Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Guide Pdf Chapter 7 Ecosystem Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Botany Solutions Chapter 7 Ecosystem
12th Bio Botany Guide Ecosystem Text Book Back Questions and Answers
![]()
I. Choose the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and write the option code and the corresponding answer.
Question 1.
Which of the following is not a abiotic component of the ecosystem?
a. Bacteria
b. Humus
c. Organic compounds
d. Inorganic compounds
Answer:
d. Inorganic compounds
Question 2.
Which of the following is / are not a natural ecosystem?
a. Forest ecosystem
b. Rice field
c. Grassland ecosystem
d. Desert ecosystem
Answer:
b. Rice field
![]()
Question 3.
Pond is a type of
a. forest ecosystem
b. grassland ecosystem
c. marine ecosystem
d. fresh water ecosystem
Answer:
d. fresh water ecosystem
Question 4.
Pond ecosystem is
a. not self sufficient and self regulating
b. partially self sufficient and self regulating
c. self sufficient and not self regulating
d. self sufficient and self regulating
Answer:
d. self sufficient and self regulating
Question 5.
Profundal zone is predominated by heterotrophs in a pond ecosystem, because of
a. with effective light penetration
b. no effective light penetration
c. complete absence of light
d. a and b
Answer:
b. no effective light penetration
![]()
Question 6.
Solar energy used by green plants for photosynthesis is only
a. 2-8%
b.2-10%
c.3-10%
d.2-9%
Ans :
b. 2 – 10%
Question 7.
Which of the following ecosystem has the highest primary productivity?
a. Pond ecosystem
b. Lake ecosystem
c. Grassland ecosystem
d. Forest ecosystem
Answer:
d. Forest ecosystem
Question 8.
Ecosystem consists of
a. decomposers
b. producers
c. consumers
d. all of the above
Answer:
d. all of the above
![]()
Question 9.
Which one is in descending order of a food chain
a. Producers → Secondary consumers → Primary consumers→ Tertiary consumers
b. Tertiary consumers → Primary consumers → Secondary consumers → Producers
c. Tertiary consumers → Secondary consumers → Primary consumers→ Producers
d. Tertiary consumers → Producers → Primary consumers → Secondary consumers
Answer:
c. Tertiary consumers → Secondary consumers → Primary consumers→ Producers
Question 10.
Significance of food web is/are
a. it does not maintain stability in nature
b. it shows patterns of energy transfer
c. it explains species interaction
d. b and c
Answer:
d. b and c
Question 11.
The following diagram represents

a. pyramid of number in a grassland ecosystem
b. pyramid of number in a pond ecosystem
c. pyramid of number in a forest ecosystem
d. pyramid of biomass in a pond ecosystem
Answer:
c. pyramid of number in a forest ecosystem
![]()
Question 12.
Which of the following is / are not the mechanism of decomposition
a. Eluviation
b. Catabolism
c. Anabolism
d. Fragmentation
Answer:
c. Anabolism
Question 13.
Which of the following is not a sedimentary cycle
a. Nitrogen cycle
b. Phosphorous cycle
c. Sulphur cycle
d. Calcium cycle
Answer:
a. Nitrogen cycle
Question 14.
Which of the following are not regulating services of ecosystem services
i) Genetic resources
ii) Recreation and aesthetic values
iii) Invasion resistance
iv) Climatic regulation
a. i and iii
b. ii and iv
c.iandii
d. iandiv
Answer:
c. i and ii
![]()
Question 15.
The productivity of the profundal zone will be low. Why?
Answer:
The producers of the pond ecosystem depend on phytoplankton through photosynthesis. The profundal zone lies below the limnetic zone with no effective light penetration, hence the productivity rate is very low.
Question 16.
Discuss the gross primary productivity is more efficient than net primary productivity.
Grass primary productivity (GPP)
Answer:
The grass primary productivity is the total amount of food energy (or) biomass produced by autotrophs through the process of photosynthesis without respiratory loss in the plant.
Net primary productivity (NPP)
- But the net primary productivity is the proportion of energy, which remains after respiration loss from the gross primary productivity in the plant. NPP = GPP – Respiration
- So, gross primary productivity is more efficient than net primary productivity.
Question 17.
Pyramid of energy is always upright. Give reasons
Answer:
The energy pyramid represents a successive energy flow at each trophic level in an ecosystem. There is a gradual decrease in energy transfer at successive tropic levels from producers to higher levels, hence the pyramid of energy is always upright.
Question 18.
What will happen if all producers are removed from ecosystem?
Answer:
- The removal of all the producers would cause the collapse of the entire food web.
- Primary consumers (or) herbivores, which feed on producers directly would die off because they would have nothing to eat.
- All the other animals in the food web would die too, because their food supplies would have gone.
- The population of the consumers would fall as the population of the producer fell.
- Producers are maintaining C02 and oxygen level in the atmosphere.
- If the producers are removed C02 and 02 cycle will be in imbalance in the atmosphere.
- It will leads to the depletion of respiratory gas oxygen as it is a by product of photosynthesis
Question 19.
Construct the food chain with the following data. Hawk, plants, frog, snake, grasshopper.
Answer:
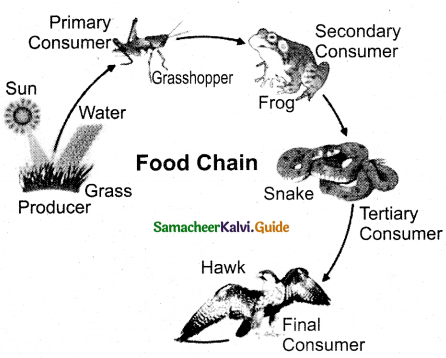
- Food chain with plants → grasshopper → frog → snake → hawk
- The movement of energy from producers upto top carnivores is known as food chain.
- In this food chain energy flows from producers (plants) to primary consumers (grasshopper) to secondary consumer (frog) to tertiary consumer (snake) to predator (hawk)
- It shows linear network link.
![]()
Question 20.
Name of the food chain which is generally present in all type of ecosystem. Explain and write their significance.
Answer:
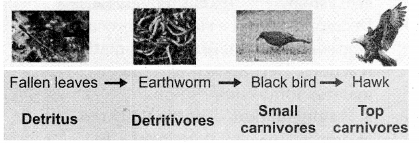
Detritus food chain is generally present in all type of ecosystem.
Detritus food chain:
This type of food chain begins with dead organic matter which is an important source of energy. A large amount of organic matter is derived from dead plants, animals, and their excreta. This type of food chain is present in all ecosystems.
The transfer of energy from the dead organic matter, is transferred through a series of organisms called detritus consumers (detritivores)- small carnivores – large (top) carnivores with repeated eating and being eaten respectively. This is called the detritus food chain.

Significance:
- The detritus (dead plants, animals and their excreta) are breakdown into simple organic matter by the decomposers.
- It is an essential process for recycling and balancing the nutrient pool in an ecosystem.
Question 21.
Shape of pyramid in a particular ecosystem is always different in shape. Explain with example.
Answer:
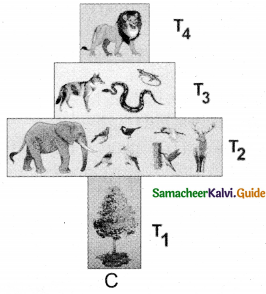
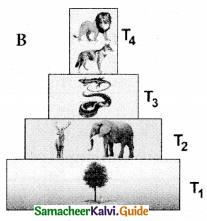
In a forest ecosystem the pyramid of number is spindle in shape, it is because the base (T1) of the pyramid occupies large sized trees (Producer) which are lesser in number. Herbivores (T2) (Fruit-eating birds, elephant and deer) occupying second trophic level, are more in number than the producers. In final trophic level (T4), .tertiary consumers (lion) are lesser in number than the secondary consumer (T3) (fox and snake).
![]()
Question 22.
Generally human activities are against to the ecosystem, whereas you a student how will you help to protect the ecosystem?
Answer:
To protect the ecosystem, we have to practice the following in our daily life.
- Buy and use only eco-friendly products and recycle them.
- Grow more trees.
- Choose sustained farm products (vegetables, fruits, greens, etc.) > Reduce the use of natural resources.
- Recycle the waste and reduce the amount of waste you produce.
- Reduce consumption of water and electricity.
- Reduce or eliminate the use of household chemicals and pesticides.
- Maintain your cars and vehicles properly. (In order to reduce carbon emission)
- Create awareness and educate about ecosystem protection among your friends and family members and ask them to find out solution to minimize this problem.
