Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Botany Guide Pdf Chapter 1 Living World Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Botany Solutions Chapter 1 Living World
11th Bio Botany Guide Living World Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part-I
Choose the Right Answer:
Question 1.
Which one of the following statements about viruses is correct?
a. Possess their own metabolic system
b. They are the facultative parasites
c. They contain DNA or RNA
d. Enzymes are present
Answer:
b. They are the facultative parasites
Question 2.
Identify the Archaebacterium
a. Acetobacteria
b. Erwinia
c. Treponema
d. Methanobacterium
Answer:
d. Methanobacterium
![]()
Question 3.
Identify the correctly matched pair
a. Actinomycete – a) Late blight
b. Mycoplasma – b) lumpy jaw
c. Bacteria – c) crown gall
d. Fungi – d) sandal spike
Answer:
a. Actinomycete – Lumpy jaw
b. Mycoplasma – sandal spike
c. Bacteria – crown gall
d. Fungi – late blight
Question 4.
Identify the incorrect statement about the gram-positive bacteria.
a. Teichoic acid absent
b. A high percentage of peptidoglycan is found in the cell wall.
c. Cell wall is single-layered
d. Lipopolysaccharide is present in the cell wall.
Answer:
a. Teichoic acid absent
![]()
Question 5.
The correct statement regarding Blue Green Algae is
a. Lack of motile structures
b. Presence of cellulose in cell wall
c. Absence of mucilage around the thallus
d. Presence of Floridian starch
Answer:
a. lack of motile structure
Question 6.
Differentiate Homoiomerous and Heteromerous lichens.
Answer:
|
Homoiomerous |
Heteromerous |
| Here algae cells evenly distributed in the thallus | Heteromerous-a distinct layer of alga and fungi present. |
Question 7.
Write the distinguishing features of Monera.
Answer:
Distinguishing Features of Monera:
- This kingdom includes all prokaryotic organisms. Example: Mycoplasma, bacteria, actinomycetes, and cyanobacteria.
- These are microscopic. They do not have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
- Many other bacteria like Rhizobium, Azotobacter, and Clostridium can fix atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia.
- Some bacteria are parasites and others live as symbionts.
![]()
Question 8.
Why do farmers plant leguminous crops in crop rotations/mixed cropping?
Answer:
Rhizobium- Nitrogen-fixing bacteria,
Living in the root modules of leguminous plants has a symbiotic association with it, fix atmospheric nitrogen, and convert it into nitrates, thereby increases the fertility of the soil. Growing legumes alternatively with paddy can help paddy to give high yield- This method of growing paddy, alternatively with leguminous plants is known as crop rotation.
Mixed cropping:
Amidst, other crops. The leguminous crop is also raised as a mixed crop – so that it enriches the soil and increases the yield by fixing atmospheric nitrogen.
Question 9.
Briefly discuss the 5 kingdom system of classification. Add a note on their merits and demerits.
Answer:
a. Proposed by R.H. Whittaker (American taxonomist)
b. Criteria considered – cell structure, Thallus Organization, Mode of Nutrition, Reproduction, and Phytogenitic Relations.
5 kingdom classifications include: –
a. Monera b. Protista c. Fungi d. Plantae e. Animalia
|
S. No |
Merits: |
Demerits: |
| 1. | Based on the complexity of cell structure & organization of thallus | Monera & Protista – Include both autotrophic & heterotrophic organisms |
| 2. | Based on mode of nutrition. | Include cell wall lacking & cell wall |
| 3. | Fungi-kept in a separate category from plants | Bearing organisms. |
| 4. | It shows the phylogeny of the organisms | So the group is more heterogeneous |
Question 10.
Give a general account of lichens
Answer:
a. Definition: A symbolic association of algae and Fungi helping each other & living together known as lichens.
b. Partners: Algal partner known as Phycobiont & Fungal partner known as Mycobiont
c. Role of Algal partner – Autotrophic prepare food – give nutrition to fungal partner also
d. Role of fungal partner – gives protection- helps in fixing to the substratum by rhizines.
Classification:
|
Character |
Phycobiont |
Mycobiont |
|
| 1 | Asexual reproduction | Akinetes, hormogonia, Aplanospore, etc. | fragmentation soredia, and isidia |
| 2 | Sexual reproduction | absent | sexual reproduction by ascocarp & ascospores |
|
Character |
Classification of lichens |
|
| 1. | Habitat | Corticolous – growing on the bark Lichnicolous – growing on wood Saxicolous – growing on rock Terricolous – growing on the ground Marine – siliceous rock sea Freshwater – siliceous rocks (freshwater habitat). |
| 2. | Morphology of thallus | Leprose – distinct fungal layer absent Crustose – crust like Foliose – Leaf-like Fruticose-branched pendulous shrub-like |
| 3. | On the basis of the distribution of algae cells | Homoiomerous – Algae cells evenly distributed Heteromerous – A distinct layer of Algae and Fungi present |
| 4. | On the basis of the fungal partner | If it is Ascomycetes – Ascolichen If it is basidiomycetes-Basidiolichen |
Economic importance:
|
Secretion of acids of lichens |
Uses |
|
| 1 | Oxalic acid | Weathering of rocks Pioneers in xerosere |
| 2 | Usnic acid | Antibacterial |
II. a. Pollution Indicators – Lichens sensitive to air pollutants- (pollution indicators)
b. Rocella Montagne – Produces a dye used in litmus paper (acid-base indicator)
c. Cladonia rangiferina – Food for animals in tundra regions
![]()
Part – II.
11th Bio Botany Guide Living World Additional Important Questions and Answers
Choose The Right Answer:
Question 1.
Earth has formed around billion years ago ……………
(a) 3.3
(b) 5.6
(c) 4.6
(d) 5.9
Answer:
(c) 4.6
Question 2.
The organism that is reproductively sterile is
a. Wasp
b. Worker bees
c. Housefly
d. Drosophila
Answer:
c. Worker bees
![]()
Question 3.
Which of the following is NOT a prokaryote?
(a) Bacteria
(b) Blue-green algae
(c) Oedogonium
(d) Nostoc
Answer:
(c) Oedogonium
Question 4.
Recombination is the result of
a. Binary fission
b. Asexual reproduction
c. Sexual reproduction.
d. Vegetative propagation
Answer:
c. sexual reproduction
![]()
Question 5.
Vaccination for smallpox was discovered by …………….
(a) W.M. Stanley
(b) Adolf Mayer
(c) Robert Koch
(d) Edward Jenner
Answer:
(d) Edward Jenner
Question 6.
Blister-like pustules occur due to
a. Chickenpox
b. Rust
c. Smut
d. Mumps
Answer:
a. Chickenpox
![]()
Question 7.
Expand Bt-toxin
a. Biotechnology
b. Biotoxin
c. Beta-toxin
d. Bacillus thuringiensis
Answer:
d. Bacillus thuringiensis
Question 8.
One nanometer equals to metres …………….
(a) 10-9
(b) 10-6
(c) 10-5
(d) 10-12
Answer:
(a) 10-9
![]()
Question 9.
Saprophytic angiosperm with mycorrhiza
a. Clostridium
b. Azolla
c. Monotropa
d. Viscum
Answer:
c. Monotropa
Question 10.
The famous roqueforti cheese is produced by employing
a. Aspergillus roquefortic
b. Penicillium camemberti
c. Penicillium notatum
d. Aspergillus terreus
Answer:
b.Penicillium camémberti
![]()
Question 11.
Identify the criteria not used in classifying viruses by Baltimore …………….
(a) ss (or) ds
(b) use of RT
(c) capsid
(d) sense or antisense
Answer:
(c) capsid
Question 12.
Both viruses and bacteria contain
a. Plasma membrane
b. Protein wat
c. Peptidoglycan
d. Nucleic acids
Answer:
d. Nucleic acids
![]()
Question 13.
Lactobacillus bulgaricus is responsible for the formation of
a. Lactic acid
b. Cheese
c. Yogurt
d. Curd
Answer:
C. Yoghurt
Question 14.
Parvo viruses have …………….
(a) ssDNA
(b) dsDNA
(c) ssRNA
(d) dsRNA
Answer:
(a) ssDNA
![]()
Question 15.
Bacterial chlorophyll is also known as
a. Chlorophyll
b. Bilirubin
c. Chromatium
d. Chioridin .
Answer:
Chromatium
Question 16.
This drug is also known as wonder drug.
a. Streptomycin
b. Aureomycin
c. Bacitracin
d. Pencillin
Answer:
Pencillin
![]()
Question 17.
The empty protein coat left outside after penetration is …………….
(a) host
(b) ghost
(c) capsid
(d) capsomeres
Answer:
(b) ghost
Question 18.
Among the given 4 – one is not viral diseases- find it out.
a. Cucumber mosaic
b. Citrus canker
c. Ricetungro
d. Potato leaf roll
Answer:
b. citrus canker
![]()
Question 19.
Bacillus thuringiensis is an
a. Biofertilizer
b. Bio-fuel
c. Bio-pesticide
d. Bio-medicine
Answer:
c. Bio-pesticide
Question 20.
Mad cow disease is caused by …………….
(a) viroids
(b) virusoids
(c) prions
(d) viruses
Answer:
(c) prions
![]()
Question 21.
Bacteria that grow in high salinity condition is known as
a. Methane bacterium
b. Halobacterium
c. Thermos aquaticus
d. Agrobacterium
Answer:
b. Halobacterium
Question 22.
Budding is an unique feature of
a. Schizo saccharomyces
b. Aspergillus
c. Penicillium
d. Neurospora
Answer:
Schizo saccharomyces
![]()
Question 23.
Mycophages infect …………….
(a) blue-green algae
(b) bacteria
(c) fungi
(d) cyanobacteria
Answer:
(c) fungi
Question 24.
The colourless cell in Nostoc in the intercalary position is responsible for nitrogen fixation is
a. Holoblast
b. Heterozygote
c. Homocyst
d. Heterocyst
Answer:
d. Heterocyst
![]()
Question 25.
Genetic trait carried in the bacterial
a. Cell wall
b. Chromosome
c. Plasmid
d. Cell membrane
Answer:
c. Plasmid
Question 26.
Three kingdom classification was proposed by …………….
(a) Copeland
(b) Theophrastus
(c) Linnaeus
(d) Haeckel
Answer:
(d) Haeckel
![]()
Question 27.
Developing a vaccine for SARS is difficult because
a. It spreads through nucleic acid
b. It is an enveloped virus
c. It has RNA
d. It constantly changes its form
Answer:
d. It constantly changes its form
Question 28.
Arrange correctly the following viruses according to the given shape and symmetry, Cuboidal, spherical, helical and complex respectively
I. a. Vaccinovirus b. Influenza, c. HIV, d. Herpes
II. a. Influenza b. HIV c, Herpes d. Vaccinovirus
III. a. Herpes b. HIV, c. Influenza d. Vaccinovirus
IV. a. HIV b. Herpes c. Vaccinio Virus d. Influenza
Answer:
III. a. Herpes, b, HIV, c, Influenza, d, Vaccinovirus
II.Match the following and find the correct answer.
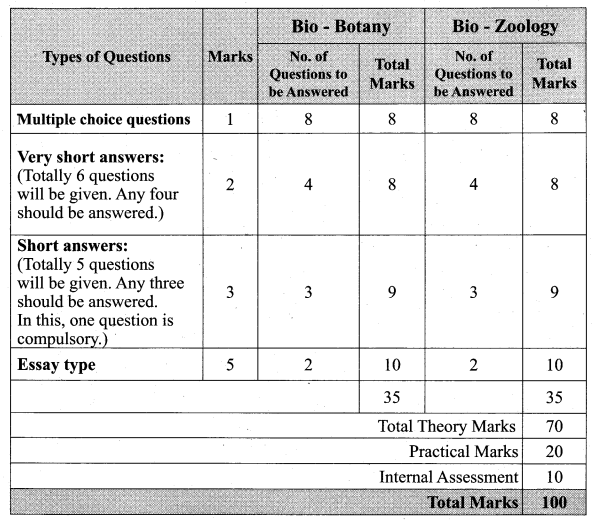
Question 1.
I. Five kingdom system of classification
II. Three kingdom system of classification
III. Four kingdom system of classification
IV. Two kingdom system of classification
Answer:
a. C-D-B-A
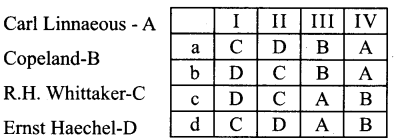
Question 2.
I. TMV Discovered by world
II. Bacterium word coined by
III. Father of Mycology
IV. Classification virus given by
Answer:
b. B-D-A-C
![]()
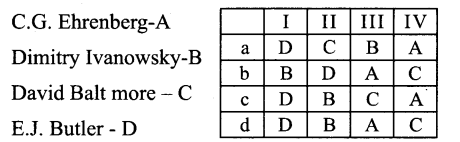
Question 3.
I. Genophore
II. Bacteria
III. Extra Chromosomal DNA
IV. Fimbrial
Answer:
b. D-A-B-C
Question 4.
I. Plasmid
II. Heterocyst
III. Glycocalyx
IV. Mesosome

Answer:
c. B-A-D-C
![]()
III.
Question 1.
Which one of the following is a false statement regarding Prions
a. Prions were discovered by B. Prusiner in 1982
b. They are infectious particles of lipo protein
c. They cause about a dozen fatal degenerative disorders of CNS
d. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease(cjD) and bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) are some commonly known diseases
Answer:
b. They are infectious particles of lipoprotein
Question 2.
Which one of the following is a false statement regarding Ribosomes
a. Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis
b. The number of ribosomes per cell varies from 1000 to 1500.
c. The ribosomes are 70s type and consists of a 2 subunits (50s and 30s)
d. The nbosomes are held together by mRNA and form polyribosomes or polysomes.
Answer:
b. The number of ribosomes per cell varies from 1000 to 1500.
IV. Find out the True and False statements from the following and on that basis find the correct answer:
Question 1.
(i) Poly-B hydroxybutysate is a microbial plastic which is biodegradable
(ii) Transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another is known as transduction
(iii) Micrococcus must have oxygen to survive-known as an obligate aerobe
(iv) Spirulina is rich in carbohydrates so treated as an alternative food.
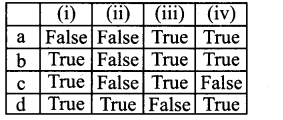
Answer:
c. True False True False
![]()
Question 2.
(i) Toad stools are known as an edible mushroom
(ii) Volvariella volvaceae and Agaricus bisporous are known for their high poisonous nature
(iii) Claviceps purpurea produces ergot-used as vasoconstrictor
(iv) Aspergillus flavus infest dried foods and produce carcinogenic toxin called -aflatoxin
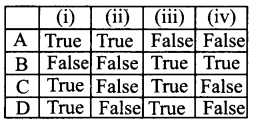
Answer:
B. False False True True
Question 3.
Which one of the following is a correct statement regarding TMV
a. David Baltimore in 1971 discovered TMV
b.First visible symptom of TMV is visible discoloration of leaves along the veins-but with typical yellow and green symptom molting-(mosaic symptom)
c. The plant grow abnormally at the nodal point
d. Infection spread by house flies and mosquitoes
Answer:
b. First visible symptom of TMV is discoloration of leaves along with the veins-but visible with typical yellow and green symptom molting-(mosaic symptom)
![]()
V.
Question 1.
Which one of the following is a correct statement regarding bacterial antibiotic
a. Chloromycetin got from Streptomyces venezuelae cure T.B
b. Bactracin is got from bacillus mycoides- used to treat UTI
c. Aurecomycin got from Streptomyces aureofaciens is used to treat whooping cough and eye infections
d. Streptomycin got from Streptmyces griseus cure typhoid fever
Answer:
c. Aurecomycin got from streptomyces aureofaciens is used to treat whooping cough and eye infections
![]()
Question 2.
Which one of the following is a correct statement regarding mycoplasma
a. Mycoplasm are very small (0.1-0.5mm) pleomorphic gram negative micro organisms
b. The have whole body appear like boiled egg-like structure in culture
c. Little leaf of tomato Witches broom of solanum.
d. Mycoplasma is also known as mollicutes
Answer:
Mycoplasm arevery small (0.1- 0.5mm) pleomorphic gram negative micro organisms
VI.
Question 1.
Sac fungi & club fungi are common names of
a. Ascomycetes
b. Basidiomycetes
c. Deuteromycetes
d. Phycomycetes
(i) a & b
(ii) b & c
(iii) a & c
(iv) c & d
Answer:
(i) a & b
Question 2.
Recurrence of fungal skin disease is due to
a. Resistance to antibiotics
b. Dormant spores become active at the onset of favourable condition
c. Non-availability of specific drugs.
d. Moisture favor fungal mycelium to spread,
(i) a & C
(ii) b & c
(iii) b & d
(iv) c & d
Answer:
(i) b & d
![]()
Question 3.
Find out the symbiotic associations from the given options.
a. Nitrogen fixing bacteria on the leguminous plants.
b. Rhizoids of Neprolepis
c. Lichens on rocks
d. Mycorrhizal roots.
(I) ac & d
(II) ab & c
(III) ab & d
(IV) a & b
Answer:
VII. Find out the wrong statement
Question 1.
Which one of the following is a wrong statement regarding ehemo lithotrophs
a. Sulphur bacteria
b. Iron bacteria
c. Methane bacteria
d. Hydrogen bacteria
Answer:
c. Methane bacteria
Question 2.
Among the following, which one is not viral?
a. Cucumber mosaic
b. Citrus canker
c. Rice tungro
d. Potato leaf roll
Answer:
b. Citrus canker
![]()
Question 3.
Which one of the following is not a Ribovirus?
a. Tobacco mosaic virus
b. Cauliflower mosaic virus
c. Human immune deficiency virus.
d. Wound tumour virus d. Pilobolus
Answer:
d. Wound tumour virus
Question 4.
Find out from the given, which one is not a Zygomycetes fungi.
a. Mucor
b. Rhizopus
c. Yeast
d. Pilobolus
Answer:
c. yeast
VIII. Read the following Assertion A and Reason R. Find the correct Answer
Question 1.
Assertion ‘A’: Viruses have genetic material but cannot divided on its own. They also don’t have in built metabolic machinery Reason ‘R’: Virus kept between living and non living
(a) A & R correct. R is explaining A
(b) A & R correct R is not explaining A
(c) A is true but R is wrong
(d) A is true but R is not explaining A
Answer:
a. A & R correct R is explaining A.
Question 2.
Assertion ‘A : Some bacteria have the capacity to retain gramstain after treatment with acid alcohol.
Reason ‘R’: Known as gram +ve as attracted towards positive pole under the influence of electric current.
Answer:
c. A is true but R is wrong.
![]()
Question 3.
Assertion’A’: Aflatoxin produced by Aspergillus flavus.
Reason ’R’: These toxin are useful to mankind to cure few disease
Answer:
c. A is true but R is wrong
Question 4.
Assertion ’A’: In septal mycelium the septa complete the partition walls between cells Reason
‘R’: There is no cytoplasmic connection between adjacent cells.
Answer:
d. A is true but R is not explaining A.
I. Additional 2 Marks
Question 1.
Define Growth.
Answer:
Growth is an intrinsic property of all living organisms through which they can increase cells both in number and mass.
Question 2.
Tabulate Milestones in Virology
Answer:
|
Year |
Name of the Scientist |
Achievement |
| 1796 | Edward Jenner | Vaccination for smallpox |
| 1886 | Adolf Mayer | Proved infectious nature of- TMV- from mosaic leaves sap |
| 1892 | Dimitry Ivanowsky | Viruses are smaller than bacteria |
Question 3.
Draw the structure of TMV and label the parts and explain in a word or two
Answer:
Answer:
a. Nucleic acid – It is ss RNA(Single Standed)
b. Capsomere – Protein Units
c. Capsid – Protein Coat.
![]()
Question 4.
Define reproduction and Mention its types.
Answer:
Reproduction is the tendency of a living organism to perpetuate its own species. There are two types of reproduction namely asexual and sexual.
Question 5.
Bacteria is a indeed friend- discuss
Answer:
Even though Bacteria cause many diseases to plants animals and human beings they are beneficial to day-to-day life also. Ex: Milk (lactobacillus acidophobus)/(lactobaci llus lacti)
a. Curd b. Butter c. Cheese d. Yogurt These are a few of the beneficial activities.
Question 6.
Draw the ultra structure of bacterial cell.
Answer:
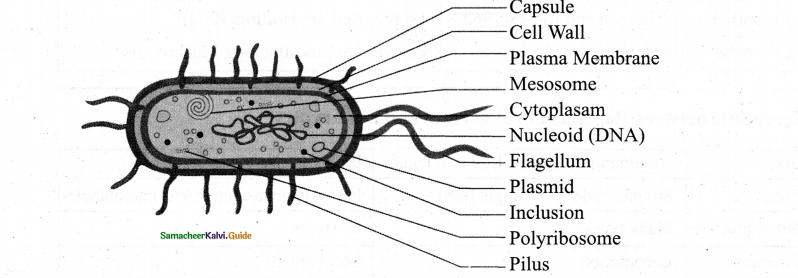
Question 7.
Name the four types of ascocarps produced by ascomycetes.
Answer:
Four Types Of Ascocarps Produced By Ascomycetes:
- Cleistothecium
- Perithecium
- Apothecium and
- Pseudothecium.
Question 8.
Why is it essential to do classification?
Answer:
- To relate on the basis of common features
- To define, on the basis of salient features
- To know the relationship among different groups.
- To understand evolutionary relationship.
![]()
Question 9.
Ruggerio etal’s recent classification-Explain.
Answer:
- Ruggerio etal in 2015-published-7-kingdom system of classification
- It is an extension of Cavalier’s 6 – Kingdom Scheme’Include 2 superkingdom
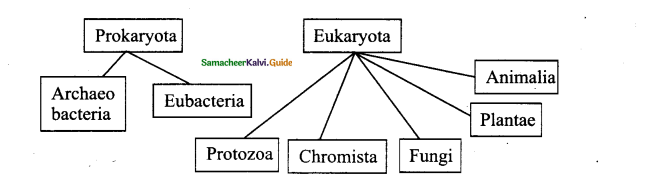
Question 10.
What is Prophage?
Answer:
a. In the lysogenic cycle, the injected phage DNA become circular and integrates into bacterial chromosome by recombination.
b. The integrated DNA of phage and bacteria is known as Prophase.
![]()
Question 11.
Distinguish between Cyanophage and Mycophage
Answer:
| Cyanophage | Mycophage | |
| 1 | Vims infecting blue green Algae are known as Cyanophage |
Vims allacking fungi are called Mycovimses or Mycophage |
| 2 | 1st reported by Safferman and Mores(1963) | 1st reported by Holling(1962) |
| 3 | Eg. Lyngbuya, Plectonema | Eg. Myc ovims attacking Mushrooms |
Question 12.
Differentiate between flagella of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Answer:
| 1 | Size | 20-30mm in diameter 15 pm in length | Bigger in size |
| 2 | Structure | Simple made up of single fibril | In C.S flagella contain 9+2 microtubules |
| 3 | No of position | Many types | few types |
| 4 | Function | Locomotion | Locomotion |
Question 13.
Differentiate between Photolithotrophs and Photo organotrophs
Answer:
|
Photolithotrophs |
Photo organotrophs |
| 1 .Hydrogen donor is an in organic substance 2 types – Green sulphur bacteria Hydrogen donor H2S Posses bacterioviridin. E.g chlorobium Purple sulphur bacteria Here hydrogen donor is thiosulphate pigment bacterial chlorophyll in chlorosomes E.g chromatium |
2. The hydrogen donor is an organic acid or alcohol e.g purple non sulphur bacteria Rhodospirillum E.g
|
Question 14.
If you think endospore formation not a reproduction method then justify you answer
Answer:
Yes Endospores are formed not during reproduction, but during unfavorable season the thick walled endospores are resting spores when favorable condition comes, they germinate and form bacteria.
![]()
Question 15.
What are the 3 different methods by which gene recombination occur in bacteria ? Or write about Sexual reproduction in bacteria?
Answer:
Sexual reproduction is so simple formation and fusion of gametes is absent. However by Three different methods gene recombination can occur
- Conjugation
- Transduction
- Transformation
2 Marks
Question 16.
Define chemolithotrophs – give examples
Answer:
- The type of bacteria oxidise in organic compound to release energy
- Eg Sulphur bacteria – Thiobacillus thio oxidants
- Iron bacteria – Ferrobacillus ferro oxidants
- Hydrogen bacteria – Hydrogenomonas
Question 17.
Label the given diagram properly
Answer:
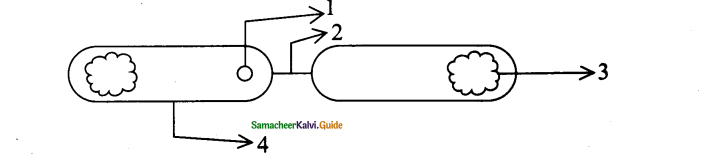
Answer:
1. F- plasmid
2. Conjugation pilus
3. Chromosome
4. F+ cell
Question 18.
Write any 2 vitamin yielding bacteria
Answer:
| Escherichia coli | Live in human intestine produce large quantities of vitamin K&B – complex |
| Clostrdiumacctobutylieum | Vitamin B2 is prepared by the fermentation of sugar |
Question 19.
Name any 2 bacteria diseases affecting Potato
Answer:
| Name of disease | Causative organism |
| 1. Ringrot_____________ | Clavi bacter michiganensis sub sp sepedonicus |
| 2. Scab_____________ | Streptomyees scabies |
Question 20.
What is meant by Probiotics
Answer:
- Microorganism such as lactobacillus bifidobacterium when consume as a dietary supplement help to maintain or restores beneficial bacteria to the digestive tract. They are called friendly or good bacteria. They keep our gut healthy
- They help to increase the immunity of the body
- Eg: Probiotic Yoghurt
- Probiotie tooth paste.
Question 21.
What is the meant by Ray fungi? Give example
Answer:
- Actinomycetes are called as ray fungi due to their mycelia like growth
- They are anaerobic or facultative anaerobic
- They are gram + ve
- Don’t produce aerial mycelium
- DNA contain high guanine and cytosine content Eg strepotmyces
![]()
Question 22.
What is this structure?
Answer:
The figure is the structure of mycoplasma
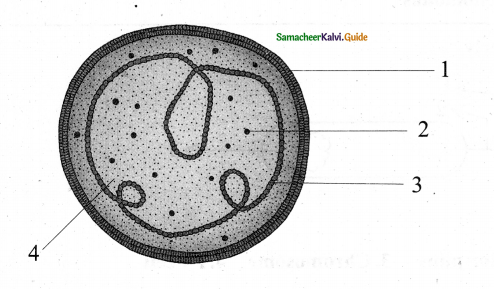
Answer:
1. Cell membrane
2. Ribosome
3. DNA strain
4. Cytoplasm
Question 23.
Name few Renowed mycologists?
Answer:
A. Arthur H.R. Buller, John Webster D.L. Hawksworth, G.C Ainsworth
B. B mundkur, K.C. Meta, C.V. Subramanian and T.S. Sadasivam & Father of Indian Mycology -E.J. Butler-
Question 24.
Identify the diagram and label any three parts.
Answer:
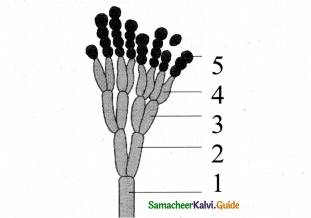
Conidia formation-Penicillium
- Conidiophores
- Ramus
- Metula
- Sterigma
- Conidium or Conidiospore
![]()
Question 25.
Define Homeostasis. Why it is essential?
Answer:
Property of self-regulation and tendency to maintain a steady-state within an external environment which is liable to change is called homeostasis. It is essential for the living organism to maintain internal conditions to survive in the environment.
Question 26.
Name 4 fungi, from which we derive organic acids.
Answer:
- Citric acid& Gluconic acid – Aspergillus niger
- Itaconicacid – Aspergillus terreus
- Kojicacid – Aspergillus oryzae
![]()
Question 27.
Name 4 common basidiomycetes
Answer:
- Puffballs,
- Toadstools,
- Birds nest’s fungi,
- Bracket fungi,
- Smuts
- Rusts,
- Smuts.
