Students get through the TN Board 11th Bio Botany Important Questions Chapter 2 Plant Kingdom which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 11th Bio Botany Important Questions Chapter 2 Plant Kingdom
Answer the following short answers.
Question 1.
Define photosynthesis.
Answer:
Plants are unique living entities as they are endowed with the power to harvest the light energy from the sun and to convert it to chemical energy in the form of food through the astounding reaction, photosynthesis.
Question 2.
What is an alternation of generation?
Answer:
Alternation of generation is common in all plants. Alternation of the haploid gametophytic phase (n) with the diploid sporophytic phase (2n) during the life cycle is called alternation of generation.
Question 3.
What do you know about Halophyte algae?
Answer:
Dunaliella salina grows in salt pans (Halophytic algae), which can tolerate high concentration of salt content.
![]()
Question 4.
Mention any two vegetative reproduction in algae.
Answer:
Vegetative reproduction includes fission in unicellular forms the cell divides mitotically to produce two daughter cells, eg. Chlamydomonas.
Fragmentation: fragments of parent thallus grow into new individual, eg. Uloihrix.
Question 5.
Describe the thallus of red algae.
Answer:
The thallus is multicellular, macroscopic and diverse in form.
Question 6.
What is Garpogohium?
Answer:
The female sex organ of red algae is called carpogonium.
Question 7.
Mention any two characteristic features of bryophytes.
Answer:
- The plant body of bryophyte is gametophyte and is not differentiated into root, stem and leaf-like structure.
- Most of them are primitive land dwellers. Some of them are aquatic (Riella, Ricciocarpus).
Question 8.
Mention any three uses of Pteridophyte.
Answer:
Cut flower arrangements, Food, Biofertilizer.
![]()
Question 9.
Define the term Solenostele.
Answer:
The stele is perforated at a place or places corresponding to the origin of the leaf trace.
Question 10.
What is meant by Amber?
Answer:
Amber is a plant secretion that is an efficient preservative that doesn’t get degraded and hence can preserve remains of extinct life forms. The amber is produced by Pinites succinifera, a Gymnosperm.
Question 11.
Why do you call some plant fossil plants?
Answer:
The term ’form genera’ is used to name the fossil plants because the whole plant is not recovered as fossils instead organs or parts of the extinct plants are obtained in fragments.
Question 12.
What are the three classes of Gymnosperms?
Answer:
- Cycadopsida,
- Coniferopsida,
- Gnetopsida
Question 13.
Define the term Gymnosperm.
Answer:
Gymnosperms (Gr. Gymnos = naked; Sperma = seed) are naked seed-producing plants. They were dominant in the Jurassic and cretaceous periods of the Mesozoic era.
![]()
Question 14.
What are the non-vascular cryptogams?
Answer:
Vascular tissue like xylem and phloem are completely absent, hence called ‘Non-vascular cryptogams’.
Question 15.
Mention any two fossil gymnosperms.
Answer:
Medullosa and Lepido-carpon.
Question 16.
List out morphological features of the dicot plant.
Answer:
- Reticulate venation is present in the leaves.
- Presence of two cotyledons in the seed.
- Primary root radicle persists as the taproot.
- Flowers tetramerous or Pentamerous.
- Tricolpate (3 furrow) pollen is present.
Question 17.
What do you know about pyrenoids?
Answer:
Storage bodies called pyrenoids are present in the chloroplast and store starch.
Question 18.
What are Epiphytic algae?
Answer:
A few algae grow on the surface of aquatic plants and are called epiphytic algae (Coleochaete, and Rhodymenia).
Question 19.
What are Bryophytes?
Answer:
Bryophytes are the simplest land inhabiting cryptogams and are restricted to moist, shady habitats.
They lack vascular tissue and hence called ‘Non- vascular cryptogams’.
![]()
Question 20.
Mention the five subdivisions of Pteridophytes.
Answer:
- Psilophytopsida,
- Psilotopsida,
- Lycopsida,
- Sphenopsida,
- Pteropsida.
Answer In brief.
Question 1.
List the life cycle patterns in plants.
Answer:
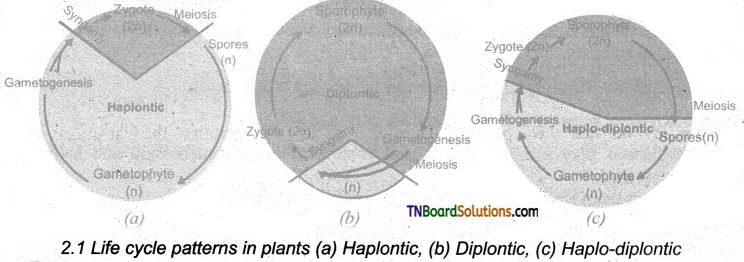
Question 2.
Name the 11 classes of Algae by which F.E. Fritsch classified.
Answer:
F.E. Fritsch proposed a classification for algae-based on pigmentation, types of flagella, reserve food materials, thallus structure and reproduction. He published his classification in the book “The structure and reproduction of Algae” (1935). He classified algae into 11 classes namely Chlorophyceae, Xanthophyceae, Chrysophyceae, Bacillariophyceae, Cryptophyceae, Dinophyceae, Chloromonodineae, Euglenophyceae, Phaeophyceae, Rhodophyceae, Cyanophyceae.
![]()
Question 3.
Describe the gametophyte phase of non-vascular cryptogams.
Answer:
- The gametophyte is a conspicuous, long-lived phase of the life cycle.
- Thalloid forms are present in liverworts and Hornworts.
- In Mosses leaf-like, stem-like structures are present.
- In Liverworts thallus grows prostrate on the ground and is attached to the substratum by means of rhizoids.
- Two types of rhizoids are present namely smooth-walled and pegged. Multicellular scales are also present.
- In Moss, the plant body is erect with a central axis bearing leaf-like expansions. Multicellular rhizoids are present.
Question 4.
Describe the sporophyte of non-vascular cryptogam.
Answer:
- The embryo divides and gives rise to the sporophyte.
- The sporophyte is dependent on the gametophyte.
- It is differentiated into three recognizable parts namely foot, seta and capsule.
- The foot is the basal portion and is embedded in the gametophyte through which water and nutrients are supplied for the sporophyte.
- The diploid spore mother cells found in the capsule region undergo meiotic division and give rise to haploid spores. Bryophytes are homosporous.
- In some sporophytes, elaters are present and help in the dispersal of spores, eg. Marchantia.
- The spores germinate to produce gametophyte.
Question 5.
Write briefly about the economic importance of non-vascular cryptogams.
Answer:
- A large amount of dead thallus of Sphagnum gets accumulated mid compressed, hardened to form peat. In northern Europe, peat is used as fuel in a commercial scale (Netherlands).
- Apart from this Nitrates, brown dye and tanning materials are derived from peat.
- Sphagnum and peat are also used in horticulture as packing material because of their water holding capacity.
- Marchantia polymorpha is used to cure pulmonary tuberculosis.
- Sphagnum, Bryum and Polytrichum are used as food.
- Bryophytes play a major role in soil formation through succession and help in soil conservation.
![]()
Question 6.
List out any four, characteristic features of pteridophytes.
Answer:
- The plant body is a sporophyte (2n) and it is the dominant phase.
- It is differentiated into root, stem and leaves. Roots are adventitious.
- The stem shows monopodial or dichotomous branching.
- Leaves may be microphyllous or megaphyllous.
Question 7.
Distinguish between Gymnosperms and Angiosperms.
Answer:
| Gymnosperms | Angiosperms |
| Vessels are absent [except Gnetales] | Vessels are present |
| Phloem lacks companion cells | Companion cells are present |
| Ovules are naked | Ovules are enclosed within the ovary |
| Wind pollination only | Insects, wind, water, animals etc., act as pollinating agents |
| Double fertilization is absent | Double fertilization is present |
| Endosperm is haploid | Endosperm is triploid |
| Fruit formation is absent | Fruit formation is present |
| Flowers absent | Flowers present |
Question 8.
List out any three Economic importance of algae.
Answer:
- Agar Agar – cell wall material used for media preparation in the microbiology lab.
- Packing canned food, cosmetic, textile paper industry.
- Carrageenan – Preparation of toothpaste, paint, blood coagulant
- Alginate – Ice cream, paints, flameproof fabrics.
![]()
Question 9.
Describe the Vegetable reproduction of non-vascular cryptogams.
Answer:
- Vegetative reproduction takes place by die formation of adventitious buds (Riccia fluitans) tubers develop in Anthoceros.
- In some forms small detachable branches or brood bodies are formed, they help in vegetative reproduction as in Bryopteris fruticulosa.
- In Marchantia propagative organs called gemmae are formed and help in reproduction.
Question 10.
List the salient features of Angiosperms.
Answer:
- Vascular tissue (Xylem and Phloem) is well developed.
- Flowers are produced instead of a cone.
- The embryosac (Ovule) remains enclosed in the ovary.
- Pollen tube helps in fertilization, so water is not essential for fertilization.
- Double fertilization is present. The endosperm is triploid.
- Angiosperms are broadly classified into two classes namely Dicotyledons and Monocotyledons.
Answer In detail.
Question 1.
Explain the asexual and sexual reproduction in algae with a suitable example.
Answer:
Asexual reproduction takes place by the production of zoospores (Ulothrix, Oedogonium),
- Aplanospore – Thin walled non motile spores, eg. Vaucheria.
- Autospores – Spores that look similar to the parent cell. eg. Chlorella.
- Hypnospore – Thick walled aplanospore. eg. Chlamydomonas nivalis. .
- Tetraspores – Diploid thallus of Polysiphonia produce haploid spores after meiosis).
![]()
Sexual reproduction in algae are of three types:
- Isogamy (Fusion of morphologically and Physiologically similar gametes eg. Ulothrix.
- Anisogamy (Fusion of either morphologically or physiologically dissimilar gametes eg. Pandorina.
- Oogamy (Fusion of both morphologically and physiologically dissimilar gametes, eg. Sargassum. The life cycle shows a distinct alternation of generation.
Question 2.
Give an account of Phaeophyceae.
Answer:
The members of this class are called ‘Brown algae’.
- The majority of the forms are found in marine habitats.
- Pleurocladia is a freshwater form.
- The thallus is filamentous (Ectocarpus) frond-like (Dictyota) or maybe giant kelps (Laminaria and Macrocystis).
- The thallus is differentiated into leaf-like photosynthetic part Called fronds, a stalk-like structure called stipe and a holdfast which attach thallus to the substratum.
- The Pigments include Chlorophyll a, c, Carotenoids and Xanthophylls.
- A golden-brown pigment called fucOxanthin is present and it gives shades of colour from olive green to brown to the algal members of this group.
- Mannitol and Laminarin are the reserve food materials. Motile reproductive structures are present.
- Two laterally inserted unequal flagella are present. Among these one is whiplash and another is tinsel.
- Although sexual reproduction ranges from isogamy to Oogamy, Most of the forms show the Oogamous type.
- Alternation of generation is present (isomorphic, heteromorphic or diplontic). eg. Sargassum, Laminaria, Fucus and Dictyota.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the method of sexual reproduction in non-vascular cryptogams.
Answer:
- Sexual reproduction is oogamous. Antheridia and Archegonia are produced in a protective covering and are multicellular.
- The antheridia produce biflagellate antherozoids which swim in a thin film of water and reach the archegonium and fuse with the egg to form a diploid zygote.
- Water is essential for fertilization.
- The zygote is the first cell of the sporophyte generation. It undergoes mitotic division to form the multicellular undifferentiated embryo. The embryogeny is exoscopic (the first division of the zygote is transverse and the apex of the embryo develops from the outer cell). The embryo divides and gives rise to the sporophyte.
- The sporophyte is dependent on the gametophyte.
- It is differentiated into three recognizable parts namely foot, seta and capsule. Foot is the basal portion and is embedded in the gametophyte through which water and nutrients are supplied for the sporophyte.
- The diploid spore mother cells found in the capsule region undergo meiotic division and give rise to haploid spores. Bryophytes are homosporous.
- In some sporophytes elaters are present and help in the dispersal of spores eg. Marchantia.
- The spores germinate to produce gametophyte.
Question 4.
Give an account of types of steles.
Answer:
The term stele refers to the central cylinder of vascular tissues consisting of xylem, phloem; pericycle and sometimes medullary rays with pith. There are two types of steles (i) Protostele, (ii) Siphonostele.
Protostele In protostele xylem surrounds phloem. The type includes Haplostele, Actinostele, Plectostele, and mixed protostele.
- Haplostele Xylem surrounded by phloem is known as haplostele. eg. Selaginella.
- Actinostele Star-shaped xylem core is surrounded by phloem is known as actinostele.
eg. Lycopodium serratum. - Plectostele Xylem plates alternate with phloem plates, eg. Lycopodium clavatum.
- Mixed protostele Xylem groups uniformly scattered in the phloem, eg. Lycopodium cernuum.
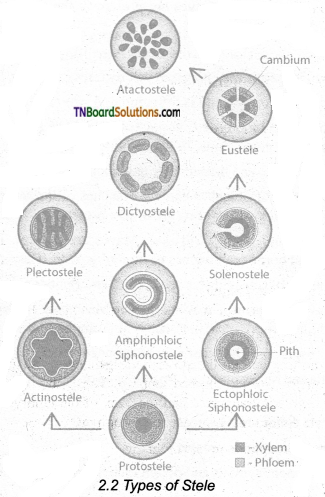
Siphonostele: In siphonostele, xylem is surrounded by phloem with pith at the centre. It includes Ectophloic siphonostele, Amphiphloic siphonostele, Solenostele, Eustele, Atactostele and Polycyclic stele.
- Ectophloic siphonostele: The phloem is restricted only on the external side of the xylem. Pith is in centre, eg. Osmunda.
- Amphiphloic siphonostele: The phloem is present on both the sides of xylem. The pith is in the centre, eg. Marsilea.
- Solenostele: The stele is perforated at a place or places corresponding the origin of the leaf trace.
(a) Ectophloic solenostele: Pith is in the centre and the xylem is surrounded by phloem, eg. Osmunda.
(b) Amphiphloic solenostele: Pith is in the centre and the phloem is present on both sides of the xylem. eg. Adiantum pedatum
(c) Dictyostele: The stele is separated into several vascular strands and each one is called meristele. eg. Adiantum capillus-veneris. - Eustele: The stele is split into distinct collateral vascular bundles around the pith, eg. Dicot stem.
- Atactostele: The stele is split into distinct collateral vascular bundles and are scattered in the ground tissue, eg. the Monocot stem.
- Polycyclicstele: The vascular tissues are present in the form of two or more concentric cylinders, eg. Pteridium.
![]()
Question 5.
Describe the general characteristics features of gymnosperms.
Answer:
- Most of the gymnosperms are evergreen woody trees or shrubs. Some are lianas (Gnetum)
- The plant body is sporophyte and is differentiated into root, stem and leaves.
- A well-developed tap root system is present. Coralloid roots of Cycas have a symbiotic association with blue-green algae. In Pinus the roots have mycorrhizae.
- The stem is aerial, erect and branched or unbranched (Cycas) with leaf scars.
- In conifers two types of branches namely branches of limited growth (Dwarf shoot) and Branches of unlimited growth (Long shoot) are present.
- Leaves are dimorphic, foliage and scale leaves are present. Foliage leaves are green, photosynthetic and borne on branches of limited growth. They show xerophytic features.
- The xylem consists of tracheids but in Gnetum and Ephedra Vessels are present.
- Secondary growth is present. The wood may be Manoxylic (Porous, soft, more parenchyma with wide medullary ray – Cycas) or Pycnoxylic (compact with narrow medullary ray-Pinus).
- They are Heterosporous. The plant may be monoecious (Pinus) or dioecious (Cycas).
- Microsporangia and Megasporangia are produced on Microsporophyll and Megasporophyll respectively.
- Male and female cones are produced.
- Anemophilous pollination is present.
- Fertilization is siphon gamous and pollen tube helps in the transfer of male nuclei.
Question 6.
List out the economic importance of gymnosperms.
Answer:
Economic importance of gymnosperms
| Plants | Products | Uses |
| Cycas circinalis, Cycas revoluta | Sago | Starch used as food. |
| Pinus gerardiana. | Roasted seed | Used as a food. |
| Abies balsamea. | Resin (Canada balsam) | Used as mounting medium in permanent slide preparation. |
| Pinus insularis, Pinus roxburghii | Rosin and Turpentine | Paper sizing and varnishes. |
| Araucaria (monkey’s puzzle), Picea and Phyllocladus. | Tannins | Bark yield tannins and is used in Leather industries. |
| Taxus brevifolia. | Taxol | Drug used for cancer treatment. |
| Ephedra gerardiana. | Ephedrine | For the treatment of asthma, bronchititis. |
| Pinus roxburghii. | Oleoresin | Used to make soap, varnishes and printing ink. |
| Pinus roxburghii, Picea smithiana | Wood pulp | Used to make papers. |
| Cedrus deodara. | Wood | Used to make doors, boats and railway sleepers. |
| Cedrus atlantica. | Oil | Used in perfumery. |
| Thuja, Cupressus, Araucaria, and Crypiomeria. | Decorative | Ornamental plants. |
![]()
Choose the correct answer.
1. Who proposed plant kingdom?
(a) Eichler
(b) G.M.Smith
(c) Chamberlain
(d) Aristotle
Answer:
(a) Eichler
2. Volvox, §pirogyra are the examples for:
(a) Diplontic
(b) Haplontic
(c) Epiphytic
(d) Haplodiplotic
Answer:
(b) Haplontic
3. Father of Indian phycology is:
(a) Went
(b) F.E. Fritsch
(c) Ainsworth
(d) M.O.P. Iyengar
Answer:
(d) M.O.P. Iyengar
4. Identify the incorrect habitat:
(a) Marine – Sargassum
(b) Freshwater – Oedogonium
(c) Soil – Ulothrix
(d) Salt pass – Dunaliella
Answer:
(c) Soil – Ulothrix
5. The study of Algae is called:
(a) Phycology
(b) Mycology
(c) Bryology
(d) Virology
Answer:
(a) Phycology
![]()
6. Which is the proteinaceous body found is
(a) Pyrenoids
(b) Siliceous walls
(c) Carrageenan
(d) Alginate
Answer:
(a) Pyrenoids
7. Oedogonium belongs to the class:
(a) Cryptophyceae
(b) Rhodophyceae
(c) Phaeophyceae
(d) Chlorophyceae
Answer:
(d) Chlorophyceae
8. Identify the incorrect pair.
(a) Green algae – Chlorophyceae
(b) Red algae – Rhodophyceae
(c) Brown algae -Phaeophyceae
(d) Blue algae – Dinophyceae
Answer:
(d) Blue algae – Dinophyceae
9. Match the following:
| (i) Carrageenin | (a) Gracilaria |
| (ii) Alginate | (b) Chlorella |
| (Hi) Chlorellin | (c) Laminaria |
| (iv) Agar agar | (d) Chondrus |
(a) (i)-(d), (ii)-(b), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(c)
(b) (i)-(d), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(b), (iv)-(a)
(c) (i)-(b), (ti)-(a), (iii)-(d), (iv)-(c)
(d) (i)-(b), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(d)
Answer:
(b) (i)-(d), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(b), (iv)-(a)
10. Amylum stars, root bulbils and amorphous bulbils are the vegetative reproductive organs of:
(a) Chora
(b) Oedogonium
(c) Selaginella
(d) Pinus
Answer:
(a) Chora
![]()
11. In which sporophyte elaters are present and help in dispersal:
(a) Riccia
(b) Anthoceros
(c) Bryopteris
(d) Marchantia
Answer:
(d) Marchantia
12. Who classified bryophytes in to 3 classes.
(a) Proskauer
(b) Kashyap
(c) G.M.Smith
(d) Chamberlain
Answer:
(a) Proskauer
13. Sphagnum is used in:
(a) Agriculture
(b) Horticulture
(c) Sericulture
(d) Monoculture
Answer:
(b) Horticulture
14. Pulmonary tuberculosis is caused by:
(a) Funaria hygrometrica
(b) Sphagnum
(c) Marchantia polynmorpha
(d) Riccia
Answer:
(c) Marchantia polynmorpha
15. Selaginalla is the example for:
(a) Plectostele
(b) Haplostele
(c) Mixed protostele
(d) Actinostele
Answer:
(b) Haplostele
![]()
16. ‘Walking fem’ is the common name for:
(a) Pinus
(b) Cycas
(c) Adiantum
(d) Selaginella
Answer:
(c) Adiantum
17. Identify the incorrect statement.
(a) presence of cambium in gymnosperm as in monocotyledons
(b) presence integument around the ovule
(c) both plant group produce seeds.
(d) pollentube helps in the transfer of male nucleus in both.
Answer:
(a) presence of cambium in gymnosperm as in monocotyledons
18. Match the following:
| (i) Cycas revoluta | (a) Drug used for cancer treatment |
| (ii) Pinus gerardiana | (b) used in perfumery |
| (iii) Taxus brevifolia | (c) used as a food |
| (iv) Cedrus atlantica | (d) starch used as food |
(a) (i)-(d), (ii)-(b), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(c)
(b) (i)-(d), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(b)
(c) (i)-(a), (ii)-(d), (iii)-(b), (iv)-(c)
(d) (i)-(a), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(b), (iv)-(d)
Answer:
(b) (i)-(d), (ti)-(c), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(b)
19. Coralloid roots are found in:
(a) Araucaria
(b) Ephedra
(c) Cycas
(d) Pinus
Answer:
(c) Cycas
20. Foliage leaves are otherwise called:
(a) Axillary leaves
(b) Scale leaves
(c) Sessile leaves
(d) Assimilatory leaves
Answer:
(d) Assimilatory leaves
![]()
21. Algae having oil as reserve food belongs to:
(a) Xanthophyceae
(b) Rhodophyceae
(c) Chlorophyceae
(d) Phaeophyceae
Answer:
(a) Xanthophyceae
22. Antheridia and Archegonia are sex organs of:
(a) Moss
(b) Mucor
(c) Spirogyra
(d) Puccinia
Answer:
(a) Moss
23. Archegonicphore is found in:
(a) Funaria
(b) Marchantia
(c) Chara
(d) Adiantum
Answer:
(b) Marchantia
24. Which one of the following in Spyrogyra is different based on its nucleus?
(a) Zygospore
(b) Azygospore
(c) Aplanspore
(d) Akinete
Answer:
(a) Zygospore
25. Nostoc fixes dinitrogen in symbiotic association with the following:
(a) Alnus
(b) Gunnera
(c) Anthocerus
(d) Casurina
The correct combination is:
(a) I & II (b) II & III (c) I & III (d) I & IV
Answer:
(b) II & III
![]()
26. Select the wrong statement:
(a) Isogametes are similar in structure, function and behaviour
(b) Anisogametes differ either in structure, function and behaviour
(c) In oomycetes , female gamete is smaller and motile, while male gamete is larger and nonmotile.
(d) Cjilamydomonas exhibits both isogamy and anisogamy and focus shows oogamy.
Answer:
(c) In oomycetes , female gamete is smaller and motile, while male gamete is larger and nonmotile.
27. The ladder like structure found in spirogyra is due to:
(a) Asexual reproduction
(b) Lateral conjugation
(c) Direct conjugation
(d) Sealiriform conjugation
Answer:
(d) Sealiriform conjugation
28. Transgenic plants are the ones:
(a) grown in artificial medium, after hybridization in the field.
(b) produced by a somatic embryo in artificial medium.
(c) generated by introducing foreign DNA into a cell and regenerating a plant from that cell.
(d) produced after protoplast fusion in artificial medium.
Answer:
(c) generated by introducing foreign DNA into a cell and regenerating a plant from that cell.
29. Which of the following is a living fossil?
(a) Spirogyra
(b) Moss
(c) Cycas
(d) Saccharomyces
Answer:
(c) Cycas
![]()
30. Which of the following species propagates through leaf-tip?
(a) Funaria
(b) Walking fern
(c) Moss
(d) Marchantia
Answer:
(b) Walking fern