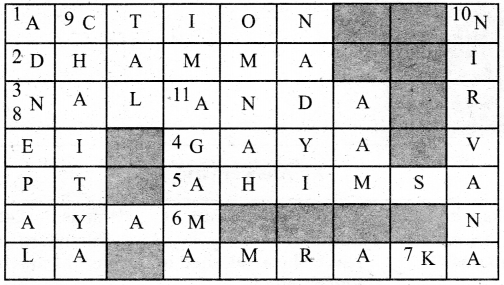
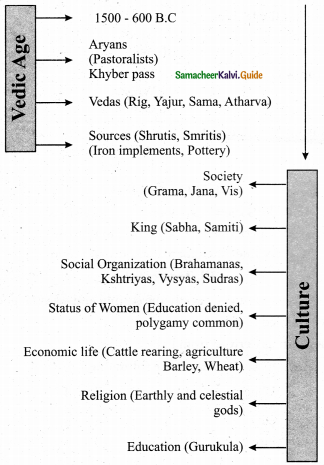
Students can download 6th Social Science Term 3 History Chapter 2 The Post-Mauryan India Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science History Solutions Term 3 Chapter 2 The Post-Mauryan India
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science The Post-Mauryan India Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The last Mauryan emperor was killed by ……………
(a) Pushyamitra
(b) Agnimitra
(c) Vasudeva
(d) Narayana
Answer:
(a) Pushyamitra
Question 2.
___________ was the founder Of Satavahana dynasty.
(a) Simuka
(b) Satakarani
(c) Kanha
(d) Sivasvati
Answer:
(a) Simuka
![]()
Question 3.
…………… was the greatest of all the Kushana emperors.
(a) Kanishka
b) Kadphises I
(c) Kadphises II
(d) Pan – Chiang
Answer:
(a) Kanishka
Question 4.
The Kantara School of Sanskrit flourished in the
(a) Deccan
(b) North-west India
(c) Punjab
(d) Gangetic valley
Answer:
(a) Deccan
![]()
Question 5.
Sakas ruled over Gandhara region …………… as their capital.
(a) Sirkap
(b) Taxila
(c) Mathura
(d) Purushpura
Answer:
(a) Sirkap
II. Match the statement with the reason and tick the appropriate answer
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : Colonies of Indo – Greeks and Indo – Parthians were established along the north-western part of India.
Reason (R) : The Bactrian and Parthian settlers gradually intermarried and intermixed with the indigenous population.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is correct but R is not correct.
(d) A is not correct but R is correct
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
Question 2.
Statement I : Indo – Greek rulers introduced die system and produced coins with inscription and symbols, engraving figures on them.
Statement II : Indo – Greek rule was ended by the Kushanas.
(a) Statement I is wrong, but statement II is correct.
(b) Statement II is wrong, but statement I is correct
(c) Both the statements are correct.
(d) Both the statements are wrong.
Answer:
(b) Statement II is wrong, but statement I is correct
Question 3.
Circle the odd one
![]()
Answer:
Kanishka
Question 4.
Answer the following in a word:
Question 1.
Who was the last Sunga ruler?
Answer:
Devabhuti
Question 2.
Who was the most important and famous king of Sakas?
Answer:
Rudradaman
![]()
Question 3.
Who established Kanva dynasty in Magadha?
Answer:
Vasudeva
Question 4.
Who converted Gondophemes into Christianity?
Answer:
St.Thomas
III. Fill in the blanks
- …………… was the founder of Indo – Parthian Kingdom.
- In the South, Satavahanas became independent after …………… death.
- Hala is famous as the author of ……………
- …………… was the last ruler of Kanva dynasty.
- Kushana’s later capital was ……………
Answer:
- Arsaces
- Susarman
- Sattasai (Saptasati)
- Susarman
- Peshawar(Purushpura)
IV. State whether True or False Answer
- Magadha continued to be a great centre of Buddhist culture True even after the fall of the Mauryan Empire.
- We get much information about Kharavela from Hathigumba True inscription.
- Simuka waged a successful war against Magadha.
- Buddhacharita was written by Asvaghosha.
Answer:
- True
- True
- False
- True
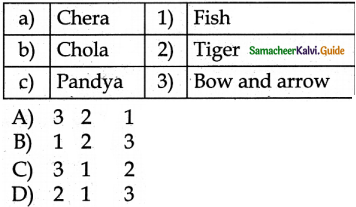
V. Match the following
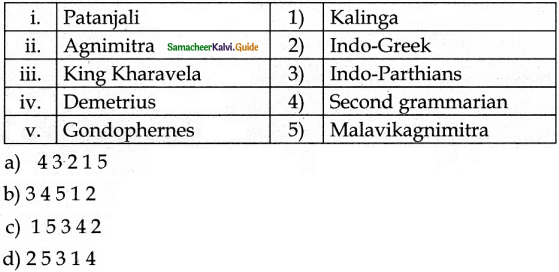
Answer:
b) 3451 2
VI. Find out the wrong statement from the following
(1) The Kushanas formed a section of the yueh-chi tribes who inhabited north-western China.
(2) Kanishka made Jainism the state religion and built many monasteries.
(3) The Great Stupa of Sanchi and the railings which enclose it belog to the Sunga period.
(4) Pan – Chiang was the Chinese general defeated by Kanishka.
Answer:
2) Kanishka made Jainism the state religion and built many monasteries.
VII. Answer in one or two sentences
Question 1.
What happened to the last Mauryan emperor?
Answer:
- The last Mauryan emperor was Brihadratha.
- He was assassinated by his own general, Pushyamitra Sunga.
Question 2.
Write a note on Kalidasa’s Malavikagnimitra.
Answer:
- Pushyamitra’s son Agnimitra is said to be the hero of Kalidasa’s Malavikagnimitra.
- This drama also refers to the victory of Vasumitra, Agnimitra’s son, over the
Greeks on the banks of the Sindhu river.
![]()
Question 3.
Name the ruler of Kanva dynasty.
Answer:
- Vasudeva
- Bhumi Mitra
- Narayana
- Susarman.
Question 4.
Highlight the literary achievements of Satavahanas.
Answer:
- The Satavahana king Hala was himself a great scholar of Sanskrit.
- The Kantara school of Sanskrit flourished in the Deccan in Second Century B.C.
- Hala is famous as the author of Sattasai (Saptasati), 700 stanzas in Prakrit.
Question 5.
Name the places where Satavahana’smounments are situated.
Answer:
- Gandhara
- Madhura
- Amaravati
- BodhGaya
- Sanchi
- Bharhut
Question 6.
Give an account of the achievements of Kadphises
Answer:
- Kadphises I was the first famous military and political leader of the Kushanas.
- He overthrew the Indo-Greek and Indo-Parthian rulers.
- He established himself as a sovereign ruler of Bactria.
- He extended his power in Kabul, Gandhara and up to the Indus.
![]()
Question 7.
Name the Buddhist saints and scholars who adorned the court of Kanishka
Answer:
- Asvaghosha
- Vasumitra
- Nagarjuna
VIII. Answer the following
Question 1.
Who invaded India after the decline of the Mauryan empire.
Answer:
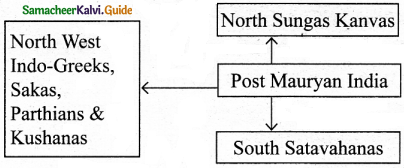
- The break-up of the Mauryan empire resulted in the invasions of Sakas, Scythians, Parthians, Indo-Greeks or Bactria Greeks, and Kushanas from the north-west.
- In the South, Satavahanas became independent after Asoka’s death.
- There were Sunga and Kanvas in the north before the emergence of the Gupta dynasty.
- Chedis (Kalinga) declared their independence.
- Though Magadha ceased to be the premier state of India, it continued to be a great center of Buddhist culture.
Question 2.
Give an account of the conquests of Pushyamitra Sunga.
Answer:
- The last Mauryan emperor, Brihadratha, was assassinated by his own general, Pushyamitra Sunga.
- He established his Sunga dynasty in Magadha. His capital was Pataliputra.
- Pushyamitra successfully repulsed the invasion of Bactria king Menander. He also conquered Vidarbha.
- He was a staunch follower of Vedic religion. He performed two Asvamedbayagnas (horse sacrifices) to assert his imperial authority.
![]()
Question 3.
Write a note on GautamiputraSatakarni
Answer:
- GautamiputraSatakarni was the greatest ruler of the family.
- In the Nasik prashasti, published by his mother GautamiBalasri, Gautamiputra Satakami is described as the destroyer of Sakas, Yavanas (Greeks), and Pahlavis (Parthians).
- The extent of the empire is also mentioned in the record.
- Their domain included Maharashtra, north Konkan, Berar, Gujarat, Kathiawar, and Malwa.
- His ship coins are suggestive of Andhras’ skill in seafaring and their naval power.
- The Bogor inscriptions suggest that South India played an important role in the process of early state formation in Southeast Asia.
Question 4.
What do you know of the Gondopharid dynasty?
Answer:
- Indo-Parthians came after the Indo-Greeks and the Indo-Scythians who were, in turn, defeated by the Kushanas in the second half of the first century A.D.
- Indo-Parthian kingdom or Gondopharid dynasty was founded by Gondophemes.
- The domain of Indo-Parthians comprised Kabul and Gandhara.
- The name of Gonodophemes is associated with the Christian apostle St. Thomas.
- According to Christian tradition, St.Thomas visited the court of Gondophemes and converted him to Christianity.
Question 5.
Who was considered the best known Indo-Greek king? Why?
Answer:
- Menander was one of the best known Indo-Greek kings.
- He is said to have ruled a large kingdom in the north-west of the country.
- His coins were found over an extensive area ranging from Kabul valley and Indus river to western Uttar Pradesh.
- MilindaPanha, a Buddhist text, is a discourse between Bactrian king Milinda and the learned Buddhist scholar Nagasena.
- This Milinda is identified with Menander.
- Menander is believed to have become a Buddhist and promoted Buddhism.
![]()
Question 6.
Who was Sakas?
Answer:
- The Indo-Greek rule in India was ended by the Sakas. Sakas as nomads came in huge number and spread all over northern and western India.
- The Sakas were against the tribe of Turki nomads.
- Sakas were Scythians, nomadic ancient Iranians, and known as Sakas in Sanskrit.
- Saka rule was founded by Maos or Mogain in the Gandhara region and his capital was ‘Sirkap’. His name is mentioned in Mora inscription. His coins bear images of Buddha and Siva.
- Rudradaman was the most important and famous king of Sakas. His Junagadh/ Gimar inscription was the first inscription in chaste Sanskrit.
- In India, the Sakas were assimilated into Indian society. They began to adopt Indian names and practice Indian religious beliefs.
- The Sakas appointed kshetras or satraps as provincial governors to administer their territories.
Question 7.
Give an account of the religious policy of Kanishka.
Answer:
- Kanishka was an ardent Buddhist.
- His empire was a Buddhist empire.
- He adopted Buddhism under the influence of Asvaghosha, a celebrated monk from Pataliputra.
- He was as equal as the exponent and champion of Mahayanism.
- He made Buddhism the state religion.
- He built many stupas and monasteries in Mathura, Taxila, and many other parts of his kingdom.
- He sent Buddhist missionaries to Tibet, China, and many countries of Central Asia for the propagation of Buddha’s gospel.
- He organised the fourth Buddhist Council at Kundalavana near Srinagar to sort out the differences between the various schools of Buddhism. It was only in this council that Buddhism was split into Hinayanism and Mahayanism.
IX. HOTS
Question 1.
The importance of the Gandhara School of Art.
Answer:
- The Gandhara School of Indian Art is heavily indebted to Greek influence.
- The Greeks were good cave builders.
- The Mahay ana Buddhists learnt the art of carving out caves from them.
- They became skilled in rock-cut architecture.
- This Gandhara art flourished during Kanishka time. The most favourite subject was the carving of Sculptures of Buddha.
Question 2.
Provide an account of trade and commerce during the Post-Mauryan period in South India.
Answer:
- Kadphises II maintained a friendly relationship with the emperors of China and Rome.
- He encouraged trade and commerce with foreign countries.
- His coins contained the inscribed figures of Lord Siva and his imperial titles.
- The inscriptions in the coins were in the Kharosthi language.
X. Activity (For Students)
- Prepare an album with centres of archaeological monuments of Satavahanas and Kushanas.
- Arrange a debate in the classroom on the cultural contribution of Indo-Greeks, Sakas, and Kushanas.
XI. Answer Grid
Question 1.
Who wrote Brihastkatha?
Answer:
Gunadhya
Question 2.
Name the Satavahana ruler who performed two Asvamedha sacrifices.
Answer:
Satakarni
Question 3.
How many years did the Satavahanas rule the Deccan?
Answer:
450 years
![]()
Question 4.
Who laid the foundation of the Saka era?
Answer:
Mao’s (or) Mogain
Question 5.
What was the favourite subject of Gandhara artists?
Answer:
Carving of Sculptures of Buddha
Question 6.
Where did Kanishka organise the fourth Buddhist Council?
Answer:
Kundalavana (near Srinagar)
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science The Post-Mauryan India Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer:
Question 1.
The Chinese Buddhist monk and traveller who wrote si-yu-ki …………….
(a) Fahien
(b) Hiuen Tsang
(c) Yuch – Chi
(d) Pan – Chiang
Answer:
(b) Hiuen Tsang
Question 2.
Asvahosha wrote
(a) Brihastkatha
(b) Mahabhasya
(c) Buddhacharita
(d) Harshacharita
Answer:
(c) Buddhacharita
![]()
Question 3.
During the Sunga period stone was replaced by railings.
(a) wood
(b) iron
(c) copper
(d) brick
Answer:
(a) wood
Question 4.
MilindaPanha is a Buddhist
(a) Statue
(b) Cave
(c) Text
(d) Monastry
Answer:
(c) Text
Question 5.
……………. gradually gained ascendancy and became the court language.
(a) Sanskrit
(b) Kharasthi
(c) Kannada
(d) Prakrit
Answer:
(a) Sanskrit
II. Match the statement with the reason and tick the appropriate answer
Question 1.
Assertion (A): The Greek rulers of Bactria and Parthia started encroaching into the northwestern borderlands of India.
Reason (R): There was a decline in the Mauryan empire.
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are correct and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is correct but R is not correct.
(d) Both the statements are wrong.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A
![]()
Question 2.
Statement I: The Mahayana Buddhists learned the art of carving out caves from the Greeks.
Statement II: The Greeks were good cave builders.
(a) Statement I is wrong, but statement II is correct.
(b) Statement II is wrong, but the statement I is correct.
(c) Both the statements are correct.
(d) Both the statements are wrong.
Answer:
(c) Both the statements are correct.
III. Fill in the blanks
- Simuka’s successor was his brother …………….
- A bronze statue of the standing Buddha was discovered in …………….
- The Indo – Greek rule in India was ended by the ……………..
- The Saka ruler Mogain’s capital was ……………..
- Rudradaman’s ……………. inscription was the first inscription in chaste Sanskrit.
Answer:
- Krishna
- OC – EO
- Sakas
- Sirkap
- Junagadh / Girnar
IV. True or False
- Satakarni was Simuka’s nephew.
- A stone seal discovered in Nakhon Pathom was in Thailand.
- Mao’s name is mentioned in the Mora inscription.
- The Kushanas appointed satraps as provincial governors.
- Kushana rulers were Buddhists.
Answer:
- True
- True
- True
- False
- True
V. Answer in one or two sentences
Question 1.
Write a short note on king Kharavela of Kalinga
Answer:
- King Kharavela was a contemporary of the Sungas.
- Hathigumba Inscription gave information about Kharavela.
Question 2.
Who laid the foundation of the Satavahana dynasty?
Answer:
- The last Kanva ruler Susarman was assassinated by his powerful feudatory chief of Andhra named Simuka.
- Simuka laid the foundation of the Satavahana dynasty.
![]()
Question 3.
How did the Sakas assimilate into Indian Society?
Answer:
- The Sakas began to adopt Indian names.
- They practiced Indian religious beliefs.
Question 4.
Under whom did the satrapies Bactria and Parthia become independent,
Answer:
Satrapies Bactria became independent under the leadership of Diodotus I and Parthia under Arsaces.
VII. Answer the following
Question 1.
Write a note on the Conquests of Kanishka.
Answer:
- Kanishka conquered and annexed Kashmir.
- He waged a successful war against Magadha.
- He also waged a war against a ruler of Parthia to maintain safety and integrity in his vast empire on the western and south-western border.
- After the conquest of Kashmir and Gandhara, he turned his attention towards China.
- He defeated the Chinese general Pan-Chiang and safeguarded the northern borders of India from Chinese intrusion.
- His empire extended from Kashmir down to Benaras, and the Vindhya mountain in the south. It included Kashgar, Yarkand touching the borders of Persia and Parthia.
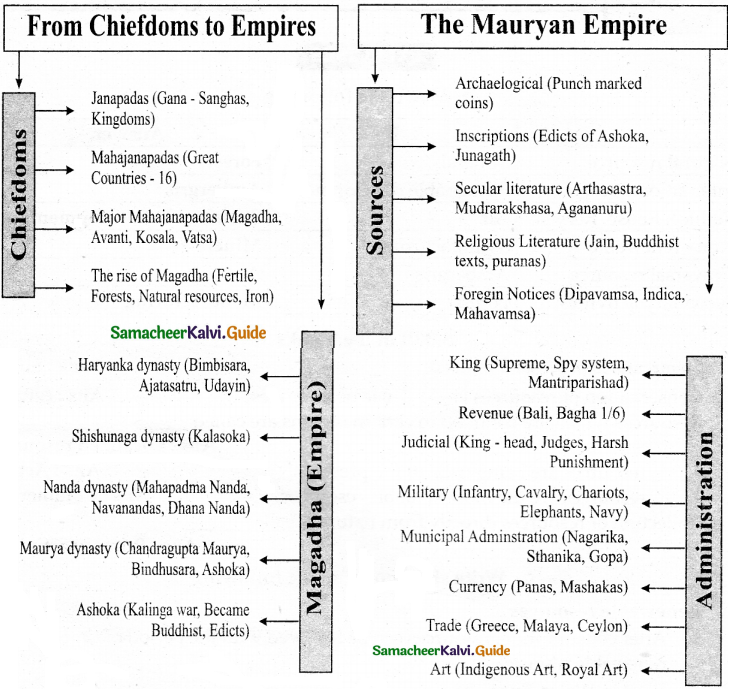
VIII. Mind map