Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Botany Guide Pdf Chapter 13 Photosynthesis Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Botany Solutions Chapter 13 Photosynthesis
11th Bio Botany Guide Photosynthesis Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part-I
Questions 1.
Assertion (A): Increase in Proton gradient inside lumen responsible for ATP synthesis.
Reason (R): Oxygen evolving complex of PS I located on the thylakoid membrane facing Stroma, releases H+ ions.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are True.
(b) Assertion is True and Reason is False.
(c) Reason is True and Assertion is False.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are False.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are True.
Question 2.
Which chlorophyll molecule does not have a phytol tail?
a) Chl – a
b) Chl – b
c) Chl – c
d) Chl – d
Answer:
(c) Chl – c
![]()
Question 3.
The correct sequence of flow of electrons in the light reaction is:
(a) PS II, plastoquinone, cytochrome, PS I, ferredoxin.
(b) PS I, plastoquinone, cytochrome, PS II ferredoxin.
(c) PS II, ferredoxin, plastoquinone, cytochrome, PS I.
(d) PS I, plastoquinone, cytochrome, PS II, ferredoxin.
Answer:
(a) PS II, plastoquinone, cytochrome, PS I, ferredoxin.
Question 4.
For every CO2 molecule entering the C3 cycle, the number of ATP & NADPH required
a) 2ATP + 2NADPH
b) 2ATP + 3NADPH
c) 3ATP + 2NADPH
d) 3ATP + 3NADPH
Answer:
(c) 3ATP + 2NADPH
![]()
Question 5.
Identify true statement regarding light reaction of photosynthesis?
(a) Splitting of water molecule is associate with PS I.
(b) PS I and PS II involved in the formation of NDPH + H+.
(c) The reaction center of PS I is Chlorophyll a with absorption peak at 680 nm.
(d) The reaction center of PS II is Chlorophyll a with absorption peak at 700 nm.
Answer:
(b) PS I and PS II involved in the formation of NDPH + H+.
Question 6.
Two groups (A&B) of bean plants of similar size and same leaf area were placed in identical conditions. Group A was exposed to light of wavelength 400 – 450 nm & Group B to light of wavelength of 500 – 550nm. Compare the photosynthetic rate of the 2 groups giving reasons.
Answer:
‘A’ group of plants exposed to light of 400 – 450nm. Chlorophyll a shows maximum absorption peak at 450nm (blue region). Hence rate of photosynthesis was high.
‘B’ group of plants exposed to light of 500 – 550nm. This wavelength refers to green region of the spectrum. Chlorophyll does not absorb light in the green region but reflects green. So plants appear green rate of photosynthesis was negligible in these plants.
![]()
Question 7.
A tree is believed to be releasing oxygen during nighttime. Do you believe the truthfulness of this statement? Justify your answer by giving reasons?
Answer:
Yes, a tree is believed to be releasing O2 during nighttime because at night CAM plants fix CO2 with the help of phospho Enol Pyruvic acid and produce oxala acetic acid, which is converted into malic acid-like C4 cycle.
Question 8.
Grasses have an adaptive mechanism to compensate for photorespiratory losses – Name and describe the mechanism.
Answer:
The photorespiratory losses are checked by certain grasses by having physiological adaptation. The process of photosynthesis occurs in mesophyll cells and bundle sheath cells.
Mesophyll cells:
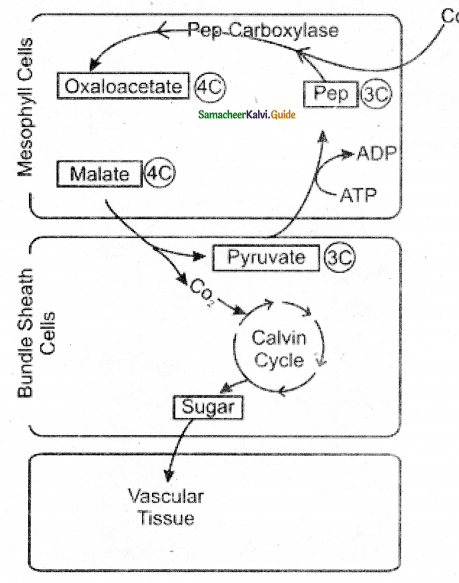
- Initially, CO2 is taken up by Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEPA) (3C) and changed to oxaloacetate (4C) in the presence of PEP carboxylase.
- Oxaloacetate is reduced to Malate/Aspartate. The product formed reaches the bundle sheath.
Bundle Sheath:
- The oxidation of Malate and Aspartate occurs with the release of carbon dioxide and the formation of Pyruvate (3C)
- Due to increased CO2 concentration RUBISCO functions as a carboxylase and not as Oxygenase.
- The photosynthetic losses are prevented.
- RUBP operates now under the Calvin cycle and pyruvate transported back to Mesophyll cells is changed into Phosphoenolpyruvate to keep the cycle going.
![]()
Question 9.
In Botany class, teacher explains, Synthesis of one glucose requires 30 ATPs in C4 plants and only 18 ATPs in C3 plants. The same teacher explains C4 plants are more advantageous than C3 plants. Can you identify the reason for this contradiction?
Answer:
C4 Plants are more advantageous than C3 plants because of the following reasons:
| C4 Plants | C3 Plants |
| CO2 fixation occurs in mesophyll cells only | CO2 fixation occurs in mesophyll and bundle sheath cells |
| RUBP is the only CO2 acceptor | PEPA Phosphoenol pyruvate in mesophyll is the acceptor in the first phase |
| Fixation of CO2 occurs if the atmospheric concentration of C02 is 50 ppm only | It can fix carbon dioxide even if the atmospheric concentration of CO2 is below 10 ppm |
| Optimum temperature is 20° to 25°C | Optimum temperature is 30° to 45°C and is thus effective in tropical regions. |
| RUBP carboxylase enzyme also functions as oxygenase if the 0, concentration is higher than carbon dioxide | PEP carboxylase enzyme functions even at low carbon – dioxide concentrations. |
| Higher rate of photorespiration and hence rate of photosynthesis is reduced. | Minimal rate of photorespiration is seen is C4 plants. |
Question 10.
When there is plenty of light and higher concentration of O2, what kind of pathway does the plant undergo? Analyse the reasons.
Answer:
The rate of photosynthesis decreases when there is an increase in oxygen concentration. This Inhibitory effect of oxygen was first discovered by Warburg (1920) using green algae, Chlorella.
Part-II.
11th Bio Botany Guide Photosynthesis Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answers
Question 1.
Photosynthesis is the major:
(a) endothermic reaction
(b) exothermic reaction
(c) endergonic reaction
(d) exergonic reaction
Answer:
(c) endergonic reaction
Question 2.
The physiological unit of photosynthesis is
a) 150-250 Chlorophyll molecules
b) 200-300 chlorophyll molecules
c) 440-660 chlorophyll molecules
d) 450- 650 chlorophyll molecules
Answer:
b) 200-300 chlorophyll molecules
![]()
Question 3.
How many million tonnes of dry matter produced annually by photosynthesis?
(a) 1700 million tonnes
(b) 1900 million tonnes
(c) 1400 million tonnes
(d) 2000 million tonnes
Answer:
(a) 1700 million tonnes
II. Match Correctly & Choose The Right Answer
Question 4.
I) Black Mann – A) the importance of Chlorophyll
II) Warburg – B) Law of limiting factor
III) Dustrochet – C) C4 cycle
IV) Hatch & Slack – Chlorella
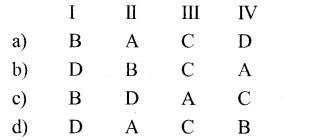
Answer:
c) B-D-A-C
![]()
Question 5.
Thylakoid disc diameter is:
(a) 0.35 to 0.75 microns
(b) 0.25 to 0.8 microns
(c) 0.45 to 0.8 microns
(d) 0.50 to 0.9 microns
Answer:
(b) 0.25 to 0.8 microns
Question 6.
The pigment responsible for the yellowing of leaves during autumn season is
a) Violaxanthin
b) Fucoxanthin
c) Phycobillin
d) Lycopene
Answer:
d) Lycopene
![]()
Question 7.
The no of quanta of light required for the release of one oxygen molecule
a) 18 quanta
b) 8 quanta
c) 81 quanta
d) 19 quanta
Answer:
b) 8 quanta
Question 8.
Each pyrrole ring comprises of:
(a) six carbons and one nitrogen atom
(b) three carbons and one nitrogen atom
(c) four carbons and one nitrogen atom
(d) four carbons and two nitrogen atom
Answer:
(c) four carbons and one nitrogen atom
![]()
Question 9.
RUBISCO – Constitute …………. of chloroplast protein
a) 17%
b) 20%
c) 18%
d) 16%
Answer:
d) 16%
Question 10.
Pheophytin resembles chlorophyll ‘a’ except that it lacks:
(a) Fe atom
(b) Mn atom
(c) Mg atom
(d) Cu atom
Answer:
(c) Mg atom
![]()
Question 11.
According to Emerson the fall in quantum yield about 680 nm is called
a) Phoisynthtic drop
b) Emerson drop
c) Airburg effect
d) Red drop
Answer:
d) Red drop
Question 12.
Which one of the photosynthetic pigments is called shield pigment:
(a) carotenes
(b) chlorophyll ‘b’
(c) pheophytin
(d) carotenoids
Answer:
(d) carotenoids
![]()
Question 13.
Which of the following equation correctly sums up photosynthesis
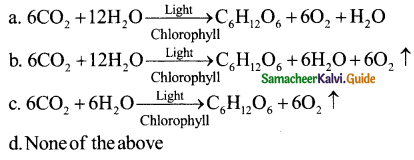
Answer:
![]()
Question 14.
Photosynthetic rate of red light (650 nm) is equal to:
(a) 42.5
(b) 10.0
(c) 43.5
(d) 40.8
Answer:
(c) 43.5
Question 15.
Which photosystem is found to be located on the outer surface of the thylakoid?
a) PS I
b) P.S II
c) P. 890
d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
a) P.S I
![]()
Question 16.
Phosphorylation taking place during respiration is called as:
(a) Photophorylation
(b) Oxidative phosphorylation
(c) Reductive phosphorylation
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Oxidative phosphorylation
Question 17.
The term Quantosome was coined by
a) Emerson
b) Liebig
c) Calvin & Melvin
d) Park & Biggins
Answer:
d) Park & Biggins
![]()
Question 18.
In bioenergetics of light reaction, to release one electron from pigment system it requires:
(a) two quanta of light
(b) four quanta of light
(c) one quantum of light
(d) eight quanta of light
Answer:
(a) two quanta of light
Question 19.
Photosynthesis produces
a) 1700 million tonnes of dry matter/year by fixing 75 x 1012 kg of carbon every year
b) 7100 million tonnes of dry matter/year by fixing 75 x 1012 kg of carbon every year
c) 1600 million tonnes of dry matter/week by fixing 56 x 1210 kg of carbon every week
d) 6100 million tonnes of dry matter/month by fixing 100 x 1012 kg of carbon every month
Answer:
a) 1700 million tonnes of dry matter/year by fixing 75 x 1012 kg of carbon every year
Question 20.
In C4 plants, how many ATPs and NADPH + H+ are utilised for the release of one oxygen molecule:
(a) 3 ATPs and 2 NADPH + H+
(b) 4 ATPs and 3 NADPH + H+
(c) 2 ATPs and 2 NADPH + H+
(d) 5 ATPs and 2 NADPH + H+
Answer:
(d) 5 ATPs and 2 NADPH + H+
![]()
Question 21.
Products of light reaction in photosynthesis are
a) ATP & NADPH2
b) ADP & glucose
c) Ferredoxin and cytochrome b6
d) Cytochrome
Answer:
a) ATP & NADPH2
Question 22.
In the sugarcane plant, the dicarboxylic acid pathway was first discovered by:
(a) Hatch and Slack
(b) Kortschak, Hart and Burr
(c) Calvin and Benson
(d) Mitchell and Root
Answer:
(b) Kortschak, Hart and Burr
![]()
Question 23.
Photosynthetic pigments in chloroplasts lie embedded in
a) Chloroplast envelope
b) Plastogloblue
c) matrix
d) thylakoids
Answer:
d) thylakoids
Question 24.
Indicate the correct answer:
(a) C4 plants are adapted to only rainy conditions
(b) C4 plants are partially adapted to drought condition
(c) C4 plants are exclusively adapted to desert condition
(d) C4 plants are adapted to aquatic condition
Answer:
(b) C4 plants are partially adapted to drought condition
![]()
Question 25.
Carotenoids and Xanthophylls are also known as
a) Respiratory pigments
b) Accessory pigments
c) Photosynthetic pigments.
d) Photolytic pigments
Answer:
b) Accessory pigments
Question 26.
Which metal ion is a
a) Iron
b) cobalt
c) Magnesium
d) Zinc
Answer:
c) Magnesium
![]()
Question 27.
The important external factors affecting photosynthesis are:
(a) light, chlorophyll, temperature
(b) light, stomatal opening, oxygen
(c) light, protoplasmic factor, oxygen
(d) light, CO2 and oxygen
Answer:
(d) light, CO2 and oxygen
Question 28.
The process of photophosphorylation was discovered by
a) Priestly
b) Calvin
c) Amon
d) Warburg
Answer:
c) Arnon
![]()
Question 29.
Which of the following is a C4 plant
a) Potato
b) Sugarcane
c) Pea
d) Papaya
Answer:
b) Sugarcane
Question 30.
Splitting of water molecule (photolysis) produces:
(a) hydrogen and oxygen
(b) electrons, protons and oxygen
(c) electrons and oxygen
(d) hydrogen, carbon dioxide and oxygen
Answer:
(b) electrons, protons and oxygen
![]()
Question 31.
Dimorphism in chloroplasts is seen in
a) C4 plants
b) C2 plants
c) CAM – plants
d) C3 plants
Answer:
a) C4 plants
Question 32.
Energy required for ATP synthesis in PSII comes from
a) Proton gradient
b) Electron gradient
c) Reduction of glucose
d) Oxidation of glucose
Answer:
a) Proton gradient
![]()
Question 33.
The by-product of Photosynthesis is
a) O2
b) CO2
c) Carbohydrate
d) H2O
Answer:
a) O2
Question 34.
Which of the following process is called reverse of Glycolysis?
a) CO2 reduction
b) RUBP carboxylation
c) RUBP regeneration
d) ATP synthesis
Answer:
a) CO2 reduction
![]()
Question 35.
The Dark reaction of Photosynthesis occurs in
a) Matrix
b) Grana
c) Stroma
d) Cytoplasm
Answer:
c) Stroma
Question 36.
A granal chloroplasts are characteristics of
a) Mesophyll of pea leaves
b) Bundle sheath of Mango leaves
c) Mesophyll of maize leaves
d) Bundle sheath of sugar cane leaves
Answer:
d) Bundle sheath of Sugar cane leaves
Question 37.
Which of the following plant is a better photosynthesis?
a) Mango
b) Sugarcane
c) Wheat
d) Rice
Answer:
b) Sugarcane
![]()
Question 38.
The enzyme that is not found in a C3 plant is
a) RUBP carboxylase
b) PEP carboxylase
c) NADP reductase
d) ATP synthase
Answer:
b) PEP carboxylase
Question 39.
Which of the following factors affect the rate of photosynthesis?
I. Light
II. Protoplasmic factor
III. Hormones Codes
IV. Haemoglobin
a) only III
b) I and II
c) only IV
d) I, II, and III
Answer:
d) I, II and III
![]()
Question 40.
Match the following columns
| Column I | Column II |
| I. The 5C sugar that | A. RUBIS Co |
| II. 3 C sugar that gives Calvin cycle its nickname | B. Glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate |
| III. Activated form of 3 PGA | C. 3 phosphoglyceric acid |
| IV. Huge enzyme complex that brings CO2 and 5C sugar together. | D. RUBP |
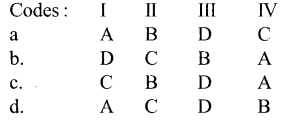
Question 41.
One complete light reaction involves light energy.
a) 30 quanta
b) 48 quanta
c) 40 quanta
d) 25 quanta
Answer:
b) 48 quanta
Question 42.
During photosynthesis which of the following event does not take place?
a) oxidation of CO2
b) Reduction of CO2
c) oxidation of H2O
d) Light absorption
Answer:
a) Oxidation of CO2
![]()
Question 43.
The site of light trapping in the chloroplast is
a) Thylakoid membrane
b) Stroma
c) Plasma fluid
d) Stromal lamellae
Answer:
a) Thylakoid membrane
Question 44.
Kranz anatomy is traced in the Leaves of
a) Wheat
b) Potato
c) Mustard
d) Sugarcane
Answer:
d) Sugarcane
![]()
Question 45.
The intermediate got from Kreb’s cycle that is used for chlorophyll synthesis is
a) Citric acid
b) Isocitric acid
c) Succinic acid
d) Fumaric acid
Answer:
c) Succinic acid
Question 46.
The existence of light and dark reaction of photosynthesis was proved by
a) Blackman
b) Emerson
c) Warburg
d) Arnon
Answer:
a) Blackman
![]()
Question 47.
Choose the wrong match.
a) Hatch & Slack – Dicarboxylic acid pathway
b) Decker – PCO cycle
c) Ruben, Kamen – CAM cycle
d) Calvin Benson – PCR cycle
Answer:
c) Ruben, Kamen – CAM cycle
Question 48.
I) Primary CO, acceptor – PEPA
II) 4C compound produced 1 st – OAA
III) 1st carboxylation occurs in – Bundle sheath cells
IV) 2nd carboxylation occurs in – Mesophy 11 cells
a) I & II
b) II & III
c) III & IV
d) I & IV
Answer:
c) III & IV
Question 49.
Say True or False with respect to C2 cycle
I) RUBISCO has the most abundant protein on earth.
II) Photorespiration does not yield any free energy in the form of ATP
III) The end product is a 2 – c compound. So the cycle is known as C2 cycle
IV) Under certain conditions 50% of the photosynthetic potential is lost because of photorespiration.

Answer:
b) True – True – False – True
Question 50.
Say True or False and choose the right option from the given choice.
I) PAR is between – 400 – 700 mil.
II) Heliophytes (Beans) require higher light intensity than sccophytes (oxalis)
III) Red light induces lowest rate of photosynthesis.
IV) Green light induces highest rate of photosynthesis.

Answer:
c) True – True – False – False
![]()
Question 51.
Choose the wrongly matched pair
a) Stephen hales – Father of plant physiology
b) Lavoisier – Purifying gas oxygen is produced in sun light
c) Vonmayer – Green plants convert solar energy into chemical energy
d) Emerson &Amoid – C4 cycle
Answer:
d) Emerson & Arnold – C4 cycle
Question 52.
Choose the rightly matched pair
a) Chlorophyll a – Accessory pigments and trap solar energy
b) Chlorophyll b – Differs from Chlorophyll a in having CH3 instead of CHO – at 3rd C atom
c) Chlorophyll c – Differs from Chlorophyll a by lacking a phytol tail
d) Chlorophyll d – It has CHO at 3rd at the 3rd carbon atom at 11 – pyrrole ring
Answer:
c) Chlorophyll c – Differs from chlorophyll a by lacking a phytol tail.
![]()
Question 53.
Choose the right matched pairs from the given options.
I) Green non sulphur bacteria – Clostridium & Lynbya
II) Green sulphur bacteria – Chlorobacterium & Chlorobium
III) Purple sulphur bacteria – Thiospirillum & Chromatium
IV) Purple non sulphur bacteria – Rhodopseudomonas & Rhodospirillum
a) I, II, & III
b) II, III & IV
C) I, II & IV
d) I, III & IV
Answer:
b) II, III & IV
II. Assertion (A) & Reason (R)
a) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion
b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true – Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
c) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
d) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are false.
Question 1.
Assertion (A): Chlorophyll appears green.
Reason (R): It absorbs light mainly in the region of green part of light spectrum.
Answer:
c) Assertion (A) is False but Reason (R) is true.
![]()
Question 2.
Assertion (A): Red of spectrum contains high energy.
Reason (R): Green light of Visible spectrum contain low energy than red light.
Answer:
c) Assertion (A) is False but Reason (R) is true.
Question 3.
Assetion (A): Non cyclic photo phosphorylation occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts
Reason (R): There is a continuous flow of electrons in this process.
Answer:
d) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are false.
Question 4.
Assetion (A): Carotenes and Xanthophylls are soluble in either
Reason (R): These are accessory pigments of photosynthesis
Answer:
b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
Question 5.
Assetion (A): Carotenoids are accessory pigments
Reason (R): Absorbed light energy is transferred to reaction centre by carotenoids.
Answer:
a) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) True and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
III. 2 Marks Questions
Question 1.
What is the function of the plant in the universe?
Answer:
Plants are the major machinery which produces organic compounds like carbohydrates,lipids, proteins, nucleic acids and other biomolecules.
Question 2.
What is PAR?
Answer:
It refers to Photosynthetically Active Radiation, which is between 400 – 700 nm photosynthetic rate is maximum in blue and red light – Green light induces lowest rate of photosynthesis.
![]()
Question 3.
What is the site of photosynthesis?
Answer:
Chloroplasts are the main site of photosynthesis and both the energy-yielding process (Light reaction) and fixation of carbon dioxide (Dark reaction) that takes place in the chloroplast.
Question 4.
Name the photosynthetic pigments of Algae?
Answer:
- Chlorophyll b – Green Algae
- Chlorophyll c – Dianoflagellates, Diatoms & Brown Algae
- Chlorophyll d – Red Algae
- Chlorophyll e – Xantho phycean Algae.
Question 5.
Endosymbiotic hypothesis says that chloroplasts evolved from bacteria. Substantiate the statement.
Answer:
Presence of 70S ribosome and DNA gives them status of semi-autonomy and proves endosymbiotic hypothesis which says chloroplast evolved from bacteria.
![]()
Question 6.
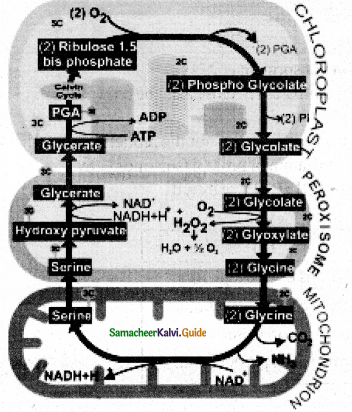
Write down the significance of photorespiration.
Answer:
- Glycine and Serine synthesized during this process are precursors of many biomolecules like Chlorophyll, Proteins, Nucleotides.
- It consumes excess NADH + H+ generated.
- Glycolate protects cells from Photooxidation.
Question 7.
What are the conclusions of Hill’s Reaction?
Answer:
- During Photosynthesis oxygen is evolved from water.
- Electrons for the reduction of CO2 are obtained from water.
- A reduced substance produced, later helps to reduce CO2
- 2H2O + 2A→ 2 AH2 + O2
Question 8.
What are Xanthophylls?
Answer:
Yellow (C40H56O2) pigments are like carotenes but contain oxygen. Lutein is responsible for yellow colour change of leaves during autumn season. Examples: Lutein, Violaxanthin and Fueoxanthin.
Question 9.
Notes on Phycobillins.
Answer:
- They are proteinaceous pigments.
- They are soluble in water.
- Lack ‘Mg’ and phytol tail.
- There are 2 forms 1. Phycocyanin 2. Phycoerythrin.
- Phycocyanin occur in Cyanobacteria.
- Phyco erythrin occur in Rhodophycean Algae.
Question 10.
Define absorption spectrum.
Answer:
Pigments absorb different wavelengths of light. A curve obtained by plotting the amount of absorption of different wavelengths of light by a pigment is called its absorption spectrum.
![]()
Question 11.
Why do we call carotenoids shield pigments?
Answer:
- Carotenoids are yellow to orange pigments mostly tetraterpens and absorb light strongly in the blue to violet region of the visible spectrum.
- These pigments protect chlorophyll from photosynthetic oxidative damage.
Question 12.
What is known as substrate-level phosphorylation?
Answer:
Phosphorylation taking place during respiration is called oxidative phosphorylation and ATP produced by the breakdown of substrate is known as substrate-level phosphorylation.
Question 13.
What are Quantosomes?
Answer:
- They are physiological photosynthetic units, located on the inner membrane of thylakoid lamellae of size 180A X 160 A length & breadth.
- It was named by Park &Pickins( 1964).
- One quantosome contains about 230 chlorophyll molecules.
- It constitutes a photosynthetic unit responsible for the production of one O2 molecule or reduction of one CO2 molecule.
Question 14.
What is Bioluminescence?
Answer:
It is the special aspect of few living organism, in which there are some biochemical substances production is responsible for the emission of light by a living organism.
![]()
Question 15.
What is the significance of photorespiration?
Answer:
Significance of photorespiration:
- Glycine and Serine synthesized during this process are precursors of many biomolecules like chlorophyll, proteins, nucleotides.
- It consumes excess NADH + H+ generated.
- Glycolate protects cells from Photooxidation.
Question 16.
Explain water oxidizing clock or S state mechanism.
Answer:
The splitting of water molecule, mechanism was studied by KoK et, al (1970).
It consists of a series of 5 states so, s1, s2, s3, s4.
Each sate acquires positive charge by a photon (hv) and after the state s4 – if acquires 4 positive charges 4 electron and evolution of oxygen.
Two molecules of water go back to the so.
At the end of photolysis 4H+, 4e– and O2 are evolved from water.
4H2O → 4H++ + 40H–
40H– → 2H2O+O2+4e–
2H2O → 4H++ O2 + 4e–.
Question 17.
Distinguish between photophosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation.
Answer:
| Photophosphorylation | Phosphorylation |
| 1. It is the process of synthesis of ATP from ADP by the addition of phosphate takes place with the help of photosynthesis light generated electron, which is known as photophosphorylation. It is of two types Cyclic and Non-cyclic photophosphorylation. | 1. The process of production of ATP via terminal oxidation of reduced coenzymes during respiration is known as oxidative phosphorylation. |
Question 18.
What are the air pollutants, that affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Answer:
Pollutants like SO2, NO2, O3 (Ozone) and Smog affect the rate of photosynthesis.
Question 19.
What are the conditions for the occurrence of Non-cyclic photophosphorylation?
Answer:
- Non-Cyclic Photo Phosphorylation occurs, when.
- There is the availability of NADP+ for reduction.
- Two molecules of water go back to the so.
- When there is the splitting of water molecules.
- When both PSI and PS II are activated.
![]()
Question 20.
Name any three photosynthetic bacteria.
Answer:
Three photosynthetic bacteria:
- Chlorobacterium
- Thiospirillum
- Rodhospirillum
Question 21.
What are the 2 phases of light reaction?
Answer:
The light reaction has 2 phases
- Photooxidation phase
- Photochemical phase.
I) Photooxidation phase (POP):
- Absorption of light energy.
- Transfer of energy from accessory pigments to the reaction centre.
- Activation of chlorophyll ‘a’ -molecule.
II) Photochemical phase (PCO):
- Photolysis of water and evolution of oxygen.
- Electron transport and synthesis of assimilatory power.
Question 22.
Greenlight induces lowest rate of photosynthesis justifies.
Answer:
- Yes green light induces the lowest rate of photosynthesis because it is not coming under photosynthetically
- Active reduction – (400 – 700 nm) known as PAR.
- PAR – (Photosynthetic rate is maximum in blue and red light not in green Light.
Question 23.
What will be the quanta requirement for the complete light reaction which releases 6 oxygen molecules?
Answer:
- Complet light reaction releases 6 oxygen molecules.
- If one molecule of oxygen evolution requires 8 quanta means for 6 oxygen molecules (6 x 8 = 48) quanta of light reaquired for a complete light reaction.
![]()
Question 24.
Give the balance sheet of Calvin or C3 cycle.
Answer:
One molecule of CO2 is fixed in one turn of the Calvin or C3 cycle.
So 6 turns of cycle will be required to fix 6 molecules of C02 – (i.e) to form one molecule of Glucose C6H12O6
| In | Out |
| 6CO2 | 1 Glucose |
| 18 ATP | 18 ADP |
| 12 NADPH | 12 NADP |
IV. 3 Mark Questions
Question 1.
Mention any three significance of photosynthesis.
Answer:
Three significance of photosynthesis:
- Photosynthetic organisms provide food for all living organisms on earth either directly or indirectly.
- It is the only natural process that liberates oxygen in the atmosphere and balances the oxygen level.
- Photosynthesis balances the oxygen and carbon cycle in nature.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the properties of light.
Answer:
- Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave.
- It consists of ocillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to each other and perpenticular to the direction of propagation of the light.
- Light moves at a speed of 3 x 108 ms-1
- Wave length is the distance between successive crests of the wave.
- Light as a particle is called photon. Each photon contains an amount of energy known as quantum.
- The energy of a photon depends on the frequency of the light.
Question 3.
Distinguish between Absorption spectrum & Action Spectrum.
Answer:
| Absorption spectrum | Action spectrum |
| A curve obtained by plotting the amount of absorption of different wavelengths of light by a pigment is called the Absorption spectrum. | The curve showing the rate of photosynthesis at different wavelengths of light is called the action spectrum. |
Question 4.
Distinguish between fluorescence and phosphorescence.
Answer:
| Fluorescence | Phosphorescence |
| 1. Immediate emission of absorbed radiations in the form of radiation energy (light) in the red region. | 1. This is the delayed emission of absorbed radiations in the form of light in the red region. |
| 2. The electrons move from S1 →SO | 2. The electrons pathway is from S2 →S1 →T1→ SO |
Question 5.
What is meant by the ground state?
Answer:
The action of photon plays a vital role in the excitation of pigment molecules to release an electron. When the molecules absorb a photon, it is in an excited state. When the light source turned off, the high-energy electrons return to their normal low-energy orbitals as the excited molecule goes back to its original stable condition known as the ground state.
Question 6.
Write down the significance of Photosynthesis.
Answer:
- Photosynthetic organisms provide food for all living organisms on earth either directly or indirectly All other organism depend on them for energy.
- It liberates oxygen in the atmosphere and balances.
- Fuels such as coal, petroleum, and other fossil fuels are preserved forms got only from photosynthetic plants.
- It also provides fodder, fibre, firewood, timber useful medicinal products and these sources come by the act of photosynthesis.
![]()
Question 7.
What is DCMU?
Answer:
- It is a chemical herbicide having an inhibiting effect on photosynthesis.
- It is Dichloro phenyl D1 Methyl Urea.
- It can inhibit electron flow during light reactions of photosynthesis.
- It is a herbicide that blocks the plastoquinone binding site of P.S II and inhibits electron flow from plastoquinone to cytochrome.
Question 8.
State black man’s law of limiting factor.
Answer:
It is a modified law proposed by Liebig’s law of minimum.
Definition:
According to Blackman at any given point of time, the lowest factor among essentials will limit the rate of Photosynthesis.
Example:
When in a condition, if light intensity is low also C02 concentration low, in this situation among the two factors which ever is the lowest is considered as the limiting factor here among the essentials CO2 concentration is the limiting factor.
![]()
Question 9.
What is meant by dicarboxylic acid pathway?
Answer:
C4 pathway is completed in two phases, first phase takes place in the stroma of mesophyll cells, where the CO2 acceptor mblecule is 3 – Carbon compound, phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to form 4 – carbon Oxalo acetic acid (OAA). The first product is a 4 – carbon and so it is named as C4 cycle. Oxalo acetic acid is a dicarboxylic acid and hence this cycle is also known as a dicarboxylic acid pathway.
Question 10.
State some interesting facts about C4 cycle.
Answer:
- C4 cycle is an alternative path way for CO2 fixation.
- It occur in nearly 1000 plant species 300 dicots but mostly 700 monocots (tropical and sub tropical grasses)
- It represent about 5% earths biomass and 1% of its known plants
- 30% terrestrial carbon fixation on earth is due to C4 So, if C4 plants on earth is increased, then by carbon sequestration by thus strategy severe climate change would be avoided in the near future.
![]()
Question 11.
What is Kranz Anatomy or what is meant by Dimorphism of Chloropiasts in C4 plants.
Answer:
| C3 plants | C4 plants |
| C3 plants kranz Anatomy not seen | C4 plants show kranz Anatomy |
| C3 plants only one type of chloroplasts seen both in bundle sheath and mesophyll cells. | C4 plants Bundle sheath surrounding the vascular bundles have larger chloroplast and have thylakoids are free, not arranged in granum. |
| Thylakoids are arranged in granum as coins. | Mesophyll cells have smaller chloroplasts thylakoid arranged in granum |
Question 12.
what is the significance of the CAM cycle?
Answer:
The significance of the CAM cycle:
- It is advantageous for succulent plants to obtain CO2 from malic acid when stomata are closed.
- During daytime, stomata are closed and CO2 is not taken but continues their photosynthesis.
- Stomata are closed during the daytime and help the plants to avoid transpiration and water loss.
Question 13.
Compare the C3 and C4 on the basis of ATP production.
Answer:
| C3 plants | C4 plants |
| The evolution of one oxygen molecule (4 electrons required) requires 8 quanta of light | |
| C3 plants utilise 2 ATPs and 2 NAD PH+H+ to evolve one oxygen molecule | C4 plants utilise 5 ATPs and 2NADPH + H+ to evolve one oxygen molecule |
| To evolve 6 molecules of oxygen or 1 molecule of Glucose 8 ATPs and 12 NADPH + H+ are utilised. | To evolve 6 molecules of oxygen 30 ATPs and 12 NADPH + H+ are utilised. |
Question 14.
What will be the quanta requirement for the complete light reaction which releases 6 oxygen molecules?
Answer:
The complete light reaction releases 6 oxygen molecules if one molecule of oxygen evolution, requires 81 quanta means for 6 oxygen molecules 6 x 8 = 48 quanta of light required for the complete light reaction.
Question 15.
Draw the Graphical representation of any 3 factors affecting photosynthesis.
Answer:
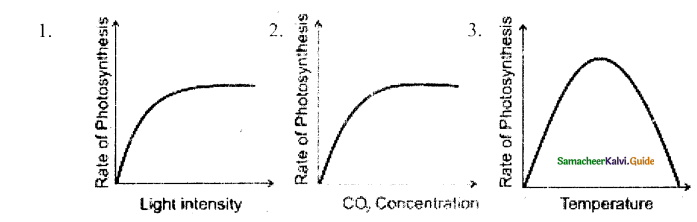
1. Light Intensity
2. CO2 Concentration
3. Temperature
![]()
V. 5 Mark Questions
Question 1.
Distinguish between Photosystem – I and photosystem – II
Answer:
Photosystem – I:
- The reaction centre is P700.
- PS I is involved in both cyclic and non – cyclic.
- Not involved in the photolysis of water and evolution of oxygen.
- It receives electrons from PS II during non – cyclic photophosphorylation.
- Located in unstacked region granum facing chloroplast stroma.
- Chlorophyll and Carotenoid ratio is 20 to 30 : 1.
Photosystem – II:
- Reaction centre is P680.
- PS II participates in Non – cyclic pathway.
- Photolysis of water and evolution of oxygen take place.
- It receives electrons by photolysis of water.
- Located in stacked region of thylakoid membrane facing lumen of thylakoid.
- Chlorophyll and Carotenoid ratio is 3 to 7 : 1.
Question 2.
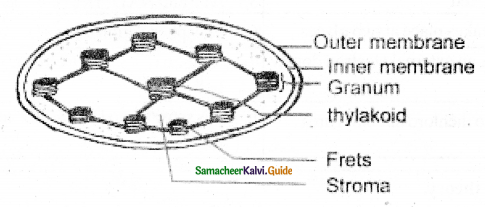
Structure of Chloroplast.
Answer:
Question 3.
Notes on photosystem and Reaction centre.
Answer:
- Thylakoid membrane contains photosystem I (PSI) and photosystem II (PSII)
- PS I is unstacked region of granum tàcing stroma ofchÍoroplast.
- PS II is found in stacked region of thylakoid membrane facing lumen of thylakoid.
- Each photosystem consists of central core complex (CC) and light harvesting complex (LHC) or Antenna molecules.
- The core complex consists of respective reaction centre associated with proteins, electron donors and acceptors.
- PSI – CCI consists of reaction centre P 700 and LHC – I
- PS II- CC II consists of reaction centre P680 and LHC – II
- Light harvesting complex consists of several chiorophylls, carotenoids and xanthophyll molecules.
- The main function of LHC is to harvesting light energy and transfer it to their respective reaction centre.
![]()
Question 4.
Difference between photosystem I and Photosystem II.
Answer:
| Photosystem I | Photosystem II |
| 1. The reaction centre is P700 | 1. Reaction centre is P 680. |
| 2. PSI is involved in Photolysis of water and evolution. | 2. PS II participates in Non – Cyclic pathway |
| 3. Not involved in photolysis of water and evolution of oxygen. | 3. Photolysis of water and evolution of oxygen take place. |
| 4. It receives electrons from PSII during non – cyclic photophosphorylation. | 4. It receives electrons by photolysis of water. |
| 5. Located in unstacked region granum racing chloroplast stroma. | 5. Located in stacked region of thylakoid membrane facing lumen of thylakoid. |
| 6. Chlorophyll and carotenoid ratio is 20 to 30:1 | 6. Chlorophyll and carotenoid ratio is 3 to 7:1 |
Question 5.
Differences between Cyclic Photophosphorylation and Non – cyclic photophosphorylation.
Answer:
| Cyclic Photophosphorylation | Non – Cyclic Photophosphorylation |
| 1. PSI only involved | 1. PS I and PS II involved. |
| 2. Reaction centre is P 700 | 2. Reaction centre is P 680. |
| 3. Electrons released are cycled back | 3. Electron released are not cycled back. |
| 4. Photolysis of water does not take place | 4. Photolysis of water takes place |
| 5. Only ATP Synthesized | 5. ATP and NADPH + H+ are synthesized. |
| 6. Phosphorylation takes place at two places | 6. Phosphorylation takes place at only one place |
| 7. It does not require an external electron donor. | 7. Requires external electron donor like H2O or H2S |
| 8. It is not sensitive to dichloro dimethyl urea (DCMU) | 8. It is sensitive to DCMU and inhibits electron flow |
Question 6.
Compare and contrast the photosynthetic processes in C3 and C4 plants.
Answer:
Contrast the photosynthetic processes in C3 and C4 plants:
C3 Plants:
- CO2 fixation takes place in mesophyll cells only.
- CO2 acceptor is RUBP only.
- First product is 3C – PGA.
- Kranz anatomy is not present.
- Granum is present in mesophyll cells.
- Normal Chloroplast.
- Optimum temperature 20° to 25° C.
- Fixation of CO2 at 50 ppm.
- Less efficient due to higher photorespiration.
- RUBP carboxylase enzyme used for fixation.
- 18 ATPs used to synthesize one glucose.
- Efficient at low CO2.
- eg: Paddy, Wheat, Potato and so on.
C4 Plants:
- CO2 fixation takes place mesophyll and bundle sheath.
- PEP in mesophyll and RUBP in bundle sheath cells.
- First product is 4C – OAA.
- Kranz anatomy is present.
- Granum present in mesophyll cells and absent in bundle sheath.
- Dimorphic chloroplast.
- Optimum temperature 30° to 45° C.
- Fixation of CO2 even less than 10 ppm.
- More efficient due to less photorespiration.
- PEP carboxylase and RUBP carboxylase used.
- 30 ATPs to produce one glucose.
- Efficient at higher CO2.
- eg: Sugar cane, Maize, Sorghum, Amaranthus and so on.
![]()
Question 7.
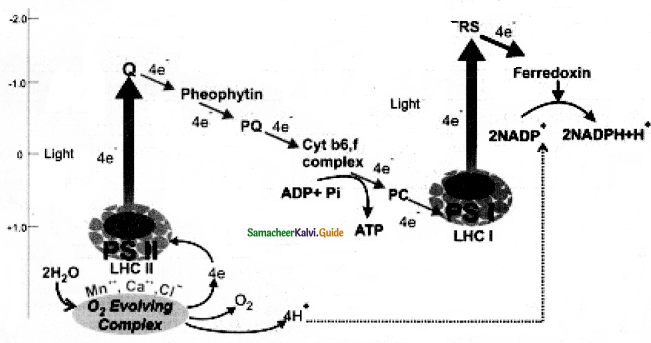
Explain Non cyclic photophosphorylation.
Answer:
When PS II (P680) gets activated, electrons from a high energy state pass through a series of electron carriers like pheophytin, plastoquinone cytochrome complex, plastocyanin, and finally accepted by PS I (P700).
During this flow ATP is generated:
- PS. I (P 700) is activated by light electrons moved to high energy state and accepted by electron acceptor (FRS) Ferredoxin Reducing Substance, during downhill passes through Ferredoxin. During this process NADPH is reduced by H+ formed during photolysis.
- Electrons released from PS II are not cycled back but used in the reduction of NADPH+ into NADPH+H+.
- During electron transport, it generates ATP and this type of Phophorylation is called.
Non Cyclic Photophosphorylation:
The electron flow looks like the letter ‘Z’ so known as Z scheme. It has 3 stages.
- Electron transport from water to P 680: Electrons lost by the PS II are replaced by electrons from splitting of the water molecule, producing electron, protons, and oxygen.
- Electron transport from P680 to P 700: The flow, through various electron carrier molecules, like pheophytin, plastoquinone (PQ) cytochrome b6 – F complex, plastocyanin (PC) finally reaches P 700 (P.S.I)
- Electron transport from P 700 to NADP+: PSI (P700) is excited now and the electrons pass through ferredoxin, NADP is reduced to NADPH + H+
Question 8.
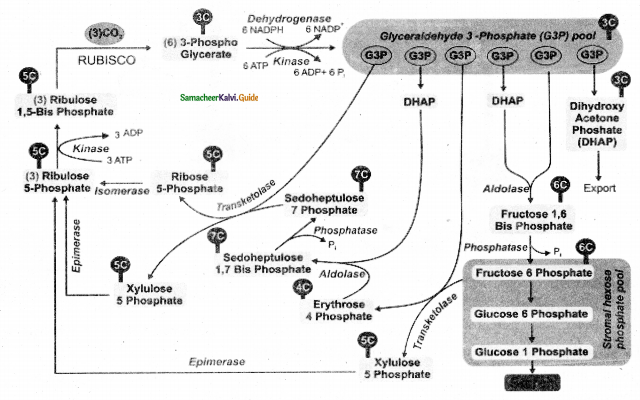
Explain Calvin cycle or C3 cycle?
Answer:
- It follows a light reaction.
- Utilises ATP and NADPH + H+ produced during the light reaction, and reduce carbon dioxide carbohydrate.
- These reactions do not require light so named as Dark reactions.
- The first formed product is a 3 carbon compound (Phospho Glyceric Acid) and so-known as C3 cycle.
- It was found by Melvin, Calvin, and Benson – so known as the Calvin cycle.
- Occur in the stroma of the chloroplast.
- It is temperature-dependent, and so it is also called a thermochemical reaction.
Phase I carboxylation (Carbon fixation):
- The 5 C compound Ribulose 1 – 5 Bisphosphate (RUBP) with the help of (RUBISCO) enzyme accepts one molecule of carbon dioxide → 6 carbon compound (unstable)
- The 6c compound is broken into → 2 molecules of 3 c compound.
![]()
Phase II – Glycolytic Reversai/Reduction :

Phase III – Regeneration:
- The regeneration of RUBP involves several intermediate compounds of 6c, 5c, 4c, and 7c compounds.
- Fixation of one CO2 require 3 ATPs + 2NADPH+ + H+
- Fixation of six CO2 require I8 ATPs+ 12NADPH+ + H+
- 6 c compound is the net gain to form hexose sugar.
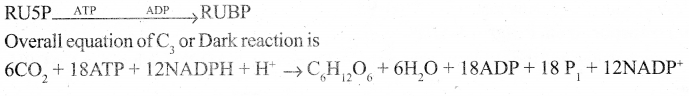
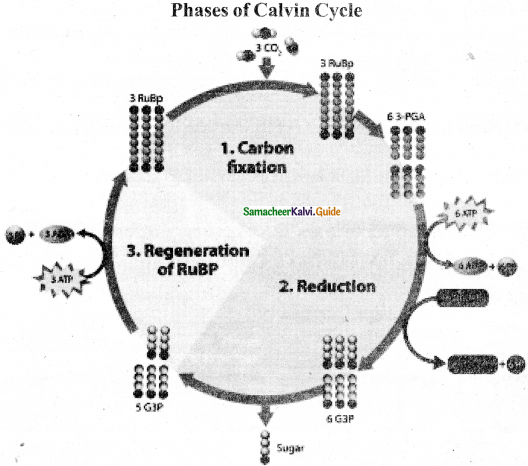
Question 9.
Draw the flow Chart of C4 pathway?
Answer:
Question 10.
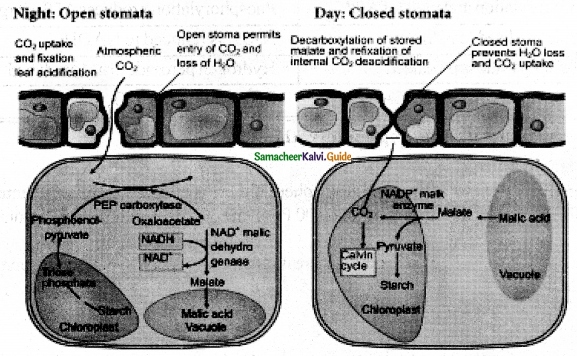
Explain CAM Cycle?
Answer:
- It is one of the carbon path ways in succulent plants growing in semi arid or xerophytic condition.
- The stomata are closed during day (scoto active) and open during night.
- This reverse rhythm help to conserve water loss through transpiration and will stop the fixation of CO2 during day.
- At night time CAM plants fix CO, with help of (PEP) phospho Enol Pyruvic acid and produce (OAA) Oxalo Acetic Acid.
- Subsequently OAA is converted into a Malic acid-like C4 cycle and get accumulated in the vacuole, increasing the acidity.
- During daytime stomata, are closed and Malic acid is decarboxylated into pyruvic acid resulting in the decrease of acidity.
- CO2 thus formed enters into the Calvin cycle and produces carbohydrates.
Question 11.
Give the flow chart of Photo respiration or C2 cycle.
Answer:
Question 12.
Differentiate Photorespiration and Dark respiration.
Answer:
| Photorespiration | Dark respiration |
| 1. It takes place in photosynthetic green cells | It takes place in all living cells |
| 2. It takes place only in the presence of light | It involves only Mitochondria |
| 3. It involves Chloroplast, Peroxisome, and Mitochondria | It involves only Mitochondria |
| 4. It does not involve Glycolysis, Kreb’s cycle, and ETS | It involves Glycolysis, Kreb’s cycle and ETS |
| 5. Substrate is Glycolic acid | Substrate is Carbohydrates protein or fats |
| 6. It is not essential for survival | Essential for survival |
| 7. No phosphorylation and yield of ATP Phosphorylation | produces ATP energy |
| 8. NADH2 is oxidised to NAD+ | NAD+ is reduced to NADH2 |
| 9. Hydrogen peroxide is produced | Hydrogen peroxide is not produced |
| 10. End products are CO2 and PGA | End products are CO2 and water |
Question 13.
Give any 5 External factors affecting photosynthesis.
Answer:
1. Carbon dioxide:
330ppm or 0.3% of CO2 is available in the atomsphere If there is an increase in CO2 concentration the rate of Photosynthesis increases -If it increases beyond 500 PPm rate of photosynthesis will be inhibited.
2. Oxygen:
When there is increase in oxygen concentration there is unhibition of photosynthesis Warburg – studied this in chlorellain 1920. This effect is known as Warburg effect.
3. Temperature:
- Optimum temperature for photosynthesis vary from plant to plant
- Normally it is 25°C to 3 5°C
- In Opuntia, it is 55°C
- In Lichens it is 20°C
- In Algae growing in hot spring it is 75°C
- At high and low temperature the stomata will close also the enzymes get inactivated.
4. Water:
- Pholysis of water provide electrons and protons for the reduction of NADP – directly.
- Affect stomatal movement and hydration of protoplasm – indirectly.
- During water stress, supply of NADPH + H+ affected
5. Minerals:
| Deficiency | Effect |
| Mg, Fe and N | Synthesis of chlorophyll |
| P | phosphorylation reactions |
| Mn, Cl- | photolysis of water |
| CU | Formation of plastocyanin |
![]()
Question 14.
Explain the test tube funnel experiment.
Answer:
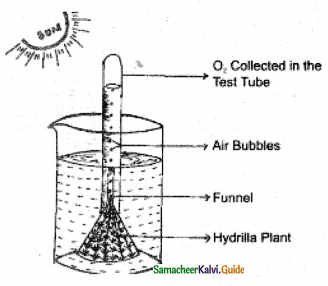
AIM: To proove that oxygen is evolved during Photosynthesis.
Procedure:
Take some hydrilla plant and place them at the bottom of a beaker containing water – Add, little NaHCO3 in to the water. Cover plant with an inverted funnel Invert a test tube over the funnel keep this set up in sun light.
Observation: Air bubbles are released from Hydrilla plant and collected in the test tube by downward displace ment of water. Take the test tube carefully by closing with a finger and then introduce a burning match stick, it bum brightly.
Inference: Hydrilla plant perform photosynthesis and oxygen is liberated during photosynthesis.
Question 15.
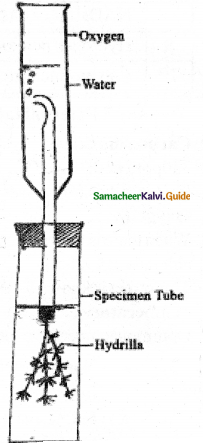
Explain the experiment to determine rate of photosynthesis by Witmott’s bubbler.
Answer:
Procedure:
- Wilmott’s bubbler consists of a wide mouth bottle fitted with a single holed cork, a glass tube with lower and having wider opening to insert hydrilla plant.
- The upper end is fitted to a narrow bottle with water.
- Fill the bottle with water and insert hydrilla living into wider part of the tube.
- Hydrilla plant should be cut inside the water to avoid entry of
air bubbles. - Fix the tube with jar which acts as water reservoir.
- Keep the apparatus in sunlight count the bubbles when they are in same size.
Question 16.
Differentiate photosynthesis in plants and Bacterial photosynthesis.
Answer:
| Photosynthesis | Bacterial photosynthesis |
| 1. Cyclic and Non – Cyclic phosphorylation takes place | Only cyclic phosphorylation takes place |
| 2. Photosystem I and II involved | Photosystem I only involved |
| 3. Electron donor is water | Electron donor is H9S |
| 4. Oxygen is evolved | Oxygen is not evolved |
| 5. Reaction centres are P700 and P680 | Reaction centre is P890 |
| 6. Reducing agent is NADPH + H+ | Reducing agent is NADH + H+ |
| 7. PAR is 400 to 700 nm | PAR is above 700nm |
| 8. Chlorophyll, Carotenoid and Xanthophyll | Bacterio chlorophyll and Bacterio viridin |
| 9. Photosynthetic apparatus – chloroplast | It is chromosomes and Chromatophores |