TN State Board 12th Economics Important Questions Chapter 9 Fiscal Economics
Question 1.
Define public finance.
Answer:
“Public finance is one of those subjects that lie on the border line between Economics and Politics. It is concerned with income and expenditure of public authorities and with the adjustment of one to the other”. – Huge Dalton “Public finance is an investigation into the nature and principles of the state revenue and expenditure”. – Adam Smith
Question 2.
What is public revenue?
Answer:
It is the methods of raising public revenue such as tax and non tax, the principles of taxation rates of taxation, shifting of taxes etc.
![]()
Question 3.
Differentiate tax and fee.
Answer:
Tax is a compulsory payment by the citizens and fees are another important source of revenue for the Government.
Question 4.
Write a short note on zero based budget.
Answer:
It involves fresh evaluation of expenditure in the Government budget, assuming it as a new item or every year is considered as a new year. The budget is done fresh. It starts from zero. The Indian Government presented Zero Based Budgeting (ZBB)first in 1987 – 88.
Question 5.
Give two examples for direct tax.
Answer:
The Tax levied on person’s income and wealth and it is paid directly to the Government.
Eg: Income tax and Wealth tax.
![]()
Question 6.
What are the components of GST?
Answer:
The components are of three types. They are COST, SGST and IGST.
Question 7.
What do you mean by public debt?
Answer:
Money or credit owned by the Government to domestic or foreign lenders.
Question 8.
Describe Canons of Taxation.
Answer:
According to Adam Smith, there are four canons or maxims of taxation.
(i) Canon of ability:
Tax should be imported based on people’s ability.
(ii) Canon of certainty:
The Government should ensure that there is no uncertainty regarding the rate of tax or the time of payment.
(iii) Canon of convenience:
The method of tax collection and the timing of tax payment should suit the convenience of the people, so the tax can be paid without any difficulty.
![]()
Question 9.
Mention any three similarities between public finance and private finance.
Answer:
(i) Rationality:
Maximisation of welfare and least cost factor.
(ii) Limit to borrowing:
Both have to apply restrain with regard to borrowing. The Government also cannot live beyond its means.
(iii) Resource utilisation:
Both have limited resources. So they have to use it at maximum.
(iv) Administration:
The effectiveness of measures of both Government and private depends on administrative machinery. If it is insufficient and corrupt, it will result in wastages and losses.
Question 10.
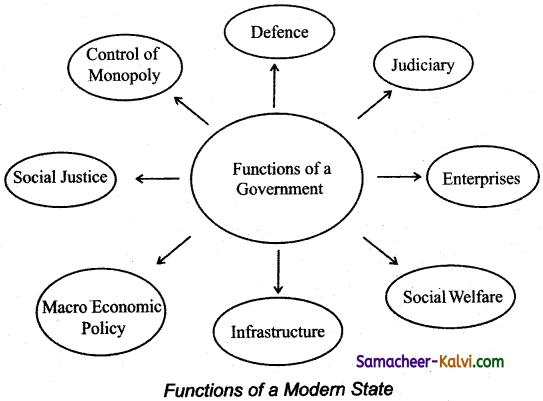
What are the functions of a modern state?
Answer:
The modern state is a welfare state and not just police state. The state assumes greater rules by creating economic and social overheads, ensuring stability both internally and externally.
![]()
Question 11.
State any three characteristics of taxation.
Answer:
- A tax is a compulsory payment made to the Government. People can’t refuse to pay the tax.
- The tax payer cannot claim any specific benefit against die payment of tax.
- Every tax involves some sacrifice or part of the tax payer.
- A tax is not levied as a fine or penalty for breaking law.
Question 12.
Point out any three differences between direct tax and indirect tax.
Answer:
| Direct tax |
Indirect tax |
| Tax levied on person’s income and wealth and it is paid directly to the Government. | A tax charged on a person who purchases the goods and services and it is paid indirectly to the Government. |
| Ultimate burden of tax payment. | Ultimate burden of tax payment: purchaser. |
| Responsibility to pay tax.
Eg: Income tax When you earn income, you are responsible for tax payment, and you also have the burden. |
Responsibility to pay tax: Shopkeeper.
Eg: GST When you buy stuff, the shopkeer is responsible for tax payment, but he can collect it from you. |
![]()
Question 13.
What is primary deficit?
Answer:
Primary Deficit:
It shows the real burden of the Government and does not include the interest burden on loans taken in the past. Thus primary deficit reflects borrowing requirement of the Government exclusive of Interest payments.
Primary Deficit (PD)= Fiscal Deficit (FD) – Interest Payment (IP).
Question 14.
Mention any three methods of redemption of public debt.
Answer:
The process of repaying public debt is called as redemption.
(i) Sinking fund:
According to this, the Government will credit a fixed amount of money to this fund and when it matures, it is paid along with the interest.
(ii) Conversion:
Old loan is converted into a new one and the interest is reduced.
(iii) Budgetary surplus:
Whenever there is surplus budget, it can be utilised to pay the debt.
Question 15.
Explain the scope of public finance.
Answer:
It is a study of the financial aspects of Government.
(i) Public revenue:
It deals with methods of raising public revenue such as tax and non tax.
(ii) Public expenditure:
It studies about fundamental principles that governs the Government expenditure and control it.
(iii) Public debt:
It is the method of raising loans from internal and external sources.
(iv) Financial administration:
It deals with the study of the different aspects of public budget. Budget is the annual master financial plan of the Government.
(v) Fiscal policy:
Taxes, subsidies, public debt and public expenditure are the instruments of fiscal policy.
![]()
Question 16.
Bring out the merits of indirect taxes over direct taxes.Answer:
(i) Wider coverage:
All the consumers have to pay indirect taxes. Indirect people cover more people than direct taxes.
(ii) Equitable:
The indirect tax satisfies the canon of equity when higher tax is imposed on luxuries used by rich people.
(iii) Economical:
The cost of collecting taxes is less because it is collected by the producers.
(iv) Checks harmful consumption:
The Government imposes indirect taxes on harmful commodities. They are known as sin taxes.
(v) Convenient:
Indirect taxes are levied on commodities and services and they don’t feel the burden of paying the tax.
Question 17.
Explain the methods of debt redemption.
Answer:
The process of repaying a public debt is called redemption.
(i) Sinking fund:
According to this the Government will credit a fixed amount of money to this fund and when it matures, it is paid along with the interest.
(ii) Conversion:
Old loan is converted into a new one and the interest is reduced.
(iii) Budgetary surplus:
Whenever there is surplus budget, it can be utilised to pay the debt.
(iv) Terminal annuity:
Government will pay of the public debt in equal annual instalments.
(v) Repudiation:
Government will get rid of the burden of payment of a loan during crisis.
(vi) Reduction in the rate of interest:
Compulsory reduction in the rate of interest during crisis.
(vii) Capital levy:
When the Government imposes levy on the capital assets owned by an individual, it is called as capital levy. Especially war time debt obligation.
![]()
Question 18.
State and explain instruments of fiscal policy.
Answer:
Fiscal policy:
It is an instrument of macro economic policy of the modem Government. It is implemented through fiscal tools, fiscal levers.
Instruments are:
(i) Taxation:
Taxes transfer income from the people to the Government, an increase in tax reduces disposable income. So the taxation should be raised to control inflation. During depression, taxes are to be reduced.
(ii) Public expenditure:
It increases wages and salaries of the employees and thereby the aggregate demand for goods and services. So public expenditure is raised to fight recursion and reduced to control inflation.
(iii) Public debt:
When Government borrows by floating a loan, there is transfer of funds from the public to the Government. At that time of interest payment and repayment of public debt, funds are transferred from Government to public.
Question 19.
Explain the principles of federal finance.
Answer:
Federal finance refers to the system of assigning the source of revenue to the Central as well as State Government for the efficient discharge of their respective functions. The principles are:
(i) Principle of independence:
The Government should have separate sources of revenue, authority to levy taxes to borrow money and to meet the expenditure.
(ii) Principle of equity:
The resources has to be distributed among the states to earn their revenue.
(iii) Principle of uniformity:
In the federal system, each state should contribute equal tax payments for federal finance. But this principle cannot be followed because the taxable capacity of each unit is not of the same.
(iv) Principle of adequacy of resource:
Resources should be adequate to execute its function. The resources should be elastic in order to meet the growing needs and unforeseen expenditure like war etc.
(v) Principle of fiscal access:
Government will make possibility for the central and state Government to develop new source of revenue with in their prescribed fields to meet the growing financial needs.
(vi) Principle of integration and coordination:
There should be perfect coordination among different layers of financial system of the country. Then only the federal system will survive. This should be done in such a way to promote the overall economic development of the country.
(vii) Principle of efficiency:
The financial system should be well organised and efficiently administered. There should be no scope for fraud. No one should be taxed more than once in a year. Double taxation should be avoided.
(viii) Principle of administrative economy:
Each Government should be accountable to its own legislature for its financial decisions, that is the Central to the Parliament and the State to the assembly.
![]()
Question 20.
Describe the various types of deficit in budget.
Answer:
Deficit budget is one where the estimated Government expenditure is more than expected revenue budget deficit is of four types.
(i) Revenue budget:
Excess of Government revenue expenditures over revenue receipts. Revenue deficit is the Government is living beyond its means to conduct day to day operations.
Revenue deficit RD = Total Revenue Expenditure (RE) – Total Revenue Receipts (RR) (when RE – RR >0)
(ii) Budget deficit:
Budget deficit is the difference between total receipts and total expenditure.
Budget Deficit = Total Expenditure – Total Revenue
(Hi) Fiscal deficit:
Fiscal deficit = Budget deficit + Government market
borrowings and liabilities.
(iv) Primary deficit:
It shows the real burden of the Government and it does . not include the interest burden on loans taken in the part.
Primary Deficit (PD) = Fiscal Deficit (FD) – Investment Payment (IP).
Question 21.
What are the reasons for the recent growth in public expenditure?
Answer:
In welfare state, the Government has to perform several functions, activities like social, economic etc., Activities are the cause for increase in public expenditure.
(i) Population growth:
The growth in population needs investment in all areas especially youth education require more investments and for old people transfer payments
(ii) Defence expenditure:
Increase in defence expenditure specially during planning period. Its increasing due to modernisation of defence equipment.
(iii) Government subsidies:
The Government has been providing subsidies on a number, of items such as food, fertilisers etc., Because of the massive amount of subsidies, the public expenditure has increased.
(iv) Debt servicing:
The Government has been borrowing heavily. As a result it has to make huge repayment towards debt servicing.
(v) Development projects: The Government has been undertaking various development projects which involve huge investment.
(vi) Urbanisation:
Now the urban population has increased to about 43%. It requires heavy expenditure on law and order education and civic amenities.
(vii) Industrialisation:
Setting up of basic and heavy industries involve huge capital and long gestation period. Under planned economy, such industries and started by Government and the UDC need a strong infrastructure like transport, communication, power etc., so there is increase in public expenditure.
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
The-modern state is:
(a) Laissez-faire state
(b) Aristocratic state
(c) Welfare state
(d) Police state
Answer:
(c) Welfare state
Question 2.
One of the following is NOT a feature of private finance:
(a) Balancing of income and expenditure
(b) Secrecy
(c) Saving some part of income
(d) Publicity
Answer:
(d) Publicity
Question 3.
The tax possesses the following characteristics:
(a) Compulsory
(b) No quid pro quo
(c) Failure to pay is offence
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
![]()
Question 4.
Which of the following canons of taxation was not listed by Adam Smith?
(a) Canon of equality
(b) Canon of certainty
(c) Canon of convenience
(d) Canon of simplicity
Answer:
(d) Canon of simplicity
Question 5.
Consider the following statements and identify the correct ones.
(i) Central Government does not have exclusive power to impose tax which is not mentioned in state or concurrent list.
(ii) The Constitution also provides for transferring certain tax revenues from un|on list to states.
(a) (i) only
(b) (ii) only
(c) both a & b
(d) none
Answer:
(b) (ii) only
Question 6.
GST is equivalence of:
(a) Sales tax
(b) Corporation tax
(c) Income tax
(d) Local tax
Answer:
(a) Sales tax
![]()
Question 7.
The direct tax has the following merits except:
(a) equity
(b) convenient
(c) certainty
(d) civic consciousness
Answer:
(b) convenient
Question 8.
Which of the following is a direct tax?
(a) Excise duty
(b) Income tax
(c) Customs duty
(d) Service tax
Answer:
(b) Income tax
Question 9.
Which of the following is not a tax under Union list?
(a) Personal Income Tax
(b) Corporation Tax
(c) Agricultural Income Tax
(d) Excise duty
Answer:
(c) Agricultural Income Tax
![]()
Question 10.
“Revenue Receipts” of the Government do not include:
(a) Interest
(b) Profits and dividents
(c) Recoveries and loans
(d) Rent from property
Answer:
(d) Rent from property
Question 11.
The difference between revenue expenditure and revenue receipts is:
(a) Revenue deficit
(b) Fiscal deficit
(c) Budget deficit
(d) Primary deficit
Answer:
(a) Revenue deficit
Question 12.
The difference between total expenditure and total receipts including loans and other liabilities is called:
(a) Fiscal deficit
(b) Budget deficit
(c) Primary deficit
(d) Revenue deficit
Answer:
(a) Fiscal deficit
![]()
Question 13.
The primary purpose of deficit financing is:
(a) Economic development
(b) Economic stability
(c) Economic equality
(d) Employment generation
Answer:
(a) Economic development
Question 14.
Deficit budget means:
(a) An excess of Government’s revenue over expenditure
(b) An excess of Government’s current expenditure over its current revenue
(c) An excess of Government’s total expenditure over its total revenue
(d) None of above
Answer:
(c) An excess of Government’s total expenditure over its total revenue
Question 15.
Methods of repayment of public debt is:
(a) Conversion
(b) Sinking fund
(c) Funded debt
(d) All these
Answer:
(d) All these
![]()
Question 16.
Conversion of public debt means exchange of:
(a) new bonds for the old ones
(b) low interest bonds for higher interest bonds
(c) long term bonds for short term bonds
(d) all the above
Answer:
(b) low interest bonds for higher interest bonds
Question 17.
The word budget has been derived from the French word “bougette” which means:
(a) A small bag
(b) An empty box
(c) A box with papers
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) A small bag
Question 18.
Which one of the following deficits does not consider borrowing as a receipt?
(a) Revenue deficit
(b) Budgetary deficit
(c) Fiscal deficit
(d) Primary deficit
Answer:
(c) Fiscal deficit
![]()
Question 19.
Finance Commission determines:
(a) The finances of Government of India
(b) The resources transfer to the States
(c) The resources transfer to the various departments
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) The resources transfer to the States
Question 20.
Consider the following statements and identify the right ones.
(i) The Finance Commission is appointed by the President.
(ii) The tenure of Finance commission is five years.
(a) (i) only
(b) (ii) only
(c) both (a) & (b)
(d) none
Answer:
(c) both (a) & (b)
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Notes Chapter 9 Fiscal Economics
→ Public finance: Study of the financial aspects of government.
→ Public expenditure: The income of the government from all sources.
→ Tax: Compulsory payment by the citizens to the government.
→ Redemption: The process of repaying public debt.
→ Public debt: Loan taken by the Government from the citizens within the country.
→ Public revenue: The income of all the Government from all sources.
→ Budget: Annual financial statement of income and expenditure of the Government.
![]()
→ Vote on account: The budget can be presented in the middle of the year. (When election are due or any political situation). This is also called as lame duck budget.
→ Zero based budget: Fresh evaluation of expenditure in Government budget. Canon of taxation: Qualities which a good tax should possess.
→ Public finance:
• “Public finance is one of those subjects that lie on the border line between Economics and Politics. It is concerned with income and expenditure ofpublic authorities and with the adjustment of one to the other” – Hugh Dalton.
• “Public finance is an investigation into the nature and principles of the state revenue and expenditure’” – Adam smith.
→ Public revenue:
• “A Tax is a compulsory payment made by a person or a firm to a Government without reference to any benefit the payer may derive from the Government” – Anatol murad.
‘ • “A Tax is a compulsory contribution imposed by public authority, irrespective of the exact amount of service rendered to the tax payer in return and not imposed as a penalty for any legal offence” – Dalton.
![]()
→ Public debt:
• “The debt is the form of promises by the Treasury to pay to the holders of these promises a principal sum and in most instances interest on the principal. Borrowing is resorted to in order to provide funds for financing a current deficit” – Philip E.Taylor.
• “The receipt from the sale of financial instruments by the Government to individuals or firms in the private sector, to induce the private sector to release manpower and real resources and to finance the purchase of these resources or to make welfare payments or subsidies” – Carl S.Shoup.
→ Budget:
• Reney Stoum – “It is a document containing a preliminary approved plan of public revenue and expenditure”.
• Bastabale – “ The budget has come to mean the financial arrangements of a given period, with the usual implication that they have been submitted to the legislature for approval’.
→ Public expenditure:
Public expenditure can be defined as, “The expenditure incurred by public authorities like central, state and local Governments to satisfy the collective social wants of the people is known as public expenditure
→ Definition of Fiscal policy:
“The term fiscal policy refers to a policy under which the Government uses its expenditure and revenue programmes to produce desirable effects and avoid undesirable effects on the national income, production and employment” – Arthur Smithies “By fiscal policy is meant the use of public finance or expenditure, taxes, borrowing and financial administration to Jurther our national economic objectives” – Buehler.