Students can download 6th Science Term 3 Chapter 4 Our Environment Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 3 Chapter 4 Our Environment
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Our Environment Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Identify the freshwater ecosystem.
a. Pond
b. Lake
c. River
d. All of them
Answer:
d. All of them
Question 2.
Producers are ________
(a) Animals
(b) Birds
(c) Plants
(d) Snakes
Answer:
(c) Plants
Question 3.
It is a biodegradable waste
a. Plastic
b. Coconut Shell
c. Glass
d. Aluminium
Answer:
b. Coconut Shell
![]()
Question 4.
It is an undesirable change that occurs in air and water.
(a) Recycling
(b) Reuse
(c) Pollution
(d) Reduce
Answer:
(c) Pollution
Question 5.
Usage of chemical pesticides and fertilisers causes ……… pollution.
a. Air pollution
b. Water pollution
c. Noise pollution
d. None of the above
Answer:
b. Water pollution
II. Fill in the Blanks
- Primary consumers that eat plants are called ……….
- Temperature, light and wind are ………… factors.
- ………. is the process of converting waste materials into new materials.
- Water pollution can spread …………. and chemicals.
- The 3R’s are Reduce, ………….. and Recycle.
Answer:
- herbivores
- physical
- Recycle
- diseases
- reuse
III. True or False. If False, give the correct statement.
- The pacific ocean is an example of an aquatic ecosystem.
- Bacteria and fungi are called decomposers.
- Human and animal wastes are examples of non-biodegradable waste.
- Excessive use of pesticides leads to air pollution.
- In schools, waste management rules say that we should separate waste in two categories.
Answer:
- True.
- True.
- False – Human and animal wastes are examples of bio-degradable waste.
- False – Excess use of pesticides leads to land pollution.
- False – In schools waste management rules say that we should separate waste in three categories.
IV. Match the following
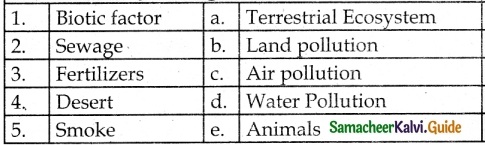
Answer:
1. – e
2. – d
3. – b
4. – a
5. – c
V. Arrange the following in a correct sequence and form a food chain
- Rabbit → Carrot → Eagle → Snake.
- Human → Insect → Algae → Fish
Answer:
- carrot → rabbit → snake → eagle.
- Algae → Insect → Fish → Human
![]()
VI. Give Very Short Answer:
Question 1.
Define ecosystem.
Answer:
An ecosystem is a community of living or biotic and non-living or a biotic things that work together.
Question 2.
What are the two types of ecosystems?
Answer:
They are terrestrial (on land) and aquatic (in water).
Question 3.
Write any two things that can be recycled.
Answer:
Examples:
- Old clothes
- Plastics
Question 4.
What are the types of pollution?
Answer:
There are four major kinds of pollution.
- Air pollution
- Water pollution
- Land (soil) pollution
- Noise pollution
Question 5.
Give one example of a food chain in an aquatic ecosystem?
Answer:
Food chain in aquatic ecosystem.
Aquatic plant → Aquatic insect → Larva → Fish.
Question 6.
Name some pollutants.
Answer:
Pollutants:
- Burning fossil fuel (petrol, coal, oil, etc).
- Toxic gases, (Carbon monoxide).
- Dust particles (ash, soot).
![]()
Question 7.
What are the pollutions caused by the objects given below?
- Loud Speaker
- Plastic
Answer:
- Loud Speaker – Noise Pollution.
- Plastic – Land Pollution.
VII. Give a short answer:
Question 1.
What is biodegradable waste?
Answer:
The term ‘Biodegradable’ is used for those things that can be easily decomposed by natural agents like water, oxygen, ultraviolet rays of the sun, microorganisms, etc. (Eg.) Vegetable and fruit peel leftover food, grass, leaves, and twigs.
Question 2.
How can we reduce water pollution?
Answer:
- Do not pour leftover oil, old medicines or waste down the drain or into the toilet.
- Reduce the use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers to grow crops.
- Reduce the use of detergents and bleach to wash clothes.
- Do not litter or dump waste always use a waste bin.
Question 3.
Write the importance of the food chain.
Answer:
- Learning about the food chain help us to understand the feeding relationship and interaction between organisms in any ecosystem.
- It also help us to appreciate the energy flow and nutrient circulation in an ecosystem. This enable us to understand the movement of toxic substances and their impacts.
VIII. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
Give two examples of how you can avoid or reduce waste?
Answer:
Examples of how we can Avoid waste:-
Avoid buying packaged foods. Refuse to buy ‘use-and-throw’ plastic products.
Examples of how we can reduce waste:-
- Write on both sides of paper
- Share newspaper and magazines with others.
![]()
Question 2.
Write a short note on noise pollution.
Answer:
- Noise pollution affects the environment. We all like a quiet and peaceful place since unpleasant or loud sounds disturb us.
- Loud music, the sounds of motor vehicles, fireworks and machines cause noise pollution. Continuous noise disturbs our sleep and does not let us study.
- Noise pollution has been directly linked to stress and health impacts such as high blood pressure and hearing loss.
- Loud noise or even loud music can damage our ears. Noise pollution also disturbs animals.
- Birds have to communicate (talk) louder so that, they can hear each other in noisy areas.
- Even underwater noise pollution from ships can make whales lose their way as they use sounds to navigate.
Reduce noise pollution :
- Turn off your electronics when you do not use them.
- Avoid fireworks.
- Speak, do not shout.
- Remind drivers not to use the horn too much.
- Lower the volume when you watch TV (or) listen to music.
IX. Questions Based on Higher Order Thinking Skills
Question 1.
What would happen if an organism is removed from the food chain?
Answer:
If an organism is removed from the food chain,
- The food chain will fall apart.
- The ecosystem will become imbalanced and collapse.
- For example, Consider a food chain: Plants → grasshoppers → frogs → snakes → hawks.
If frogs were to die off in this chain, (due to disease/pollutants), then, there will be an increase in the number of grasshoppers. This will cause a major problem.
Question 2.
Explain the link between waste and dangerous diseases like dengue and malaria?
Answer:
- The substances consist of plastic materials, metal scraps, aluminium cans, and bottles which cannot be broken down or decomposed into the soil by natural agents are labelled as non-biodegradable.
- When it rains, some of the water never reaches the ground as it collects in the plastic garbage at the dump.
- Little pools of water let mosquitoes breed and they can spread unwanted diseases like dengue and malaria.
- Aedes aegypti is the vector responsible for dengue transmission.
- It breeds in solid waste mud pots and other junk materials.
- We must know mosquitoes tend to breed in places which are dirty.
X. See the diagram and answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Explain what is happening in the picture?
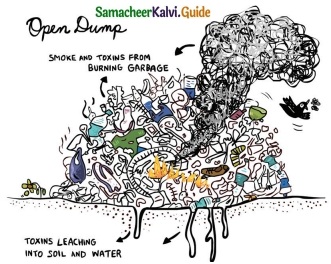
Answer:
- We can see the mixed waste dumped in the open ground.
- There is a fire in the open dump and the garbage is burning.
- By the burning of plastic materials, pipes, leather, and garbage smoke and toxins are coming out and pollute the air.
- The leftover ash from burning waste pollutes the soil.
- When it rains some of the dangerous chemicals leaching into the soil and groundwater.
- Thus the unhealthy chemicals from the garbage pollute the ecosystem.
![]()
Question 2.
What types of pollution are caused by open dumps?
Answer:
The following types of pollution are caused by open dumps:
- Water pollution
- Land pollution
- Air pollution
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Our Environment Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the best Answer:
Question 1.
The ecosystem that originated without human intervention is called
(a) natural ecosystem
(b) artificial ecosystem
(c) aquarium
(d) terrarium
Answer:
(a) natural ecosystem
Question 2.
