Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Botany Guide Pdf Chapter 15 Plant Growth and Development Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Botany Solutions Chapter 15 Plant Growth and Development
11th Bio Botany Guide Plant Growth and Development Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part – I.
Question 1.
Select the wrong statement from the following:
(a) Formative phase of the cells retain the capability of cell division.
(b) In elongation phase development of central vacuole takes place.
(c) In maturation phase thickening and differentiation takes place.
(d) In maturation phase, the cells grow further.
Answer:
(d) In maturation phase, the cells grow further.
Question 2.
If the diameter of the pulley is 6 inches, length of pointer is 10 inches and distance travelled by pointer is 5 inches. Calculate the actual growth in length of plant.
a) 3 inches
b) 6 inches
c) 12 inches
d) 30 inches
Answer:
options are wrong, (correct Ans = 1.5 inches)
Solution:
Step I:
Diameter of the Pulley=6 inches
Radius of the pulley \(=\frac{6}{2}\)= 3 inches
Actual growth in length= Distance travailed by pointer x Radius of the pulley Length of the pointer
=\(\frac{5 \times 3}{10}\) =1.5=1.5.
Answer:
1.5 inches
![]()
Question 3.
In unisexual plants, sex can changed by the application of
a) Ethanol
b) Cytokinins
c) ABA
d) Auxin
Answer:
c) ABA
Question 4.
Select the correctly matched one
A) Humanurine i) Auxin-B
B) Corn gram oil ii) GA3
C) Fungs iii) Abscisic acid II
D) Herring fish sperm iv) Kinetin
E) Unripcrnaizegrains v) AuxinA
F) Young cotton boils vi) Zeatin
Answer:
b) A – v, B – i, C – ii, D – iv, E – vi, F – iii
![]()
Question 5.
Seed dormancy allows the plants to:
(a) overcome unfavorable climatic conditions
(b) develop healthy seeds
(c) reduce viability
(d) prevent deterioration of seeds
Answer:
(a) overcome unfavorable climatic conditions
Question 6.
What are the parameters used to measure growth of plants?
Answer:
Growth in plants can be measured in terms, of
- Increase in length or girth (roots and stems)
- Increase in fresh or dry weight
- Increase in area or volume (fruits and leaves)
- Increase in a number of cells produced.
![]()
Question 7.
What is plasticity?
Answer:
Plasticity refers to the environmental heterophylly seen in Butter cup plant (Ranunculus). In this aquatic plant, the leaves in the air is normal, where as the leaves submerged underwater are highly thin and hairy highly adapted to do carbon assimilation Developmental heterophlly seen in the juvenile plant leaves of cotton and corianter. Where the young leaves have a different shape from the mature leaves is not considered as plasticity.
Question 8.
Write the physiological effects of Cytokinins.
Answer:
- Cytokinin promotes cell division in the presence of auxin (IAA).
- Induces cell enlargement associated with IAA and gibberellins
- Cytokinin can break the dormancy of certain light-sensitive seeds like tobacco and induces seed germination.
- Cytokinin promotes the growth of lateral bud in the presence of apical bud.
- Application of cytokinin delays the process of aging by nutrient mobilization. It is known as the Richmond Lang effect.
- Cytokinin:
- increases rate protein synthesis
- induces the formation of inter-fascicular cambium
- overcomes apical dominance
- induces the formation of new leaves, chloroplast and lateral shoots.
- Plants accumulate solutes very actively with the help of cytokinins.
![]()
Question 9.
Describe the mechanism of photoperiodic induction of flowering.
Answer:
Mechanism of photoperiodic induction of flowering.
- The physiological change on flowering due to the relative length of light and darkness (photoperiod) is called Photoperiodism.
- The photoperiod required to induce flowering is called critical day length. Eg. 12 hours in Maryland Mammoth’s Tobacco Xanthium 15.05 hours.
Photoperiodic induction:
- An appropriate photoperiod in 24 hours cycle constitutes one inductive cycle. Plants may require one or more inductive cycles for flowering.
- The phenomenon of conversion of leaf primordia into flower primordia under the influence of suitable inductive cycles is called photoperiodic induction. Example: Xanthium (SDP) -1 inductive cycle and Plantago (LDP) -25 inductive cycles.
Site of photoconductive perception:
- Leaves are the parts that receive photoperiodic stimulus (PPS), again it is only leaves that synthesize floral hormones and translocate them to the apical tip to promote flowering.
- This can be demonstrated by experiments conducted in the Cocklebur plant. Which is an SD plant. The nature of flower-producing stimulus has been elusive so far. It is believed by physiologists that a hormone is responsible for it, Chailakyan (1936) named it as Florigen It is not possible to isolate it.
| Procedure | Observation | Inference |
| 1. Take potted plant A and defoliate the plant subject it to SD – a condition | There is no induction of flowering | No leaf to receive stimulus or induction of flowering |
| 2. Take potted plant B – and defoliate all, except one leaf subject it to SD – condition. | There is the induction of flowering | One leaf is enough to receive stimulus or induction of flowering. |
| 3. Take potted plant C – and defoliate it and subject it to LD condition | There is no induction of flowering | no leaf to receive stimulus or induction of flowering |
| 4. Take potted plant D and subject all leaves to LD but one leaf to SD | There is the induction of flowering | One leaf is enough to receive an induction in the SD condition |
Question 10.
Give a brief account of programmed cell death (PCD).
Answer:
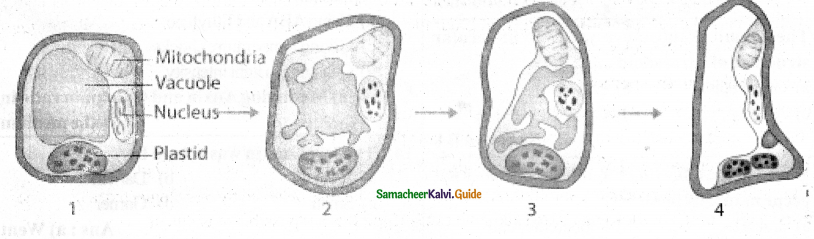
Senescence is controlled by plants’ own genetic program and the death of the plant or plants part consequent to senescence is called Programmed Cell Death. In short senescence of an individual cell is called PCD. The proteolytic enzymes involving PCD in plants are phytases and in animals are caspases. The nutrients and other substrates from senescing cells and tissues are remobilized and reallocated to other parts of the plant that survives.
