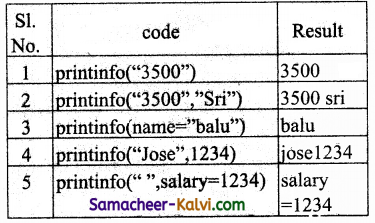
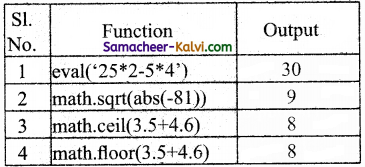
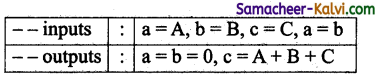TN State Board 12th Computer Science Important Questions Chapter 4 Algorithmic Strategies
Question 1.
Write the some examples of Data structures.
Answer:
Examples for data structures are arrays, structures, list, tuples, dictionary etc.
Question 2.
Write any four an algorithm characteristics.
Answer:
Any four an algorithm characteristics are Input, Output, Finiteness, Definiteness.
![]()
Question 3.
Write the Analysis of algorithms.
Answer:
Analysis of algorithms can be divided into two different phrases.
- A prior estimates – This is a theoretical performance analysis of an algorithm.
- A posteriori testing- This is a performance measurement analysis of an algorithm.
Question 4.
What are the two components of space complexity?
Answer:
The two components of space complexity are
- A Fixed part-is defined as the total space required to store certain data and variables for an algorithm, Eg:variables.
- A variable part-is defined as the total space required by variable, which sizes depends on the problem and its iteration.
Eg: Recursion.
Question 5.
What is space-time trade off?
Answer:
- A space – time or time-memory trade off is a way of solving in less time by using more storage space.
- By solving a given algorithm in very little space by spending more time.
![]()
Question 6.
What is the advantage for space / time Tradeoff?
Answer:
- Time/space trade off can reduce the use of memory at the cost of slower program execution.
- To reduce the running time at the cost of increased memory usage.
Question 7.
What is a insertion sort?
Answer:
Insertion sort is a simple sorting algorithm. It works by taking elements from the list one by one and inserting then in their correct position in to a new sorted list.
Question 8.
What is mean by memorization?
Answer:
Memorization is an optimization technique used primarily to speed up computer programs by sorting the results of expensive function calls and returning the cached result when the same inputs occur again.
![]()
Question 9.
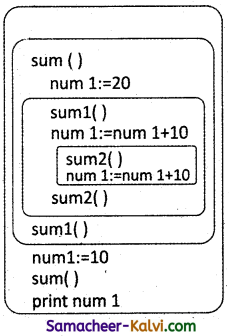
What is algorithmic strategy? Explain with example.
Answer:
- The way of defining an algorithm is called algorithmic strategy.
- For example to calculate factorial for the given value n.
- To calculate factorial for the iteration then it can be called recursively until the number of required iteration is reached.
Question 10.
Write the algorithm for preparing coffee?
Answer:
Step 1: Take a bowl with coffee powder.
Step 2: Boil the water and pour it into the bowl.
Step 3: Filter it.
Step 4: Boil Milk.
Step 5: Mix sugar and filtered coffee along with boiled milk.
Step 6: Pour the coffee into the cup to serve.
![]()
Question 11.
Write an algorithm to find square of this given number.
Answer:
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Get the input X
Step 3: Calculate the square by x*x
Step 4: Display the result
Step 5: Stop
Question 12.
What are the factors depends the time efficiency of an algorithm?
Answer:
- Speed of the machine
- Compiler and other system software tools
- Operating system
- Programming language used
- Volume of data required.
![]()
Question 13.
Write the steps to do Dynamic programming.
Answer:
- The given problem will be divided into smaller overlapping sub-problems.
- An optimum solution for the given problem can be achieved by using result of smaller sub-problem.
- Dynamic algorithms uses memorization.
Question 14.
What are the differences have algorithm and program?
Answer:
| Algorithm | Program |
| Algorithm helps to solve a given problem logically. | Program is an expression of algorithm in a programming language. |
| Algorithm based on their implementation method, design techniques etc. | It is object oriental programming approach. |
| There is no specific rules for algorithm writing. | Program should be written for the selected language with specific syntax. |
| Algorithm resembles a pseudo code. | Program is more specific to a programming language. |
![]()
Question 15.
Explain Best, Worst and Average case efficiency of an algorithm.
Answer:
(i) Assume that a list of n number of values stored in an array sequentially.
(ii) The Best case would be if the first element in the list matches with the key element to be searched in a list of elements.
(iii) The efficiency in that case would be expressed as 0(1) because only one comparison is enough.
(iv) The Worst case is, if the complete list is searched and element is found only at the end of the list or not found.
(v) The efficiency of an algorithm in that case would be expressed as 0(n).
(vi) The Average case of an algorithm can be obtained by finding the average number of comparisons.
(vii) The average number of comparisons = (n + 1)/2 Hence the average case efficiency will be expressed as 0(n).
![]()
Question 16.
Explain the selection sort with example.
Answer:
- The selection sort is a simple, sorting algorithm that improves on the performance of bubble sort by making only one exchange for every pass through the list.
- This algorithm will first find the smallest elements in array and swap it with element in the first position of an array.
- Then it will find the second smallest element and swap that element with the element in the second position.
- And it will continue until the entire array is sorted in respective order.
- For example an array with values {13,16, 11,18,14,15} this algorithm repeatedly select the first element and next smallest element and swaps into the right place for every pass.
- Finally we will get the sorted array end of the pass.
Question 17.
Explain the insertion sort with example.
Answer:
- Insertion sort is a simple sorting algorithm.
- It works by taking element from the list one by one and inserting then in their correct position in to a new sorted list.
- The algorithm builds the final sorted array at the end.
- For example, compare with all elements in the sorted sub-list.
- Shift all the elements in the sorted sub – list that is greater than the value to be sorted.
- At the end of the pass the insertion sort algorithm gives the sorted output in ascending order.
![]()
Question 18.
Write the steps of Fibonacci iterative algorithm with Dynamic programming approach.
Answer:
Step 1: Initialize F0 = 0, f1 = 1,
Step 2: print the initial value of Fibonacci f0 and f1.
Step 3: Calculate fib = f0 + f1
Step 4: Assign fo = F1, f1 =f1 b
Step 5: Go to step-2 and repeat until the specified number of terms generated.
Step 6: print the value of Fibonacci terms.
Question 19.
What is an Algorithm?
Answer:
- An algorithm is a finite set of instructions to accomplish a particular task.
- It is a step-by-step procedure for solving a given problem.
Question 20.
Define Pseudo code.
Answer:
Pseudo code is a simpler version of a programming code in plain Bhglish which uses- short phrases to write code for a program before it is implemented in a specific programming language.
![]()
Question 21.
Who is an Algorist?
Answer:
One who practices algorism is known as an algorist. An Algorist is a Persian author, Abu Jafar Mohammed ibn Musa al Khowarizmi, who wrote a textbook on Mathematics.
Question 22.
What is Sorting?
Answer:
- Sorting is nothing but arranging the data in ascending or descending order.
- Sorting arranges data in a sequence which makes searching easier.
Question 23.
What is searching? Write its types.
Answer:
- Searching is a process of locating a particular element present in a given set of elements.
- The element may be a record, a table, or a file. Searching types are Linear search, Binary search, Jump search, Interpolation search, Exponential search, Fibonacci search etc..
![]()
Question 24.
List the characteristics of an algorithm.
Answer:
The characteristics of an algorithm are:
- Input
- Output
- Finiteness
- Definiteness
- Effectiveness
- Correctness
- Simplicity
- Unambiguous
- Feasibility
- Portable
Question 25.
Discuss about Algorithmic complexity and its types.
Answer:
- f(n) is the complexity to an algorithm, it gives the running time and / or storage space required but the algorithm in terms of n as the size of input data.
- Time complexity and space complexity are two types of algorithmic complexity.
- Space complexity has two components, are a fixed part and variable part.
![]()
Question 26.
What are the factors that influence time and space complexity?
Answer:
Time Factor and Space Factor are that influence time and space complexity.
Time Factor: Time is measured by counting the number of key operations like comparisons in the sorting algorithm.
Space Factor: Space is measured by the maximum memory space required by the algorithm.
Question 27.
Write a note on Asymptotic notation.
Answer:
Asymptotic notations are languages that uses meaningful statements about time and space complexity. They are 3 types.
- Big O – is used to describe the worst case of an algorithm.
- Big Ω (omega) – is used to describe the lower bound that is best case.
- Big
 – When an algorithm has complexity which lower bound – upper bound, say that an algorithm has complexity.
– When an algorithm has complexity which lower bound – upper bound, say that an algorithm has complexity.
Question 28.
What do you understand by Dynamic programming?
Answer:
- Dynamic programming is an algorithmic design method that can be used when the solution to a problem can be viewed as the result of a sequence of decisions.
- Dynamic programming approach is similar to divide and conquer.
- Dynamic programming is used whenever problems can be divided into similar sub problems. So that their results can be reused to complete the process.
![]()
Question 29.
Explain the characteristics of an algorithm
Answer:
The Characteristics of an algorithm are:
- Input: Zero or more quantities to be supplied.
- Output: At least one quantity is produced.
- Finiteness: Algorithms must terminate after finite number of steps.
- Definiteness: All operations should be well defined.
- Effectiveness: Every instruction must be carried out effectively.
- Simplicity, unambiguous, feasibility, portable and independent are other important algorithm characteristics.
Question 30.
Discuss about Linear search algorithm.
Answer:
- Linear search algorithm is a method of technique to find a particular value in a list.
- Linear search also called sequential search.
- Sequential method checks the search element in sequential order until the desired element is found.
- Linear searching algorithm, list need not be ordered.
- Eg:
Input: values [ ] = {5,34, 65,12,77,35} target =12 output: 3
In this example number 12 is found at index number 3.
To search the number 12 in the array of 4th place at index number 3 .
![]()
Question 31.
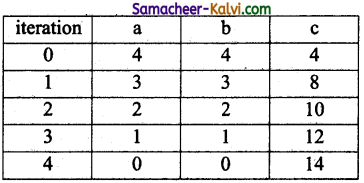
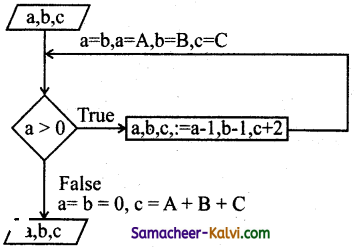
What is Binary search? Discuss with example.
Answer:
- (i) Binary search also called half-interval search algorithm.
- It finds the position of a search element within a sorted array.
- The binary search algorithm can be done as divide-and-conquer search algorithm and executes in algorithmic time.
- We use binary search, First find index of middle element of the array by using this formula mid = low + (high – low) /2 and compare the search element. If it is not found that element, using this formula again.
- The search element still not found, hence, we calculated the mid again by using the formula.
high. = mid – 1
mid = low + (high – low)/2
Question 32.
Explain the Bubble sort algorithm with example.
Answer:
- Bubble sort algorithm is simple sorting algorithm.
- This type of algorithm starts at the begining of the list of values stored in an array. W
- It compares each pair of adjacent elements and swaps them if they are in the unsorted order.
- This comparison and passed to be continued until no swaps are needed, which indicates that the list of values stored in an array is sorted.
- This type is too slow and less efficient when compared to other sorting methods.
- For example an array values {15, 11, 16, 12, 14, 13} using Bubble sort will sort the values. The swap function swaps the values of the given array elements.
- At the end of all the iteration we will get the sorted values as
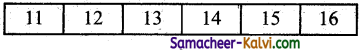
![]()
Question 33.
Explain the concept of Dynamic programming with suitable example.
Answer:
- Dynamic programming is an algorithmic design method that can be used when the solution to a problem can be viewed as the result of a sequence of decisions.
- Dynamic programming approach is similar to divide and conquer.
- Dynamic programming is used whenever problems can be divided into similar sub-problems. So that, their results can be re-used to complete the process.
- the subsequent number by adding two previous numbers FibO and Fib 1.
- Then Fib<sub>n</sub> = Fib<sub>n – 1</sub> + Fib<sub>n – 2</sub> Hence, a Fibonacci series for the n values of can look like this Fib<sub>8</sub> = 0 1 1 2 3 5 8 1 3
- Input, output, Finiteness, Definiteness, Effectiveness, correctness, simplicity, unambiguous, Feasibility, portable and independent.
![]()
Choose the best answer:
Question 1.
Which one is maintained and manipulated effectively through data structures?
(a) Data
(b) File
(c) Recorde
(d) List
Answer:
(a) Data
Question 2.
Which can be developed to store, manipulate and retrieve data from such data structures?
(a) File
(b) Algorithm
(c) Sorting
(d) Searching
Answer:
(b) Algorithm
![]()
Question 3.
Match the following:
| (i) Finiteness | (A) Well defined |
| (ii) Definiteness | (B) Must terminate |
| (iii) Effectiveness | (C) Clear |
| (iv) Unambiguous | (D) Error Free |
(a) (i) – B, (ii) – C, (iii) – D, (iv) – A
(b) (i) – B, (ii) – A, (iii) – D, (iv) – C
(c) (i) – C, (ii) – D, (iii) – B, (iv) – A
(d) (i) – C, (ii) – B, (iii) – A, (iv) – D
Answer:
(b) (i) – B, (ii) – A, (iii) – D, (iv) – C
Question 4.
Match the following:
| (i) Big O | (A) Best case |
| (ii) Big Ω (omega) | (B) Key operation |
| (iii) Time | (C) Memory space |
| (iv) Space | (D) Worst case |
(a) (i) – D, (ii) – A, (iii) – B, (iv) – C
(b) (i) – D, (ii) – C, (iii) – B, (iv) – A
(c) (i) – C, (ii) – B, (iii) – A, (iv) – D
(d) (i) – C, (ii) – A, (iii) – D, (iv) – B
Answer:
(a) (i) – D, (ii) – A, (iii) – B, (iv) – C
![]()
Question 5.
Match the following:
| (i) Linear | (A) Comparison |
| (ii) Binary | (B) Exchange |
| (iii) Bubble | (C) half – interval |
| (iv) Selection | (D) Sequential |
(a) (i) – D, (ii) – A, (iii) – B, (iv) – C
(b) (i) – B, (ii) – C, (iii) – D, (iv) – A
(c) (i) – D, (ii) – C, (iii) – A, (iv) – B
(d) (i) – B, (ii) – D, (iii) – A, (iv) – C
Answer:
(c) (i) – D, (ii) – C, (iii) – A, (iv) – B
Question 6.
Choose the incorrect pair:
(a) Search – Linear
(b) Sort – Order
(c) insert – Update
(d) Delete – Remove
Answer:
(c) insert – Update
![]()
Question 7.
Choose the incorrect pair:
(a) Finiteness – Terminate
(b) Definiteness – Defined
(c) Effectiveness – Carried
(d) Correctness – Unambiguous
Answer:
(d) Correctness – Unambiguous
Question 8.
Choose the incorrect pair:
(a) A priori estimates – Theoretical
(b) A posteri testing – Measurement
(c) Time factor – Key operation
(d) Space factor – Instructions
Answer:
(d) Space factor – Instructions
![]()
Question 9.
Choose the correct pair:
(a) Space complexity – Size of input
(b) A fixed part – Performance
(c) A variable part – Recursion
(d) Time complexity – Variables
Answer:
(c) A variable part – Recursion
Question 10.
Choose the correct pair:
(a) 0 (1) – Worst case
(b) 0 (n) – Best case
(c) 0 (n+1) – Best and Worst case
(d) Big Question (omega) – Best case
Answer:
(d) Big Question (omega) – Best case
Question 11.
Choose the incorrect statement:
(a) Binary search also called half-interval search algorithm.
(b) The binary search algorithm can be done as divide-and-conquer.
(c) Linear search also called Random search
(d) List of elements in an array must be sorted first for Binary search.
Answer:
(c) Linear search also called Random search
![]()
Question 12.
Choose the incorrect statement:
(a) Bubble sort is a simple sorting algorithm.
(b) Insertion sort is a update sorting.
(c) The selection sort is that improves on the performance of bubble sort.
(d) Insertion sort works by taking elements from the list one by one.
Answer:
(b) Insertion sort is a update sorting.
Question 13.
Choose the incorrect statement:
(i) Dynamic programming is an algorithmic design method.
(ii) Dynamic programming approach is similar to the selection sort.
(ii) Dynamic algorithms uses memorization.
(iv) Dynamic algorithms will try to check the results of solved problems.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (iv) and (ii)
Answer:
(a) (i) and (ii)
Question 14.
Choose the correct statement:
(a) Two main measures for the efficiency of an algorithm are Time and Space.
(b) Search is the way of defining algorithm.
(c) There is a specific rules for algorithm writing.
(d) Algorithm is not to be solve any problem logically.
Answer:
(a) Two main measures for the efficiency of an algorithm are Time and Space.
![]()
Question 15.
Choose the correct statement:
(a) Program is a group of files.
(b) Algorithm can be implemented by operating system.
(c) Program should be written for any language.
(d) Program is more specific to a programming language.
Answer:
(d) Program is more specific to a programming language.
Question 16.
Assertion (A):
An algorithm is a finite set of instructions.
Reason (R):
An algorithm can be implemented in any suitable programming language
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation for A.
(b) A is True, But R is False.
(c) A is False, But R is True.
(d) Both A and R are False.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation for
Question 17.
Assertion (A):
Computer resources are limited that should be utilized efficiently.
Reason (R):
The efficiency of an algorithm can be measured based on computer type.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation for A.
(b) A is True, But R is False.
(c) A is False, But R is True.
(d) Both A and R are False.
Answer:
(b) A is True, But R is False.
![]()
Question 18.
Assertion (A):
The Time efficiency of an algorithm is measured by same factors.
Reason (R):
The efficiency of an algorithm depends on time and memory space.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation for A.
(b) A is True, But R is False.
(c) A is False, But R is True.
(d) Both A and R are False.
Answer:
(c) A is False, But R is True.
Question 19.
Assertion (A):
Big O is often used to describe the best case of an algorithm.
Reason (R):
Big omega is used to describe the worst case of an algorithm.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation for A.
(b) A is True, But R is False.
(c) A is False, But R is True.
(d) Both A and R are False.
Answer:
(d) Both A and R are False.
![]()
Question 20.
Assertion (A):
Dynamic programming approach is similar to divide and conquer.
Reason (R):
The given problem is divided into smaller and yet smaller possible sub¬problems.
(a) Both A and R are correct, and R is the correct explanation for A.
(b) A is True, But R is False.
(c) A is False, But R is True.
(d) Both A and R are False.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct, and R is the correct explanation for A.
Question 21.
Pick the odd one out:
(a) Array
(b) Structure
(c) List
(d) Algorithm
Answer:
(d) Algorithm
Question 22.
Pick the odd one out:
(a) Search
(b) Sort
(c) Syntax
(d) Update
Answer:
(c) Syntax
![]()
Question 23.
Pick the odd one out:
(a) Simplicity
(b) Flowchart
(c) Feasibility
(d) Portable
Answer:
(b) Flowchart
Question 24.
Pick the odd one out:
(a) Time
(b) Space
(c) Efficiency
(d) Program
Answer:
(d) Program
Question 25.
Pick the odd one out:
(a) Binary
(b) Bubble
(c) Selection
(d) Insertion
Answer:
(a) Binary
![]()
Question 26.
Which of the following is a sorting technique?
(a) Quick
(b) Bubble
(c) Insertion
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question 27.
Which of the following is a finite set of instructions to accomplish a particular task?
(a) Algorithm
(b) Flow chart
(c) Pseudo code
(d) Program
Answer:
(a) Algorithm
![]()
Question 28.
Which is called, the way of defining an algorithm?
(a) Algorithmic strategy
(b) Program strategy
(c) Running program strategy
(d) Compiling strategy
Answer:
(a) Algorithmic strategy
Question 29.
How many asymptotic notations are mostly used to represent time complexity of algorithms?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(b) 3
Question 30.
Which of the following is to describe the worst-case algorithm?
(a) Big O
(b) Big α
(c) Big Ω
(d) Big β
Answer:
(a) Big O
![]()
Question 31.
Which of the following is reverse of Big O?
(a) Big O
(b) Big α
(c) Big Ω
(d) Big β
Answer:
(c) Big Ω
Question 32.
Linear search also called:
(a) Sequential search
(b) Binary search
(c) Quick search
(d) Selection search
Answer:
(a) Sequential search
Question 33.
Binary search also called:
(a) Sequential search
(b) Quick search
(c) Half-interval search
(d) Linear search
Answer:
(c) Half-interval search
![]()
Question 34.
Bubble sort is also called:
(a) Sequential search
(b) Quick search
(c) Comparison soft
(d) Binary sort
Answer:
(c) Comparison soft
Question 35.
Which of the following algorithm used memorization?
(a) Static
(b) Dynamic
(c) Modular
(d) Object
Answer:
(b) Dynamic
Question 36.
The word comes from the name of a Persian mathematician Abu Ja’far Mohammed ibn-i Musa al Khowarizmi is called?
(a) Flowchart
(b) Flow
(c) Algorithm
(d) Syntax
Answer:
(c) Algorithm
Question 37.
From the following sorting algorithms which algorithm needs the minimum number of swaps?
(a) Bubble sort
(b) Quick sort
(c) Merge sort
(d) Selection sort
Answer:
(d) Selection sort
Question 38.
Two main measures for the efficiency of an algorithm are:
(a) Processor and memory
(b) Complexity and capacity
(c) Time and space
(d) Data and space
Answer:
(c) Time and space
![]()
Question 39.
The complexity of linear search algorithm is:
(a) O(n)
(b) O(logn)
(c) O(n2)
(d) O(n log n)
Answer:
(d) O(n log n)
Question 40.
From the following sorting algorithms which has the lowest worst case complexity?
(a) Bubble sort
(b) Quick sort
(c) Merge sort
(d) Selection sort
Answer:
(a) Bubble sort
Question 41.
Which of the following is not a stable sorting algorithm?
(a) Insertion sort
(b) Selection sort
(c) Bubble sort
(d) Merge sort
Answer:
(d) Merge sort
![]()
Question 42.
Time complexity of bubble sort in best case is:
(a) θ (n)
(b) θ (nlogn)
(c) θ (n2)
(d) θ (n(logn) 2)
Answer:
(b) θ (nlogn)
Question 43.
The 0 notation in asymptotic evaluation represents
(a) Base case
(b) Average case
(c) Worst case
(d) NULL case
Answer:
(c) Worst case
Question 44.
If a problem can be broken into subproblems which are reused several times, the problem possesses which property?
(a) Overlapping subproblems
(b) Optimal substructure
(c) Memoization
(d) Greedy
Answer:
(b) Optimal substructure
![]()
Question 45.
In dynamic programming, the technique of
storing the previously calculated values is called ?
(a) Saving value property
(b) Storing value property
(c) Memoization
(d) Mapping
Answer:
(c) Memoization