An example for artificial aquatic ecosystem is _______
(a) Forest
(b) Pond
(c) Garden
(d) Aquarium
Answer:
(d) Aquarium
Question 3.
Ecosystems created and maintained by humans are called?
(a) lake
(b) river
(c) artificial ecosystem
(d) natural ecosystem
Answer:
(c) artificial ecosystem
Question 4.
Plants are producers because they make their own food by _______
(a) Respiration
(b) Consumer
(c) Photosynthesis
(d) Decomposing
Answer:
(c) Photosynthesis
![]()
Question 5.
The micro-organisms that obtain energy from the chemical breakdown of dead organisms is called
(a) consumers
(b) decomposers
(c) omnivores
(d) producers
Answer:
(b) decomposers
II. True or False. If False, Give the correct statement.
- The abiotic factors are the non-living parts such as sunlight, air, water, and minerals in the soil.
- A Zoo is a natural ecosystem.
- A food web is very useful to show the many different feeding relationships between different species within an ecosystem.
- India produces 532 million kilos of solid waste every day.
- Certain toxic gases from industries mix with raindrops and make rain unusually acidic.
Answer:
- True
- False – A Zoo is an artificial ecosystem.
- True
- True.
- True.
III. Match the Following:
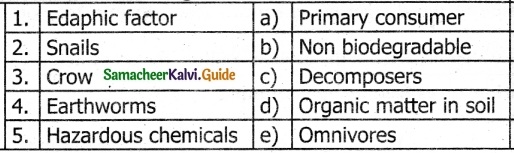
Answer:
1. – d
2. – a
3. – e
4. – c
5. – b
IV. Arrange the following statements in the correct sequence and form a food chain:
Question 1.
Grasshopper → Frog → Grass → Crow.
Answer:
Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Crow
Question 2.
Peacock → Rat → Grains → Snake
Answer:
Grains → Rat → Snake → Peacock
![]()
V. Very Short Answer:
Question 1.
Give two examples of artificial terrestrial ecosystems?
Answer:
- Paddy fields
- Garden
Question 2.
What are called producers?
Answer:
Producers are organisms that are able to produce their own organic food.
(Eg) Plants.
Question 3.
What do plants need in order to photosynthesis?
Answer:
Plants need chlorophyll, water, carbon-di-oxide, and sunlight.
Question 4.
What are the two major types of solid wastes?
Answer:
- Biodegradable
- Non-biodegradable.
Question 5.
What happens to the dead organisms of animals and plants?
Answer:
- They are broken down into simple organic substances by decomposers.
- These substances go into the soil and are used by plants.
VI. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
How do we reduce noise pollution?
Answer:
- Turn off your electronics when we do not use them.
- Lower the volume when we watch TV or listen to music.
- Remind drivers not to use the horn too much.
- Avoid fireworks.
- Speak do not shout.
![]()
Question 2.
Differentiate the artificial ecosystem and natural ecosystem.
Answer:
Natural Ecosystem:
- Ecosystem Originated without human intervention
- Ex: Sea, River, Lake, Forest
Artificial Ecosystem:
- Ecosystem Originated by human
- Ex: Paddy field, garden, aquarium
VII. Questions based on higher-order thinking levels:
Question 1.
Are animal bones biodegradable?
Answer:
- The microorganisms that break down tissues will also cause bones to decompose in a suitable aerated peaty soil.
- In warm damp environments, bacteria and fungi attack the protein in the skeleton and it will break down in a matter of a decade or so.
- But in a dry climate, it could take thousands of years
- So bones do decay at a slower rate than other types of organic material and tissue.
Question 2.
Are all types of clothes biodegradable?
Answer:
- Not all fabrics are safely biodegradable as they are made with artificial and chemical components.
- It depends on what fibres or fabric is made from.
- And also the more chemicals used the longer it takes to biodegrade.
- Polyester has been introduced since 1951 created not by the textile industry but by American Chemical Company Dupont went on sale.
- Polyester is a polymer or a long chain of repeating molecular units.
- That basically means that our clothes are increasingly made of plastic.
- In theory cotton, silk hemp is biodegradable and polyester is not.
![]()