The protoplasts of developing xylem vessels and tracheids die and disappear at maturity to make them functionally efficient to conduct water for transport. In aquatic plants, aerenchyma is normally formed in different parts of the plant such as roots and stems which enclose large air spaces that are created through PCD. In the development of unisexual flowers, male and female flowers are present in earlier stages, but only one of these two completes its development while the other aborts through PCD.
Part-II.
11th Bio Botany Guide Plant Growth and Development Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
The open form of the growth occurs in:
(a) leaves and flowers
(b) stem and root
(c) leaves and stem
(d) stem and flowers
Answer:
(b) stem and root
Question 2.
An example of a De-Differentiating cell is ………………
a) Tracheary element
b) shoot apex
c) Cork cambium
d) root apex
Answer:
c) Cork cambium
![]()
Question 3.
Primary growth of the plant is due to the activity of:
(a) phloem parenchyma
(b) phloem meristem
(c) vascular cambium
(d) apical meristem
Answer:
(d) apical meristem
Question 4
Choose the natural Auxin of the following
a) Anti Auxin
b) NAA
c) 2.4.D
d) IndoleAcetic Acid (IAA)
Answer:
d) Indole Acetic Acid (IAA)
![]()
Question 5.
Thickening and differentiation of cells take place during:
(a) elongation phase
(b) formative phase
(c) maturation phase
(d) flowering phase
Answer:
(c) maturation phase
Question 6.
The hormone present in Coconut milk is
a) Gibberellins
b) Ethylene
c) Cytokinin
d) Auxin
Answer:
c) Cytokinin
![]()
Question 7.
The total growth of the plant consists of four phases in the following order.
(a) Log phase, lag phase, decelerating phase and maturation phase
(b) Log phase, lag phase, maturation phase and decelerating phase
(c) Lag phase, log phase, maturation phase and decelerating phase
(d) Lag phase, log phase, decelerating phase and maturation phase
Answer:
(d) Lag phase, log phase, decelerating phase and maturation phase
Question 8.
Which of the following Phytóhormone does not occur naturally in plants?
a) 2. 4. D
b) GibberellicAcid
c) 6. Furfuryl amino purine
d) IAA
Answer:
a) 2.4.D
![]()
Question 9.
Absence of light may lead to the yellowish color in plants and this is called:
(a) venation
(b) etiolation
(c) estivation
(d) vernation
Answer:
(b) etiolation
Question 10.
Apical dominance is caused when Auxin
a) Concentration is more than Cytokinins
b) Concentration is less than Cytokinins
c) and Cytokinin concentration are equal
d) and Cytokinin concentration are fluctuating
Answer:
a) Concentration is more than Cytokinins
![]()
Question 11.
Indicate a plant growth regulator from the following:
(a) cytocin
(b) cytokinins
(c) acetic acid
(d) methylene
Answer:
(b) cytokinins
Question 12.
Which prevents premature fall of fruit?
a) NAA
b) Ethylene
c) GA3
d) Zeatin
Answer:
a) NAA
![]()
Question 13.
The activity of synergistic effect involves the activity of:
(a) auxin and gibberellins
(b) auxin and ethylene
(c) ABA and gibberellins
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(a) auxin and gibberellins
Question 14.
The term Auxin was coined by
a) Went
b) Darwin
c) Smith
d) Garner
Answer:
a) Went
![]()
Question 15.
The term auxin was first coined by:
(a) Charles Darwin
(b) Kogl
(c) F.W. Went
(d) Smith
Answer:
(c) F.W. Went
Question 16.
The term Gibberellin was coined by
a) Went
b) Kurosawa
c) Skoog
d) Yabuta
Answer:
d) Yabuta
![]()
Question 17.
Indicate a synthetic auxin.
(a) Indole Acetic Acid
(b) Phenyl Acetic Acid
(c) Indole Butyric Acid
(d) Naphthalene Acetic Acid
Answer:
(d) Naphthalene Acetic Acid
Question 18.
The mineral required for the synthesis of IAA is
a) Copper
b) Magnesium
c) Zinc
d) Boron
Answer:
c) Zinc
![]()
Question 19.
Auxin stimulates:
(a) transpiration
(b) respiration
(c) flowering
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(b) respiration
Question 20.
The most widely occurring Cytokinin in plants is
a) ABA
b) NAA
c) TNT
d) IPA
Answer:
d) IPA
![]()
Question 21.
Who established the structure of gibberellic acid?
(a) Brain etal
(b) Kurosawa
(c) Cross et al
(d) Yabuta and Sumiki
Answer:
(c) Cross etal
Question 22.
The term Florigen was coined by
a) Maheswari
b) Chailakyan
c) R Gane
d) Richmond Lang
Answer:
b) Chailakyan
![]()
Question 23.
Cytokinins inducing cell division was first demonstrated by:
(a) Haberlandt
(b) Charles Darwin
(c) Clarke
(d) Hubert
Answer:
(a) Haberlandt
Question 24.
Which of the following is a bioassay for Cytokinins?
a) Chlorophyll preservation test
b) Dwarf maize Assay
c) Seed germination Assay test
d) Neem cotyledon Assay
Answer:
d) Neem cotyledon Assay
![]()
Question 25.
Indicate correct statements.
(i) Genes are intracellular factors for growth.
(ii) Temperature has no role in the growth of plant.
(iii) Oxygen has a vital role in the growth of plants.
(iv) CIN ratio of soil does not affect the growth of plant.
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Answer:
(c) (i) and (iii)
Question 26.
Avena curvature test as a BioAssay for
a) Auxins
b) GA3
c) Cytokinin
d) Ethylene
Answer:
a) Auxins
![]()
Question 27.
The stress phytohormones (Abscisic acid) was first isolated by:
(a) Linn et al
(b) Addicott et al
(c) Edward et al
(d) Stone and Black
Answer:
(b) Addicott et al
Question 28.
The Gibberellins have been commercially exploited for
a) increasing the size of grapefruits
b) inducing rooting in stem cuttings
c) breaking the dormancy in seeds
d) production of disease-resistant varieties
Answer:
c) breaking the dormancy in seeds
![]()
Question 29.
Pick out the correct statement from the following:
(i) Abscisic acid is found abundantly inside the chloroplast of green cells.
(ii) ABA is a powerful growth promotor.
(iii) ABA is formed from the pentose phosphate pathway.
(iv) ABA has anti-auxin and anti-gibberellin properties.
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (i) and (ii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer:
(a) (i) and (iv)
Question 30.
Biennials can be induced to flower in the first season itself by treatment with
a) Auxin
b) Kinetin
c) GA
d) ABA
Answer:
c) GA
![]()
Question 31.
Pea and barley are classified under:
(a) short-day plants
(b) short long day plants
(c) long day plants
(d) long short day plants
Answer:
(c) long day plants
Question 32.
Auxin a was isolated from human urine by
a) F.W. went
b) Charles Darwin
c) Kogl and Haugen Smith
d) Denny
Answer:
c) Kogl and Haugen smith
![]()
Question 33.
Usually, Xanthiumpensylvanicum will flower under:
(a) long day condition
(b) short long day condition
(c) photo neutral condition
(d) short-day condition
Answer:
(d) short-day condition
Question 34.
The most widely occurring Cytokinin in plants is
a) Indole Acetic Acid (LAA)
b) Indole Butyric Acid (IBA)
c) Pentenyl Adenine (IPA)
d) Naphthalene Acetic Acid (NAA)
Answer:
c) Pentenyl Adenine (IPA)
![]()
Question 35.
Who found out the phytochrome in plants?
(a) Butler et al
(b) Michell et al
(c) Boumick et al
(d) Gamers and Allard
Answer:
(a) Butler et al
Question 36.
Scientists, those who are connected with Ethylene
(I) Denny
(II) R. Gane
(III) Kurosawa
(IV) Cocken
Options:
a) (I) (II) & (III)
b) (II) (III) & (IV)
c) (I) (II) & (IV)
d) (I) (III) & (IV)
Answer:
c) (I)(II)& (IV)
![]()
Question 37.
Pick out the wrong statement from the following:
(a) Vernalization increases the cold resistance of plants
(b) It increases the resistance of plants to fungal disease
(c) Vemalizatiqn increase the vegetative period of the plant
(d) It accelerates the plant breeding
Answer:
(c) Vemalizatiqn increase the vegetative period of the plant
Question 38.
Day-neutral plants are
a) Sugarcane & Coleus
b) Bryophyllum& Night Jasmine
c) Wheat, rice & Oats.
d) Potato, Tomato & Cotton
Answer:
d) Potato, Tomato & Cotton
![]()
Question 39.
In apple and plum, the method of breaking seed dormancy involves the process of:
(a) impaction
(b) Scarification
(c) exposing to red light
(d) Stratification
Answer:
(d) Stratification
Question 40.
Xanthium (Cocklebur) requires …………….. hours of light to induce flowering,
a) 12
b) 9
c) 15.05
d) 13.05
Answer:
c) 15.05
![]()
Question 41.
The hormone that cannot be isolated
a) IAA
b) ABA
c) NAA
d) Florigen
Answer:
d) Florigen
Question 42.
The term Photoperiodism was coined by
a) Went
b) Butler
c) Gamer
d) Skoog
Answer:
c) Garner
![]()
Question 43.
ABA acts as antagonistic to
a) Ethylene
b) Cytokinin
c) Gibberellic acid
d) IAA
Answer:
c) Gibberellic acid
Question 44.
If a short-day plant, flowering is induced by
a) Long nights
b) Photo periods less than 12 hrs
c) Photoperiods shorter than critical value and uninterrupted long night
d) Short photoperiods and interrupted long nights
Answer:
c) Photoperiods shorter than critical value and uninterrupted long night.
![]()
Question 45.
Phytochrome is
a) Reddish phytohormone
b) Bluish biliprotein pigment
c) Photoreceptor of apical bud
d) Unstable pigment molecule
Answer:
b) Bluish biliprotein pigment
Question 46.
The growth & ripening is induced by Ethylene in
a) Tropical fruits
b) Temperate fruits
c) Climacteric fruits
d) Nonclimacteric fruits
Answer:
c) Climacteric fruits
![]()
Question 47.
The bioassay of ABA was done with
a) Rice
b) Wheat
c) Maize
d) Barley
Answer:
a) Rice
Question 48.
Four types of senescence were recognized by
a) Leopold
b) Gamer
c) Addicott
d) Cocken et al
Answer:
a) Leopold
![]()
Question 49.
The final stage of senescence is
a) PCD
b) Scarification
c) Yellowing
d) Abscission
Answer:
d) Abscission
Question 50.
Match & Find out the Correct Answer
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Yabuta&Sumiki | a) Identified Ethylene |
| 2. Lethan & Miller | b) Isolated Auxin from Human urine |
| 3. Cockenetal | c) Isolated and identified Zeatin |
| 4. Kogi & Haugen Smith | d) Isolated Gibberellin in Crystal form |

Answer:
b) D C A B
![]()
Question 51.
Match the following and Find the Correct Answer
| I. Auxin | a) Bolting |
| II. ABA | b) Induces Respiration |
| III. Gibberellin | c) Cell division |
| IV. Ethylene | d) Weedicide |
| V. Cytokinin | e) Closure of stomata |

Answer:
b) D E A B C
II. Assertion (A) & Reason (R)
Question 52.
a. Both A & R are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation of A
b. Both A & R are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation of A
c. A is true but R is False
d. Both A and ‘R’ are False
Assertion (A): The shoot Apical meristems are the only source of Auxin synthesis
Reason (R): Dormancy of lateral buds over Apical buds is due to Auxin
Answer:
C. A is true but R is False
Question 53.
Assertion (A): Hormones are also called Growth regulator
Reason (R): Hormones promote or inhibit plant growth
Answer:
A. Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
![]()
Question 54.
Assertion (A): In many land Mammoth flowering occurred at different times at different latitude
Reason (R): Many land Mammoth is a tobacco variety
Answer:
b. Both Assertion (A) and, Reason (R) are true and Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
III. 2 Mark Questions
Question 1.
Define closed form of growth in plants.
Answer:
Leaves, flowers, and fruits are limited in growth or of determinate or closed-form growth.
Question 2.
Compare between Absolute and Relative growth rates
Answer:
| Absolute growth | Relative growth |
| An increase in the total growth of two organs measured and compared per unit time is called Absolute growth rate | The growth of the given system per unit time expressed per unit initial parameter is called relative growth rate |
Question 3.
Name the phases of growth in ‘S’ shaped growth curve.
Answer:
- Lag phase
- Log phase
- Decelerating phase
- Maturation phase
![]()
Question 4.
Mention the phase of growth in plants
Answer:
I. Formative phase
II. Elongation phase
III. Maturation phase
Question 5.
Distinguish between absolute growth rate and relative growth, rate.
Answer:
Absolute growth rate:
An increase in total growth of two organs measured and compared per unit time is called absolute growth rate.
Relative growth rate:
The growth of the given system per unit time expressed per unit initial parameter is called relative growth rate.
Question 6.
What is the Grand period of growth
Answer:
The total period from initial to the final stage of growth is called Grand period of growth.
When plotted against time the growth curve is ‘S’ shaped, (sigma curve) it is also known as Grand Period curie consists of 4 phases
- Lag,
- Log,
- Decelerating,
- Maturation.
![]()
Question 7.
What is meant by the dedifferentiation of plant cells?
Answer:
Differentiated cells, after multiplication again lose the ability to divide and mature to perform specific functions. This is called redifferentiation, eg: Secondary xylem and Secondary phloem.
Question 8.
Define Phytohormone.
Answer:
The chemical substances synthesized by plants and thus naturally occuring are known as Phytohormones. Eg. Auxin, Gibberellins.
Recently 2 groups – Brassinosteroids, Polyamines were also known to behave like hormones.
![]()
Question 9.
Mention any two synthetic auxins.
Answer:
- 2, 4 – Dichloro Phenoxy Acetic Acid (2, 4 – D)
- 2, 4, 5 – Trichloro Phenoxy Acetic Acid (2, 4, 5 – T)
Question 10.
State 3 characteristic features of phytohormones.
Answer:
- They are produced in root tips and stem tips and leaves (do not have specialized cells or organs for secretion)
- The transfer of hormones takes place through the conducting system (xylem and phloem)
- They are required in trace quantities
- They either promote, inhibit or modify growth.
Question 11.
Name the natural auxins present in plants.
Answer:
- Indole Acetic Acid (IAA)
- Indole Propionic Acid (IPA)
- Indole Butyric Acid (IBA)
- Phenyl Acetic Acid (PAA)
Question 12.
Give the historial significance of Agent Orange
Answer:
- Mixture of two phenoxy herbicides – 2.4. D and 2.4.5 T together known as Agent orange.
- This Agent orange, was used by USA in Vietnam war as chemical warfare weapon to defoliate forests in Vietnam.
![]()
Question 13.
Does the trimming of plants in gardens have any scientific explanation?
Answer:
- Yes, trimming of plants removes apical buds and hence apical dominance is prevented the lateral buds sprout and give a beautiful bushy appearance and aesthetic value.
- Also in tea estates, this trimming develops more lateral branches and more tea leaves thus it has commercial significance.
Question 14.
Where do you find cytokinin hormone in plants?
Answer:
The distribution of cytokinin in plants is not as wide as those of auxin and gibberellins but found mostly in roots. Cytokinins appear to be translocated through xylem.
Question 15.
What is bolting?
Answer:
- When treated with Gibberellins the rose the plants (genetic dwarf) exhibit excessive internodal growth.
- This sudden elongation of a stem followed by flowering is called bolting.
![]()
Question 16.
What is Richmond Lang effect?
Answer:
Application of Cytokinin delays the process of aging by nuitrient mobilization.
Question 17.
Why do you call Abscisic acid (ABA) as stress hormone?
Answer:
It inhibits the shoot growth and promotes growth of root system. This character protect the plants from water stress. Hence, ABA is called as stress hormone.
Question 18.
Define photoperiodism & Critical day length.
Answer:
- The physiological change on flowering due to relative length of light and darkness (Photoperiod) is called
Photoperiodism. - The photoperiod required to induce flowering is called critical day length Eg.
- Mary land mammoth (tobacco variety) requires 12 hours of light.
- Cocklebur required 15.05 hours of light.
Question 19.
Write down the importance of photoperiodism in plants.
Answer:
- The knowledge of photoperiodism plays an important role in hybridisation experiments.
- Photoperiodism is an excellent example of physiological pre-conditioning that is using an external factor to induce physiological changes in the plant.
Question 20.
What is the importance of photoperiodism?
Answer:
- The knowledge of photoperiodism an important role in hybridization experiments.
- It is an excellent example of physiological preconditioning that is using an external factor to induce physiological changes in the plant.
![]()
Question 21.
What is meant by Epigeal germination?
Answer:
During epigeal germination, cotyledons are pushed out of the soil. This happens due to the elongation of the hypocotyl.
Eg: Castor and Bean.
Question 22.
Define Vernalization.
Answer:
- It is a process by which many annuals and biennials are induced to flower when subjected to low-temperature exposure.
- T.d. Lysenko first used the term.
Question 23.
Define the term phytogerontology.
Answer:
The branch of botany which deals with ageing, abscission and senescence is called Phytogerontology.
![]()
Question 24.
Distinguish between Epigeal and Hypogeal germination.
Answer:
| Epigeal | Hypogeal |
| Cotyledons pussed out of the soil | Cotyledons remain below the soil due to rapid elongation of epicotyls. |
| Happens due to the elongation of the hypocotyl Eg. Castor & Bean | Eg. Maize |
Question 25.
Define seed dormancy and what are its types.
Answer:
The condition of a seed when it fails to germinate even in suitable environmental condition is called seed dormancy.
There are two types
(I) Innate dormancy (II) Imposed dormancy.
Question 26.
What is Scarification?
Answer:
- By mechanical and chemical treatments like cutting or chipping of hard tough sed coat and use of organic solvents to remove waxy or fatty compounds are called scarification.
- It is a method of breaking dormancy of the seeds.
Question 27.
Distinguish between Re differentiation and Devernalization.
Answer:
| Redifferentiation | Devernalization |
| Differentiated cells after multiplication again lose the ability to divide and mature to perform specific functions, is called Re differentiation. Eg. Sec.Xylem & Sec. |
Phloem The reversal of the effect of vernalization is called Devemalization. |
Question 28.
Define Senescence.
Answer:
- Ageing or getting old is called senescence.
- It refers to all collective, progressive and deteriorative processes which ultimately lead to complete loss of organization and function (Eg. leaves turn yellow and fall off from plant).
![]()
Question 29.
What is impaction in seed dormancy.
Answer:
- In some seeds water and oxygen are unable to penetrate micropyle due to blockage by cork cells.
- These seeds are shaken vigorously to remove the plug
- The process of removing the plug or block is called impactation.
Question 30.
What is called stratification in seed dormancy?
Answer:
- The break dormancy, some plant seeds have to be exposed to well aerated, moist conditions under low temperature (0°c to 10°c) for weeks to months.
- This kind of seed dormancy breaking treatment is known as stratification.
- The stratified soil layers should be given a low-temperature treatment for a certain period so as to induce germination.
- Eg. the Seeds of Rosaceae plants Apple, Plum, Peach, etc.
Question 31.
What are the 4 types of Senescence?
Answer:
Leopold (1961) explained 4 types they are
- Overall senescence
- Top senescence
- Deciduous senescence
- Progressive senescence.
Question 32.
What is the Abscission layer or Abscission Zone?
Answer:
Abscission is marked internally at the place of petiole by a distance zone of few layers of thin-walled cells arranged transversely. This zone is called Abscission Zone, which leads to Abscission of the leaf.
Question 33.
The photoperiodic response will not be possible in a defoliated plant. Give scientific reasons.
Answer:
Yes, a defoliated plant will not respond to photoperiodic change because the hormonal substance responsible for flowering is present in the leaves of the plant.
![]()
Question 34.
What is gas chromatography?
Answer:
- It is a bioassay technique by which Ethylene can be measured.
- It helps in the detection of the exact amount of ethylene from different plant tissues like lemon and orange.
Question 35.
Give the occurrence and precursors of Gibberellins and Cytokinins.
Answer:
| Character | Gibberellins | Cytokinin |
| Occurrence | Produced by plant parts like an embryo, roots, and young leaves near the tip. Immature seeds are rich in Gibberellins. | Formed in root apex shoot apex like Auxin. Also formed in buds & young fruits. |
| Precursor | Formed by 5C precursor, Iso prenoidunit called Iso Pentenyl Pyrophosphate (IPP) through a number of intermediates primary precursor – Acetate. | Derived from purine-Adenine. |
IV. 3 Mark Questions
Question 1.
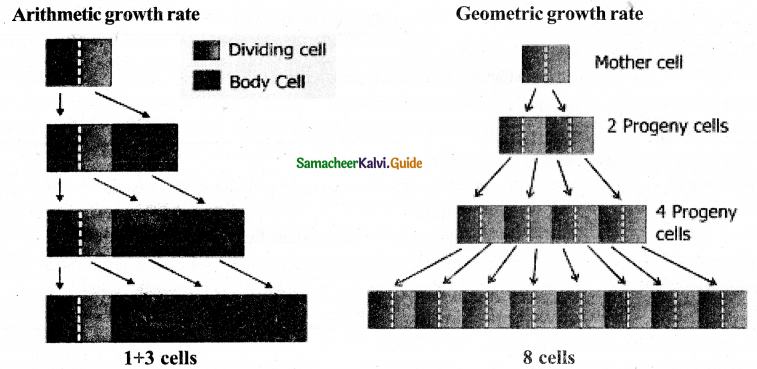
Explain Arithmetic growth rate and Geometric growth rate by diagrams.
Answer:
Question 2.
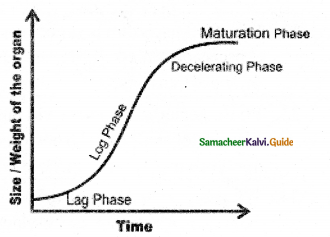
Explain stages in growth by drawing the sigmoid curve.
Answer:
- The total period from the initial to the final stage of growth is called the Grand period of growth.
- The graph that is drawn by taking time and rate of growth is ‘S’ shaped. It is known as a sigmoid curve.
It has 4 stages:
- Lag phase
- Log phase
- Decelerating phase
- Maturation phase
Question 3.
Mention the internal factors, that affect the growth of plants.
Answer:
- Genes are intracellular factors for growth.
- Phytohormones are intracellular factors for growth, eg: auxin, gibberellin, cytokinin.
- C/N ratio.
Question 4.
Mention the Agricultural role of Auxin.
Answer:
- Eradicate weeds: Eg. 2.4 D and 2.4.5.7
- Formation of seedless fruits: (Parthenocarpic fruits) Eg. Synthetic Auxin.
- Break dormancy.
- Induction of flowering: In pineapple NAA induce flowering
- Increase the number of female flowers: Eg. Cucurbita.
![]()
Question 5.
List out the agricultural applications of auxins.
Answer:
- It is used to eradicate weeds, eg: 2,4 – D and 2,4,5 – T.
- Synthetic auxins are used in the formation of seedless fruits (Parthenocarpic fruit).
- It is used to break the dormancy in seeds.
- Induce flowering in Pineapple by NAA & 2,4 – D.
- Increase the number of female flowers and fruits in cucurbits.
Question 6.
What are the Precursors of Gibberellins?
Answer:
- Gibberellins are chemically related to terpenoids (natural rubber, Carotenoids, and steroids) formed by 5-C precursors and an Isoprenoid unit called Iso Pentenyl Pyrophosphate (IPP) through a number of intermediates.
- The primary precursors are Acetate.
Question 7.
What are the uses of ethylene in agriculture?
Answer:
- Ethylene normally reduces flowering in plants except in Pineapple and Mango.
- It increases the number of female flowers and decreases the number of male flowers.
- Ethylene spray in the cucumber crop produces female flowers and increases the yield.
Question 8.
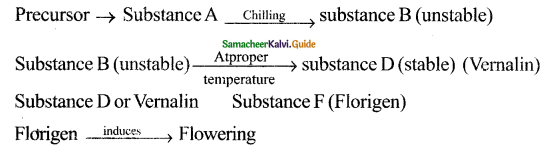
Explain the mechanism of Vernalization by Hypothesis of hormonal involvement.
Answer:
I. Vernalization: According to Purvis
II. Devernalization

Question 9.
What are the practical applications of Vernalization?
Answer:
- It shortens the vegetative period and induces the plant to flower earlier.
- It increases the cold resistance of the plants.
- It increases the resistance of plants to fungal disease.
- Plant breeding can be accelerated.
![]()
Question 10.
What is meant by the viability of seeds?
Answer:
- Viable means the living condition of the seed
- The shelf life of the seed after which it cannot germinate is known as the viable period
- It varies from plant to plant
| Name of the plant | Viability |
| 1. Oxalis seeds | Few days |
| 2. Lotus seeds | More than 1000 years |
| 3. Judean Dale palm (Methuselah) | More than 2000 years |
Question 11.
Differentiate between climacteric and Non-climacteric fruits.
Answer:
| Climacteric fruits | Non-Climacteric fruits |
| 1.There is a sharp rise in respiration rate near the end of the development of fruit. 2. The ripening on demand can be induced in these fruits by exposing them to normal air conditioning. 3. Epthan secrete Ethylene continuously about 1 ppm of ethylene Eg. Lemon, Apples, Banana, Mango |
These fruits cannot be ripened by exposure to ethylene so-known as non-climacteric fruits. Eg. Grapes, Watermelon orange. |
Question 12.
Differentiate between scarification & Stratification in breaking seed dormacy
Answer:
| Scarification | Stratification |
| Mechanical and chemical treatment either by cutting, chipping or use of organic solvents to remove waxy or fatty compounds is called scarification. | Rosaceous plants (Apple, Plum Peach, and Cherry) will not germinate until they have been exposed to well derated, moist conditions under low temperature (1°c to 10°c) for weeks to months and this treatment is known as stratification. |
Question 13.
Mention the factors causing dormancy of seeds.
Answer:
- Hard, tough seed coat causes barrier effect as impermeability of water, gas and restriction of the expansion of embryo prevents seed germination.
- Many species of seeds produce imperfectly developed embryos called rudimentary embryos which promotes dormancy.
- Lack of specific light requirement leads to seed dormancy.
- A range of temperatures either higher or lower cause dormancy.
- The presence of inhibitors like phenolic compounds which inhibits seed germination cause dormancy.
Question 14.
What are the factors that affect senescence?
Answer:
| Name of the factor | Effect of senescence |
| ABA & Ethylene | Accelerates |
| Auxin & Cytokinin Nitrogen deficiency | reduces increases |
| Nitrogen supply | retards |
| High temperature in vernalized seeds | Accelerates |
| Low temperature | Retards |
| Water stress | Accumulation of ABA leading to senescence |
Question 15.
What are the morphological and Anatomical changes due to Abscission?
Answer:
- Abscission Zone: formed at the base of petiole
- Greenish grey in colour by rows of 2 to 15 cells thick primary wall and middle lamella
- The dissolution of by pectinase & Cellulase
- Formation tyloses – that block conduction of vessels
- Degradation of chlorophyll – Colour of leaves changes and leaves fall off.
- After Abscission – Suberization of outer layer of cells by the development of periderm.
![]()
Question 16.
Write down the significance of Abscission.
Answer:
1. Abscission separates dead parts of the plant like old leaves and ripe fruits.
2. Helps in dispersal of fruits and continuing the life cycle.
3. Abscission of leaves (in deciduous plants) helps in water conservation during summer.
4. Helps in vegetative propagation (Shedding of gemmae or plantlets) Eg. Bryophyta.
V. 5 Mark Questions
Question 1.
Describe an experiment to measure the growth of a plant or By lever Auxanometer measure the rate of growth in stem tip.
Answer:
Experiment:
1. Arc auxanometer:
The increase in the length of the stem tip can easily by measured by an arc auxanometer. If consists of a small pulley to the axis of which is attached a long pointer sliding over a graduated arc. A thread one end of which is tied to the stem tip and another and to a weight passes over the pulley tightly. As soon as the stem tip increases in length, the pulley moves and the pointer slide over the graduated arc (Refer Figure) The reading is taken. The acutal increase in the lengthwm stem is then calculated by knowing the length of the pointer and the radius of the pulley. If the radius of the pulley is 4 inches and the length of pointer 20 inches the actual growth is measured as follows:
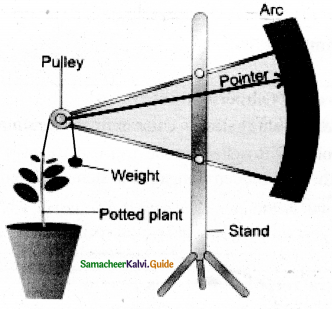
Actual growth in length\(=\frac{\text { Distance travelled by the pointer radius of the }}{\text { Length of the pointer }}\)
For example, actual growth in length \(=\frac{10 \times 4 \text { inches }}{20 \text { inches }}\) = 2 inches
Question 2.
Explain the physiological effect of Auxin? Add a note on its agricultural applications.
Answer:
Cell elongation:
Promotes cell elongation in stem & Coleoptile
Root growth:
At extremely low concentration – promote root growth, at high concentrations it inhibits elongation of roots, but induce more lateral roots
Apical dominance:
Suppression of growth of lateral buds – by apical bud is known as Apical dominance
Prevents Abscission
Secondary growth:
Promotion of cell division in the cambium, responsible for secondary growth this property is exploited in tissue culture. (Callus foundation)
Respiration Stimulates respiration Induces Vascular differentiation.
![]()
Question 3.
Give the Agricultural application of Auxin.
Answer:
Weedicide
2.4.D & 2.4.5. T – Weedicides to remove weeds
Induce parthenocarpy
Synthetic auxins used to induce parthenocarpy (formation of seedless fruits).
Break dormancy
Used to break seed dormancy.
Induce flowering in Pineapple Eg. NAA & 2.4.D
Induce female flowers (numbers)
Eg. Cucumber.
Question 4.
Explain physiological effects of Gibberellins
Answer:
- Induction of cell division & cell elongation – Extraordinary stem elongation.
- Reversal of dwarfism & Bolting – Rosette (genetic dwarfism) plants when treated with Gibberellins exhibit excessive enter nodal growth – This sudden elongation of a stem followed by flowering is called Bolting.
- Breaks dormancy – in Potato tubers.
- Biennials flower in the 1 st year – Instead of cold exposure, if biennials treated with Gibberellins flower in the 1st year itself.
Question 5.
Write an essay on the role of ethylene on plant physiology and agriculture.
Answer:
Almost all plant tissues produce ethylene gas in minute quantities.
1. Discovery:
In 1924, Denny found that ethylene stimulates the ripening of lemons. In 1934, R. Gane found that ripe bananas contain abundant ethylene. In 1935, Cocken et al., identified ethylene as a natural plant hormone.
2. Occurrence:
Maximum synthesis occurs during climacteric ripening of fruits and tissues undergoing senescence. It is formed in almost all plant parts like roots, leaves, flowers, fruits and seeds.
3. Transport in plants:
Ethylene can easily diffuse inside the plant through intercellular spaces.
4. Precursor:
It is a derivative of amino acid methionine, linolenic acid and fumaric acid.
5. Bioassay (Gas Chromatography):
Ethylene can be measured by gas chromatography. This technique helps in the detection of exact amount of ethylene from different plant tissues like lemon and orange.
6. Physiological Effects:
- Ethylene stimulates respiration and ripening in fruits.
- It stimulates radial growth in sterft and roof and inhibits linear growth.
- It breaks the dormancy of buds, seeds and storage organs.
- It stimulates the formation of an abscission zone in leaves, flowers and fruits. This makes the leaves to shed prematurely.
- Inhibition of stem elongation (shortening the internode).
- In low concentration, ethylene helps in root initiation.
- Growth of lateral roots and root hairs. This increases the absorption surface of the plant roots.
- The growth of fruits is stimulated by ethylene in some plants. It is more marked in climacteric fruits.
- Ethylene causes epinasty.
7. Agricultural role:
- Ethylene normally reduces flowering in plants except in Pineapple and Mango.
- It increases the number of female flowers and decreases the number of male flowers.
- Ethylene spray in cucumber crops produces female flowers and increases the yield.
Question 6.
Explain the physiological Effects of Cytokinins.
Answer:
- With IAA – Promotes cell division With IAA & GA – Induces cell enlargement
- Breaks dormancy of light-sensitive seeds (tobacco) induces seed germination.
- Promotes growth of lateral
- buds even in the presence of apical bud.
- Delays the process of aging by nutrient mobilization known as Richmond Lang effect.
- Induces rate of protein synthesis.
- Induces the formation of interfascicular cambium Overcomes apical dominance
- Induces the formation of new leaves chloroplast and lateral shoots.
- Induces Accumulation of solutes.
![]()
Question 7.
Write down the physiological effects of Ethylene
Answer:
- Stimulates respiration and thereby ripening of fruits
- Stimulates radial growth in stem and root and inhibits linear growth.
- breaks dormancy of
- buds
- Seeds
- Storage Organs
- Stimulates abscission 2 one formation in
- leaves
- flowers
- fruits (so leaves shed prematurely)
- Prevents stem elongation by preventing internodal growth
- Root growth in low concentration
- Stimulates growth of lateral roots and root hairs and increase the absorptive surface
- Ripening of fruits – Increases ripening in climacteric fruits (Mango, banana) etc.
- It causes epinasty
Question 8.
Describe the methods of breaking the dormancy of seeds in plants.
Answer:
The dormancy of seeds can be broken by different methods. These are:
1. Scarification:
Mechanical and chemical treatments like cutting or chipping of hard tough seed coat and use of organic solvents to remove waxy or fatty compounds are called Scarification.
2. impaction:
in some seeds, water and oxygen are unable to penetrate micropyle due to blockage by cork cells. These seeds are shaken vigorously to remove the plug which is called Impaction.
3. Stratification:
Seeds of rosaceous plants (Apple, Plum, Peach, and Cherry) will not germinate until they have been exposed to well aerated, moist conditions under low temperature (0°C to 10°C) for weeks to months. Such treatment is called Stratification.
4. Alternating temperatures: Germination of some seeds is strongly promoted by alternating daily temperatures. An alternation of low and high temperature improves the germination of seeds.
5. Light:
The dormancy of photoelastic seeds can be broken by exposing them to red light.
![]()
Question 9.
Define photoperiodism – Classify plants based on photoperiodism
Answer:
a. The physiological change on flowering due to the relative length of light and darkness is called photoperiodism.
- Gamer and Allard (1920) coined the term
- They studied photoperiodism in Biloxi variety of soybean (Glycine max) and Many land mammoth varieties of tobacco.
b. Depending on photoperiodic responses plants are classified into several types.
1. L.D. Plants (Long Day) The photoperiod required to induce flowering is called critical day length depending on critical day length if it is long (more than 12 hours) and with short nights. Eg. Pea Barley and Oats
Short LD Plants: These are Long day plants but need short day length during the early period of growth for flowering Eg. Wheat, Rye
2. SD Plants: Plants requiring short critical day length for flowering or a long night.
Eg. Tobacco, Cocklebur, Soya, Rice, and Chrysanthemum.
Long SD Plants: Actually SD plants but need long days during the early period of growth for flowering Eg. Some SPS of Bryophyllum & Night Jasmine.
3. Intermediate day plants:
These require a photoperiod between a long day and a short day for flowering Eg. Sugarcane and coleus.
4. Day Neutral plants:
There are a number of plants which can flower in all possible photoperiods, known as photo neutral or hiterterminate plants. Eg. Potato, Rhododendron, Tomato & Cotton.
Question 10.
Describe the role of phytochrome in inducing Flowering
Answer:
Definition:
It is a bluish biliprotein responsible for the perception of light in the photophysiological process, existing in two different forms is mainly involved in flower induction, (i.e) Pr and PFr.
- Butler et al(1959) named the pigment.
- It exists in two interconvertible forms
| Pr | PFr |
| 1. red light absorbing form 2. Absorbs red lgiht of wavelength 660 nm 3. Biologically inactive form & stable found in the diffused state in cytoplasm 4. Promotes flowering in SD plants and inhibits flowering LD plants. |
1. Far-red light absorbing form 2. Absorbs far-red light of wavelength 730 nm 3. Biologically active and it is unstable Associated with a hydrophobic area of the membrane system 4. Promotes flowering in LD plants and inhibit flowering in SD plants. |
Mechanism:
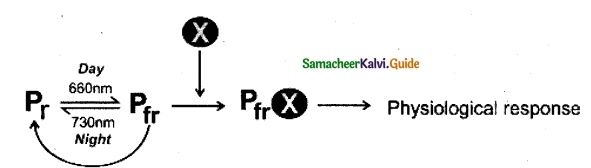
Other functions:
Play a role in seed germination and changes in membrane conformation.
![]()
Question 11.
Write an Essay on Vernalization
Answer:
Definition:
- Many biennials and perennials are induced to flower by low-temperature exposure (O°c to 5°c) This process is called Vernalization.
- T.D. Lysenko – Coined the term.
Mechanism of Vernalization:
2 theories explain the mechanism of vernalization.
1. Hypothesis of Phasic development (T.D. Lysenko),
The development of the annual plant has 2 phases.
- Thermostate-Vegetatine stage requiring low temperature and suitable moisture.
- Photo stage -high temperature needs to synthesize florigen.
2. Hypothesis of hormonal involvement (Purvis 1961)
Vernalization has several steps
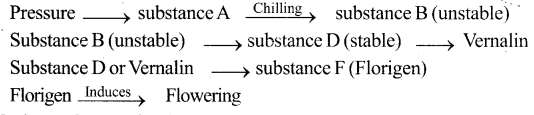
The technique of Vernalization:
- Seeds soaked in water
- Allowed to germinate at 10°C to 12°C
- Transferred to low temperature for few days to 30 days (3°C to 5°C).
- Germinated seeds after the low temp, treatment are allowed to dry & then sown.
- Quickened flowering than untreated (control seedling)
Devernalization:
The reversal of the effect of vernalization is called Devemalization.
- Practical Applications:
- Vernalization shortens the vegetative period and induces the plant to flower earlier
- It increases cold resistance
- It increases fungal resistance
- It accelerates Plant Breeding.
Question 12.
Define Senescence and give its types
Answer:
Definition:
Getting old or Ageing is call d senescence in plants.
It refers to all collective, progressive, and deteriorative processes which ultimately lead to complete loss of organization and function.
Types – 4 types (Leopold -1961)
- Overall senescence: When the entire plant gets affected and dies – Eg. Annuals – Wheat & Soybeans, Perennials – Agave & Bamboo
- Top senescence: Occur in aerial parts only Eg. Parrennials – Banana and Gladiolus
- Deciduous senescence: Occur only in leaves Eg. Decidual plants – Elm and Maple
- Progressive Senescence: Occur in Annuals occur in old leaves first followed by new leaves than stem and finally root system.
![]()
Question 13.
Explain the physiology of senescence and Factors affecting senescence Physiology of Senescence :
Answer:
- Change in the structure of cells
- Vacuoles act like lysosome-secrete hydrolytic enzymes.
- Reducation in photosynthetic rate (due to loss of chlorophyll & accumulation of anthocyanin)
- The decrease in Starch content, Protein content
- Decrease in …………. r RNA level due to increased activity of enzyme RNA ase
- Degeneration of DNA – by increased activity of enzyme DNA ase
Factors affecting senescence :
| Name of the factor | Effect of senescence |
| ABA & Ethylene | Accelerates |
| Auxin & Cytokinin Nitrogen deficiency | reduces increases |
| Nitrogen supply | retards |
| High temperature in vernalized seeds | Accelerates |
| Low temperature | Retards |
| Water stress | Accumulation of ABA leading to senescence |