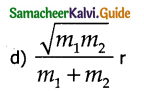Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Guide Pdf Chapter 22 Types of Trade Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Solutions Chapter 22 Types of Trade
11th Commerce Guide Types of Trade Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
The purchase of goods from a foreign country is called ………………..
a. Import
b. Export
c. Entrepot
d. Re-export
Answer:
a. Import
Question 2.
When goods are imported for the purpose of export it is called as …………..
a. Foreign Trade
b. Home Trade
c. Entrepot
d. Trade
Answer:
c. Entrepot
![]()
Question 3.
………………… acts as a connective link between the producer and the consumer.
a. Trade
b. Industry
c. Commerce
d. Business
answer:
a. Trade
Question 4.
The aim of home trade is ……………………
a. To raise the standard of living
b.To provide the essential goods and services economically
c. To raise the national income
d.To obtain all types of goods.
Answer:
b.To provide the essential goods and services economically
![]()
Question 5.
Internal trade can be classified into ……………… categories
a. Three
b. Four
c. Two
d. Five
Answer:
c. Two
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Give the meaning of Trade?
Answer:
The buying and selling of goods and services consist of trade. Trade is conducted in order to earn a profit.
Question 2.
What is Internal Trade?
Answer:
Buying and selling of goods and services within the boundaries of a nation are called internal trade. It takes place between buyers and sellers in the same locality, village, town or city or in different states, but definitely within the same country.
![]()
Question 3.
Mr.Vikram who runs a textile industry regularly procures cotton from Germany. Name the type of trade he is engaged in.
Answer:
This is Import trade because Mr. Vikram procures (purchases) cotton from Germany Import means buying of goods from a foreign country for domestic use.
Question 4.
When Vikram of India sells cotton shirts to Amal of England, what type of trade he is engaged in?
Answer:
It is called Export Trade.
Question 5.
How do you classify Trade?
Answer:
On the basis of the geographical location of buyers and sellers, trade can be broadly classified into two categories
- Internal trade
- External trade
![]()
Question 6.
What are the classifications of internal trade?
Answer:
Internal trade can be classified into Wholesale trade and Retail Trade.
Question 7.
What is import trade?
Answer:
Import trade means buying goods from a foreign country for domestic use.
Example. India imports petroleum products from Gulf Countries.
![]()
Question 8.
Explain the meaning of the Entrepot trade.
Answer:
Entrepot trade means importing goods from one country and exporting the same to foreign countries. It is also known as ‘Re-export trade’.
Question 9.
TVS is selling motorbikes in Europe. Under which type of trade can this be classified?
Answer:
TVS is selling motorbikes in Europe. This trade can be classified under Foreign trade.
![]()
Question 10.
What is the currency used in India in internal trade?
Answer:
The currency used in India for internal trade is RUPEE.
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is the classification of Foreign trade?
Answer:
Types of Foreign Trade:
- Import Trade: Import trade means buying goods from a foreign country for domestic use.
- Export Trade: Export trade means the sale of domestic goods to foreign countries.
- Entrepot Trade: Entrepot trade means importing goods from one country and exporting the same to foreign countries.
Question 2.
Give two examples of Entrepot trade.
Answer:
Indian diamond merchants in Surat import uncut raw diamonds from South Africa. They cut and polish the diamonds in their units in India and re-export them to the International Diamond Market in Amsterdam. An Indian Company imports rubber from Thailand and exports it to Japan.
![]()
Question 3.
What do you mean by Export trade?
Answer:
Export trade means the sale of domestic goods to foreign countries. Export trade is necessary to sell domestic surplus goods, to make better utilization of resources, to earn foreign exchange, to increase national income, to generate employment, and to increase Government revenue.
Question 4.
What is Wholesale trade?
Answer:
“Purchase of goods in bulk from the manufacturers and selling them in smaller quantities to other intermediaries” is known as wholesale trade.
![]()
Question 5.
State the meaning of Retail trade.
Answer:
Retail trade deals with the distribution of goods in small quantities to consumers.
Question 6.
Name any three retail traders in your locality
Answer:
Sree Akshaya Traders, Hari Traders, and Thomas Traders. (Any three)
![]()
Question 7.
State the main aim of trade.
Answer:
The essence of trade is to make goods and services available to those persons who need them and are able and willing to pay for them. Trade is conducted in order to earn a profit.
IV. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the features of Internal trade?
Answer:
- The buying and selling of goods take place within the boundaries of the same country.
- Payment for goods and services is made in the currency of the home country.
- It involves transactions between the producers, consumers, and middlemen.
- It consists of a distribution network of middlemen and agencies engaged in an exchange of goods and services.
- In-home trade, the risk of transportation is very less when compared to foreign trade.
- In-home trade, the laws prevailing in that country only have to be followed.
- The aim of home trade is to provide goods and services economically.
- The goods must be a part of domestic production.
- Goods must be purchased from an individual or a firm established within a country.
- Goods can be delivered using locally available modes of transport.
- It does not involve any custom/import duty, but buyers need to pay the taxes to the Government.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain briefly the different types of Foreign trade?
Answer:
Meaning:
Foreign trade is a trade between a seller and buyer of different countries. It involves the exchange of goods and services of one country with another country.
Types of Foreign Trade
A. Import Trade:
Import trade means buying goods from a foreign country for domestic use. Example. India imports petroleum products from Gulf Countries. India imports machinery, equipment, materials, etc. It is necessary to speed-up industrialization, meet consumer demands, and improve the standard of living.
B. Export Trade:
Export trade means the sale of domestic goods to foreign countries.
Examples:
- Export of Iron ore from India to Japan
- Selling of Tea from India to England.
- Export of jasmine flowers from Madurai to Singapore.
![]()
11th Commerce Guide Types of Trade Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer :
Question 1.
……………… trade is a trade between a seller and buyer of different countries.
(a) Foreign
(b) Export
(c) Entrepot
(d) Home
Answer:
(a) Foreign
Question 2.
The internal trade is also called…………….
a. Wholesale Trade
b. Retail Trade
c. Entrepot Trade
d. Home Trade
Answer:
d. Home Trade
![]()
Question 3.
Selling of Tea from India to England – What type of trade is this?
Answer:
(a) Export
(b) Import
(c) Entrepot
(d) Home
Answer:
(a) Export
Question 4.
India imports petroleum products from Gulf countries. This is the example for ………………….
a. Wholesale Trade
b. Retail Trade
c. Entrepot Trade
d. Import Trade
Answer:
d. Import Trade
![]()
Question 5.
Hero pens produced in China and sold in India is an example for ……………… trade.
(a) Foreign
(b) Home
(c) Export
(d) Entrepot
Answer:
(a) Foreign
II. Very Short Answer Questions:
Question 1.
Where does Internal Trade take place?
Answer:
Internal takes place between the buyers and sellers in the same locality, village, town, or city or in different states but with the same country.
III. Short Answer Questions:
Question 1.
Write a short note on Entrepot Trade:
Entrepot trade means importing goods from one country and exporting the same to foreign countries. It is also known as ‘Re-export trade’.
E.g. Indian diamond merchants in Surat import uncut raw diamonds from South Africa. They cut and polish the diamonds in their units in India and re-export them to the International Diamond Market in Amsterdam.
![]()
IV. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the types of Internal Trade
Answer:
Home trade consists of two main subdivisions namely
- Wholesale trade: “Purchase of goods in bulk from the manufacturers and selling them in smaller quantities .to other intermediaries” is known as wholesale trade.
- Retail Trade: Retail trade deals with the distribution of goods in small quantities to consumers.
![]()