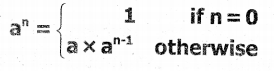Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Guide Pdf Chapter 2 Number Systems Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Solutions Chapter 2 Number Systems
11th Computer Science Guide Number Systems Text Book Questions and Answers
![]()
Part – I
I. Choose The Correct Answer:
Question 1.
Which refers to the number of bits processed by a computer’s CPU? .
a) Byte
b) Nibble
c) Word length
d) Bit
Answer:
c) Word length
Question 2.
How many bytes does 1 KiloByte contain?
a) 1000
b) 8
c) 4
d) 1024
Answer:
d) 1024
![]()
Question 3.
Expansion for ASCII
a) American School Code for Information Interchange
b) American Standard Code for Information Interchange
c) All Standard Code for Information Interchange
d) American Society Code for Information Interchange
Answer:
b) American Standard Code for Information Interchange
Question 4.
2^50 is referred as
a) Kilo
b) Tera
c) Peta
d) Zetta
Answer:
c) Peta
Question 5.
How many characters can be handled in Binary Coded Decimal System?.
a) 64
b) 255
c) 256
d) 128
Answer:
a) 64
![]()
Question 6.
For 11012 whai is the Hexadecimal equivalent?
a) F
b) E
c) D
d) B
Answer:
c) D
Question 7.
What is the 1’s complement of 00100110?
a) 00100110
b) 11011001
c) 11010001
d) 00101001
Answer:
b) 11011001
![]()
Question 8.
Which amongst this is not an Octal number?
a) 645
b) 234
c) 876
d) 123
Answer:
c) 876
Part II
Very Short Answers.
Question 1.
What is data?
Answer:
The term data comes from the word datum which means a raw fact. The data is a fact about people, places, or some objects.
Example: Rajesh, 16, XI.
Question 2.
Write the l’s complement procedure.
Answer:
The steps to be followed to find l’s complement of a number:
Step 1: Convert given Decimal number into Binary
Step 2: Check if the binary number contains 8 bits, if less add O at the left most bit, to make it as 8 bits.
Step 3: Invert all bits (i.e. Change 1 as 0 and 0 as 1)
Example: Find 1’s complement for (-24)10

Question 3.
Convert (46)10 into a Binary number.
Answer:
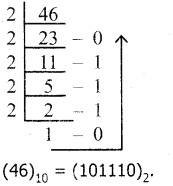
Question 4.
We cannot find l’s complement for (28)10 State reason.
Answer:
Since it is a positive number. 1’s complement will come only for negative numbers.
Question 5.
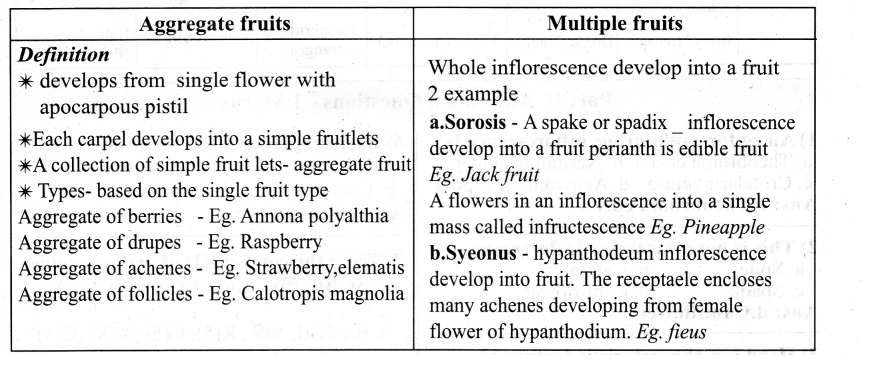
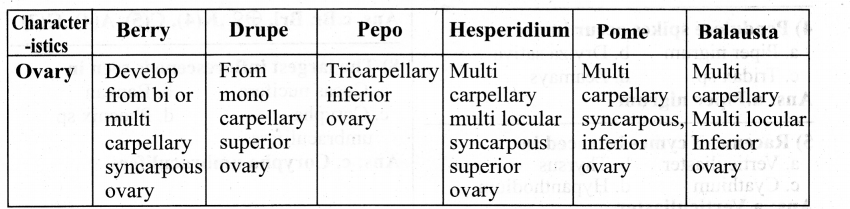
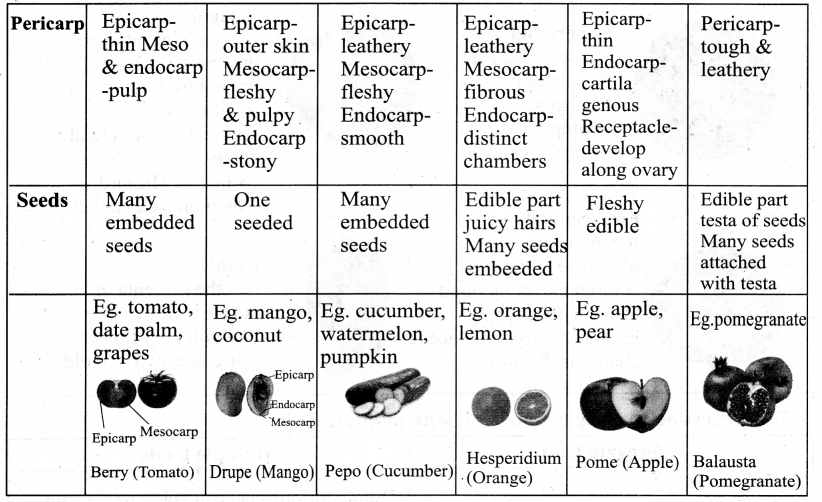
List the encoding systems for characters in memory.
Answer:
There are several encoding systems used for computers. They are
- BCD – Binary Coded Decimal
- EBCDIC – Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code
- ASCII – American Standard Code for Information Interchange
- Unicode
- ISCII – Indian Standard Code for Information Interchange
![]()
Part III
III. Very Short Answers
Question 1.
What is radix of a number system? Give example.
Answer:
Each number system Is uniquely Identified by Its base value or radix. Radix or base Is the count of number of digits In each number system. Radix or base is the general Idea behind positional numbering system. Ex.
| Number system | Base / Radix |
| Binary | 2 |
| Octal | 8 |
| Decimal | 10 |
| Hexadecimal | 16 |
![]()
Question 2.
Write a note on the binary number system.
Answer:
There are only two digits in the Binary system, namely, 0 and 1. The numbers in the binary system are represented to the base 2 and the positional multipliers are the powers of 2.
The leftmost bit in the binary number is called the Most Significant Bit (MSB) and it has the largest positional weight. The rightmost bit is the Least Significant Bit (LSB) and has the smallest positional weight.

![]()
Question 3.
Convert (150)10 into Binary, then convert that Binary number to Octal.
Answer:
Decimal to Binary conversion 150
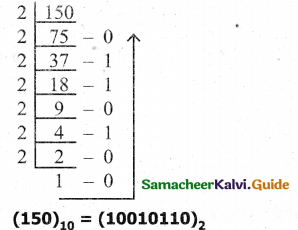
Binary to octal conversion
LSB to MSB divide the number into three-digit binary and write the equivalent octal digit
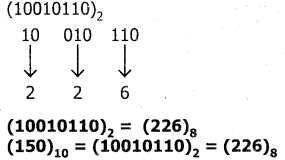
Question 4.
Write a short note on ISCII.
Answer:
ISCII – Indian Standard Code for Information Interchange (ISCII) is the system of handling the character of Indian local languages. This is an 8 – bit coding system. Therefore it can handle 256 (28) characters. It is recognized by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS). It is integrated with Unicode.
This system is formulated by the Department of Electronics in India in the year 1986-88 and recognized by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS). Now, this coding system is integrated with Unicode.
Question 5.
Add : a) -2210 + 1510 b) 2010 + 2510.
Answer:
a) -2210 + 1510
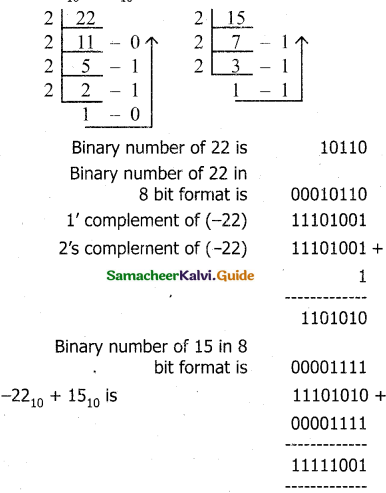
Answer in 2’s complement form . 11111001 is 2’s complement of 7 which is the answer.
![]()
Part IV
IV. Detail Answers.
Question 1.
a) Write the procedure to convert fractional Decimal to Binary.
Answer:
Conversion of fractional Decimal to Binary
The method of repeated multiplication by 2 has to be used to convert such kinds of decimal fractions.
The steps involved in the method of repeated multiplication by 2:
Step 1. : Multiply the decimal fraction by 2 and note the integer part. The integer part is either 0 or 1.
Step 2: Discard the integer part of the previous product. Multiply the fractional part of the previous product by 2. Repeat Step 1 until the same fraction repeats or terminates (0).
Step 3: The resulting integer part forms a sequence of 0’s and 1’s that becomes the binary equivalent of a decimal fraction.
Step 4: The final answer is to be written from the first integer part obtained till the last integer part obtained.
Integer part (last integer part obtained)
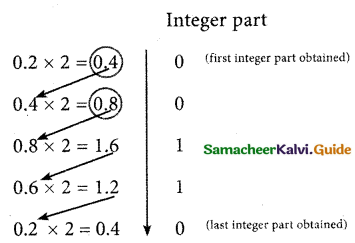
Write the integer parts from top to bottom to obtain the equivalent fractional binary number.
Hence
(0.2)10 = (0.00110011.,.)2 = (0.00110011)2.
![]()
b) Convert (98.46)10 to Binary.
Convert (98.46)10 to Binary
Procedure: Conversion of an integral part:
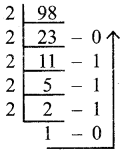
(98)10 = (1100010)2 Conversion of fractional part:

Question 2.
Find l’s Complement and 2’s Complement for the following Decimal number.
a) -98
b) -135
Answer:
a) Conversion of (98)10 into binary
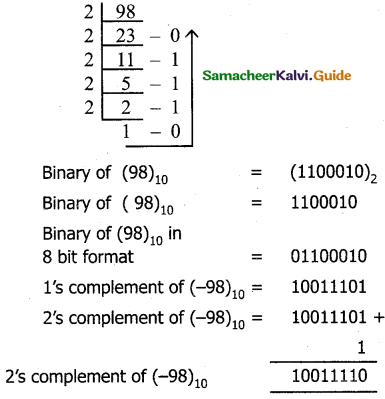
Conversion of (135)10 into binary
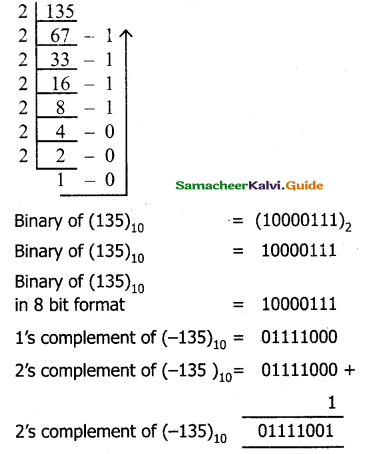
Question 3.
a) Add 11010102 + 101101)2
Answer:
a) Add 11010102 + 1011012

b) Subtract 11010112 – 1110102.
Subtract 11010112 – 1110102

![]()
11th Computer Science Guide Number Systems Additional Questions and Answers
Part I
Choose The Correct Answer.
Question 1.
The simplest method to represent a negative binary number is called ………………..
(a) signed magnitude
(b) sign bit or parity bit
(c) binary
(d) decimal
Answer:
(a) signed magnitude
Question 2.
Computer understand ________________language.
a) High level
b) Assembly
c) Machine
d) All the above
Answer:
c) Machine
Question 3.
Expansion for BCD ………………..
(a) Binary coded decimal
(b) binary complement decimal
(c) binary computer decimal
(d) binary convert decimal
Answer:
(a) Binary coded decimal
Question 4.
__________is the basic unit of data in computer.
a) BIT
b) BYTE
c) NIBBLE
d) WORD
Answer:
a) BIT
![]()
Question 5.
The ……………….. operator is defined in boolean algebra by the use of the dot (.) operator.
(a) AND
(b) OR
(c) NOT
(d) NAND
Answer:
(a) AND
Question 6.
Binary digit means __________
a) 0
b) 1
c) either 0 or 1
d) None of these
Answer:
c) either 0 or 1
Question 7.
The convert (65)10 into its equivalent octal number ………………..
(a) (101)8
(b) (101)10
(c) (101)12
(d) (101)4
Answer:
(a) (101)8
Question 8.
A collection of 8 bits is called __________
a) BIT
b) BYTE
C) NIBBLE
d) WORD
Answer:
b) BYTE
Question 9.
……………….. is the general idea behind the positional numbering system.
(a) Radix
(b) Computer memory
(c) Binary number
(d) Decimal number
Answer:
(a) Radix
![]()
Question 10.
__________refers to the number of bits processed by a computer’s CPU.
a) Word length
b) Nibble
c) Word size
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Word length
Question 11.
Bit means ………………..
(a) nibble
(b) byte
(c) word length
(d) binary digit
Answer:
(d) binary digit
Question 12.
__________is a valid word length of a computer.
a) 64
b) 32
c) 16
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 13.
The computer can understand ……………….. languages.
(a) computer
(b) machine
(c) post
(d) pre
Answer:
(b) machine
Question 14.
1 KiloByte equals to __________bytes.
a) 1024
b) 256
c) 1000
d) 128
Answer:
a) 1024
![]()
Question 15.
How many bytes does 1 zettabyte contain?
(a) 290
(b) 280
(c) 270
(d) 260
Answer:
(c) 270
Question 16.
1024 MegaBytes equals to _________
a) 1 GigaByte
b) 1 TeraByte
c) 1 YottaByte
d) None of these
Answer:
a) 1 GigaByte
Question 18.
1-kilo byte represents ……………….. bytes.
(a) 512
(b) 256
(c) 1024
(d) 64
Answer:
(c) 1024
Question 18.
1Kb equals to _________bytes.
a) 210
b) 220
c) 230
d) 240
Answer:
a) 210
Question 19.
How many megabytes does 1 GB contain?
(a) 220
(b) 210
(c) 230
(d) 240
Answer:
(b) 210
Question 20.
1 GB equals to ________ bytes.
a) 210
b) 220
c) 230
d) 240
Answer:
c) 230
Question 21.
What is the 1’ s complement of 11001?
(a) 11100110
(b) 01010101
(c) 11110000
(d) 100100111
Answer:
(a) 11100110
Question 22.
1 PetaByte(PB) equals to _________bytes.
a) 250
b) 260
c) 270
d) 280
Answer:
a) 250
Question 23.
The hexadecimal equivalent of 15 is ………………..
(a) A
(b) B
(c) E
(d) F
Answer:
(d) F
![]()
Question 24.
1 ZettaByte (1ZB) equals to _______ bytes.
a) 250
b) 260
c) 270
d) 280
Answer:
c) 270
Question 25.
The radix of a hexadecimal number is ………………..
(a) 2
(b) 8
(c) 16
(d) 10
Answer:
(c) 16
Question 26.
Computer memory is normally represented in terms of ________ bytes.
a) Kilo
b) Mega
c) Kilo or Mega
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Kilo or Mega
![]()
Question 27.
The most commonly used number system is ………………..
(a) binary
(b) decimal
(c) octal
(d) hexadecimal
Answer:
(b) decimal
Question 28.
The most commonly used coding scheme to represent character set and the number is ________
a) BCD
b) ASCII
c) EBCDIC
d) All the above
Answer:
b) ASCII
Question 29.
What does MSB mean?
(a) Major sign bit
(b) Most sign bit
(c) Minor sign bit
(d) Most significant bit
Answer:
(d) Most significant bit
Question 30.
The ASCII value for blank space is _________
a) 43
b) 42
c) 32
d) 62
Answer:
c) 32
![]()
Question 31.
The binary equivalent of hexadecimal number B is ………………..
(a) 1011
(b) 1100
(c) 1001
(d) 1010
Answer:
(a) 1011
Question 32.
The most commonly used numbering system in real life is the _________number system.
a) Hexadecimal
b) Octal
c) Binary
d) Decimal
Answer:
d) Decimal
Question 33.
What is the range of ASCII values for lower case alphabets?
(a) 65 to 90
(b) 65 to 122
(c) 97 to 122
(d) 98 to 122
Answer:
(c) 97 to 122
Question 34.
_________is the count of number of digits in each number system.
a) base
b) radix
c) base or radix
d) symbols
Answer:
c) base or radix
Question 35.
What is the ASCII value for blank space?
(a) 8
(b) 2
(c) 18
(d) 32
Answer:
(d) 32
![]()
Question 36.
Identify the true statement from the following.
a) In the positional number system, each decimal digit is weighted relative to its position in the number.
b) A numbering system is a way of representing numbers.
c) The speed of a computer depends on the number of bits it can process at once.
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 37.
Which one of the following bits has the smallest positional weight?
(a) MSB
(b) LSB
(c) UPS
(d) USB
Answer:
(b) LSB
Question 38.
The rightmost bit in the binary number is called as the __________
a) MSB
b) LSB
c) FSB
d) None of these
Answer:
b) LSB
Question 39.
Name the person who proposed the basic principles of Boolean Algebra?
(a) Wiliam Boole
(b) George Boole
(c) James Boole
(d) Boolean George
Answer:
(b) George Boole
Question 40.
_______ numbers are used as a shorthand form of a binary sequence.
a) Hexadecimal
b) Octal
c) Decimal
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Hexadecimal
![]()
Question 41.
What is the other name for a logical statement?
(a) Truth values
(b) Truth functions
(c) Truth table
(d) Truth variables
Answer:
(b) Truth functions
Question 42.
In hexadecimal number system letter ‘E’ represents _______
a) 12
b) 13
c) 14
d) 15
Answer:
c) 14
Question 43.
The NOT operator is represented by the symbol.
(a) over bar
(b) single apostrophe
(c) a and b
(d) plus
Answer:
(c) a and b
Question 44.
_______is a method to convert decimal number to binary number.
a) Repeated division by 2
b) Sum of powers of 2
c) Repeated addition by 2
d) Either A or B
Answer:
d) Either A or B
Question 45.
The output for the AND operator is ………………..
(a) A + B
(b) –
(c) A.B
(d) AB + C
Answer:
(c) A.B
![]()
Question 46.
Computer can handle _______ numbers.
a) signed
b) unsigned
c) signed and unsigned
d) None of these
Answer:
c) signed and unsigned
Question 47.
Which gate takes only one input?
(a) OR
(b) AND
(c) NOT
(d) XOR
Answer:
(c) NOT
Question 48.
In the signed magnitude method, the leftmost bit is called _______bit.
a) sign
b) parity
c) sign or parity
d) None of these
Answer:
c) sign or parity
Question 49.
Which is not a derived date?
(a) AND
(b) NAND
(c) NOR
(d) XOR
Answer:
(a) AND
Question 50.
The numbers are represented in computers in _______method.
a) Signed magnitude representation
b) 1’s complement
c) 2’s complement
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 51.
The statement “C equal the complement of A or B” means
(a) C = A + B
(b) C = \(\overline{\mathrm{A}}+\overline{\mathrm{B}}\)
(c) C = \(\overline{\mathrm{A}}\) + \(\overline{\mathrm{B}}\)
(d) C = \(\overline{\mathrm{A}\mathrm{B}}\)
Answer:
(a) C = A + B
![]()
Question 52.
If the number has_______sign, it will be considered as negative in signed magnitude representation.
a) +
b) no
c) –
d) A or B
Answer:
c) –
Question 54.
What is the output of the XOR gate?
(a) C = A% B
(b) C = A \(\otimes\) A
(c) C = A \(\odot\) B
(d) C = A \(\oplus\) B
Answer:
(d) C = A \(\oplus\) B
Question 54.
2’s complement of (0001i000)2 is_______
a) 11100111
b) 00011001
c) 11101000
d) None of these
Answer:
c) 11101000
Question 55.
Find A + \(\overline{\mathrm{A}}\) .B = ………………..
(a) A + B
(b) A.B
(c) \(\overline{\mathrm{A}}\).B
(d) A.\(\overline{\mathrm{B}}\)
Answer:
(d) A.\(\overline{\mathrm{B}}\)
Question 56.
When two binary numbers are added _______will be the output.
a) sum
b) carry
c) sum and carry
d) None of these
Answer:
c) sum and carry
![]()
Question 57.
When subtracting 1 from 0, borrow 1 from the next _______
a) LSB
b) MSB
c) either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
b) MSB
Question 58.
Find the wrong pair from the following:
(a) Null element : A + 1 = 1
(b) Involution : \(\overset { = }{ A }\) = A
(c) Demorgan’s : \(\overline{\mathrm{A+B}}\) =\(\overline{\mathrm{A}}\) . \(\overline{\mathrm{A}}\)
(d) Commutative : A + B = B . A
Answer:
(d) Commutative : A + B = B . A
Question 59.
_______ is the character encoding system.
a) BCD and ISCII
b) EBCDIC
c) ASCII and Unicode
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 60.
With 2 inputs in the truth table, how many sets of values will be obtained.
(a) 4
(b) 8
(c) 2
(d) 1
Answer:
(a) 4
Question 61.
EBCDIC stands for _______
a) Extensive Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code
b) Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code
c) Extended Binary Coded Digit Interchange Code
d) Extended Bit Coded Decimal Interchange Code.
Answer:
b) Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code
![]()
Question 62.
ASCII stands for _______
a) Arithmetic Standard Code for Information Interchange
b) American Structured Code for Information Interchange
c) American Standard Code for Information Interchange
d) American Standard Code for Instant Interchange
Answer:
c) American Standard Code for Information Interchange
Question 63.
ISCII stands for_______
a) International Standard Code for Information Interchange
b) Indian Structured Code for Information Interchange
c) India’s Standard Code for Information Interchange
d) Indian Standard Code for Information Interchange
Answer:
d) Indian Standard Code for Information Interchange
Question 64.
BCD is _______bit code.
a) 6
b) 7
c) 8
d) None of these
Answer:
a) 6
Question 65.
EBCDIC is_______ bit code
a) 6
b) 7
c) 8
d) None of these
Answer:
c) 8
Question 66.
ASCII is________ bit code
a) 6
b) 7
c) 8
d) None of these
Answer:
b) 7
![]()
Question 67.
Unicode is _______ bit code
a) 16
b) 7
c) 8
d) None of these
Answer:
a) 16
Question 68.
ISCII is_______ bit code
a) 16
b) 7
c) 8
d) None of these
Answer:
c) 8
Question 69.
_______coding system is formulated by IBM.
a) BCD
b) EBCDIC
c) ISCII
d) None of these
Answer:
b) EBCDIC
Question 70.
IBM stands for_______
a) Indian Business Machine
b) International Basic Machine
c) International Business Method
d) International Business Machine
Answer:
d) International Business Machine
![]()
Question 71.
_______is the system of handling the characters of Indian local languages.
a) ASCII
b) Unicode
c) BCD
d) ISCII
Answer:
d) ISCII
Question 72.
ISCII system is formulated fay the _______ in India.
a) Department of Electronics
b) Department of Electricity
c) Department of E-commerce
d) Department of Economics
Answer:
a) Department of Electronics
Question 73.
SCO system can handle___________characterscharacters.
a) 64
b) 128
c) 256
d) 65536
Answer:
a) 64
Question 74.
EBCDIC system can handle _______ characters.
a) 64
b) 128
c) 256
d) None of these
Answer:
c) 256
Question 75.
ASCII system can handle _______characters.
a) 64
b) 128
c) 256
d) None of these
Answer:
c) 256
![]()
Question 76.
Unicode system can handle _______ characters.
a) 64
b) 128
c) 256
d) 65536
Answer:
d) 65536
Question 77.
ISCII system can handle _______ characters.
a) 64
b) 128
c) 256
d) 65535
Answer:
c) 256
Question 78.
__________ language characters are not represented by ASCII.
a) Tamil
b) Malayalam
c) Telugu and Kannada
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 79.
Tamil, Malayalam, Telugu, and Kannada language characters are represented by _______ code.
a) ASCII
b) Unicode
c) BCD
d) ISCII
Answer:
b) Unicode
Question 80.
_______scheme is denoted by hexadecimal numbers
a) ASCII
b) Unicode
c) BCD
d) ISCII
Answer:
b) Unicode
![]()
Question 81.
ISCII code was formulated in the year_______
a) 1986 – 88
b) 1984 – 86
c) 1988
d) 1987
Answer:
a) 1986 – 88
Question 82.
_______coding system is integrated with Unicode.
a) ASCII
b) EBCDIC
c) BCD
d) ISCII
Answer:
d) ISCII
Question 83.
_______was generated to handle all the coding system of Universal languages.
a) ASCII
b) Unicode
c) BCD
d) ISCII
Answer:
b) Unicode
Question 84.
The popular coding scheme after ASCII is_______
a) EBCDIC
b) Unicode
c) BCD
d) ISCII
Answer:
b) Unicode
Question 85.
BCD system is_______bit encoding system.
a) 28
b) 216
c) 26
d) 24
Answer:
c) 26
![]()
Question 86.
EBCDIC system is _______bit encoding system.
a) 28
b) 216
c) 26
d) 27
Answer:
a) 28
Question 87.
ASCII system is a bit encoding system.
a) 28
b) 216
c) 26
d) 27
Answer:
d) 27
Question 88.
Unicode system is _________bit encoding system.
a) 28
b) 216
c) 26
d) 27
Answer:
b) 216
Question 89.
ISCII svstem is _________bit encoding system.
a) 28
b) 216
c) 26
d) 27
Answer:
a) 28
Question 90.
The input code in ASCII can be converted into _________system.
a) EBCDIC
b) Unicode
c) BCD
d) ISCII
Answer:
a) EBCDIC
Question 91.
What is ASCII value for ‘A’ in a decimal number,
a) 97
b) 65
c) 98
d) 32
Answer:
b) 65
![]()
Question 92.
What is the ASCII value for ‘A’ in a binary number?
a) 01100001
b) 01000001
c) 01100010
d) 00100000
Answer:
b) 01000001
Question 93.
What is the ASCII value for ‘A’ in an octal number?
a) 141
b) 101
c) 142
d) 40
Answer:
b) 101
Question 94.
What is the ASCII value for ‘A’ in hexadecimal numbers?
a) 61
b) 41
c) 62
d) 20
Answer:
b) 41
Question 95.
Find the false statement in the following.
a) Computers can handle positive and negative numbers.
b) MSB is called a sign bit
c) LSB is called a parity bit
d) All the above
Answer:
c) LSB is called a parity bit
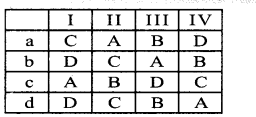
Question 96.
Match the following.
a) 78 – (1) Binary number
b) linn – (2) Octal number
c) CAFE – (3) Decimal number
d) 71 – (4) Hexadecimal number
a) 3, 1, 4, 2
b) 4, 3, 2, 1
c) 1, 3, 2, 4
d) 3, 1, 2, 4
Answer:
a) 78 – (1) Binary number
![]()
Question 97.
In signed magnitude representation,_________ in the sign bit represents negative number.
a) 0
b) 1
c) No symbol
d) None of these
Answer:
b) 1
Question 98.
In signed magnitude representation, __________in the sign bit represents positive number.
a) 0
b) 1
c) No symbol
d) None of these
Answer:
a) 0
Question 99.
The term data comes from the word __________
a) datum
b) date
c) fact
d) None of these
Answer:
a) datum
Part II
Very Short Answers.
Question 1.
What is nibble?
Answer:
Nibble is a collection of 4 bits. A nibble is half a byte.
Question 2.
Define information.
Answer:
Information is a processed fact and obtained from the computer as output. It conveys meaning.
Question 3.
What is radix?
Answer:
The base value of a number is also known as the radix.
Question 4.
Define Bit and Byte.
Answer:
Bit: A bit is the short form of a Binary digit which can be ‘0’ or ‘1’. It is the basic unit of data in computers.
Byte: A collection of 8 bits is called Byte. It is the basic unit of measuring the memory size in the computer.
Question 5.
Expand: BCD, EBCDIC, ASCII
Answer:
BCD – Binary Coded Decimal; EBCDIC – Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code; ASCII – American Standard Code for Information Interchange.
![]()
Question 6.
What are the different types of coding schemes to represent the character sets?
Answer:
The different coding schemes are
- BCD – Binary Coded Decimal
- EBCDIC – Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code
- ASCII – American Standard Code for Information Interchange
- Unicode
- ISCII – Indian Standard Code for Information Interchange.
Question 7.
What are the methods of converting a number from decimal to binary?
Answer:
- Repeated division by two.
- Sum of powers of 2.
Question 8.
What does base or radix mean?
Answer:
Radix or base is the count of a number of digits in each number system. Radix or base is the general idea behind the positional numbering system.
Question 9.
What are the various ways for Binary representation of signed numbers?
Answer:
- Signed magnitude representation
- 1’s complement
- 2’s complement
Question 10.
Write a note on the decimal number system.
Answer:
It consists of 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9(10 digits). It is the oldest and most popular number system used in our day-to-day life. In the positional number system, each decimal digit is weighted relative to its position in the number.
Its base or radix is 10.
Question 11.
Write about the octal number system.
Answer:
Octal number system uses digits 0,1,2,3,4,5,6 and 7 (8 digits). Each octal digit has its own positional value or weight as a power of 8. Its base or radix is 8.
![]()
Question 12.
How will you convert decimal to hexadecimal?
Answer:
To convert Decimal to Hexadecimal, “Repeated division by 16” method can be used) In this method, we have to divide the given number by 16.
Example: Convert (31)10 into its equivalent hexadecimal number.
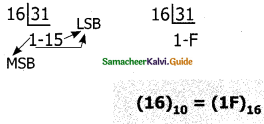
Question 13.
Give the procedure to Octal to Binary.
Answer:
Procedure: For each octal digit in the given number write its 3 digits binary equivalent using positional notation.
Example: Convert (6213)8 to equivalent Binary number.
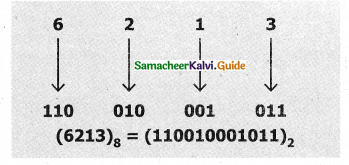
Question 14.
How will you convert Hexadecimal to Binary?
Answer:
Procedure: Write 4 bits Binary equivalent for each Hexadecimal digit for the given number using the positional notation method.
Example:
Convert (8BC)16 into an equivalent Binary number.
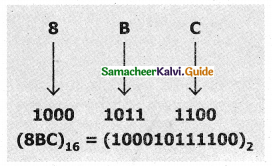
Question 15.
Write short note on Binary Coded Decimal (BCD).
Answer:
This is 26 bit encoding system. This can handle 26 = 64 characters only. This encoding system is not
in the practice right now.
Question 16.
Write note on EBCDIC encoding system.
Answer:
Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBCDIC) is similar to ASCII Code with 8 bit representation. This coding system is formulated by International Business Machine (IBM). The coding system can handle 256 characters. The input code in ASCII can be converted to EBCDIC system and vice – versa.
![]()
Question 17.
Write a note on the ISCII encoding system.
Answer:
ISCII is the system of handling the character of Indian local languages. This is an 8-bit coding system. Therefore it can handle 256 (28) characters. This system is formulated by the Department of Electronics in India in the year 1986-88 and recognized by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS). Now, this coding system is integrated with Unicode.
Part III
III. Very Short Answers
Question 1.
Write about the binary number system.
Answer:
There are only two digits in the Binary system, namely, 0 and 1. The numbers in the binary system are represented to the base 2 and the positional multipliers are the powers of 2.
The leftmost bit in the binary number is called the Most Significant Bit (MSB) and it has the largest positional weight. The rightmost bit is the Least Significant Bit (LSB) and has the smallest positional weight.

Question 2.
What is the octal number system?
Answer:
The octal number system uses digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 (8 digits): Each octal digit has its own positional value or weight as a power of 8.
Example: The Octal sequence (547)8 has the decimal equivalent:
Question 3.
Give the procedure to convert decimal to octal.
Answer:
To convert Decimal to Octal, “Repeated Division by 8” method can be used) In this method, we have to divide the given number by 8.
Example:
Convert (65)10 into its equivalent Octal number.
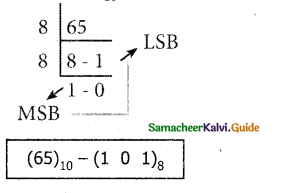
Question 4.
Give the procedure to convert Octal to Decimal
Answer:
To convert Octal to Decimal, we can use positional notation method)
- Write down the Octal digits and list the powers of 8 from right to left (Positional Notation).
- For each positional notation of the digit write the equivalent weight.
- Multiply each digit with its corresponding weight.
- Add all the values.
Example:
Convert (1265)8 to equivalent Decimal number.
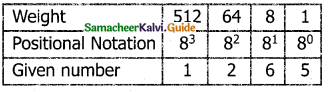
(1265)8 = 512 x 1 + 64 x 2 + 8 x 6 + 1 x 5
= 512 + 128 + 48 + 5
(1265)8 = (693)10
![]()
Question 5.
How will you convert Hexadecimal to Decimal?
Answer:
To convert Hexadecimal to Decimal we can use the positional notation method.
- Write down the Hexadecimal digits and list the powers of 16 from right to left (Positional Notation)
- For each positional notation written for the digit, now write the equivalent weight.
- Multiply each digit with its corresponding weight
- Add all the values to get one final value.
Example:
Convert (25F)16 into its equivalent Decimal number.
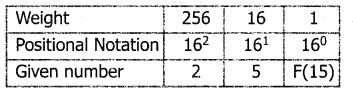
(25F)16 = 2 x 256 + 5 x 16 + 15 x 1
= 512 + 80 + 15 (25F)16
= (607)10
Question 6.
Write about binary representation for signed numbers.
Answer:
Computers can handle both positive (unsigned) and negative (signed) numbers. The simplest method to represent negative binary numbers is called Signed Magnitude. In signed magnitude method, the leftmost bit is the Most Significant Bit (MSB), which is called the sign bit or parity bit.
The numbers are represented in computers in different ways:
- Signed Magnitude representation
- 1’s Complement
- 2’s Complement
Question 7.
Explain ASCII code in detail.
Answer:
This is the most popular encoding system recognized by the United States. Most of the computers use this system. Remember this encoding system can handle English characters only. This can handle 27 bit which means 128 characters.
In this system, each character has an individual number. The new edition ASCII -8, has 28 bits and can handle 256 characters are represented from 0 to 255 unique numbers.
The ASCII code equivalent to the uppercase letter ‘A’ is 65. The binary representation of the ASCII (7 bit) value is 1000001. Also 01000001 in ASCII-8 bit.
Question 8.
Explain Unicode in detail.
Answer:
This coding system is used in most modern computers. The popular coding scheme after ASCII is Unicode. ASCII can represent only 256 characters. Therefore English and European Languages alone can be handled by ASCII. Particularly there was a situation when the languages like Tamil, Malayalam, Kannada, and Telugu could not be represented by ASCII.
Hence, Unicode was generated to handle all the coding system of Universal languages. This is a 16-bit code and can handle 65536 characters. The unicode scheme is denoted by hexadecimal numbers.
![]()
Part IV
IV. Detail Answers.
Question 1.
Explain decimal to binary conversion using Repeated Division by 2 methods.
Answer:
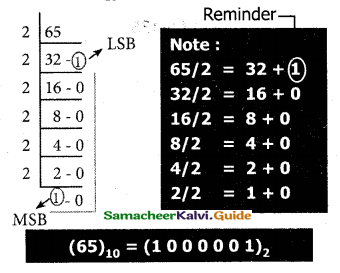
To convert Decimal to Binary “Repeated Division by 2” method can be used. Any Decimal number divided by 2 will leave a remainder of 0 or 1. Repeated division by 2 will leave a sequence of 0s and Is that become the binary equivalent of the decimal number.
Suppose it is required to convert the decimal number N into binary form, dividing N by 2 in the decimal system, we will obtain a quotient N1 and a remainder Rl, where R1 can have a value of either 0 or 1. The process is repeated until the quotient becomes 0 or 1. When the quotient is ‘0’ or ‘1’, it is the final remainder value. Write the final answer starting from the final remainder value obtained to the first remainder value obtained.
Example:
Convert (65)10 into its equivalent binary number
Question 2.
Explain decimal to binary conversion using Sum of powers of 2 methods.
Answer:
A decimal number can be converted into a binary number by adding up the powers of 2 and then adding bits as needed to obtain the total value of the number.
a) Find the largest power of 2 that is smaller than or equal to 65.
6510 > 6410
b) Set the 64’s bit to 1 and subtract 64 from the original number
65 – 64 = 1
c) 32 is greater than the remaining total.
Therefore, set the 32’s bit to 0.
d) 16 is greater than the remaining total.
Therefore, set the 16’s bit to 0
.
e) 8 is greater than the remaining total.
Therefore, set the 8’s bit to 0.
f) 4 is greater than the remaining total.
Therefore, set the 4’s bit to 0.
g) 2 is greater than the remaining total.
Therefore, set the 2’s bit to 0.
h) As the remaining value is equivalent to l’s bit, set it to 1.
1 – 1 = 0
Conversion is complete 6510 = (1000001)2
Example:
The conversion steps can be given as follows:
Given Number: 65
Equivalent or value less than the power of 2 is: 64
(1) 65 – 64 = 1
(2) 1 – 1= 0
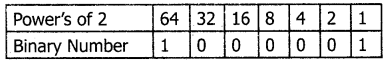
6510 = (1000001)2.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the procedure to convert fractional decimal to Binary.
Answer:
The method of repeated multiplication by 2
has to be used to convert such kind of decimal fractions.
The steps involved in the method of repeated multiplication by 2:
Step 1: Multiply the decimal fraction by 2 and note the integer part. The integer part is either 0 or 1.
Step 2: Discard the integer part of the previous product. Multiply the fractional part of the previous product by 2. Repeat Step 1 until the same fraction repeats or terminates (0).
Step 3: The resulting integer part forms a sequence of Os and Is that becomes the binary equivalent of a decimal fraction.
Step 4: The final answer is to be written from the first integer part obtained till the last integer part obtained.
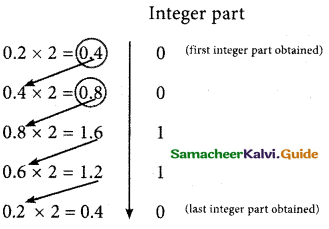
Write the integer parts from top to bottom to obtain the equivalent fractional binary number. Hence (0.2)10= (0.00110011…)2 = 0.00110011)2
Question 4.
How will you convert Binary to Decimal?
Answer:
To convert Binary to Decimal we can use the positional notation method.
Step 1: Write down the Binary digits and list the powers of 2 from right to left (Positional Notation)
Step 2: For each positional notation written for the digit, now write the equivalent weight.
Step 3; Multiply each digit with its corresponding weight
Step 4: Add all the values.
Example:
Convert (111011)2 into its equivalent decimal number.
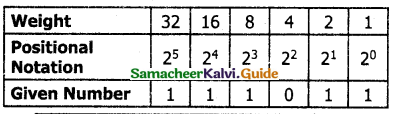
32 + 16 + 8 + 0 + 2 + 1 = (59)10
(111011)2 = (59)10
Question 5.
How will you convert Binary to Octal?
Answer:
Step 1.: Group the given binary number into 3 bits from right to left.
Step 2: You can add preceding O to make a group of 3 bits if the leftmost group has less than 3 bits.
Step 3: Convert equivalent octal value using “2’s power positional weight method”
Example
Convert (11010110)2 into an octal equivalent number
Step 1: Group the given number into 3 bits from right to left.
011 010 110
The left-most groups have less than 3 bits, so 0 is added to its left to make a group of 3 bits.
Step-2: Find the Octal equivalent of each group.
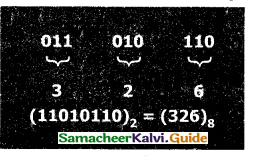
![]()
Question 6.
Give the procedure to convert Binary to Hexadecimal.
Answer:
Step 1: Group the given number into 4 bits from right to left.
Step 2: You can add preceding 0’s to make a group of 4 bits if the leftmost group has less than 4 bits.
Step 3: Convert equivalent Hexadecimal value using “2’s power positional weight method”.
Example
Convert (1111010110)2 into Hexadecimal number
Step 1: Group the given number into 4 bits from right to left. 1
0011 1101 0110
0’s are added to the leftmost group to make it a group of 4 bits.

Question 7.
Give the procedure to convert fractional Binary to Decimal equivalent.
Answer:
The steps to convert fractional Binary number to its decimal equivalent:
Step 1 : Convert an integral part of Binary to Decimal equivalent using positional notation method.
Step 2 : To convert the fractional part of binary to its decimal equivalent.
Step 2,1 : Write down the Binary digits in the fractional part.
Step 2,2 : For all the digits write powers of 2 from left to right starting
from 2-1, 2-2, 2-3 2-n, now write the equivalent weight.
Step 2.3 : Multiply each digit with its corresponding weight.
Step 2.4 : Add all the values which you obtained in Step 2.3.
Step 3 : To get final answer write the integral
part (after conversion), followed by a decimal point(.) and the answer arrived at Step 2.4
Example:
Convert the given Binary number (11.011)2 into its decimal equivalent Integer part (11)2 = 3
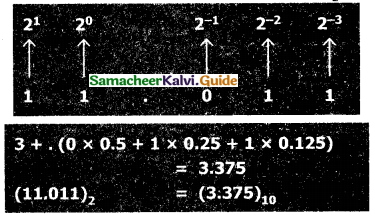
![]()
Question 8.
Explain the method of representing signed binary numbers in the Signed Magnitude representation.
Answer:
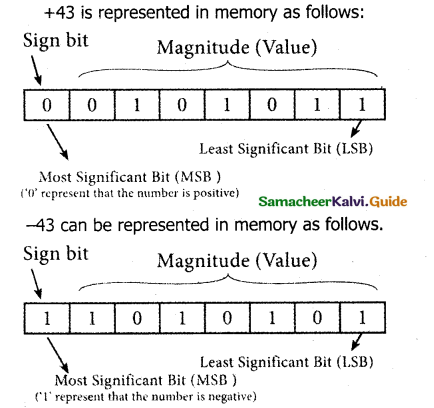
The value of the whole numbers can be determined by the sign used before it. If the number has a ‘+’ sign or no sign it will be considered as positive. If the number has signed it will be considered negative.
Example:
+ 43 or 43 is a positive number
– 43 is a negative number
In signed binary representation, the leftmost bit is considered as a sign bit. If this bit is 0, it is a positive number and if it 1, it is a negative number. Therefore a signed binary number has 8 bits, only 7 bits used for storing values (magnitude), and 1 bit is used for signs.
Question 9.
Explain the method of representing signed binary numbers in l’s complement representation.
Answer:
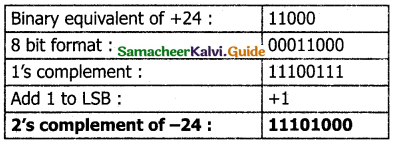
This is an easier approach to represent signed numbers. This is for negative numbers only i.e. the number whose MSB is 1.
The steps to be followed to find l’s complement of a number:
Step 1: Convert given Decimal number into Binary
Step 2: Check if the binary number contains 8 bits, if less add 0 at the left most bit, to make it as 8 bits.
Step 3: Invert all bits (i.e. Change 1 as 0 and 0 as 1)
Example: Find 1’s complement for (-24)10

![]()
Question 10.
Explain the method of representing signed binary numbers in 2’s complement representation.
Answer:
The 2’s-complement method for the negative number is as follows:
a) Invert all the bits in the binary sequence (i.e., change every 0 to 1 and every 1 to 0 ie.,l’s complement)
b) Add 1 to the result to the Least Significant Bit (LSB).
Example: 2’s Complement represent of (-24)10
Question 11.
Explain binary addition with a suitable example.
Answer:
The following table is useful when adding two binary numbers.
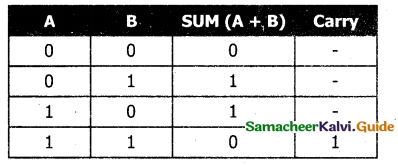
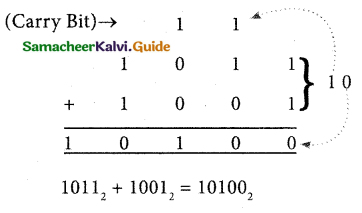
In 1 + 1 = 10, is considered as sum 0 and the 1 as carry bit. This carry bit is added with the previous position of the bit pattern.
Example: Add: 10112 + 10012
Example: Perform Binary addition for the following:
2310 + 1210
Step 1: Convert 23 and 12 into binary form
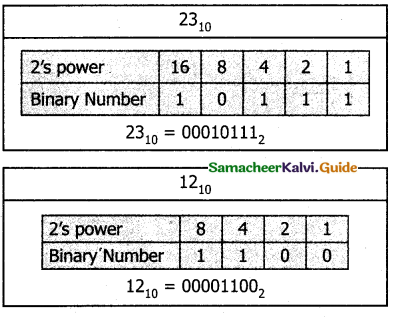
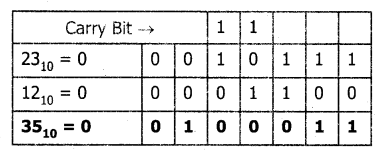
Step 2: Binary addition of 23 and 12:
![]()
Question 11.
Explain binary subtraction with a suitable example.
Answer:
The table for Binary Subtraction is as follows:
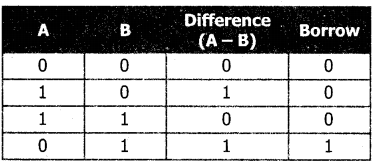
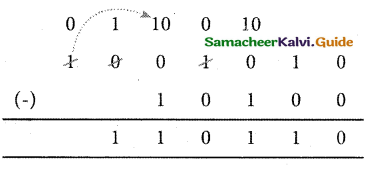
When subtracting 1 from 0, borrow 1 from the next Most Significant Bit, when borrowing from the next Most Significant Bit, if it is 1, replace it with 0. If the next Most Significant Bit is 0, you must borrow from a more significant bit that contains 1 and replace it with 0 and 0s upto that point become Is.
Example : Subtract 10010102 — 101002.
Example: Perform Binary addition for the
following:
(-21)10 + (5)10
Step 1: Change -21 and 5 into binary form
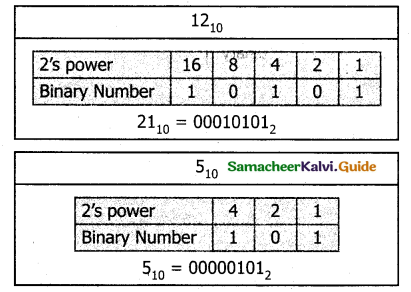
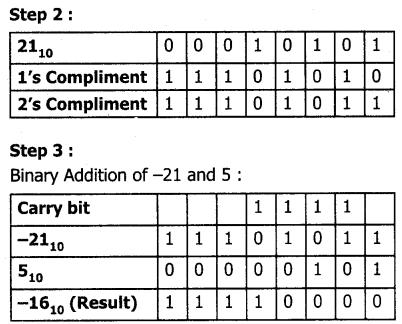
Workshop
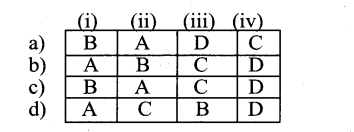
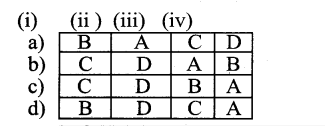
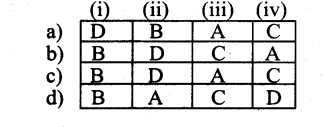
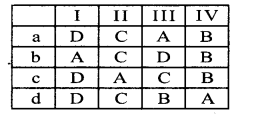
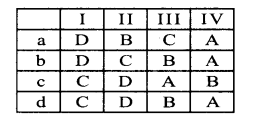
Question 1.
Identify the number system for the following numbers.
Answer:
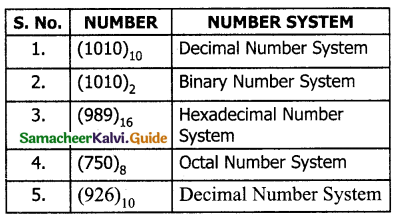
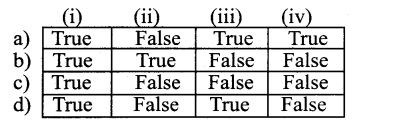
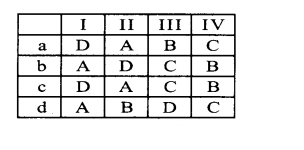
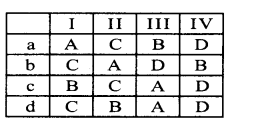
Question 2.
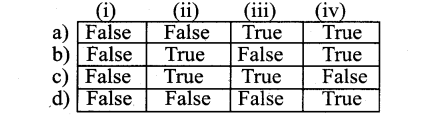
State whether the following numbers are valid or not. If invalid, give a reason.
Answer:
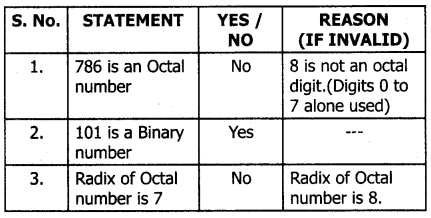
![]()
Question 3.
Convert the following Decimal numbers to their equivalent Binary, Octal, Hexadecimal.
i) 1920
ii) 255
iii) 126
Answer:
i) 1920
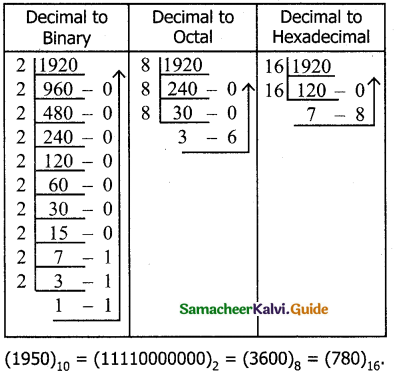
ii) 255
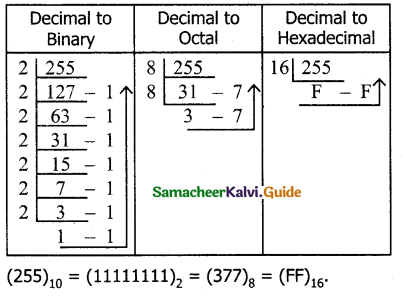
iii) 126
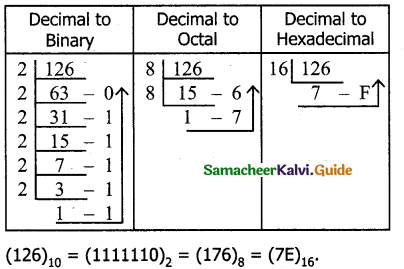
![]()
Question 4.
Convert the given Binary number into its equivalent Decimal, Octal, and Hexadecimal numbers.
i)101110101
ii) 1011010
iii) 101011111
Answer:
i) 101110101
Binary to Decimal (Multiply by positional value and then add)
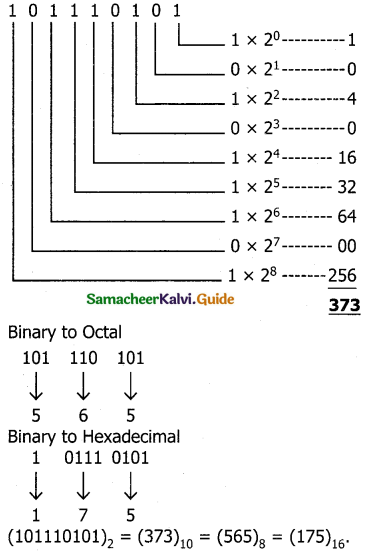
ii) 1011010
Binary to decimal
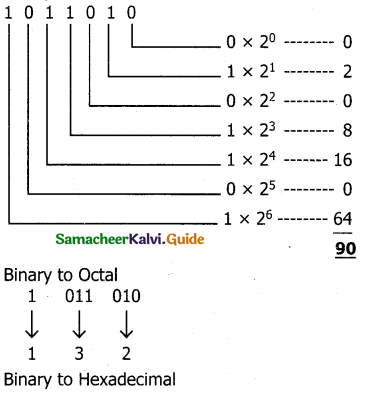
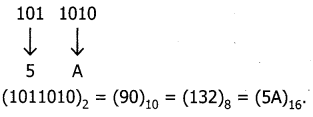
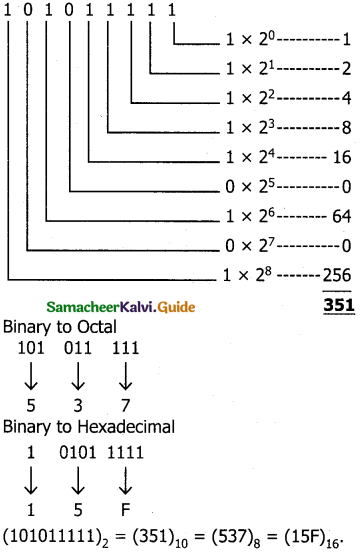
iii) 101011111
Binary to decimal
![]()
Question 5.
Convert the following Octal numbers into Binary numbers.
a) 472
b) 145
c) 347
d) 6247
e) 645
Answer:
Procedure: Write three digits binary number for every octal digit that will give the equivalent binary number.

