Students can Download Tamil Nadu 12th Commerce Model Question Paper 3 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 12th Commerce Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
TN State Board 12th Commerce Model Question Paper 3 English Medium
Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II. III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 20 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer.
- Question numbers 21 to 30 in Part II are two-mark questions. These are to be answered in about 50 words.
- Question numbers 31 to 40 in Part III are three-mark questions. These are to be answered in about 150 words.
- Question numbers 41 to 47 in Part IV are five-mark questions. These are to be answered in about 250 words. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Max Marks: 90
Part -I
Choose the correct answer. Answer all the questions: [20 x 1 = 20]
Question 1.
How many times a security can be sold in a secondary market?
(a) Only one time
(b) Two times
(c) Three times
(d) Multiple times
Answer:
(d) Multiple times
Question 2.
Money market Institutions are ………………
(a) Investment Houses
(b) Mortgage Banks
(c) Reserve Bank of India
(d) Commercial Banks and Discount Houses
Answer:
(d) Commercial Banks and Discount Houses
Question 3.
Risk in the Money Market is ………………
(a) High
(b) Market Risk
(c) Low credit and Market Risk
(d) Medium Risk
Answer:
(c) Low credit and Market Risk
![]()
Question 4.
A pessimistic speculator is ………………
(a) Stag
(b) Bear
(c) Bull
(d) Lame Duck
Answer:
(b) Bear
Question 5.
An optimistic speculator is ……………
(a) Bull
(b) Bear
(c) stag
(d) Lame Duck
Answer:
(a) Bull
Question 6.
SEBI is empowered by the Finance Ministry nominate ……………. mumbers on the governing body of every stock exchange.
(a) 5
(b) 3
(c) 6
(d) 7
Answer:
(b) 3
![]()
Question 7.
The process of converting physical shares into electronic from is called from is called …………..
(a) Dematerialisation
(b) Delisting
(c) Materialisation
(d) Debarring
Answer:
(a) Dematerialisation
Question 8.
Labour turnover is the rate at which employees the organisation.
(a) enter
(b) leave
(c) salary
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(b) leave
Question 9.
Which of the following test is used to measure the various characteristics of the candidate?
(a) physical Test
(b) psychological Test
(c) attitude Test
(d) proficiency Tests
Answer:
(b) psychological Test
Question 10.
When trainees are trained by supervisor or by superior at the job is called …………..
(a) Vestibule training
(b) Refresher training
(c) Role Pay
(d) Apprenticeship training
Answer:
(d) Apprenticeship training
![]()
Question 11.
Stock Exchange Market is also called …………..
(a) Spot Market
(b) Local Market
(c) Security Market
(d) National Market
Answer:
(c) Security Market
Question 12.
Marketing mix means a marketing program that is offered by a firm to to its target ………….. to earn profits through satisfaction of their wants.
(a) Wholesaler
(b) Retailer
(c) Consumer
(d) Seller
Answer:
(c) Consumer
Question 13.
Effective use of Social media marketing increase conversion rates of ……………..
(a) Customer to buyers
(b) Retailer to customers
(c) One buyer to another buyer’s
(d) Direct contact of marketer
Answer:
(a) Customer to buyers
Question 14.
The Consumer protection Act came into force with effect from ……………
(a) 1.1. 1986
(b) 1.4.1986
(c) 15.4. 1987
(d) 15.4.1990
Answer:
(c) 15.4. 1987
Question 15.
Which of the following is not consumer right summed up by John F. Kennedy
(a) Right to safety
(b) Right to choose
(c) Right’to consume
(d) Right to he informed
Answer:
(a) Right to safety
Question 16.
The National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission has jurisdiction to entertain complaints where the value of goods/services complained against and the compensation, if any, claimed is………………..
(a) Exceeding ₹ 1 crore
(b) Exceeding ₹ 10 lakhs
(c) Exceeding ₹ 5 lakhs
(d) Exceeding ₹ 12 lakhs
Answer:
(a) Exceeding ₹ 1 crore
![]()
Question 17.
New Economic Policy was introduced in the year
(a) 1980
(b) 1991
(c) 2013
(d) 2015
Answer:
(b) 1991
Question 18.
In which of the following types, the ownership is immediately transferred to buyer?
(a) When goods are ascertained
(b) When goods are appropriate
(c) Delivery to the carrier
(d) Sale or return basis
Answer:
(c) Delivery to the carrier
Question 19.
………………. cannot be a bearer instrument.
(a) Cheque
(b) Promissory Note
(c) Bills of exchange
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Cheque
![]()
Question 20.
Which of the below is not classified into managerial functions?
(a) Planning
(b) Marketing
(c) Organising
(d) Controlling
Answer:
(c) Organising
Part – II
Answer any seven in which Question No. 30 is compulsory. [7 x 2 = 14]
Question 21.
What do you mean by Span of Management?
Answer
The Span of Management refers to the number of subordinates who can be managed efficiently by a superior. Simply, the manager having the group of subordinates who report him directly is called as the span of management.
Question 22.
What is Mutual Fund?
Answer
Financial institutions that provide facilities for channeling savings of small investors into avenues of productive investments are called ‘Mutual Funds’. A mutual fund company invests the funds pooled from shareholders and gives them the benefit of diversified investment portfolio and a reasonable return.
Question 23.
Who is called a Broker?
Answer
Broker is a commission agent. He acts as an intermediary between buyers and sellers of securities. He charges a commission for his services from both the parties.
Question 24.
What is Mentoring training method?
Answer
Mentoring is the process of sharing knowledge and experience of an employee. The focus in this training is on the development of attitude of trainees. It is mostly used for managerial employees.
![]()
Question 25.
Define E-Marketing.
Answer
“E-Marketing is achieving marketing objectives through use of digital technologies like Internet, world wide web, e-mail, wireless media, and management of digital customer data and electronic customer management systems.
Question 26.
What is caveat Venditor?
Answer
Today, most sales in the U.S. fall under the principle of caveat venditor, which means “let the seller beware,” by which goods are covered by an implied warranty of merchantability.
Question 27.
What is Privatisation.
Answer
Privatization is the incidence or process of transferring ownership of a business enterprise, agency or public service from the government to the private sector.
Question 28.
List three characteristics of a promissory Note.
Answer
Characteristics of a Promissory Note:
- A promissory note must be in writing.
- The promise to pay must be unconditional.
- It must be signed by the maker.
Question 29.
List down the promotional functions of entrepreneurs.
Answer
- Discovery of Idea
- Determining the business objectives
- Detailed Investigation
- Choice of form of enterprise
- Fulfilment of the formalities
- Preparation of Business Plan
- Mobilisation of funds
- Procurement of Machines and Materials
![]()
Question 30.
Name the companies required to appoint KMP?
Answer
Following Companies are required to appoint KMP:
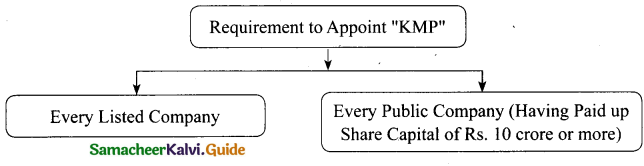
Part – III
Answer any seven in which question No. 40 is compulsory. [7 x 3 = 21]
Question 31.
What determines the span of management?
Answer:
The Span of Management has two implications:
- Influences the complexities of the individual manager’s job.
- Determine the shape or configuration of the organisation.
- There is a wide and a narrow span of management.
Question 32.
Bring out the scope of financial market in India.
Answer:
The financial market provides financial assistance to individuals, agricultural sectors, industrial sectors, service sectors, financial institutions like banks, insurance sectors, provident funds and the government as a whole. With the help of the financial market all the above stated individuals, institutions and the Government can get their required funds in time. Through the financial market the institutions get their short term as well as long term financial assistance. It leads to overall economic development.
Question 33.
Explain the types of Treasury Bills?
Answer:
Treasury Bills are issued to the public and other financial institutions for meeting the short-term financial requirements of the Central Government. Treasury Bills may be classified into three. They are:
- 91 days Treasury Bills
- 182 days Treasury Bills and
- 64 days Treasury Bills 34.
Question 34.
Explain National Stock Exchange. (NSE)
Answer:
National Stock Exchange was incorporated in November, 1992. It uses satellite link to spread trading throughout the country. Through computer network, members’ orders for buying and selling within prescribed price are matched by central computer.
Question 35.
Name the types of Selection Test.
Answer:
Selection tests are of two types:
- Ability Tests and Personality Tests. Ability tests can further be divided into: aptitude test, achievement test, intelligence test, and judgement test.
- Personality tests can further be divided into: interest test, personality inventory test, projective test or thematic appreciation test, and attitude test.
Question 36.
Write the importance of Consumerism.
