TN State Board Kalvi 12th Commerce Notes Chapter 7 Stock Exchange
Question 1.
What is meant Stock Exchange?
Answer:
- Stock exchange is an organized market for the purchase and sale of industrial and financial security.
- It is a convenient place where trading in securities is conducted in a systematic manner that is as per certain rules and regulations.
- It is an investment intermediary and facilitates economic and industrial development of a country.
Question 2.
Define Stock Exchange.
Answer:
According to Hastings “Stock exchange or securities market comprises all the places where buyers and sellers of stocks and bonds or their representatives undertake transactions involving the sale of securities”.
![]()
Question 3.
Write any 5 Stock Exchanges in India.
Answer:
- The Bombay stock exchange.
- Bangalore stock exchange Limited.
- The Calcutta stock exchange association.
- The Madras stock exchange association Limited.
- The Delhi stock exchange association.
Question 4.
What is meant by Remisier?
Answer:
He acts as an agent of a member of a stock exchange. He obtains business for his principle that is the member and gets a commission for that service.
Question 5.
Who is called a Broker?
Answer:
Brokers are commission agents, who acts as an intermediaries between buyers and sellers of securities. They do not purchase or sell securities on their behalf. They bring together the buyers and sellers and help them in making a deal. Brokers charge a commission from both the parties for their service.
![]()
Question 6.
What are the types of Speculator?
Answer:
Speculators in a stock market are of different types.
- Bull
- Bear
- Stag
- Lame duck
Question 7.
What is meant by Commodity Exchange?
Answer:
A Commodity Exchange is an exchange where commodities are traded. Tradable commodities fall into the following categories.
Metals (Eg: silver, copper)
Energy (Eg: crude oil, natural gas)
Agricultural (Eg: rice, wheat)
Live stock (Eg: live cattle)
Question 8.
Mention the Recent Development in Stock Exchange.
Answer:
- National Stock Exchange of India Limited (NSE)
- Stock Holding Corporation of India Limited (SHCIL)
- National Clearing and Depository System (NCDS)
- Securities Trading Corporation of India (STCI)
- National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL)
![]()
Question 9.
What is the stock trading time in India?
Answer:
(i) The normal trading time for equity market is between 9.15 am to 3.30 pm, Monday to Friday.
(ii) The trading time for commodity (MCX) market is between 10.00 am to 11.30 am, Monday to Friday.
(iii) The timings of the Indian stock markets are divided into three sessions. They are:
(a) Normal sessions
(b) Pre opening sessions and
(c) Post closing sessions.
Question 10.
Explain Dalai Street.
Answer:
- Dalai street is an area in downtown, Mumbai, India, that houses the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE). The largest stock exchange in India and other reputable financial institutions.
- It received the name Dalai street after the Bombay stock exchange moved to the area in 1874 and become the first stock exchange recognized by the Indian Government.
Question 11.
What are the limitations of Stock exchange?
Answer:
- Lack of uniformity and control of stock exchanges.
- Absence of restriction on the membership of stock exchanges.
- Failure to control unhealthy speculations.
- Allowing more than one charge in the place.
- No proper regulations of listing of securities on the stock exchange.
![]()
Question 12.
Explain Bull and Bear.
Answer:
Bull:
- A bull or Tejiwala is an operator who expects a rise in prices of securities in the future. In anticipation of price rise he makes purchases of shares at present and other securities with intention to sell at higher prices in future.
- He is called bull because just like a bull tends to throw his victim up in the air, the bull speculator stimulates the price to rise. He is an optimistic speculator.
Bear:
- A bear or Mandiwala speculator expects prices to fall in future and sells securities at present with a view to purchase them at lower prices in future.
- A bear does not have securities at present but sells them at higher prices in anticipation that he will supply them at lower prices in future.
- The bear speculator tends to force down ms prices of securities. A bear is pessimistic speculator.
Question 13.
Explain Stag and Lame Duck.
Answer:
Stag:
A stag is a cautious speculator in the stock exchange. He applies for shares in new companies and expects to sell them at a premium, if he gets an allotment. He sells the shares before being called to pay the allotment money. He is also called a premium hunter.
Lame duck:
When a bear finds it difficult to fulfill his commitment, he is said to be struggling like a lame duck. A bear speculator contracts to sell securities at a later date. On the appointed time he is not able to get the securities as the holders are not willing to part with them. Moreover, the buyer is not willing to carry over the transaction.
![]()
Question 14.
Explain National Stock Market System (NSMS).
Answer:
National Stock Market System was advocated by the – high powered group on the establishment of new stock exchanges headed by shri. M.J. Pherwani. (Popularly known as Pherwani committee). At present the national stock market in India comprises the following.
- National Stock Exchange of India Limited. (NSE)
- Stock Holding Corporation of India Limited. (SHCIL)
- National Clearing and Depository System.(NCDS)
- Securities Trading Corporation of India. (STCI)
- National Securities Depository Limited. (NSDL)
Question 15.
Explain National Stock Exchange (NSE).
Answer:
- NSE was incorporated in November 1992. It is a country wide, screen based online and order driven trading system.
- It uses satellite link to spread trading throughout the country thereby connecting members scattered all over India.
- NSE has two segments that is debt segment and capital segment.
- It has ushered in transparent, screen based and user friendly trading of global standards. It has revolutionised stock trading in India.
![]()
Question 16.
Explain the functions of Stock Exchange.
Answer:
The various functions of a stock exchange are explained below:
(i) Ready and continuous market:
If an investor wants to sell his securities he can easily and quickly dispose them off on a stock exchange. This easy marketability of securities increases their liquidity (cash) and consequently raises their value.
(ii) Correct evaluation of securities:
The prices at which securities are bought are sold are recorded and made public. These prices are called “market quotations”. One can easily evaluate the worth of one’s securities on the basis of these quotations.
(iii) Protection to investors:
All dealings in a stock exchange are in accordance with well defined rules and regulations. Any malpractices will be severely punished.
(iv) Aid to capital formation:
Stock exchanges thus ensure a steady flow of capital into industry and assists flow of capital into industry and assists industrial development.
(v) Facilities for speculations:
Speculation is an integral part of stock exchange operations. As a result of speculation, demand for and supply of securities are equalized.
![]()
Question 17.
Explain the features of Stock Exchange.
Answer:
(i) Market for securities:
Stock exchanges is a market, where securities of corporate bodies, Government and semi Government bodies are bought and sold.
(ii) Deals in second hand securities:
It deals with shares, debentures, bonds and such securities already issued by a companies. It deals with existing on secondhand securities and hence it is called secondary market.
(iii) Allows dealings only in listed securities:
Stock exchanges maintain an official list of securities that could be purchased and sold on this floor. Securities which do not figure in the official list that unlisted securities cannot be traded in the stock exchanges.
(iv) Transactions effected only through Members:
All the transactions insecurities at the stock exchange are affected only through its authorized brokers and members. Investors have to buy and sell the securities at the stock exchange through the authorized brokers only.
(v) Specific location:
Stock exchange is a particular market place where authorized brokers come together daily (on working days) on the floor of market called trading circles and conduct trading activities. All the working of stock exchanges is conducted and controlled through computers and electronic systems.
![]()
Question 18.
Explain the Benefits of Stock Exchange.
Answer:
Benefits of the community:
- Economic development: It accelerates the economic development by ensuring steady flow savings into productive purpose.
- Fund raising platform: It enables the well managed, profit making companies to raise limitless funds by fresh issue of shares from time to time.
- Capital formation: It encourages capital formation.
Benefits to the company:
- Enhances goodwill or reputation: Companies whose shares are quoted on a stock exchanges enjoy greater goodwill and credit standing.
- Wide market: There is a wide and ready market for such securities.
- Raise huge funds: Stock exchange can raise huge funds easily by issue of shares and debentures.
Benefits of investors:
- Liquidity: Stock exchange helps an investors to convert his shares into cash quickly and thus increases the liquidity of his investments.
- Investors protection: The stock exchange safeguards investors interest and ensures fair dealing by strictly enforcing its rules and regulations.
- Mechanism to trade security: Stock exchange provides a mechanism by which purchase and sale of listed securities take place in a matter of few minutes.
Question 19.
Distinguish between Stock Exchange and Commodity Exchange.
Answer:
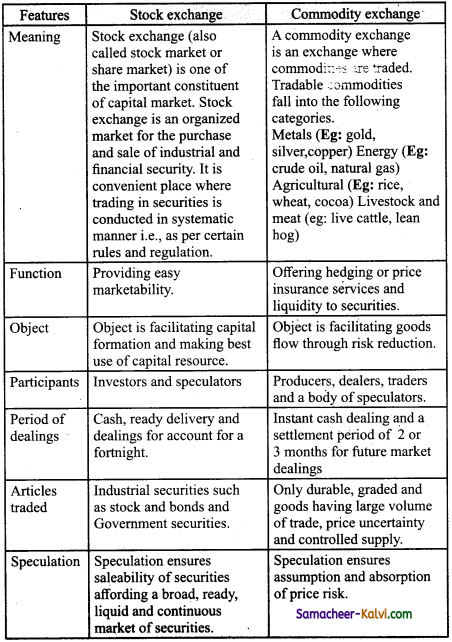
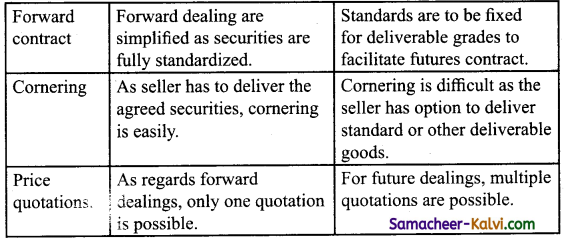
![]()
Question 20.
Explain Lombard street and Wall street.
Answer:
Lombard street:
Lombard street, London is a street notable for its connections with the city of London’s merchant, banking and insurance industries, stretching back to medieval times.
From bank junction where nine streets’ coverage by the Bank of England, Lombard street runs southeast for a distance before bearing into a more easterly direction. It terminates at a junction with grace church street and Fenchurch street.
It is overall length is 260 meters. It has often been compared with wall street in New York city.
Wail street:
Wall street is a street in lower Manhatten that is the original home of the New York Stock Exchange and historic headquarters of the largest U.S. brokerages and investment bank.
The term wall street is also used as a collective name for the financial and investment community, which includes stock exchanges and large banks, brokerages, securities and underwriting firms and big business.
Today, brokerages are geographically diverse, allowing investors free access to the same information available to wall street’s tycoons.
![]()
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
________ is the oldest stock exchange in the world.
(a) London Stock Exchange
(b) Bombay Stock Exchange
(c) National Stock Exchange
(d) Amsterdam Stock Exchange
Answer:
(a) London Stock Exchange
Question 2.
There are ______ stock exchange in the country.
(a) 21
(b) 24
(c) 20
(d) 25
Answer:
(a) 21
Question 3.
Stock exchanges deal in:
(a) Goods
(b) Services
(c) Financial Securities
(d) Country’s Currency
Answer:
(c) Financial Securities
![]()
Question 4.
Stock exchange allow trading in:
(a) All types of Shares of any Company
(b) Bonds issued by the Govt
(c) Listed Securities
(d) Unlisted Securities
Answer:
(c) Listed Securities
Question 5.
Jobbers transact in a stock exchange:
(a) For their Clients
(b) For their Own Transactions
(c) For other Brokers
(d) For other Members
Answer:
(b) For their Own Transactions
Question 6.
A pessimistic speculator is:
(a) Stag
(b) Bear
(c) Bull
(d) Lame Duck
Answer:
(b) Bear
![]()
Question 7.
An optimistic speculator is:
(a) Bull
(b) Bear
(c) Stag
(d) Lame duck
Answer:
(a) Bull
Question 8.
A bull operator believes in:
(a) Increase in Prices
(b) Decrease in Prices
(c) Stability in Prices
(d) No change in Prices
Answer:
(a) Increase in Prices
Question 9.
_________ means the price at which securities are bought and sold are recorded and made public.
(a) Market Quotations
(b) Trade Quotations
(c) Business Quotations
(d) Buyers Quotations
Answer:
(a) Market Quotations
![]()
Question 10.
The rules and regulations of Stock exchange is framed by ________ guide lines.
(a) RBI
(b) Central Government
(c) SEBI
(d) BSE
Answer:
(c) SEBI