Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Business Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 2 Integral Calculus I Ex 2.8 Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Business Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Integral Calculus I Ex 2.8
Using second fundamental theorem, evaluate the following:
Question 1.
\(\int_{0}^{1}\) e2x dx
Solution:
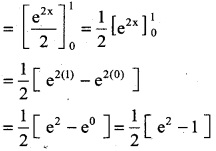
![]()
Question 2.
\(\int_{0}^{1/4}\) \(\sqrt { 1 -4x}\) dx
Solution:
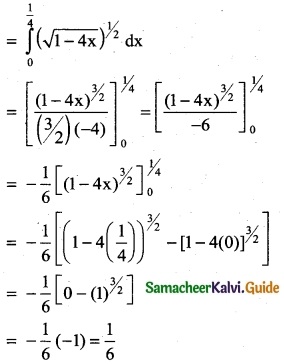
Question 3.
\(\int_{0}^{1}\) \(\frac { xdx }{x^2+1}\)
Solution:
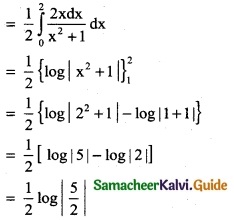
![]()
Question 4.
\(\int_{0}^{3}\) \(\frac { e^xdx }{1+e^x}\)
Solution:
\(\int_{0}^{3}\) \(\frac { e^xdx }{1+e^x}\)
= {log |1 + ex|}\(_{0}^{3}\)
= log |1 + e³| – log |1 + e°|
= log |1 + e³| – log |1 + 1|
= log |1 + e³| – log |2|
= log |\(\frac { 1+e^3 }{2}\)|
Question 5.
\(\int_{0}^{1}\) xex² dx
Solution:
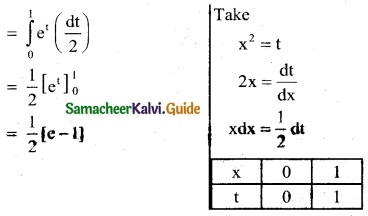
![]()
Question 6.
\(\int_{1}^{e}\) \(\frac { dx }{x(1+logx)^3}\)
Solution:
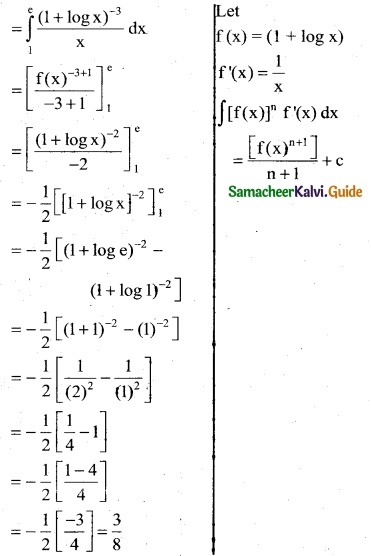
Question 7.
\(\int_{-1}^{1}\) \(\frac { 2x+3 }{x^2+3x+7}\) dx
Solution:
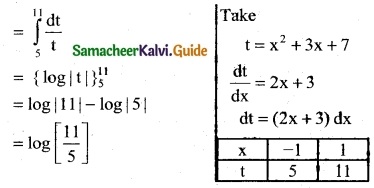
Question 8.
\(\int_{0}^{π/2}\) \(\sqrt { 1 +cosx} \) dx
Solution:
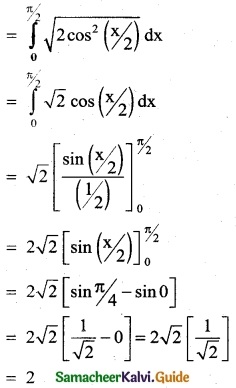
![]()
Question 9.
\(\int_{1}^{2}\) \(\frac { x-1 }{x^2}\) dx
Solution:
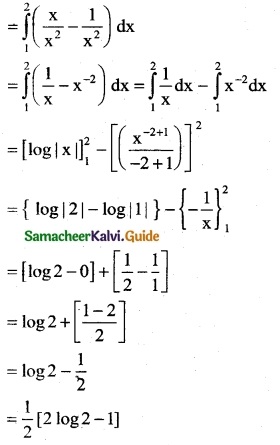
Evaluate the following
Question 10.
\(\int_{1}^{4}\) f(x) dx where f(x) = \(\left\{\begin{array}{l}
4 x+3,1 \leq x \leq 2 \\
3 x+5,2 \end{array}\right.\)
Solution:
\(\int_{1}^{4}\) f(x) dx
= \(\int_{1}^{2}\) f(x) dx + \(\int_{2}^{4}\) f(x) dx
= \(\int_{1}^{2}\) (4x + 3) dx + \(\int_{2}^{4}\) (3x + 5) dx
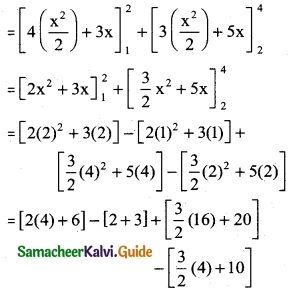
(8 + 6) – [5] + [24 + 20] – [6 + 10]
= 14 – 5 + 44 – 16
= 58 – 21
= 37
![]()
Question 11.
\(\int_{0}^{2}\) f(x) dx where f(x) = \(\left\{\begin{array}{ll}
3-2 x-x^{2}, & x \leq 1 \\
x^{2}+2 x-3, & 1<x \leq 2
\end{array}\right.\)
Solution:
\(\int_{0}^{2}\) f(x) dx
= \(\int_{0}^{1}\) f(x) dx + \(\int_{1}^{2}\) f(x) dx
= \(\int_{0}^{1}\) (3 – 2x – x²) dx + \(\int_{1}^{2}\) (x² + 2x – 3) dx
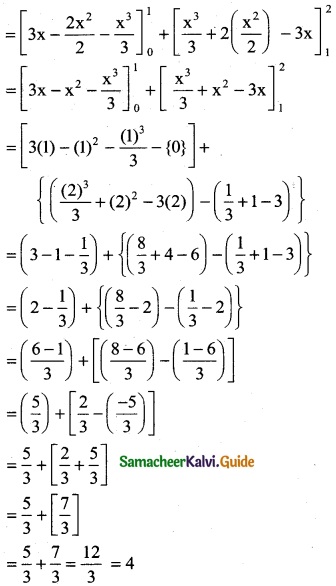
Question 12.
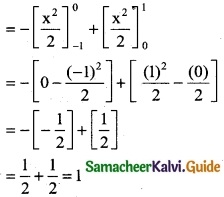
\(\int_{-1}^{1}\) f(x) dx where f(x) = \(\left\{\begin{array}{ll}
x, & x \geq 0 \\
-x, & x<0
\end{array}\right.\)
Solution:
\(\int_{-1}^{1}\) f(x) dx
\(\int_{-1}^{0}\) f(x) dx + \(\int_{0}^{1}\) f(x) dx
= \(\int_{-1}^{0}\) (-x) dx + \(\int_{0}^{1}\) x dx
![]()
Question 13.
f(x) = \(\left\{\begin{array}{l}
c x, \quad 0<x<1 \\
0, \text { otherwise }
\end{array}\right.\) find ‘c’ if \(\int_{0}^{1}\) f(x) dx = 2
Solution:
Given
f(x) = \(\left\{\begin{array}{l}
c x, \quad 0<x<1 \\
0, \text { otherwise }
\end{array}\right.\)
⇒ \(\int_{0}^{1}\) f(x) dx = 2
⇒ \(\int_{0}^{1}\) cx dx = 2
c[ \(\frac { x^2 }{ 2 }\) ]\(_{0}^{1}\) = 2
c[ \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) – 0 ] = 2
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) = 2
⇒ c = 4
![]()
Must Read: