Students can download 6th Science Term 3 Chapter 3 Chemistry in Everyday Life Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 3 Chapter 3 Chemistry in Everyday Life
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Chemistry in Everyday Life Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct Answer:
Question 1.
Soaps were originally made from ………
a. proteins
b. animal fats and vegetable oils
c. chemicals extracted from the soil
d. foam booster
Answer:
b. animal fats and vegetable oils.
Question 2.
The saponification of a fat or oil is done using _______ solution for hot process.
(a) Potassium hydroxide
(b) Sodium hydroxide
(c) Hydrochloric acid
(d) Sodium chloride
Answer:
(b) Sodium hydroxide
Question 3.
Gypsum is added to the cement for ………..
a. fast setting
b. delayed setting
c. hardening
d. making paste
Answer:
b. delayed setting
Question 4.
Phenol is ……..
a. carbolic acid
b. acetic acid
c. benzoic acid
d. hydrochloric acid
Answer:
a. carbolic acid
![]()
Question 5.
Natural adhesives are made from ………..
a. Protein
b. fat
c. starch
d. vitamins
Answer:
c. starch
II. Fill in the Blanks
- ………… gas causes tears in our eyes while cutting onions.
- Water, coconut oil and ……….. are necessary for soap preparation.
- ………..is called a farmer’s best friend.
- …………. fertilizer is ecofriendly.
- ………… is an example for natural adhesive.
Answer:
- Propane Thiol Oxide
- NaOH
- Earthworm
- Artificial
- Starch
III. True or False. If False, give the correct statement.
- Concentrated phenol is used as a disinfectant.
- Gypsum is largely used in medical industries.
- Plaster of Paris is obtained from heating gypsum.
- Adhesives are the substances used to separate the components.
- NPK are the primary nutrients for plants.
Answer:
- False. – Low concentrated Phenol is used as a disinfectant.
- False – Epsum is largely used in medical industry.
- True.
- False – Adhesives are substances that are used to join two (or) more components.
- True
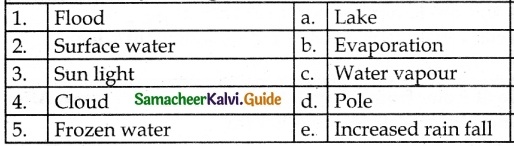
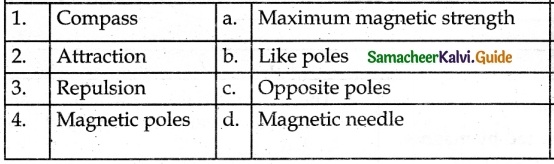
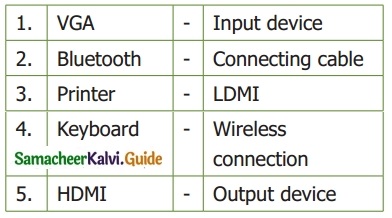
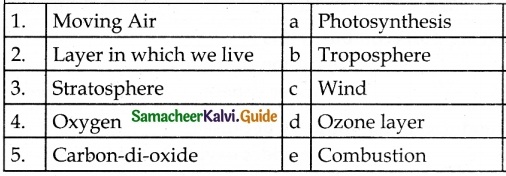
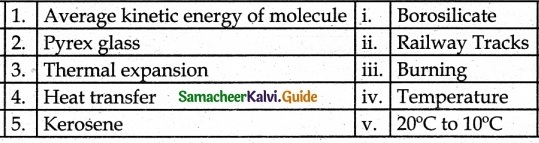
IV. Match the following:
Answer
1. – c
2. – d
3. – e
4. – b
5. – a
V. Arrange the following statements in the correct sequence:
- Pour that solution into an empty matchbox, soap can be obtained after drying.
- Take the necessary quantity of water in a jar.
- Then add coconut oil drop by drop and stir it well.
- Add concentrated sodium hydroxide in the jar and allow it to cool.
- Try this soap to wash your handkerchief.
- Cover your work area with old newspaper.
Answer:
- Cover your work area with old newspaper.
- Take the necessary quantity of water in a jar.
- Add concentrated sodium hydroxide in the jar and allow it to cool.
- Then add coconut oil drop by drop and stir it well.
- Pour that solution into an empty matchbox, soap can be obtained after drying.
- Try this soap to wash your handkerchief.
![]()
VI. Analogy:
- Urea : Inorganic fertilizer :: Vermi Compost: …………
- ……….. : Natural Adhesives :: Cello tape : Artificial Adhesives
Answer:
- Natural Fertilizer
- Starch
VII. Give Very Short Answer:
Question 1.
What are the three main constituents of soap?
Answer:
The three main constituents of soap are Lye (Sodium hydroxide), coconut oil, and water.
Question 2.
What are the two different types of molecules found in the soap?
Answer:
The two types of molecules found in the soap are
- water-loving
- water-hating.
Question 3.
Give an example of inorganic fertilizer.
Answer:
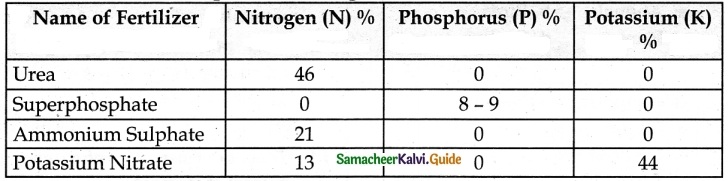
The Inorganic fertilizers are Urea, Ammonium sulphate, and Superphosphate.
Question 4.
Mention any three physical properties of phenol.
Answer:
Phenol properties:
- It is a weak acid.
- It is a volatile, white crystalline powder.
- It is a colourless solution but changes into the red in the presence of dust.
Question 5.
Explain the uses of plaster of Paris.
Answer:
Uses of plaster of pairs:
- In making blackboard chalks.
- In surgery for setting fractured bones.
- For making casts for statues and toys etc.
- In the construction industry.
Question 6.
What are the ingredients of the cement?
Answer:
The ingredients of the cement are lime, clay, and gypsum.
![]()
Question 7.
Why gypsum is used in cement production?
Answer:
Gypsum is added to control the setting of cement.
VIII. Give Short Answer:
Question 1.
Why earthworm is called a farmer’s friend?
Answer:
- Earthworms take organic wastes as food and produce compost castings.
- They provide a multitude of services to improve soil health and consequently plant health.
- So earthworm is called a farmer’s friend.
Question 2.
Explain the process of manufacturing cement.
Answer:
The cement is manufactured by crushing naturally occurring minerals such as limestone, clay, and gypsum through a milling process.
Question 3.
What are the uses of Gypsum?
Answer:
- Used as fertilizers
- Used in the process of making cement and plaster of Paris.
IX. Answer in detail
Question 1.
How are detergents manufactured?
Answer:
Manufacture of Detergents:
Materials used:
Acid slurry, Soda ash (or) Sodium Carbonate, Trisodium phosphate (TSP), sodium tripolyphosphate (STPP), Carboxy Methyl Chloride (or) Cellulose, Glauber’s salt, colour perfume and brightner.
Preparation:
- Acid slurry is first neutralised.
- Then neutralised Acid Slurry is mixed with Soda ash and kept for one hour for completion of reaction.
- Other ingredients such as Trisodium phosphate (TSP), Sodium tripolyphosphate (STPP), Carboxy Methyl Chloride (or) Cellulose, Glauber’s salt, colour, perfume, brightner are then blended to the neutralised Acid Slurry with continuous mixing.
- Then the mixture is dried.
- Now we get detergent powder.
![]()
X. Questions based on Higher Order Thinking Skills
Question 1.
Ravi is a farmer; he rears many cattle in his farm. His field has many biowastes. Advise Ravi on how to change this biowaste to compost by using vermicomposting techniques. Explain the benefits of vermi castings?
Answer:

- Make a pit of 30 cm or take a wooden box.
- Place a thin net on the base of the pit or wooden box.
- Fill it with sand for about 1-2 cm.
- Spread some plant wastes (like a dry leaf, flower) and biodegradable wastes on it.
- Sprinkle some water.
- Add some earthworms to these substances and cover them with an old cloth or dried coconut leaf.
- We can find that vermicompost is formed after four weeks.
- Use this vermicompost as manure for plants and conserve soil fertility.
Advantages of using vermicompost:
- Vermicompost is an excellent organic manure for sustainable agro-practices.
- Vermicompost is rich in essential plant nutrients.
- In improves soil structure texture, aeration, and water holding capacity and prevents soil erosion.
- Vermicompost is rich in nutrients and an eco-friendly amendment to the soil for farming and terrace gardening.
- It enhances seed germination and ensures good plant growth.
- Vermicompost can be prepared easily.
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Chemistry in Everyday Life Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the right answer:
Question 1.
………. to remove strong strains on the clothes.
(a) Detergents soap
(b) Bathing soap
(c) Bleaching powder
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Bleaching powder
Question 2.
_______ are the substances which can undergo chemical changes to produce certain materials.
(a) Soaps
(b) Fertilizers
(c) Plastics
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question 3.
If 50 kg of Superphosphate is added to the soil, how much phosphorus would the soil get?
(a) 4 – 4.5 kg
(b) 8 – 9 kg
(c) 12 – 13 kg
(d) 16 – 18 kg
Answer:
(a) 4 – 4.5 kg
![]()
Question 4.
All the plants get their _______ from the soil.
(a) Nutrients
(b) Water
(c) Nitrogen
(d) All the above
Answer:
(a) Nutrients
Question 5.
The molecular formula of Epsom is _______
(a) CaSO41/2H2O
(b) C6H5OH
(c) MgSO4.7H2O
(d) CaSO4.2H2O
Answer:
(c) MgSO4.7H2O
II. Fill in the blanks:
- ……… is a natural indicator.
- ……….. molecules goes and joins with dirt and oil in the cloth.
- Fertilizer facilitates the growth of ………….
- ………….. is used to fix bone fractures.
- Epsom salt is ………….
Answer:
- turmeric powder
- Water hating molecules
- plants
- Plaster of Paris
- Magnesium Sulphate Hydrate
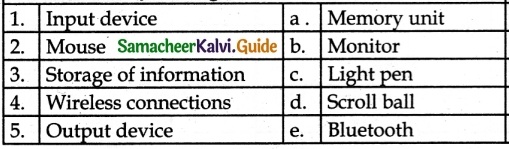
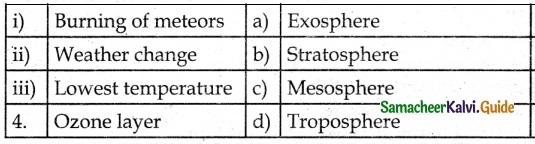
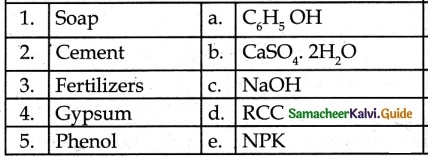
III. Match the Following:
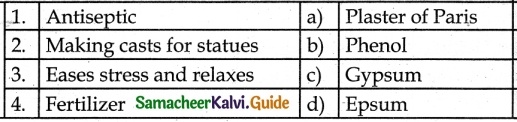
Answer:
1. – b
2. – a
3. – d
4. – c
IV. Arrange the following statements in correct sequence:
- One side water-loving and other water-hating molecules.
- When you agitate the cloth, the dirt is surrounded by many molecules and taken away from the cloth.
- The dirt surrounded by the detergent molecules floats in the water making it dirty.
- Finally, the cloth is clean.
- The detergent molecules have two sides.
- Water hating goes and joins with dirt and oil in the cloth while the water-loving joins with the water molecules.
Answer:
- The detergent molecules have two sides.
- One side water-loving and other water-hating molecules.
- Water hating goes and joins with dirt and oil in the cloth while the water-loving joins with the water molecules.
- When you agitate the cloth, the dirt is surrounded by many molecules and taken away from the cloth.
- The dirt surrounded by the detergent molecules floats in the water making it dirty.
- Finally, the cloth is clean.
![]()
V. Analogy:
- Black board chalks : ………….. : : Plant growth : Epsum
- …………. : Calcium Sulphate Dihydrate : : Plaster of Paris : Calcium Sulphate Hemihvdrate
- ………. : Mortar : : Construction of bridges : Concrete
Answer:
- Plaster of Paris
- Gypsum
- Construction of house walls.
VI. Give Very Short Answer
Question 1.
What are the principal nutrients?
Answer:
Principal nutrients are NPK
- Nitrogen (N)
- Phosphorus (P)
- Potassium (K)
Question 2.
What are fertilizers?
Answer:
Fertilizers are organic (or) inorganic materials that we add to the soil to provide one (or) more nutrients to the soil.
Question 3.
Give two examples of organic fertilizers?
Answer:
- Compost
- Vermicompost
Question 4.
Why is called inorganic fertilizers?
Answer:
The fertilizers prepared by using natural elements by making them undergo chemical changes in the laboratories are called inorganic fertilizers.
![]()
Question 5.
Why is called Portland cement?
Answer:
It was named “Portland” cement because it resembled the high-quality building stones found in Portland, England.
VII. Answer in details:
Question 1.
What is Epsum? Mention it’s used.
Answer:
Epsum:
- Epsum salt is magnesium Sulphate Hydrate.
- Its molecular formula – MgSO4. 7H2O
Uses:
- Eases stress and relaxes the body.
- Helps muscles and nerves to function properly.
- Medicine for skin problems.
- Improving plant growth in agriculture.
Question 2.
Write about the Phenol and its uses.
Answer:
Phenol:
- Phenol is a Carbolic acid of an organic compound.
- It’s molecular formula C6H5OH
- It is a weak acid.
- It is a volatile, white crystalline powder.
- It is a colourless solution but changes into the red in the presence of dust.
- It irritates when exposed to human skin.
Uses:
- It’s used industrial.
- Low concentration of Phenol is used in mouth wash, disinfectant in household cleaners.
- It is used as a surgical antiseptic since it kills microorganisms.
![]()
Question 3.
Tabulate the nutrients present in inorganic fertilizers.
Answer: