Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology Guide Pdf Chapter 4 Organ and Organ Systems in Animals Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology Guide Chapter 4 Organ and Organ Systems in Animals
11th Bio Zoology Guide Organ and Organ Systems in Animals Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part I
I. Choose The Best Options
Question 1.
The clitellum is a distinct part in the body of earthworm Lampito mauritii, it is found in?
a. Segments 13-14
b. Segments 14-17
c. Segments 12 -13
d. Segments 14-16
Answer:
b. Segments 14-17
Question 2.
Sexually, earthworms are
a. Sexes are separate
b. Hermaphroditic but not self – fertilizing
c. Hermaphroditic and self – fertilizing
d. Parthenogenic
Answer:
b. Hermaphroditic but not self – fertilizing
![]()
Question 3.
To sustain themselves, earthworms must guide their way through the soil using their powerful muscles. They gather nutrients by ingesting organic matter and soil, absorbing what they need into their bodies. Say whether the statement is True or False: The two ends of the earthworm can equally ingest soil.
Answer:
a. True
b. False
Question 4.
The head region of Cockroach ……………….. pairs of …………….. and …………….. shaped eyes occur.
a. One pair, sessile compound and kidney shaped
b. Two pairs, stalked compound and round shaped
c. Many pairs, sessile simple and kidney shaped
d. Many pairs, stalked compound and kidney shaped
Answer:
a. One pair, sessile compound and kidney shaped
![]()
Question 5.
The location and numbers of malpighian tubules in Periplaneta.
a. At the junction of midgut and hindgut, about 150.
b. At the junction of foregut and midgut, about 150.
c. Surrounding gizzard, eight.
d. At the junction of colon and rectum, eight.
Answer:
a. At the junction of midgut and hindgut, about 150.
Question 6.
The type of vision in Cockroach is
a. Three dimensional
b. Two dimensional
c. Mosaic
d. Cockroachdonot have vision
Answer:
c. Mosaic
![]()
Question 7.
How many abdominal segments are present in male and female Cockroaches?
a. 10,10
b. 9,10
c. 8,10
d. 9,9
Answer:
d. 9,9
Question 8.
Which of the following have an open circulatory system?
a. Frog
b. Earthworm
c. Pigeon
d. Cockroach
Answer:
d. Cockroach
![]()
Question 9.
Buccopharyngeal respiration in frog
a. is increased when nostrils are closed
b. Stops when there is pulmonary respiration
c. is increased when it is catching fly
d. stops when mouth is opened.
Answer:
b. Stops when there is pulmonary respiration
Question 10.
Kidney of frog is
a. Archinephros
b. Pronephros
c. Mesonephros
d. Metanephros
Answer:
c. Mesonephros
![]()
Question 11.
Presence of gills in the tadpole of frog indicates that
a. fishes were amphibious in the past
b. fishes involved from frog -like ancestors
c. frogs will have gills in future
d. frogs evolved from gilled ancestor
Answer:
d. frogs evolved from a gilled ancestor
Question 12.
Choose the wrong statement among the following:
a. In earthworm, a pair of male genital pore is present.
b. Setae help in the locomotion of earthworms.
c. Muscular layer in the body wall of an earthworm is made up of circular muscles and longitudinal muscles
d. Typhlosole is part of the intestine of earthworms.
Answer:
d. Typhlosole is part of the intestine of earthworm.
![]()
Question 13.
Which of the following are the sense organs of Cockroach?
a. Antennae, compound eyes, maxillary palps, anal cerci
b. Antennae, compound eye, maxillary palps and tegmina
c. Antennae, ommatidia, maxillary palps, sternum and anal style.
d. Antennae, eyes, maxillary palps, and tarsus of walking legs and coxa
Answer:
a. Antennae, compound eyes, maxillary palps, anal cerci
(2 marks)
II. Very Short Questions
Question 14.
What characteristics are used to identify the earthworms?
Answer:
In gardens, earthworms can be traced by their fecal deposits known as worm castings on the soil surface.
The earthworms can be identified using the following characteristics:
- Long and cylindrical narrow body.
- Bilateral symmetry
- It is light brown in colour with a purple tinge at the anterior end.
- The division of the body into many segments or metameres.
- The dorsal surface of the body is marked by a dark mid-dorsal line.
- In mature worms, segments 14-17 may be found swollen with a glandular thickening of the skin called the clitellum.
![]()
Question 15.
What are earthworm casts?
Answer:
The undigested particles along with soil are passed out through the anus as worm castings or vermicasts.
Question 16.
How do earthworms breathe?
Answer:
- There are no lungs and gills.
- They respire through the body surface.
- The surface blood vessel helps in gaseous exchange.
Question 17.
Why do you call cockroaches a pest?
Answer:
Cockroaches destroy food and contaminate it with their offensive odour. They are carriers of a number of bacterial diseases. The cockroach allergen can cause asthma in sensitive people.
Question 18.
Comment on the functions of alary muscles?
Answer:
The triangular muscles that are present on both side of the heart are responsible for blood circulation.
![]()
Question 19.
Name the visual units of the compound eyes of cockroach.
Answer:
- The photoreceptors of the cockroach consist of a pair of compound eye on the dorsal surface of the head.
- Each eye is formed of about 2000 simple eyes called the ommatidia.
Question 20.
How does the male frog attract the female for mating?
Answer:
- The male frog has a pair of vocal sacs and a copulatory or nuptial pad on the ventral side of the first digit of each forelimb.
- Vocal sacs produce croaking sound to attract females and nuptial pad is also helpful in mating.
Question 21.
Write the types of respiration seen in frogs.
Answer:
Frog respires on land and in the water by two different methods. In water, the skin acts as an aquatic respiratory organ (cutaneous respiration). Dissolved oxygen in the water gets exchanged through the skin by diffusion. On land, the buccal cavity, skin, and lungs act as the respiratory organs. In buccal respiration on land, the mouth remains permanently closed while the nostrils remain open.
The floor of the buccal cavity is alternately raised and lowered, so air is drawn into and expelled out of the buccal cavity repeatedly through the open nostrils. Respiration by the lungs is called pulmonary respiration. The lungs are a pair of elongated, pink-colored sac-like structures present in the upper part of the trunk region (thorax). Air enters through the nostrils into the buccal cavity and then to the lungs. During aestivation and hibernation, gaseous exchange takes place through the skin.
![]()
Question 22.
Differentiate between peristomium and prostomium in earthworms.
Answer:
| Peristomium | Prostomium |
| 1. The mouth is present in the centre of the first segment of the body called peristomium | Overhanging the mouth is a small flap called the upperlip or prostomium. |
Question 23
Give the location of clitellum and spermathecal openings in Lampito mauritii.
Answer:
- Clitellum -14 -17 segment.
- Spermatheca – There are three pairs of spermathecae lying in segments 6/ 7,7/ 8,8/9
Question 24.
Differentiate between tergum and a sternum.
Answer:
| Tergum |
| 1.The scierites of dorsal side of cockroach Sternum |
| Sternum |
| The sclerites of ventral side of cockroach |
Question 25.
Head of cockroach is called hypognathous. Why?
Answer:
The mouth parts of cockroach are directed downwards. The head is small, triangular lies at a right angle to the longitudinal body axis. Hence it is called hypognathous.
Question 26.
What are the components of blood in frogs?
Answer:
1. Plasma-60%
2. Red blood cells, white blood cells platelets 40 %
![]()
Question 27.
Draw a neat labeled diagram of the digestives system of frog.
Answer:
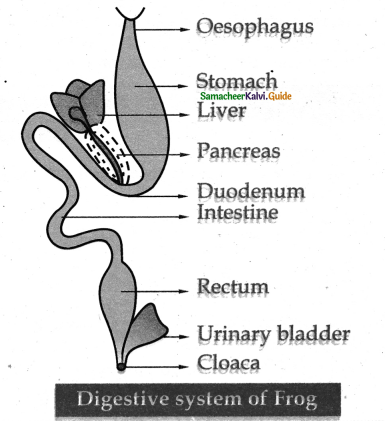
Question 28.
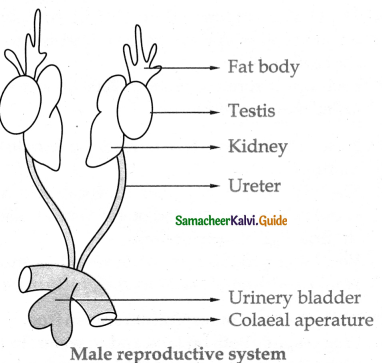
Explain the reproductive system of frog
1. Male reproductive organ:
- There are pair of testes. Each test is attached with kidney and dorsal body wall with the peritoneal membrane mesorchium.
- The vasa efferentia arises from each test is opened into the bladder canal and it communicates with the urinogenital duct that comes out of kidneys and opens into the cloaca.
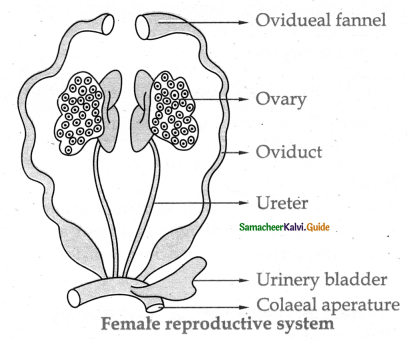
2. Female reproductive system:
- It consists of paired ovaries attached to the kidney and dorsal body wall by folds of peritoneum called mesovarium.
- Each oviduct opens into the body cavity at the anterior end by a funnel like opening called ostia and posteriority the oviducts dilated to form ovisac before they open into cloaca.
- Fertilization is external.
- The eggs hatch into tadpoles.
- Tadpole develops three pairs of gills.
- The tadpole grows into an air-breathing carnivorous adult frog through a process metamorphosis.
Part II
11th Bio Zoology Guide Organ and Organ Systems in Animals Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose The Best Options
Question 1.
We can locate the earth worm’s living area through ……………………….
a. Small hole in the ground
b. Worm costings
c. Debris
d. Excreta of cattle.
Answer:
b. Worm costings
Question 2.
The region between 14 – 17 segments in earthworm is called as …………………
a. Pygidium
b. Prostomium
c. Clitellum
d. Peristomium
Answer:
c. Clitellum
![]()
Question 3.
What is the shape of the setae?
a. ‘S’ shaped
b. C shaped
c. Round shaped
d. Curved shaped
Answer:
a. ‘S’ shaped
Question 4.
Find the correct pair.
a. First segment -Clitellum
b. Last segment – Peristomium
c. 14-17 -Pygidium
d. Vascular fold -Typhlosole
Answer:
d. Vascular fold -Typhlosole
![]()
Question 5.
In which segment the lateral hearts are situated?
a. 7-13
b. 6-13
c. 6-15
d. 7-15
Answer:
b. 6-13
Question 6.
Find out the correct statement
a. In male cockroach the reproductive sac lie anteriorily.
b. In female cockroaches chitinous plates gonapophyses are present around the female genital aperature.
c. In male cockroach the sternum of 10th segment have pair of anal cerci.
d. In the 12th segment anal styes are seen.
Answer:
b. In female cockroaches chitinous plates gonapophyses are present around the female genital aperature.
![]()
Question 7.
What is the length of lampito mauritii.
a. 80-210 mm
b. 85-350 mm
c. 80 – 220 mm
d. 80 – 200 mm
Answer:
a. 80-210 mm
Question 8.
The pale brown the purplish tinge colour of earthworm is due to the pigment
a. Haemolymph
b. Porphyrin
c. Choloroquin
d. Flaemoglobin
Answer:
b. Porphyrin
![]()
Question 9.
In which segments the spermatheca are situated
a. 6-7 segments, 7-8 segments 8-9 segments
b. 6-7 segments, 8-9 segments 9-10 segments
c. 8-9 segments, 9-10 segments 10-11 segments
d. 7-8 segments, 8-9 segments 9-10 segments
Answer:
a. 6-7 segments, 7-8 segments 8-9 segments
Question 10.
Find out the wrong statement?
a. The wall of earthworm is thin and moist.
b. There are cuticle and epithelial layer.
c. The body cavity which lies between the digestive system and body wall does not act as a fluid-filled structure.
d. The coelomic fluid is alkaline and milky in nature.
Answer:
c. The body cavity which lies between the digestive system and body wall does not act as a fluid-filled structure.
![]()
Question 11.
Whether the following statement is correct or wrong. Justify.
a. In earthworm the digestive tract runs from the mouth to anus.
b. In earthworm the mouth is seen in the first segment.
c. In the second segment lies buccal cavity.
d. In the 3 – 4th segment lies the pharynx.
a. True, False, False, True
b. True, True, True, True
c. False, False, False, True
d. True, False, True, False
Answer:
b. True, True, True, True
Question 12.
The large complex molecules which consist of organic-rich soil eaten by earthworm with the help of digestive enzymes is converted into the simple absorptive unit is
a. Intestinal digestion
b. Digestion
c. Rectal digestion
d. Enzymatic digestion
Answer:
b. Digestion
![]()
Question 13.
Find the odd one out.
The earthworm receptors are
a. Photoreceptors
b. Vision receptors
c. Taste receptors
d. Gustatory receptors
Answer:
b. Vision receptors
Question 14.
Which of the following is true with an excretory system of earthworm.
a. Nephridia
b. Nephron minute tubules
c. Nephridia – minute coiled tubules
d. Nephron – coiled tubule
Answer:
c. Nephridia – minute coiled tubules
![]()
Question 15.
Apart from nephridia, there is specialised cell present in the intestinal walls.
a. Chlorogogen
b. Chloricgen
c. Chlorajan
d. Chlorojin
Answer:
a. Chlorogogen
Question 16.
What is the other name for the seminal funnel?
a. Ciliary
b. Ciliary rosettes
c. Ciliary flagella
d. Ciliary antennae
Answer:
b. Ciliary rosettes
![]()
Question 17.
How many days are taken by the earthworm to complete its life cycle?
a. 70 days
b. 65 days
c. 69 days
d. 60 days
Answer:
d. 60 days
Question 18.
What is the fluid manure of earthworm consist of?
a. Vermicomposting
b. Vermiculture
c. Vermiwash
d. Earthworm manure
Answer:
c. Vermiwash
![]()
Question 19.
Find out the unrelated one
a. Vermi compose
b. Vermin
c. Vermiculture
d. Vermi wash
Answer:
b. Vermin
Question 20.
Match and find out correct
I. Coxa – a. Thick
II. Trochanter – b. Long
III. Femur – c. Small
IV. Tibia – d. Large
a. I – a, II – b, III – c, IV – d
b. I-d, II-c, III-b, IV-a
c. I-a, II-c , III-d ,IV-b
d. I – b, II – a, III – c, IV – d
Answer:
b. I-d, II-c, III-b, IV-a
![]()
Question 21.
Find out the wrong pair of cockroaches.
a. Tarsus – Podomeres
b. Genital opening Sclerites – Parametabolus
c. Sclerites of the dorsal side – Tergites
d. Sclerites of the ventral side – Sternites
Answer:
b. Genital opening Sclerites – Parametabolus
Question 22.
Find out the wrong pair of cockroaches.
a. Spiracles – Stigmata
b. Ostia – Colourless coelomic fluid
c. Ostia – Digestive system cockroach
d. Supra oesophageal ganglion – Brain
Answer:
c. Ostia – Digestive system cockroach
![]()
Question 23.
Which is the ancient organism of insect?
a. Cockroach
b. Cricket
c. Grasshopper
d. Scorpion
Answer:
a. Cockroach
Question 24.
Cockroach belongs to …………………………………………… period about 320 million years ago.
a. Devonian
b. Carboniferous
c. Missisipian
d. Pensylvanian.
Answer:
b. Carboniferous
![]()
Question 25.
One of the fastest moving land insect is the cockroach. What is it’s speed?
a. 6.4 km/hr
b. 5.0 km/hr
c. 5.4 km/hr
d. 6.5 km/hr
Answer:
c. 5.4 km/hr
Question 26.
Which makes the wings of insect?
a. Chitin
b. Pecten
c. Cellulose
d. Hemicellulose
Answer:
a. Chitin
(2 marks)
II. Very Short Questions
Question 1.
Name the earthworms of India.
Answer:
- Lampito mauritii (Megascolex mauritii)
- Perioynx excavatus
- Metaphire posthuma (Pheretima Posthuma)
Question 2.
What are the regions of clitellum?
Answer:
- Preclitellar region (1st – 13th segments)
- Clitellar region (14th – 17th segment)
- Post – Clitellar region (after 17th segment)
Question 3.
Name the structure that helps in locomotion where is it seen?
Answer:
Locomotion is effected through setae. In all the segments of the body except the first last and clitellum there is a ring of chitinous body setae.
![]()
Question 4.
What is the composition of the coelom of earthworms?
Answer:
The coelomic fluid is milky and alkaline. It consists of granulocytes or eleocytes amoebocytes, mucocytes and leucocytes.
Question 5.
Classify earthworms based on their ecological strategies.
Answer:
- Earthworms are classified as epigeics, anecics and endogeics based on their ecological strategies.
- Epigeics are the surface dwellers e.g., Perionyx excavaus and Eudrilus eugeniae.
- Anecics are found in the upper layers of the soil e.g., Lampiro mauritii, Lumbricus terrestris.
- Endogeics are found in deeper layers of the soil e.g., Octochaetona thursoni.
![]()
Question 6.
What are the mouthparts of the cockroach?
Answer:
- Labrum (i) pair of mandibles Labrum (ii) pair of maxillae
- Labium and hypopharynx or tongue.
Question 7.
Give notes on sclerites?
Answer:
In each segment, exoskeleton has hardened plates called sclerites, which are joined together by a delicate and elastic articular membrane or arthrodial membrane.
![]()
Question 8.
When is cockroach evolved?
Answer:
The cockroaches are ancient among all groups of insects dating back to the carboniferous period about 320 million years ago.
Question 9.
Name the five segments of the leg of the cockroach?
Answer:
- Coxa -Large
- Trochanter-Small
- Femur -Long and broad
- Tibia – Long and thick
- Tarsus -has five movable joints
Question 10.
Where are hepatic caeca seen in cockroaches?
Answer:
At the junctional region of the gizzard are eight finger-like tubular blind processes called hepatic caecae.
Question 11.
Trace the air paths of respiration.
Answer:
Spiracle trachea tracheoles Tissues.
![]()
Question 12.
Write a note on coelom of earthworm.
Answer;
A spacious body cavity called the coelom is seen between the alimentary canal and the body wall. The coelom contains the coelomic fluid and serves as a hydrostatic skeleton, in which the coelomocytes are known to play a major role in regeneration. immunity and wound healing. The coelomic fluid of the earthworm is milky and alkaline, which consists of granulocytes or cicocytes. amoebocytes, mucocytes and leucocytes.
Question 13.
What are the structures that is not present in frog?
Answer:
In frog there is no external ear neck and tail.
Question 14.
Give notes on chyme?
Answer:
Digestion of food takes place by the action of hydrochloric acid and gastric juices secreted from the walls of the stomach. This partially digested food is called as chyme.
![]()
Question 15.
What are the regions of nervous system?
Answer:
Central nervous system peripheral nervous system autonomous nervous system.
Question 16.
A cockroach produces nutritionally dense milk to feed their young ones. It may be considered as a superfood of the future. How?
Answer:
- It contains crystalline milk.
- It is synthesised by diploptera punctata.
Question 17.
What are the economic importance of frog?
Answer:
- Frogs feed on insects and helps in reducing insect pest population.
- Frogs are used in traditional medicine for controlling blood pressure and for antiaging properties.
Question 18.
What are the types of cockroach?
Answer:
- American cockroach
- Brown – banded cockroach
- German cockroach
- Oriental cockroach
- Viviparous cockroach
Question 19.
Name the cells that helps in excretion of cockroach?
Answer:
- Fat bodies
- Nephrocytes
- Cuticle
- Urecose glands
Question 20.
Define uricotelic organism.
Answer:
The nitrogenous wastes are eliminated through uric acid. (Eg.) Hence cockroach excretes uric acid as a waste it is said to be uricotelic.
![]()
Question 21.
What is typhiosole?
Answer:
- The dorsal wall of the intestine of earthworm is folded into the cavity as the typhiosole.
- This fold contains blood vessels and increases the absorptive area of the intestine.
Question 22.
What are the glands seen in male reproductive system ?
Answer:
- Mushroom-shaped gland
- conglobate gland.
Question 23.
What is clitellum?
Answer:
In mature worms 14 – 17 segments may be found swollen with a glandular thickening of the skin called the clitellum. This helps in the formation of cocoon.
Question 24.
Where is spermathecal openings seen in the earthworm?
Answer:
They are lying inter segmentally between the grooves of the segments 6/7,7/S and 8/9.
![]()
Question 25.
Where is genital openings seen in the earthworm?
Answer:
- The female genital aperture lies on the ventral side in the 14th segment.
- A pair of male genital apertures are situated latero-ventrally in the 18th segment.
Question 26.
Name the body muscles of earthworm.
Answer:
- Cuticle
- Epidermis
- Coelomic epithelium
Question 27.
Name the cells t at makes the epidermis?
Answer:
- Supportive cells
- Glandular cells
- Basal cells
- Sensory cells
Question 28.
What is the functions of coelomocytes of earthworm?
Answer:
Uses of coelomocytes
- Regeneration
- Immunity
- Woundhealing
Question 29.
Name the cells of coelom of earthworm
Answer:
- Granulocytes or eleocytes
- Amoebocytes
- Mucocytes
- Leucocytes
Question 30.
What are lateral hearts ?
Answer:
In the anterior part of body of earthworm the dorsal vessel is connected with the ventral vessel by eight pairs of commissural vessels or lateral hearts lying in the 6th – 13th segment.
![]()
Question 31.
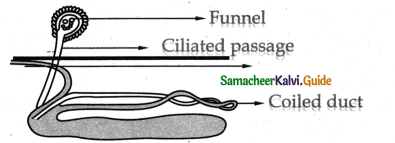
Give notes on nephrostome.
Answer:
The mega nephridium of earthworm has an internal funnel like opening called the nephrostome which is fully ciliated.
Question 32.
What is chloragogen cell?
Answer:
Besides nephridia special cells on the coelomic wall of the intestine called chloragogen cells are present. They excrete nitrogenous wastes in the blood.
Question 33.
Whatisprotandrous?
Answer:
- The two sex organs of earthworm mature at different times and hence self fertilisation is prevented.
- The sperm develops earlier than the production of ova. This process is known as protandrous.
It transmits the diseases like cholera, dysentery and tuberculosis hence it is known as vectors.
Question 38.
Whatishypognathous?
Answer:
The mouth parts of cockroach are directed downwards so its is hypognathous.
Question 39.
What is compound eyes?
Answer:
The head of cockroach bears a pair of large sessile and reniform compound eyes. Each eye is formed of about 2000 simple eyes called the ommatidia and the vision caused by the ommatidia is mosaic vision.
![]()
Question 40.
Name the segments of the legs of cockroach?
Answer:
There are five segments in the legs of cockroach.
- Coxa
- Trochanter
- Femur
- Tibia
- Tarsus
Question 41.
What is podomeres?
Answer:
The last segment of the leg tarsus has five movable joints called podomeres or tarsomeres.
Question 42.
Give notes on wings of cockroach?
Answer:
Cockroach has two pairs of wing. The first pair of wings protects the hind wings when rest is called elytra or tegmina. The second pair of wings used in flight.
Question 43.
Name the plates of the abdomen of cockroach?
Answer:
There are 10 segments in the abdomen. The sclerites of the dorsal side are called tergites.
The sclerites on the ventral side are called sternites and the sclerites on the lateral sides are called pleurites.
Question 44.
What are the sensory receptors seen in cockroach?
Answer:
- Antenna
- Compound eyes
- Labrum
- Mandibles
- Labialpalps
- Analcerci
Question 45.
Name the fat bodies of cockroach?
Answer:
Nephrocytes, Cuticle, Urecose glands.
Question 46.
What are the glands seen in the male cockroach?
Answer:
- Mushroom shaped gland
- Conglobate gland.
Question 47.
What is meant by paurometabolus?
Answer:
- In cockroach the embryonic development occurs in the ootheca for 5-13 weeks.
- The development of cockroach is gradual through nymphal stages. Hence it is called as paurometabolus.
Question 48.
What are pokilotherms?
Answer:
The organisms which change its temperature according to the temperature of the environment is known as pokilotherms.
Question 49.
What is nictitating membrane?
Answer:
The third eyelid of frog is nictitating membrane. It protects the eye.
![]()
Question 50.
What is cloaca?
Answer:
As the digestive excretory reproductive system opens commonly through a aperture this is called as cloaca.
Question 51.
What is spiracle?
Answer:
In cockroach the trachea open through 10 pairs of small holes called spiracles.
Question 52.
What is meant by chordotonal receptor?
Answer:
Chordotonal receptor is found on the anal cerci which are receptive to vibrations in air and land.
Question 53.
How can a earthwom senses its burrow?
Answer:
In the prostomium of earthworm there are thermal and chemical receptors with the help of this they can find it’s habitat.
![]()
Question 54.
Compare the respiration of human with the respiration of cockroach?
Answer:
In the respiratory system of cockroach there are spiracles and trachea. Each spiracles can open and close. During inspiration spiracles open. This oxygen enters into the haemocoel through spiracles and exchange of gases taking place.
Question 55.
List the very special features of cockroach.
Answer:
- Cockroach can survive being submerged under water upto 45 minutes.
- They hold their breath often to help regulate loss of water.
Question 56.
Cockroach can live without ahead? How?
Answer:
A cockroach can live for a week without its head. There is no connection between head and respiration. There is no nostrils and lungs.
The abdomen has 10 pairs of spiracles. These spiracles are communicated with the tracheoles and haemolymph and exchange of gases taking place.
![]()
Question 57.
Why is mosaic vision with less resolution in cockroaches ?
Answer:
The unit of compound eye is ommatidium. There are hundreds of ommatidia. Each ommatidium forms a image. Each image formed in all the ommatidia forms a vision. This image is a mosaic vision.
Question 58.
List the charcteristic features of order Aneura?
Answer:
Frogs and Toads have elongated hindlimbs. This helps in jumping, Frogs can live in water and on trees. Parental care is seen in few species.
Question 59.
Differentiate the compound eyes from simple eye.
Answer:
| Compound eye | Simple eye |
| 1. Formed of hundreds of small units | Single eye |
| 2. Each ommatidium contains lens cornea retina and optic nerve | Only one lens cornea retina and optic nerve |
| 3. Each ommatidium forms a separate image and forms a unclear mosaic vision | A single image informed. The image is clear |
Question 60.
Why three chambered heart of frog is not as efficient as the four chambered heart of birds and mammals?
Answer:
- The heart of birds and mammals have four chambers. The oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is carried by separate blood vessels and transports to body parts and the purifying organ.
- The frog has three chambered heart. The oxygenated and deoxygenated blood mixeshere. This mixed blood is reaching all the parts.
![]()
Question 61.
What is meant by cloaca a Common digestive and excretary opening ?
Answer:
- In the elasmobranhs amphibians, reptiles egg laying mammals the faeces and urine pass through this opening.
- This passage is also a genital passage for the deposition of sperm. This is called cloacal aperature.
Question 62.
Give notes on setae of earthworm?
Answer:
- Earthworm have setae which are small hair like bristles. They are not composed of the same material as human hair.
- They will be helpful in feeding mating and locomotion.
Question 63.
Give notes on intestinal caeca of earthworm?
Answer:
In 26th segment of metaphire posthuma a pair of cone shaped bulging is seen. It is known as intestinal caecum. This secretes amylolytic enzymes. This helps in starch digestion.
( 3 marks)
III. Short Questions
Question 1.
Based on their ecological strategies classify the earthworms?
Answer:
| Ecological strata | Earthworm type |
| 1. Epigeics – up on the earth | Perionyx excavatus |
| 2. Anecics – out of the earth | Lampito mauritii |
| 3. Endogeics – with in the earth | Octohaetona thurstoni |
Question 2.
Where is longest earthworm seen?
Answer:
- Micro chaetus rappi is an African giant earthworm can reach a length of 6.7 meter (22 feet)
- Drawida nilamburansis is a species of earthworm in Kerala reaches a maximum length upto 1 meter (3 feet).
![]()
Question 3.
What is the significance of coelomic fluid of earthworm?
Answer:
- In the coelomic fluid coelomocytes are present.
- It helps in regeneration.
- It helps in immunity and healing of wounds.
Question 4.
What are the sensory receptors seen in the earthworm?
Answer:
- Photo receptors – Found on the dorsal surface of the body.
- Gustatory – Sense of taste are found in the buccal cavity.
- Tactile receptors Sense of touch
- Chemo receptors Seen in the prostomium and the bodywall.
- Thermo receptors
![]()
Question 5.
Draw the diagram of nephridia of earthworm and name the parts.
Answer:
Question 6.
What are the other name for sclerites ?
Answer:
On the basis of their location they gets their name.
- Dorsal sclerites – Tergites
- Ventral sclerites – Stemites
- Lateral sclerites – Plurites
Question 7.
The cockroach can survive with out the head. Whether the statement is correct or wrong if it is so give reason?
Answer:
This statement is correct.
Reason:
- A cockroach can live for a week without its head.
- Due to their open circulatory system they breath through little holes on each of their body segment hence they are not dependent on the mouth or head to breath.
Question 8.
What are the parts of the nervous system ?
Answer:
Supraoesophagial nerve ganglion or brain sub- oesophagial ganglion – circum oesophageal connectives double ventral nerve cord.
![]()
Question 9.
What are the significance of nervous system.
Answer:
- Brain or supra oesophageal ganglion or brain.
- It acts as a sensory and an endocrine centre.
- Sub – oesophageal ganglion
- It acts as a motor centre controls the movements of the mouthparts legs and wings.
Question 10.
Give notes on ommatidia?
Answer:
- The photo receptors of the cockroach consists of a pair of compound eyes at the dorsal surface of the head.
- Each eye is formed of about 2000 simple eyes called ommatidia.
Question 11.
Give notes on ‘Mosaic vision’?
Answer:
- The cockroach perceives the vision through each ommatidia. This vision is mosaic vision.
- Though there is sensitivity but the vision is not a clear one.
Question 12.
Why is sexual dimorphism exhibited clearly during breeding season in frog?
Answer:
- During breeding the sexual dimorphism is seen clearly.
- The male frog has a pair of vocal sac and a ; nuptial pad on the ventral side of the first digit i of each fore limb.
- Vocal sacs assist in amplifying the croaking sound of frog.
![]()
Question 13.
How will you classify the earthworm based on their living in relation to ecological strata?
Answer:
- Epigeics – Surface living (Eg.) Eudrilus eugeniae
- Anecics-Found in upper layers of the soil. (Eg.) Lampito mauritii.
- Endogeics – Found in deeper layers of the soil. (Eg.) Octochaetona thurstoni.
Question 14.
Give an account of respiratory system of earthworm?
Answer:
- Earthworm has no special respiratory organ like lungs or gills.
- Respiration takes place through the body wall.
- The outer surface of the skin is richly supplied with blood capillaries which helps in the diffusion of gases.
- Oxygen diffuses through the skin into the blood.
- Carbondi-oxide from the blood diffuses out.
- The skin is kept moist by mucous and coelomic j fluid and facilitates exchange of gases.
Question 15.
Give an account of nervous system of earthworm?
Answer:
- The brain composed of bilobed mass of supra- pharyngeal ganglia. On the third segment j supra-pharyngeal nerve ganglion and on the 4th segment sub-pharyngeal nerve ganglion is seen.
- The brain and the sub-pharyngeal ganglia are connected by a pair of cirum-pharyngeal connectives.
- The double ventral nerve cord runs backward from the sub-pharyngeal ganglion.
Question 16.
What is the excretory organ of earthworm? What are its type?
Answer:
The nephridia is the excretory organ of earthworm
They are three types.
- Pharyngeal or tufted nephridia seen in 5-9 segments
- Micro nephridia or Integumentary nephridia seen 14 – 19th -segment.
- Mega nephridia or septal nephridia seen from 19th – last segment.
![]()
Question 17.
Give notes on vermiwash.
Answer:
- Vermi wash is a liquid manure or plant tonic obtained from earthworm.
- It is used as a foliar spray and helps to induce plant growth.
- It is a collection of excretory products, mucus secretion micro nutrients from the soil organic molecules.
Question 18.
What is wormery or wormbin?
Answer:
Earth worm can be used for recycling of waste food leaf litter and biomass to prepare a good fertilizer in container is known as wormery or wormbin. It makes superior compost.
Question 19.
Give the systematic classification of earthworm?
Answer:
- Phylum – Annelida
- Class – Oligocheata
- Order – Haplotaxida
- Genus – Lampito
- Species – Mauriitii
Question 20.
In which part of the cockroach’s body the sensory receptors are seen?
Answer:
| Receptors | Organs |
| 1. Thigmo receptor | Antenna, maxillary paips and anal cerci |
| 2. Olfactory | Antennae |
| 3. Gustatory | Maxillary paips labium |
| 4. Thermo receptors | Tarsal segments on the legs. |
| 5. Chordotonal which responds to air or earth borne vibrations | Anal cerci |
Question 21.
Give the systematic classification of frog?
Answer:
- Phylum – Chordata
- Class – Amphibia
- Order – Aneura
- Genus – Rana
- Species – Hexatacdyla
Question 22.
Give the systematic classification of cockroach?
Answer:
- Phylum – Arthropoda
- Class – Insecta
- Order – Orthroptera
- Genus – Periplanata
- Species – Americana
Question 23.
Give an account of exo skeleton of cockroach?
Answer:
- The entire body is covered by a hard chitinous exoskeleton.
- In each segment exoskeleton has hardened plates called sclerites which are joined together by a delicate and elastic articular membrane.
- The sclerites of the dorsal side are called tergites. Ventral side are called sternites lateral side are called pleurites.
![]()
Question 24.
Give an account of mouth parts of cockroach?
Answer:
- The appendages form the mouth parts which are of biting and chewing type.
- These are mandibulate or orthopterus.
Mouth parts
- Labrum – Upperlip
- A pair of mandibles
- Pair of maxillae.
- Labium-Lower lip
- Tongue – Hypopharynx.
Question 25.
Name the digestive glands of cockroach.
Answer:
- Salivary glands.
- Hepatic caeca or entericcaeca
Question 26.
Draw the male frog with vocal sac and nuptial pad and marks the parts.
Answer:
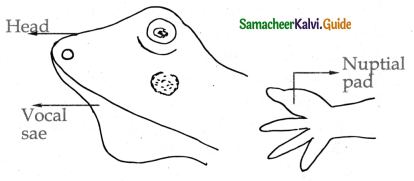
Question 27.
Give an account of buccal cavity of frog.
Answer:
- The wide mouth opens into the buccal cavity.
- On the floor of the buccal cavity lies a large muscular sticky tongue.
- The tongue is attached in front and free behind.
- The free edge of the tongue is forked.
- A row of small and maxillary teeth is found on the inner region of the upper jaw.
- Vomerine teeth are present one on each side of the internal nosteils.
![]()
Question 28.
Give an account of blood of frog ?
Answer:
60% of frog’s blood is plasma and 40% is red blood cells. The blood cells composed of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets.
White blood cells
- Neutrophil
- Basophil
- Eosinophils
- Lymphocytes
- Monocytes
( 5 marks)
IV. Essay Questions
Question 1.
Describe the external features of the earthworm?
Answer:
- Earthworm has along and cylindrical body.
- It is 80-210 mm in length. It is light brown in colour.
- The body is encircled by a large number of grooves which divides it into a number of compartments called segments ormetameres.
- The mouth is found in the centre of the first segment of the body called the peristomium.
- Overhanging the mouth is a small flab called prostomium.
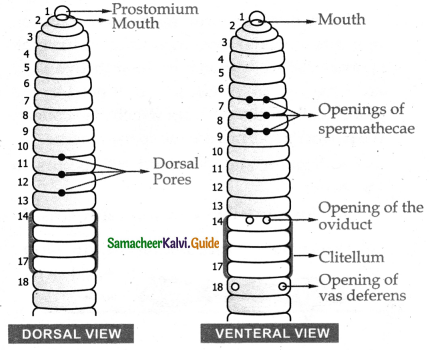
- The 14 – 17th segments become swollen called clitellum.
- There are pair of female genital opening in the 14th segment and pair of male genital opening in the 18th segment.
- In the segments 6/7, 7/8, 8/9 lies the spermatheca.
- In all the segments of the body except the first last and clitellum there is ring of chitinous body setae. They all involved in locomotion.
- The last segments bear anus.
Question 2.
Give an account of digestive system of earthworm?
Answer:
1. The alimentary canal runs as a straight tube throughout the length of the body from the mouth to anus.
2. The mouth opens into the buccal cavity which occupies the 1st and 2nd segments.
3. The thick muscular pharynx lies in the 3rd and 4th segment and is surrounded by the pharyngeal glands.
4. A small narrow oesophagus lies in the 5th segment and 6th segment contains muscular gizzardes. Which helps in grinding the soil and decaying leaves.
5. The intestine starts from the 7th segment and ’ continues upto the last segment.
6. The dorsal wall of the intestine is folded into the vascular cavity called typhlosole.
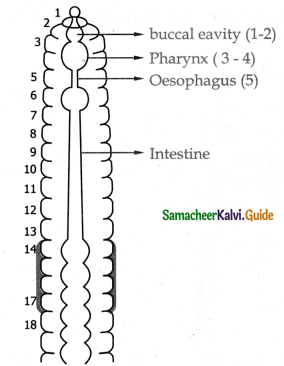
Question 3.
Describe the structure of circulatory system of earthworm?
Answer:
- In earthworm closed type of blood vascular system is seen which contains blood vessels, capillaries and lateral hearts.
- Two median longitudinal vessels run above and below the alimentary canal as dorsal and ventral vessels of the earthworm.
- There are paired valves in the dorsal vessels which prevent the backward flow of the blood.
- From 6 to 13 segments with the 8 pairs of commissural vessels which connects the dorsal and the ventral vessel called lateral hearts.
- The blood is pumped from the dorsal vessel to the ventral vessel.
The blood glands present in the anterior segments of the earthworm produce blood cells and haemoglobin and gives red colour to the blood.
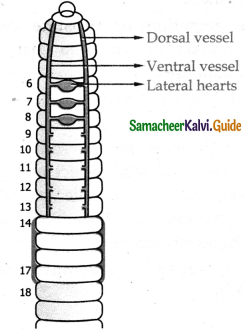
Question 4.
Describe the structure of reproductive system of earthworm ?
Answer:
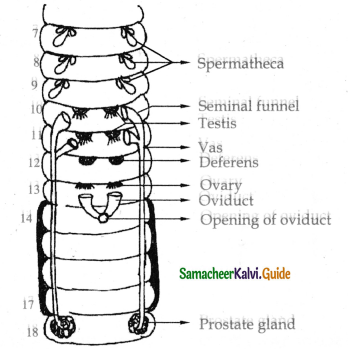
Earth worm is a hermaphrodite organism the male and female reproductive organs are found in the same individual.
Male reproductive system:
- Two pairs of testes are present in the 10th and 11th segments. The testes give rise to the germ cellor spermatogonia.
- Two pairs of seminal funnels called ciliary rosettes are situated in the same segments as the testes. Three pairs of spermathecalies in the 7,8,9 segments.
- The vas deferens arise from the ciliary rosettes run upto the 18th segment and open exterior through the male genital aperture which contains two pairs of penial setae.
- A pair of prostate glands lie in the 18th and 19th segments.
- The secretion of prostate cement the spermatozoa into a bundles of spermatophores.
Female reproductive system:
- A pair of ovaries lying in the 13th segment. Ovarian funnels are present beneath the ovaries continue as a oviduct and opens in the 14th segment as a female genital opening. There are three pairs of spermathecae lie in the 7th, 8th and 9th segment.
- They receive spermatozoa during copulation.
- The two earthworm mate juxta position opposite gonadal openings and exchanging sperms mature egg cells in the nutritive fluid are deposited in the cocoons produced by the glands cells of the citellum which also collects the partner’s sperm from the spermathecae.
- Fertilization and developments occurs in the cocoon.
- After 3 weeks baby earthworm are released.
![]()
Question 5.
Give an account of locomotion of earthworm?
Answer:

- The earthworm normally crawls with the help of their body muscles setae and buccal chamber. The outer circular and inner longitudinal muscle layers lies below the epidermis of the body wall.
- The contraction of circular muscles make the body long and narrow while the longitudinal muscles make the body short and broad and hence due to the contraction of longitudinal muscle the earthworm moves.
- The alternate waves of extensions and contractions are aided by the leverage afforded by the buccal chamber and setae.
Question 6.
Describe the morphological features of cockroach?
Answer:
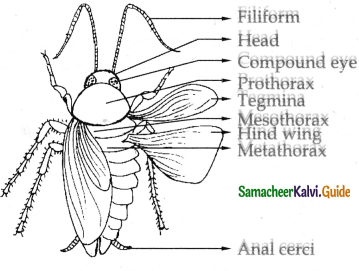
- Cockroach is a bilaterally symmetrical segmented animal which is divisible into head thorax and abdomen.
- The entire body is covered with chitinous exo-skeleton.
- Each segment consists of sclerites. The head is small and triangular and the mouth parts are directed downwards hence known as hypognathous. The head bears a pair of compound eye. Each compound eye is composed of unit of ommatidia.
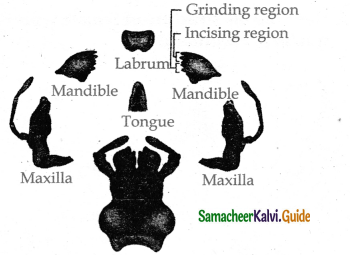
- The mouth parts are of mandibulatetype. It consists of labrum pair of mandibles a pair of maxillae labium and tongue.
- The thorax consists of prothorax mesothorax and metathorax. Each thoracic segment bears a pair of walking legs.
- Due to the presence of 3 pairs of leg they are called as hexapoda. Each leg consists of five segments they are coxa, trochanter femur tibia and tarsus.
- It has two pairs of wings. It is called as tegmina or elytra. The wings arise from the mesothorax protects the hind wings when at rest. The second pair of wings arise from metathoraxa and used inflight.
Question 7.
Draw the diagram of mouth parts of cockroach ?
Answer:
![]()
Question 8.
Describe the structure of digestive system of cockroach with a diagram ?
Answer:
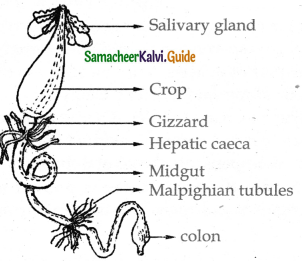
The alimentary canal is divided into three regions namely foregut midgut and hindgut.
Foregut:
- It includes pre-oral cavity mouth pharynx oesophagus and the posterior region contains crop.
- The food is stored in the crop. The crop is followed by gizzard which have chitinous teeth helps in the grinding of the food particles.
Midgut:
- At the junctional region of the gizzard are eight finger like tubular blind processes called the hepatic caecae or enteric caecae.
- At the junction of midgut and hind gut lies 100 – 150 yellow coloured malphigian tubules. It excretes the nitrogenous wastes from the haemolymph.
Hindgut:
- The hind gut is broader than the midgut.
- It consists of ileum colon andrectum. The rectum opens out through anus.
Digestive glands
Salivary glands
Hepatic caeca
Question 9.
Describe the structure of circulatory system of cockroach ?
Answer:
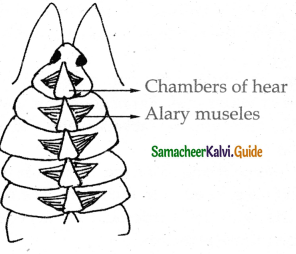
Cockroach has an open type of circulatory system.
The coelom is filled with haemolymph. Heart is an elongated tube with muscular wall lying mid dorsally beneath the thorax.
The heart consists of 13 chambers with ostia on either side.
The blood from the sinuses enter the heart through the ostia and is pumped anteriorilly to sinuses again. In each segment there is triangular muscle called alary muscles are seen. It is responsible for blood circulation.
There is a pulsatile vesicle lies at the base of each antenna also pumps blood.
![]()
Question 10.
Give an account of excretory system of cockroach?
Answer:
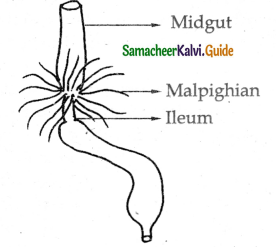
- The malphighian tubules are the main excretory organs of cockroach which help in eliminating the nitrogenous wastes from the body in the form of uric acid. Excretion is uricotelic.
- In addition fat body, nephrocytes cuticle and urecose glands are also excretory in function. The malpighian tubules are attached at the junction of midgut and hindgut. There are about 100-150 in number present in 6 – 9 bundles.
- Each tubule is lined by glandular and ciliated cells and the waste is excreted out through the hindgut.
- The glandular cells of malpighian tubules absorb water salts and nitrogenous wastes. The cells of the tubules reabsorb water and inorganic salts.
- By the contraction of the tubules nitrogenous waste is pushed in to the ileum. The remaining waste with solid uric acid is exceeded along with the faecal matter.
Question 11.
Describe the structure of reproductive system of male cockroach?
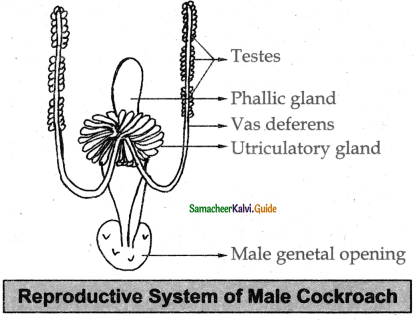
Answer:
- The male reproductive system consists of a pair of testes vasa deferentia an ejaculatory duct utricular gland phallic gland and the external genitalia.
- A pair of 3 lobed testes lies on the 4th and 6th abdominal segments. The vas deferens opens into the male gonopore which lies ventral to anus.
- The mushroom shaped gland is a large reproductive gland which opens into the anterior part of the ejaculatory duet.
- The sperms are stored in the seminal vesicles as bundles of spermatophores. Surrounding the male genital opening are few chitinous structures called phallomeres or gonopophyses which help in copulation.
Question 12.
Describe the structure of female reproductive system of cockroach?
Answer:
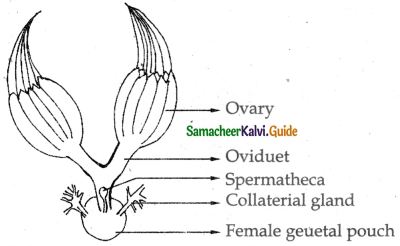
- The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries vagina genital pouch collaterial glands speromthecae and the external genitalia.
- A pair of ovaries lie in the segmetn of 2nd and 6th abdominal segment. Each ovary is formed of eight ovarian tubules. Oviducts of each ovary unite into a common oviduct known as vagina which opens into the genital chamber.
- A pair of spermathecae is present in the 6th segment and opens in to the genital pouch.
- During copulation the ova descend to the genital chamber and fertilised by the sperm. The collateral gland secreta a hard case called ootheeca around the egg.
- The ootheca is dropped to a crack or crevice of high relative humidity near a food source. The nymphs are released from this ootheca and they grows by moulting about 13 times to reach the adult form.
![]()
Question 13.
Describe the morphological features of frog?
Answer:
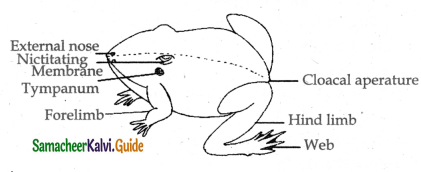
The body of frog is streamlined to help in swimming. Body is divided into head and trunk.
Head:
- The head is triangular and has an apex which forms the snout.
- The mouth is at the anterior end on the head contains pair of external nostrils, pair of eyes with unmovable upper eyelid movable lower eye lid which protects the eye.
- The nictitating membrane protects the eye when the frog is underwater.
- A pair of ear drum lies behind the eyes. There is no external ear neck and tail.
Trunk:
- It bears a pair of fore limbs and a pair of hind limbs. The hind limbs are longer than the forelimbs. At the posterior end between the hind limbs is the cloacal aperture.
- Fore limbs help to bear the weight of the body. It consists of upper arm fore arm and a hand. The hind limbs consist of thigh shank and foot.
- Foot bears five long webbed toes and one small spot called the sixth toe cloacal aperture.
- Fore limbs help to bear the weight of the body. It consists of upper arm fore arm anda hand.
- The hind limbs consist of thigh shank and foot. Foot bears five long webbed toes and one small spot called the sixth toe.
Question 14.
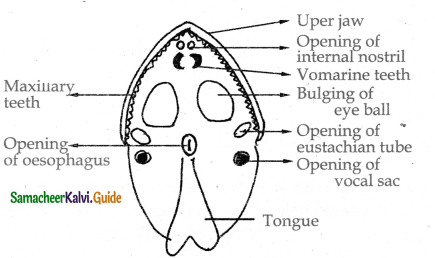
Describe about the digestive system of frog?
Answer:
The digestive system extends from mouth to the cloaca.
Digestive tract organs:
- The alimentary canal consists of the buccal cavity pharynx oesophagus duodenum ileum and the rectum which opens outside by the cloacal aperture.
- The mouth opens into the buccal cavity.
Tongue:
- On the floor of the buccal cavity lies a large muscular sticky tongue. The tongue is attached in front and free behind.
- The free edge of tongue is forked.
Teeth:
- A row of small and pointed maxillary teeth is found on the inner region of the upper jaw. Vomerine teeth are also present as two groups. One on each side of the internal nostrils.
- The lower jaw is devoid of teeth. The mouth opens into the buccal cavity and then to esophagus through pharynx. Oesophagus opens into stomach
- Stomach opens in to intestine then to rectum and finally to the cloaca. Liver, Pancresa are the structures of digestive system.
![]()
Question 15.
Describe the structure of the heart of frog ?
Answer:
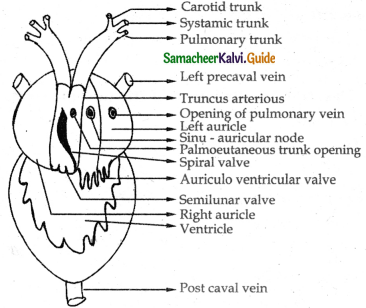
- The heart consists of three chamber. Two auricle and one ventricle. Heart is covered by pericardium. On the dorsal side of the heart is a triangular chamber called sinus venosus.
- Truncus arteriosus is a thick walled structure which is obliquely placed on the ventral surface of the heart.
- It divides into right and left aortic trunk. Each divides into carotid systemic and pulmocutaneous arteries.
- The systemic trunk of each side is joined posteriorly to form the dorsal aorta. They supply blood to the posterior part of the body. The pulmo-cutaneous trunk supplies blood to lungs and skin.
- The sinus venosus receives the deoxygenated blood from the pre and post venacava and delivers the blood to the right auricle.
- The left auricle receives oxygenated blood through pulmonary vein.
Question 16.
Describe the structure of the respiratory system of frog?
Answer:
- Frog respires on land and in the water by two different methods. In water the dissolved oxygen in the water gets exchanged through the skin by diffusion.
- On land the buccal cavity skin and lungs act as the respiratory organ.
Buccal respiration:
- Mouth remains permanently closed while the nostrils remain open. The floor of the buccal cavity is raised and lowered so air drawn into and expelled out of the buccal cavity repeatedly through the open nostrils.
- A pair of elongated pink coloured sac like lungs are present in the upper part of the trunk.
- Air enters through the nostrils into the buccal cavity and then to the lungs.
Question 17.
Describe the structure of the nervous system
Answer:
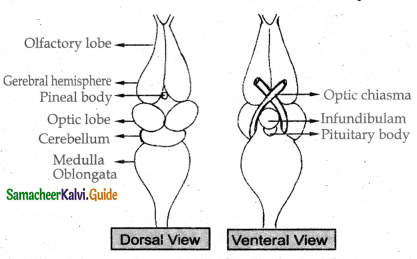
- The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system, peripheral nervous system and the autonomous nervous system.
- Peripheral nervous system consists of 10 pairs of cranial nerves and 10 pairs of spinal nerves. The autonomous nervous system is divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system.
- CNS consists of brain and spinal cord. Brain is covered with pia mater and dura mater. The brain is divided into forebrain mid brain and hind brain
- Fore brain Consists of a pair of olfactory lobes and cerebral hemisphere and diencephalon. The olfactory lobes contain a small cavity called olfactory ventricle.
- The midbrain includes two large optic lobes and has cavities called optic ventricles.
- Hind brain consists of cerebellum and medulla oblongata. The medulla oblongata passes out through the foramen magnum and continues as spinal cord.
![]()
Question 18.
Draw the diagram of buccal cavity of frog and name the parts?
Answer:
Question 19.
Describe the locomotion of earthworm?
Answer:

- The earthworm normally crawl with the help of their body muscles setae and buccal chamber.
- The outer circular and inner longitudinal muscle layers lies below the epidermis of the body wall.
- The contraction of circular muscles make the body long and narrow while the longitudinal muscle make the body short and broad and hence due to the contraction of longitudinal muscle the earthworm moves.
- The alternate waves of extensions and contractions are aided by the leverage afforded by the buccal chamber and setae.
Question 20.
Tabulate the morphological differences between lampito mauritii and metaphire posthuma.
Answer:
| Characters | Lampito mauritii | Metaphire posthuma |
| 1. Shape and size | Cylindrical 80 mm – 210 mm in length 3.5mm – 5.0 mm in width |
Cylindrical 115 – 130 mm in length 5 mm in width |
| 2. Colouration | Light Brown | Dark Brown |
| 3. Segmentation | 165-190 Segments | About 140 Segments |
| 4. Clitellum | 14th – 17th Segments (4) | 14th – 16th Segments (3) |
| 5. Intestinal caeca | Absent | Present in 26th segment |
| 6. Male genital pore | 18th segment | 18th segment |
| 7. Female genital pore | 14th segment | 14th segment |
Question 21.
Tabulate anatomical differences between lampitomaritii and metaphire posthuma
Answer:
| Characters | Lampito mauritii | Metaphire posthuma |
| 1. Sperma thecal opening | Three pairs 6/7, 7/8 and 8/9 | Four pairs 5/6, 6/7, 7/8 and 8/9 |
| 2. Pharynx | 3rd – 4th segment | Runs up to 4th Segment |
| 3. Oesophagus | 5th segment | 8th segment |
| 4. Gizzard | 6th segment | 8th – 9th segment |
| 5. Intestine | 7th segment to anus | 15th segment to anus |
| 6. Lateral hearts | 8 pairs from 6th to 13th segments | 3 pairs from 7th to 9th segments |
| 7. Pharyngeal nephridia | 5th _ 9th segment | 4th – 6th segment |
| 8. Micronephridia | 14th to last segment | 7th to last segment |
| 9. Meganephridia | 19th to last segment | 15th to last segment |
![]()
Question 22.
Differentiate the male cockroach from female cockroach.
Answer:
| Characters | Male cockroach | Female cockroach |
| 1. Abdomen | Long and narrow | Short and broad |
| 2. Segments | In the abdomen, nine segments are visible | In the abdomen, seven segments are visible |
| 3. Anal styles | Present | Absent |
| 4. Terga | 7th ter gum covers 8 th tergum | 7th ter gum covers 8 th and 9th terga |
| 5. Brood pouch | Absent | Present |
| 6. Antenna | Longer in length | Shorter in length |
| 7. Wings | Extends beyond the tip of abdomen | Extends up to the end of abdomen |
23. Draw the life cycle of lampito mauritii.
Answer:
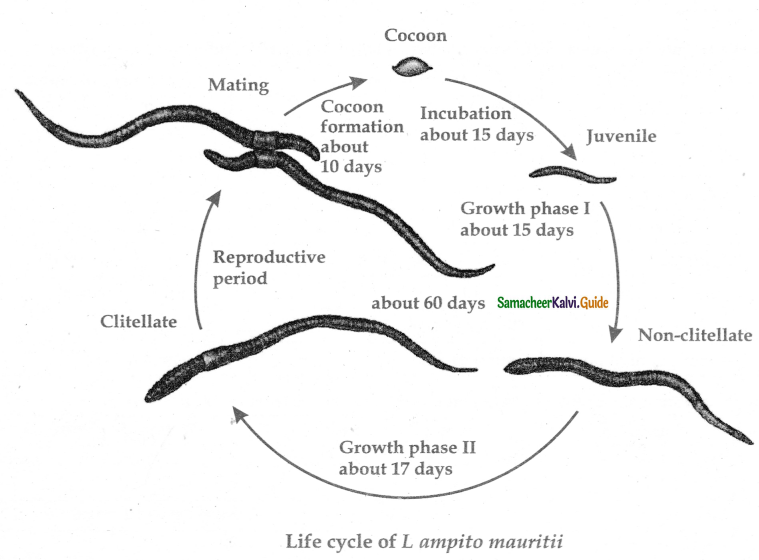
![]()
Question 24.
Differentiate the frog from toad.
Answer:
| Characters | Frog | Toad |
| 1. Family | Ranidae | Buforudae |
| 2. Body shape | Slender | More Bulky |
| 3. Legs | Longer | Shorter |
| 4. Webbed feet | present | Absent |
| 5. Skin | Smooth and moist skin | Dry skin covered with wart like glands |
| 6. Teeth | Maxillary and vomerine teeth. | Teeth absent |
| 7. Egg formation | Lays eggs in clusters | Lays eggs in strings |