Ans.
(472)8 = (100111010)2

Answer:
(145)8 = (001100101)2

Answer:
(347)8 = (011100111)2
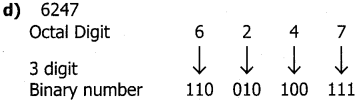
Answer:
(6247)8 = (110010100111)2

Answer:
(645)8 = (110100101)2.
![]()
Question 6.
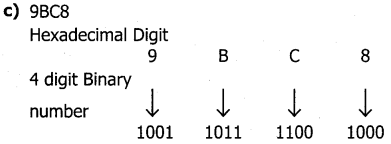
Convert the following Hexadecimal numbers to Binary numbers
a) A6
b) BE
c) 9BC8
d) BC9
Answer:
Procedure: Write four digits binary number for every Hexadecimal digit that will give the equivalent binary number.

Answer:
(A6)16 = (10100110)2.

Answer:
(BE)16 = (1011 1110)2
Answer:
(9BC8)16 = (1001101111001000)2

Answer:
(BC9)16 = (101111001001)2
Question 7.
Write the l’s complement number and 2’s complement number for the following decimal numbers:
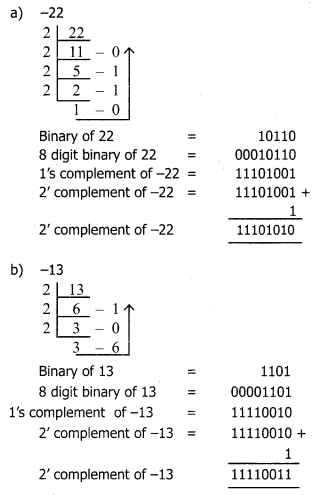
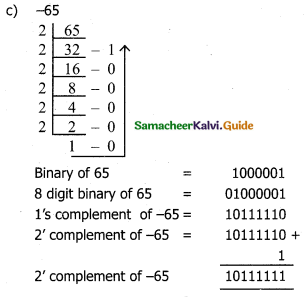
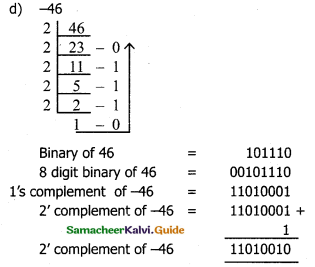
Perform the following binary computations:
a) -22
b) -13
c) -65
d) -46
Answer:
a) -22
![]()
Question 8.
a) 1010 + 1510
b) – 1210 + 510
c) 1410 – 1210
d) (-2)10 – (-6)10
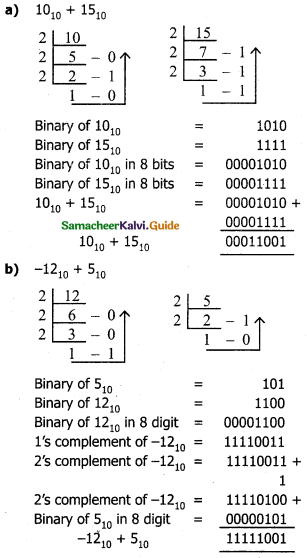
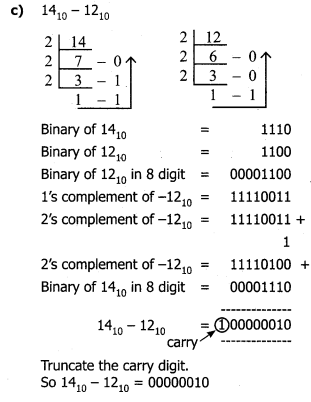
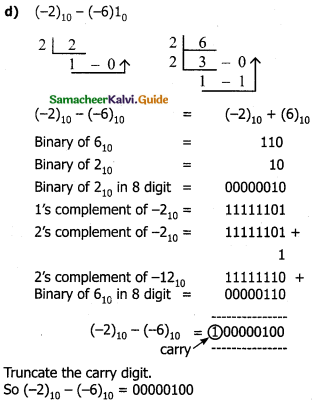
Answer: