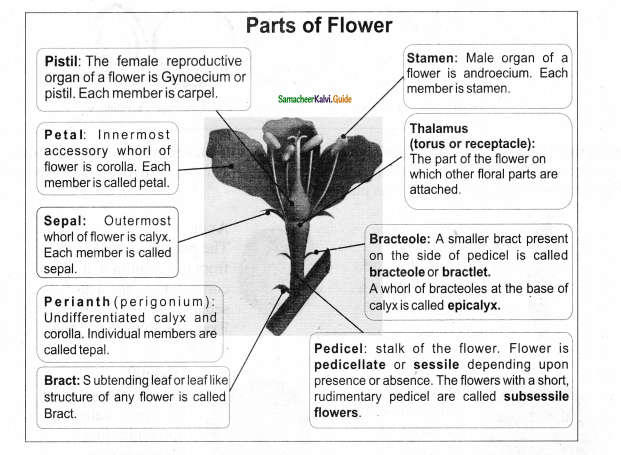
Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Guide Pdf Chapter 5 Working with Typical Operating System (Windows & Linux) Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Solutions Chapter 5 Working with Typical Operating System (Windows & Linux)
11th Computer Science Guide Working with Typical Operating System (Windows & Linux) Text Book Questions and Answers
Part I
Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
From the options given below, choose the operations managed by the operating system.
a) Memory
b) Processor
c) I/O devices
d) all of the above
Answer:
d) all of the above
![]()
Question 2.
Which is the default folder for many Windows Applications to save your file?
a) My Document
b) My Pictures
c) Documents and Settings
d) My Computer
Answer:
a) My Document
Question 3.
Under which of the following OS, the option Shift + Delete – permanently delete a file or folder?
a) Windows 7
b) Windows 8
c) Windows 10
d) None of the OS
Answer:
a) Windows 7
![]()
Question 4.
What is the meaning of “Hibernate” in Windows XP/Windows 7?
a) Restart the Computer in safe mode
b) Restart the Computer in hibernate mode
c) Shutdown the Computer terminating a!! the running applications
d) Shutdown the Computer without closing the running applications
Answer:
d) Shutdown the Computer without closing the running applications
Question 5.
Which of the following OS is not based on Linux?
a) Ubuntu
b) Redhat
c) CentOs
d) BSD
Answer:
d) BSD
Question 6.
Which of the following in Ubuntu OS is used to view the options for the devices installed?
a) Settings
b) Files
c) Dash
d) VBox_GAs_5.2.2
Answer:
b) Files
![]()
Question 7.
Identify the default email client in Ubuntu.
a) Thunderbird
b) Firefox
c) Internet Explorer
d) Chrome
Answer:
a) Thunderbird
Question 8.
Which is the default application for spreadsheets in Ubuntu? This is available in the software launcher.
a) LibreOffice Writer
b) LibreOffice Calc
c) LibreOffice Impress
d) LibreOffice Spreadsheet
Answer:
b) LibreOffice Calc
![]()
Question 9.
Which is the default browser for Ubuntu?
a) Firefox
b) Internet Explorer
c) Chrome
d) Thunderbird
Answer:
a) Firefox
![]()
Question 10.
Where will you select the option to log out, suspend, restart, or shut down from the desktop of Ubuntu OS?
a) Session Indicator
b) Launcher
c) Files
d) Search
Answer:
a) Session Indicator
Part – II
Short Answers
Question 1.
Differentiate cut and copy options.
Answer:
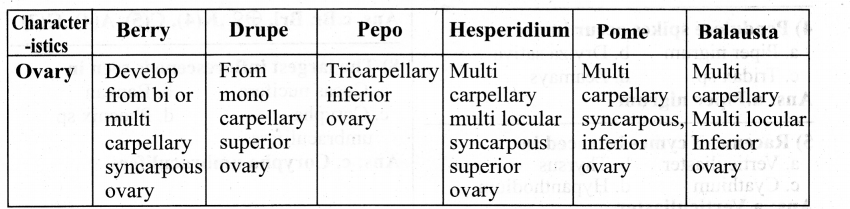
| COPY | CUT |
| Copy text will leave the source as it is and place a copy in the destination. | Move text will shift the source to the destination i.e., the text will change its position. |
| After the copy, the text available in both source and destination locations. | After the move, the text available in the destination location alone. |
![]()
Question 2.
What is the use of a file extension?
Answer:
File Extension is the second part of the file name. It succeeds the decimal point in the file name. It is used to identify the type of file and it is normally upto 3 to 4 characters long.
Example: exe, html.
![]()
Question 3.
Differentiate Files and Folders.
Answer:
| Files | Folders |
| The files store data of any kind. | The folders store files and other sub-folders. |
| Information stored in the computer only in the form of file. | The folders often referred to as directories, are used to organize files on your computer. |
Question 4.
Differentiate Save and Save As option.
Answer:
| Save | Save As |
| The save command automatically saves the file using the same name, format and location, as when it was last saved or opened from. Save command opens a dialog box only first time saved. | The save as command opens a dialog box every time in which the user can change the name of the file, the format, as well as the location of where the file is saved if needed. |
Question 5.
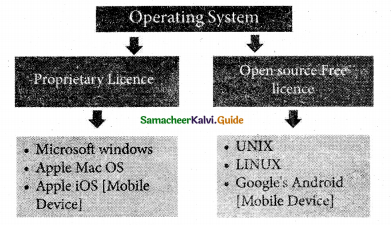
What is open source?
Answer:
Open source refers to a program or software in which the source code is available in the web to all public, without any cost.
Question 6.
What are the advantages of open source?
Answer:
The reasons individuals or organizations choose open source software are:
- lower cost
- security
- no vendor ‘lock-in’
- better quality
![]()
Question 7.
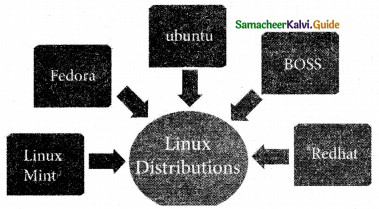
Mention the different server distributions in Linux OS.
Answer:
The server distribution in Linux OS:
- Ubuntu Linux
- Linux Mint
- Arch Linux
- Deepin
- Fedora
- Debian
- Centos
Question 8.
How will you log off from Ubuntu OS?
Answer:
When you have finished working on your computer, you can choose to Log Out through the Session Indicator on the far right side of the top panel.
Part – III
Explain in brief
Question 1.
Analyse: Why the drives are segregated?
Answer:
- It saves space and increases system performance.
- Sharing and protection.
- Segment and segregate the data to defend it from cyber-attacks.
![]()
Question 2.
If you are working on multiple files at a time, sometimes the system may hang. What is the reason behind it. How can you reduce it?
Answer:
Too Many Applications Running :
Each application open on the system takes some internal and hardware resources to keep it running. If multiple apps and programs are running, your PC may run low on resources as memory is used by a number of applications.
Device Driver Issues:
Outdated or damaged drivers can also be the reason behind frequent computer freezes. If video drivers being installed on your system are not updated, the computer might hang up while you attempt to play a video or game on the system.
Operating System Issues:
To ensure the smooth functioning of the machine, make sure that all updates are installed. To be able to keep the system updated, it is vital that you use a legal copy of the operating system.
Excess Heating Up:
If the temperature of your system processor is higher than usual, the chances are that the computer may freeze.
Hardware Misconfigyratioo:
One major reason behind the computer freeze issue is hardware misconfiguration, This may have occurred due to misconfigured hardware component that you recently added to the computer. Alternatively, the hardware component you added recently may be incompatible with the computer.
Question 3.
Are drives such as hard drive and floppy drives represented with drive letters? If so why, if not why?
Answer:
Yes, hard drives and floppy drives are represented with drive letters.
A: drive is used for floppy disk of 3.5 inches and storage capacity of 1.44 MB.
B: drive is for floppy of size 5.25 inches and of storage capacity of 1.2 MB
So, we can say like
A: First Floppy Drive
B: Second Floppy Drive
C: D : E: …………….. Z: Hard Disk Drives, CD/DVD
![]()
Question 4.
Write the specific use of Cortana.
Answer:
Cortana is your personal digital assistant on Windows 10 to help you find virtually anything on your device, track your packages and flights, inform you about weather and traffic information, manage your calendar and create reminders, and it can even tell you jokes.
Question 5.
List out the major differences between Windows and Ubuntu OS.
Answer:
| Windows | Ubuntu |
| Windows NT’ is the kernel used in Windows | Linux is the kernel used in Ubuntu |
| Needs to pay for Windows | It is completely free and available as open-source |
| It support executable files (.exe), Virus threatening exists | It does not support executable files (.exe) so, mostly it is virus-free OS |
| Desktop OS does not support server | Desktop OS can also work as a server |
| It does not support multiple desktop environments | It supports multiple desktop environments |
| Installation is very simple | Installation is quite complex process |
| Separately install MS Office in Windows | OS comes with many useful software like Office |
| It does not have own software manager | It has its own software manager |
| Software installation does that by simple installation package and instructions. | It normally installs the software and tools by terminal |
| User friendly | It is not user friendly |
![]()
Question 6.
Are there any difficulties you face while using Ubuntu? If so, mention it with reasons.
Answer:
- Ubuntu has less hardware support for commercial/industrial/medical/ logistical therefore it’s less voted for use in big-time backends.
- Ubuntu doesn’t support middlewares such as C panel, cloud Linux and a plethora of other infrastructure or monitoring tools.
- Hard to install graphic drivers especially for old hardware. It is not possible to play modern games, because of poor graphics quality.
- The user switching from windows will not like the user experience on Ubuntu and will have difficulty in operating the OS.
- Ubuntu is not capable of playing MP3 files by default.
![]()
Question 7.
Differentiate Thunderbird and Firefox in Ubuntu OS.
Answer:
- Firefox is a browser is access the internet.
- Thunderbird is an email client. We can install it on our computer and view our emails.
- Both Firefox and Thunderbird are Mozilla products.
Question 8.
Differentiate Save, Save As, and Save a Copy in Ubuntu OS.
Answer:
Save: This will save the document without asking for a new name or location. It will overwrite the original.
Save As: This will prompt you to save the document using a dialog box. You will have the ability to change the file name and/or location.
Save A Copy: This will prompt you to save a ‘copy’ using the same dialog box as ‘save as’. You will have the ability to change the file name and/or location. If you choose the same file name and location it will overwrite the original.
If you changed the name or location of the document you will be working on the original document, not the copy. This means that if you make additional changes and then hit save the original will be overwritten with the new changes, but the copy you saved earlier will be left at the state of the Save A Copy.
Part IV
Explain in detail
Question 1.
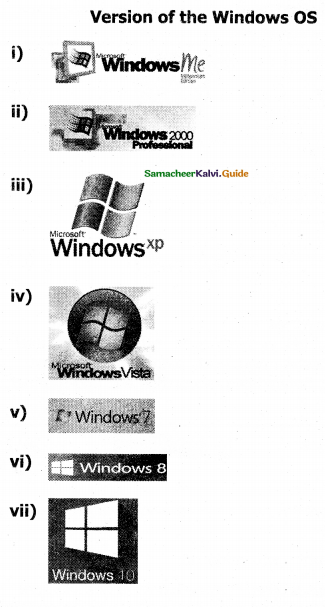
Explain the versions of the Windows Operating System.
Answer:
Versions of Windows Operating System
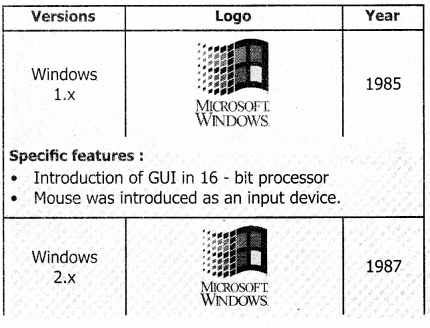
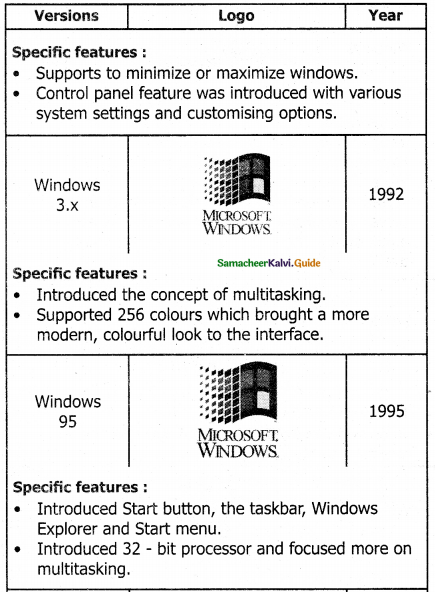
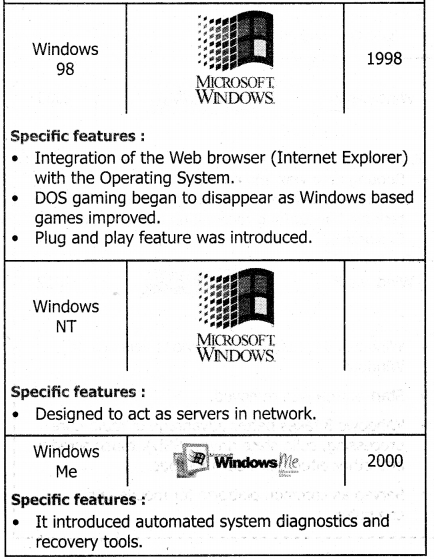

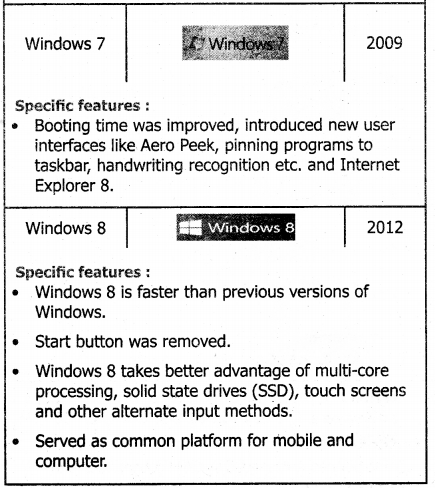
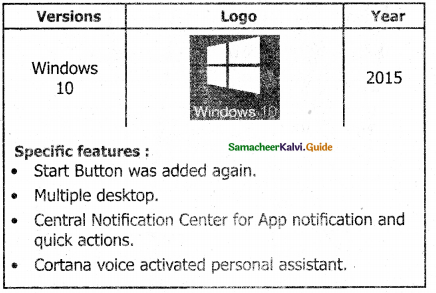
![]()
Question 2.
Draw and compare the scan equivalence in Windows and Ubuntu.
Answer:


Question 3.
Complete the following matrix.
| Navigational method | Located on | Ideally suited for |
| Start button | Taskbar | |
| Desktop | Exploring your disk drives and using system tools | |
| Windows
Explorer |
Seeing hierarchy of ail computer contents and resources in one window. | |
| Quick Launch |
Answer:
| Navigational method | Located on | Ideally suited for |
| Start button | Taskbar | To open the applications |
| My Computer | Desktop | Exploring your disk drives and using system tools |
| Windows Explorer | Start Button | Seeing hierarchy of all computer contents and resources in one window. |
| Quick Launch | Taskbar | To quickly launch programs that we place in it |
![]()
Question 4.
Observe the figure and mark all the window elements. Identify the version of the Windows OS.
Answer:
The element of a windows
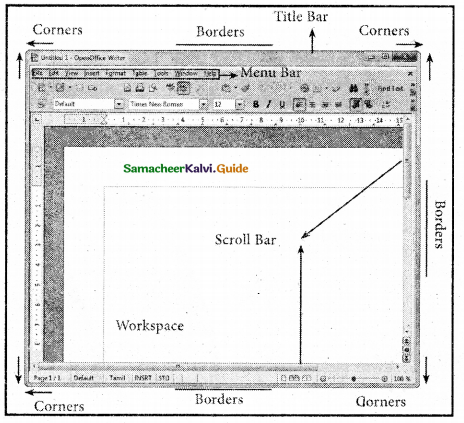
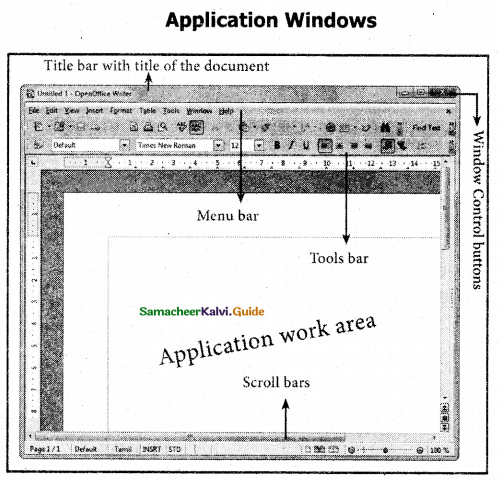
![]()
Question 5.
Write the procedure to create, rename, delete and save a file in Ubuntu OS. Compare it with Windows OS.
Answer:
The procedure to create, rename, delete and save a file in Ubuntu OS
Creating Files:
- We can create the files with the same procedure by clicking the Files icon,
- The following Figure shows the method of creating a File by right-clicking on the Desktop,
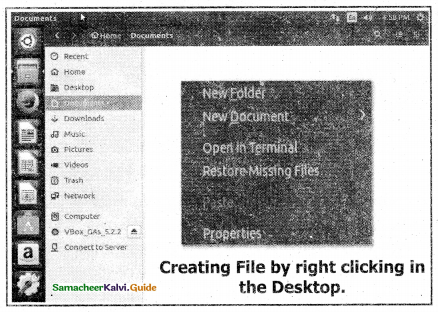
A new File can also be created by using File menu.

Deleting a File: A file created by us can be moved to trash by using right-click or by using the menu.
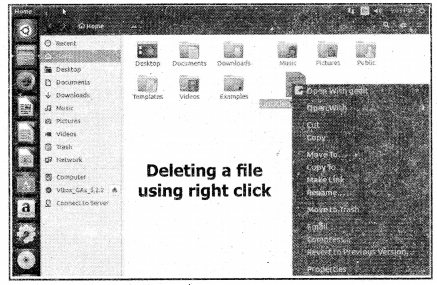
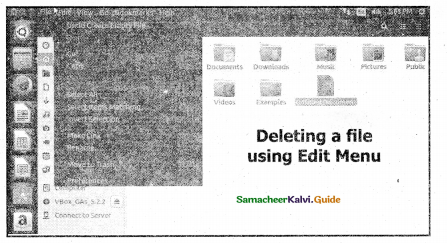
Deleting a File: Deleting a File by using the Edit menu.
Rename a file:
- Select the file.
- Right dick on the selected file and select Rename.
- Type the new filename and then, press Enter
The procedure to create, rename, delete and save a file in Windows OS
To create a file:
- Open the application using the Start button or through Icon or using the Run command.
- Enter the content.
- Save the file using Ctrl + S.
Renaming Files:
Using the FILE Menu
- Select the File you wish to Rename.
- Click File → Rename.
- Type in the new name.
- To finalize the renaming operation, press Enter.