Question 23.
Generally in summer the forest are affected by natural fire. Over a period of time it recovers itself by the process of successions. Find out the types of succession and explain.
Answer:
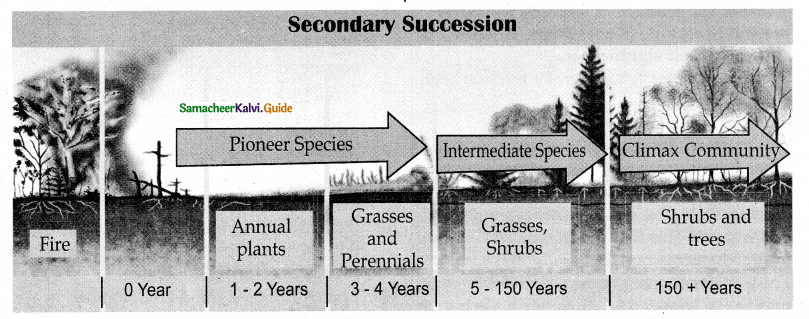
1. Primary succession:
The development of plant community in a barren area where no community existed before is called primary succession. The plants which colonize first in a barren area is called pioneer species or primary community or primary colonies. Generally, Primary succession takes a very long time for the occurrence in any region.
Example: Microbes, Lichen, Mosses.
2. Secondary succession:
The development of a plant community in an area where an already developed community has been destroyed by some natural disturbance (Fire, flood, human activity) is known as secondary succession.
| Primary succession | Secondary succession |
| 1. Developing in an barren area | Developing in disturbed area |
| 2. Initiated due to a biological or any other external factors | Starts due to external factors only |
| 3. No soil, while primary succession starts | It starts where soil covers is already present |
| 4. Pioneer species come from outside environment | Pioneer species develop from existing environment |
| 5. It takes more time to complete | It takes comparatively less time to complete |

Generally, This succession takes less time than the time taken for primary succession. Example: The forest destroyed by fire may be re-occupied by herbs over period of times.
3. Autogenic succession:
Autogenic succession occurs as a result of biotic factors. The vegetation reacts with its environment and modifies its own environment causing its own replacement by new communities. This is known as autogenic succession.
Example: In forest ecosystem, the larger trees produce broader leaves providing shade to the forest floor area. It affects the shrubs and herbs which require more light (heliophytes) but supports the shade tolerant species (sciophytes) to grow well.
4. Allogenic succession:
Allogeneic succession occurs as a result of abiotic factors. The replacement of existing community is caused by other external factors (soil erosion, leaching, etc.,) and not by existing organisms.
Example : In a forest ecosystem soil erosion and leaching alter the nutrient value of the soil leading to the change of vegetation in that area.
5. Autotrophic succession:
If the autotrophic organisms like green plants are dominant during the early stages of succession it is called autotrophic succession, this occurs in the habitat which is rich in inorganic substances. Since, green plants dominate in the beginning of this succession, there is a gradual increase in organic matter and subsequently the energy flow in the ecosystem.
6. Heterotrophic succession:
If heterotrophic organisms like bacteria, fungi, actinomycetes, and animals are dominant during the early stages of succession it is called heterotrophic succession. Such a succession takes place in organic habitats. Since heterotrophs dominate in the beginning of such succession, there will be a gradual decrease in the energy content.
![]()
Question 24.
Draw a pyramid from following details and explain in brief.
Quantities of organisms are given – Hawks – 50, plants – 1000. rabbit and mouse – 250 +250, pythons and lizard- 100 + 50 respectively.
Answer:
- A graphical representation of the amount of organic material (biomass) present at each successive trophic level in an ecosystem is called pyramid of biomass.
- In grassland and forest ecosystems there is a gradual decrease in biomass of organisms at successive trophic levels from producers to top carnivores (tertiary consumer)
- Therefore these two ecosystems show pyramids as upright

- No.of producers → 1000
- No.of primary consumers → 500
- No.of secondary consumer → 150
- No.of the tertiary consumer is lesser than Secondary consumers (50)
Question 25.
Various stages of succession are given below. From that rearrange them accordingly. Find out the type of succession and explain in detail.
Reed-swamp stage, phytoplankton stage, shrub stage, submerged plant stage, forest stage, submerged free-floating stage, marsh meadow stage.
Answer:
Reed-swamp stage, phytoplankton stage, shrub stage, submerged plant stage, forest stage, submerged free floating stage and marsh medow stage.
(1) Phytoplankton stage – It is the first stage of succession consisting of the pioneer community like blue green algae, green algae, diatoms, bacteria, etc., The colonization of these organisms enrich the amount of organic matter and nutrients of pond due to their life activities and death. This favors the development of the next serai stages.
(2) Submerged plant stage – As the result of death and decomposition of planktons, silt brought from land by rain water, lead to a loose mud formation at the bottom of the pond. Hence, the rooted submerged hydrophytes begin to appear on the new substratum.
Example: Vallisneria and Hydrilla etc. The death and decay of these plants will build up the substratum of pond to become shallow.
(3) Submerged free floating stage – During this stage, the depth of the pond will become almost 2-5 feet Hence, the rooted hydrophytic plants and with floating large leaves start colonising the pond.
Example: Rooted floating plants like Nelumbo, Nymphaea and some free floating species like Azolla, and Pistia are also present in this stage. By death and decomposition of these plants, further the pond becomes more shallow.
(4) Reed-swamp stage – It is also called an amphibious stage. During this stage, rooted floating plants are replaced by plants which can live successfully in aquatic as well as aerial environment.
Example: Typha, Phragmites, Sagittaria and Scirpus etc. At the end of this stage, water level is very much reduced, making it unsuitable for the continuous growth of amphibious plants.
(5) Marsh meadow stage – When the pond becomes swallowed due to decreasing water level, species of Cyperaceae and Poaceae colonise the area. They form a mat-like vegetation with the help of their much branched root system. This leads to an absorption and loss of large quantity of water. At the end of this stage, the soil becomes dry and the marshy vegetation disappears gradually and leads to shurb stage.
(6) Shrub stage – Here areas are invaded by terrestrial plants like shrubs (Salix and Comus) and trees (Populus and Alnus). These plants absorb large quantity of water and make the habitat dry. Further, the accumulation of humus with a rich flora of microorganisms produce minerals in the soil, ultimately favouring the arrival of new tree species in the area.
(7) Forest stage – It is the climax community of hydrosere. A variety of trees invade the area and develop any one of the diverse type of vegetation.
Example.Temperate mixed forest (Ulmus, Acer and Quercus), Tropical rain forest (Artocarpus and Cinnamomum ) and Tropical deciduous forest (Bamboo and Tectona).
![]()
12th Bio Botany Guide Ecosystem Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The most stable and productive ecosystem seen on the earth is _____
a. Mangrove ecosystem
b. Grassland ecosystem
c. Pond ecosystem
d. Forest ecosystem
Answer:
d. Forest ecosystem
Question 2.
In an ecosystem, the energy flow is always
a. Unidirectional
b. Top to bottom
c. Chain form
d. Multi directional
Answer:
a. Unidirectional
![]()
Question 3.
Grass 2 Goat 2 Man. This is the grazing food chain choose the correct option.
a. Goat is primary producer, secondary trophic level and herbivore
b. Grass is a primary producer, herbivore, and first trophic level.
c. Goat is a primary consumer, herbivore, second trophic level
d. Goat is a primary consumer, herbivore, first trophil level
Answer:
c. Goat is a primary consumer, herbivore, second trophic level
Question 4.
Choose the incorrect statement from following
a. Pyramid of energy is always upright
b. In grass land and forest ecosystem pyramid of biomass as upright.
c. Pyramid of number shows three different shape of pyramids like upright, spindle and inverted
d. Food web is used for the construction of ecological pyramid.
Answer:
d. Food web is used for the construction of ecological pyramid.
Question 5.
Assertion : If the decomposers were removed completely from the ecosystem the functioning of ecosystem will be adversely affected.
Reason : The cycling of nutrients between abiotic and biotic components will be blocked
a. A and R are correct
b. A and R are not correct
c. A is correct R is wrong
d. R is not a correct explanation for A
Answer:
a. A and R are correct
![]()
Question 6.
Assertion : An ecological pyramid is a diagrammatic (or) graphic representation of the trophic structure and function.
Reason : Various trophic levels of a food chain are considered in ecological pyramid.
a. Both are not correct
b. R is not related to A
c. Both A and R are wrong
d. R is the correct explanation of A
Answer:
d. R is the correct explanation of A
Question 7.
Match the following
Read this statement and fill it with correct (A) and (B)
Carbon stored in fossil fuel is ……(A)……….. and carbon stored in the biosphere is …………..(B)……..
The only one correct option for the two blank is
| A | B |
| a. Brown carbon | Black carbon |
| b. Grey carbon | Green carbon |
| c. Black carbon | Brown carbon |
| d. Green carbon | Blue carbon |
Answer:
b. Grey carbon – Green carbon
![]()
Question 8.
Match the following and find the correct answer
| Column I | Column II |
| i. Green carbon | A. Carbon in industrialised forest |
| ii. Grey carbon | B. Carbon in atmosphere |
| iii. Blue carbon | C. Carbon in fossil fuel |
| iv. Brown carbon | D. Carbon in biosphere |
a. (i) – B; (ii) – C; (iii) – D; (iv) – A
b. (i) – C; (ii) – D; (iii) – B; (iv) – A
c. (i) – B; (ii) – A; (iii) – D; (iv) – C
d. (i) – D; (ii) – C; (iii) – B; (iv) – A
Answer:
d. (i) – D; (ii) – C; (iii) – B; (iv) – A
![]()
Question 9.
Choose the incorrect pair
| a) Humification | Detritus to dark humus |
| b) Eluviation | Movement of organic and inorganic compound to lower layer of soil |
| c) Detritus | Dead plants and animal waste |
| d) Fragmentation | Release of inorganic nutrients from the humus. |
Answer:
d. Fragmentation – Release of inorganic nutrients from the humus.
Question 10.
Choose the correct pair
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Grasses, shrubs | 5 -150 years |
| B. Grasses and perennials | 3-4 years |
| C. Annual plants | 1-7 years |
| D. Shrubs and trees | 150 + years |
a. B and C
b. A and C
c. B, C and D
d. A, B and D
Answer:
d. A, B and D
![]()
Question 11.
The plants which colonize first in a barren …………..
area is called
a. Pioneers
b. Serai
c. Autogenic
d. Allogenic
Answer:
a. Pioneers
Question 12.
The term ‘ecosystem’ was proposed by……………..in the year 1935.
a. A.G. Hoxley
b. A.G.Tansley
c. Odum
d. Lindeman
Answer:
b. A.G. Tansley
![]()
Question 13.
The position of organisms in food chain is refers to
a. Ecosystem
b. Trophic level
c. Food chain
d. Ten percent law
Answer:
b. Trophic level
Question 14.
Temperate mixed forest, tropical rain forest tropical deciduous forest are
a. Climax communities
b. T ertiary communities
c. Primary communities
d. Secondary communities
Answer:
a. Climax communities
Question 15.
Assertion and Reason
Assertion : Photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) which is between the range of 400 – 700 nm wave length.
Reason : At night PAR is zero and during midday in the summer, PAR often reaches 2000 – 3000 millimoles/square meter/second
a. R does not explains A
b. R explaining A
c. A is correct R is wrong
d. Both A and R are wrong
Answer:
a. R does not explains A
Question 16.
Choose the correct statement:
| Column I | Column II |
| a. Herbivore | Zooplankton and grass hopper |
| b. Carnivore | First trophic level |
| c. Secondary consumer | Cow, goat |
| d. Top carnivore | Birds, snake and wolf |
Question 17.
Choose the correct statement
a. Only 2 – 10% of solar energy is used by green plants for photo synthesis
b. Only 56% of the solar energy is used by green plants for photosynthesis.
c. Productivity can be expressed in terms of kcal / m2 / 10 year
d. Limnology is the study about ocean.
Answer:
a. Only 2 – 10% of solar energy is used by green plants for photo synthesis
![]()
Question 18.
Blue carbon ecosystems is related to …………….
a. Carbon sequestration
b. Productivity
c. Visibility
d. Phosphorus cycle
Answer:
a) Carbon sequestration
Question 19.
Choose the correct pair related to this statement
Secondary productivity can be defined as
a. Amount of energy in the tissues of consumer (or) heterotrophs
b. Amount of biomas formation
c. Rate of energy formation
d. Rate of energy utilization
Answer:
a. Amount of energy in the tissues of consumer (or) heterotrophs
Question 20.
Which one of the following will be the shape of the pyramid. If you consider the following statement.
“No. of fruit eating birds, elephant, deer depends on large sized tree (producer) which are lesser in number and lesser number of secondary consumer (fox and snake) and final trophic level tertiary consumer lion.
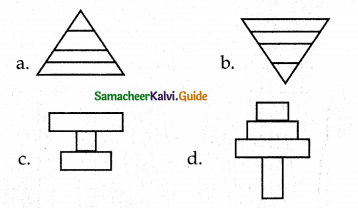
Answer:
d.
Question 21.
Choose the odd one out
a. Flagship species
b. Rehabilitation
c. Maintaining biodiversity
d. Anthropogenic activities
Answer:
d. Anthropogenic activities
![]()
Question 22.
Ecological succession refers to …………………
a. Gradual, fairly changes and pH development of a given area
b. Linking of ecosystem
c. Energy transfer
d. Biotic communities
Answer:
a. Gradual, fairly changes and pH development of a given area
Question 23.
Succession occur in which area ?
Answer:
Flooded, earthquake and anthropogenic area
Question 24.
Plant succession in saline water is…………
Answer:
Halosere
Question 25.
The replacement of existing community by other factors like soil erosion, leaching etc. is …………..
Answer:
Allogenic succession.
![]()
Question 26.
The type of succession takes less time to the time taken for primary succession ?
Answer:
Secondary succession
Question 27.
The type of succession in which organisms like bacteria, fungi, actinomycetes and animals are dominant during its early stages is …………..
a. Heterotrophic
b. Allogenic
c. Autotrophic
d. Autogenic
Answer:
a. Heterotrophic
Question 28.
Match the following:
| Column I | Column II |
| A) Allogenic succession | i) Rock, Disturbed area |
| B) Autotrophic succession | ii) Biotic factors |
| C) Autogenic succession | iii) Rich in inorganic substances |
| D) Secondary succession | iv) Abiotic factors |
a. A – iv), B – iii), C – ii), D – i)
b. A – i), B – ii), C – iii), D – iv)
c. A – ii), B – iii), C – iv), D – i)
d. A – iii), B – ii), C – i), D – iv)
Answer:
a. A – iv), B – iii), C – ii), D-i)
![]()
Question 29.
Pioneer community like blue green algae, green algae, diatoms, bacteria etc are present in ……….. stage of hydrosere.
Answer:
Phytoplankton stage
Question 30.
Rooted floating plants like Nelumbo Nymphaea and Trapa and free floating SPS wolffia and lemna are present in this stage is
Answer:
Submerged free floating stage
Question 31.
Submerged hydrophytes like char a, utricularia, vallisneria, hydrilla are present in the ………… stage of hydrosere.
Answer:
Submerged plant.
Question 32.
Mat – like vegetation with the help of much branched root system is the character of ………….. stage of hydrosere
Answer:
Marsh meadow.
Question 33.
Species of cyperaceae and poaceae like carex, juncus cyperus and eleocharis colonise in this i area is
Answer:
Marsh meadow stage
Question 34.
Salix and cornus (shrubs) and trees like populous and alnus are present in the …………… stage.
Answer:
Shrub stage
![]()
Question 35.
Say true or false
Reduce, reuse, recycle are “three R” s for waste management.
Answer:
True
Question 36.
…………… is the best example for urban eco restoration in the state of Tamilnadu.
Answer:
Urban ecosystem restoration model.
Question 37.
Initiation of plant succession on barren rock is …………………
Answer:
Lithosere
Question 38.
Succession with minimal amount of water is
a. Merosere
b. Psammosere
c. Halosere
d. Xerosere
Answer:
d. Xerosere
Question 39.
Succession in a fresh water ecosystem is
a. Merosere
b. Hydrosere
c. Lithosere
d. Halosere
Answer:
b. Hydrosere
Question 40.
Study of interaction between living and non- living components is
a. Biomass
b. Food chain
c. Food web
d. Ecosystem
Answer:
d. Ecosystem
![]()
Question 41.
Which of the following is not related to photosynthetic active radiation.
a. 400-700 nm
b. 10% is held by ozone
c. 2-10% by green plants
d. 46% reaches earth surface
Answer:
d. 46% reaches earth surface
Question 42.
Which of the following light is efficient for
photo-synthesis.
a. Blue and red
b. Blue and green
c. Blue and white
d. Blue and violet
Answer:
a. Blue and red
Question 43.
Which of the following determine the productivity of different ecosystem.
a. Fixation of radiant energy
b. Population
c. Size of ecosystem
d. Number of plants
Answer:
a. Fixation of radiant energy
![]()
Question 44.
Which is the right representation of detritus food chain?
a. Grass Earthworm → Black bird → Hawk
b. Grass Mouse → Snake Eagle
c. Fallen leaves → Earthworm → Black bird →Hawk
d. Plants → Rabbit → Snake → Eagle
Answer:
c. Fallen leaves → Earthworm → Black bird →Hawk
Question 45.
NPP of whole biosphere is estimated to be …………. about billion tons dry weight/year
a. 140
b. 170
c. 150
d.160
Answer:
b. 170
Question 46.
NPP of oceanic producers is only ……………… billiob tons/year in unit time.
a. 55
b. 45
c. 56
d. 54
Answer:
a. 55
Question 47.
During energy transfer from one trophic level to other only 10% stored at every level this is related to
a. First law of thermodynamics
b. Second law of thermodynamics
c. Ten percent law
d. Law of thermodynamics
Answer:
c. Ten percent law
![]()
Question 48.
The commonly occurring pioneer species in
xerich succession
a. Lichens
b. Mosses
c. Bryophytes
d. Pteridophytes
Answer:
a. Lichens
Question 49.
Lowest productivity is seen in
a. Ocean
b. Grass land
c. forest
d. savannah
Answer:
a. Ocean
Question 50.
The term biosphere is used for
a. Ecosystem
b. Plants and animals
c. All living organism
d. The part of the earth with life
Answer:
d. The part of the earth with life
Question 51.
Bio geo chemical cycle refers to
a. Cycling of nutrients
b. Cycling of nutrients with ecosystem
c. Water cycle
d. Cycling of chemicals substrances
Answer:
b. Cycling of nutrients with ecosystem
![]()
Question 52.
Which of the following does not contain phosphorous?
a. Phospholipids
b. DNA, RNA
c. ATP, NADP
d. Respiration
Answer:
d. Respiration
Question 53.
The ecosystem with (or) without human interference is
a. Terrestrial
b. Natural
c. Artificial
d. Lotic
Answer:
b. Natural
Question 54.
Examine the ecological pyramid given below and select the type of it represent
a. Upright pyramid of biomass
b. Upright pyramid of number
c. Inverted pyramid of biomass
d. Inverted pyramid of number
Answer:
a. Upright pyramid of biomass
![]()
Question 55.
The organisms which eat both plants and animals are called ……………….
Answer:
Omnivores
Question 56.
When sparrow eats insects and worms it is a
a. Primary consumer
b. Secondary consumer
c. Tertiary consumer
d. Carnivore
Answer:
b. Secondary consumer
Question 57.
Imagine number of fruit eating birds and insects feeding or a big tree what kind of pyramid would be ?
a. Inverted pyramid of number
b. Inverted pyramid of energy
c. Upright pyramid
d. Upright pyramid of energy
Answer:
a. Inverted pyramid of number
Question 58.
Which of the following is natural ecosystem.
a. Pond and lake
b. Rice field
c. Maize fi eld
d. Aquarium
Answer:
a. Pond and lake
![]()
Question 59.
Which one of the following food chain refers inverted pyrmid? Q23D
a. Grasses → Rats → Snake → Hawk
b. Banyan tree → Birds → Beetles → Fungi
c. Phytoplanktons → Zooplanktons → Fishes → snakes
d. Plants Rabbits → Fox → Hawk
Answer:
c. Phytoplanktons → Zooplanktons → Fishes → snakes
Question 60.
The quantity of energy present in the universe is constant it is related to
a. Second law of thermodynamics
b. First law of thermodynamics
c. Ten percent lawd. Law of thermodynamics
Answer:
b. First law of thermodynamics
II. Two Marks
Question 1.
What do you mean standing quality (or) Standing state of abiotic components ?
Answer:
- Abiotic components play vital role in an ecosystem.
- The total inorganic substances present in any ecosystem at a given time is called standing quality (or) standing state.
Question 2.
In most of the ecosystem, which one is called autotrophs why?
Answer:
- Autotrophs are organism which can manufacture the organic compounds from simple inorganic components through a process called photo synthesis.
- Eg. Green plants. They are called as producers.
![]()
Question 3.
What is standing crop?
Answer:
- The amount of living materials present in a population at a given time is known as standing crop.
- Which is expressed in terms of number (or) biomass per unit area.
Question 4.
What are the functions of an ecosystem?
Answer:
- Its functions are energy creation and sharing of energy.
- It is the way to cycling of materials between the living and nonliving component of the ecosystem.
Question 5.
Why biomass production is called productivity of an ecosystem?
Answer:
- The rate of biomass production per unit area in a unit time is called productivity.
- It can be expressed in terms of gm / m2 / yr (or) kcal / m2 / yr
Question 6.
What is biomass? How it is measured?
Answer:
- The total quantity (or) weight of organism in a give area is called biomass.
- It can be measured as fresh weight (or) dry weight (or) carbon weight of organisms.
![]()
Question 7.
Write the difference between gross primary productivity and gross secondary productivity ?
Answer:
Grass Primary Productivity :
- The total amount of food energy (or) biomass produced in an ecosystem
- It is done by autotrophs through the process called photosynthesis
Grass Secondary Productivity :
- The total amount of plant material ingested minus (-) materials lost as faeces.
- It is done by herbivores by the process called ingestion.
Question 8.
Differentiate net primary productivity from net secondary productivity ?
Answer:
Net Primary Productivity :
- The proportion of energy which remains after respiration loss in the plant.
- Net primary productivity is calculated in producers.
Net Secondary Productivity:
- Stored energy (or) biomass per unit area per unit time after respiratory loss.
- Net secondary productivity is calculated in consumers.
![]()
Question 10.
Which factors may affect the primary productivity of plants (or) producers ?
Answer:
Primary productivity of plants affected by
- Plant species of an area.
- Photosynthetic capacity
- Availability of nutrients
- Solar radiation
- Precipitation
- Soil type
- opographic factors
- Environmental factors.
Question 11.
How does NPP calculated from GPP?
Answer:
- NPP = GPP – Respiration
- Thus it is the difference between gross primary productivity and respiration is net primary productivity.
Question 12.
Why grey carbon different from brown carbon?
Answer:
- Grey carbon is stored in fossil fuel like coal, oil and biogas deposits in the lithosphere
- Brown carbon is stored in industrialized forest wood used in making commercial articles.
Question 13.
What are the sources for blue carbon and black carbon
Answer:
- Blue carbon is stored in the atmosphere.
- Black carbon is emitted from diesel engine gas and coal fired power plants.
Question 14.
What is energy flow ?
Answer:
- The transfer of energy in an ecosystem between trophic levels can be termed as energy flow.
- It is the key function in an ecosystem.
![]()
Question 15.
If crow is absent in an ecosystem what would happen?
Answer:
- The crow has omnivorous type of Nutrition.
- They eat cereals, fruit and seeds, small insects and worms.
- They eat dead & decaying animals body and keep the environment clean, so known as scavengers of the sky.
- They occupy several trophic levels in the food chain.
- When they eat some fruits they swallow the seeds which are dispersed along with the excreta.
- However unlike certain pollination and insects they are not considered vital organisms because their loss from the ecu system mav cause drastic impacts, leading to the extinction of rhe. it partk ular plant species which can’t be pollinated in the absence of the particular insect/bird.
- However when crow is absent, then its niche in the food chain will be kept vacant ecological, this will be drastic change occur some other organism mav evolve to occupy the same neche in the long run.
Question 17.
Conversion of light energy into chemical energy which law is related to this ?
Answer:
The first law of thermodynamics is related to this statement.
![]()
Question 18.
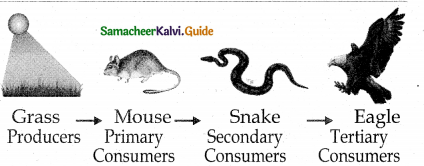
Construct the diagrammatic representation of grazing food chain.
Answer:
Question 19.
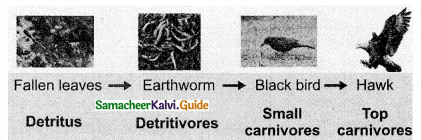
Draw the diagrammatic representation of detritus food chain.
Answer:
![]()
Question 20.
Food web is known as basic unit of ecosystem. Why ?
Answer:
- The interlocking pattern of a number of food chain form a weblike arrangement called food web.
- It is known as basic unit of ecosystem to maintain its stability in nature.
- It is called homeostasis.
Question 21.
Why ecological pyramids are called Eltonianpyramids ?
Answer:
- The concept of ecological pyramids was introduced by Charles Elton in the year 1927.
- Thus ecological pyramids are called Eltonian pyramids.
Question 22.
What is ecological pyramid ?
Answer:
Graphic representation of the trophic structure and function at successive trophic levels of an ecosystem is called ecological pyramid.
Question 23.
Why the pyramids of energy is always upright?
Answer:
- There is a gradual decrease in energy transfer at successive tropic levels from producers to the upper levels.
- Therefore, the pyramid of energy is always upright.
![]()
Question 24.
Define pyramid of energy.
Answer:
The graphical representation of energy flow of each successive trophic level in an ecosystem is called pyramids of energy.
Question 25.
Name the process which is essential for recycling and balancing the nutrient in an ecosystem?
Answer:
Decomposition is a process in which the detritus are breakdown into simple organic matter by the decomposers.
Question 26.
Write the difference between limnology and oceanography ?
Answer:
Limnology
It is the studv of biological, chemical physical and geological components of inland fresh water aquatic ecosystem (ponds, lakes etc)
Oceanography :
It is the study of biological, chemical, physica I and geological components of ocean.
Question 27.
Blue carbon ecosystems are very important to nature. Why?
Answer:
- Sea grasses and mangroves of estuarine and coastal ecosystems are the most efficient in carbon sequestration.
- Hence these ecosystems are called blue carbon ecosystem.
Question 28.
What is carbon sequestration?
Answer:
Carbon sequestration is the process of capturing and storing carbondioxide from the atmosphere in carbon sinks such as ocean and forest.
![]()
Question 29.
Odd one out and give reason.
Answer:
Provision of habitat, nutrient recycling, primary production, succession Odd one out: Succession.
Reason : Replacement of one type of plant community by other of the same place is known as succession. While others are supporting services of ecosystem services.
Question 30.
Odd one out and give reason.
Lichen, blue green algae, green algae diatoms, bacteria.
Answer:
Odd one out: Lichen
Reason : Lichen is related to primary succession. While others are related to phytoplankton stage of hydrosere.
Question 31.
Write the slogan for the safety of the environment.
Answer:
“Use Ecosystem. But don’t lost ecosystem. Make it sustainable.”
![]()
Question 32.
Define fragmentation.
Answer:
The breaking down of detritus in to smaller particles by detritivores like bacteria, fungi and earth worm is known as Fragmentation.
Question 33.
What is Humification?
Answer:
It is a process by which simplified detritus is changed into dark coloured amorphous substance called humus.
Question 34.
Define oceanography.
Answer:
It is the study of biological chemical, physical and geogical components of ocean.
Question 35.
In different food chains of different ecosystem the placement of man is not mentioned. You give placement in a suitable food chain and give reason for your answer.
Answer:
- Placement of man in the food chain is not clear, due to the various dietary choices of each human.
- Many are omnivores – consuming both plants & meat.
- They may be kept on the 3rd or even on the 4th trophic level.
- Meat eaters (cow, goat are herbivores) are a part of 3rd trophic level.
- If you were to eat Salmon, – Salmon consume other fish – and so you are in the 4th trophic
![]()
III. Three Marks
Question 1.
What is photosynthetically active radiation ?
Answer:
- The amount of light available for photosynthesis of plants is called photosynthetically active radiation.
- Which is between the range of 400 – 700 nm of wave length.
- Generally plants absorb move blue and red light for efficient photosynthesis.
- Only 2 -10% of the solar energy is used by green plants for photosynthesis.
Question 2.
Differentiate green carbon from grey carbon.
Answer:
Green Carbon :
- It is the carbon stored in the biosphere.
- It is done by the process of photosynthesis by green plants.
Grey Carbon :
- It is the carbon stored in fossil fuel. (Coal, oil, biogas)
- It is done by the process of decomposition in the lithosphere.
Question 3.
Differentiate primary productivity from secondary productivity.
Answer:
| Primary Productivity | Secondary Productivity |
| 1. It is the chemical energy (or) organic matter generated by autotrophs | It is the amount of energy stored in the tissues. |
| 2. It is produced by the process called photosynthesis and chemosynthesis. | It is consumed by heterotrophs (or) consumers from the producers. |
| 3. It is the source of energy for all organisms from bacteria to human | It is the source of energy present in theparticular organism. |
![]()
Question 4.
“The energy transformation results in the education of the free energy of the system”. What does it states ?
Answer:
- It states second law of thermodynamics.
- Usually energy transformation cannot be 100% efficient.
- As energy is transformed from one organism to another in the form of food, where as a large part of energy is dissipated as heat through respiration. (Eg.) Ten percent law.
Question 5.
What is ten percent law?
Answer:
- This law was proposed by Lindeman (1942)
- During transfer of food energy from one trophic level to other, only about 10% stored at every level and rest of them 90% is lost in respiration, decomposition in the form of heat.
- Hence the law is called ten percent law.
Question 6.
Which type of food chain is present in all ecosystem ? (or) What is detritus food chain?
Answer:
- It begins with dead organic matter.
Which is an important source of energy - Transfer of energy from Detritus → Detritivores → Small carnivores → Top carnivores
- This type of food chain is present in all ecosystems.
Question 7.
Complete the missing organisms of food web in grassland ecosystem.
Answer:
- A – Rabbit
- B – Mouse
- C – Lizard
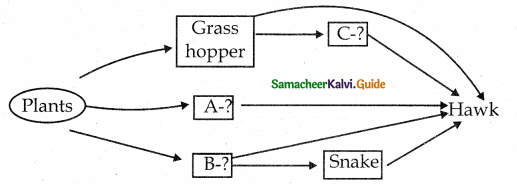
![]()
Question 8.
What are the importance of studying food web ? (or) What are significant of food web? Is there any significance in maintaining food web?
Answer:
- Food web is constructed to describe species interaction called direct interaction.
- It can be used to illustrate indirect interaction among different species.
- It can be used to reveal different patterns of energy transfer in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
Question 9.
What are the different shapes of pyramids present in pyramids of number?
Answer:
- There are three different shapes of pyramids present in pyramid of number.
- Pyramid of number in grassland and pond ecosystem are always upright in shape.
- In forest ecosystem it is spindle shaped.
- In parasite ecosystem it is inverted.
Question 10.
What are the different shapes of pyramids present in pyramid of biomass?
Answer:
According to pyramid of biomass
Eco System – Shape :
Grassland and forest – Upright
Pond ecosystem – Inverted
![]()
Question 11.
Why pyramids of biomass in grass land and forest ecosystem is always upright ?
Answer:
- In grassland and forest there is a gradual decrease in biomass of organisms from producers to top carnivore.
- There fore it is always upright.
Question 12.
Why pyramids of biomass in pond ecosystem is always inverted in shape?
Answer:
- In pond ecosystem the bottom of the pyramid is occupied by the producers which are small organisms posses least biomass.
- So the value gradually increases towards the tip of the pyramid.
- Therefore pyramid of biomass is always inverted in shape.
Question 13.
Differentiate humification and mineralisation.
Answer:
Humification :
- It is the process by which simplified detritus into dark coloured amorphous substance called humus.
- Humus is resistant to microbial action.
Mineralisation :
- Release of inorganic nutrients from the humus is called mineralisation.
- Some microbes are involved in release of nutrients.
Question 14.
Define catabolism:
Answer:
The decomposers produce some extracellular enzymes in their surroundings to break down complex organic and inorganic compounds into simpler ones called catabolism.
![]()
Question 15.
What is leaching or eluviation ? (or) Which process of decomposition helpful to enrich lower layer of soil ?
Answer:
The movement of decomposed water soluble organic and inorganic compounds from the surface to the lower layer of soil by water is called eluviation (or) leaching.
Question 16.
What is bio-geo chemical cycle ?
Answer:
Circulation of nutrients within the ecosystem (or) biosphere is known as biogeo chemical cycles, (or) Cycling of materials.
Question 17.
Which cycles are called sedimentary cycles ? Why?
Answer:
- Phosphorus, sulphur, calcium are called as sedimentary cycles.
- Which are present as sediments on earth.
- Sedimentary cycles are very slow its take a long time to complete its circulation, because nutrient elements may get locked in the reservoir pool.
Question 18.
Wihat is carbon cycle?
Answer:
- The circulation of carbon between organisms and environment is known as carbon cycle.
- Cycling of carbon between organisms and atmosphere is consequence (event) of two reciprocal process of photosynthesis and respiration.
![]()
Question 19.
What is ecosystem resilience ? (or) Ecosystem robustness?
Answer:
Ecosystem is damaged by disturbances from fire, flood, predation, infection, drought, etc., removing a great amount of biomass. However, ecosystem is endowed with the ability to resist the damage and recover quickly. This ability of ecosystem is called ecosystem resilience or ecosystem robustness.
Question 20.
What are the ways to go green and save green?
Answer:
- Close the tap when not in use.
- Switch off the electrical gadgets when not in use.
- Never use plastics and replace them with biodegradable products.
- Always use ecofriendly technology and products.
Question 21.
Draw and write the 3 Rs for the safety and benefits of the environment.
Answer:

The three R’s are – reduce, reuse and recycle. It refers to the changing of one’s lifestyle for the safety and benefits of the environments (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle)
Question 22.
Which is significance of food web?
Answer:
- Food web is constructed to describe species interaction called direct interaction
- It can be used to illustrate indirect interaction among different species.
- It can be used to study bottom up or top down control of community structure.
- It can be used to reveal different patterns of energy transfer in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
![]()
Question 23.
What are the types of carbon?
Answer:
- Green carbon : carbon stored in the biosphere by the process of photosynthesis.
- ray carbon: carbon stored in fossil fuel (Coal, oil and biogas deposits in the lithosphere).
- Blue carbon : carbon stored in the atmosphere and oceans.
- Brown carbon: carbon stored in industrialized forests (wood used in making commercial articles)
- Black carbon : carbon emitted from gas, diesel engine and coal fired power plants.
IV. Five Marks
Question 1.
Define ecosystem. Describe the components of ecosystem
Answer:
The term ecosystem was proposed by A.G. Tansley (1935), who defined it as.
- The system resulting from the integration of all the living and non living factors of the environment.
Whereas Odum (1962) defined ecosystem as - Eco system is structural and functional unit of ecology.
- Ecosystem comprises of two major components
i) Abiotic ii) Biotic components
i) Abiotic (non-living) components:
Edaphic Factors – Soil, air, soil water and pH of soil.
Topography factors – Latitude altitude Organic components – Carbohydrates, protein’s lipids and humic substances
Inorganic substances:
C, H, O, N and P . Abiotic components play vital role in any ecosystem hence it is important for standing quality.
ii) Biotic (living) components:
It includes all living organisms like plants, animal, fungi and bacteria.
- They form the trophic structures of any ecosystem.
- It has two components
i) Autotrophic components ii) Heterotrophic components
i) Autotrophic components:
Autotrophs are plants (or) producers which can manufacture the organic compounds from simple inorganic components through a process called photosynthesis.
ii) Heterotrophic components:
Heterotrophs are organisms which consume the producers are called consumers. They are two types
i) Macro consumers ii) Micro consumers
- Macro consumers are herbivores, carnivores and omnivores.
- Micro consumers are called decomposers. (Eg.) Bacteria, actinomycetes and fungi
- Biotic components are essential to construct the food chain, food web and ecological pyramids.
![]()
Question 2.
What kind of solar radiation is used in photosynthesis ? (OR)
AR is not always constant because of clouds, tree shades, air, dust particles, seasons latitudes and length of the daylight availability. (OR)
What is photosynthetically active radiation ? (OR)
How it is calculated for active photosynthesis in plants ? (OR)
From the sunlight, only 2-10% of the solar energy is used by green plants for photosynthesis. Explain why?
Answer:
- The amount of light available for photosynthesis of plants is called photosynthetically active radiation.
- Which is between the range of 400 -700 nm wavelength. Which is essential for photosynthesis and plant growth.
- Generally plants absorb more blue and red light for efficient photosynthesis.
- Of the total sunlight, 34 percent that reaching the atmosphere is reflected back into the atmosphere, moreover 10% is held by ozone.
- Remaining 56% reaches the earths surface out of this 56%, only 2 – 10% of solar energy is used by green plants for photosynthesis while the remaining portion is dissipated as heat
- PAR is generally reported as millimoles / square meter / second by using silicon photo voltic detector.
- Which detect only 400 – 700 nm wavelength of light.
- PAR values range from 0 to 3000 millimoles / square meter / second.
- At night PAR is zero and during midday in summer, PAR often reaches 2000 – 3000 millimoles /square meter / second.
Question 3.
What is primary productivity ? What are its types ? What are the factors affecting primary productivity ? (or)
What is primary productivity ? How net primary productivity is calculated ? What are the factors affecting primary productivity.
Answer:
1.Primary productivity:
The chemical energy or organic matter generated by autotrophs during the process of photosynthesis and chemosynthesis is called primary productivity. It is the source of energy for all organisms, from bacteria to human.
a. Gross Primary Productivity (GPP):
The total amount of food energy or organic matter or biomass produced in an ecosystem by autotrophs through the process of photosynthesis is called gross primary pro-ductivity
b. Net Primary Productivity (NPP):
The proportion of energy which remains after respiration loss in the plant is called net primary productivity. It is also called as apparent photosynthesis. Thus the difference between GPP and respiration is known as NPP.
NPP = GPP – Respiration
NPP of whole biosphere is estimated to be
about 170 billion tons (dry weight) per year. Out of which NPP of oceanic producers is only 55 billion tons per year in unit time.
Factors affecting primary productivity:
- Factors affecting primary productivity depends upon the plant species of an area
- Their photosynthetic capacity, availability of nutrients solar radiation, precipitation, soil type and other environmental factors.
- It varies in different types of ecosystems.
![]()
Question 4.
What is secondary productivity and its types ? In what way community productivity calculated ?
Answer:
Secondary productivity:
The amount of energy stored in the tissues of heterotrophs or consumers is called secondary productivity.
a. Gross secondary productivity:
It is equivalent to the total amount of plant material is ingested by the herbivores minus the materials lost as faeces.
b. Net secondary productivity:
Storage of energy or biomass by consumers per unit area per unit time, after respiratory loss is called net secondary productivity.
Community productivity:
The rate of net synthesis of organic matter (biomass) by a group of plants per unit area per unit time is known as community productivity.
Question 5.
How does energy flow in an ecosystem, (or)
Describe about the concept of trophic level in an ecosystem, (or)
Write about various trophic level of food chain in an ecosystem.
Answer:
- A trophic level refers to the position of an organism in the food chain.
- The number of trophic levels is equal to the number of steps in the food chain.
- The green plants (producers) occupying the first trophic level (TA are called producers.
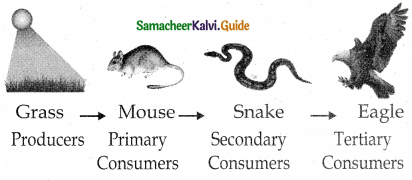
- The energy produced by the producers is utilized by the plant eaters (herbivores) they are called primary consumers and occupies the second trophic level (T2).
- Herbivores are eaten by carnivores, which occupy the third trophic level (T3).
They are also called secondary consumers or primary carnivores. - Carnivores are eaten by the other carnivores, which occupy the fourth trophic level (T4). They are called the tertiary consumers or secondary carnivores.
- Some organisms which eat both plants and animals are called as omnivores (Crow). Such organisms may occupy more than one trophic level in the food chain.

![]()
Question 6.
How does the laws of thermodynamics explain the storage and loss of energy in an ecosystem ? (or) Write about laws of thermodynamics in an ecosystem.
Answer:
Laws of thermodynamics:
The storage and loss of energy in an ecosystem is based on two basic laws of thermodynamics.
i) First law of thermodynamics
- It states that energy can be transmitted from one system to another in various forms. Energy cannot be destroyed or created.
- As a result, the quantity of energy present in the universe is constant.
- Example: In photosynthesis, the product of starch (chemical energy) is formed by the combination of reactants (chlorophyll, H2O, CO2). ‘ “
Starch is acquired from the external sources (light energy) and so there is no gain or loss in total energy. Here light energy is converted into chemical energy.
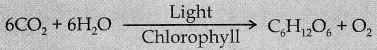
- Light energyv → Chemical energy
ii) Second law of thermodynamics Usually energy transformation cannot be 100% efficient. As energy is transferred from one organism to another in the form of food, a portion of it is stored as energy in living tissue, whereas a large part of energy is dissipated as heat through respiration. Example: Ten percent law Ten percent law : During transfer of food energy from one trophic level to other, only about 10% stored at every level and rest of them (90%) is lost in respiration, decomposition and in the form of heat. Hence, the law is called ten percent law.
Question 7.
What is food chain ? (or) How does movement takes place from producers to top carnivore? What are its types.
Answer:
- The movement of energy from producers upto top carnivores is known as food chain,
- Generally, there are two types of food chain, (1) Grazing food chain and (2) Detritus food chain.
1. Grazing food chain : Main source of energy for the grazing food chain is the Sun. It begins with the first link, producers (plants) The second link in the food chain is primary consumers (mouse) which get their food from producers. The third link in the food chain is secondary consumers (snake) which get their food from primary consumers. Fourth link in the food chain is tertiary consumers (eagle) which get their food from secondary consumers.
2. Detritus food chain : This type of food chain begins with dead organic matter which is an important source of energv. A large amount of organic matter is derived from the dead plants, animals and their excreta. This type of food chain is present in all ecosystems.
The transfer of energy from the dead organic matter, is transferred through a series of organisms called detritus consumers (detritivores)- small carnivores – large (top) carnivores with repeated eating and being eaten respectively. This is called the detritus food chain.
![]()
Question 8.
What is ecological pyramid ? Write about ecological pyramid of number.
Answer:
Graphic representation of trophic structure and function in successive trophic levels of an ecosystem is called ecological pyramid (or) Eltonian pyramid.
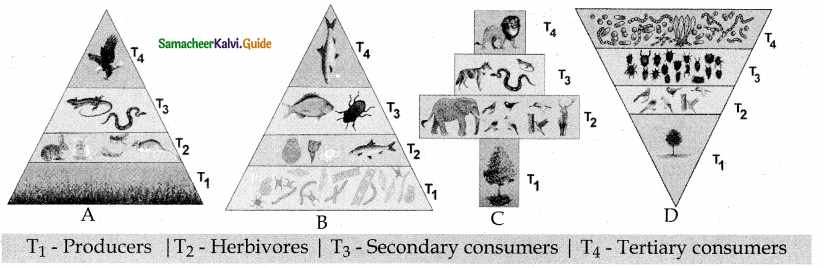
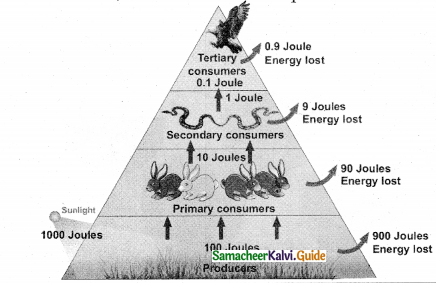
Figure 7.8 : Pyramids of numbers (individuals per unit area) in different types of ecosystems, Upright – A) Grassland ecosystem B) Pond ecosystem, Spindle shaped – C) Forest ecosystem,
Inverted – D) Parasite ecosystem
Pyramid of number:
- A graphical representation of the number of organism present at each successive trophic level in an ecosystem is called pyramid of number.
- There are different shapes, pyramid of number in grassland and pond ecosystem are always upright. Because
- There is a gradual decrease in number of organisms in each trophic level from Producer → Primary consumer then → Secondary consumer and finally → Tertiary consumer.
- Pyramid of number in forest ecosystem looks spindle shaped. Because
- In forest ecosystem, large sized tree (producer) which are lesser in number, herbivores are more in number than produces.
- In final tertiary consumers are lesser in number than the secondary consumer.
- In a parasite ecosystem the pyramid of number is always inverted because
- Its starts with single tree, there is gradual increase in the number of organisms in successive
trophic levels from producers to tertiary consumers. - Question 9.
Write about the mechanism of decomposition ? What are the factors affecting decomposition, (or) Describe about an essential process for recycling and balancing the nutrient pool in an ecosystem.
Answer:
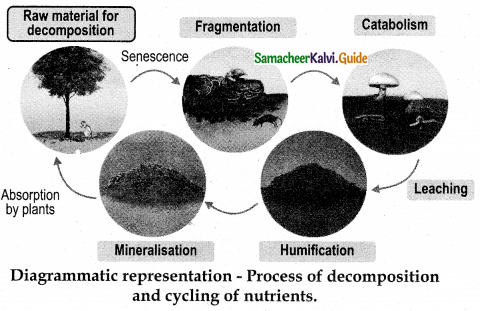
- Decomposition is a step wise process of degradation mediated by enzymatic reactions. Detritus acts as a raw material for decomposition.
- a. Fragmentation – The breaking down of detritus into smaller particles by detritivores like bacteria, fungi and earth worm is known as fragmentation.
- b. Catabolism – The decomposers produce some extracellular enzymes in their surroundings to break down complex organic and inorganic compounds in to simpler ones. This is called catabolism
- c. Leaching or Eluviation – The movement of decomposed, water soluble organic and inorganic compounds from the surface to the lower layer of soil or the carrying away of the same by water is called leaching or eluviation.
- d. Humification – Detritus is changed into dark coloured amorphous substance called humus. It is highly resistant to microbial action, therefore decomposition is very slow.
- e. Mineralisation – The release of inorganic nutrients from the humus is called mineralisation.
- Decomposition is affected by climatic factors like temperature, soil moisture, soil pH oxygen and also the chemical quality of detritus.
![]()
Question 10.
Define pyramid of biomass. What are its types based on shape ?
Answer:
- A graphical representation of the amount of organic material (biomass) present at each successive trophic level in an ecosystem is called pyramid of biomass.
- In grassland and forest ecosystems, there is a gradual decrease in biomass of organisms at successive trophic levels from producers to top carnivores (Tertiary consumer). Therefore, these two ecosystems show pyramids as upright pyramids of biomass.
- However, in pond ecosystem, the bottom of the pyramid is occupied by the producers, which comprise very small organisms possessing the least biomass and so, the value gradually increases towards the tip of the pyramid. Therefore, the pyramid of biomass is always inverted in shape.
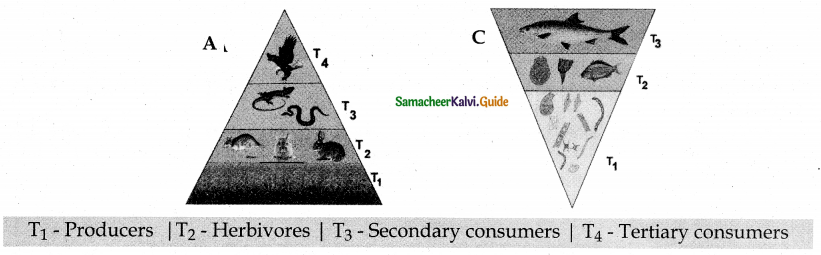
Figure 7.9: Pyramids of biomass (dry weight per unit area) in different types of ecosystems.
Upright – A) Grassland ecosystem Inverted – C) Pond ecosystem
Question 11.
Write about the structure of pond ecosystem with diagram.
Answer:
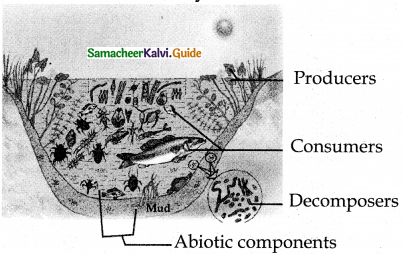
- Pond ecosystem is a self sustaining and self regulatory fresh water ecosystem, which shows a complex interaction between the abiotic and biotic components in it.
- A pond ecosystem consists of dissolved inorganic (CO2, O2, Ca, N, Phosphate) and organic substances (amino acids and humic acid) formed from the dead organic matter.
- The function of pond ecosystem is regulated by few factors like the amount of light, temperature, pH value of water and other climatic conditions.
- Biotic components : They constitute the producers, variety of consumers and decomposers (microorganisms).
- A variety of phytoplankton like Oscillatoria, Anabaena, Eudorina, Volvox and Diatoms. Filamentous algae, floating plants, rooted floating plants are the major producers of a pond ecosystem.
- zooplanktons, benthos, secondary consumers like water beetles and frogs tertiary consumers (carnivores) like duck, crane and some top carnivores which include large fish, hawk ,man, etc.
- They are also called as microconsumers. They help to recycle the nutrients in the ecosystem.
- The cycling of nutrients between abiotic and biotic components is evident in the pond ecosystem, making itself self sufficient and self regulating.
![]()
Question 12.
Write important features of a sedimentation cycle in an ecosystem.
Answer:
Sedimentary cycles are very slow. They take a long time to complete their circulation. Because during recycling, nutrient elements may get locked in the reservoir pool there by taking a very long to come out and continue circulation.
- It is a type of sedimentary cycle. Already we know that phosphorus is found in the biomolecules like DNA, RNA, ATP, NADP and phospholipid molecules of living organisms.
- Bulk quantity of phosphorus is present in rock deposits, marine sediments and guano.
It is released from these deposits by weathering process. - The producers absorb phosphorus in the form of phosphate ions, and then it is transferred to each trophic level of food chain through food.
- Again death of the organisms and degradation by the action of decomposers, the phosphorus is released back into the lithosphere and hydrosphere to maintain phosphorus cycle.
Question 13.
Based on the varieties of benefits obtained from ecosystem what are the various types ecosystem services ?
Answer:
The varieties of benefits obtained from the ecosystem are generally categorized into the follo wing four types
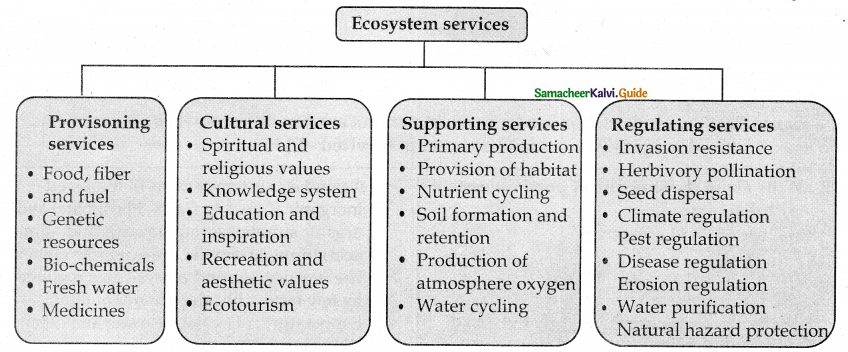
![]()
Question 14.
Discuss about the various benefits of mangrove ecosystem services, (or) What are the various benefits of mangrove ecosystem services to nature and human being?
Answer:
Mangrove ecosystem services:
- Offers habitat and act as nursery for aquatic plants and animals Provides medicine, fuel wood and timber.
- Act as bridge between sea and rivers by balancing sedimentation and soil erosion.
- Help to reduce water force during cyclones, tsunamis and high tide periods.
- Help in wind break, O2 production, carbon sequestration and prevents salt spray from waves.
Question 15.
If we fail to protect environment, we will fail to save posterity? (or) What are the practices we have to follow to protect the ecosystem ? (or) How to protect the ecosystem ?
Answer:
To protect ecosystem, we have to practice the following in our daily life.
- Buy and use only ecofriendly products and recycle them.
- Grow more trees.
- Choose sustained farm products (vegetables, fruits, greens, etc.)
- Reduce the use of natural resources.
- Recycle the waste and reduce the amount of waste you produce.
- educe consumption of water and electricity.
- Reduce or eliminate the use of house-hold chemicals and pesticides.
- Maintain your cars and vehicles properly. (In order to reduce carbon emission)
Create awareness and educate about ecosystem protection among your friends and family members and ask them to find out solution to minimise this problem.
![]()
Question 16.
What are the strategy of ecosystem management ?
Answer:
Strategy of ecosystem management:
- It is used to maintain biodiversity of ecosystems.
- It helps in indicating the damaged ecosystem (Some species indicate the health of the ecosystem: such species are called a flagship species).
- It is used to recognize unavoidance of ecosystem change and plan accordingly.
- It is one of the tools used for achieving sustainability of ecosystem through sustainable development programme (or projects).
- It is also helpful in identifying ecosystems which are in need of rehabilitation.
Question 17.
What are various steps involved in ecological succession ? (or) What are the characteristics of ecological succession ?
Answer:
Characteristics of ecological succession:
- It is a systematic process which causes changes in specific structure of plant community.
- It is resultant of changes of abiotic and biotic factors.
- It transforms unstable community into a stable community.
- Gradual progression in species diversity, total biomass, niche specialisation, and humus content of soil takes place.
- It progresses from simple food chain to complex food web.
- It modifies the lower and simple life form to the higher life forms.
- It creates inter-dependence of plants and animals.
Question 18.
Tabulate the differences between primary and secondary succession?
Answer:
| Primary succession | Secondary succession |
| 1. Developing in an barren area | Developing in disturbed area |
| 2. Initiated due to a biological or any other external factors | Starts due to external factors only |
| 3. No soil, while primary succession starts | It starts where soil covers is already present |
| 4. Pioneer species come from outside envinormet |
Pioneer species develop from existing environment |
| 5. It takes more time to complete | It takes comparatively less time to complete |
![]()
Question 19.
Write about the different stages of hydrosere? (or) Write about the different substages of hydrosere in plant succession.
Answer:
The type of succession is hydrosere. It includes the following stages.
- Phytoplankton stage
- Submerged plant stage
- Submerged free floating stage
- Reed-swamp stage
- Marsh rnedow stage
- Shr ub stage
- Forest stage
1. Phytoplankton stage:
It is the first stage of succession consisting of the pioneer community like blue green algae, green algae, diatoms, bacteria, etc., The colonization of these organisms enrich the amount of organic matter and nutrients of pond due to their life activities and death. This favours the development of the next serai stages.
2. Submerged plant stage:
As the result of death and decomposition of planktons, silt brought from land by rain water, lead to a loose mud formation at the bottom of the pond. Hence, the rooted submerged hydrophytes begin to appear on the new substratum. Example: Chara, Utricularia. The death and decay of these plants will build up the substratum of pond to become shallow. Therefore, this habitat now replaces another group of plants which are of floating type.
3. Submerged free floating stage:
During this stage, the depth of the pond will become almost 2-5 feet. Hence, the rooted hydrophytic plants and with floating large leaves start colonising the pond. Example: Rooted floating plants like Nelumbo, Nymphaea and Trapa. By death and decomposition of these plants, further the pond becomes more shallow. Due to this reason, floating plant species is gradually replaced by another species which makes new serai stage.
4. Reed-swamp stage:
It is also called an amphibious stage. During this stage, rooted floating plants are replaced by plants which can live successfully in aquatic as well as aerial environment. Example: Typha
5. Marsh meadow stage:
When the pond becomes swallowed due to decreasing water level, species of Cyperaceae and Poaceae. They form a mat-like vegetation with the help of their much branched root system. This leads to an absorption and loss of large quantity of water. At the end of this stage, the soil becomes dry and the marshy vegetation disappears gradually and leads to shurb stage.
6. Shrub stage:
As the disappearance of marshy vegetation continues, soil becomes dry. Hence, these areas are now invaded by terrestrial plants like shrubs (Salix and Cornus) and trees (Populus and Alnus). These plants absorb large quantity of water and make the habitat dry. Further, the accumulation of humus with a rich flora of microorganisms produce minerals in the soil, ultimately favouring the arrival of new tree species in the area.
7. Forest stage:
It is the climax community of hydrosere. A variety of trees invade the area and develop any one of the diverse type of vegetation. Example: Temperate mixed forest 207
Question 20.
Write about the significance of plant succession.
Answer:
Significance of Plant Succession:
- Succession is a dynamic process. Hence an ecologist can access and study the serai stages of a plant community found in a particular area.
- The knowledge of ecological succession helps to understand the controlled growth of one or more species in a forest.
- Utilizing the knowledge of succession, even dams can be protected by preventing siltation
- It gives information about the techniques to be used during reforestation and afforestation.
- It helps in the maintenance of pastures.
- Plant succession helps to maintain species diversity in an ecosystem.
- Patterns of diversity during succession are influenced by resource availability and disturbance by various factors.
- Primary succession involves the colonization of habitat of an area devoid of life.
- Secondary succession involves the reestablishment of a plant community in disturbed area or habitat.
- Forests and vegetation that we come across all over the world are the result of plant succession.
![]()
Question 21.
What is carbon cycle ? Draw the diagrammatic sketch showing carbon cycle ?
Answer:
The circulation of carbon between organisms and environment is known as the carbon cycle
