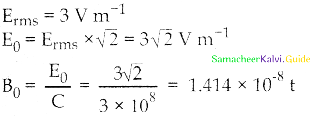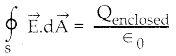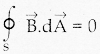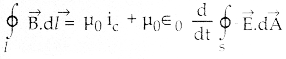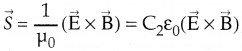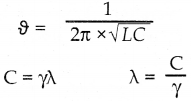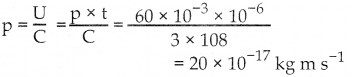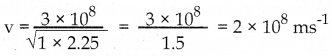Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Business Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 4 Differential Equations Ex 4.2 Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Business Maths Solutions Chapter 4 Differential Equations Ex 4.2
Question 1.
Solve:
(i) \(\frac { dy }{dx}\) = aey
Solution:
\(\frac { dy }{dx}\) = aey
\(\frac { dy }{e^y}\) = adx ⇒ e-y dy = adx
Integrating on both sides
∫e-y dy = ∫adx
\(\frac { e^y }{(-1)}\) = ax + c
-e-y = ax + c ⇒ e-y + ax + c = 0
![]()
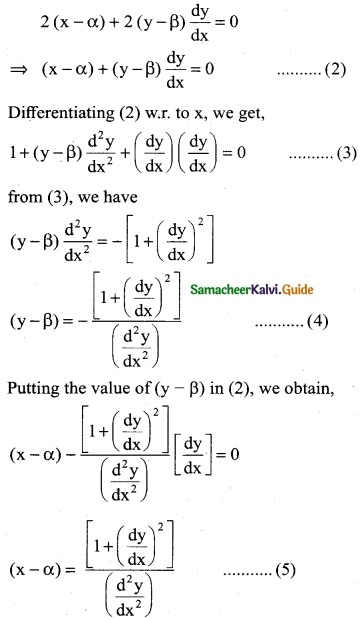
(ii) \(\frac { 1+x^2 }{1+y}\) = xy \(\frac { dy }{dx}\)
Solution:
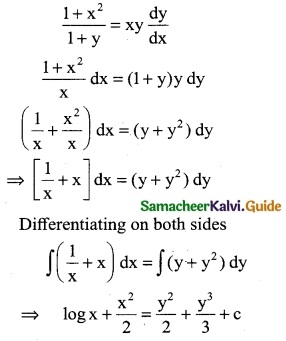
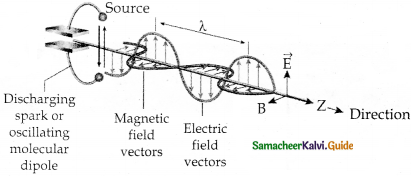
Question 2.
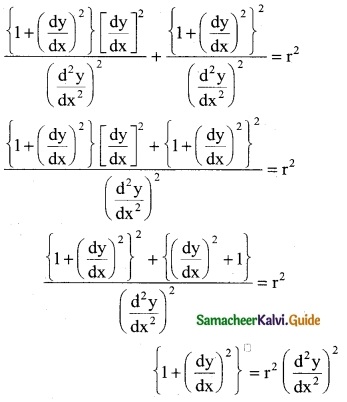
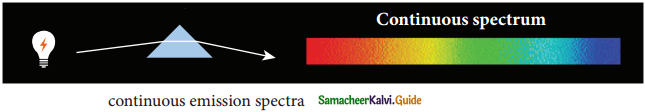
y(1 – x) – x \(\frac { dy }{dx}\) = 0
Solution:
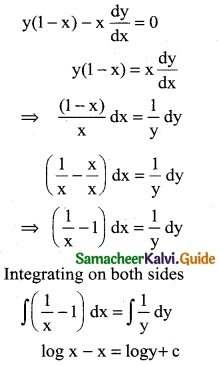
![]()
Question 3.
(i) ydx – xdy = 0 dy
Solution:
ydx – xdy = 0
ydx = xdy
\(\frac { 1 }{x}\) dx = \(\frac { 1 }{y}\) dy
Integrating on both sides
∫\(\frac { 1 }{x}\)dx = ∫\(\frac { 1 }{y}\)dy
log x = log y + log c
log x = log cy
⇒ x = cy
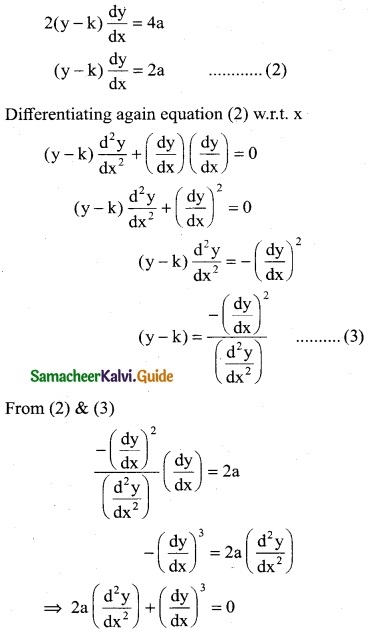
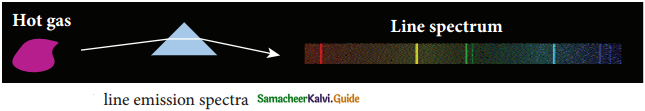
(ii) \(\frac { dy }{dx}\) + ex + yex = 0
Solution:
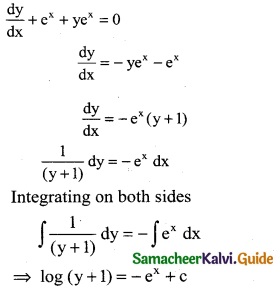
![]()
Question 4.
Solve : cosx (1 + cosy) dx – siny (1 + sinx) dy = 0
Solution:
cos x (1 + cos y) dx – sin y (1 + sin x) dy = 0
cos x (1 + cos y) dx = sin y (1 + sin x) dy
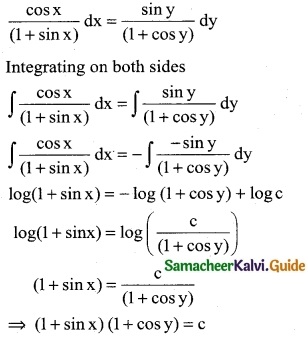
Question 5.
Solve: (1 – x) dy – (1 + y) dx = 0
Solution:
(1 – x) dy – (1 + y) dx = 0
(1 – x) dy = (1 + y) dx
\(\frac { dy }{(1+y)}\) = \(\frac { dx }{(1-x)}\)
Integrating on both sides
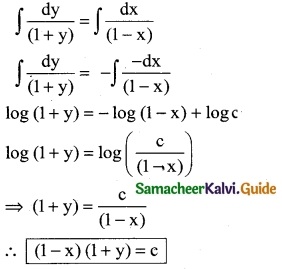
![]()
Question 6.
Solve:
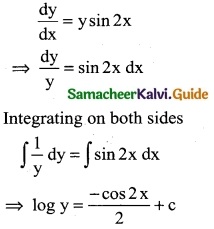
(i) \(\frac { dy }{dx}\) = y sin 2x
Solution:
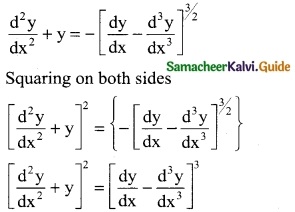
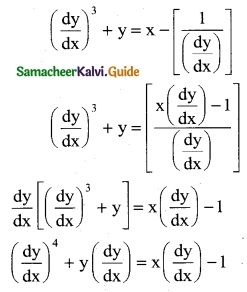
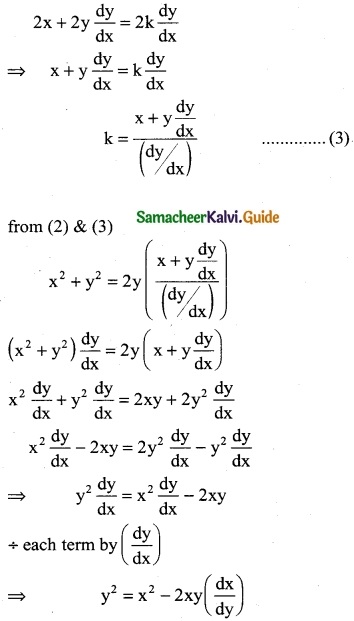
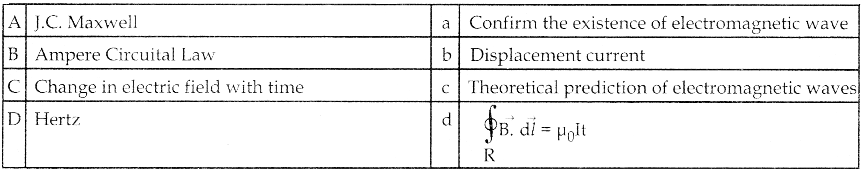
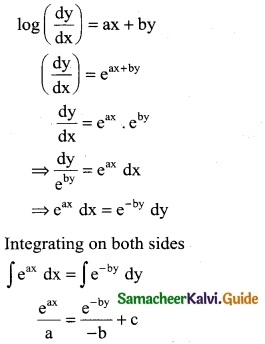
(ii) log(\(\frac { dy }{dx}\)) = ax + by
Solution:
![]()
Question 7.
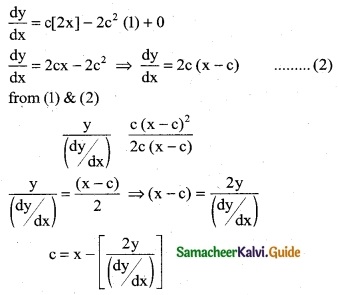
Find the curve whose gradient at any point P (x, y) on it is \(\frac { x-a }{y-b}\) and which passes through the origin.
Solution:
The gradient of the curve at P (x, y)
\(\frac { dy }{dx}\) = \(\frac { x-a }{y-b}\)
(y – b) dy = (x – a) dx
Integrating on both sides
∫(y – b)dy = ∫(x – a)dx
⇒ \(\frac { (y-b)^2 }{2}\) = \(\frac { (x-a)^2 }{2}\) + c
(Multiply each term by 2)
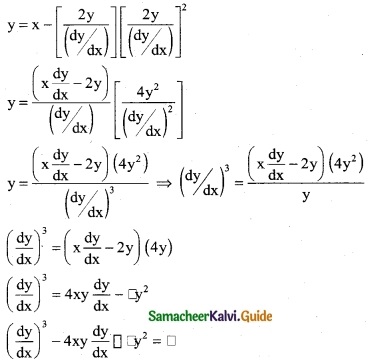
∴ (y – b)² = (x – a)² + 2c ……… (1)
Since the curve passes through the origin (0, 0)
eqn (1) (0 – b)² = (0 – a)² + 2c
b² = a² + 2c
b² – a² = 2c ………. (2)
Substitute eqn (2) in eqn (1)
(y – b)² = (x – a)² + b² – a²
![]()