Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Guide Pdf Chapter 6 Banking
Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Solutions Chapter 6 Banking
12th Economics Guide Banking Text Book Back Questions and Answers
PART – A
Multiple Choice questions
Question 1.
A Bank is a
a) Financial institutions
b) Corporate
c) An Industry
d) Service institutions
Answer:
a) Financial institutions
Question 2.
A commercial Bank is an institution that provides services
a) Accepting deposits
b) Providing loans
c) Both a and b
d) None of the above
Answer:
c) Both a and b
![]()
Question 3.
The Functions of commercial banks are broadly classified into
a) Primary Functions
b) Secondary Functions
c) Other Functions
d) a, b, and c
Answer:
d) a, b, and c
Question 4.
Bank credit refers to
a) Bank loañs
b) Advances
c) Bank loans and advances
d) Borrowing
Answer:
c) Bank loans and advances
Question 5.
Credit creation means.
a) Multiplication of loans and advances
b) Revenue
c) Expenditure
d) Debt
Answer:
a) Multiplication of loans and advances
![]()
Question 6.
NBFI does not have.
a) Banking license
b) government approval
c) Money market approval
d) Finance ministry approval
Answer:
a) Banking license
![]()
Question 7.
Central bank is …………………… authority of any country.
a) Monétary
b) Fiscal
c) Wage
d) National Income
Answer:
a) Monétary
Question 8.
Who will act as the banker to the Government of India?
a) SBI
b) NABARD
c) ICICI
d) RBI
Answer:
d) RBI
Question 9.
Lender of the last resort is one of the functions of.
a) Central Bank
b) Commercial banks
c) Land Development Banks
d) Co – operative banks
Answer:
a) Central Bank
![]()
Question 10.
Bank Rate means.
a) Re – discounting the first class securities
b) Interest rate
c) Exchange rate
d) Growth rate Repo Rate means.
Answer:
a) Re – discounting the first class securities
Question 11.
Repo Ràte means.
a) Rate at which the Commercial Banks are willing to lend to RBI
b) Rate at which the RBI is willing to lend to commercial banks
c) Exchange rate of the foreign bank
d) Growth rate of the economy .
Answer:
b) Rate at which the RBI is willing to lend to commercial banks
![]()
Question 12.
Moral suasion refers.
a) Optimization
b) Maximization,
c) Persuasion
d) Miñimization
Answer:
c) Persuasion
Question 13.
ARDC started functioning from
a) June 3 1963
b) July 5, 1963
c)July 1,1963
d) July 1, 1963
Answer:
d) July 1, 1963
![]()
Question 14.
NABARD was set up in .
a) July 1962
b) July 1972
c) July 1982
d) July 1992
Answer:
c) July 1982
Question 15.
EXIM bank was established in ……………..
a) June 1982
b) April 1982
c) May 1982
d) March 1982
Answer:
d) March 1982
![]()
Question 16.
The State Financial Corporation Act was passed by .
a) Governnent of India
b) Government of Tamilnadu
c) Government of Union Territòries
d) Local Government
Answer:
a) Governnent of India
Question 17.
Monetary policy is formulated by.
a) Co – operative banks
b) Commercial banks
c) Central bank
d) Foreign banks
Answer:
c) Central bank
![]()
Question 18.
Online Banking is also known as
a) E Banking.
b) Internet Banking
c) RTGS
d) NEFT
Answer:
b) Internet Banking
Question 19.
Expansions of ATM.
a) Automated Teller Machine
b) Adjustment Teller Machine
c) Automatic Teller mechanism
d) Any Time Money
Answer:
a) Automated Teller Machine
Question 20.
2016 Demonetization of currency includes denominations of
a) ₹ 500 and ₹ 1000
b) ₹ 1000 and ₹ 2000
c) ₹ 200 and ₹ 500
d) All the above
Answer:
a) ₹ 500 and ₹ 1000
![]()
PART – B
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences.
Question 21.
Define Commercial banks.
Answer:
Commercial bank refers to a bank, or a division of a large bank, which more specifically deals with deposit and loan services provided to corporations or large/middle-sized business – as opposed to individual members of the public/small business.
Question 22.
What is credit creation?