To delete a file:
Select the file or folder you wish to delete.
- Right-click the file or folder, select the Delete option from the pop-up menu, or Click
File → Delete or press the Delete key from the keyboard. - The file will be deleted and moved to the Recycle bin.
To save a file:
Select the Save option from File Menu OR press Ctrl + S and then enter the file name and press OK.
![]()
11th Computer Science Guide Working with Typical Operating System (Windows & Linux) Additional Questions and Answers
Part I & Part II
Part – I
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
………………. is an Open source Operating System for desktop and server.
(a) Windows series
(b) Android
(c) iOS
(d) Linux
Answer:
(d) Linux
Question 2.
__________enables the hardware to communicate and operate with other software.
a) Loader
b) Compiler
c) Interpreter
d) Operating System
Answer:
d) Operating System
Question 3.
If you want to select multiple files or folders, use ……………….
(a) Ctrl + shift
(b) Ctrl + click
(c) shift + click
(d) Ctrl + shift + click
Answer:
(b) Ctrl + click
![]()
Question 4.
__________controls the overall execution of the computer.
a) Loader
b) Compiler
c) Interpreter
d) Operating System
Answer:
d) Operating System
Question 5.
………………. is one of the popular Open Source versions of the UNIX Operating System.
(a) Windows 7
(b) Windows 8
(c) Linux
(d) Android
Answer:
(c) Linux
Question 6.
The most popular Operating System for desktop and laptop computers.
a) Windows Series
b) Android
c) iOS
d) Linux
Answer:
a) Windows Series
Question 7.
………………. icon is the equivalent of Recycle bin of windows OS. All the deleted Files and Folders are moved here.
(a) Trash
(b) Files
(c) Online shopping
(d) Libre Office Impress
Answer:
(a) Trash
Question 8.
The most popular Operating System for Apple phones, iPad, and iPods.
a) Windows Series
b) Android
c) iOS
d) Linux
Answer:
c) iOS
![]()
Question 9.
………………. manages network connections, allowing you to connect to a wired or wireless network.
(a) Toolbar
(b) Title bar
(c) Session indicator
(d) Network indicator
Answer:
(d) Network indicator
Question 10.
Multiple applications can execute simultaneously in Windows, and this is known as __________
a) Multitasking
b) Multiuser
c) Parallel processing
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Multitasking
Question 11.
Clock is available in ……………….
(a) system tray
(b) Files
(c) start
(d) My documents
Answer:
(a) system tray
Question 12.
Windows Operating System uses __________as input device.
a) Keyboard
b) Mouse
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 13.
The menu bar is present below the ……………….
(a) Taskbar
(b) Scroll bar
(c) Title bar
(d) Function bar
Answer:
(c) Title bar
![]()
Question 14.
__________ is used to enter alphabets, numerals and special characters.
a) Keyboard
b) Mouse
c) Scanner
d) Optical Character Reader
Answer:
a) Keyboard
Question 15.
………………. has the task for frequently used applications?
(a) Quick Launch Tool bar
(b) Settings
(c) My pc
(d) This pc
Answer:
(a) Quick Launch Toolbar
Question 16.
__________program is an application program.
a) Word processing
b) Games and Spreadsheets
c) Calculator
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 17.
SSD stands for ……………….
(a) Solid State Devices
(b) Simple Stage Driver
(c) Single State Drivers
(d) Synchronized State Devices
Answer:
(a) Solid State Devices
![]()
Question 18.
__________is a file management activity.
a) Creating and Modifying file
b) Saving a file
c) Deleting a file
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 19.
What is the name given to the document window to enter or type the text?
(a) Workspace
(b) Work Area
(c) Typing Area
(d) Space
Answer:
(a) Workspace
Question 20.
Windows 1.x introduced in the year __________
a) 1992
b) 1987
c) 1985
d) 1982
Answer:
c) 1985
Question 21.
The disk drives mounted in the system can be seen by clicking ……………….
(a) Disk drive Icon
(b) Drive Icon
(c) Device Driver Icon
(d) My Computer Icon
Answer:
(d) My Computer Icon
Question 22.
Windows 3.x introduced in the year __________
a) 1992
b) 1987
c) 1985
d) 1982
Answer:
a) 1992
![]()
Question 23.
Windows 10 was developed in the year ……………….
(a) 2009
(b) 2012
(c) 2015
(d) 2018
Answer:
(c) 2015
Question 24.
Windows 98 introduced in the year __________
a) 1992
b) 1988
c) 1998
d) 1995
Answer:
c) 1998
Question 25.
The Rulers are used to set ……………….
(a) Orientations
(b) Header
(c) Footer
(d) Margins
Answer:
(d) Margins
Question 26.
Windows-XP introduced in the year __________
a) 2002
b) 2000
c) 1990
d) 2001
Answer:
d) 2001
Question 27.
Which functional key is used to bring the focus on, the first menu of the menu bar?
(a) F5
(b) F10
(c) F11
(d) F7
Answer:
(b) F10
![]()
Question 28.
Windows-7 introduced in the year __________
a) 2002
b) 2007
c) 2009
d) 2010
Answer:
c) 2009
Question 29.
Which one of the following is used to open the search results dialog box?
(a) search
(b) See more results
(c) search more results
(d) searching web
Answer:
(b) See more results
Question 30.
Windows-10 introduced in the year __________
a) 2012
b) 2015
c) 2009
d) 2010
Answer:
b) 2015
Question 31.
The keyboard shortcut to save a file is ……………….
(a) alt + s
(b) Ctrl + s
(c) Ctrl + alt + s
(d) winkey + s
Answer:
(b) Ctrl + s
![]()
Question 32.
In which version Start button window introduced.
a) Windows-XP
c) Windows 2.x
b) Windows 3.x
d) Windows 95
Answer:
d) Windows 95
Question 33.
Applications or files or folders are opened using related shortcut icons by ……………….
(a) Click and drag
(b) double click
(c) click
(d) drag and drop
Answer:
(b) double click
Question 34.
In which Windows version plug and play was introduced.
a) Windows-XP
b) Windows 98
c) Windows-Vista
d) Windows 95
Answer:
b) Windows 98
Question 35.
Which option is used to save the file?
(a) Ctrl + s
(b) Save
(c) File + save
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question 36.
Which Windows version was designed to act as servers in the network.
a) Windows-XP
b) Windows 98
c) Windows-Vista
d) Windows-NT
Answer:
d) Windows-NT
![]()
Question 37.
ubuntu supports an office suite called ……………….
(a) Open Office
(b) Star Office
(c) Libre Office
(d) MS – Office
Answer:
(c) Libre Office
Question 38.
__________versions of Windows 2000 were released.
a) 6
b) 5
c) 4
d) 3
Answer:
c) 4
Question 39.
Which one of the following is a server distribution of Linux?
(a) Deepin
(b) Firefox
(c) MS.word
(d) Files
Answer:
(a) Deepin
Question 40.
Which version of Windows 2000 released for both a Web server and an office server.
a) Professional
b) Data Centre Server
c) Advanced Server
d) Server
Answer:
d) Server
Question 41.
Which option is used to delete all files in the Recycle bin?
(a) Remove the Recycle bin
(b) Empty the Recycle bin
(c) Clear the Recycle bin
(d) Clean the Recycle bin
Answer:
(b) Empty the Recycle bin
Question 42.
Which version of Windows 2000 released for high-traffic computer networks.
a) Professional
b) Data Centre Server
c) Advanced Server
d) Server
Answer:
b) Data Centre Server
![]()
Question 43.
Which version of Windows introduced as a stable version.
a) Windows-XP
b) Windows Me
c) Windows-Vista
d) Windows-NT
Answer:
a) Windows-XP
Question 44.
In which version of Windows booting time was improved.
a) Windows-7
b) Windows Me
c) Windows-Vista
d) Windows-NT
Answer:
a) Windows-7
Question 45.
__________feature is introduced in Windows-7.
a) Aero peek
b) Pinning programms to the taskbar
c) Handwriting recognition
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 46.
What is used to interact with windows by clicking icons?
(a) Mouse
(b) Keyboard
(c) Monitor
(d) Printer
Answer:
(a) Mouse
Question 47.
Which version of Windows served as a common platform for mobile and computer.
a) Windows-7
b) Windows – 8
c) Windows-Vista
d) Windows-NT
Answer:
b) Windows – 8
![]()
Question 48.
Windows-8 takes better advantage of_________
a) multi-core processing
b) solid-state drives
c) touch screens
d) all the above
Answer:
d) all the above
Question 49.
The start button was added again in the version of Windows.
a) Windows-7
b) Windows-8
c) Windows-Vista
d) Windows-10
Answer:
d) Windows-10
Question 50.
Hardware settings are used in which option?
(a) Monitor
(b) Display
(c) Theme
(d) My Computer
Answer:
(b) Display
![]()
Question 51.
Cortana voice activated personal assistance introduced in _________version of Windows.
a) Windows-7
b) Windows-8
c) Windows-Vista
d) Windows-10
Answer:
d) Windows-10
Question 52.
The opening screen of Windows is called
a) taskbar
b) system tray
c) desktop
d) none of the above
Answer:
c) desktop
Question 53.
The notification area of ubuntu-desktop is otherwise called……………….
(a) Task bar
(b) Desktop
(c) status bar
(d) Indicator area
Answer:
(d) Indicator area
Question 54.
_________is a graphic symbol representing the window elements like files, folders, shortcuts etc.
a) Taskbar
b) Icon
c) Shortcut key
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Icon
Question 55.
_________play a vital role in GUI based applications.
a) Taskbar
b) Icon
c) Shortcut key
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Icon
Question 56.
