TN State Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 16 Emerging Service Business in India
Question 1.
Who is a Franchisee?
Answer:
The individual who acquires the right to operate the business or use the trademark of the seller is known as the franchisee.
Question 2.
State two disadvantages of franchising?
Answer:
(i) Franchising fees:
The initial franchising fee and the subsequent renewal fee can be very high.
(ii) Fixed royalty payment:
The franchisee has to make payment of royalty to the franchiser on a regular basis.
This considerably reduce the income of the franchisee.
![]()
Question 3.
Who is a factor?
Answer:
Firms sell goods on cash and credit basis. When goods are sold on credit basis, bills are drawn on the buyer by the seller. In case of small and medium business.
Question 4.
Define outsourcing.
Answer:
Recently a new type of business in service sector has become popular in the world. It is called the Business Process Outsourcing (BPO). BPO refers to outsourcing the work which is routine in nature, to an outside agency. This practice was initiated in United States of America in few companies.
Question 5.
What is need for outsourcing?
Answer:
- Focussing on core activities.
- Operational efficiency through outsourcing .
- Improved customer satisfaction.
- Increasing profit.
![]()
Question 6.
State the importance Of BPO.
Answer:
- To focus on key function.
- Benefit of specialization / efficiency.
- Cost cutting.
- Economic growth and development.
- Increasing profit.
- Catering to the dynamic demand.
Question 7.
What are the benefits of KPO?
Answer:
- Usage of best skills.
- Ultimate use of knowledge.
- Finding solution to complex problem.
- Reduction of expenditure.
- Special focus on principal functions.
- Outsources reduces risk.
![]()
Question 8.
Define Logistics.
Answer:
Logistics can be viewed as a logical extension of transportation and related areas to achieve an efficient and effective goods distribution system.
Question 9.
What is the need for logistics?
Answer:
- Logistics implies that a integrated view of member of different activities and functions may be required.
- All firms are viewed as a collection of primary and secondary activities.
Question 10.
Write about the importance of Logistics.
Answer:
Logistics management is also important for creating visibility into a company’s supply chain. Logistics managers can use this information for process optimisation and avoiding potential disruptions.
![]()
Question 11.
What are the types of Logistics Applications?
Answer:
The Logistrics Management can be classified on the basis of applications from various dimensions in the process of examining and evaluating alternatives.
They are:
- Decision-wise.
- Actor-wise.
- Inbound logistics and outbound logistics.
Question 12.
What do you mean by e.-commerce?
Answer:
e- commerce or Electronic Commerce is the buying and selling of goods and services through electronic networks like internet.
Question 13.
What are the type of franchising?
Answer:
(i) Product / trade name franchising:
In this type, the franchisee exclusively deals with a manufacturer’s product. Examples include Kidzee, French Loaf outlets, Bharat Petroleum bunks,Patanjali products, etc.
(ii) Business format franchising:
When a franchiser awards rights covering all business aspects as a complete business package to the franchisee it is called as business format franchising, eg: McDonald’s, Pizza Hut. KFC, Hot > breads, Titan, Color plus, Zodiac, Lakme beauty parlour.
![]()
Question 14.
List the steps in factoring process.
Answer:
(i) The firm enters into a factoring arrangement with a factor, which is generally a financial institution, for invoice purchasing.
(ii) Whenever goods are sold on credit basis, an invoice is raised and a copy of the same is sent to the factor.
(iii) The debt amount due to the firm is transferred to the factor through assignment and the same is intimated to the customer.
(iv) On the due date, the amount is collected by the factor from the customer.
(v) After retaining the service fees, the remaining amount is sent to the firm by the factor.
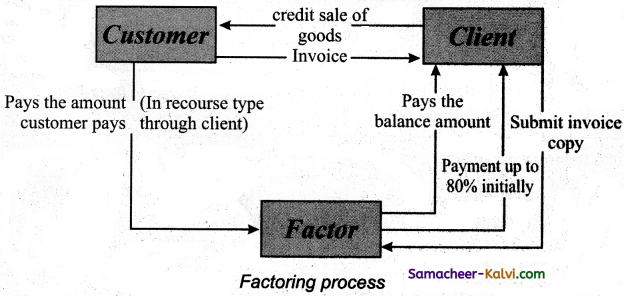
Question 15.
Describe the benefits of Logistics.
Answer:
Generally a good transportation, storage, handling and information infrastructure helps in efficient logistics management. In India most of the transportation happens through road and rail. Pipeline and Water transport are to be fully utilized further. Air transportation is used for high value commodities. In transportation infrastructure the following framework can be used to identify the problem areas like Right of way, Vehicle, Motive power, Terminals, Operations/systems.
![]()
Question 16.
Explain the points of differences between Logistics and Supply Chain Management.
Answer:
|
Logistics |
Supply chain management |
| Logistics Management deals with the efficient management of a static gap between demand and supply. | Supply Chain Management tries to identify the dynamic nature of the value creation itself such as responsiveness, quality and design. |
| Logistics management focuses on cost minimisation. | Supply chain management focuses only profit maximisation. |
| Logistics management activity is supply driven. | Supply chain management is more demand driven. |
whereas Hence, it aims for an effective management response over the longer run. SCM focuses on profit maximization rather than cost minimization. LM activity is supply driven and SCM is more demand driven.
Question 17.
What is the impact of e-commerce on buyers?
Answer:
- Buyers could have a global access to information about variety of products and services available in the market.
- They could buy the products/services round the clock from anywhere in world.
- The prices of products bought through e-commerce tend to be relatively lower than those purchased physically in the conventional shops due to offers, discount etc.
- Electronic and software products could be downloaded immediately after purchase through e-commerce mode.
- Customers could participate in e auction which is one of the facets of e-commerce and get contract in a free and fair manner.
![]()
Question 18.
Enumerate the characteristics of franchising.
Answer:
Characteristics of franchising:
- Franchise relationship is based on an agreement which lays down terms and conditions of this relationship.
- The term of franchise may be for 5 years or more. The franchise agreement may be renewed with the mutual consent of the parties.
- The franchisee gives an undertaking not to carry any other competing business during the term of the franchise; and the franchiser gives an undertaking not to terminate the franchise agreement before its expiry except under situations which may justify the termination of the franchise agreement.
- The franchisee agrees to pay specified royalty to the franchiser, as per terms of the franchise agreement.
- Franchise means selling the same product and maintaining a similar type of shop decor (i.e. style of interior decoration) for which franchiser provides assistance to franchisee in organising, merchandising and management. The franchiser virtually sets up the business for the franchisee.
Question 19.
Elucidate the features of factoring.
Answer:
Features of Factoring:
(i) Maintenance of book-debts:
A factor takes the responsibility of maintaining the accounts of debtors of a business institution.
(ii) Credit coverage:
The factor accepts the risk burden of loss of bad debts leaving the seller to concentrate on his core business.
(iii) Cash advances:
Around eighty percent of the total amount of accounts receivables is paid as advance cash to the client.
(iv) Collection service:
Issuing reminders, receiving part payments, collection of cheques form part of the factoring service.
(v) Advice to clients:
From the past history of debtors, the factor is able to provide advices regarding the credit worthiness of customers, perception of customers about the products of the client, etc.
![]()
Question 20.
Describe the benefits of Outsourcing.
Answer:
(i) Focusing on Core Activities:
Companies can focus on their core competence, a few areas where the company has distinct capability. The rest of the activities (non core) can be outsource to outside agencies.
(ii) To Fill up Economic Development:
Outsourcing stimulates entrepreneurship, encourages employment opportunities,. expands exports, enables tremendous growth of the economy.
(iii) Encourages Employment Opportunities:
Companies that are outsourcing their non core activities provide chances for other small business units to take up the activities. This paves way for more job opportunities and new employment avenues.
(iv) Reduction in Investment:
Companies through outsourcing avails the services of outsiders which in turn reduces the investment requirements. The amount so available can.be utilized productively and this increases the profits.
(v) Quest for Excellence:
Outsourcing enables the firms to pursue excellence in two ways namely excelling themselves inthe activities they do and excel outsiders by extending their capabilities through contracting out.
Question 21.
Explain the points of differences between BPO and KPO.
Answer:
| BPO |
KPO |
| BPO means getting contractual services of external companies or group of companies to complete special work or process of a company. | KPO refer to outsourcing of Knowledge based Process. It means obtaining high end knowledge work from outside the organization in order to run the business successfully and in cost effective manner. |
| For example call centres, data entry etc. This reduces the expenditure by using cheap labour available in developing countries like India, China etc. | In short KPO firms get knowledge related, information related, work done from outside firm and it involves high value work carried highly skilled staff. |
| To focus on key function. | Usage of best skills. |
| Benefit of specialization / efficiency. | Ultimate use of knowledge. |
| Cost cutting. | Finding solution to complex problem. |
![]()
Question 22.
Write a note on e-commerce models.
Answer:
(i) Business to Customers (B2C):
This is fastest growing segment in e-commerce spare. Under this model, business concern sells directly to consumers.
(ii) Business to Business (B2B):
Under the model, business concerns transact with one another through internet. For instance, Snapdeal, Flipkart, Alibaba, Indamart, Trade India. Com etc.
(iii) Consumer to Consumer (C2C):
Under this model, customers sell directly to other customers through online classified advertisement or through auction or through mobile or through market places. Example. Indian ventures in C2C are Kraftly App (buying and selling anythings) which deals in hand made products of a wide range once again store.com is a Website that buys pre-owned women’s fashion products. Other players are quirkr,01x, ebay etc.
(iv) Customer to Business (C2B):
This model is reverse to auction model. Products like automobile, electronic items furniture and similar product are traded by customer through websites.
eg: Naukri.com and Monster.com are examples of Indian companies operating in this domain.
(v) Business to Government (B2G):
This model envisages selling products and servicesby business consumerto Government organization For instance TCS operates the passport application process for the Government of India as part offline process.
![]()
Question 23.
You are a small scale manufacturer of ignition coils for automobiles, located near Ranipet. Explain how will you avail of financial credits through factoring if you get orders from
a. Ford India, Chennai
b. Maruti Suzuki, Gucgaon
c. Kun Hyundai, Seoul.
Answer:
Mainly used in advertising industry, construction, house hold appliances industry, electrical industry, furniture industry and transportation.
Question 24.
Identify methods of moving goods.
Answer:
In contrast of pull and push methods. Push method is a system that is used in traditional production when work or output finished it is pushed to the station. While pull method is pulling output from the proceeding station as it needed.
Question 25.
Draft ways and means of overcoming the problems in Logistics.
Answer:
International organisations have a key role to play in meeting this challenge, including by rapidly but accurately assessing the extent of available host nation support in order to plan for the delivery of the necessary additional logistic support from other sources.
![]()
Question 26.
Project the future of Logistics Management in India.
Answer:
Logistics management functions that are apart of ERP systems are usually integrated with other business function in the system. Like sales finance procurement and human resources. More specialized and warehouse management.
Choose the Correct Answer:
Question 1.
A continuing relationship which provides a licence privileges to do business and provides training, merchandising for a consideration is called:
(a) franchising
(b) factoring
(c) supply chain management
(d) exchange
Answer:
(a) franchising
Question 2.
A condition where a factor agrees to provide complete set of services like financing, debt collection, consultancy is called:
(a) maturity factoring
(b) national factoring
(c) full service factoring
(d) recourse factoring
Answer:
(c) full service factoring
![]()
Question 3.
Buying and selling of goods through electronic network is known as:
(a) e-commerce
(b) internet
(c) website
(d) trade
Answer:
(a) e-commerce
Question 4.
An organization carrying out activities to move goods from producer to consumer is:
(a) transport
(b) logistics
(c) channels
(d) marketing
Answer:
(a) transport
Question 5.
The role of government in logistics management is through:
(a) legislations
(b) governance
(c) transport
(d) distribution
Answer:
(d) distribution
![]()
Question 6.
The main benefit of Logistics is:
(a) productivity
(b) cost minimisation
(c) profitability
(d) storage
Answer:
(b) cost minimisation
Question 7.
What aims for an effective management response over the longer run?
(a) Logistics
(b) Supply Chain Management
(c) Demand
(d) Supply
Answer:
(a) Logistics
Question 8.
The model that identifies alternatives, criteria for decision making and analyse alternatives to arrive at the best choice is:
(a) routing model
(b) scheduling model
(c) inventory model
(d) alternative Analysis
Answer:
(b) scheduling model
![]()
Question 9.
A company under outsourcing transfers activities which are:
(a) core
(b) non-core
(c) business
(d) non business
Answer:
(b) non-core
Question 10.
Business units can reduce expenditure by outsourcing front office work like:
(a) paper work
(b) file work
(c) billing
(d) manufacturing
Answer:
(b) file work
Question 11.
The main benefit of outsourcing is:
(a) productivity
(b) cost reduction
(c) skill
(d) units
Answer:
(b) cost reduction
![]()
Question 12.
Outsourcing job is given to developing countries specifically for:
(a) cheap labour
(b) land
(c) capital
(d) factors
Answer:
(a) cheap labour
Question 13.
Outsourcing is carried out for the benefit of:
(a) global village
(b) transport
(c) factory
(d) time and money
Answer:
(d) time and money
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Notes Chapter 16 Emerging Service Business in India
→ Franchising is used by Business for marketing and distributing products and services. Franchiser means the owner of the Business who provides the Business.
→ Franchisee:
The individual who acquires the right to operate the business or use the trademark of the seller is known as the franchisee.
→ Factoring:
Firms sell goods on cash and credit basis. When goods are sold on credit basis bills are drawn on the buyer by the seller in case of small and medium business a considerable part of their working capital is tied down in bills receivables.
→ Logistics:
Logistics can be viewed as a logical extension of transportation and related areas to achieve an efficient and effective goods distribution system.
→ Outsourcing:
Recently a new type of business in service. Sector has become popular in the world. It is called the Business process outsourcing (BPO). BPO refers to outsourcing the work which is routine in nature, to an outside agency. This practice was initiated in united states of America in few companies.