Answer:
Credit creation means the multiplication of loans and advances. Commercial banks receive deposits from the public and use these deposits to give loans.
![]()
Question 23.
Define central bank.
Answer:
A central bank is an institution that manages a state’s currency, money supply, and interest rates.
Question 24.
Distinguish between CRR and SLR.
CRR is the percentage of money, which a bank has to keep with RBI in the form of cash.
SLR is the proportion of liquid assets to time and demand liabilities.
![]()
Question 25.
Write the meaning of Open market operations
Answer:
- In a narrow sense, the Central Bank starts the purchase and sale of Government securities in the money market.
- In Broad Sense, the Central Bank purchases and sells not only Government securities but also other proper eligible securities like bills and securities of private concerns.
- When the banks and the private individuals purchase these securities they have to make payments for these securities to the Central Bank.
Question 26.
What is rationing of credit?
Answer:
Rationing of credit is an instrument of credit control. It aims to control and regulate the purposes for which credit is granted by commercial banks.
![]()
Question 27.
Mention the functions of the agriculture credit department.
Answer:
Functions of Agriculture Credit Department:
- To maintain an expert staff to study all questions on agricultural credit;
- To provide expert advice to Central and State Government, State Co-operative Banks, and other banking activities.
- To finance the rural sector through eligible institutions engaged in the business of agricultural credit and to co-ordinate their activities.
PART – C
Answer the following questions in one paragraph.
Question 28.
Write the mechanism of crédit creation by commercial banks.
Answer:
- Bank credit refers to bank loans and advances. Money is said to be created when the banks, through their lending activities, make a net addition to the total supply of money in the economy.
- Likewise, money is said to be destroyed when the loans are repaid by the borrowers. Consequently the credit creáted are wiped out.
- Banks have the power to expand or contract demand deposits. This power of the commercial banks to create deposits through their loans and advances is known as credit creation.
Question 29.
Give a brief note on NBFI.
Answer:
Non – Banking Financial Institution (NBFI):
1. A non – banking financial institution (NBFI) or non-bank financial company (NBFC) is a financial institution that does not have a full banking license or is not supervised by the central bank.
2. The NBFIs do not carry on pure banking business, but they will carry on other financial transactions. They receive deposits and give loans. They mobilize people’s savings and use the funds to finance expenditure on investment activities. In short, they are institutions which undertake borrowing and lending. They operate in both the money and the capital markets.
3. NBFIs can be broadly classified into two categories. Viz.., (1) Stock Exchange; and (2) Other Financial institutions. Under the latter category comes Finance Companies, Finance Corporations, ChitFunds, Building Societies, Issue Houses, Investment Trusts and Unit Trusts and Insurance Companies.
![]()
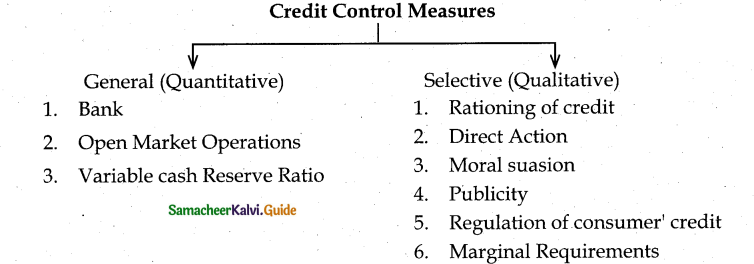
Question 30.
Bring out the methods of credit control.
Answer:
Credit Control Measures
Question 31.
What are the functions of NABARD?
Answer:
Functions of NABARD:
NABARD has inherited its apex role from RBI i.e, it is performing all the functions performed
by RBI with regard to agricultural credit.
1. NABARD acts as a refinancing institution for all kinds of production and investment credit to agriculture, small-scale industries, cottage, and village industries, handicrafts and rural crafts and real artisans and other allied economic activities with a view to promoting integrated rural development.
2. NABARD gives long-term loans (upto 20 Years) to State Government to enable them to subscribe to the share capital of cooperative credit societies.
3. NABARD gives long-term loans to any institution approved by the Central Government or contribute to the share capital or invests in securities of any institution concerned with agriculture and rural development.
4. NABARD has the responsibility of coordinating the activities of Central and State Governments, the Planning Commission (now NITI Aayog) and other all India and State level institutions entrusted with the development of small scale industries, village and cottage industries, rural crafts, industries in the tiny and decentralized sectors, etc.
5. It maintains a Research and Development Fund to promote research in agriculture and rural development.
Question 32.
Specify the function of IFCI.
Answer:
The functions of the Industrial Finance Corporation of India are
- Long term loans; both in rupees and foreign currencies.
- Underwriting of equity, preference and debenture issues.
- Subscribing to equity, preference and debenture issues. .
- Guaranteeing the deferred payments in respect of machinery imported from abroad or purchased in India.
- Guaranteeing of loans raised in foreign currency from foreign financial institutions.
Question 33.
Distinguish between money market and capital market.
Answer:
|
Money market |
Capital market |
| 1. Money market is the mechanism through which short term funds are loaned and borrowed. | The market where investment instruments like bonds, equities and mortgages are traded is known as the capital market. |
| 2. It is a part of financial system It designates financial institutions which handle the purchase, sale and transfer of short term credit instruments. | It is a part of financial system which is concerned with raising and transfer of short term credit capital by dealing in shares, bonds instruments, and other long term investments. |
Question 34.
Mention the Objectives of demonetizations.
Answer:
Objectives of Demonetisation:
- Removing Black Money from the country.
- Stopping of Corruption.
- Stopping Terror Funds.
- Curbing Fake Notes.
Demonetisation is the act of stripping a currency unit of its status as legal tender. It occurs whenever there is a change of national currency. The current form or forms of money is pulled from circulation, often to be replaced with new coins or notes.
![]()
PART – D
Answer the following questions in about a page.
Question 35.
Explain the role of Commercial Banks in economic development.
Answer:
Role of Commercial Banks in Economic Development of a Country Role of Commercial Banks:
- Capital Formation
- Creation of Credit
- Channelizing the funds
- Encouraging Rights Type of Industries
- Banks Monetize Debt
- Finance to Government
- Employment Generation
- Bank Promote Entrepreneurship
1. Capital Formation:
- Banks play an important role in capital formation, which is essential for the economic development of a country.
- They mobilize the small savings of the people scattered over a wide area through their network of branches all over the country and make it available for productive purposes.
2. Creation of Credit:
- Banks create credit for the purpose of providing more funds for development projects.
- Credit creation leads to increased production, employment, sales and prices and thereby they bring about faster economic development.
3. Channelizing the Funds towards Productive Investment:
- Banks invest the savings mobilized by them for productive purposes.
- Capital formation is not the only function of commercial banks.
4. Encouraging Right Type of Industries:
- Many banks help in the development of the right type of industries by extending loan to right type of persons.
- In this way, they help not only for industrialization of the country but also for the economic development of the country.
- They grant loans and advances to manufacturers whose products are in great demand.
5. Banks Monetize Debt:
- Commercial banks transform the loan to be repaid after a certain period into cash, which can be immediately used for business activities.
- Manufacturers and wholesale traders cannot increase their sales without selling goods on credit basis.
6. Finance to Government:
- The government is acting as the promoter of industries in underdeveloped countries for which finance is needed for it.
- Banks provide long – term credit to Government by investing their funds in Government securities and short-term finance by purchasing Treasury Bills.
7. Employment Generation:
- After the nationalization of big banks, banking industry has grown to a great extent.
- Bank’s branches are opened frequently, which leads to the creation of new employment opportunities.
8. Banks Promote Entrepreneurship:
- In recent days, banks have assumed the role of developing entrepreneurship particularly in developing countries like India by inducing new entrepreneurs to take up well-formulated projects and provision of counseling services like technical and managerial guidance.
![]()
Question 36.
Elucidate the functions of commercial Banks.
Answer:
The functions of commercial Banks are classified as primary secondary and other functions.
(a) Primary Functions:
1. Accepting Deposits:
It implies that Commercial banks are mainly dependent on public deposits. There are two types of deposits, which are :
- Demand Deposits:
It refers to deposits that can be with drawn by individuals without any prior notice to the bank - Time Deposit:
It refers to deposits that are made for certain committed period of time.
2. Advancing Loans:
It refers to granting loans to individuals and businesses. Commercial banks grant loans in the form of overdraft, cash credit and discounting bills of exchange.
b) Secondary Functions:
1. Agency Functions
It implies that commercial banks act as agents of customers by performing various functions. They are
- Collecting cheques
- Collecting Income
- Paying Expenses
2) General utility Function
It implies that commercial banks provide some utility to customers by performing various functions .
- Providing Locker Facilities
- Issuing Traveler’s cheques
- Dealing in Foreign Exchange
3) Transferring Funds :
It refers to transferring of funds from one bank to another. Funds are transferred by means of draft, telephonic transfer, and electronic transfer.
4) Letter of credit:
Commercial banks issue letters of credit to their customers to certify their creditworthiness.
- Underwriting securities
- Electronic Banking
(c) Other Functions:
- Money supply
It refers to one of the important functions of commercial banks that help in increasing money supply. With this function without printing additional money, the supply of money is increased. - Credit creation
Credit creation means the multiplication of loans and advances. - Collection of statistics
Banks collect and publish statistics relating to trade, commerce, and industry.
![]()
Question 37.
Describe the functions of Reserve Bank of India.
Answer:
Functions of Central Bank (Reserve Bank of India):
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is India’s central banking institution, which controls the monetary policy of the Indian rupee.
1. Monetary Authority:
It controls the supply of money in the economy to stabilize exchange rate, maintain healthy balance of payment, attain financial stability, control inflation, strengthen banking system.
2. The issuer of currency:
The objective is to maintain the currency and credit system of the country. It is the sole authority to issue currency. It also takes action to control the circulation of fake currency.
3. The issuer of Banking License:
As per Sec 22 of Banking Regulation Act, every bank has to obtain a banking license from RBI to conduct banking business in India.
4. Banker to the Government:
It acts as banker both to the central and the state governments. It provides short-term credit. It manages all new issues of government loans, servicing the government debt outstanding and nurturing the market for government securities. It advises the government on banking and financial subjects.
5. Banker’s Bank:
RBI is the bank of all banks in India as it provides loan to banks, accept the deposit of banks, and rediscount the bills of banks.
6. Lender of last resort:
The banks can borrow from the RBI by keeping eligible securities as collateral at the time of need or crisis, when there is no other source.
7. Act as clearing house:
For settlement of banking transactions, RBI manages 14 clearing houses. It facilitates the exchange of instruments and processing of payment instructions.
8. Custodian of foreign exchange reserves:
It acts as a custodian of FOREX. It administers and enforces the provision of Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999. RBI buys and sells foreign currency to maintain the exchange rate of Indian rupee v/s foreign currencies.
9. Regulator of Economy:
It controls the money supply in the system, monitors different key indicators like GDP, Inflation, etc.
10. Managing Government securities:
RBI administers investments in institutions when they invest specified minimum proportions of their total assets/liabilities in government securities.
11. Regulator and Supervisor of Payment and Settlement Systems:
The Payment and Settlement Systems Act of 2007 (PSS Act) gives RBI oversight authority for the payment and settlement systems in the country. RBI focuses on the development and functioning of safe, secure and efficient payment and settlement mechanisms.
12. Developmental Role:
This role includes the development of the quality banking system in India and ensuring that credit is available to the productive sectors of the economy. It provides a wide range of promotional functions to support national objectives.
It also includes establishing institutions designed to build the country’s financial infrastructure. It also helps in expanding access to affordable financial services and promoting financial education and literacy.
13. Publisher of monetary data and other data:
RBI maintains and provides all essential banking and other economic data, formulating and critically evaluating the economic policies in India. RBI collects, collates and publishes data regularly.
14. Exchange manager and controller:
RBI represents India as a member of the International Monetary Fund [IMF], Most of the commercial banks are authorized dealers of RBI.
15. Banking Ombudsman Scheme:
RBI introduced the Banking Ombudsman Scheme in 1995. Under this scheme, the complainants can file their complaints in any form, including online and can also appeal to the Ombudsman against the awards and the other decisions of the Banks.
16. Banking Codes and Standards Board of India:
To measure the performance of banks against Codes and standards based on established global practices, the RBI has set up the Banking Codes and Standards Board of India (BCSBI).
![]()
Question 38.
What are the objectives of Monetary policy? Explain.
Answer:
1) Neutrality of money :
Neutralists hold the view that monetary authority should aim at neutrality of money in the economy. Monetary changes could be the root cause of all economic fluctuations.
2) Exchange Rate stability :
Exchange rate stability was the traditional objective of monetary authority. This was the main objective under Gold standard among different countries. Instability in the Exchange rates results in unfavourable balance of payments. Therefore, stable exchange rates are advocated.
3) Price stability:
Price stability is considered the most genuine objective of monetary policy Stable prices repose public confidence. It promotes business activity and ensures equitable distribution of income and wealth. As a result, there is general wave of prosperity and welfare in the community.
But, price stability does not mean “price rigidity or price stagnation”
4) Full employment:
Full employment was considered as the main goal of monetary policy. With the publication of keynes General Theory of Employment, Interest and money in 1936, the objective of full employment gained full support as the chief objective of monetary policy.
5) Economic Growth:
Monetary policy should promote sustained and continuous economic growth by maintaining equilibrium between the total demand for money and total production capacity and further creating favourable conditions for saving and investment.
For bringing equality between demand and supply, a flexible monetary policy is the best course.
6) Equilibrium in the Balance of Payments:
Equilibrium in the balance of payments is another objective of monetary policy which emerged significantly in the post-war years. Monetary authority makes efforts to maintain equilibrium in the balance of payments.
12th Economics Guide Banking Additional Important Questions and Answers
One Mark Questions.
Question 1.
Reserve Bank of India was nationalised in …………………………
(a) 1947
(b) 1948
(c) 1949
(d)1950
Answer:
(c) 1949
Question 2.
Under British rule the first bank of India was …………………….
a) Bank of Bengal
b) Bank of Hindustan
c) Bank of Bombay
d) Bank of Madras
Answer:
b) Bank of Hindustan
![]()
Question 3.
The ……………………… Bank of India was changed into SBI
a) Mumbai
b) Chennai
c) Imperial
d) Presidency
Answer:
c) Imperial
Question 4.
Primary functions of the commercial bank is …………………………
(a) Accepting deposits from the public
(b) Making loans and advances to public
(c) Discounting bills of exchange
(d) Inter bank borrowing
Answer:
(a) Accepting deposits from the public
![]()
Question 5.
RBI commenced its operations on …………………………..
a) April 1,1934
b) April 1,1935
c) January 1,1949
d) April 1,1937
Answer:
b) April 1,1935
Question 6.
The coins are issued by …………………………
(a) Ministry of Finance
(b) RBI
(c) Central Bank
(d) State Bank
Answer:
(a) Ministry of Finance
![]()
Question 7.
The name Rupee was derived from the Sanskrit word …………….
a) Nomia
b) Rupay
c) Raupya
d) None of the above
Answer:
c) Raupya
Question 8.
The rate at which the RBI is willing to borrow from the commercial banks is called …………….
a) Reverse Repo Rate
b) Repo rate
c) Cash Reserve Ratio
d) Bank rate
Answer:
a) Reverse Repo Rate
![]()
Question 9.
Open Market operations enable the ………………………… to reduce the money supply in the economy.
(o) Commercial bank
(b) SBI
(c) ICICI
(d) RBI
Answer:
(d) RBI
Question 10.
Each Indian bank note has its amount written in …………….. language.
a) 15
b) 20
c) 17
d) 14
Answer:
c) 17
![]()
Question 11.
Regional Rural Banks were set up on ……………………
a) 1950
b) 1967
c)1970
d) 1975
Answer :
d) 1975
Question 12.
Industrial credit and Investment Corporation of India (ICICI) was set up on ………………
a) January 5, 1955
b) January 5,1973
c) February 15, 1976
d) February 5,1955
Answer:
a) January 5,1955
![]()
Question 13.
“Monetary History of the United states, 1867 -1960” was written by ………………
a) Milton Friedman
b) Irving Fisher
c) Walker
d) Culbertson.
Answer:
a) Milton Friedman
Question 14.
The qualitative credit control methods are also called …………………………
(a) Selective cash control
(b) Selective expenditure control
(c) Selective credit control
(d) Selective money control
Answer:
(c) Selective credit control
![]()
Question 15.
…………………. is the act of stripping a currency unit of its status as legal tender.
a) Fiscal policy
b) Demonitisation
c) Monetary policy
d) Money market.
Answer:
b) Demonetisation
II. Match the following:
Question 1.
A) Bank of Bengal – 1) 1843
B) Bank of Bombay – 2) 1809
C) Bank of Madras – 3) 1935
D) Reserve Bank of India – 4)1840

Answer:
a) 2 4 1 3
Question 2.
A) NEFT – 1) Automated Teller Machine
B) RTGS – 2) Payment Bank
C) ATM – 3) National Electronic Fund Transfer
D) Paytm – 4) Real Time Gross Settlement.

Answer:
c) 3 4 1 2
Question 3.
A) Expansionary monetary policy – 1) Milton Friedman
B) Contractionary monetary policy – 2) Cassel, Keynes
c) Monetary policy – 3) Cheap money policy
D) Price stability – 4) Dear money policy

Answer :
a) 3 4 1 2
III. Choose the correct pair
Question 1.
a) Nobel prize – J.M. Keynes
b) Monetary policy – Macro-Economic Policy
c) Money Market – Long term credit instruments
d) Capital Market – Short term credit instruments
Answer :
b) Monetary policy – Macro-Economic Policy
Question 2.
a) RBI – 1945
b) ARDC – 1968
c) RRB – 1975
d) NABARD – 1984
Answer:
c) RRB -1975
![]()
Question 3.
a) Neutrality of Money – Cassel, Keynes
b) Price stability – Wicksteed, Robertson
c) E-banking – Internet banking
d) Merger of banks – 2018
Answer:
c) E-banking – Internet banking
IV. Choose the incorrect pair
Question 1.
a)NABARD – Agricultural credit
b) All-India level Institutions – IFCI, ICICI, IDBI
c) State level Institutions – SFC, SIDC
d) RRB – Industrial Development Bank
Answer:
d) RRB – Industrial Development Bank
![]()
Question 2.
a) First Central Bank – The Ricks Bank
b) Commercial banks – Service motivated
c) Time Deposit – Recurring deposit
d) Primary Deposit -. Passive Deposits
Answer:
b) Commercial banks – Service motivated
Question 3.
a) Reserve Bank of India Act – 1935
b) Foreign Exchange Management Act – 1999
c) Banking Ombudsman Scheme -‘1995
d) Banking Regulation Act – 1949
Answer:
a) Reserve Bank of India Act -1935
![]()
V. Choose the correct statement.
Question 1.
a) Central Government is the sole authority to issue currency in India.
b)Variable cash Reserve Ratio as an objective of monetary policy was first suggested by J.M.Keynes.
c) SBI represents India as a member of the International Monetary Fund.
d )Variable cash Reserve Ratio was first followed by RBI.
Answer:
b) Variable cash Reserve Ratio as an objective of monetary policy was first suggested by J.M.Keynes.
Question 2.
a) RRBS provides credit and other facilities to urban Industries.
b)Contractionary Monetary policy decreases unemployment.
c) Expansionary Monetary policy is a cheap money policy.
d) Price stability means price rigidity or price stagnation.
Answer:
c) Expansionary Monetary policy is a cheap money policy.
Question 3.
a) The Minimum amount for NEFT transfer is 2 lakhs.
b) RTGS means National electronic fund transfer.
c) Capital market is concerned with raising capital by dealing in shares, bonds, and other long-term investments.
d) The rate at which the RBI is willing to borrow from the commercial banks is called Repo Rate.
Answer:
c) Capital market is concerned with raising capital by dealing in shares, bonds, and other long-term investments.
VI. Choose the incorrect statement
Question 1.
a) Variable cash Reserve Ratio was first introduced by J.M.Keynes.
b) Bank rate is otherwise called Discount Rate.
c) Commercial Banks are profit-motivated.
d) Public deposits are classified as Demand deposits, Time deposits, and Primary deposits.
Answer:
d) Public deposits are classified as Demand deposits, Time deposits, and Primary deposits.
Question 2.
a) Commercial banks provide long-term credit to maintain liquidity of assets.
b) Credit creation literally means the multiplication of loans and advances.
c) Rationing of credit is the oldest method of credit Control.
d) The modern banks create deposits in two ways such as primary deposit and derived deposit.
Answer:
a) Commercial banks provide long-term credit to maintain liquidity of assets.
![]()
Question 3.
a) The Agricultural Refinance Development Corporation was established on July 1, 1963.
b) Non – Banking Financial Institutions are supervised by the Central Bank.
c) If the Central Bank wants to control credit, it will raise the bank rate.
d) The share capital of NABARD was equally contributed by the RBI and the GOI.
Answer:
b) Non – Banking Financial Institutions are supervised by the Central Bank.
VII. Pick the odd one out:
Question 1.
a) State Financial Corporations.
b) Industrial Finance Corporation of India
c) Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India
d) Industrial Development Bank of India.
Answer:
a) State Financial Corporations.
Question 2.
a) Bank Rate Policy
b) Open Market Operations
c) Rationing of Credit
d) Variable Reserve Ratio
Answer:
c) Rationing of Credit
![]()
Analyse the reason:
Question 1.
Assertion (A): Reserve Bank of India had set up a separate Agricultural Credit Department.
Reason (R): RBI’s responsibility in the field of agriculture had been creased due to the predominance of agriculture in the Indian economy and the inadequacy of the formal agencies to cater to the huge requirements of the sector.
Answer:
a) Assertion (A): and Reason (R) both are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Question 2.
Assertion (A): A central bank is an institution that manages a state’s currency, money supply, and interest rates.
Reason (R): Central bank through monetary policy controls the supply of money.
Answer:
a) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) both are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
![]()
Question 3.
Assertion (A) : RBI was given oversight authority for the payment and settlement systems in the country. .
Reason (R) : The payment and settlement systems Act came into force in 2007.
Answer:
a) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) both are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Option:
a) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) both are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) both are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
d) Both (A) and (R) are false.
IX. 2 Mark Questions
Question 1.
When and where was the first central bank established?
Answer:
- The Ricks Banks of Sweden, which had sprung from a private bank established in 1656 is the oldest central bank in the world.
- The Bank of England (1864) is the first bank of issues.
Question 2.
What are the functions of primary deposits?
Answer:
Primary Deposits:
- It is out of these primary deposits that the bank makes loans and advances to its customers.
- The initiative is taken by the customers themselves. In this case, the role of the bank is passive.
- So these deposits are also called “Passive deposits”.
![]()
Question 3.
Name the classification of NBFIs.
Answer:
- Stock Exchange
- Other financial institutions Under the latter category comes Finance companies, Finance corporations, Chit funds, Building societies, etc.
Question 4.
Name the institutions for industrial finance.
Answer:
All-India level Institution:
- Industrial Finance Corporation of India
- Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India
- Industrial Development Bank of India.
State-level Institutions:
- State Financial Corporations
- State Industrial Development Corporation
![]()
Question 5.
Write RBI granting Regional Rural Banks concessions?
Answer:
The RBI has been granting many concessions to RRBs:
- They are allowed to maintain the cash reserve ratio at 3 percent and statutory liquidity ratio at 25 percent; and
- They also provide refinance facilities through NABARD.
Question 6.
State the specific objectives of monetary policy.
Answer:
- Neutrality of Money
- Stability of Exchange Rates
- Price stability
- Full employment
- Economic Growth
- Equilibrium in the Balance of Payments.
Question 7.
What is E-Banking?
Answer:
Online banking also known as internet banking, is an electronic payment system that enables customers of a bank or other financial institution to conduct a range of financial transactions through the financial institution’s website.
![]()
Question 8.
What do you know about Automated Teller Machine?
Answer:
ATMs were first introduced in 1967. Biometric authentication is already used in India, and its recognition is in place at Qatar National Bank ATMs.
Question 9.
Write a note on Paytm.
Answer:
Payments bank or Paytm is one of India’s e-commerce payment system and digital wallet company. It was established on August 2015, by the license of RBI.
Question 10.
Write a note on Debit Card.
Answer:
A Debit card is a card allowing the holder to transfer money electronically from their bank account when making a purchase.
Question 11.
What is demonetization?
Answer:
Demonetization is the act of stripping a currency unit of its status as legal tender. The current form or forms of money is pulled from circulation, often to be replaced with new coins or notes.
X. 3 Mark Questions
Question 1.
What are the functions of RBI agricultural credit?
Answer:
Role of RBI in agricultural credit:
- RBI has been playing a very vital role in the provision of agricultural finance in the country.
- The Bank’s responsibility in this field had been increased due to the predominance of agriculture in the Indian economy and the inadequacy of the formal agencies to cater to the huge requirements of the sector.
- In order to fulfill this important role effectively, the RBI set up a separate Agriculture Credit Department.
- However, the volume of informal loans has not declined sufficiently.
Question 2.
Write a note on Regional Rural Banks.
Answer:
- Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) was setup by the Government of India in 1975.
- The main objective of the RRBs is to provide credit and other facilities particularly to the small and marginal farmers, agricultural labourers, artisans, and smalls entrepreneurs so as to develop agriculture, trade, commerce, industry, and other productive activities in the rural areas.
- RBI provides refinance facilities to RRBs through NABARD.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the functions of ICICI.
Answer:
ICICI was set up on 5th January 1955. The principal purpose of this institution is to channelize the world bank funds to the industry in India and also to help build up a capital market.
Functions:
- Assistance to industries
- Provision of foreign currency loans
- Merchant banking
- Letter of credit
- Project promotion
- Housing loans
- Leasing operations
Question 4.
What is E-Banking?
Answer:
- Online banking, also known as internet banking, is an electronic payment system that enables customers of a bank or other financial institution to conduct a range of financial transactions through the financial institution’s website.
- The online banking system typically connects to or be part of the core banking system operated by a bank and is in contrast to branch banking which was the traditional way customers accessed banking services.
![]()
Question 5.
Differentiate NEFT and RTGS.
Answer:
|
NEFT |
RTGS |
| 1. National Electronic Fund Transfer | 1. Real Time Gross Settlement |
| 2. Transactions happen in batches hence slow | 2. Transactions happens in real-time hence fast. |
| 3. No minimum limit | 3. Minimum amount for RTGS transfer is Rs.2 Lakhs. |
XI. 5 Mark Questions
Question 1.
Differentiate Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate.
Answer:
|
Repo Rate RR |
Reverse Repo Rate RRR |
| 1. The rate at which the RBI is willing to lend to commercial banks is called Repo Rate | 1. The rate at which the RBI is willing to borrow from the commercial banks is called the reverse repo rate. |
| 2. To central inflation, RBI increases the Repo Rate. | 2. If the RBI increases the reverse repo rate, it means that the RBI wants the banks to park their money with the RBI. |
| 3. Similarly RBI reduces the Repo rate to control deflation. | 3. To control deflation RBI also reduces the Reverse Repo rate. |
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the functions of the Industrial Development Bank of India.
Answer:
- The functions of IDBI fall into two groups.
- Assistance to other financial institutions.
- Direct assistance to industrial concerns either on its own or in participation with other institutions.
- The IDBI can provide refinance in respect of term loans to industrial concerns given by the IFC, the SFCs, other financial institutions notified by the government, scheduled banks, and state cooperative banks.
- A special feature of the IDBI is the provision for the creation of a special fund known as the Development assistance fund.
- The fund is intended to provide assistance to industries which require heavy investments with a low anticipated rate of return.
Question 3.
Explain the State level institutions of Industrial Finance.
Answer:
1. State Financial Corporation (SFCs):
The government of India passed 1951 the State Financial corporations Act and SFCs were set up in many states. The SFCs are mainly intended for the development of small and medium industrial units within their respective states. However, in some cases, they extend to neighbouring states as well.
SFCs depend upon the IDBI for refinancing in respect of the term loans granted by them. Apart from these, the SFCs can also make temporary borrowings from the RBI and borrowings from IDBI and by the sale of bonds.
2. State Industrial Development Corporations(SIDCOs):
The Industrial Development Corporations have been set up by the state governments and they are wholly owned by them. These institutions are not merely financing agencies, are entrusted with the responsibility of accelerating the industrialization of their states.
![]()