The icons which are available on the desktop by default while installing Windows OS are called __________icons.
a) quick launch
b) standard
c) default
d) desktop
Answer:
b) standard
Question 57.
Which menu has the rename option?
(a) File
(b) Edit
(c) View
(d) Window
Answer:
(a) File
Question 58.
_________icons can be created for any application or file or folder.
a) Standard
b) Default
c) Shortcut
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Shortcut
Question 59.
By double-clicking the _________icon, the related application or file or folder will open.
a) Standard
b) Default
c) Shortcut
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Shortcut
Question 60.
The disk drive icons graphically represent _________disk drive options.
a) six
b) five
c) three
d) four
Answer:
b) five
Question 61.
Which option reboot the computer?
(a) Restart
(b) Boot
(c) Reboot
(d) Reselect
Answer:
(a) Restart
Question 62.
The disk drive icons available for __________
a) Removable storage
b) Network drive
c) Pen drive
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 63.
__________is a typical rectangular area in an application or a document.
a) Cell pointer
b) Window
c) Table cell
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Window
Question 64.
_________ is an area on the screen that displays information for a specific program.
a) Cell pointer
b) Window
c) Table cell
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Window
Question 65.
Who developed Ubuntu OS?
(a) Mark Shuttleworth
(b) Ricki Mascitti
(c) Dan Bricklin
(d) Bob Frankston
Answer:
(a) Mark Shuttleworth
Question 66.
Application window can be __________
a) resized
b) maximized or minimized
c) placed side by side or overlap
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 67.
When two or more windows are open, only one of them is active and the rest are__________
a) inactive
b) hidden
c) minimized
d) maximized
Answer:
a) inactive
Question 68.
A __________is a section of the screen used to display the contents of a document.
a) System Window
b) Application Box
c) Application Window
d) Document Window
Answer:
d) Document Window
Question 69.
How many sets of scroll bars are there?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(a) 2
Question 70.
__________ window is used for typing, editing, drawing, and formatting the text and graphics.
a) System Window
b) Application Box
c) Application Window
d) Document Window
Answer:
d) Document Window
Question 71.
__________window helps the user to communicate with the Application program.
a) System Window
b) Application Box
c) Application Window
d) Document Window
Answer:
c) Application Window
Question 72.
The title bar of a window will contain __________button.
a) minimize
b) maximize
c) close
d) all the above
Answer:
d) all the above
Question 73.
What is the name given to the larger window?
(a) Work window
(b) Document window
(c) Application window
(d) Desktop
Answer:
(c) Application window
Question 74.
__________in the menu bar can be accessed by pressing the Alt key and the letter that appears underlined in the menu title.
a) Menu
b) Title
c) Tool
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Menu
Question 75.
In Windows 7, in the absence of the menu bar, click __________and from the drop-down menu, click the Layout option and select the desired item from that list.
a) System Properties
b) Install
c) Uninstall
d) Organize
Answer:
d) Organize
Question 76.
The __________is the area in the document window to enter or type the text of your document.
a) application space
b) text space
c) content space
d) workspace
Answer:
d) workspace
Question 77.
The scroll bars are used to scroll the workspace __________
a) horizontally
b) vertically
c) either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) either A or B
Question 78.
Which option is used as a part of installing new software or windows update?
(a) Lock
(b) Restart
(c) Sleep
(d) Hibernate
Answer:
(b) Restart
Question 79.
Using the __________menu, we can start any application.
a) Start
b) File
c) Format
d) Tools
Answer:
a) Start
Question 80.
At the bottom of the screen is a horizontal bar called the __________
a) scrollbar
b) taskbar
c) quick launch toolbar
d) system tray
Answer:
b) taskbar
Question 81.
Task bar contains __________
a) Start button
b) shortcuts to various programs
c) minimized programs
d) all the above
Answer:
d) all the above
Question 82.
In the taskbar, the extreme right corner we can see the __________.
a) Start button
b) shortcuts to various programs
c) minimized programs
d) system tray
Answer:
d) system tray
Question 83.
System trays contains __________
a) volume control
b) network
c) date and time
d) all the above
Answer:
d) all the above
Question 84.
In the taskbar, __________contains task for frequently used applications.
a) scroll bar
b) start button
c) quick launch toolbar
d) system tray
Answer:
c) quick launch toolbar
Question 85.
By clicking the __________icon, the user can see the disk drivers mounted in the system in windows-XP and Windows Vista.
a) This PC
b) My Document
c) Computer
d) My Computer
Answer:
c) Computer
Question 86.
By clicking the __________icon, the user can see the disk drivers mounted in the system in Windows-8.
a) This PC
b) My Document
c) Computer
d) My Computer
Answer:
d) My Computer
Question 87.
The functionality of computer icon _________in all versions of Windows.
a) differs
b) remains the same
c) slightly change
d) None of these
Answer:
b) remains the same
Question 88.
By clicking the _________ icon, the user can see the disk drivers mounted in the system in Windows-7.
a) This PC
b) My Document
c) Computer
d) My Computer
Answer:
c) Computer
Question 89.
We can also open an application by clicking __________on the Start menu, and the name of the application.
a) Run
b) All Programs
c) Accessories
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Run
Question 90.
To quit an application, click the __________ button in the upper right corner of the application window.
a) Minimize
b) Maximize
c) Resize
d) Close
Answer:
d) Close
Question 91.
We can also quit an application by clicking on the option in Windows 7.
a) File → Exit
b) File → Close
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 92.
In Windows-7, we can organize your documents and programs in the form of_________
a) files
b) folder
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 93.
We can_________ the files and folders.
a) move and copy
b) rename and delete
c) search
d) all the above
Answer:
d) all the above
Question 94.
To better organise our files, we can store them in __________
a) shortcut
b) folder
c) recycle bin
d) None of these
Answer:
b) folder
Question 95.
There are __________ways in to create a new folder.
a) 5
b) 4
c) 3
d) 2
Answer:
d) 2
Question 96.
__________is a command to create a new folder.
a) File → New → Directory
b) File → New → Folder
c) File → Open → Folder
d) File → New → New Folder
Answer:
b) File → New → Folder
Question 97.
The default name of the new folder is__________
a) New folder
b) Untitled
c) Noname
d) None of these
Answer:
a) New folder
Question 98.
To create a folder in the desktop __________command is used.
a) left-click → New → Folder
b) right-click → New → Directory
c) double click → New → Folder
d) right-click → New → Folder
Answer:
d) right-click → New → Folder
Question 99.
_________ is an in-built word processor application in Windows OS.
a) Word
b) Wordstar
c) Wordpad
d) Notepad
Answer:
c) Wordpad
Question 100.
In Windows OS to create and manipulate text documents __________is used by default.
a) Word
b) Wordstar
c) Wordpad
d) Notepad
Answer:
c) Wordpad
Question 101.
__________is used to open Wordpad.
a) Click Start → All Programs → Accessories → Wordpad.
b) Run → type Wordpad, click OK
c) Either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Either A or B
Question 102.
In Wordpad, save the file using __________
a) File → Save
b) Ctrl + S
c) Either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Either A or B
Question 103.
In the Save As dialog box, select the location where you want to save the file by using the _______drop down list box.
a) filename
b) look in
c) file type
d) None of these
Answer:
b) look in
Question 104.
We can use the _______ box on the Start menu to quickly search a particular folder or file in the computer or in a specific drive.
a) Find
b) Search
c) Look in
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Search
Question 105.
The most common way of opening a file or a Folder is to _______on it.
a) right-click
b) double click
c) click and drag
d) move the mouse
Answer:
b) double click
Question 106.
How many methods are there to rename a file?
a) 4
b) 3
c) 2
d) only one
Answer:
b) 3
Question 107.
_______is the command for cut operation.
a) Edit → Cut
b) File → Cut
c) Format → Cut
d) Window → Cut
Answer:
a) Edit → Cut
Question 108.
_______is the shortcut for cut operation.
a) Ctrl + C
b) Ctrl + X
c) Ctrl + P
d) Ctrl + V
Answer:
b) Ctrl + X
Question 109.
_______is the command for copy operation.
a) Edit → Copy
b) File → Copy
c) Format → Copy
d) Window → Copy
Answer:
a) Edit → Copy
Question 110.
_______is the shortcut for copy operation.
a) Ctrl + C
b) Ctrl + X
c) Ctrl + P
d) Ctrl + V
Answer:
a) Ctrl + C
Question 111.
_______is the command for paste operation.
a) Edit → Paste
b) File → Paste
c) Format → Paste
d) Window → Paste
Answer:
a) Edit → Paste
Question 112.
_______is the shortcut for paste operation.
a) Ctrl + C
b) Ctrl + X
c) Ctrl + P
d) Ctrl + V
Answer:
d) Ctrl + V
Question 113.
_______is used for copy operation.
a) Click Edit Copy
b) Press Ctrl + C
c) Right click → Copy from the pop-up menu
d) all the above
Answer:
d) all the above
Question 114.
_______is used for cut operation.
a) Click Edit → Cut
b) Press Ctrl + X
c) Right click Cut from the pop-up menu
d) all the above
Answer:
d) all the above
Question 115.
_______is used for paste operation.
a) Click Edit → Paste
b) Press Ctrl + V
c) Right click → Paste from the pop-up menu
d) all the above
Answer:
d) all the above
Question 116.
There are _______methods of transferring files to or from a removable disk.
a) 2
b) 3
c) only one
d) None of these
Answer:
a) 2
Question 117.
_______is a method of transferring files to or from a removable disk.
a) Copy and Paste
b) Send To
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 118.
If you want to select multiple files or folders, use _______
a) Ctrl + Click
b) Shift + Click
c) Alt + Click
d) All the above
Answer:
a) Ctrl + Click
Question 119.