Answer:
Importance of consumerism lies in
- Awakening and uniting consumers
- Discouraging unfair trade practices
- Protecting against exploitation
- Awakening the government.
- Effective implementation of consumer protection laws
- Providing complete and latest information
- Discouraging anti-social activities
![]()
Question 37.
What are the advantages of disinvestment?
Answer:
Disinvestment in PSUs: The Govt, has started the process of disinvestment in those PSUs which had been running into loss. It means that Govt, has been selling out these industries to private sector. So disinvestment is a system of privatizing government enterprises.
Question 38.
Explain the promotional functions of entrepreneur.
(i) Discovery of Idea: The first and foremost function of entrepreneur is idea generation. A person may conceive his own ideas or develop the ideas contributed by others. Ideas can be generated through several ways like own experience and exposure of entrepreneur, keen observation of environment, education, training, market survey, environmental scanning and so on.
(ii) Determining the business objectives: Entrepreneur has to develop business objectives in the backdrop of nature of business and type of business activity i.e. nature of business, manufacturing or trading, type of business organisation chosen so that he/she can organise the venture in accordance with the objectives determined by him/her.
(iii) Detailed Investigation: Entrepreneur should investigate commercial feasibility of the product proposed to be produced and conduct market study to ascertain the potential demand for the product.
(iv) Choice of form of enterprise: Entrepreneur has to choose the appropriate form of organisation suited to implement the venture. There are various forms of organisation namely sole proprietor, partnership, company and co-operatives etc. which are in existence.
(v) Fulfilment of the formalities: Having chosen the appropriate type of organisation, entrepreneur has to take necessary steps to establish the form of organisation chosen. As regards sole trader, the formalities are barest minimum. In the case of partnership firm, entrepreneur has to arrange for partnership deed and he has to get the deed registered.
(vi) Preparation of Business Plan: Entrepreneur has to prepare a business plan or project report
of the venture that he is proposing to take up.
(vii) Mobilisation of funds: Entrepreneur has to take steps to mobilise capital needed to implement the venture. Entrepreneur has to estimate the fixed capital and working capital required for running the project.
(viii) Procurement of Machines and Materials: Entrepreneur has to locate the various sources of supply of machineries, equipments and materials.
Question 39.
What is Causal Vacancy?
Answer:
If a director is absent from India, for a period which is not less than three months, then it is called casual vacancy. It may be filled by the appointment of alternate director. The appointment must be authorised by the articles of association by passing a resolution in the meeting.
![]()
Question 40.
Give any three cases in which an ordinary resolution need to be passed.
Answer:
An ordinary resolution is one which can be passed by a simple majority, i.e. if the members of votes cast by members, entitled to vote in favour of the resolution is more than the votes cast against the resolution.
Ordinary Resolution is required for the following matters:
- To change or rectify the name of the company
- To alter the share capital of the company
- To redeem the debentures
Part – IV
Answer all the following questions. [7 x 5 = 35]
Question 41
(a) Explain Lombard Street and Wall Street.
Answer:
Lombard Street
Lombard Street is in London. It is a street notable for its connections with the merchants, banking and insurance industries of London. From bank junction, where nine streets converge by the bank of England, Lombard Street runs southeast for a short distance.
Wall Street
Wall Street is a street in New York. It is the original home of the New York Stock exchange.
Also it is the historic headquarters of the largest U.S. brokerages and investment banks.
Wall Street is also used as a collective name for the financial and investment community.
[OR]
(b) Discuss the Operating functions of HRM.
Answer:
Operating functions of HRM:
- Procurement: Acquisition deals with job analysis, human resource planning, recruitment, selection, placement and promotion.
- Development: It includes performance appraisal, training, executive development, and organisational development.
- Compensation: It deals with job evaluation, wage and salary administration, incentives, bonus schemes.
- Retention: This is made possible through health and safety, social security, job satisfaction and quality of work life.
- Maintenance: This encourages employees to work with job satisfaction, reducing labour turnover, for human resource.
![]()
Question 42.
(a) Differentiate Recruitment and Selection.
Answer:
| Basis for comparison | Recruitment | Selection |
| 1. Meaning | It means searching candidates for the right job. | It refers to the process of selecting the suitable candidates and offering them job. |
| 2. Objective | Inviting large number of candidates to apply for the vacant post. | Picking up the most suitable candidates. |
| 3. Method | It is an economical method. | It is an expensive method. |
| 4. Contractual relation | It involves the communication of vacancies. There is no contractual relation. | It creates contractual relation between employer and employee. |
| 5. Process | Recruitment process is very simple. | Selection process is very complex and complicated. |
| 6. Time | Requires less time since it involves merely identifying vacancies and advertising them. | It is more time-consuming because each and every candidate has to be tested on various aspects before finally being selected. |
[OR]
(b) Explain the principles of placement.
Answer:
The following are the principles of placement:
- Job First, Man Next: Man should be placed on the job according to the requirements
of the job. - Job Offer: The job should be offered to the man based on his qualification.
- Terms and conditions: The employee should be informed about the terms and conditions of the organisation.
- Aware about the Penalties: The employee should also be made aware of the penalties if he / she commits a mistake.
- Loyalty and Co-operation: When placing a person in a new job, an effort should be made to develop a sense of loyalty and co-operation in him.
Question 43.
(a) What is Marketing?
Answer:
- Marketing is the performance of buying activities that facilitate to more flow of goods and services. It is one of the oldest profession in the world.
- Objective: The traditional objective of marketing had been to make the goods available at places where they are needed.
- Later on this idea was changed from ‘exchange’ to “Satisfaction of human wants”. Marketing is linking the consumer and the producer. Also marketing helps to maintain economic stability and economic development.
![]()
[OR]
(b) What are the salient features of the Consumer Protection Act 1986?
Answer:
Salient features of The Indian Consumer Protection Act, 1986:
- Protecting consumers against products and services which are harmful to the health of the consumers.
- Ensuring consumers with supply of goods at fair quality.
- Ensuring the availability of goods in correct quantity and right size.
- Protecting the consumers against pollution of various kinds.
- Ensuring that consumers are charged fair price.
- Protecting the consumers against unfair trade practices of unscrupulous trader.
Question 44.
(a) What are the responsibilities of consumers?
Answer:
Rights and responsibilities are two sides of the same coin. The responsibilities of consumers are listed below:
- The consumer must pay the price of the goods according to the terms and conditions.
- The consumer has the responsibility to make the seller to deliver the goods in time.
- The consumer has to bear any loss, which may arise to the seller, due to delay in taking delivery.
- The consumer has to follow the instructions and precautions while using the product.
- The consumer must collect the cash receipt as a proof of goods purchased from the seller.
- The consumer must file a complaint with the seller about the defects in products or deficiency in service.
[OR]
(b) Discuss in detail the rights of an unpaid seller against the goods.
Answer
A seller is deemed to be an unpaid seller when :
(a) the whole of the price has not been paid or
(b) a bill of exchange or other negotiable instrument given to him has been dishonoured. Rights of an Unpaid Seller against the Goods: Where the Property in the Goods has Passed to the Buyer:
Right of Lien: An unpaid seller has a right to retain the goods till he receives the price. But to exercise this lien-
(i) He must be in possession of goods
(ii) The goods must have been sold without any condition.
- Right of Stoppage in Transit: Where the seller has delivered the goods to a carrier or other bailee for the purpose of transmission to the buyer, but the buyer has not acquired them, then the seller can stop the goods.
- Right of Resale: The unpaid seller can resell the goods
(iii) Where they are of a perishable nature or
(iv) Where the seller has expressly reserved the right of resale in the contract itself.
Question 45.
(a) Discuss the problems faced by Women Entrepreneurs?
Answer:
There is a tremendous growth in the women entrepreneurship in India. But there are certain problems met by women entrepreneurs. They are as follows
(i) Problem of Finance: The external sources of funds for the women is limited because they do not generally own properties in their own name. They are depending on their own savings and loan from friends and relatives.
(ii) Lack of Education: Illiterate and semi-literate women entrepreneurs face difficulties in respect of accounts, money matters, marketing and day-to-day operations
![]()
(iii) Lack of Network Support: The success of business depends on the support of family members, friends and relatives. But it is reported that the women entrepreneurs get very limited support in times of crisis.
(iv) Stiff Competition: They have to face acute competition for their goods from organised sector and from their male counterparts.
(v) Lack of Information: The lack of knowledge or limited knowledge about subsidies, concessions and incentives given by Government will affect the business.
[OR]
(b) Discuss the Preparation of a project report.
Answer:
An entrepreneur can get the report prepared by technical consultancy organisations or by auditors or by government agencies. The report should include the following:
(i) Technical feasibility: It should contain the description of product, raw materials, quality control measures, water, power and transport.
(it) Economic viability: It involves compilation of demand for domestic and export market.
(iii) Financial viability: It should cover the aspects like: Non-recurring expenses like cost of land, and building. Recurring expenses like wages and salaries.
(iv) Managerial competency: Entrepreneurs has to include the mechanism for managing the venture in the project report.
![]()
(v) Provisional registration certificate: He has to apply for provisional registration certificate. It will be issued after certain conditions for a period of one year.
(vi) Permanent registration certificate: If the venture has commenced production, or is ready to commence production, it is eligible to get permanent registration certificate.
(vii) Statutory licence: He should obtain Municipal Licence from the authority concerned.
(viii) Power connection: He has to make application to Assistant Divisional Engineer of Electricity Board for power connection.
(ix) Arrangement of finance: Entrepreneur requires two types of finance namely Long term and Short term.
Question 46.
(a) Explain how director of a company can be removed from the office?
Answer:
A Director of Company can be removed from his Office before the expiry of his term by
- the Shareholders
- the Central Government
- the Company Law Board
(i) Removal by shareholders (Sec- 169): A company may, by giving a special notice and passing an ordinary resolution, remove a director before the expiry of his period of office.
(ii) Removal by the Central Government: The Central Government has been empowered to remove managerial personnel from office on the recommendation of the Company Law Board under the following situations:
- Where a person concerned in the conduct and management of the affairs of a company has been guilty of fraud and negligence.
- If the business is managed by a person without sound business principles.
- Where the business of a company has been managed by such a person, who likes to cause injury or damage to the business.
(iii) Removal by the Company Law Board: If an application has been made to the Company Law Board against the oppression and mismanagement of the company’s affairs by a director, then the Company Law Board may order to terminate the director.
[OR]
![]()
(b) Describe the different types of resolutions which company may pass in the suitable matters required for each type of resolution.
Answer:
A motion, with or without the amendments which is put to vote at a meeting and passed with the required quorum becomes resolution. Resolution may be classified into three types. They are: Ordinary resolution, Special resolution and resolution requiring special notice.
(i) Ordinary Resolution: An ordinary resolution is one which can be passed by a simple majority.
Ordinary Resolution is required for the following matters:
- To change or rectify the name of the company
- To alter the share capital of the company
- To redeem the debentures
- To declare the dividends
- To appoint the directors
(ii) Special Resolution: A special resolution is the one which is passed by not less than 75% of majority.
Special Resolution is required for the following matters:
- To change the registered office of the company
- To alter the Articles of Association
- To commence any new business
- To appoint the auditor for the company
(iii) Resolution requiring Special Notice: There are certain matters specified in the Companies Act, 2013 which may be discussed at a general meeting only if a special notice is given at least 14 days before the meeting.
The following matters require special notice:
- To remove a director before the expiry of his period
- To appoint a director in the place of a director so removed
Question 47.
(a) Discuss the significance of understanding business environment and the internal factors affecting business.
Answer:
A business in order to remain successful and competitive has to adapt to the constantly changing environment. The significance of understanding the business environment is as follows:
- Helps in formulating strategy and future planning.
- The analysis of business environment helps a business to identify new opportunities.
- Environment scanning helps the firms to identify threats which affect the business.
Internal factors of environment:
- Value system: The success of an organisation depends upon the sharing of value system by all members.
- Vision and objectives: The vision and objectives of a business guides its operations and strategic decisions.
- Management structure: The structure of management/board and their style of functioning, the composition of the board.
- Internal power relations: This refers to the internal power relations that exist in an organisation. The relations among board members, and the CEO and employees, shareholders are the factors affecting in taking decisions.
![]()
[OR]
(b) What is Voluntary Consumer Organisations? Explain its Functions.
Answer:
Voluntary consumer organisations refer to the organisation formed voluntarily by the consumers to protect their rights and interests.
Functions:
- Collecting Data on Different Products: These organizations collect samples of different products from time to time and test them.
- Filing Suit on Behalf of Consumers: If a consumer is not able to protest regarding his complaints, these organisations file case in the court, on behalf of a consumer.
- Protests against Adulteration: The consumer organisations play a significant role in eliminating the evil of adulteration, hoarding, black-marketing.
- Helping Educational Institutions: These organizations advice the educational institutions the way to prepare courses of study.
- Extending Support to Government: Consumer organisations keep informing the government agencies about adulteration, artificial scarcity, inferior quality products.