Students can download 6th Science Term 1 Chapter 7 Computer – An Introduction Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 1 Chapter 7 Computer – An Introduction
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Computer – An Introduction Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Who is the father of computer?
a. Martin Luther King
b. Graham Bell
c. Charlie Chaplin
d. Charles Babbage
Answer:
d. Charles Babbage
Question 2.
Which of the following is another form of computer?
(a) Blackboard
(b) Mobile
(c) Radio
(d) Book
Answer:
(b) Mobile
![]()
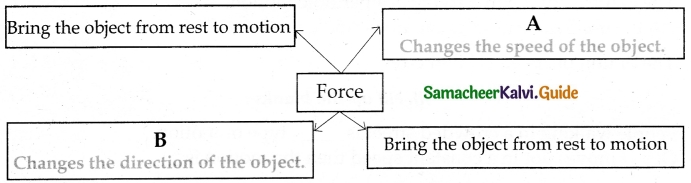
Question 3.
When was the first computer introduced?
a. 1980
b. 1947
c. 1946
d. 1985
Answer:
c. 1946
Question 4.
Who is the computer’s first programmer?
(a) Lady Wellington
(b) Augusta ado Lovelace
(c) Mary Curie
(d) Mary Comb
Answer:
(b) Augusta ado Lovelace
![]()
Question 5.
Pick out the odd one?
a. Calculator
b. Abacus
c. Flash Card
d. Laptop
Answer:
c. Flash Card
II. Fill in the blanks:
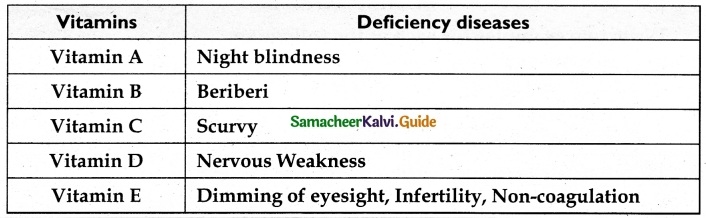
- Data is ………… Information.
- World’s first general purpose computer is ……….
- Information is ……… data
- Fifth generation computer has ………. Intelligence.
- ………… is the device that uses Index number.
Answer:
- Processed
- Electronic Numerical Integrator and computer
- a form of processed
- Artificial
- Analog Computer
![]()
III. State True or false.
- The computer is an Electronic device.
- Sir Isaac Newton invented the Computer.
- The computer can do calculations fast.
Answer:
- True
- False
- True
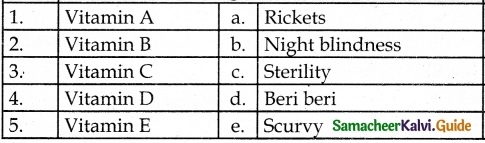
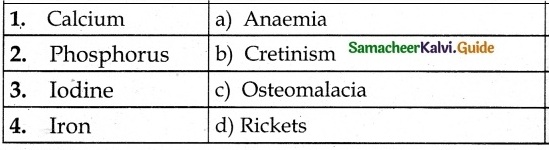
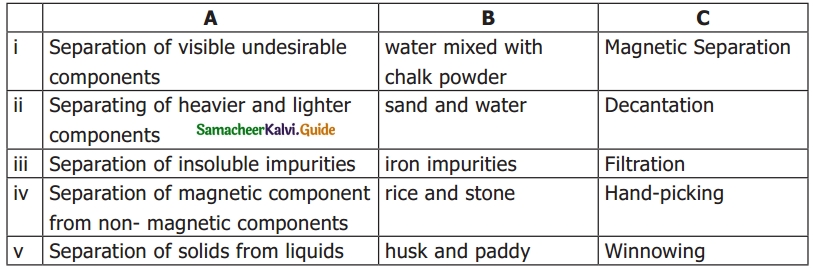
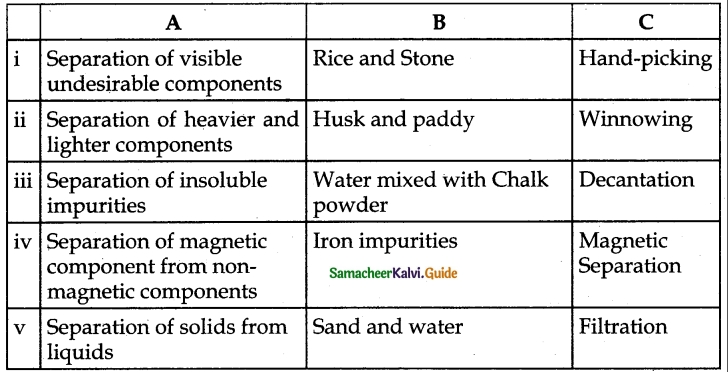
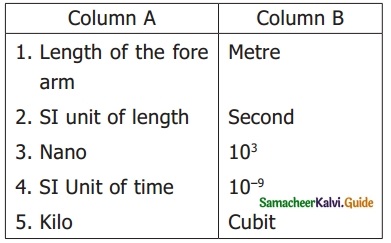
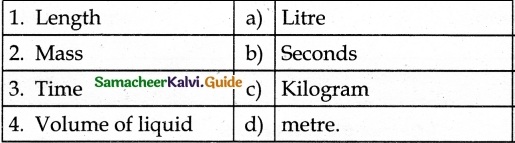
IV. Match the following:
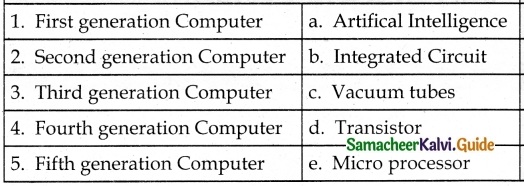
Answer:
1. – c
2. – d
3. – b
4. – e
5. – a
![]()
V. Answer the following
Question 1.
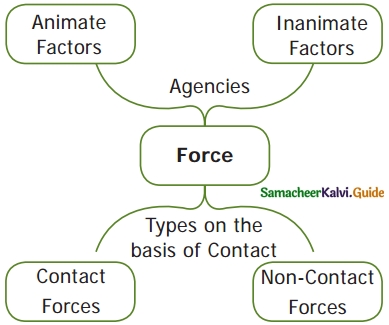
What is a Computer?
Answer:
Computer is an electronic device that processes data and information according to our needs.
Question 2.
Who are the pioneers/forerunners of computers?
Answer:
1. Charles Babbage: a professor in mathematics has designed an analog computer. He is known as the father of computers.
2. Augusta Ada Lovelace: the first programmer as she developed essential commands for mathematical operations.
Question 3.
Write a short note on Data.
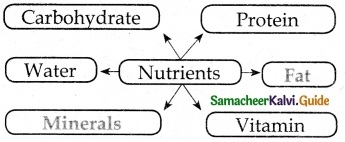
Answer:
- Data is the information that has to be processed.
- They are in the form of numbers, alphabets, and images.
![]()
Question 4.
Name any four input devices.
Answer:
Keyboard, Mouse, Bar code reader, Digital camera, etc.
Question 5.
Differentiate Hardware and Software.
Answer:
Hardware: The parts that are available on the computer that helps the software to work.
Software: The commands or programs that are used on a computer.
VI. Answer in Details.
Question 1.
Explain in detail the Applications of the computer.
Answer:
- The computer is used in textile shops for billing purposes.
- It is used in the railway station for issuing tickets.
- It is used in the banks for multi-purpose.
- It is used in ATMs.
- It is used in the Post office.
![]()