TN State Board 11th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 15 Environmental Chemistry
Question 1.
Define Environmental Chemistry.
Answer:
Environmental chemistry is a branch of chemistry which deals with the study of chemicals and chemical processes occurring in the environment by direct human activities, It also deals with sources, causes and methods of controlling air, water and soil pollution.
Question 2.
Explain the term:
(i) Environmental pollution
(ii) Pollutants.
Answer:
(i) Any undesirable change in our environment ; that has harmful effects on plants, animals and human beings is called environmental pollution.
(ii) The substances which cause pollution of environment are called pollutants.
Question 3.
Give the composition of air.
Answer:
Air contains roughly 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.04% carbon dioxide, trace amounts of other gases and little amount of water vapour.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain various regions of atmosphere.
Answer:
The lowest layer of the atmosphere is called the troposphere and it extends from 0 – 10 km from the earth surface. About 80% of the mass of the atmosphere is in this layer. This troposphere in further divided as follows.
(i) Hydrosphere:
It includes all types of water sources like oceans, seas, rivers, lakes, streams, underground water, polar icecaps, clouds etc., It covers about 75% of the earth’s surface. Hence the earth is called as a blue planet.
(ii) Lithosphere:
It includes soil, rocks and mountains which are solid components of earth.
(iii) Biosphere:
It includes the lithosphere hydrosphere and atmosphere integrating the living organism present in the , lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere.
Question 5.
Explain the term air pollution and mention the causes of air pollution.
Answer:
Any undesirable change in air which adversely affects living organisms is called air pollution. Air pollution is limited to troposphere and stratosphere. Air pollution is mainly due to the excessive discharge of undesirable foreign matter into the atmospheric air.
![]()
Question 6.
Give examples for gaseous air pollutants.
Answer:
Oxides of sulphur, oxides of nitrogen, oxides of carbon, and hydrocarbons are the gaseous air pollutants.
Question 7.
Briefly outline the sources of air pollution? How are the gaseous air pollutants produced?
Answer:
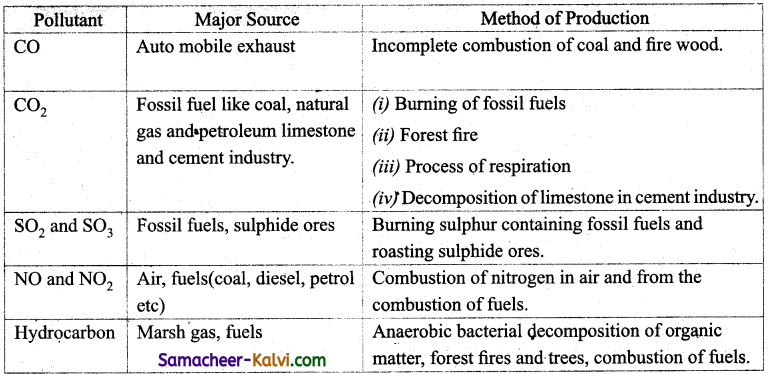
![]()
Question 8.
Mention the harmful effect of the gaseous air pollutants.
Answer:

Question 9.
Explain briefly ‘acid rain’. How is it caused?
Answer:
(i) Acid rain refers to any precipitation which has pH less than 5.6. The pH of acid rain ranges between 5.6 to 3.5 and in some cases evenupto 2.
(ii) Acid rain results from the presence of two strong acids in polluted air i.e., H2SO4 and to a lesser extent HNO3.
(iii) The presence of nitric acid in air is explained by the chemical reactions indicated below.
N2 + O2 ![]() 2NO
2NO
2 NO + O2 → 2 NO2
2 NO2 + H2O → HNO3 + HNO2
i.e., Nitric oxide is formed from its elements in air at high temperatures (i.e., during lightening). This is oxidised to NO2 which dissolves in H2O (from rain) to form nitric acid.
(iv) The sulphur dioxide present in air as a pollutant dissolves in water (i.e., rain) forming sulphuric acid as follows.
2 SO2 + O2 + 2H2O → 2H2SO4
![]()
Question 10.
Give examples for (i) viable particulate (ii) non-viable particulate.
Answer:
(i)Viable particulate:
Bacteria, fungi, moulds, algae etc…
(ii)Non-viable particulate:
Smoke, dust, mist, fumes, etc…
Question 11.
How the non-viable particulates pollute the air? Briefly explain.
Answer:
(i) Smoke:
Cigarette smoke, oil smoke, smokes from burning of fossil fuel, garbage and dry leaves mix in air and pollute the atmosphere.
(ii)Dust:
Sand from sand blasting, saw dust from wood works, cement dust from cement factories and fly ash from power generating units mix with atmosphere and pollute the air.
(iii) Mists:
They are formed by particles of spray liquids and condensation of vapours in air. Sulphuric acid mist, herbicides and insecticides sprays can form mists.
(iv)Fumes:
Organic solvents, metals and metallic oxides form fume particles.
![]()
Question 12.
Briefly outline the harmful health effects of particulate pollutants.
Answer:
(i) Effect on human beings:
Small sized particulates can pass through the nose and enter into lungs. These particulates in lungs adsorbs the particulates and produce lung diseases such as lung cancer, bronchital asthma etc., Different types of particulates cause different types of lung diseases.
(a) Coal mines suffer from black lung disease.
(b) Textile workers suffer from white lung disease.
(c) Lead particulates affect children’s brain.
(ii) Effect on plants:
Particulates deposit on the leaves of the plants. They destroy chlorophyll and retards the process of photosynthesis.
(iii) Effect on visibility:
Particulates cause scattering and absorption of sunlight and reduce visibility. This affects the free movement of vehicles and aircrafts.
(iv) Formation of artificial rain:
Particulates provide nuclei for cloud formation and induce the formation of fog and rain.
Question 13.
How will you reduce particulate pollutants in air? [OR] Outline the techniques to reduce particulate pollutants in air.
Answer:
The particulates from air can be removed by using electrostatic precipitators, gravity settling chambers, and wet scrubbers or by cyclone collectors. These techniques are based on washing away or settling of the particulates.
Question 14.
What are the effects of
(i) Classical smog,
(ii) Photochemical smog.
Answer:
(i)Effects of classical smog:
It decreases visibility and is responsible for breathing troubles like bronchitis and asthma. It produces irritation to eyes, nose and throat.
(ii) Effect of photochemical smog:
(a) It causes irritation to eyes, skin and lungs. Ozone causes reduction in plant growth. High concentration of ozone damage forests.
(b) Photochemical smog causes eye irritation, cough, chest discomfort, fatigue in humans.
(c) Peroxy Acetyl Nitrate (PAN) affects vegetation.
(d) Metal surfaces, building materials and ‘ painted surfaces get corroded by the smog.
![]()
Question 15.
Explain how photochemical smog be controlled.
Answer:
Use of catalytic convertors: This method involves the use of efficient catalytic converters in the automobiles. The harmful gases are converted to harmless gases. A catalytic converter minimize the release of oxides of nitrogen and hydrocarbons to the atmosphere.
Question 16.
Mention the pollutants that cause the depletion of ozone layer.
Answer:
The pollutants that cause ozone depletion in the atmosphere are oxides of nitrogen (NO2), chlorofluoro carbon (CFC). The oxides of nitrogen deplete ozone concentration by photochemical reactions. CFC’s reduce the ozone concentration by photochemical decomposition of O3.
Question 17.
Explain by means of a chemical equation. How nitric oxide cause the depletion of ozone layer? Nitrous oxide present in the stratosphere is photo chemically converted to nitric oxide.
Answer:
N2O + hv → NO + N
The nitric oxide thus formed undergoes the following chain reactions.
NO + O3 → NO2 + O2
O3 + hv → O2 + [O]
NO2 + [O] → NO + O2
The net reaction is
![]()
![]()
Question 18.
Discuss the environmental impact of ozone depletion.
Answer:
(i) As a result of ozone depletion, move uv , rays from the sun will reach the earth’s surface. As a result of this exposure, humans are prove to develop skin cancer and decrease in immunity level.
(ii) Exposure to UV radiations affect plants and retard their growth and harmful mutation of plant cells.
(iii) Exposure to uv radiation affect the growth of phytoplankton, as a result ocean chain is disturbed and even damages fish productivity.
Question 19.
Define water pollution.
Answer:
Water pollution is defined as “The addition of foreign substances or factors like heat which degrades the quality of water, so that it – becomes health hazard or unfit to use.”
Question 20.
Mention the sources of water pollution.
Answer:
The source of water pollution is from
(i) point and
(ii) non point sources.
(i) Point source is the one which can be easily identify the place of pollution.
eg: municipal and industrial discharge.
(ii) Non-point source cannot be identified easily.
eg: agricultural run off, mining wastes, acid rain, storm, water drainage and construction sediments.
![]()
Question 21.
Give a brief account of water pollution caused by (i) Microbiological organisms (pathogen) (ii) Organic wastes.
Answer:
(i) Microbiological (Pathogens):
Disease causing microorganisms like bacteria, viruses and protozoa are most serious water pollutants. They come from domestic sewage and animal excreta. Fish and shellfish can become contaminated and people who eat them can become ill. Some serious diseases like polio and cholera are water borne diseases. Human excreta contain bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Streptococcus faecalis which cause gastrointestinal diseases.
(ii) Organic wastes:
Organic matter such as leaves, grass, trash etc., can also pollute water. Water pollution is caused by excessive phytoplankton growth within water. Microorganisms present in water decompose these organic matter and consume dissolved oxygen in water.
Question 22.
What is Eutrophication?
Answer:
Eutrophication is a process by which water bodies receive excess nutrients that stimulates excessive plant growth (algae, other plant weeds) .This enhanced plant growth in water bodies is called as algae bloom.
Question 23.
What is the role of fluoride ion in the drinking water? What will happen if one drinks water in which the fluoride ion concentration exceeds 2 ppm?
Answer:
The Fluoride ions make the enamel on teeth much harder by converting hydroxyapatite, [3(Ca3(PO4)2.Ca(OH)2], the enamel on the surface of the teeth, into much harder fluorapatite, [3(Ca3(PO4)2.CaF2].
However, Fluoride ion concentration above 2 ppm causes brown mottling of teeth. Excess fluoride causes damage to bone and teeth.
![]()
Question 24.
What are the acceptable level of (i) Lead, (ii) Sulphate, (Hi) Nitrate in drinking water? Mention the harmful effects of these if present in excess of acceptable level in drinking water.
Answer:
(i) Lead:
The acceptable level of lead to be present in drinking water is less than 50 ppm. Excessive amount present in drinking water cause damage to liver, kidney and reproductive system.
(ii) Sulphate:
The acceptable level of sulphate ion concentration in drinking water is less than 500 ppm. Excess of sulphate ion concentration in drinking water produces laxative effect.
(iii) Nitrate:
The acceptable level of nitrate ion concentration in drinking water is less than 45 ppm. Anything in excess of their value causes methemoglobinemia disease in children.
Question 25.
What do you understand by the term Total , Dissolved Solid (TDS) in drinking water? What is the maximum concentration of these in drinking water? Mention the effect of excess concentration of TDS in drinking water if one drinks such water?
Answer:
A total dissolved solid (TDS) is a measure of the combined total of organic and inorganic substances contained in water. These solids are primarily minerals, salts and organic matter that can be general indicator of water quality.
For drinking water, the maximum concentration level is 500 mg/L or 500 ppm. This is the acceptable limit of total dissolved solids in drinking Water.
The dissolved salts contain cations like Ca+2, Mg+2, Na+, K+ and anions like CO3-2, HCO3-1, Cl– SO42, PO4-3 and NO3– The other substances that cause harmful effects if present in drinking water are fluoride in lead salts.
(a) If fluoride ions are present in drinking water (exceeding 2 ppm to 10 ppm), teeth and bones are affected.
(b) The presence of lead salts exceeding 50 ppm can damage liver, kidney and reproductive system.
(c) Sulphate ion concentration exceeding 500 ppm cause laxative effect and hyper tension.
(d) Excess nitrate ion concentration (> 50 ppm) can cause methemoglobinemia (blue baby syndrome).
![]()
Question 26.
Define soil pollution.
Answer:
Soil pollution is defined as the buildup of persistent toxic compounds /radioactive materials, chemical salts and disease causing agents in soils which have harmful effects on plant growth and animal health.
Question 27.
What is the effect of soil pollution?
Answer:
Soil pollution affects the structure and fertility of soil, groundwater quality and food chain in biological ecosystem.
Question 28.
Briefly outline the sources of soil pollution.
Answer:
Artificial fertilizers:
Phosphate fertilizers, NPK fertilizers are added to the soil to ensure good yield.
Pesticides:
These are chemicals which are used to kill or stop the growth of unwanted organisms. They, are
(i) insecticides like DDT, BHC,
(ii) fungicide eg: Organo mercury compounds,
(iii) herbicides which is also known as weed killer, eg: Sodium chlorate.
Industrial wastes:
Large number of toxic wastes like cyanides, chromates, acids, alkalis, and metals like mercury, copper, zinc, cadmium and lead etc., are released from industries. These waste lie in the soil for a long time and prevents the growth of the plants.
![]()
Question 29.
Explain with an example how to produce eco- friendly compounds.
Answer:
Styrene is produced both by traditional and greener routes.
Traditional route:
This method involves two steps. Carcinogenic benzene reacts with ethylene to form ethyl benzene. Then ethyl benzene on dehydrogenation using Fe2O3 / Al2O3 gives styrene.
Greener route:
To avoid carcinogenic benzene, greener route is to start with cheaper and environmentally safer xylenes.
Question 30.
Give a brief account of Green chemistry in – day-to-day life.
Answer:
(i) For dry cleaning of clothes, the solvents used (eg: tetra chloro methane) pollute the ground water and it is also carcinogenic. This is replaced by liquid carbondioxide with a suitable detergent, which acts as a solvent, to prevent the harmful effect of carcinogenic substances.
(ii) In the bleaching of paper, chlorine is used as a bleaching agent. This is replaced by H2O2 in the presence of a catalyst.
(iii) Synthesis of chemicals:
Acetaldehyde is now commercially prepared by one step oxidation of ethene in the presence of ionic catalyst in aqueous medium with 90%
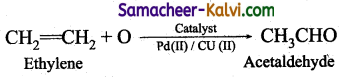
(iv) Instead of petrol, methanol is used as a fuel in automobiles.
(v) Neem based pesticides have been synthesised, which are more safer than the chlorinated hydrocarbons.
![]()
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Which of the following is the upper most region of the atmosphere?
(a) Stratosphere
(b) Troposphere
(c) Exosphere
(d) Ionosphere
Answer:
(c) Exosphere
Hint:
There is one region above thermosphere. It is called exosphere and is considered to be the highest region of the atmosphere. It lies in the range of 500 – 1600 km. Mesosphere and thermosphere are collectively known as ionosphere.
Question 2.
Which of the following is not considered to be a pollutant?
(a) CO
(b) CO2
(c) O3
(d) CxRy
Answer:
(b) CO2
Question 3.
Ozone in the stratosphere is depleted by:
(a) CF2Cl2
(b) C7F16
(c) C6H6C16
(d) C6H6
Answer:
(a) CF2Cl2
Hint:
Chlorofluorocarbons deplete the ozone layer.
![]()
Question 4.
Which of the following is not involved in the formation of photochemical smog?
(a) NO
(b) O3
(c) CxHy
(d) SO2
Answer:
(d) SO2
Hint:
(a) NO is formed by the action of N2 and O2.
(b) O3 is formed by the reaction
2NO + O2 → 2 NO2
NO2 ![]() NO + (O)
NO + (O)
(O) + O2 → O3
(c) Hydrocarbons are also present in the atmosphere.
Question 5.
Which of the following statement is false?
(a) Photochemical smog causes irritation to eyes.
(b) London smog is a mixture of smoke and fog.
(c) Photochemical smog results in the formation of PAN.
(d) London smog is oxidising in nature.
Answer:
(d) London smog is oxidising in nature.
Question 6.
Identify the wrong statement in the following:
(a) Ozone layer does not permit infrared radiation from the Sun to reach the Earth.
(b) Acid rain is mostly because of oxides of nitrogen and sulphur.
(c) Chlorofluorocarbons are responsible for ozone depletion.
(d) Green house effect is responsible for global warming.
Answer:
(a) Ozone layer does not permit infrared radiation from the Sun to reach the Earth.
![]()
Question 7.
The process ‘Eutrophication’ is due to:
(a) increase in concentration of insecticide in water.
(b) increase in concentration of fluoride ion in water.
(c) the reduction in concentration of the dissolved oxygen in water due to phosphate pollution in water.
(d) attack of younger leaves of a plant by peroxyacetyl nitrate.
Answer:
(c) the reduction in concentration of the dissolved oxygen in water due to phosphate pollution in water.
Question 8.
Excess of nitrate in drinking water can cause:
(a) methemoglobinemia
(b) kidney damage
(c) liver damage
(d) laxative effect
Answer:
(a) methemoglobinemia
Question 9.
The three main components of photo chemical smog are:
(a) nitrogen oxide, ozone and peroxy acetyl nitrate
(b) oxides of sulphur, oxides of nitrogen and ozone
(c) carbondioxide, ozone, acrolein
(d) formaldehyde, ozone, carbon monoxide
Answer:
(a) nitrogen oxide, ozone and peroxy acetyl nitrate
![]()
Question 10.
Highly polluted water has a BOD value of:
(a) 17 ppm or more
(b) 5.6 ppm
(c) 10 ppm
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(a) 17 ppm or more
Question 11.
DDT is a/an:
(a) fungicide
(b) herbicide
(c) insecticide
(d) fertilizer
Answer:
(c) insecticide
Question 12.
CFCl3 is responsible for decomposition of ozone to form oxygen. Which of the following reacts with ozone to form oxygen?
(a) Cl2
(b) Cl–
(c) F–
(d) Cl.
Answer:
(d) Cl.
Hint:
CFCl3 ![]() CFCl2 + Cl.
CFCl2 + Cl.
Cl. + O3 → ClO. + O2
ClO. + O. → Cl. + O3
![]()
Question 13.
An object is located at a height of 5 km from the surface of the Earth. The object is located in which part of the atmosphere?
(a) Thermosphere
(b) Mesosphere
(c) Stratosphere
(d) Troposphere
Answer:
(d) Troposphere
Question 14.
Lead is considered as:
(a) water pollutant
(b) soil pollutant
(c) air pollutant
(d) radioactive pollutant
Answer:
(a) water pollutant
Question 15.
If there was no carbondioxide in Earth’s atmosphere, the temperature of the Earth’s surface would be:
(a) same as present
(b) less than the present
(c) more than the present
(d) dependent on the amount of oxygen in the atmosphere.
Answer:
(b) less than the present
Hint:
CO2 present in normal concentration helps to maintain the temperature of the Earth for living organisms. A balance of CO2 is maintained in the air because CO2 produced from respiration, burning of fossil fuels and decomposition of lime stone but at the same time it is consumed by the green plants for photosynthesis.
If CO2 was not present in atmosphere global warming could not take place and the temperature of the Earth is lowered.
![]()
Question 16.
Catalytic converter is used in automobiles to control:
(a) water pollution
(b) soil pollution
(c) air pollution
(d) noise pollution
Answer:
(c) air pollution
Hint:
Catalytic converters remove particulates from air.
Question 17.
BOD5 meAnswer:
(a) water decomposed in 5 days
(b) oxygen used in 5 days
(c) micro organisms killed in 5 days
(d) dissolved oxygen left after 5 days
Answer:
(b) oxygen used in 5 days
Question 18.
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) is a measure of organic material present in water. BOD value less than 5 ppm indicates a water sample to be:
(a) rich in dissolved oxygen
(b) poor in dissolved oxygen
(c) highly polluted
(d) not suitable for aquatic life
Answer:
(a) rich in dissolved oxygen
![]()
Question 19.
The pollutants which come directly in the air from sources are, called primary pollutants. Primary pollutants are sometimes converted into secondary pollutants. Which of the following belongs to secondary air pollutants?
(a) CO
(b) Hydrocarbon
(c) Peroxy Acetyl Nitrate (PAN)
(d) NO
Answer:
(c) Peroxy Acetyl Nitrate (PAN)
Hint:
The following reactions occur in the presence of sun light.
NO2 ![]() NO + [O]
NO + [O]
(in atmosphere)
O + O2 → O3
(in atmosphere)
O3 + NO → NO2 + O2
If hydrocarbons were present in atmosphere, they combine with the oxygen produced by reaction (1) to form free radicals as intermediates (RCO.). These free radicals j initiate a variety of reactions.
eg: RCO + O2 → RCO3
RCO3 + hydrocarbon → RCHO + R2C = O
RCO3– + NO → RCO2 + NO2
RCO3– + O2 → O3 + RCO2
RCO3– + NO2 → RCO3– NO2
(peroxy acetyl nitrate, PAN)
Question 20.
Assertion:
Green house effect was observed in houses used to grow plants and these are made of green glass.
Reason:
Green house name has been given because glass houses are made of green glass.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(c) Both (A) and (R) are not correct
(d) (A) is correct but (R) is not correct
Answer:
(c) Both (A) and (R) are not correct
Hint:
Correct A: Green house effect was observed in frouses used to grow plants and these are not made of green glass but transparent glass.
Correct R: Green house name was given because it was used to grow plants.
![]()
Question 21.
Assertion:
The pH of acid rain is 5.6
Reason:
Carbon dioxide present in atmosphere dissolves in rain water and forms carbonic acid.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(c) Both (A) and (R) are not correct
(d) (A) is correct but (R) is not correct
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Hint:
Correct Explanation: CO2 as well as oxides of nitrogen and sulphur (NO2 and SO2) dissolves in water to form acid rain which has pH < 5.6.
Question 22.
Assertion:
Photochemical smog is oxidising in nature.
Reason:
Photochemical smog contains NO2 and O3 which are formed during the sequence of reactions.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(c) Both (A) and (R) are not correct
(d) (A) is correct but (R) is not correct
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
Question 23.
Assertion:
Carbondioxide is one of the important green house gases.
Reason:
It is largely produced by respiratory function of animals and plants.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(c) Both (A) and (R) are not correct
(d) (A) is correct but (R) is not correct
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Hint:
Correct Explanation Itis largely produced by combustion of fossil fuels like coal, natural gas, petroleum etc.
![]()
Question 24.
Assertion:
Ozone is destroyed by chloro fluorocarbons and nitric oxide.
Reason:
Thinning of the ozone layer allows excessive UV radiations to reach the surface of the Earth.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(c) Both (A) and (R) are not correct
(d) (A) is correct but (R) is not correct
Answer:
(A) is correct but (R) is not correct
Question 25.
Photochemical smog occurs in warm, dry and sunny climates. One of the following is not amongst the components of photochemical smog. Identify it.
(a) NO2
(b) O3
(c) SO2
(d) unsaturated hydrocarbons
Answer:
(c) SO2
Question 26.
The pollutants which come directly in the air from sources are called primary pollutants. Primary pollutants are sometimes converted into secondary pollutants. Which of the following belongs to secondary air pollutants?
(a) CO
(b) hydrocarbon
(c) peroxy acetyl nitrate
(d) NO
Answer:
(c) peroxy acetyl nitrate
![]()
Question 27.
The presence of which of the following cause smog?
(a) O2 and O3
(b) O2 and N2
(c) SO2 and NO2
(d) O3 and N2
Answer:
(c) SO2 and NO2
Question 28.
Which of the following pairs of compounds does not cause depletion of ozone layers?
(a) NO and CF2Cl2
(b) NO2 and O3
(c) O2 and N2
(d) CF2Cl2 and CFCl3
Answer:
(c) O2 and N2
Question 29.
Assertion:
The temperature in the stratosphere . increases with altitude.
Reason:
Ozone present absorbs the ultra violet radiation.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
![]()
Question 30.
Assertion:
For green house effect, presence of green plants is essential.
Reason:
Chlorophyll of the green plants cause green house effect.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
Hint:
Correct Assertion: Green house effect is due to presence of CO2 and water vapour near the earth’s surface.
Correct Reason: CO2 and H2O vapour present near the earth’s surface cause green house effect.
Question 31.
Assertion :
The catalytic converter in the car exhaust system converts polluting exhaust gases into non-toxic gases.
Reason Catalytic converter contains a mixture of transition metals and their oxides embedded in the inner support.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 32.
Assertion:
The pH of acid rain is 4 – 5.
Reason:
Normal rain water has a pH value of about 5 – 6 due to dissolution of carbon dioxide.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
![]()
Question 33.
Assertion:
London smog is found in summerduring morning time.
Reason:
Photochemical smog is formed in winter during morning time.
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
Hint:
Correct Assertion: Condon smog is found in winter during morning time.
Correct Reason: photochemical smog is formed in summer during day time.
Question 34.
Which one of the following statements is false?
(a) Photochemical smog causes irritation in eyes.
(b) London smog is a mixture of smoke and fog.
(c) Photochemical smog results in the formation of PAN.
(d) London smog is oxidising in nature.
Answer:
(d) London smog is oxidising in nature.
Hint:
London smog is reducing in nature.
Question 35.
Pick up the correct statement:
(a) CO which is a major pollutant resulting from combustion of fuels in automobile plays a major role in photochemical smog.
(b) Classical smog has an oxidising character while photochemical smog is reducing in character.
(c) Classical smog is good for health but not photochemical smog.
(d) Photochemical smog occurs in a day time, while classical smog occurs in the morning time.
Answer:
(d) Photochemical smog occurs in a day time, while classical smog occurs in the morning time.
![]()
Question 36.
Identify the incorrect statement in the following:
(a) Ozone layer does not permit infra red radiations from the Sun to reach the earth.
(b) Acid rain is mostly because of oxides of nitrogen and sulphur.
(c) Chlorofluorocarbons are responsible for ozone layer depletion.
(d) Green house effect is responsible for global warming.
Answer:
(a) Ozone layer does not permit infrared radiations from the Sun to reach the earth.
Question 37.
Choose the correct statement:
The process of eutrophication is due to:
(a) increase in concentration of insecticide in water.
(b) increase in concentration of fluoride ion in water.
(c) attack of younger leaves of a plant by j peroxy acetyl nitrate.
(d) the reduction of yi concentration of dissolved oxygen in water due to phosphate pollution in water.
Answer:
(d) the reduction of yi concentration of dissolved oxygen in water due to phosphate pollution in water.
Question 38.
Which one of the following statements is not true?
(a) Oxides of sulphur, nitrogen and carbon are the most widespread air pollutant.
(b) pH of drinking water should be 5.5 to 9.5.
(c) Concentration of DO below 6 ppm is good for growth of fish.
(d) Clean water would have a BOD value of less than 5 ppm.
Answer:
(c) Concentration of DO below 6 ppm is good for growth of fish.
![]()
Question 39.
Match the entities of column I with appropriate entities of column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Acid rain | (A) CHCl2CHF2 |
| (ii) Photochemical smog | (B) CO |
| (iii) Combination with haemoglobin | (C) CO2 |
| (iv) Depletion of ozone layer | (D) unsaturated hydrocarbon |
(a) (i) – (C), (ii) – (D), (iii) – (B), (iv) – (A)
(b) (i) – (D), (ii) – (B), (iii) – (A), (iv) – (C)
(c) (i) – (D), (ii) – (C), (iii) – (B), (iv) – (A)
(d) (i) – (A), (ii) – (D), (iii) – (B), (iv) – (C)
Answer:
(a) (i) – (C), (ii) – (D), (iii) – (B), (iv) – (A)
Question 40.
Match the entities of column I with appropriate entities of column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Inorganic pollutants | (A) Municipal waste water coming from slums, hotels and residential area |
| (ii) Organic pollutants | (B) laundry waste |
| (iii) Synthetic detergents | (C) Food processing industries, chemical industries |
| (iv) Infectious agents | (D) Acid and alkalis from chemical industries |
(a) (i) – (D), (ii) – (C), (iii) – (B), (iv) – (A)
(b) (i)- (B), (ii) – (D), (iii) – (A), (iv) – (C)
(c) (i) – (D), (ii) – (A), (iii) – (B), (iv) – (C)
(d) (i) – (D), (ii) – (B), (iii) – (A), (iv) – (C)
Answer:
(a) (i) – (D), (ii) – (C), (iii) – (B), (iv) – (A)