TN State Board 12th Economics Important Questions Chapter 11 Economics of Development and Planning
Question 1.
Define economic development.
Answer:
Michael P. Todaro, “Development must, therefore, be conceived as a multidimensional process involving major changes in social structures, popular attitudes and national institutions as well as the acceleration of growth, the reduction of inequality and the eradication of absolute poverty.
Question 2.
Mention the indicators of development.
Answer:
- GDP – Gross Domestic Product
- Gross National Product (GNP)
- GND per capita
- The Human Development Index.
![]()
Question 3.
Distinguish between economic growth and development.
Answer:
| Economic Growth |
Economic Development |
| Deals with the problems of Developed countries. | Deals with the problems of UDCs. |
| Change is gradual and steady. | Change is discontinuous and spontaneous. |
| Means more output. | Means not only more output but also its composition. |
| Concerns Quantitative aspects i.e., increase in per capita income. | Quantitative as well as Qualitative. |
| Narrow | Wider concept Development = Growth + Change |
Question 4.
What is GNP?
Answer:
Gross National Product is the total market value of all final goods and services produced within a nation in a particular year, plus income earned by its citizens, (including income of those located abroad) minus income of non residents located in that country.
![]()
Question 5.
Define economic planning.
Answer:
Economic Planning is “collective control or suppression of private activities of production and exchange ”. – Robbins
“Economic Planning in the widest sense is the deliberate direction by, persons in-charge of large resources of economic activity towards chosen ends – Dalton.
Question 6.
What are the social indicators of economic development?
Answer:
Social indicators: It is referred to as basic and collective needs of the people. The direct provision of basic needs such as health, education etc check social backwardness.
Question 7.
Write a short note on NITI Aayog.
Answer:
National Institution for transforming India was formed in 1st January 2015 by union Cabinet Resolution. It is the policy of Government of India. It has replaced the Planning Commission from 13 August 2014.
![]()
Question 8.
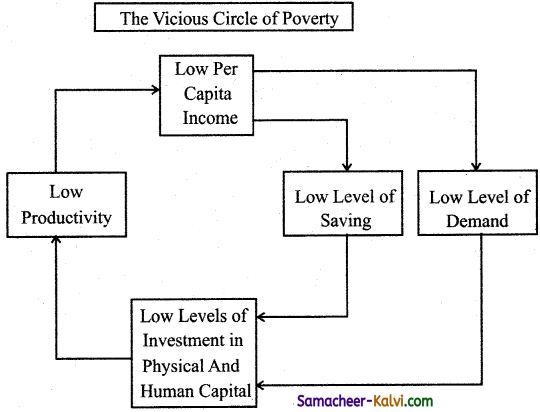
Elucidate major causes of vicious circle of poverty with diagram.
Answer:
There are circular relationship known as vicious circle of poverty on Low production, Low investment, Low conception.
Example, A poor man may not have enough to eat, being underfed his health is lost and so his working capacity is low. It operates both on demand and supply side – the cause and the effect is the same.(vicious)
Question 9.
What are the non-economic factors determining development?
Answer:
- Human Resource
- Technical Know-how
- Political Freedom
- Social Organization
- Corruption free administration
- Desire for Development
- Moral, ethical and social values
- Casino Capitalism
- Patrimonial Capitalism
![]()
Question 10.
How would you break the vicious circle of poverty?
Answer:
Vicious circle is associated with low rate of saving and investment on supply side. In underdeveloped country, the rate of investment and capital formation can be stepped up without reduction in consumption. For this the marginal rate of savings is to be greater than aggregate of saving.
To break this, the strategy of balanced growth was suggested by Nurkse. Simultaneously investment in large number of industries create mutual demand. Through the strategy of balanced growth, vicious circle of poverty operating on demand side of capital formation can be broken.
Question 11.
Trace the evolution of economic planning in India.
Answer:
- Sir M. Vishveshwarya (1934) – He made foundation for economic planning in India in 1934. It was 10 year plan.
- Jawaharlal Nehru (1938) – He set up “National planning commission” and there was changes in political era.
- Bombay plan (1940) – Formed by 8 leading industrialist, 15 year investment plan.
- S.N.Agarwal (1944) – He gave ‘Gandhian Plan” focusing on agriculture and rural area.
- M.N.Roy(1945)- ‘People’s Plan’ aiming at mechanization of agriculture.
- J.P.Narayanan – ‘Sarvodhaya Plan’ with the idea of Vinobabhave.
![]()
Question 12.
Describe the case for planning.
Answer:
The Economic planning is justified on the following grounds.
- To accelerate and strengthen market mechanism.
- To remove unemployment.
- To achieve balanced development.
Question 13.
Distinguish between functional and structural planning.
Answer:
Functional planning:
It refers to that planning which seeks to remove economic difficulties by directing all the planning activities within the existing economic and social structure.
Structural planning:
It refers to a good deal of changes in the socio economic frame work of the country. This type of planning is adopted mostly in under developed countries.
Question 14.
What are the functions of NITI Aayog?
Answer:
- Co-operative and Competitive Federalism.
- Shared National Agenda
- Decentralized Planning
- Vision and Scenario Planning
- Network of Expertise
- Harmonization
- Conflict Resolution
- Co-ordinating Interface with the World
- Internal Consultancy
- Capacity Building
- Monitoring and Evaluation
![]()
Question 15.
Discuss the economic determinants of economic development.
Answer:
Economic Factors:
(i) Natural Resources:
The existence of natural resources in abundance is essential for development. But India with larger resources is poor.
(ii) Capital formation:
It is the net addition to the existing stock of capital goods. Capital formation helps to increase productivity of labour and there by production and income.
(iii) Size of market:
It stimulate production, increase employment and increase National per capita income.
(iv) Structural change:
Change in occupational structure of the economy. If the economy is agricultural predominant, then it remains backward.
(v) Financial system:
Efficient and organized Banking System in the country.
(vi) Marketable surplus:
Total amount of output cultivated above consumption of their own. This can be sold in the market for earning income.
(vii) Foreign trade:
When the country has huge FOREX then it is developed.
(viii) Economic System:
Free market system (Laissez faire policy) enjoy between growth rate.
Question 16.
Describe different types of Planning.
Answer:
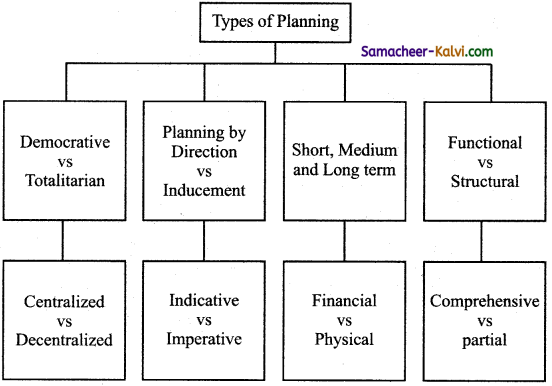
There are different types of planning which differ in ideology and the procedure.
(i) Democratic Vs totalitarian:
Democratic – Planning within democracy
Totalitarian – There is control of Central Government
(ii) Centralized Vs Decentralized:
Centralized – It is by Central planning Authority
Decentralized – Planning by local organization
(iii) Planning by direction Vs Inducement:
Planning by direction – There is central authority which plans.
Inducement – People are induced to act under certain way.
(iv) Indicative Vs Imperative:
Indicative – The outline of the plan is prepared by the Government and executed by private in mixed economy.
Imperative – The government policies and procedures are rigid.
Eg: China, Russia.
(v) Short medium long: Term
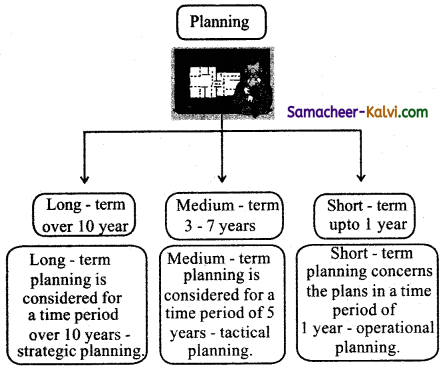
(vi) Financial Vs Physical:
Financial – Resources are allocated as money.
Physical – Human resource.
(vii) Functional Vs Structural:
Functional – To remove economic difficulty.
Structural – socio economic frame work.
(viii) Comprehensive Vs Partial:
Comprehensive – General planning,
Partial planning – It is to consider only few important sector.
![]()
Question 17.
Bring out the arguments against planning.
Answer:
The failure of market mechanism is the cause for economic planning. The argument against planning are
(i) Loss of Freedom:
The absence of freedom in decision making act as an obstacle for economic growth under planning, the crucial decisions are made by the Central Planning Authority.
(ii) Elimination of Initiating:
Under centralized planning, there will be no incentive for initiatives and innovations. The absence of private ownership discourages the entrepreneur from taking bold decisions. The red-tapism is also prevalent in the economy.
(iii) High Cost Management:
Cost management of economic affairs outweighs the benefits of planning. As Lewis says, “The better we try to plan, the more planners we need”.
(iv) Difficulty in advance calculations:
The producers and consumers adjust their supply and demand based on price changes. There is no such mechanism in a planned economy. The arguments against planning are concerned with centralized and totalitarian planning.
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
“Redistribution with Growth” became popular slogan under which approach?
(a) Traditional approach
(b) New welfare oriented approach
(c) Industrial approach
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) New welfare oriented approach
Question 2.
Which is not the feature of econofnic growth?
(a) Concerned with developed nations
(b) Gradual change
(c) Concerned with quantitative aspect
(d) Wider concept
Answer:
(d) Wider concept
Question 3.
Which among the following is a characteristic of underdevelopment?
(a) Vicious circle of poverty
(b) Rising mass consumption
(c) Growth of Industries
(d) High rate of urbanization
Answer:
(a) Vicious circle of poverty
![]()
Question 4.
The non-economic determinant of economic development:
(a) Natural resources
(b) Human resource
(c) Capital formation
(d) Foreign trade
Answer:
(b) Human resource
Question 5.
Economic growth measures the:
(a) Growth of productivity
(b) Increase in nominal income
(c) Increase in output
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Increase in output
Question 6.
The supply side vicious circle of poverty suggests that poor nations remain poor because:
(a) Saving remains low
(b) Investment remains low
(c) There is a lack of effective government
(d) (a) and (b) above
Answer:
(d) (a) and (b) above
![]()
Question 7.
Which of the following plan has focused on the agriculture and rural economy?
(a) People’s Plan
(b) Bombay Plan
(c) Gandhian Plan
(d) Vishveshwarya Plan
Answer:
(c) Gandhian Plan
Question 8.
Arrange following plans in correct chronological order.
(a) People’s Plan
(b) Bombay Plan
(c) Jawaharlal Nehru Plan
(d) Vishveshwarya Plan
Answer choices
(a) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
(b) (iv) (iii) (ii) (i)
(c) (i) (ii) (iv) (iii)
(d) (ii) (i) (iv) (iii)
Answer:
(b) (iv) (iii) (ii) (i)
Question 9.
M.N. Roy was associated with:
(a) Congress Plan
(b) People’s Plan
(c) Bombay Plan
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) People’s Plan
![]()
Question 10.
Which of the following country adopts indicative planning?
(a) France
(b) Germany
(c) Italy
(d) Russia
Answer:
(b) Germany
Question 11.
Short-term plan is also known as:
(a) Controlling Plans
(b) De-Controlling Plans
(c) Rolling Plans
(d) De-rolling Plans
Answer:
(a) Controlling Plans
Question 12.
Long-term plan is also known as:
(a) Progressive Plans
(b) Non-Progressive Plans
(c) Perspective Plans
(d) Non-Perspective Plans
Answer:
(c) Perspective Plans
![]()
Question 13.
The basic philosophy behind long-term planning is to bring _________ changes in the economy.
(a) Financial
(b) Agricultural
(c) Industrial
(d) Structural
Answer:
(c) Industrial
Question 14.
Sarvodaya Plan was advocated by:
(a) Mahatma Gandhi
(b) J.P. Narayan
(c) S. N. Agarwal
(d) M.N. Roy
Answer:
(b) J.P. Narayan
Question 15.
Planning Commission was set up in the year:
(a) 1950
(b) 1951
(c) 1947
(d) 1948
Answer:
(a) 1950
![]()
Question 16.
Who wrote the book ‘The Road to Serfdom’?
(a) Friedrich Hayek
(b) H.R. Hicks
(c) David Ricardo
(d) Thomas Robert Malthus
Answer:
(a) Friedrich Hayek
Question 17.
Perspective plan is also known as:
(a) Short-term plan
(b) Medium-term plan
(c) Long-term plan
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Long-term plan
Question 18.
NITI Aayog is formed through:
(a) Presidential Ordinance
(b) Allocation of business rules by President of India
(c) Cabinet resolution
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Cabinet resolution
![]()
Question 19.
Expansion of NITI Aayog?
(a) National Institute to Transform India
(b) National Institute for Transforming India
(c) National Institution to Transform India
(d) National Institution for Transforming India
Answer:
(d) National Institution for Transforming India
Question 20.
The Chair Person of NITI Aayog is:
(a) Prime Minister
(b) President
(c) Vice – President
(d) Finance Minister
Answer:
(a) Prime Minister
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Notes Chapter 11 Economics of Development and Planning
→ Political freedom: The process of development is linked with political freedom.
→ Crony capitalism: People do not participate in the process of development.
→ Long Term plan: Plan period for a time period of 10 years.
→ Decentralized Planning: To restructure the planning process.
→ Marketable Surplus: Refers to the total amount of farm output cultivated by farmers over and above their family consumption needs.
![]()
→ Economic development:
“Development must, therefore, be conceived as a multidimensional process involving major changes in social structures, popular attitudes and national institutions as well as the acceleration of growth, the reduction of inequality and the eradication ofabsolute poverty. – Michael P. Todaro.
→ Non – Economic factors:
“Economic Development has much to do with human endowments, social attitudes, political conditions and historical accidents. Capital is a necessary but not a sufficient condition of progress ”. – Ragnar Nurkse.
→ Vicious circle of poverty:
Nurkse explains the idea in these words: “It implies a circular constellation of forces tending to act and react upon one another in such a way as to keep a poor country in a state of poverty.
→ Planning:
Economic Planning is “collective control or suppression of private activities of production and exchange -Robbins
“Economic Planning in the widest sense is the deliberate direction by persons in-charge of large resources of economic activity towards chosen ends”. -Dalton