Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Guide Pdf Chapter 6 PHP Conditional Statements Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Solutions Chapter 6 PHP Conditional Statements
12th Computer Applications Guide PHP Conditional Statements Text Book Questions and Answers
Part I
Choose The Correct Answers
Question 1.
What will be the output of the following PHP code?
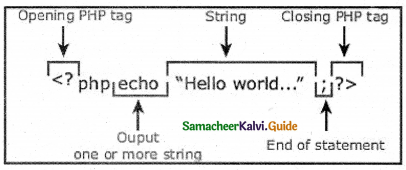
<?php
$x;
if ($x)
print “hi”;
else
print “how are u”;
?>
a) how are u
b) hi
c) error
d) no output
Answer:
c) error
![]()
Question 2.
What will be the output of the following PHP code ?
<?php
$x = 0;
if ($x++)
print “hi”;
else
print “how are u”;
?>
a) hi
b) no output
c) error
d) how are u
Answer:
a) hi
Question 3.
What will be the output of the following PHP code ?
<?php
$x;
if ($x == 0)
print “hi”;
else
print “how are u”;
print “hello”
?>
a) how are uhello
b) hihello
c) hi
d) no output
Answer:
a) how are uhello
![]()
Question 4.
Statement which is used to make choice between two options and only option is to be performed is written as
a) if statement
b) if else statement
c) then else statement
d) else one statement
Answer:
b) if else statement
Question 5.
What will be the output of the following PHP code ?
<?php
$a =
if ($a)
print “all”;
if
else
print “some”;
?>
a) all
b) some
c) error
d) no output
Answer:
c) error
![]()
Question 6.
What will be the output of the following PHP code ?
<?php
$a = “”;
if ($a)
print “all”;
if
else
print “some”;
?>
a) all
b) some
c) error
d) no output
Question 7.
What will be the output of the following PHP code ?
<?php
$x = 10;
$y = 20;
if ($x > $y + $y != 3)
print “hi”;
else
print “how are u”;
?>
a) how are u
b) hi
c) error
d) no output
Answer:
b) hi
![]()
Question 8.
What will be the output of the following PHP code ?
<?php
$x = 10;
$y = 20;
if ($x > $y && 1||1)
print “hi”;
else
print “how are u”;
?>
a) how are u
b) hi
c) error
d) no output
Answer:
b) hi
Question 9.
What will be the output of the following PHP code ?
<?php
if (-100)
print “hi”;
else
print “how are u”;
?>
a) how are u
b) hi
c) error
d) no output
Answer:
a) how are u
![]()
Part II
Short Answers
Question 1.
Define Conditional Statements in PHP
Answer:
Conditional statements are useful for writing decision-making logics. It is the most important feature of many programming languages, including PHP. They are implemented by the following types:
- if Statement
- if…else Statement
- if…else if….else Statement
- switch Statement
Question 2.
Define if statement in PHP.
Answer:
If a statement executes a statement or a group of statements if a specific condition is satisfied as per the user expectation.
Syntax:
if (condition)
{
Execute statement(s) if condition is true;
}
Question 3.
What is an if-else statement in PHP?
Answer:
If else statement in PHP:
- If a statement executes a statement or a group of statements if a specific condition is satisfied by the user expectation.
- When the condition gets false (fail) the else block is executed.
Syntax:
if (condition)
{
Execute statement(s) if condition is true;
}
else
{
Execute statement(s) if condition is false;
}
![]()
Question 4.
List out Conditional Statements in PHP.
Answer:
- if Statement
- if…else Statement
- if…else if….else Statement
- switch Statement
Question 5.
Write Syntax of the If else statement in PHP.
Answer:
if (condition)
{
Execute statement(s) if condition is true;
}
else
{
Execute statement(s) if condition is false;
}
Question 6.
Define if…elseif….else Statement in PHP.
Answer:
- If-elseif-else statement is a combination of if-else statement.
- More than one statement can execute the condition based on user needs.
![]()
Question 7.
Usage of Switch Statement in PHP.
Answer:
- The switch statement is used to perform different actions based on different conditions.
- Switch statements work the same as if statements but they can check for multiple values at a time.
Question 8.
Write Syntax of the Switch statement.
Answer:
switch (n)
{
case label1:
code to be executed if n=la bel1;
break;
case Iabel2:
code to be executed if n=label2;
break;
case label3:
code to be executed if n=iabel3;
break;
…
default:
code to be executed if n is different from all labels;
}
Question 9.
Compare if and if-else statement.
Answer:
| If Statement | If else Statement |
| if statement checks a condition and executes a set of statements when this condition is true, it does not do anything when the condition is false. | if-else statement checks a condition and executes a set of statements when this condition is true, it executes another set of statements when the condition is false. |
Part III
Explain in brief answer
Question 1.
Write the features Conditional Statements in PHP.
Answer:
PHP Conditional statements:
- Conditional statements are useful for writing decision-making logics.
- It is most important feature of many programming languages, including PHP.
- They are implemented by the following types:
- if Statement
- if…else Statement
- if…elseif….else Statement
- switch Statement
![]()
Question 2.
Write is the purpose of if elseif else stament.
Answer:
- A user can decide among multiple options.
- The if statements are executed from the top I down.
- As soon as one of the conditions controlling the if is true, the statement associated with that if is executed, and the rest of the ladder is bypassed.
- If none of the conditions is true, then the final else statement will be executed.
- More than one statement can execute the condition based on user needs.
Question 3.
Differentiate Switch and if-else statement.
Answer:
| Switch statement | if-else statement |
| Switch statement uses single expression for multiple choices. | the if-else statement uses multiple statements for multiple choices. |
| Switch statement test only for equality. | if-else statement test for equality as well as for logical expression. |
| Switch statement execute one case after another till a break statement is appeared or the end of switch statement is reached. | Either if statement will be executed or else statement is executed. |
Question 4.
Write Short notes on the Switch statement.
Answer:
- The switch statement is used to perform different actions based on different conditions.
- It tests for equality only.
- It uses default value when all the case values are not matched.
- It can have multiple ease values.
![]()
Question 5.
Differentiate if statement and if-else statement.
Answer:
| If statement | if else if else stamen |
| If-else if-else statement is a combination of if-else statement. | It consists of a single “if statement”. There is no “else” statement here. |
| More than one statement can execute the condition based on user needs | Only one statement can execute |
| If the condition is false, there are more alternatives are there | If the condition is false, there is no alternatives |
Part IV
Explain in detail
Question 1.
Explain Functions of Conditional Statements in PHP.
Answer:
Function Conditional Statements:
- Function conditional statement is the function specified inside the conditional statements.
- We can’t call a conditional function before its definition.
Syntax:
if(expression)
{
function function_name( )
{
block of statements;
}
}
function_name( ); // calling function.
Eg:
<? php
display( );
if(TRUE)
{
function display( )
{
echo “condition and function”;
}
}
Output: condition and function
Question 2.
Discuss in detail about Switch statement with an example.
Answer:
- The switch statement is used to perform different actions based on different conditions.
- Switch statement test only for equality.
- Switch statement execute one case after another till a break statement has appeared or the end of the switch statement is reached.
Syntax;
switch (n)
{
case label 1:
code to be executed if n=label1;
break;
case label 2:
code to be executed If n=label2;
break;
case label3:
code to be executed if n=label3;
break;
…
default:
code to be executed if n is different from all labels;
}
Example;
<?php
$favcolor = “red”;
switch ($favco!or) {
case “red”:
echo “Your favorite color is red!”;
break;
case “blue”:
echo “Your favorite color is blue!”;
break;
case “green”:
echo “Your favorite color is green!”;
break;
default:
echo “Your favorite color is neither red, blue, nor green!”;
}
?>
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the process of Conditional Statements in PHP?
Answer:
Conditional statements are useful for writing decision-making logics. It is the most important feature of many programming languages, including PHP. They are implemented by the following types:
(i) if Statement:
If statement executes a statement or a group of statements if a specific condition is satisfied as per the user expectation.
(ii) if…else Statement:
If statement executes a statement or a group of statements if a specific condition is satisfied by the user expectation. When the condition gets false (fail) the else block is executed.
(iii) if…elseif….else Statement:
If-elseif-else statement is a combination of if-else statement. More than one statement can execute the condition based on user needs.
(iv) Switch Case:
The switch statement is used to perform different actions based on different conditions.
Question 4.
Explain concepts of if elseif else statement.
Answer:
- If-elseif-else statement is a combination of if-else statement.
- More than one statement can execute the condition based on user needs.
Syntax:
if (1st condition)
{
Execute statement(s) if condition is true;
}
elseif(2nd condition)
{
Execute statement(s) if 2ndcondition is true;
}
else
{
Execute statement(s) if both conditions are false;
}
Example Program:
<?php
$Pass_Mark=35;
$first_class=60;
$Student_Mark=70;
if ($Student_Mark>= $first_class){ echo “The Student is eligible for the promotion with First Class”;
}
elseif ($Student_Mark>= $Pass_Mark){ echo “The Student is eligible for the promotion”;
}
else {
echo “The Student is not eligible for the promotion”;
}?>
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the if-else statement in PHP.
Answer:
If else statement in PHP:
If a statement executes a statement or a group of statements if a specific condition is satisfied by the user expectation. When the condition gets false (fail) the else block is executed.
Syntax:
if (condition)
{
Execute statement(s) if condition is true;
} else
{
Execute statement(s) if condition is false;
}
Example:
<?php
$Pass_Mark=35;
$Student_Mark=70;
if ($Student_Mark>= $Pass_Mark)
{
echo “The Student is eligible for the promotion”;
}
else
{
echo “The Student is not eligible for the promotion”; }
?>
12th Computer Applications Guide PHP Conditional Statements Additional Important Questions and Answers
Part A
Choose The Correct Answers:
Question 1.
How many types of PHP conditional statements are there?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(c) 4
![]()
Question 2.
What will be the output of the following PHP code ?
<?php
if(0.0)
print”hi”;
else
print”how are u”;
?>
a) how are u
b) hi
c) error
d) no output
Answer:
a) how are u
Question 3.
The ……………………….. statement is used to perform different actions based on different conditions.
Answer:
switch
![]()
Question 4.
What will be the output of the following PHP code ?
<?php
$a=”l”;
switch($a)
{
case1:
break;
print”hi”;
case2:
print’tiello”;
break;
default:
print”hil”;
>
?>
a) hihellohi1
b) hi
c) hihi1
d) hi1
Answer:
a) hihellohi1
Question 5.
What will be the output of the following PHP code ?
<?php
$x=l;
if($x=$x&0)
print$x;
else
break;
?>
a) 0
b) 1
c) error
d) no output
Answer:
c) error
![]()
Question 6.
Which of the following can check for multiple values at a time?
(a) If
(b) If else
(c) Nested else
(d) Switch
Answer:
(d) Switch
Very Short Answers
Question 1.
How conditional statements perform?
Answer:
It performs different actions for different decisions in programing language
Question 2.
What is an “if statement” in PHP?
Answer:
The If Statement is a way to make decisions based upon the result of a condition.
Question 3.
How switch statement and if statement differs?
Answer:
Switch statements work the same as if statements but they can check for multiple values at a time
![]()
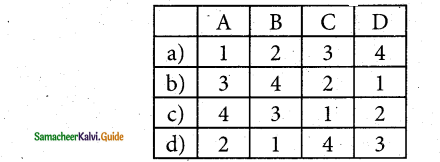
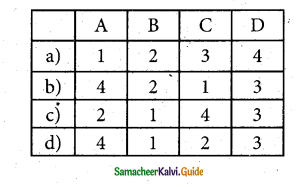
Match the following:
1. Simple if statements – Multiple branching
2. If-else statement – Combination of if-else statement
3. If elseif else statement – Only one option
4. Switch case statement – Alternative statement
Part B
Short Answers
Question 1.
Write the syntax of the If statement.
Answer:
if (condition)
{
Execute statement(s) if condition is true;
}
Question 2.
What is mean by If else ladder?
Answer:
- Else executes the following block of statements if the condition in the corresponding if is false.
- After the else, if another condition is to be checked, then an if statement follows the else. This is else if and is called as if-else ladder.
SYNTAX:
1. If statement
Answer:
if (condition)
{
Execute statement(s) if condition is true;
}
![]()
2. If else statement
if (condition)
{
Execute statement(s) if condition is true;
}
else
{
Execute statement(s) if condition is false;
}
3. If elseif else statement
if (1st condition)
{
Execute statement(s) if condition is true;
}
elseif(2nd condition)
{
Execute statement(s) if 2ndcondition is true;
}
else
{
Execute statement(s) if both conditions are false;
}
4. Switch Case:
switch (n) { case label 1:
code to be executed if n=label1;
break;
case Iabel2:
code to be executed if n=label2;
break;
case Iabel3:
code to be executed if n=label3;
break;
…
default:
code to be executed if n is different from all labels;
}
![]()
Part C
Explain in brief answer
Question 1.
Give the Syntax for If else statements in PHP?
Answer:
if (1st condition)
{
Execute statement(s) if condition is true;
}
elseif(2nd condition)
{
Execute statement(s) if 2nd condition is true;
}
else
{
Execute statement(s) if both conditions are false;
}
Programs
Question 1.
Write a php program to birthday greetings using if statement.
Answer:
<?php
$date=date(“m-d”);
if ($date==»01T0»)
{
echo “Wishing you a very Happy Birthday”;
}
?>
Question 2.
Write a php program to check whether the given number is positive or negative.
Answer:
<?php
$x = -12;
if ($x > 0)
{
echo “The number is positive”;
}
else{
echo “The number is negative”;
}
?>
![]()
Question 3.
Write a PHP program to display independence day and republic day the greetings using If elseif else statement
Answer:
<?php
$x = “August”;
if ($x == “January”) {
echo “Happy Republic Day”;
}
elseif ($x == “August”) {
echo “Happy Independence Day!!!”;
}
else{
echo “Nothing to show”;
}
?>
Part D
Explain in detail
Question 1.
Write a PHP code to display the days of weak using switch statement
Answer:
<?php
$today=date(“D”);
switch($today)
{
case”Mon”:
echo’Today is Monday.
break;
case”Tue”:
echo’Today is Tuesday.”;
break;
case”Wed”:
echo’Today is Wednesday.”;
break;
case’Thu”:echo’Today is Thursday.”;
break;
case”Fri”:
echo’Today is Friday. Party tonight.”;
break;
case”Sat”:echo’Today is Saturday.”;
break;
case”Sun”:
echo’Today is Sunday.”;
break;
default:
echo”No information available for that day.”;
break;
}
?>
![]()
Question 2.
Write a PHP program to display week days using switch case statement.
Answer:
<?php
$n = “February”;
switch($n) {
case “January”:
echo “Its January”;
break;
case “February”:
echo “Its February”;
break;
case “March”:
echo “Its March”;
break;
case “April”:
echo “Its April”;
break;
case “May”:
echo “Its May”;
break;
case “June”:
echo “Its June”;
break;
case “July”:
echo “Its July”;
break;
case “August”:
echo “Its August”;
break;
case “September”:
echo “Its September”;
break;
case “October”:
echo “Its October”;
break;
case “November”:
echo “Its November”;
break;
case “December”:
echo “Its December”;
break;
default:
echo “Doesn’t exist”;
}
?>