If you want to select consecutive files or folders, click on the first file and then use_______at the last file.
a) Ctrl + Click
b) Shift + Click
c) Alt + Click
d) All the above
Answer:
b) Shift + Click
Question 120.
When we delete a file or folder, it will move into the _______
a) My Document
b) My Computer
c) Recycle Bin
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Recycle Bin
Question 121.
To permanently delete a file or folder (i.e. to avoid sending a file or folder to the Recycle Bin), hold down the _______key, and press deletes on the keyboard.
a) ALT
b) SHIFT
c) CTRL
d) None of these
Answer:
b) SHIFT
Question 122.
_______is a special folder to keep the files or folders deleted by the user.
a) My Document
b) My Computer
c) Recycle Bin
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Recycle Bin
Question 123.
The user cannot access the files or folders available in the Recycle bin without _______it.
a) deleting
b) copy
c) restoring
d) None of these
Answer:
c) restoring
Question 124.
To delete all files in the Recycle bin, select _______option.
a) Empty the Recycle Bin
b) Clear the Recycle bin
c) Trash
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Empty the Recycle Bin
Question 125.
_______option is used to switch to another user account on the computer without closing our open programs and Windows processes.
a) log-off
b) switch user
c) sleep
d) restart
Answer:
b) switch user
Question 126.
_________ option is used to switch to another user account on the computer after closing all your open programs and Windows processes.
a) log-off
b) switch user
c) sleep
d) restart
Answer:
a) log-off
Question 127.
_______ option is used to reboot the computer.
a) log-off
b) switch user
c) sleep
d) restart
Answer:
d) restart
Question 128.
_______option is often required as part of installing new software or Windows update.
a) log-off
b) switch user
c) sleep
d) restart
Answer:
d) restart
Question 129.
_______option puts the computer into a low-power mode that retains all running programs and open Windows in computer memory for a super-quick restart.
a) log-off
b) switch user
c) sleep
d) restart
Answer:
c) sleep
Question 130.
_______option found only on laptop computers.
a) hibernate
b) shutdown
c) sleep
d) restart
Answer:
a) hibernate
Part II
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
_______refers to a program or software in which the source code is available on the web to the general public free of cost.
a) malware
b) free source
c) open-source
d) None of these
Answer:
c) open-source
Question 2.
_______is typically created as a collaborative effort in which programmers continuously improve upon the source code on the web and share the changes within the community.
a) malware
b) free source code
c) open-source code
d) None of these
Answer:
c) open-source code
Question 3.
_______is one of the popular Open Source versions of the UNIX Operating System.
a) Linux
b) MSDOS
c) Oracle
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Linux
Question 4.
_______is open source as its source code is freely available.
a) Linux
b) MSDOS
c) Oracle
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Linux
Question 5.
The most popular Linux server distributor is_______
a) Ubuntu Linux
b) Linux Mint
c) Arch Linux
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 6.
The most popular Linux server distributor is_______
a) Deepin and Fedora
b) Debian
c) CentOS
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 7.
_______ is a Linux-based operating system.
a) Ubuntu
b) MSDOS
c) Oracle
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Ubuntu
Question 8.
_______ is designed for computers, smartphones, and network servers.
a) Ubuntu
b) MSDOS
c) Oracle
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Ubuntu
Question 9.
The Ubuntu system is developed by a UK based company called ._______
a) Microsoft
b) Borland International
c) Cambridge
d) Canonical Ltd
Answer:
d) Canonical Ltd
Question 10.
Ubuntu was conceived in the year _______
a) 1994
b) 2004
c) 2014
d) 2012
Answer:
b) 2004
Question 11.
Ubuntu was conceived by_______
a) Mark Shuttleworth
b) Mark Zuckerberg
c) Mark Shuttleberg
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Mark Shuttleworth
Question 12.
The desktop version of Ubuntu supports _______ software.
a) Firefox
b) Chrome
c) VLC
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 13.
Ubundu supports the office suite called_______
a) MS-Office
b) Star Office
c) Libre Office
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Libre Office
Question 14.
Ubuntu has in-built email software called_______
a) Firefox
b) Thunderfox
c) Firebird
d) Thunderbird
Answer:
d) Thunderbird
Question 15.
_______ gives the user access to email such as Exchange, Gmail, Hotmail, etc.
a) Firefox
b) Thunderfox
c) Firebird
d) Thunderbird
Answer:
d) Thunderbird
Question 16.
The best feature of Ubundu is _______
a) It is a free operating system
b) It is backed by a huge open source community
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 17.
_______ is based on the concept of a Graphical User Interface.
a) Ubundu
b) Microsoft Windows
c) Apple
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 18.
_______ is the icons in the Ubuntu OS.
a) Search your Computer
b) Files
c) Firefox Web browser
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 19.
_______ is a word processor software of Ubundu.
a) LibreOffice Writer
b) LibreOfficeCalc
c) LibreOffice Impress
d) None of these
Answer:
a) LibreOffice Writer
Question 20.
_______ is a spreadsheet software of Ubundu.
a) LibreOffice Writer
b) LibreOfficeCalc
c) LibreOffice Impress
d) None of these
Answer:
b) LibreOfficeCalc
Question 21.
_______ is a Presentation software of Ubundu.
a) LibreOffice Writer
b) LibreOfficeCalc
c) LibreOffice Impress
d) None of these
Answer:
c) LibreOffice Impress
Question 22.
_______ is the online shopping icon of Ubundu.
a) Amazon
b) Firefox
c) Bigshop
d) Wallmart
Answer:
a) Amazon
Question 23.
_______ is a Recycle Bin Icon of Ubundu.
a) Amazon
b) Firefox
c) Files
d) Trash
Answer:
d) Trash
Question 24.
In Unundu, the frequently used icons in the menu bar are found on the _______
a) left
b) middle
c) right
d) Either A or B or C
Answer:
c) right
Question 25.
The most common indicators in the Menu bar are located in the _______ .
a) Indicator
b) Notification area
c) Either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Either A or B
Question 26.
_______ manages network connections, allowing you to connect to a wired or wireless network.
a) Indicator
b) Notification area
c) Either A or B
d) Network Indicator
Answer:
d) Network Indicator
Question 27.
_______ shows the current keyboard layout.
a) Indicator
b) Notification area
c) Text Entry Settings
d) Network Indicator
Answer:
c) Text Entry Settings
Question 28.
The keyboard indicator menu contains the_______ menu items.
a) Character Map
b) Keyboard Layout Chart
c) Text Entry Settings
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 29.
_______ indicator incorporates your social applications.
a) Messaging
b) Sound
c) Session
d) Network
Answer:
a) Messaging
Question 30.
From Messaging indicator, we can access _______
a) instant messenger
b) email clients
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 31.
_______ indicator provides an easy way to adjust the volume as well as access your music player.
a) Messaging
b) Sound
c) Session
d) Network
Answer:
b) Sound
Question 32.
_______ indicator is a link to the system settings, Ubuntu Help, and session options
a) Messaging
b) Sound
c) Session
d) Network
Answer:
c) Session
Question 33.
_______ displays the current time and provides a link to your calendar and time and date settings.
a) Indicator
b) Clock
c) System Tray
d) Notification Area
Answer:
b) Clock
Question 34.
_______ is a session option.
a) locking your computer and user/guest session
b) logging out of a session
c) restarting the computer or shutting down completely
d) all the above
Answer:
d) all the above
Question 35.
The _______ shows the name of the currently selected directory.
a) Title bar
b) System Tray
c) Notification Area
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Title bar
Question 36.
The toolbar displays _______
a) your directory browsing history
b) your location in the file system
c) a search button and options for your current directory view
d) all the above
Answer:
d) all the above
Question 37.
The default Ubuntu 16.04 theme known as_______
a) Ambiance
b) Aspirant
c) Environment
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Ambiance
Question 38.
The Launcher is equivalent to _______
a) System Tray
b) Taskbar
c) Desktop
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Taskbar
Question 39.
The vertical bar of icons on the left side of the desktop is called _______
a) System Tray
b) Taskbar
c) Launcher
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Launcher
Question 40.
The Launcher provides easy access to _______
a) applications
b) mounted devices
c) Trash
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 41.
All current applications on your system will place an icon in the _______
a) System Tray
b) Taskbar
c) Launcher
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Launcher
Question 42.
_______ icon is equal to the search button in Windows OS.
a) Search Your Computer
b) Find
c) Quick Search
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Search Your Computer
Question 43.
_______ icon is equivalent to My Computer icon.
a) Your Computer
b) Files
c) Quick Search
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Files
Question 44.
We can directly go to Desktop, Documents using_______ icon.
a) Your Computer
b) Files
c) Quick Search
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Files
Question 45.
By clicking the _______ icon, we can directly browse the internet.
a) Amazon
b) Firefox Web Browser
c) Bishop
d) Walmart
Answer:
b) Firefox Web Browser
Question 46.
_______ is equivalent to clicking the Web Browser in Taskbar in Windows.
a) Amazon
b) Firefox Web Browser
c) Bigshop
d) Walmart
Answer:
b) Firefox Web Browser
Question 47.
_______ icon will directly take you to document preparation applications like MS Word in Windows.
a) LibreOffice Writer
b) LibreOfficeCalc
c) LibreOffice Impress
d) None of these
Answer:
a) LibreOffice Writer
Question 48.
_______ icon will open LibreOffice Calc application.
a) LibreOffice Writer
b) Libre Office Caic
c) LibreOffice Impress
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Libre Office Caic
Question 49.
_______ is similar to MS Excel in Windows.
a) LibreOffice Writer
b) Libre Office Caic
c) LibreOffice Impress
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Libre Office Caic
Question 50.
_______ icon is used to prepare any presentations in Ubuntu like MS PowerPoint.
a) LibreOffice Writer
b) LibreOfficeCaic
c) LibreOffice Impress
d) None of these
Answer:
c) LibreOffice Impress
Question 51.
_______ icon will let you add any additional applications you want.
a) LibreOffice Writer
b) LibreOfficeCalc
c) LibreOffice Impress
d) Ubundu Software
Answer:
d) Ubundu Software
Question 52.
Using _______ icon users can buy and sell any products online.
a) Amazon
b) Firefox Web Browser
c) Online Shopping
d) Wallnnart
Answer:
c) Online Shopping
Question 53.
_______ icon is similar to the Control panel in the Windows Operating System.
a) System Settings
b) Your Computer
c) Launcher
d) None of these
Answer:
a) System Settings
Question 54.
Match the following:
table
a) Trash 1. Online Shopping App
b) System Settings 2. Recycle Bin
c) LibreOffice Impress 3. Control Panel
d) Amazon 4. Presentation software
a) 2, 1, 4, 3
b) 4, 3, 1, 2
c) 3, 1, 4, 2
d) 2, 3, 4, 1
Answer:
d) 2, 3, 4, 1
Question 55.
Identify the correct statement from the following:
a) In Ubundu, all the deleted Files and Folders are moved to Trash
b) Similar to Windows OS, we can create, delete the files and folders with the same procedure by clicking the Files icon in Ubundu.
c) A new File or new Folder can also be created by using File menu in Ubundu
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 56.
Shutting down Ubuntu using Session _______ option.
a) Log out
b) Suspend
c) Shutdown
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Part – I
Shot Answers
Question 1.
Name some distributions of Linux.
Answer:
- Fedora
- Ubuntu
- BOSS
- RedHat
- Linux Mint.
Question 2.
What are the most popular operating systems suitable for desktop and laptop computers?
Answer:
All the Windows Series like Windows Vista, Windows-7, etc operating systems are suitable for desktop and laptop computers.
Question 3.
What is Open source Operating system?
Answer:
It is the software in which the source code is available to the general public for use and modification from its original design, free of charge.
Question 4.
Which operating system suitable for Apple phones, iPad, and iPods?
Answer:
iOS operating systems are suitable for Apple phones, iPad, and iPod.
Question 5.
What are the similarities between Ubuntu and other operating systems?
Answer:
All are based on the concepts of Graphical User Interface.
Question 6.
What is multitasking?
Answer:
Multiple applications can execute simultaneously in Windows, and this is known as multitasking.
Question 7.
What is a workspace of a window?
Answer:
The workspace is the area in the document window to enter or type the text of your document. The workspace is the element of a window.
Question 8.
What are the file management activities?
Answer:
File management activities are creating, modifying, saving, deleting files and folders.
Question 9.
What are the four versions of Windows 2000 and its application?
Answer:
The four versions of Windows 2000 are:
- Windows 2000 – Professional – for business desktop and laptop systems.
- Windows 2000 – Server – for both a Web server and an office server.
- Windows 2000 – Advanced Server – for line-of-business applications.
- Windows 2000 – Data Centre Server – for high-traffic computer networks.
Question 10.
What is Firefox?
Answer:
It is a browser.
Question 11.
What is a desktop?
Answer:
The opening screen of Windows is called Desktop.
Question 12.
Write a note on Icons.
Answer:
Icon is a graphic symbol representing the window elements like files, folders, shortcuts etc. Icons play a vital role in GUI based applications.
Question 13.
What do you mean by standard icon? Give an example.
Answer:
The icons which are available on desktop by default while installing Windows OS are called standard icons. The standard icons available in all Windows OS are My Computer, Documents and Recycle Bin.
Question 14.
How will you switch to desktop?
Answer:
We can move to the Desktop any time by pressing the Winkey + D or using Aero Peek while working in any application.
Question 15.
Define Window.
Answer:
Window is a typical rectangular area in an application or a document. It is an area on the screen that displays information for a specific program.
Question 16.
Write note on document window.
Answer:
A document window is a section of the screen used to display the contents of a document.
Question 17.
Write a note on Recycle Bin.
Answer:
Recycle Bin: Recycle bin is a special folder to keep the files or folders deleted by the user, which means you still have an opportunity to recover them. The user cannot access the files or folders available in the Recycle bin without restoring it.
Question 18.
How will you restore file or folder from Recycle Bin?
Answer:
To restore file or folder from the Recycle Bin
- Open Recycle bin.
- Right-click on a file or folder to be restored and select the Restore option from the pop-up menu.
- To restore multiple files or folders, select Restore all items.
- To delete all files in the Recycle bin, select Empty the Recycle Bin.
Question 19.
How will you create a desktop shortcut?
Answer:
Creating Shortcuts on the Desktop:
Shortcuts to your most often used folders and files may be created and placed on the Desktop to help automate your work.
- Select the file or folder that you wish to have as a shortcut on the Desktop.
- Right-click on the file or folder.
- Select Send to from the shortcut menu, then select Desktop (Create Shortcut) from the sub¬menu.
- A shortcut for the file or folder will now appear on your desktop and you can open it from the desktop in the same way as any other icon.
Question 20.
How will you log off/shut down the computer?
Answer:
To Log off/Shut down the computer :
- Click start to → log off (click the arrow next to Shut down) or Start Shutdown.
- If you have any open programs, then you will be asked to close them or windows will Force shut down, you will lose any unsaved information if you do this.
Question 21.
Compare switch user and log off options.
Answer:
- Switch User: Switch to another user account on the computer without closing your open programs and Windows processes.
- Log Off: Switch to another user account on the computer after closing all your open programs and Windows processes.
Question 22.
When we use the Lock and Restart option?
Answer:
- Lock: Lock the computer while you’re away from it.
- Restart: Reboot the computer. This option is often required as part of installing new software or Windows update.
Question 23.
Write a note on the Sleep mode option.
Answer:
Sleep: Puts the computer into a low-power mode that retains all running programs and open Windows in computer memory for a super-quick restart.
Question 24.
Write a note on Hibernate mode option? Where it is available?
Answer:
The Hibernate option is found only on laptop computers. It puts the computer into a low-power mode after saving all running programs and open windows on the machine’s hard drive for a quick restart.
Part – II
Short Answers
Question 1.
How will you rename the files or folders?
Answer:
Using the FILE Menu
- Select the File or Folder you wish to Rename.
- Click File → Rename.
- Type in the new name.
- To finalize the renaming operation, press Enter
Question 2.
What are the merits of open source code?
Answer:
Open Source code is typically created as a collaborative effort in which programmers continuously improve upon the source code on the web and share the changes within the community.
Question 3.
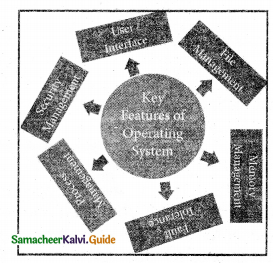
List out the important functions of an OS?
Answer:
Following are some of the important functions of an Operating System:
- Memory Management
- Process Management
- Device Management
- File Management
- Security Management
- Control overall system performance
- Error detecting aids
- Coordination between other software and users
Question 4.
List the distributors of Linux.
Answer:
The most popular Linux server distributors are: Ubuntu Linux
- Linux Mint
- Arch Linux
- Deepin
- Fedora
- Debian
- CentOS
Question 5.
Write about Ubuntu.
Answer:
Ubuntu is a Linux-based operating system. It is designed for computers, smartphones, and network servers. The system is developed by a UK-based company called Canonical Ltd. Ubuntu was conceived in 2004 by Mark Shuttleworth, a successful South African entrepreneur.
Question 6.
Write note on the Network indicator.
Answer:
Network indicator – This manages network connections, allowing you to connect to a wired or wireless network.
Question 7.
What are the four versions of Windows 2000?
Answer:
- Professional – business desktop and laptop systems.
- Server – used as both a web server and an office server.
- Advanced server – for a line of business applications.
- Datacenter server – for high-traffic computer networks.
Question 8.
Write note on the Sound indicator.
Answer:
Sound indicator – This provides an easy way to adjust the volume as well as access your music player.
Question 9.
What is a Window?
Answer:
Window is a typical rectangular area in an application or a document. It is an area on the screen that displays information for a specific program. The two types of windows are the application window and the document window.
Question 10.
Write about session indicators.
Answer:
Session indicator – This is a link to the system settings, Ubuntu Help, and session options like locking your computer, user/guest session, logging out of a session, restarting the computer, or shutting down completely.
Question 11.
How will you start an application?
Answer:
- Click the start button and then point to all programs. The program menu appears. Point to the group that contains the application you want to start and then click the application name.
- Click Run on the start menu and type the name of the application and click ok.
Question 12.
Write about Toolbar of Ubuntu.
Answer:
Toolbar – The toolbar displays your directory browsing history, your location in the file system, a search button, and options for your current directory view.
Question 13.
Write a note on Recycle bin.
Answer:
Recycle bin is a special folder to keep the files or folders deleted by the user. From the recycle bin, files can be restored back.
Part – I
Explain brief
Question 1.
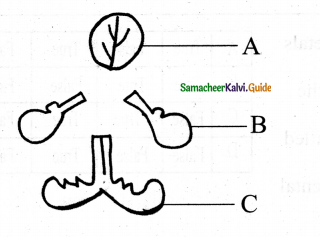
Discuss the following Icons.
Answer:
Shortcut Icons:
Shortcut icons can be created for any application or file or folder. By double-clicking the icon, the related application or file, or folder will open. This represents the shortcut to open a particular application.
Disk drive icons:
The disk drive icons graphically represent five disk drive options.
- Hard disk.
- CD – ROM/DVD Drive.
- Pen drive.
- Other removable storage such as mobile, smartphone, tablet, etc.
- Network drives if your system is connected with another system.
Question 2.
What is a shortcut icon? Mention its types.
Answer:
Shortcut icons can be created for any application or file or folder. By double-clicking the icon, the related application or file, or folder will open.
Type of shortcuts:
- Desktop shortcut
- Keyboard shortcut
Question 3.
Write notes on disk drive icons.
Answer:
The disk drive icons graphically represent five disk drive options.
- Hard disk.
- CD-ROM/DVD Drive
- Pen drive
- Other removable storage such as mobile, smartphone, tablet, etc.
- Network drives if your system is connected with another system.
Question 4.
What is the application window? Explain with an example.
Answer:
It is an area on a computer screen with defined boundaries, and within which information is displayed.
Such windows can be resized, maximized, minimized, placed side by side, overlap, and so on.
An Application Window contains an open application i.e. current application such as Word or Paint. When two or more windows are open, only one of them is active and the rest are inactive.
Question 5.
Explain various methods of creating Files and Folders.
Answer:
Creating files and Folders:
Creating Folders:
You can store your files in many locations – on the hard disk or in other devices. To better organise your files, you can store them in folders.
There are two ways in which you can create a new folder:
Method I:
Step 1: Open Computer Icon.
Step 2: Open any drive where you want to create a new folder. (For example select D:)
Step 3: Click on File → New → Folder.
Step 4: A new folder is created with the default name “New folder”.
Step 5: Type in the folder name and press Enter key.
Method II:
In order to create a folder in the desktop:
Step 1: In the Desktop, right-click → New → Folder.
Step 2: A Folder appears with the default name “New folder” and it will be highlighted.
Step 3: Type the name you want and press Enter Key.
Step 4: The name of the folder will change.
Question 6.
Write about Taskbar.
Answer:
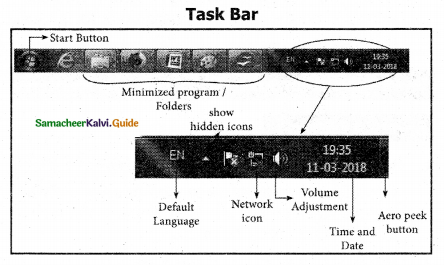
At the bottom of the screen there- is a horizontal bar called the taskbar. This bar contains the Start button(left side), shortcuts to various programs, minimized programs, and in the extreme right corner you can see the system tray which consists of volume control, network, date and time, etc. Next to the Start button is the quick Launch Toolbar which contains tasks for frequently used applications.
Question 7.
Explain Computer Icon.
Answer:
Computer Icon – By clicking this icon, the user can see the disk drivers mounted in the system. In Windows XP, Vista, this icon is called “My computer” in Windows 8 and 10, it is called “This PC”.
The functionality of the computer icon remains the same in all versions of windows as shown in the following Figure.

Question 8.
How will you copy files and folders?
Answer:
Copying Files and Folders:
There are variety of ways to copy files and folders:
The method I – COPY and PASTE:
To copy a file or folder, first, select the file or folder and then choose one of the following:
- Click Edit → Copy or Ctrl + C or right-click → Copy from the pop-up menu.
- To paste the file(s) or folder(s) in the new location, navigate to the target location then do one of the following:
- Click Edit → Paste or Ctrl + V.
- Or Right-click → Paste from the pop-up menu.
Method II – Drag and Drop:
- In the RIGHT pane, select the file or folder you want to copy.
- Click and drag the selected file and/or folder to the folder list on the left, and drop it where you want to copy the file and/or folder.
- Your file(s) and folder(s) will now appear in the new area.
Question 9.
How will you search files or folders using the Computer icon?
Answer:
Procedure:
- Click Computer Icon from desktop or from the Start menu.
- The Computer disk drive screen will appear and at the top right corner of that screen, there is a search box option.
- Type the name of the file or the folder you want to search. Even if you give the part of the file or folder name, it will display the list of files or folders starting with the specified name.
- Just click and open that file or the folder.
Question 10.
How will you delete a file or folder?
Answer:
To delete a file or folder: Select the file or folder you wish to delete.
- Right-click the file or folder, select the Delete option from the pop-up menu or Click File → Delete or press the Delete key from the keyboard.
- The file will be deleted and moved to the Recycle bin.
Question 11.
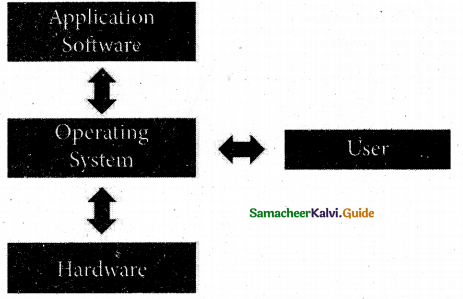
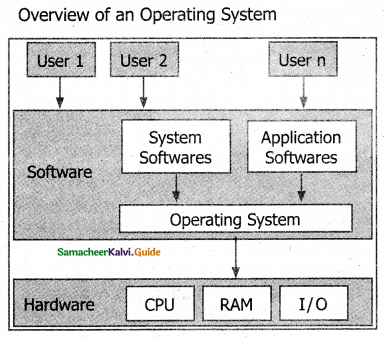
Represent overview of an operating system using a diagram.
Answer:
Part II
Explain brief
Question 1.
What are the features of Ubuntu?
Answer:
Features of Ubuntu
- The desktop version of Ubuntu supports all norma! software like Windows such as Firefox, Chrome, VLC, etc.
- It supports the office suite called LibreOffice.
- Ubuntu has in-built email software called Thunderbird, which gives the user access to email such as Exchange, Gmail, Hotmail, etc.
- There are free applications for users to view and edit photos, to manage and share videos.
- It is easy to find content on Ubuntu with the smart searching facility.
- The best feature is, it is a free operating system and is backed by a huge open source community.
Question 2.
What are the names of the icons in the Ubuntu OS?
Answer:
- Search your Computer
- Files
- Firefox Webbrowser
- LibreOffice Writer
- LibreOfficeCalc
- LibreOffice Impress
- Ubuntu Software
- Amazon
- System Settings
- Trash
Question 3.
Explain about Ubuntu menu bar.
Answer:
Menu bar – The menu bar is located at the top of the screen, The menu bar Incorporates common functions used in Ubuntu. The frequently used icons in the menu bar are found on the right. The most common indicators in the Menu bar are located in the indicator or notification area.

Question 4.
Write a note on Text entry settings.
Answer:
Text entry settings: This shows the current keyboard layout (such as En, Fr, Ku, and so on. If more than one keyboard layout is shown, it allows you to select a keyboard layout out of those choices. The keyboard indicator menu contains the following menu items: Character Map, Keyboard Layout Chart, and Text Entry Settings.
Question 5.
Write about Ubundu desktop background.
Answer:
The desktop background Below the menu bar at the top of the screen is an image covering the entire desktop. This is the default desktop background or wallpaper;, belonging to the default Ubuntu 16.04 theme known as Ambiance.
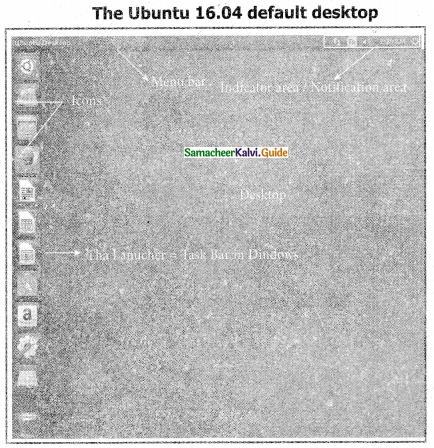
Question 6.
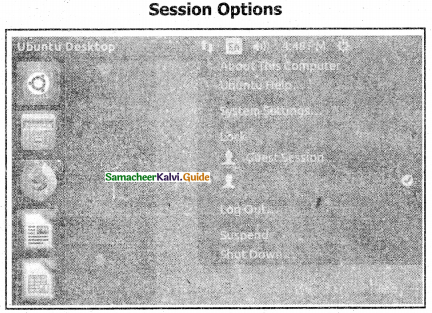
Explain Ubuntu Shutting down method.
Answer:
Shutting down Ubuntu using Session options
When you have finished working on your computer, you can choose to Log Out, Suspend or Shut down through the Session Indicator on the far right side of the top panel.
Part – I
Explain brief
Question 1.
Explain the various mouse actions.
Answer:
The following are the mouse actions:
| Action | Reaction |
| Point to an item | Move the mouse pointer over the item. |
| Click | Point to the item on the screen, press and release the left mouse button. |
| Right-click | Point to the item on the screen, press and release the right mouse button. Clicking the right mouse button displays a pop-up menu with various options. |
| Double-click | Point to the item on the screen, quickly press twice the left mouse button. |
| Drag and drop | Point to an item then hold the left mouse button as you move the pointer press and you have reached the desired position, release the mouse button. |
Question 2.
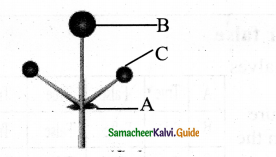
Draw and explain the Elements of a window.
Answer:
The elements of a window
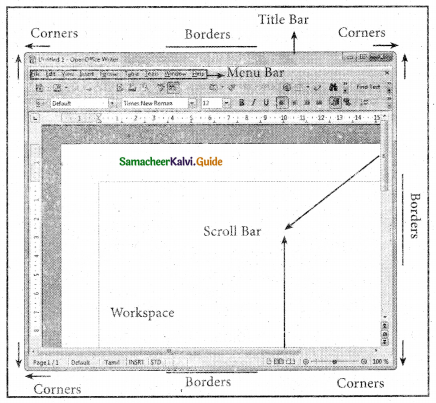
Menu Bar:
The menu bar is seen under the title bar. Menus in the menu bar can be accessed by pressing the Alt key and the letter that appears underlined in the menu title. Additionally, pressing Alt or F10 brings the focus on the first menu of the menu bar.
The Workspace:
The workspace is the area in the document window to enter or type the text of your document.
Scroll bars:
The scroll bars are used to scroll the workspace horizontally or vertically.
Corners and borders:
The corners and borders of the window help to drag and resize the windows. The mouse pointer changes to a double-headed arrow when positioned over a border or a corner. Drag the border or corner in the direction indicated by the double-headed arrow to the desired size. The window can be resized by dragging the corners diagonally across the screen.
Title bar:
The first line of the window is called the title bar. It contains the name of the application on its left and the sizing buttons on its right.
Question 3.
How will you create a folder? Explain its methods with an example.
Answer:
There are two ways in which you can create a new folder:
Method I:
Step 1: Open Computer Icon.
Step 2: Open any drive where you want to create a new folder. (For example select D:.
Step 3: Click on File → New Folder.
Step 4: A new folder is created with the default name “New folder”.
Step 5: Type in the folder name and press Enter key.
Method II:
In order to create a folder on the desktop:
Step 1: In the Desktop, right-click New → Folder.
Step 2: A Folder appears with the default name “New folder” and it will be highlighted.
Step 3: Type the name you want and press Enter Key.
Step 4: The name of the folder will change.
Question 4.
How will you create a file in Wordpad?
Answer:
To create files in Wordpad we need to follow the steps given below.
- Click Start → All Programs → Accessories → Wordpad or Run → type Wordpad, click OK. Wordpad window will be opened.
- Type the contents in the workspace and save the file using File → Save or Ctrl + S.
- Save As dialog box will be opened.
- In the dialog box, select the location where you want to save the file by using the Look in the drop-down list box.
- Type the name of the file in the file name text box.
- Click the save button.
Question 5.
Explain the method of finding Files and Folders.
Answer:
You can use the search box on the Start menu to quickly search a particular folder or file in the computer or in a specific drive.
To find a file or folder
- Click the Start button, the search box appears at the bottom of the start menu.
- Type the name of the file or the folder you want to search. Even if you give the part of the file or folder name, it will display the list of files or folders starting with the specified name.
- The files or the folders with the specified names will appear, if you click that file, it will directly open that file or the folder.
- There is another option called “See more results” which appears above the search box.
- If you click it, it will lead you to a Search Results dialog box where you can click and open that file or the folder.
Question 6.
Explain the various methods to Rename a file.
Answer:
You can rename using the File menu, left mouse button, or right mouse button.
Method 1:
Using the FILE Menu
- Select the File or Folder you wish to Rename.
- Click File → Rename.
- Type in the new name.
- To finalise the renaming operation, press Enter.
Method 2:
Using the Right Mouse Button
- Select the file or folder you wish to rename.
- Click the right mouse button over the file or folder.
- Select Rename from the pop-up menu.
- Type in the new name.
- To finalise the renaming operation, press Enter.
Method 3:
Using the Left Mouse Button
- Select the file or folder you wish to rename.
- Press F2 or click over the file or folder. A surrounding rectangle will appear around the name.
- Type in the new name.
- To finalise the renaming operation, press Enter.
Question 7.
How will you move the files and folders? Explain various methods.
Answer:
Method I:
CUT and PASTE: To move a file or folder, first select the file or folder and then choose one of the following:
- Click on the Edit → Cut or Ctrl + X Or right-click → cut from the pop-up menu.
- To move the file(s) or folder(s) in the new location, navigate to the new location and paste it using Click Edit → Paste from the edit menu or Ctrl + V using the keyboard.
- Or Right-click → Paste from the pop-up menu. The file will be pasted in the new location.
Method II:
Drag and Drop: In the disk drive window, we have two panes called left and right panes. In the left pane, the files or folders are displayed like a tree structure. In the right pane, the files inside the specific folders in the left pane are displayed with various options.
- In the right pane of the Disk drive window, select the file or folder we want to move.
- Click and drag the selected file or folder from the right pane to the folder list on the left pane.
- Release the mouse button when the target folder is highlighted (active).
- Our file or folder will now appear in the new area.
Question 8.
How will you copy the files and folders? Explain various methods.
Answer:
Copying Files and Folders Method I – COPY and PASTE
To copy a file or folder, first, select the file or folder and then choose one of the following:
- Click Edit Copy or Ctrl + C or right-click Copy from the pop-up menu.
- To paste the file(s) or folder(s) in the new location, navigate to the target location then do one of the following:
- Click Edit Paste or Ctrl + V.
- Or Right-click → Paste from the pop-up menu.
Method II – Drag and Drop
- In the RIGHT pane, select the file or folder we want to copy.
- Click and drag the selected file and/or folder to the folder list on the left, and drop it where you want to copy the file and/or folder.
- Our file(s) and folder(s) will now appear in the new area.
Question 9.
How will you copy the files and folders to a removable disk? Explain various methods.
Answer:
Copying Files and Folders to a removable disk
The following are methods of transferring files to or from a removable disk:
- Copy and Paste
- Send To
METHOD I: Copy and Paste
- Plug the USB flash drive directly into an available USB port.
- If the USB flash drive or external drive folder does NOT open automatically, follow these steps:
- Click Start → Computer.
- Double-click on the Removable Disk associated with the USB flash drive.
- Navigate to the folders in your computer containing files you want to transfer.
- Right-click on the file you want to copy, then select Copy.
- Return to the Removable Disk window, right-click within the window, then select Paste.
METHOD II: Send To
- Plug the USB flash drive directly into an available USB port.
- Navigate to the folders in our computer containing files you want to transfer.
- Right-click on the file we want to transfer to your removable disk.
- Click Send To and select the Removable Disk associated with the USB flash drive.
Part – II
Explain detail
Question 1.
Explain the elements of Ubuntu,
Answer:
Search your Computer Icon
This icon is equal to the search button in Windows OS. Here, you have to give the name of the File or Folder for searching them.
Files :
This icon is equivalent to the My Computer icon. From here, you can directly go to Desktop, Documents, and so on.
Firefox Web Browser:
By clicking this icon, you can directly browse the internet. This is equivalent to clicking the Web Browser in Taskbar in Windows.
Online Shopping icon:
Using this icon users can buy and sell any products online.
System Settings Icons :
This icon is similar to the Control panel in the Windows Operating System. But here, you need to authenticate the changes by giving your password. You cannot simply change as you do in Windows.
Trash :
This icon is the equivalent of Recycle bin of windows OS. All the deleted Flies and Folders are
moved here.
Question 2.
Explain the method of creating, deleting files/folders in Ubuntu.
Answer:
Creating, Deleting Files/Folders
Similar to Windows OS, you can create, delete the files and folders with the same procedure by clicking the Files icon. The following Figure shows the method of creating a File or Folder by right-clicking on the Desktop.
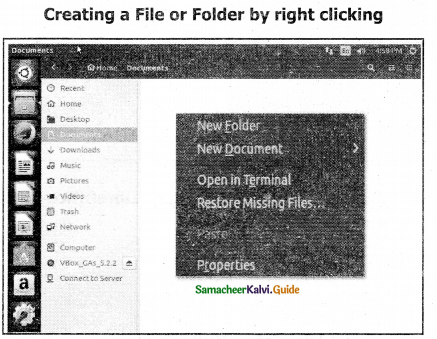
A new File or new Folder can also be created by using the File menu.
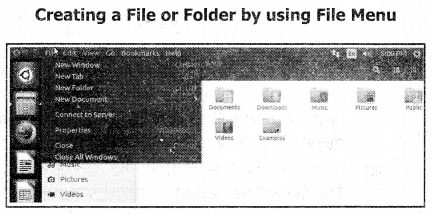
Deleting a File/Folder: A file/folder created by you can be moved to trash by using right-click or by using the menu.
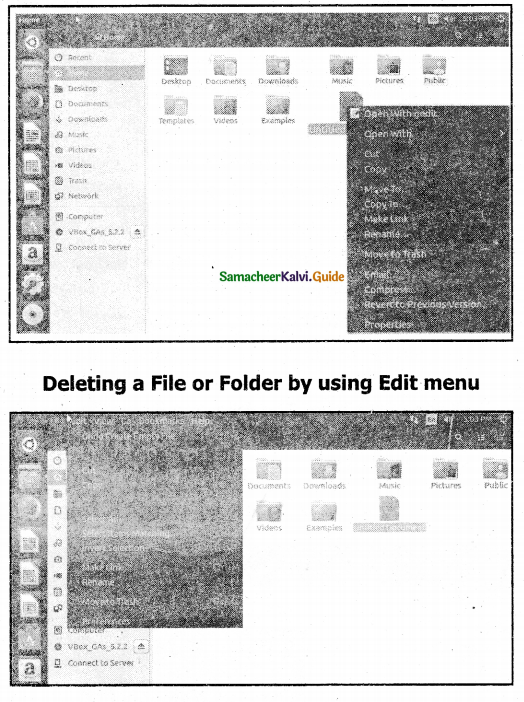
Question 3.
Explain LibreOffice Writer, LibreOffice Cacl and LibreOffice Impress.
Answer:
LibreOffice Writer
This icon will directly take you to document preparation applications like MS Word in Windows.

Libre Office Cac: This icon will open the LibreOffice Calc application. It is similar to MS Excel in Windows.
LibreOffice Impress: By clicking this icon, you can open LibreOffice Impress to prepare any presentations in Ubuntu like MS PowerPoint.