Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Commerce Model Question Paper 5 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th Commerce Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
TN State Board 11th Commerce Model Question Paper 5 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 20 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each.
These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer - Question numbers 21 to 30 in Part II are two-mark questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 31 to 40 in Part III are three-mark questions. These are to be answered in above three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 41 to 47 in Part IV are five-mark questions. These are to be answered in detail Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 2:30 Hours
Maximum Marks: 90
PART – I
Choose the correct answer. Answer all the questions. [20 × 1 = 20]
Question 1.
The document which authorises to deliver the goods either in part or full is called …………………..
(a) Warehouse warrant
(b) Dock receipt
(c) Dock warrant
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Dock warrant
![]()
Question 2.
Which of the following is not correctly matched?
(a) Franchisee – An agent who buys the accounts receivables
(b) Factor – Trade mark of the seller
(c) Logistics – Knowledge process outsourcing
(d) BPO – Extension of transportation
Answer:
(d) BPO – Extension of transportation
Question 3.
WTO was established on ……………………..
(a) 1-1-1996
(b) 1-1-1997
(c) 1-1-1995
(d) 1-1-1994
Answer:
(c) 1-1-1995
![]()
Question 4.
Charter Party is a document related to which of the following transport?
(a) Air Transport
(b) Ocean Transport
(c) Railway Transport
(d) Motor transport
Answer:
(b) Ocean Transport
Question 5.
Charter party may also be known as ………………………
(a) Bill of lading
(b) Voyage charter
(c) Airway note
(d) Way bill
Answer:
(b) Voyage charter
![]()
Question 6.
Occupation of a bank official is …………………………
(a) Employment
(b) Business
(c) Profession
(d) Sole trader
Answer:
(a) Employment
Question 7.
Who is not an intermediary in the export trade from the following?
(a) Indent house
(b) Forwarding agent
(c) Commission agent
(d) Export trading house
Answer:
(a) Indent house
Question 8.
What is IGST?
(a) Integrated Goods and Services Tax
(b) Indian Goods and Services Tax
(c) Initial Goods and Services Tax
(d) All the above
Answer:
(a) Integrated Goods and Services Tax
![]()
Question 9.
Dock Receipt is a document issued by ………………………….
(a) Dock authorities
(b) Warehouse keeper
(c) Owner of the goods
(d) Manufacturer
Answer:
(a) Dock authorities
Question 10.
………………………… is not a type of general insurance.
(a) Marine insurance
(b) Life insurance
(c) Fidelity insurance
(d) Fire insurance
Answer:
(b) Life insurance
Question 11.
Trade middleman who acts as a link between wholesaler and customers refers to a ………………………..
(a) Producer
(b) Broker
(c) Retailer
(d) Customer
Answer:
(c) Retailer
![]()
Question 12.
……………………… are mobile traders who deal in low priced articles with no fixed place of business.
(a) Shopping malls
(b) Super markets
(c) Street stalls
(d) Itinerant traders
Answer:
(d) Itinerant traders
Question 13.
Public deposits are the deposits which are raised directly from ………………………
(a) The public
(b) The director
(c) The auditors
(d) The owners
Answer:
(a) The public
Question 14.
Income Tax is ………………………..
(a) A business tax
(b) A direct tax
(c) An indirect tax
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) A business tax
![]()
Question 15.
Which bank has the power to issue bank notes?
(a) Central bank
(b) Commercial bank
(c) Co – operative banks
(d) Foreign banks
Answer:
(a) Central bank
Question 16.
The compensation given for a breach of contract is …………………………..
(a) Damage
(b) Remuneration
(c) Money
(d) Cheque
Answer:
(a) Damage
![]()
Question 17.
Which one of the following is not correctly matched?
(a) Sony Corporation – MNC
(b) Post and Telegraph – Departmental undertaking
(c) IDBI – Agricultural bank
(d) Steel Authority of India Ltd – Government company
Answer:
(c) IDBI – Agricultural bank
Question 18.
Find out which is not the classification of manufacturing Industries?
(a) Micro industries
(b) Synthetic industry
(c) Processing industry
(d) Assembling industry
Answer:
(a) Micro industries
![]()
Question 19.
Match List – I with List – II and select the correct answer using the codes given below:
|
List – I |
List – II |
| (i) Indian Bank | 1. Private sector bank |
| (ii) Karur vysya bank | 2. Government company |
| (iii) Indian Airlines | 3. Nationalised bank |
| (iv) Coal India Ltd | 4. Public corporation |
Answer:
Codes:
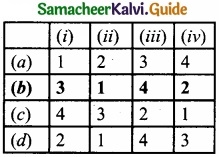
Question 20.
Socially responsible business provides goods at ……………………..
(a) High price
(b) Low price
(c) Reasonable price
(d) Moderate price
Answer:
(c) Reasonable price
PART – II
Answer any seven questions in which question No. 30 is compulsory. [7 × 2 = 14]
Question 21.
Give the meaning of crop insurance?
Answer:
This policy is to provide financial support to fanners in case of a crop failure due to drought or flood. It generally covers all risks of loss or damages relating to production of rice, wheat, millets, oil seeds and pulses etc.
![]()
Question 22.
Mention any four examples of public corporation?
Answer:
Examples of public corporation:
- Life Insurance Corporation of India
- The Indian Airlines
- The Air India International
- Food Corporation of India
Question 23.
What is meant by foreign bank?
Answer:
Banks which have registered office in a foreign country and branches in India are called foreign banks.
![]()
Question 24.
What is GATT?
Answer:
The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade. (GATT) was signed at Geneva on 30th October 1947 by 23 countries. It came into effect on 1st January 1948.
Question 25.
Describe any two advantages of water transport?
Answer:
Advantages of water transport:
- It is the cheapest mode of transport.
- It is most suitable for heavy loads.
Question 26.
A transport which is useful in hilly and remote areas. It is a means of transport in naval lifting device. What does it mean?
Answer:
It is the type of transport called pack animals. Animals like horse, mule, donkey, camel and elephant are known as pack animals. They are used for carrying small loads in backward areas, hilly tracks, forest regimes and deserts. They serve areas which are inaccessible to modem means of transport.
![]()
Question 27.
What is unlimited liability?
Answer:
The liability of the proprietor for the debts of the business is unlimited. The creditors have the right to recover their dues even from the personal property of the proprietor in case the business assets are not sufficient to pay their debts.
Question 28.
What are the services included in service business?
Answer:
Educational, medical, hospitality and banking are the services included in service businesses. Bank service is the nerve center of industry and commerce in a country.
![]()
Question 29.
What is meant by Marine Insurance?
Answer:
Marine insurance is a contract of insurance under which the insurer undertakes to indemnify the insured against marine losses. The insured pays the premium for the insurer’s guarantee to make good the looses arising from marine perils. Marine perils may be damage of ship, fire, etc.
Question 30.
What is credit co – operatives?
Answer:
Co – operative credit societies are societies formed for providing short-term financial help to their members. Agriculturists, artisans, industrial workers, salaried employees, etc., form these credit societies.
PART – III
Answer any seven questions in which question No. 40 is compulsory. [7 × 3 = 21]
Question 31.
The functions of commercial banks are:
(a) Primary functions
(b) Secondary functions. Secondary functions may be of agency and general utility functions? Describe any three utility services?
Answer:
General utility functions:
- Accepting bills on behalf of customers: Banks accept bills on behalf of customers and make payments to the foreign exporter.
- Issue of demand drafts and Banker’s cheques: Demand drafts and banker’s cheques are issued to the public and customers.
- Safety lockers: Valuable documents, jewels can be kept in a vault provided by the bank for rent.
![]()
Question 32.
Goods are manufactured in one place and it may be demanded throughout the world. Goods may reach the consumers by a number of middlemen. Who is the first middleman in the trade? Explain any three features of that middleman?
Answer:
The first middleman in the trade or distribution is called wholesaler. A wholesaler buys goods directly from manufacturers and sells them to the retailers.
Features:
- Wholesalers buy goods directly from producers.
- Wholesalers buy goods in large quantities and sell in small quantities.
- Wholesalers sell different varieties of a particular kind of product.
Question 33.
The importer places the order either directly or through an indent house. It is known as indent. Indent may be of three types. What are the three types of indents? Explain?
Answer:
There are three types of indent:
- Open Indent: It gives complete freedom to exporter to choose type of goods, price, quality, method of packing, etc.
- Closed Indent: It does not give any freedom to exporter. Importer specifies the type of goods, price, quality, etc.
- Confirmatory Indent: An indent is to be confirmed by importer/his agent and the final indent is sent by importer thereafter.
![]()
Question 34.
Explain the differences between Direct tax and Indirect tax?
Answer:
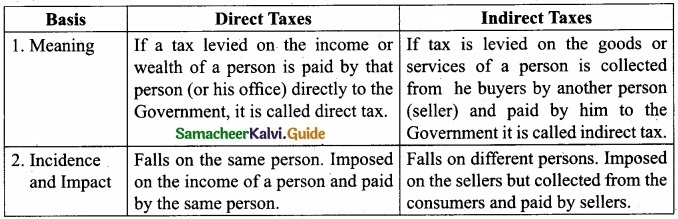
Question 35.
Mention the importance of banking service?
Answer:
Banking service is the nerve center of industry and commerce in a country. It plays a vital role by providing the money required for their regular functioning and development. There are many types of banks rendering different types of services.
Question 36.
This organisation is useful to the farmers in a village. It helps in the purpose of cultivation. Identify the form of organisation and briefly explain about it?
Answer:
This form of organisation is ‘co-operative farming societies’. The societies in a village collect their land together for the purpose of cultivation, purchase the inputs for cultivation and market the crops for the sales.
![]()
Question 37.
State the meaning of retail trade?
Answer:
Retail trade deals with the distribution of goods in small quantities to the end consumers. It represents the final stage in the distribution where goods are transferred from the hands of manufacturers or wholesalers to the users. If the sales are made directly to the end consumers it will be considered as retailing.
Question 38.
What is the classification of foreign trade?
Answer:
Types of Foreign Trade:
- Import Trade: Import trade means buying goods from a foreign country for domestic use.
- Export Trade: Export trade means the sale of domestic goods to foreign countries.
- Entrepot Trade: Entrepot trade means importing of goods from one country and exporting the same to foreign countries.
Question 39.
What are the various rules regarding damages?
Answer:
Generally in the following cases, the court grants specific performance:
- When the act agreed to be done is such that compensation in money for its non-performance is not sufficient.
- When it is probable that compensation in money cannot be received for the non-performance of the act agreed to be done.
- When there is no standard for ascertaining the actual damage caused by the non-performance of the act agreed to be done.
![]()
Question 40.
The scheme was introduced by the RBI in August 1996. These are small private sector banks established in rural and semi urban areas. What is the name of the bank? Explain?
Answer:
Local Area Bank (LAB) scheme was introduced by the RBI in August 1996. LABs are small private sector banks established in rural and semi-urban areas. Each bank serves two or three adjoining districts only. Their main objective is to mobilise rural savings (accept deposits) and invest them in the same areas.
Examples:
- Coastal Local Area Bank, Vijayawada, Andhra Pradesh.
- Subhadra Local Area Bank Limited, Kolhapur, Maharashtra
PART – IV
Answer all the questions. [7 × 5 = 35]
Question 41.
(a) Discuss the advantages of transport?
Answer:
Advantages of railway transport:
- Railways are well suited for carrying heavy and bulky goods over long distances.
- It can provide long distance travel throughout the day and night with unbroken services.
Advantages of inland waterways:
- It is considered as the cheapest mode of transport among the other modes of transport.
- It is most suitable for heavy loads.
Advantages of air transport:
- It provides a regular, convenient, efficient and quick service.
- Perishable goods like fruits, vegetables, egg, meat, etc., can be transported quickly.
[OR]
(b) Discuss the causes of risk?
Answer:
Business risk arises due to a variety of causes which are classified as follows:
1. Natural Causes:
Human beings have little control over natural calamities like flood, earthquake, lightning, heavy rains, famine, etc. These result in heavy loss of life, property, and income in business.
2. Human Causes:
Human causes include such unexpected events like dishonesty, carelessness or negligence of employees, stoppage of work due to power failure, strikes, riots, management inefficiency, etc.
3. Economic Causes:
These include uncertainties relating to demand for goods, competition, price, collection of dues from customers, change of technology or method of production, etc. Financial problems like rise in interest rate for borrowing, levy of higher taxes,, etc., also come under this type of causes as they result in higher unexpected cost of operation of business.
4. Other Causes:
These are unforeseen events like political disturbances, mechanical failures such as the bursting of boiler, fluctuations in exchange rates, etc. which lead to the possibility of business risks.
![]()
Question 42 (a).
Sole proprietorship is a form of business organisation in which an individual introduces his own capital, uses his own skill and intelligence in the management of the business? Explain the characteristics of a sole trader?
Answer:
Business owned and controlled by a single person is known as sole trading business.
The following are the characteristics of a sole trader:
- Ownership by one man: This is owned by single person. The sole trader contributes the required capital.
- Freedom of work and Quick decisions: The sole trader is the owner, so he need not consult with others. Hence he can take quick decision.
- Unlimited liability: When his business assets are not sufficient to pay off the business debts he has to pay from his personal property.
- Enjoying Entire Profit: All the benefits earned by the sole trader is enjoyed by him alone.
- Absence of Government Regulation: A sole trading concern is free from Government regulations. No legal formalities are to be observed in its formation and management.
- Maintenance of Secrecy: Since the trader manages all the affairs of the business, the secrecy can be maintained easily.
[OR]
(b) Partnership is the relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits of a business carried on by all. It is the result of an agreement. Closing of business is also by an agreement. It is called Dissolution of Partnership. Explain the dissolution of partnership firm without the order of the court?
Answer:
Dissolution of a partnership firm takes place in two ways:
- Without the order of the court and
- By the order of the court
1. Without the order of the court:
- By agreement or mutual consent: A firm may be dissolved when all the partners agree to close the affairs of the firm.
- By insolvency of all the partners but one: If any one of the partners is adjudged as insolvent, it is necessary to dissolve the firm.
- When the objective becomes illegal: When the business carried on by the partnership becomes illegal, the partnership firm is automatically dissolved.
- By notice of dissolution: In the case of partnership at will, if any partner gives in writing to close the firm, the firm will be dissolved.
- On certain contingencies:
- On the expiry of the period of the firm.
- On the completion of a business.
- On the death of a partner.
- On the retirement of a partner.
- On the insolvency of a partner.
![]()
Question 43 (a).
What are the features of public corporation?
Answer:
1. Special Statute:
A public corporation is created by a special Act of the Parliament or the State Legislature. The Act defines its powers, objectives, functions and relations with the ministry and the Parliament (or State Legislature).
2. Separate Legal Entity:
A public corporation is a separate legal entity with perpetual succession and common seal It has an existence, independent of the Government. It can own property; can make contracts and file suits, in its own name.
3. Capital Provided by the Government:
The capital of a public corporation is provided by the Government or by agencies controlled by the government. However, many public corporations have also begun to raise money from the capital market.
4. Financial Autonomy:
A public corporation enjoys financial autonomy. It prepares its own budget; and has authority to retain and utilize its earnings for its business.
5. Management by Board of Directors:
Its management is vested in a Board of Directors, appointed or nominated by the Government. But there is no Governmental interference in the day-to-day working of the corporation.
[OR]
(b) Partnership is formed according to Partnership Act. There are various kinds of partners based on capital and administration. Explain any five kinds of partners?
Answer:
Partnership is formed by agreement. In this partnership, the member in a firm is called as partner. There are various kinds of partners. They are as follows:
1. Active partner:
A partner who takes an active part in the conduct of the partnership business is known as an active partner.
2. Sleeping or Dormant partner:
A partner contributes capital and shares in the profits or losses of the firm, but does not take part in the management of the business is known as sleeping partner.
3. Nominal partner:
Such a partner neither contributes any capital nor is he entitled to manage the affairs of the business. He lends only his name to strengthen the firm.
4. Partner in profits only:
When a person joins a firm as a partner on the condition that he is entitled to share profits in the firm, he is called as a partner in profits only.
5. Secret partner:
A secret partner is one whose association is not known to the general public.
![]()
Question 44 (a).
Explain various types of insurance?
Answer:
Insurance covers various types of risks. All contract of insurance can be broadly classified as follows:
- Life Insurance (or) Life Assurance
- Non – life Insurance (or) General Insurance
It can be further classified into:
- Fire Insurance
- Marine Insurance
- Health Insurance and
- Miscellaneous Insurance
1. Life Insurance:
Life Insurance may be defined as a contract in which the insurance company called insurer undertakes to insure the life of a person called assured in exchange of a sum of money called premium which may be paid in one lump sum or monthly, quarterly, half yearly or yearly and promises to pay a certain sum of money either on the death of the assured or on expiry of certain period.
2. Non – Life Insurance or General insurance:
It refers as the insurance not related to human but related to properties.
3. Fire Insurance:
Fire insurance is a contract whereby the insurer, in consideration of the premium paid, undertakes to make good any loss or damage caused by a fire during a specified period upto the amount specified in the policy.
4. Marine Insurance:
Marine insurance is a contract of insurance under which the insurer undertakes to indemnify the insured in the manner and to the extent thereby agreed against marine losses. The insured pays the premium in consideration of the insurer’s (underwriter’s) guarantee to make good the losses arising from marine perils or perils of the sea.
5. Health Insurance:
In mid 80’s, most of the hospitals in India were government owned and treatment was free of cost. With the advent of Private Medical Care, the need for Health Insurance was felt and various Insurance Companies introduced Health Insurance as a Product. Presently the health insurance exists primarily in the form of ‘Mediclaim policy’.
[OR]
(b) Explain the functions of retailers?
Answer:
- Buying: A retailer buys a wide variety of goods from different wholesalers after estimating customer’s demand.
- Storage: A retailer maintains a ready stock of goods and displays them in the shop.
- Selling: The retailer sells the goods in small quantities according to the demand taste and preference of consumers.
- Grading and Packing: The retailer grades the goods which are not graded by manufacturers and wholesalers.
- Risk – bearing: A retailer always keeps stock of goods in anticipation of demand and bears the risk of loss due to fire, theft, spoilage, price fluctuations, etc.
- Transportation: Retailers often carry goods from manufacturers to their retail outlets.
- Financing: Some retailers grant credit facilities to his customers and provide the facility of return or exchange of goods.
![]()
Question 45 (a).
Explain any four personal investment avenues?
Answer:
1. Public Provident Fund (PPF):
It is the safest long – term investment option for the investors in India. It is totally tax – free. PPF account can be opened in bank or post office. The money deposited cannot be withdrawn before 15 years and an investor can earn compound interest from this account.
However the investor can extend the time frame for the next five years if the investor does not opt to withdraw the amount matured for payment at maturity date. PPF investor can take loan against PPF account when he/she experiences financial difficulties.
2. Mutual Funds:
An individual investor who wants to invest in equities and bond with a balance of risk and return generally can invest in mutual funds. Nowadays people invest in stock markets through a mutual fund. Systematic investment plan is one of the best investment options in India.
3. Direct Equity or Share Purchase:
An individual can opt for investment in shares. But he has to analyse the market price of various shares traded in stock exchange, reputation of the company, consistency in the payment of dividend, the nature of the project undertaken by the company, growth prospects of industry in which a company is operating, before investing in shares. If the investment is made for a long time, it may yield good return.
4. Real Estate Investment:
Real estate is one of the fastest growing sectors in India. Buying a flat or plot is supposed to be the best decision amongst the investment options. The value of the real asset may increase substantially depending upon the area of location and other support facilities available therein.
[OR]
(b) Explain any four warehousing documents?
Answer:
Warehouses means a place where goods are stored for future use. For keeping the goods, the various documents are needed; they are as follows:
- Warehousing Warrants: It is a document issued in favour of goods by the warehouse keeper. It is also used as a document of title to goods.
- Warehouse Keeper’s receipt: It is a document issued by the warehouse keeper, which acknowledges there receipt of goods from the owner of the goods.
- Dock Warrant: Dock warrant is a document of title of goods issued by the dock authorities. This document certifies that the dock authorities hold the goods.
- Dock Receipt: Dock receipt is an acknowledgement of receipt of goods issued by the dock authorities to the owner of the goods. It is not a document of title to goods.
- Delivery Order: This is a document through which the depositor directs the warehouse keepers to deliver the goods to the party mentioned in the document.
![]()
Question 46 (a).
Industry means, which is connected with conversion of raw materials into finished goods. It may be of various types. Explain: (a) Analytical industry (b) Genetic industry and (c) Construction industry?
Answer:
- Analytical Industry: It analyses and separates different elements from the same materials, as in the case of oil refinery.
- Genetic Industries: These industries remain engaged in breeding plants and animals for their use in further reproduction. The seeds, nursery companies, poultry, diary, piggery, hatcheries, nursery, fisheries, apiary etc are classic examples of genetic industries.
- Construction Industries: These industries are involved in the ,construction of building, dams, bridges, roads, as well as tunnels and canals.
[OR]
(b) Explain the procedure for the registration of partnership firm?
Answer:
- Name of the firm.
- The principal place of business.
- Name of other places where the firm carried on business.
- Names and addresses of all the partners.
- The date on which each partner joined the firm.
- The duration of the firm.
This statement signed by all the partners should be produced to the Registrar of Firms along with the necessary registration fee of Rs.3. Any change in the above particulars must be communicated to the Registrar within 14 days of such alteration.
![]()
Question 47 (a).
Partnership is formed by agreement. It is desirable to have a written agreement. What is the name of the agreement? Explain the contents of it?
Answer:
- Name: Name of the Firm.
- Nature of Business: Nature of the proposed business to be carried on by the partners.
- Duration of Partnership: Duration of the partnership business whether it is to be run for a fixed period of time or whether it is to be dissolved after completing a particular venture,
- Capital Contribution: The capital is to be contributed by the partners. It must be remembered that capital contribution is not necessary to become a partner for, one contribute his organizing power, business acumen, managerial skill etc., instead of capital.
- Withdrawal from the Firm: The amount that can be withdrawn from the firm by each partner.
- Profit/Loss Sharing: The ratio in which the profits or losses are to be shared. If the profit sharing ratio is not specified in the deed, all the partners must share the profits and bear the losses equally.
- Interest on Capital: Whether any interest is to be allowed on capital and if so, the rate of interest.
- Rate of Interest on Drawing: Rate of interest on drawings, if any.
- Loan from Partners: Whether loans can be accepted from the partners and if so the rate of interest payable thereon.
- Account Keeping: Maintenance of accounts and audit.
- Salary and Commission to Partners: Amount of salary or commission payable to partners for their services. (Unless this is specifically provided, no partner is entitled to any salary).
- Retirement: Matters relating to retirement of a partner. The arrangement to be made for paying out the amount due to a retired or deceased partner must also be stated.
- Goodwill Valuation: Method of valuing goodwill on the admission, death or retirement of a partner.
- Distribution of Responsibility: Distribution of managerial responsibilities. The work that is entrusted to each partner is better stated in the deed itself.
- Dissolution Procedure: Procedure for dissolution of the firm and the mode of settlement of accounts thereafter.
- Arbitration of Dispute: Arbitration in case of disputes among partners. The deed should provide the method for settling disputes or difference of opinion. This clause will avoid costly litigations.
[OR]
(b) Explain any five principles of co – operatives?
Answer:
1. Voluntary and Open Membership:
Co – operatives are voluntary organisations, open to all people able to use its services and willing to accept the responsibilities of membership, without gender, social, racial, political or religious discrimination.
2. Democratic Member Control:
Co – operatives are democratic organisations controlled by their members those who buy the goods or use the services of the co – operative who actively participate in setting policies and making decisions.
3. Member’s Economic Participation:
Members contribute equally to, and democratically control, the capital of the co – operative. This benefits members in proportion to the business they conduct with the co-operative rather than on the capital invested.
4. Autonomy and Independence:
Co – operatives are autonomous, self – help organisations controlled by their members. If the co – operative enters into agreements with other organisations or raises capital from external sources, it is done so based on terms that ensure democratic control by the members and maintains the co – operative’s autonomy.
5. Education, Training, and Information:
Co – operatives provide education and training for members, elected representatives, managers and employees so they can contribute effectively to the development of their cooperative. Members also inform the general public about the nature and benefits of cooperatives.