Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Notes Chapter 27 Company Management
→ The group of human beings who undertake the responsibility to run the business of the company are known as board of directors and the members of the board individually called as directors. The directors play a vital role in the functioning of the company by controlling, guiding, directing and managing the affairs of the company.
→ In the company management board of directors get nucleus position and their selection is according to the procedure prescribed lay down in the act and the articles of association.
→ The success of any company depends on the efficient functioning of its directors, they can be called as eyes, ears, brain, hands, nerves and other essential parts of a company.
→ The governing body of a company incorporated under companies act called board. They are empowered to take decisions on the major issues to lead the company in the right way.
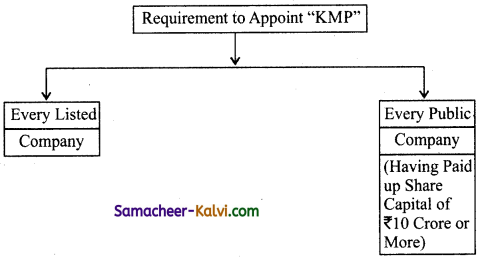
→ Types of directors as per companies act 2013 are residential director, independent director, small share holders, nominee additional, alternative and shadow director.
→ Directors are the person duly appointed by the company to lead and manage its affairs and their legal position. At times they have to act as agents, managing partner, trustees, employee and officer.
→ Directors are appointed to lead the company in relation to third parties. They can enjoy the rights and privileges of an agent.
→ A director of company can be removed from his office the expiry of his term by:
- The share holders,
- The Central Government
- The company law board
→ The powers of directors grouped into four different heads.
- Statutory powers of directors
- Managerial powers of directors
- Powers only with a resolution
- Other powers
→ Director as a part of board perform certain duties collectively the liabilities of directors may be discussed under three heads, liability to outsiders, liability to company and criminal liability.
→ In corporate law, the director register refers to a list of the directors elected by the share holders generally recorded in the company’s minute book.