Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Guide Pdf Chapter 3 Management By Objectives (MBO) and Management By Exception (MBE) Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Solutions Chapter 3 Management By Objectives (MBO) and Management By Exception (MBE)
12th Commerce Guide Management By Objectives (MBO) and Management By Exception (MBE) Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
…………………… System gives full Scope to the Individual Strength and Responsibility.
a) MBO
b) MBE
c) MBM
d) MBA
Answer:
a) MBO
![]()
Question 2.
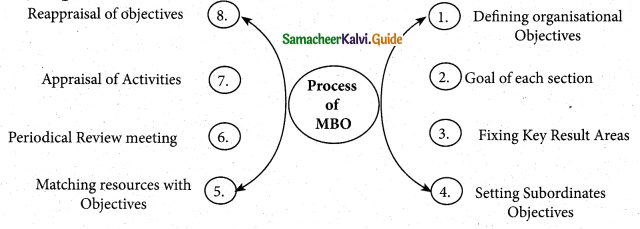
Which is the First step in Process of MBO?.
a) Fixing Key Result Area
b) Appraisal of Activities
c) Matching Resources with Activities
d) Defining Organisational Objectives
Answer:
d) Defining Organisational Objectives
Question 3.
…………………. keeps Management Alert to Opportunities and Threats by Identifying Critical Problems.
a) MBA
b) MBE
c) MBM
d) MBO
Answer:
b) MBE
Question 4.
Delegation of Authority is Easily Done with the Help of
a) MBM
b) MBE
c) MBO
d) MBA
Answer:
c) MBO
![]()
II. Very short answer questions.
Question 1.
Define-MBO
Answer:
MBO is popularised in the USA by George Odiome. According to him, “MBO is a system wherein the superior and the subordinate managers of an organisation jointly identify its common goals, define each individual’s major area of responsibility in terms of the result expected of him and use these measures as guides for operating the unit and assessing the contribution of each of its members”.
Question 2.
What are the objectives of MBO?
Answer:
- To measure and judge performance.
- To relate individual goals to organisation goals.
- To stimulate the subordinate’s motivation.
- To serve as a device for organisational control and integration.
Question 3.
Bring out the meaning of MBE.
Answer:
Management By Exception is an important principle of managerial control suggested by the classical writers on management. It is based on the belief that an attempt to control everything results in controlling nothing. Management by exception is a style of business management that focuses on identifying and handling cases that deviate from the norm.
![]()
Question 4.
Mention any two advantages of MBO?
Answer:
- MBO process helps the managers to understand their role in the total organization.
- Delegation of Authority is easily done with the help of MBO.
Question 5.
What is known as KRA?
Answer:
- Key Result Areas [KRA] are fixed on the basis of organisational objective premises.
- KRA arranged on a priority basis.
- It indicates the strength of an organisation. (Profitability – Market standing – innovation)
- MBE is helpful for the better utilisation of managerial talents.
- MBE facilitates delegation of authority. TOP level Management concentrates on strategic decisions and operational decisions are left to lower-level management.
- MBE keeps management alert to opportunities and threats by identifying critical problems.
- MBE avoids uniform and impulsive action.
- MBE provides better yardsticks for judging results.
- MBE is helpful in objective performance appraisal.
- MBE is a technique of separating important information from unimportant one.
- MBE forces managers to review past history and study-related business data for identifying deviations.
Question 3.
Explain the various disadvantages of MBO.
Answer:
- MBO fails to explain the philosophy; most of the executives do not know how MBO
works? what is MBO? and why is MBO necessary? and how participants can benefit from MBO. - MBO is a time-consuming process. Much time is needed by senior people for framing the MBO. Next, it leads to heavy expenditure and also requires heavy paperwork.
- MBO emphasizes only short-term objectives and does not consider long-term objectives.
- The status of subordinates is necessary for proper objectives setting. But, this is not possible in the process of MBO.
- MBO is a rigid one. Objectives should be changed according to the changed circumstances, external or internal. If it is not done, the planned results cannot be obtained.
Question 4.
Discuss the disadvantages of MBE.
Answer:
- The main disadvantage of MBE is, only managers have the power over really important decisions, which can be demotivating for employees at a lower level.
- Furthermore, it takes time to pass the issues to managers. Managing employees who deviate from the normal procedures. Because of compliance failures are considered difficult to manage and typically find themselves with limited job duties and ultimately dismissed/ terminated.
12th Commerce Guide Management By Objectives (MBO) and Management By Exception (MBE) Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
MBO refers to ……………………………
a) Management By Objective
b) Management By Officers
c) Management By Orders
d) Management By Organisation
Answer:
a) Management By Objective
![]()
Question 2.
_______ harmonises the goal of an individual with the organisation’s goal.
(a) MBO
(b) MBE
(c) MBA
(d) MBM
Answer:
(a) MBO
Question 3.
It is based on the belief that any attempt to control everything results in controlling nothing.
a) MBA
b) MBM
c) MBO
d) MBE
Answer:
d) MBE
![]()
Question 4.
KRA refers to …………………….
a) Key Result Areas
c) Known Result Areas
b) Key Reference Action
d) Knowledge Resource Aim.
Answer:
a) Key Result Areas
Question 5.
“Exception has occured”
(a) MBO
(b) MBE
(c) MBM
(c) Appraisal
Answer:
(b) MBE
Question 6.
The examples of KRA are _______
(a) profitability
(b) loss
(c) market standing
(d) innovation
Answer:
(b) loss
![]()
II. Match the following
1. Match List I with List II
| List -I | List -II |
| i. Matching Resources | 1. Subordinate objective fixed. |
| ii. Appraisal of Activities | 2. Framed on the basis of resources. |
| iii. Periodical Review | 3. Discussion between superiors and subordinates |
| iv. Targets | 4. Hold meeting periodically |
a) i-2, ii-3, iii-4, iv-1
b) i-2, ii-4, iii-3, iv-1
b) i-2, ii-4, iii-3, iv-1
d) i-1, ii-3, iii-4, iv-2
Answer:
a) i-2, ii-3, iii-4, iv-1
![]()
III. Assertion and Reason
Question 1.
Assertion (A): KRA indicates the strength of an organisation.
Reason (R): Objectives are expressed in a meaningful manner.
a) (A) is true (R) is true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
b) (A) is true (R) is false but (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
c) (A) and (R) are False.
d) (A) and (R) are true.
Answer:
a) (A) is true (R) is true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
IV. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is Appraisal of Activities?
Answer:
At the end of the fixed period for achieving the objectives, there should be a discussion between the superior and subordinates. The discussion is related to subordinates’ performance against I the specified standards. The superior should take corrective action.
Question 2.
What are the processes involved in MBO?