power. It also followed the imperialistic aggression policy of the European powers faithfully. It surprised the world by giving a crushing defeat to China in the Sino-Japanese War during the period of 1894-95. Japan also defeated Russia in Russo- Japanese War in 1904 and got back Port Arthur from it. In this way it emerged as an imperial power.
(iii) An ever-growing demand for markets and raw materials made the industrial countries hungry for colonies in the nineteenth century.
(iv) Capitalism produced huge contrasts. Those contrasts were: extreme poverty and extreme wealth, slum and skyscraper, empire-state and dependent exploited colony.
(b) Non-Aligned Movement (NAM)
(i) When and where was the first conference on Non-Aligned Movement held?
(ii) Who were the prominent personalities present in the first conference?
(iii) What were the objectives of NAM?
(iv) List out any two basic principles of Non-Alignment Movement enunciated in the Belgrade Conference.
Answer:
(b) Non-Aligned Movement (NAM)
(i) The first conference on NAM was held at Belgrade in 1961.
(ii) The prominent personalities present in the first conference were Tito (Yugoslavia), Nasser (Egypt), Nehru (India), Nkrumah (Ghana) and Sukarno (Indonesia).
(iii) To fight all forms of colonialism and imperialism.
(iv) Two basic principles of NAM eximiated in the Belgrade conference were:
- peaceful cooperation, commitment to peace and security
- no military alliance with any super power.
[OR]
(c) Non-Brahmin Movement
(i) Why was the South Indian Liberal Federation formed?
(ii) What is the Non-Brahmin Manifesto?
(iii) Why did EVR join the Non-Brahmin Movement?
(iv) What do you know about anti-Hindi agitation?
Answer:
(c) Non-Brahmin Movement
(i) The South Indian Liberal Federation was formed to promote the interests of non-Brahmins.
(ii) The Non-Brahmin Manifesto had objectives such as reservation of jobs for non-Brahmins in government service and seats in representative bodies. It opposed the Home Rule Movement and criticised Congress as a party of Brahmins.
(iii) EVR joined the non-Brahmin movement because he felt the Congress was promoting the
interests of Brahmins alone.
(iv) A massive campaign was led by EVR against the introduction of Hindi as a compulsory subject in schools. The anti-Hindi agitation was popular because Hindi was considered a form of Aryan and North Indian imposition. EVR organised an anti-Hindi conference. More than 1200 protesters were arrested at a rally. The subject was later removed after protests.
(d) Maraimalai Adigal
(i) Name the Sangam texts for which Maraimalai Adigal wrote commentaries.
(ii) Name the Journal where he worked as a young man.
(iii) Why did he oppose imposition of Hindi?
(iv) Who were the key influences in Maraimalai Adigal’s life?
Answer:
(d) Maraimalai Adigal
(i) Pattinappalai and Mullaipattu
(ii) Siddhanta Deepika
(iii) Adigal promoted the use of pure Tamil words and removal of the Sanskrit influences from Tamil language. He painted out that Tamil language would suffer with the introduction of Hindi.
(iv) His teachers P. Sundaram Pillai and Somasundara Nayagar were the key influences in Maraimalai Adigal’s life.
![]()
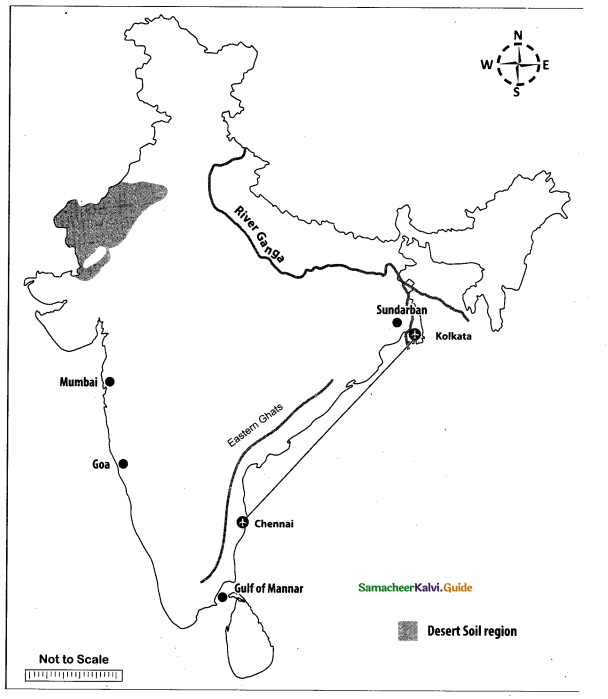
Question 44.
Mark the following places on the given outline map of India.
(i) Eastern Ghats
(ii) Gulf of Mannar
(iii) Sundarban
(iv) Desert soil region
(v) Mumbai
(vi) Chennai to Kolkata Air route
(vii) Goa
(viii) River Ganga
Answer:
[OR]
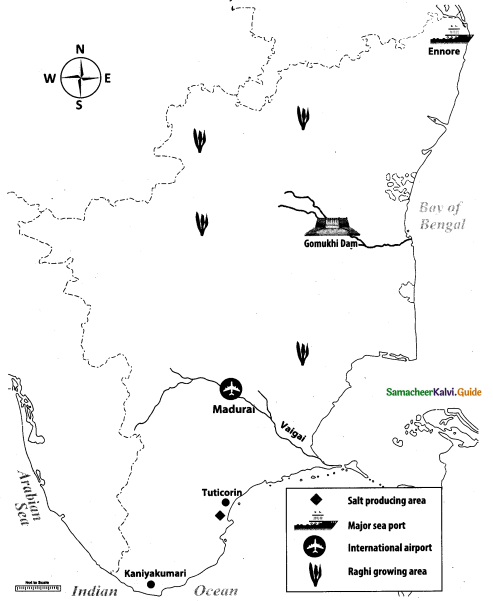
Mark the following places on the given outline map of Tamil Nadu:
(i) Tuticorin
(ii) Salt region
(iii) Raghi growing area
(iv) Gomukhi dam
(v) Vaigai river
(vi) Kanniyakumari
(vii) One international airport
(viii) One major sea port
Answer:
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Model Question Paper 1 English Medium – 8
Map for Q. 42
(i) San Francisco
(ii) Hawai Island
(iii) Hiroshima
(iv) Moscow
(v) Nagasaki
Answer:
Map for Q. 44
(i) Eastern Ghats
(ii) GulfofMannar
(iii) Sundarban
(iv) Desert soil region
(v) Mumbai
(vi) Chennai to Kolkata Air route
(vii) Goa
(viii) River Ganga
Answer:
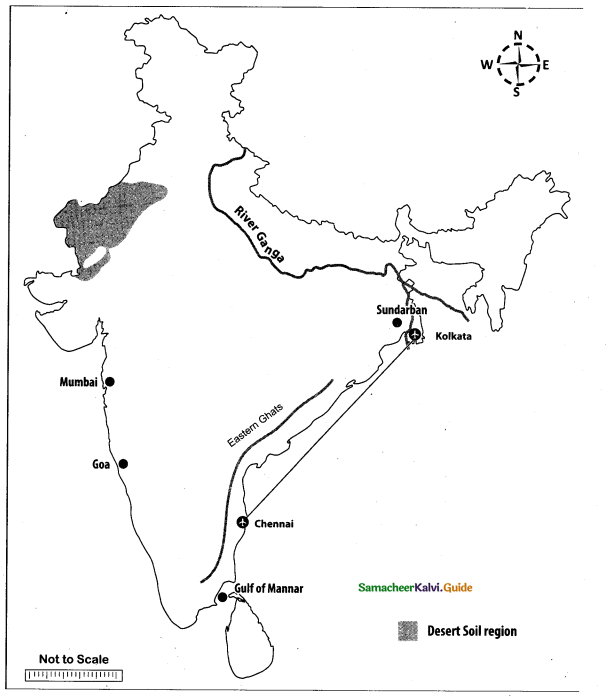
Map for Q. 44
(I) Tuticorin
(ii) Salt region
(iii) Ragi growing area
(iv) Gomukhi dam
(y) Vaigai river
(vi) Kanniyakumari
(vii) One international airport
(viii) One major sea port
Answer: