Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Guide Pdf Chapter 9 Applications of Biotechnology Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter 9 Applications of Biotechnology
12th Bio Zoology Guide Applications of Biotechnology Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The first clinical gene therapy was done for the treatment of ……………………..
(a) AIDS
(b) Cancer
(c) Cystic fibrosis
(d) SCID
Answer:
(d) SCID
Question 2.
Dolly, the sheep was obtained by a technique known as ……………………..
(a) Cloning by gene transfer
(b) Cloning without the help of gametes
(c) Cloning by tissue culture of somatic cells
(d) Cloning by nuclear transfer
Answer:
(d) Cloning by nuclear transfer
![]()
Question 3.
The genetic defect adenosine deaminase deficiency may be cured permanently by ……………………..
(a) Enzyme replacement therapy
(b) periodic infusion of genetically engineered lymphocytes having ADA cDNA
(c) administering adenosine deaminase activators
(d) introducing bone marrow cells producing ADA into embryo at an early stage of development.
Answer:
(d) introducing bone marrow cells producing ADA into embryo at an early stage of development.
Question 4.
How many amino acids are arranged in the two chains of Insulin?
(a) Chain A has 12 and Chain B has 13
(b) Chain A has 21 and Chain B has 30 amino acids
(c) Chain A has 20 and chain B has 30 amino acids
(d) Chain A has 12 and chain B has 20 amino acids
Answer:
(b) Chain A has 21 and Chain B has 30 amino acids
![]()
Question 5.
PCR proceeds in three distinct steps governed by temperature, they are in order of………………………
(a) Denaturation, Annealing, Synthesis
(b) Synthesis, Annealing, Denaturation
(c) Annealing, Synthesis, Denaturation
(d) Denaturation, Synthesis, Annealing
Answer:
(a) Denaturation, Annealing, Synthesis
Question 6.
Which one of the following statements is true regarding DNA polymerase used in PCR?
(a) It is used to ligate introduced DNA in recipient cells
(b) It serves as a selectable marker
(c) It is isolated from a Virus
(d) It remains active at a high temperature
Answer:
(d) It remains active at a high temperature
Question 7.
ELISA is mainly used for……………………..
(a) Detection of mutations
(b) Detection of pathogens
(c) Selecting animals having desired traits
(d) Selecting plants having desired traits
Answer:
(b) Detection of pathogens
Question 8.
Transgenic animals are those which have
(a) Foreign DNA in some of their cells
(b) Foreign DNA in all their cells
(c) Foreign RNA in some of their cells
(d) Foreign RNA in all their cells
Answer:
(b) Foreign DNA in all their cells
![]()
Question 9.
Recombinant Factor VIII is produced in the …………………….. cells of the Chinese Hamster
(a) Liver cells
(b) blood cells
(c) ovarian cells
(d) brain cells
Answer:
(c) ovarian cells
Question 10.
Vaccines that use components of a pathogenic organism rather than the whole organism are called ……………………..
(a) Subunit recombinant vaccines
(b) attenuated recombinant vaccines
(c) DNA vaccines
(d) conventional vaccines
Answer:
(a) Subunit recombinant vaccines
Question 11.
Mention the number of primers required in each cycle of PCR. Write the role of primers and DNA polymerase in PCR. Name the source organism of the DNA polymerase used in PCR.
Answer:
- For each cycle of PCR two primers are required.
- Primers are the small fragments of single-stranded DNA or RNA that serve as a template for initiating DNA polymerization.
- DNA polymerase is an enzyme that synthesizes DNA molecules by pairing the Deoxyribo Nucleotides leading to the formation of new strands.
- DNA polymerase used in PCR is Taq polymerase which is isolated from a thermophilic bacteria called Thermus aquatics.
- Taq polymerase will remain active ever at a very high temperature (80°C) and hence used in the PCR amplification technique.
![]()
Question 12.
How is the amplification of a gene sample of interest carried out using PCR?
Answer:
Denaturation, renaturation or primer annealing, and synthesis or primer extension, are the three steps involved in PCR. The double-stranded DNA of interest is denatured to separate into two individual strands by high temperature. This is called denaturation. Each strand is allowed to hybridize with a primer (renaturation or primer-annealing). The primer-template is used to synthesize DNA by using Taq – DNA polymerase.
During denaturation, the reaction mixture is heated to 95 °C for a short time to denature the target DNA into single strands that will act as a template for DNA synthesis. Annealing is done by the rapid cooling of the mixture, allowing the primers to bind to the sequences on each of the two strands flanking the target DNA.
During primer extension or synthesis the temperature of the mixture is increased to 75°C for a sufficient period of time to allow Taq DNA polymerase to extend each primer by copying the single-stranded template. At the end of incubation, both single template strands will be made partially double-stranded. The new strand of each double-stranded DNA extends to a variable distance downstream. These steps are repeated again and again to generate multiple forms of the desired DNA. This process is also called DNA amplification.
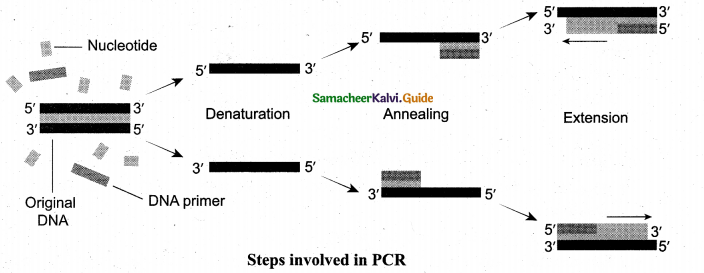
Question 13.
What has genetically engineered Insulin?
Answer:
The insulin synthesized by recombinant DNA technology is called genetically engineered Insulin. It was the first-ever pharmaceutical product of rDNA technology. In 1986, human insulin was marked under the trade name Humulin.
![]()
Question 14.
Explain how “Rosie” is different from a normal cow.
Answer:
Rosie was the first transgenic cow. It produced human protein-enriched milk, which contained the human alpha-lactalbumin (2.4 gm/liter). This milk was a nutritionally balanced food for infants than the normal milk of cows.
Question 15.
How was Insulin obtained before the advent of rDNA technology? What were the problems encountered?
Answer:
Conventionally, Insulin was isolated and refined from the pancreas of pigs and cows to treat diabetic patients. Though it is effective, due to minor structural changes, the animal insulin caused allergic reaction in a few patients.
Question 16.
ELISA is a technique based on the principles of antigen-antibody reactions. Can ~ this technique be used in the molecular diagnosis of a genetic disorder such as Phenylketonuria?
Answer:
Yes, ELISA test can be done to diagnose phenylketonuria. The affected person does not produce the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase. If specific antibodies are developed against the enzyme and ELISA is performed, the unaffected person will show positive result due to antigen and antibody reaction, whereas the affected individual produces negative results. [Note: phenylketonuria is an inherited metabolic disorder that causes the accumulation of phenylalanine (an amino acid) in body cells due to defect in the synthesizing of an enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase]
Question 17.
Gene therapy is an attempt to correct a Genetic defect by providing a normal gene into the individual. By this the function can be restored. An alternate method would be to provide gene product known as enzyme replacement therapy, which would also restore the function. Which in your opinion is a better option? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer:
Though both Gene therapy and Enzyme replacement therapy helps to restore genetic defects, Gene therapy is much better than Enzyme replacement therapy. Because, in Gene therapy, once the defective gene is repaired using a normal gene, the affected individual gains complete recovery whereas, in Enzyme replacement therapy, the respective enzyme or protein has to be provided periodically and does not offer a permanent cure. Moreover, when compared to Gene therapy, Enzyme replacement therapy is highly expensive.
![]()
Question 18.
What are transgenic animals? Give examples.
Answer:
Transgenesis is the process of introduction of extra (foreign/exogenous) DNA into the genome of the animals to create and maintain stable heritable characters. The foreign DNA that is introduced is called the transgene and the animals that are produced by DNA manipulations are called transgenic animals or genetically engineered or genetically modified organisms. e.g. Mice, Cow
Question 19.
If a person thinks he is infected with HIV, due to unprotected sex, and goes for a blood test. Do you think a test such as ELISA will help? If so why? If not, why?
Answer:
Yes, ELISA is a highly sensitive and precise procedure and can detect antigens even in the range of a nanogram. So, it can be used to detect HIV in blood.’
Question 20.
Explain how ADA deficiency can be corrected?
Answer:
The right approach for SCID treatment would be to give the patient a functioning ADA which breaks down toxic biological products.
In some children ADA deficiency could be cured by bone marrow transplantation, where defective immune cells could be replaced with healthy immune cells from a donor. In some patients it can be treated by enzyme replacement therapy, in which functional ADA is injected into the patient.
During gene therapy the lymphocytes from the blood of the patient are removed and grown in a nutrient culture medium. A healthy and functional human gene, ADA cDNA encoding this enzyme is introduced into the lymphocytes using a retrovirus. The genetically engineered lymphocytes are subsequently returned to the patient. Since these cells are not immortal, the patient requires periodic infusion of such genetically engineered lymphocytes. The disease could be cured permanently if the gene for ADA isolated from bone marrow cells are introduced into the cells of the early embryonic stages.
![]()
Question 21.
What are DNA vaccines?
Answer:
Genetic immunization by using DNA vaccines is a novel approach that came into being in 1990. The immune response of the body is stimulated by a DNA molecule. A DNA vaccine consists of a gene encoding an antigenic protein, inserted onto a plasmid, and then incorporated into the cells in a target animal. DNA instructs the cells to make antigenic molecules which are displayed on its surfaces. This would evoke an antibody response to the free-floating antigen secreted by the cells. The DNA vaccine cannot cause the disease as it contains only copies of a few of its genes. DNA vaccines are relatively easy and inexpensive to design and produce.
Question 22.
Differentiate between Somatic cell gene therapy and Germline gene therapy.
Answer:
Somatic Cell Gene Therapy:
- Therapeutic genes transferred into the somatic cells.
- Introduction of genes into bone marrow cells, blood cells, skin cells, etc.
- It Will not be inherited in later generations.
Germ Line Gene Therapy:
- Therapeutic genes transferred into the germ cells.
- Genes introduced into eggs and sperms.
- Heritable and passed on to later generations.
![]()
Question 23.
What are stem cells? Explain its role in the field of medicine.
Answer:
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells found in most of multicellular animals. These cells maintain their undifferentiated state even after undergoing numerous mitotic divisions.
Stem cell research has the potential to revolutionize the future of medicine with the ability to regenerate damaged and diseased organs. Stem cells are capable of self-renewal and exhibit ‘cellular potency’. Stem cells can differentiate into all types of cells that are derived from any of the three germ layers ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm.
Question 24.
One of the applications of biotechnology is ‘gene therapy” to treat a person born with a hereditary disease
(i) What does “gene therapy” mean?
(ii) Name the hereditary disease for which the first clinical gene therapy was used.
(iii) Mention the steps involved in gene therapy to treat this disease.
Answer:
(i) Gene therapy is the process in which the defective genes are replaced with normal genes leading to the expression of the proper phenotype.
(ii) SCID (Severe Combined Immuno Deficiency) disease was the first disease treated by using gene therapy.
(iii) There are two strategies involved in gene therapy namely; Gene augmentation therapy, which involves the insertion of DNA into the genome to replace the missing gene product; and Gene inhibition therapy, which involves insertion of the anti-sense gene which inhibits the expression of the dominant gene.
Question 25.
PCR is a useful tool for early diagnosis of Infectious disease. Elaborate.
Answer:
The specificity and sensitivity of PCR is useful for the diagnosis of inherited disorders (genetic diseases), viral diseases, bacterial diseases, etc., The diagnosis and treatment of a particular disease often require identifying a particular pathogen. Traditional methods of identification involve culturing these organisms from clinical specimens and performing metabolic and other tests to identify them.
The concept behind PCR-based diagnosis of infectious diseases is simple – if the pathogen is present in a clinical specimen its DNA will be present.
Its DNA has unique sequences that can be detected by PCR, often using the clinical specimen (for example, blood, stool, spinal fluid, or sputum) in the PCR mixture.
![]()
Question 26.
What are recombinant vaccines? Explain the types.
Answer:
Vaccines developed by using recombinant DNA technology are called recombinant vaccines. Subunit recombinant vaccines, attenuated recombinant vaccines, DNA vaccines are the types of recombinant vaccines.
Question 27.
Explain why cloning of Dolly, the sheep was such a major scientific breakthrough?
Answer:
The development of Dolly was a remarkable achievement in the scientific field and it demonstrates that the DNA from differentiated adult cells can also be used to develop into an entire organism.
Question 28.
Mention the advantages and disadvantages of cloning.
Answer:
- Offers benefits for clinical trials and medical research. It can help in the production of proteins and drugs in the field of medicine.
- Aids stem cell research.
- Animal cloning could help to save endangered species.
- Animal and human activists see it as a threat to biodiversity saying that this alters evolution which will have an impact on populations and the ecosystem.
- The process is tedious and very expensive.
- It can cause animals to suffer.
- Reports show that animal surrogates were manifesting adverse outcomes and cloned animals were affected with the disease and have a high mortality rate.
- It might compromise human health through the consumption of cloned animal meat.
- Cloned animals age faster than normal animals and are less healthy than the parent organism as discovered in Dolly
- Cloning can lead to the occurrence of genetic disorders in animals.
- More than 90% of cloning attempts fail to produce viable offspring.
![]()
Question 29.
Explain how recombinant Insulin can be produced.
Answer:
Production of insulin by recombinant DNA technology started in the late 1970s. This technique involved the insertion of a human insulin gene on the plasmids of E. coli. The polypeptide chains are synthesized as a precursor called pre-pro insulin, which contains A and B segments linked by a third chain (C) and preceded by a leader sequence. The leader sequence is removed after translation and the C chain is excised, leaving the A and B polypeptide chains
Question 30.
Explain the steps involved in the production of recombinant hGH.
Answer:
Using recombinant DNA technology hGH can be produced. The gene for hGH is isolated from the human pituitary gland cells. The isolated gene is inserted into a plasmid vector and then is transferred into E. coli. The recombinant E. coli then starts producing human growth hormone. The recombinant E. coli are isolated from the culture and mass production of hGH is carried out by fermentation technology.
12th Bio Zoology Guide Applications of Biotechnology Additional Important Questions and Answers
12th Bio Zoology Guide Applications of Biotechnology One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Statement 1: Human Insulin is a polypeptide Statement 2: It is composed of 52 amino acids
(a) Statement 1 is true. Statement 2 is false.
(b) Statement 1 is false. Statement 2 is true.
(c) Both statements 1 and 2 are true.
(d) Both statements 1 and 2 are false.
Answer:
(a) Statement 1 is true. Statement 2 is false.
Question 2.
Statement 1: Rosie was the first transgenic goat.
Statement 2: Meat is enriched with human protein.
(a) Statement 1 is true. Statement 2 is false.
(b) Statement 1 is false. Statement 2 is true.
(c) Both statements 1 and 2 are true. ‘
(d) Both statements 1 and 2 are false.
Answer:
(d) Both statements 1 and 2 are false.
![]()
Question 3.
Statement 1: Recombinant Hepatitis B vaccine is a live vaccine.
Statement 2: It is obtained by cloning HB antigen gene in yeast.
(a) Statement 1 is true. Statement 2 is false.
(b) Statement 1 is false. Statement 2 is true.
(c) Both statements 1 and 2 are true.
(d) Both statements 1 and 2 are false.
Answer:
(b) Statement 1 is false. Statement 2 is true.
Question 4.
Statement 1: ADA deficiency was the first disease treated by gene therapy.
Statement 2: ADA is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder.
(a) Statement 4 is true. Statement 2 is false.
(b) Statement 1 is false. Statement 2 is true.
(c) Both statements 1 and 2 are true.
(d) Both statements 1 and 2 are false.
Answer:
(c) Both statements 1 and 2 are true.
Question 5.
Statement 1: Attenuated recombinant vaccines are live vaccines.
Statement 2: Polio is a live vaccine.
(a) Statement 1 is true. Statement 2 is false.
(b) Statement 1 is false. Statement 2 is true.
(c) Both statements 1 and 2 are true.
(d) Both statements 1 and 2 are false.
Answer:
(c) Both statements 1 and 2 are true.
![]()
Question 6.
Assertion (A): Interferons are used to treat herpes zoster.
Reason (R): Interferons are antiviral proteins.
(a) R explains A.
(b) Both A and Rare incorrect.
(c) A is correct. R is incorrect. y
(d) A and R are correct. R does not explain A.
Answer:
(a) R explains A.
Question 7.
Assertion (A): PCR is an amplification technique used in biotechnology.
Reason (R): Using PCR multiple copies of DNA can be generated.
(a) R explains A.
(b) Both A and Rare incorrect.
(c) A is correct. R is incorrect.
(d) A and R are correct. R does not explain A.
Answer:
(a) R explains A.
Question 8.
The B-chain of Insulin is composed of ………………….. amino acids
(a) 70
(b) 30
(c) 45
(d) 60
Answer:
(b) 30
![]()
Question 9.
The gene for the formation of factor VIII is located in ……………….
(a) 20th Chromosome
(b) 12th Chromosome
(c) X-chromosome
(d) Y-chromosome
Answer:
(c) X-chromosome
Question 10.
The genetic defect in the synthesis of factor VIII results in……………….
(a) Polycythemia
(b) Anaemia
(c) Thalassemia
(d) Haemophilia
Answer:
(c) Haemophilia
Question 11.
Name the scientists who discovered Interferons?
Answer:
Alick Issac and Jean Lindemann
Question 12.
Which is the first synthetic vaccine produced?
(a) Polio Vaccine
(b) Hepatitis B Vaccine
(c) BCG Vaccine
(d) MMR Vaccine
Answer:
(A) Hepatitis B Vaccine
Question 13.
Identify the incorrect statement.
(i) The first clinical gene therapy was given by French Anderson.
(ii) For a four-year-old boy with ADA deficiency.
(iii) ACD is an autosomal dominant metabolic disorder.
(iv) Where patients have non-functioning B – lymphocytes.
(a) i and iv only
(b) ii, iii and iv
(c) i, ii and iv
(d) all the above
Answer:
(b) ii, iii and iv
![]()
Question 14.
Identify the correct statement(s).
(i) Totipotency is the ability of single cell to produce a whole organism.
(ii) Pluripotency refers to ability of stem cell with apotential to differentiate into any kind of germ layers.
(iii) Unipotency refers to ability of stem cell to differentiate into one cell type.
(iv) Oligopotency refers to stem cells to differentiate into few cell types.
(a) i and iii (b) ii and iv (c) i and iv (d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
Question 15.
Identify those proper sequence of ELISA testing.
(a) Coating → Blocking → Detection → Read out
(b) Detection → Read out → Coating → Blocking
(c) Read out→ Coating→ Detection → Blocking
(d) Blocking → Detection → Read out → Coating
Answer:
(a) Coating → Blocking → Detection→ Read out
Question 16.
PCR technique was developed by
(a) Eva Engvall
(b) Peter Perlmanin
(c) Kary Mullis
(d) Wilmut
Answer:
(c) Kary Mullis
![]()
Question 17.
Arrange the steps of PCR in proper sequence.
(a) Denaturation, Primer extension, Renaturation
(b) Renaturation, Denaturation, Primer extension
(c) Primer extension, Denaturation, Renaturation
(d) Denaturation, Renaturation, Primer extension
Answer:
(d) Denaturation, Renaturation, Primer extension
Question 18.
The first cloned organism was………….
(a) Goat
(b) Cow
(c) Sheep
(d) Pig
Answer:
(c) Sheep
Question 19.
The first transgenic clone of sheep was called as ……………….
(a) Rosie
(b) Dolly
(c) Sameera
(d) Joel
Answer:
(b) Dolly
![]()
Question 20.
In the cloning process of Dolly, how many embryos were implemented by Ian Wilmut and Campbell, out of which one successful Dolly was developed?
(a) 267
(b) 211
(c) 287
(d) 307
Answer:
(b) 277
Question 21.
The term Biotechnology was coined by…………..
Answer:
Karl Ereky
![]()
12th Bio Zoology Guide Applications of Biotechnology Two Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
How insulin controls blood sugar level?
Answer:
Insulin controls the blood sugar level by facilitating the cellular uptake and utilisation of glucose for the release of energy.
Question 2.
State the role of Somatostatin and Somatotropin in human beings.
Answer:
Both somatostatin and somatotropin are peptide hormones which helps in growth and development by increasing the uptake of amino acids and promoting protein synthesis.
Question 3.
Mention the manifestation of the disease – Haemophilia-A
Answer:
Haemophilia A is a X-linked disease which is characterized by prolonged clotting time and * internal bleeding.
Question 4.
Define Interferons.
Answer:
Interferons are proteinaceous, antiviral, species specific substances produced by mammalian cells when infected with viruses. They stimulate the cellular DNA to produce antiviral enzymes which inhibit viral replication and protect the cells.
![]()
Question 5.
Who discovered Interferons? On which basis it was classified?’
Answer:
Interferons were discovered by Alick Isaacs and Jean Lindemann in 1957. It is classified as a, P and y interferons based on the structure.
Question 6.
Name the disease that are treated by using interferons.
Answer:
Interferons are used for the treatment of various diseases like cancer, AIDS, multiple sclerosis, hepatitis C and herpes zoster.
Question 7.
Recombinant vaccines are better than conventional ones – Justify.
Answer:
The recombinant vaccines are generally of uniform quality and produce less side effects as compared to the vaccines produced by conventional methods.
![]()
Question 8.
Point out four types of recombinant vaccines.
Answer:
- Subunit recombinant vaccines
- Attenuated recombinant vaccines
- Edible vaccines
- DNA vaccines
Question 9.
What are subunit recombinant vaccines? Mention its advantages.
Answer:
Vaccines that use components of a pathogenic organism rather than the whole organism are called subunit vaccines. The advantages of these vaccines include their purity in preparation, stability and safe use.
Question 10.
Define Attenuated recombinant vaccines.
Answer:
Attenuated recombinant vaccines include genetically modified pathogenic organisms (bacteria or viruses) that are made nonpathogenic and are used as vaccines. Such vaccines are referred to as attenuated recombinant vaccines.
![]()
Question 11.
List out the benefits of recombinant vaccines.
Answer:
Vaccines produced by recombinant techniques have definite advantages like producing target proteins, long-lasting immunity and trigger immune response only against specific pathogens with less toxic effects.
Question 12.
Name the two strategies involved in gene therapy
Answer:
- Gene augmentation therapy.
- Gene inhibition therapy.
Question 13.
Comment on SCID.
Answer:
ADA deficiency or SCID (Severe Combined Immuno Deficiency) is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder. It is caused by the deletion or dysfunction of the gene coding for ADA enzyme. In these patients the nonfunctioning T-Lymphocytes cannot elicit immune responses against invading pathogens.
Question 14.
Differentiate between Gene augmentation therapy and gene inhibition therapy.
Answer:
Gene augmentation therapy which involves insertion of DNA into the genome to replace the missing gene product and Gene inhibition therapy which involves insertion of the anti sense gene which inhibits the expression of the dominant gene.
![]()
Question 15.
Define the terms (a) Totipotency (b) Unipotency
Answer:
Totipotency is the ability of a single cell to divide and produce all of the differentiated cells in an organism.
Unipotency refers to the ability of the stem cells to differentiate into only one cell type.
Question 16.
What are the best sources of stem cells in mammals?
Answer:
Placenta, Umbilical cord, amniotic sac, amniotic fluid.
Question 17.
Write the names of any two molecular diagnostic techniques used for early diagnosis of diseases?\
Answer:
(a) Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) technique.
(b) Enzyme Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay (ELISA)
Question 18.
What does ELISA stands for? Who invented this technique?
Answer:
Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay (ELISA). It was invented by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlman.
Question 19.
Name the various kinds of ELISA.
Answer:
There are four kinds of ELISA namely, Direct ELISA, Indirect ELISA, sandwich ELISA and competitive ELISA.
![]()
Question 20.
Simply define the PCR technique. Also mention its inventor.
Answer:
The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is an invitro amplification technique used for synthesizing multiple identical copies (billions) of DNA of interest. The technique was developed by Kary Mullis in the year 1983.
Question 21.
Expand PCR and name the steps involved in the process.
Answer:
PCR – Polymerase Chain Reaction.
Denaturation, Renaturation or Primer annealing and Primer extension are the three steps in PCR technique.
Question 22.
For which disease does the first clinical gene therapy was done? Who accomplished it?
Answer:
The first clinical gene therapy was done for SCID. Severe Combined Immuno Deficiency disease is caused by ADA deficiency. It was done by French Anderson in 1990.
Question 23.
Define Transgenesis.
Answer:
Transgenesis is the process of introduction of foreign DNA (exogenous DNA) into the genome of the other organism to create and maintain stable heritable characters.
![]()
Question 24.
What are the Genetically Modified Organisms?
Answer:
Transgenesis is the process of introduction of extra (foreign/ exogenous) DNA into the genome of the animals to create and maintain stable heritable characters. The foreign DNA that is introduced is called the transgene and the animals that are produced by DNA manipulations are called transgenic animals or the genetically engineered or genetically modified organisms.
Question 25.
What does Biological Product refers to?
Answer:
A biological product is a substance derived from a living organism and used for the prevention or treatment of disease. These products include antitoxins, bacterial and viral vaccines, blood products and hormone extracts.
Question 26.
Define cloning. Name the first organism developed by cloning.
Answer:
Cloning is the process of producing genetically identical individuals of an organism either naturally or artificially. The first cloned organism is a sheep named Dolly.
![]()
Question 27.
Who developed Dolly? How many embryos were aborted to develop a single Dolly?
Answer:
Dolly- The first cloned organism (sheep) was developed by Ian Wilmut and Campbell. Out of 29 embryos implanted only one Dolly was developed.
Question 28.
Define Biotechnology.
Answer:
Biotechnology is defined as “any technological application that uses biological systems, living organisms or derivatives thereof, to make or modify products or processes for specific use”.
12th Bio Zoology Guide Applications of Biotechnology Three Marks Questions and Answers
Question 29.
Briefly explain the structure of insulin.
Answer:
Human insulin is synthesized by the (5 cells of Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. It is formed of 51 amino acids which are arranged in two polypeptide chains, A and B. Polypeptide chain A has 21 amino acids while the polypeptide chain B has 30 amino acids. Both A and B chains are attached together by disulfide bonds.
![]()
Question 30.
Who was the first to discover the role of insulin against diabetes? From which organism does was insulin isolated?
Answer:
Best and Banting in 1921, isolated insulin from the pancreatic islets of a dog and demonstrated its effectiveness against diabetes.
Question 31.
How “Rosie” differs from a normal cow? Explain.
Answer:
Rosie, the first transgenic cow produced human protein-enriched milk, which contained the human alpha-lactalbumin. The protein-rich milk (2.4 gm/litre) was a nutritionally balanced food for new bom babies than the normal milk produced by the cows.
Question 32.
Point out any two microbes that play a crucial role in recombinant DNA technology.
Answer:
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Escherichia coli
![]()
Question 33.
What are Edible vaccines?
Answer:
Edible vaccines are prepared by molecular pharming using the science of genetic engineering. Selected genes are introduced into plants and the transgenic plants are induced to manufacture the encoded protein. Edible vaccines are mucosal targeted vaccines which cause stimulation of both systemic and mucosal immune response. At present edible vaccines are produced for human and animal diseases like measles, cholera, foot and mouth disease and hepatitis.
Question 34.
How the recombinant hepatitis B vaccine is produced in the laboratory?
Answer:
Recombinant hepatitis B vaccine as a subunit vaccine is produced by cloning hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg) gene in the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Question 35.
Suggest few methods to treat SCID.
Asnwer:
SCID caused by ADA deficiency could be cured by bone marrow transplantation where defective immune cells could be replaced with healthy immune cells from donor. It can also be treated by enzyme replacement therapy in which functional ADA is injected into patient’s body where it breaks down toxic biological product.
![]()
Question 36.
How gene therapy is done to treat ADA deficiency?
Answer:
During gene therapy, the lymphocytes from the blood of the patient are removed and grown in a nutrient culture medium. A healthy and functional human gene, ADA cDNA encoding this enzyme is introduced into the lymphocytes using a retrovirus. The genetically engineered lymphocytes are subsequently returned to the patient. Since these cells are not immortal, the patient requires a periodic infusion of such genetically engineered lymphocytes. The disease could be cured permanently if the gene for ADA isolated from bone marrow cells is introduced into the cells of the early embryonic stages.
Question 37.
How does Somatic cell therapy differ from germline gene therapy?
Answer:
Somatic cell therapy involves the insertion of a fully functional and expressible gene into a target somatic cell to correct a genetic disease permanently whereas Germline gene therapy involves the introduction of DNA into germ cells which is passed on to successive generations. Gene therapy involves the isolation of a specific gene and making its copies and inserting them into target cells ’to make the desired proteins.
Question 38.
Differentiate between Pluripotency and Multipotency.
Answer:
Pluripotency: refers to a stem cell that has the potential to differentiate into any of the three germ layers-ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm.
Multipotency: refers to the stem cells that can differentiate into various types of cells that are related. For example, blood stem cells can differentiate into lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils etc.
![]()
Question 39.
Write a short note on stem cell banks.
Answer:
Stem cell banking is the extraction, processing and storage of stem cells, so that they may be used for treatment in the future, when required. Amniotic cell bank is a facility that stores stem cells derived from amniotic fluid for future use. Stem cells are stored in banks specifically for use by the individual from whom such cells have been collected and the banking costs are paid. Cord Blood Banking is the extraction of stem cells from the umbilical cord during childbirth. While the umbilical cord and cord blood are the most popular sources of stem cells, the placenta, amniotic sac and amniotic fluid are also rich sources in terms of both quantity and quality.
Question 40.
State any two uniqueness of the ELISA test.
Answer:
ELISA is highly sensitive and can detect antigen even in nanograms.
ELISA test does not require radioisotopes or radiation counting apparatus.
Question 41.
What is the ELISA test?
Answer:
ELISA – Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay is a biochemical procedure done to detect the presence of specific antibodies or antigens or hormones in a sample of serum, urine etc.
![]()
Question 42.
Elucidate the methodology of the ELISA test.
Answer:
During diagnosis, the sample suspected to contain the antigen is immobilized on the surface of an ELISA plate. The antibody specific to this antigen is added and allowed to react with the immobilized antigen. The anti-antibody is linked to an appropriate enzyme-like peroxidase. The unreacted anti-antibody is washed away and the substrate of the enzyme (hydrogen peroxidase) is added with certain reagents such as 4-chloronaphthol. The activity of the enzyme yields a coloured product indicating the presence of the antigen.
Question 43.
Whether PCR is applicable for RNA molecules? Explain.
Answer:
The PCR technique can also be used for amplification of RNA in which case it is referred to as reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR). In this process, the RNA molecules (mRNA) must be converted to complementary DNA by the enzyme reverse transcriptase. The cDNA then serves as the template for PCR.
Question 44.
How PCR helps forensic personnel?
Answer:
PCR technique can also be used in the field of forensic medicine. A single molecule of DNA from bloodstains, hair, semen of an individual is adequate for amplification by PCR. The amplified DNA is used to develop a DNA fingerprint which is used as an important tool in forensic science. Thus, PCR is very useful for the identification of criminals. PCR is also used in the amplification of a specific DNA segments to be used in gene therapy.
![]()
Question 45.
Role of PCR in phylogenetics. Explain.
Answer:
The differences in the genomes of two different organisms can be studied by PCR. PCR is very important in the study of evolutions, more specifically phylogenetics. As a technique that can amplify even minute quantities of DNA from any source, like hair, mummified tissues, bones or any fossilized materials.
Question 46.
Enumerate the use of biological products.
Answer:
Antibodies are substances that react against the disease-causing antigens and these can be produced using transgenic animals as bioreactors. Monoclonal antibodies, which are used to treat cancer, heart disease and transplant rejection are produced by this technology. Natural protein adhesives are non-toxic, biodegradable and rarely trigger an immune response, hence could be used to reattach tendons and tissues, fill cavities in teeth, and repair broken bones.
Question 47.
Name the principles underlying the cloning technique.
Answer:
(a) Nuclear transfer (b) Totipotency (the ability of a cell to develop into an entire organism)
![]()
12th Bio Zoology Guide Applications of Biotechnology Five Marks Questions and Answers
Question 48.
Explain in detail about stem cell therapy.
Answer:
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells found in most multicellular animals. These cells maintain their undifferentiated state even after undergoing numerous mitotic divisions.
Stem cell research has the potential to revolutionize the future of medicine with the ability to regenerate damaged and diseased organs. Stem cells are capable of self-renewal and exhibit ‘cellular potency’. Stem cells can differentiate into all types of cells that are derived from any of the three germ layers ectoderm, endoderm arid mesoderm.
In mammals, there are two main types of stem cells – embryonic stem cells (ES cells) and ‘ adult stem cells. ES cells are pluripotent and can produce the three primary germ layers ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. Embryonic stem cells are multipotent stem cells that can differentiate into a number of types of cells. ES cells are isolated from the epiblast tissue of the inner cell mass of a blastocyst. When stimulated ES can develop into more than 200 cells types of the adult body. ES cells are immortal ie. they can proliferate in a sterile culture medium and maintain their undifferentiated state.
Adult stem cells are found in various tissues of children as well as adults. An adult stem cell or somatic stem cell can divide and create another cell similar to it. Most of the adult stem cells are multipotent and can act as a repair system of the body, replenishing adult tissues. The red bone marrow is a rich source of adult stem cells.
The most important and potential application of human stem cells is the generation of cells and tissues that could be used for cell-based therapies. Human stem cells could be used to test new drugs.
![]()
Question 49.
Describe the role of PCR in clinical field.
Answer:
PCR In Clinical Diagnosis: The specificity and sensitivity of PCR is useful for the diagnosis of inherited disorders (genetic diseases), viral diseases, bacterial diseases, etc., The diagnosis and treatment of a particular disease often require identifying a particular pathogen. Traditional methods of identification involve culturing these organisms from clinical specimens and performing metabolic and other tests to identify them.
The concept behind PCR-based diagnosis of infectious diseases is simple – if the pathogen is present in a clinical specimen its DNA will be present. Its DNA has unique sequences that can be detected by PCR, often using the clinical specimen (for example, blood, stool, spinal fluid, or sputum) in the PCR mixture. PCR is also employed in the prenatal diagnosis of inherited diseases by using chorionic villi samples or cells from amniocentesis. Diseases like sickle cell anemia, P-thalassemia and phenylketonuria can be detected by PCR in these samples. cDNA from PCR is a valuable tool for diagnosis and monitoring retroviral infections – eg. Tuberculosis by Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Several virally induced cancers, like cervical cancer caused by Papillomavirus, can be detected by PCR. Sex of human beings and live stocks, embryos fertilized in-vitro can be determined by PCR by using primers and DNA probes specific for sex chromosomes. PCR technique is also used to detect sexlinked disorders in fertilized embryos.
Question 50.
Enumerate the steps involved in producing transgenic animals.
Answer:
The various steps involved in the production of transgenic organisms are,
- Identification and separation of the desired gene.
- Selection of a vector (generally a virus) or direct transmission.
- Combining the desired gene with the vector.
- Introduction of the transferred vector into cells, tissues, embryo or mature individual.
- Demonstration of integration and expression of a foreign gene in transgenic tissue or animals. Transgenic animals such as mice, rat, rabbit, pig, cow, goat, sheep and fish have been produced.
![]()
Question 51.
List out the uses of Transgenesis.
Answer:
- Transgenesis is a powerful tool to study gene expression and developmental processes in higher organisms.
- Transgenesis helps in the improvement of genetic characters in animals.Transgenic animals serve as good models for understanding human diseases which help in the investigation of new treatments for diseases. Transgenic models exist for many human diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer’s, cystic fibrosis, rheumatoid arthritis and sickle cell anemia.
- Transgenic animals are used to produce proteins which are important for medical and pharmaceutical applications.
- Transgenic mice are used for testing the safety of vaccines.
- Transgenic animals are used for testing toxicity in animals that carry genes which make them sensitive to toxic substances than non-transgenic animals exposed to toxic substances and their effects are studied.
- Transgenesis is important for improving the quality and quantity of milk, meat, eggs and wool production in addition to testing drug resistance.
Question 52.
Describe the procedure by which Dolly was developed.
Answer:
Dolly was the first mammal (Sheep) clone developed by Ian Wilmut and Campbell in 1997. Dolly, the transgenic clone was developed by the nuclear transfer technique and the phenomenon of totipotency. Totipotency refers to the potential of a cell to develop different cells, tissues, organs and finally an organism.
The mammary gland udder cells (somatic cells) from a donor sheep (ewe) were isolated and subjected to starvation for 5 days. The udder cells could not undergo normal growth cycle, entered a dormant stage and became totipotent. An ovum (egg cell) was taken from another sheep (ewe) and its nucleus was removed to form an enucleated ovum. The dormant mammary gland cell/udder cell and the enucleated ovum were fused. The outer membrane of the mammary cell was ruptured allowing the ovum to envelop the nucleus.
The fused cell was implanted into another ewe which served as a surrogate mother. Five months later dolly was bom. Dolly was the first animal to be cloned from a differentiated somatic cell taken from an adult animal without the process of fertilization.
![]()
Question 53.
What are the ethical issues about cloning.
Answer:
Biotechnology has given to the soceity cheap drugs, better fruits and vegetables, pest-resistant crops, indigenous cure to diseases and lot of controversy. This is mainly because the major part of the modem biotechnology deals with genetic manipulations. People fear that these genetic manipulations may lead to unknown consequences.
The major apprehension of recombinant DNA technology is that unique microorganism either inadvertently or deliberately for the purpose of war may be developed that could cause epidemics or environmental catastrophe. Although many are concerned about the possible risk of genetic engineering, the risks are in fact slight and the potential benefits are substantial.
Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTs) Questions
Question 1.
The immune system of a person is suppressed,. In ELISA test, the result is positive (i) Name the disease associated with this.
(ii) Why did he loose his immunity?
Answer:
AIDS caused by Human Immuno Virus.
In AIDS, the pathogen destroys the T-lymphocytes which forms the major immune resouce of our body.
Question 2.
Why do children cured by enzyme replacement therapy for ADA deficiency need periodic treatment? Suggest a permanent solution for this issue.
Answer:
During gene therapy the lymphocytes from the blood of the patient are removed and grown in a nutrient culture medium. A healthy and functional human gene, ADA cDNA encoding this enzyme is introduced into the lymphocytes using a retrovirus. The genetically engineered lymphocytes are subsequently returned to the patient. Since these cells are not immortal, the patient requires periodic infusion of such genetically engineered lymphocytes. The disease could be cured permanently if the gene for ADA isolated from bone marrow cells are introduced into the cells of the early embryonic stages.
Question 3.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae, acts as a best host than Encherichia coli for the production of recombinant interferons. Yes or No? Support your answer.
Answer:
Yes. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is the best source of recombinant interferon than E-coli. Since E-coli does not possess the machinery for glycolysation of protein.
![]()
Question 4.
Isolation of blood to treat Haemophilia A is practically impossible. Give reason.
Answer:
a) Requirement of large quantity of blood.
b) Risk of transmission of blood related diseases like AIDS.
Question 5.
Functional Insulin differs from its pre-hormonal form. How?
Answer:
Pro-Insulin contains A and B segments linked by a C – chain and preceded by a leader sequence. Whereas the functional Insulin contains only A and B chain formed by the excision of C-chain and leaders sequence after translation.
Question 6.
Whether PCR can be done for RNA molecules? Explain.
Answer:
The PCR technique can also be used for amplification of RNA in which case it is referred to as reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR). In this process, the RNA molecules (mRNA) must be converted to complementary DNA by the enzyme reverse transcriptase. The cDNA then serves as the template for PCR.
![]()
Question 7.
Suggest any two techniques for early diagnosis of bacterial/viral human diseases.
Answer:
PCR and ELISA