Question 28.
Define aflatoxin.
Answer:
Aspergillus, Polyporus, Mucor and Penicillium are involved in spoilage of food material Aspergillus flavus infest dried food & produce caranogenic toxin known as aflatoxin.
Question 29.
Name 3 Dermatophytes
Answer:
- Trichophyton
- Tinea
- Microsporum
- Epidermophyton are some fungi causing skin problems
3 Marks Additional Questions
Question 1.
State the living and Non-living character of the Virus.
Answer:
(i) Living characters:
- Presence of nucleic acid & protein
- Capable of mutation
- Ability to multiply with living cells
- Able to infect and cause diseases
- Show irritability and host-specific.
(ii) Non-living characters:
- Can be crystallized
- Don’t have metabolic machinery or functional autonomy
- In active outside the host
- Energy producing enzyme system is absent
Question 2.
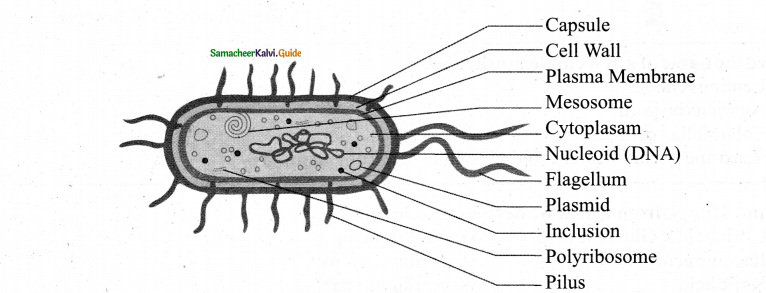
Draw the ultra structure of bacterial cell. Image Parts:
Answer:
Question 3.
What are the economic importance of Cyanophyceae
Answer:
|
SNO |
NAME OF THE ORGANISM |
ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE |
| 1 | Microcystis aeruginosa anabaeria Anabaena Flos aquae | Waterbloom-release toxins-affect aqualic organisms |
| 2 | Nostoc, Anabaena | Fix atmospheric nitrogen(bio fertilizer) |
| 3 | Spirulina | Used to prepare SCP |
Question 4.
Explain any 3 asexual method of reproduction in fungi
Answer:
| 1. | Zoospores | Flagellate structures-produced zoosporangia e.g. chytrids |
| 2. | Conidia | Spores produced on conidiosphores e.g. penicillillium, Aspergillus |
| 3. | Budding | A small out growth of parental cell, gets detached E.g. Saccharomyces. |
![]()
Question 5.
Tabulate animal diseases caused by bacteria
Answer:
| S.NO | Name of the animal | Name of the diseases | Name of the pathogen |
| 1. | Sheep | Anthrax | Bacillus anthracis |
| 2. | Cattle | Brucellosis | Bacillus abortus |
| 3. | Cattle | Bovine Tuberculosis | Mycobacterium bovis |
| 4. | Cattle | Black leg | Clostridium chanvei |
Question 6.
Distinguish between Ammonification & Nitrification.
Answer:
| Ammonification | Nitrification |
| 1. Convert protein of dead plant animal bodies ↓ Ammonia ↓ Ammonium salt |
After Ammonification the ammonium salts converted into Nitrites & nitrates |
| 2. The bacteria bringing forth this conversion is known as Ammonifying Bacteria. | This conversion of Ammonia into nitrites & nitrates is known as Nitrification. |
Question 7.
By drawing diagrams, classify bacteria on the basis of flagellatin
Answer:
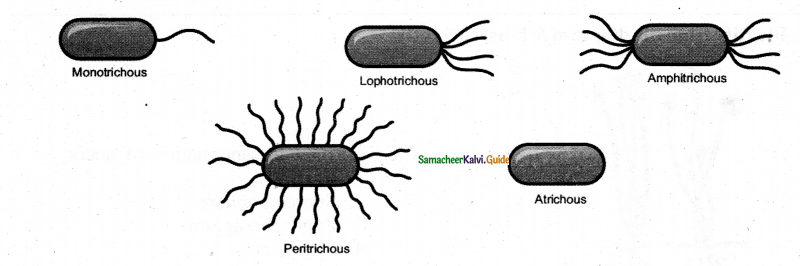
Question 8.
What are the prominent symptoms of TMV-affected tobacco plants?
Answer:
The first visible symptom of TMV is discoloration of leaf colour along the veins and show typical yellow and green mottling which is the mosaic symptom. The downward curling and distortion of young apical leaves occurs, plant becomes stunted and yield is affected.
![]()
Question 9.
Define Transduction and explain
Answer:
The three types of Transduction
- Phage mediated DNAtransfer is Transduction
- Zinder and Lederberg (1952) discovered it in Salmonella typhimurum
- 2 types – Generalised and Specalised
I. Generalised Transduction:
a. Ability of bacteriophage to carry the genetic material of any region of bacteria DNA is called generalized transduction.
II. Specialised Transduction:
a. Ability of bacteriophage to carry only a specific region of the bacterial DNA is called Specialized or Restricted Transduction.
Question 10.
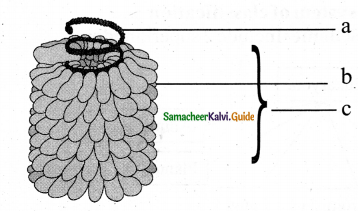
Identify from the diagram – & table correctly
Answer:
The given diagram is Basidiocarp of Agaricus
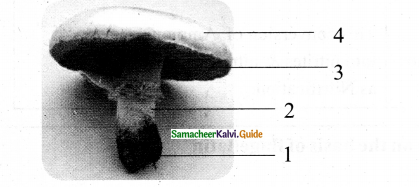
Answer:
1. Rhizoids
2. Stipe
3. Pileus
4. Gills
Question 11.
Identify from the diagram & label correctly.
Answer:
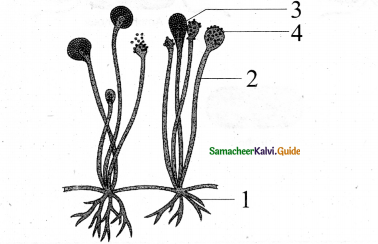
The given diagrams sporangium of mucor
1. Rhizoids
2. Sporangiophore
3. Zygosporangium
4. Zygospores
![]()
Question 12.
Define biopesticides and give 2 examples from fungi.
Answer:
- The substances derived from microbes and plants can be used to kill or eradicate pests weeds and diseases causing germs of crops.
- This is known Bio-pesticide. They are ecofriendly, non hazardous, non phytotoxic, e.g. Beauveria bassiana Metarhizium anisopliae
Question 13.
Write down any 4 uses of Mycorrhiza.
Answer:
- Nutrition – Saprophytic Angiosperm cant prepare food-due to absence of green leaves & it get nutrition via mycorrhiza e.g. Monotropa
- Availability of water and minerals: improve availability of water & minerals
- Protection-help plant to resist drought & attack of plant pathogen
Question 14.
Progametangium is formed at the tip.
Answer:
The fusion occurs & Zygosporangium is formed then undergo meiosis & zygospores These zygospores germinate are formed, during favourable condition into fungal hyphae.
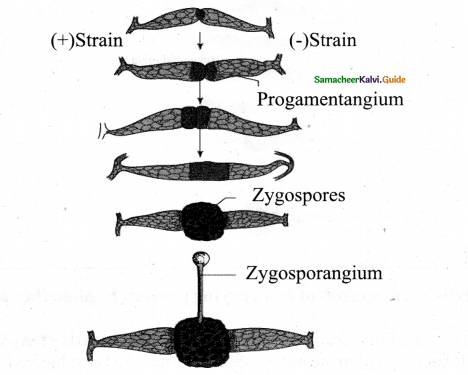
Question 15.
Explain briefly the characteristics of Oomycetes
Answer:
| Mycelium Cell wall Asexual reproduction Sexual reproduction |
Branched & Coenocytic (multinucleate made up of Glucan & Cellulose) Heterokont with one whiplash & one tinsel flagellum Oogamous-in nature E.g. Albugo |
![]()
Question 16.
Explain briefly the characteristics of zygomycetes
Answer:
|
Mostly saprophytic Chitin & Cellulose Branched & Coenocylic Zygospore produced in Zygosporangia fusion of gametangia result in zygospores |
Question 17.
Planogametic copulation in fungi has 3 types Explain.
Answer:
Planogametic copulation means fusion of motile gametes it has 3 types
- Isogamy
- Anisogamy
- Oogamy
Isogamy — Morphologically smilar gametes Anisogamy Morphologically dissimilar gametes
Oogamy – But in Oogamy it is highly advanced anisogamy
Question 18.
Explain gametangial copulation in Rhizopus with the help of diagrams.
Answer:
- In rhizopus & in Mucor there occur heterothallism- there are 2 strains of the hyphae.
- In a sexual copulation only the 2 opposite strains +ve and -ve strains come together.
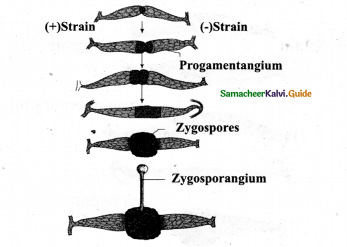
Question 19.
The tea or tobacco is not a result of mere drying process. Explain the value addition in these things?
Answer:
Yes tea & tobacco they are not mere dried leaves of Camellia sinensis (tea) & Nicotiana tobaccum so tea and tobacco to reach the utility stage, they have to be subjected to biological process known as curing, where specific bacteria are added & curing occur by a process of fermentation specific flavor and aroma of tea and tobacco are due to this fermentation process.
Tea – Mycococcus candisans
Tobacco – Bacillus megatherium
![]()
Question 20.
Write about the harmful activities of fungi.
Answer:
| Amanita phalloides Amanita yema Boletus satanus known as toad stools |
Poisonous – toxins are produced |
| Aspergillus Rhizopus Mucor Penicillum |
Cause food spoilage |
| Aspergillus flavus | infest dried foods produce carcinogenic toxin called aflatoxin |
| Patutin ochratoxin A arc other toxins produced by fungi | |
| Diseases | Various diseases are caused to plants animals & human beings. |
Question 21.
Mycorrhiza is known as bio fertilizer. Explain
Answer:
- Symbolic association between fungal mycelium and roots of higher plants is known as mycorrhiza.
- Fungi absorbs nutrition from root of higher plant, and intum fungal hyphae helps the paint to absorb water and minerals nutrients from soil.
- Any nutrient of biological orgin is biofertilizer & This is Bio fertilizer it is non hazardous, Non phytotoxic and ecofriendly.
Question 22.
Name the Antibiotics derived from fungi.
Answer:
| Organism | Antibiotics | Uses |
| Penicillium notatum | Penicillin | To treat Pneumonia and throat infections |
| Penicillium griseofulvum | Grisofulvin | To treat ring worm athletes foot & fungal infections of scalp. |
| Acremorium chrysogenum | Cephatosporin | To treat respiratory tract infections skin infections & UTI (urinary tract infections) |
| Claviceps purpurea | Ergotamine | To treat migraine head aches induce uterus contraction at the time of child birth. |
5 Marks
Question 1.
Compare the five-kingdom system of classification
Answer:
Kingdom
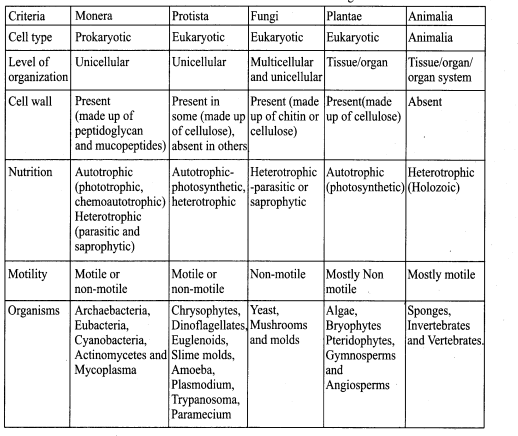
![]()
Question 2.
Ultrastructure of a typical bacterial cell.
Answer:
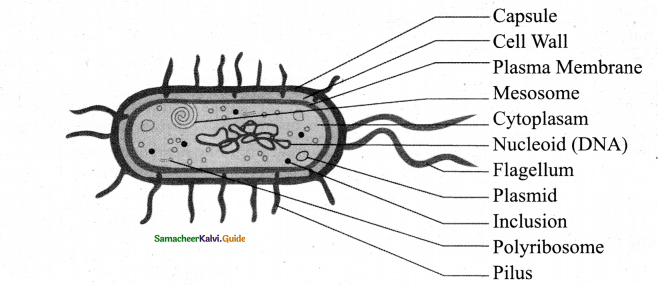
Question 3.
Explain industrial uses of bacteria.
Answer:
Industrial Uses
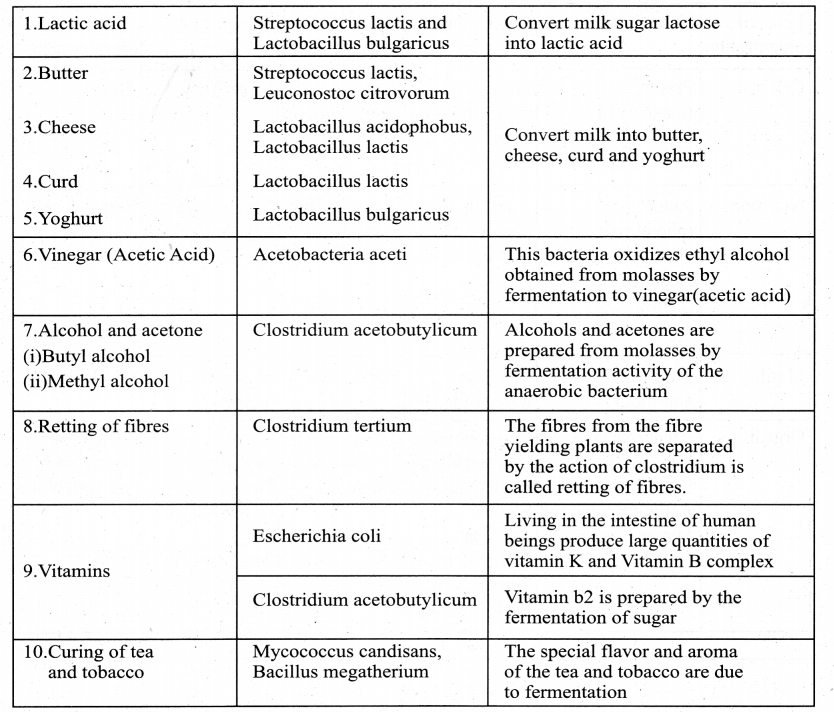
Question 4.
List out bacterial diseases caused to plants, animals & human brings.
Answer:
Plant diseases caused by bacteria
|
SNo |
Name of the host | Name of the disease |
Name of the pathogen |
| 1 | Rice | Bacterial blight | Xanthomonas oryzae |
| 2 | Apple | Fire blight | Erwinia amylovora |
| 3 | Carrot | Soft rot | Erwinia caratovora |
| 4 | Citrus | Citrus canker | Xanthomonas citri |
| 5 | Cotton | Angular leaf spot | Xanthomonas malvacearum |
| 6 | Potato | Ring rot | Clavibacter michiganesis subsp sepdonicus |
| 7 | Potato | scab | Sterptomyces scabies |
Animal diseases caused by bacteria
|
S.No |
Name of the animal | Name of the diseases |
Name of the pathogen |
| 1 | Sheep | anthrax | Bacillus anthracis |
| 2 | Cattle | brucellosis | Brucella abortus |
| 3 | Cattle | Bovine tuberculosis | Mycobacterium bovis |
| 4 | Cattle | Black leg | Clostridium chanvei |
Human diseases caused by bacteria
|
S.NO |
Name of the disease |
Name of the pathogen |
| 1. | Cholera | Vibrio cholerae |
| 2. | Typhoid | Salmonella typhi |
| 3. | Tuberculosis | Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
| 4. | Leprosy | Mycobacterium leprae |
| 5. | Pneumonia | Diplococcus pneumonie |
| 6. | Plague | Yersinia pestis |
| 7. | Diphtheria | Corynebacterium diptheriae |
| 8. | Tetanus | Clostridium tetani |
| 9. | Food poisoning | Clostridium botulinum |
| 10. | Syphilis | Treponema pallidum |
![]()
Question 5.
Tabulate the salient features of Cyanophyceae?
Answer:
| Thallus | Unicellular- Eg. Chroococcus Colonial- Eg. Gleocapsa Filamentous trichome- Eg. Nostoc |
| Movement | Gliding movement – Eg. Oscillatoria |
| Protoplasm | Central – centroplasm Peripheral – chromoplast |
| Photosynthetic pigments | c. phyco cyanin & c. phyco erythrin Myxo xanthum Myxo xanthophyll |
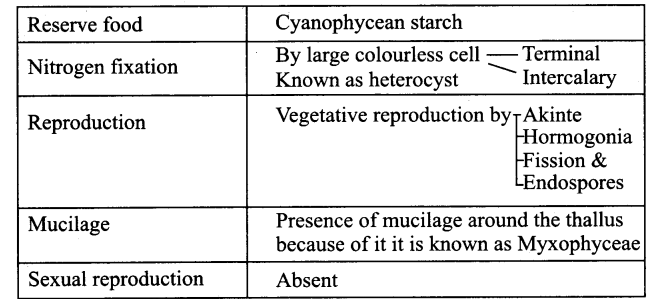
Question 6.
Give an account of Mycoplasma as Mollicutes.
Answer:
- Small-(0.1-0.5gm)
- Pieomorphic- gram-negative
- 1 st isolation by Nocard & co in 1898-from pleural fluid of cattle affected with bovine pleuropneumonia.
- Cell wall-absent
- In culture appear as fried egg.
- DNA contains low guanine and cytosine than true bacteria
- Cause disease in Animals / Plants
- Little leaf of brinjal – Witches broom of legumes Phyllody of cloves Sandal spike, -plant diseases
- Pleuropneumonia – animal disease caused by Mycoplasma mycoide.
![]()
Question 7.
Differentiate between Gram-positive and Gram-Negative bacteria.
Answer:
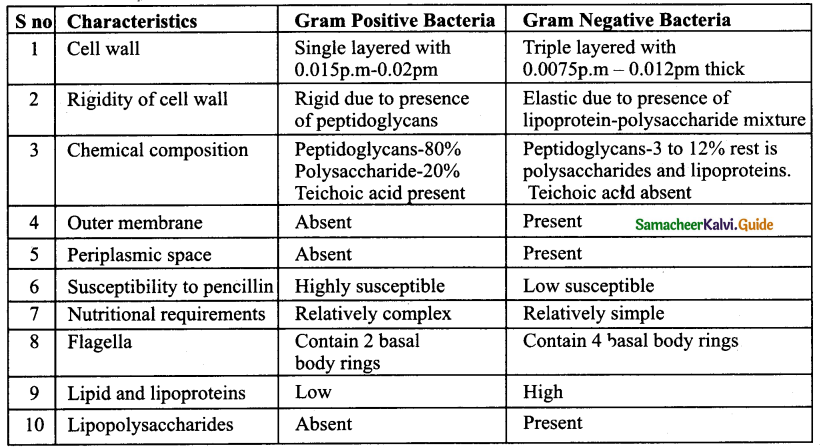
Question 8.
Explain transformation in bacteria.
Answer:
Definition: Transfer of DNA from one bacteria to another is called transformation.
- 1928 Frederick Griffth demonstrated it in mice using Diplococcus pneumonia.
- 2 strains
- Smooth colonies – virulent type (S)
- Rough colonies – Avirulent type (R)
- S type injected – mouse died because it is virulent
- R type injected – mouse lived because R type is Avirulent
- Heat killed S type injected-mouse lived
- Heat killed S type + R type called when injected mixedly} mouse died

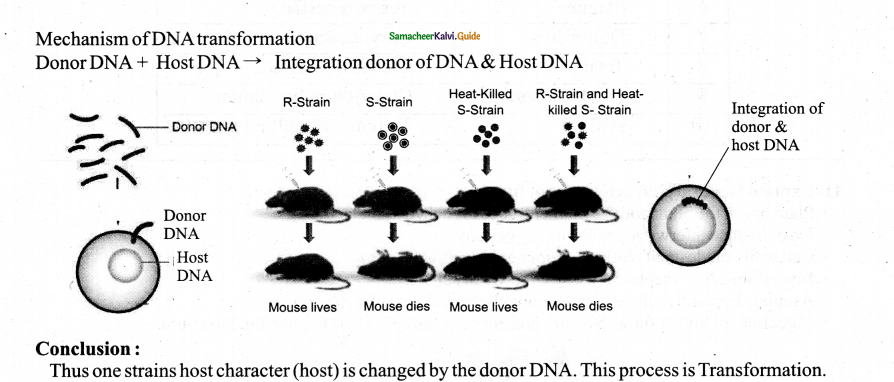
Question 9.
Classify the nitrogen-fixing biological systems.
Answer:
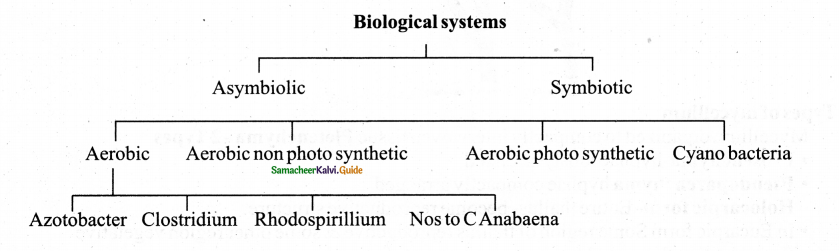
I. Symbiolic Angiosperm:
Leguminous Rhizobium root nodules of Ground nut Peas etc. (soil bacterium) Non-Leguminous (Alnus casuarinas) Frankia actinomycetes (root nodules)
II. Symbiolic gymnosperm Cycas unidentified spices of Blule green algae (corolloid roots)
III. Symbiotic ferns Azolla- Anbaena azollae – leaf pockets
IV. Symbiotic (fungi & Algae) Lichen (phycobiont mycobiont mutually benefited).
![]()
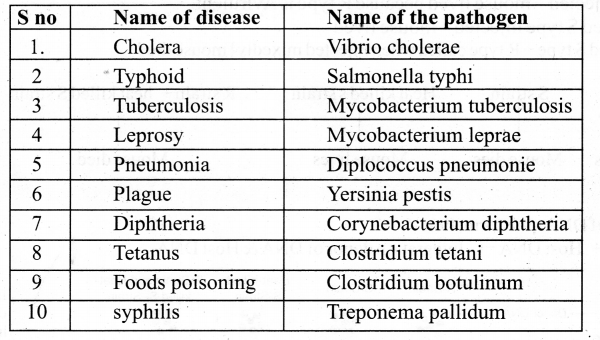
Question 10.
Tabulate the human disease caused by bacteria.
Answer:
Question 11.
Explain General characteristics of fungi
Answer:
- Plant body- the plant body is filamentous & branched hyphae No of hyphae interwoven to form – my celium
- Cell wall – made up of chitin (polymer of N acetyl glucose)
- Mycelium 2 types septate cross wall between cells Aseptate hyphae (multi nucleus coenocytic mycelium) E.g Albugo
- Mycelium of higher fungi. Septum present between cells if the hyphae Eg. Fusarium.
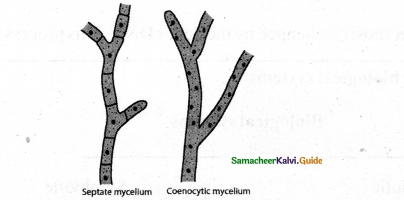
Types of mycelium
Mycelium organized to compactly interwoven tissue Pletenchyma – 2 Types
- Prosenchyma-hyphae loosely arranged
- Pseudoparenchyma hyphae compactly arranged Holocarpic form- Entire thallus- become reproductive structure.
- In Eucarpic form Some region of thallus reproductive & some other region vegetative Reproduction there are 3 types
- Anamorph-Asexual
- Teleomorph -Sexual
- Holomorph-both sexual & Asexual.
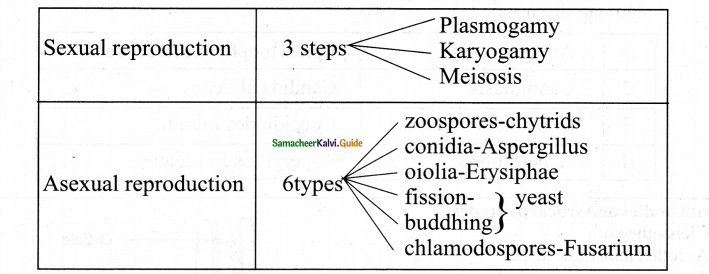
Question 12.
Tabulate various types of Mycorrhizae
Answer:
Mycorrhizae – 3 Types
|
Ectotropic mycorrhizae |
Endotropicmycorrhizae |
Ectrndotrophicmycorrhizae |
| The fungal mycelium forms a dense sheath around the root called mantle. The hypha network penetrate the intercellular spaces of the epidermis, and cortex to form Hartignet. Example pisolithus tinctorius. | The hyphae grows mainly inside the roots, penetrate the outer cortical cells of the plant root. A small portion of the mycelium is found outside the root. This form is also called Vesicular Arbuscular Mycorrhizal fungi (VAM fungi) due to the presence of vesicle or arbuscle like haustoria.
1. Arbuscular mycorrhizae(VAM)- Example Gigaspora |
The fungi form both mantle and also penetrates the cortical cells. |
![]()
Question 13.
List out diseases caused by fungi
Answer:
Diseases caused by fungi
|
S no |
Name of the disease |
Causative organism |
| Plant diseases | ||
| 1 | Blast of paddy | Magnoporthegriesea |
| 2 | Red rot of sugarcane | Colletotrichum falcatum |
| 3 | Anthracnose of beans | Colletotrichum lindemuthianum |
| 4 | White rust of crucifers | Albugo Candida |
| 5 | Peach leaf curl | Taphrina deformans |
| 6 | Rust of wheat | Puccinia graminis tritici |
Human diseases
| 1 | Athlete’s foot | Epidermophyton floccosum |
| 2 | Candidiasis | Candida albicans |
| 3 | Coccidioidomycosis | Coccidiosis immitis |
| 4 | Aspergillosis | Aspergillus fumigatus |
Question 14.
Fruit bodies or Ascocarps 4types
Answer:
- Cleistothecium
- Ascothecium(flask shape)
- Apothecium(cup shape)
- Psedothecium
1. Image structure of cleistothecium
2. Structure of PeritheciumV.S
3. Structure of Apothecium
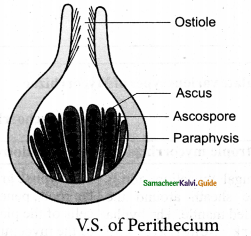
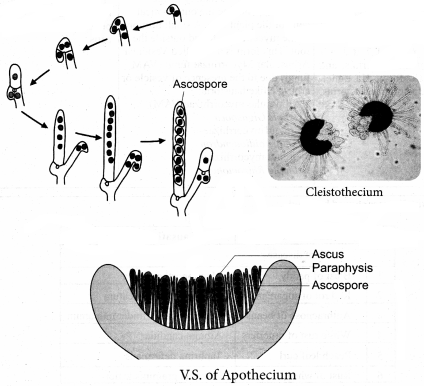
Question 15.
Give an account of Basidiomycetes (club fungi).
Answer:
| Fungi included | Puffballs, toadstools, bird nest’s fungi. Bracket fungi- stinkhorns, rusts smuts etc. |
| Habitat | Mostly terrestrial Saprophytic Parasitic mode of life |
| Mycelium | Well-developed, septate with a bracket like 3 types Monokaryotic mycelium Dikaryotic mycelium (Primary & Secondary) Tertiary mycelium |
| Sexual reproduction steps Plasmogamy Karyogamy &Meiosis | Occur – but sex organs absent Somatogamy or – Spermatisation result in Plasmogamy Karyogamy delayed & dikaryotic phase is prolonged followed by meiosis |
| image | 4 nuclei become basidiospores bom on sterigmata -(exogenous) Club-shaped basidium bear basidiospores so-known as club fungi. |
![]()