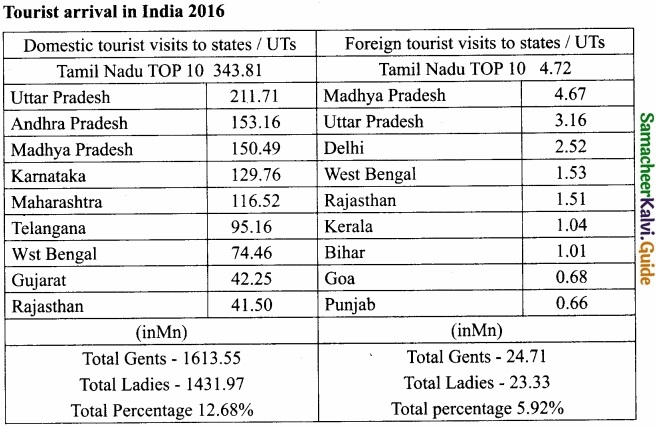
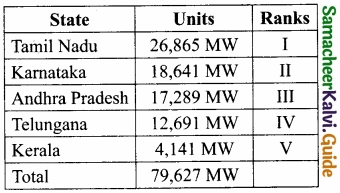
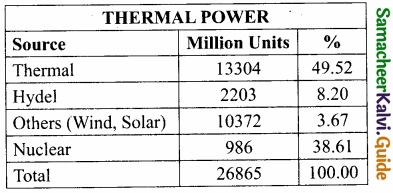
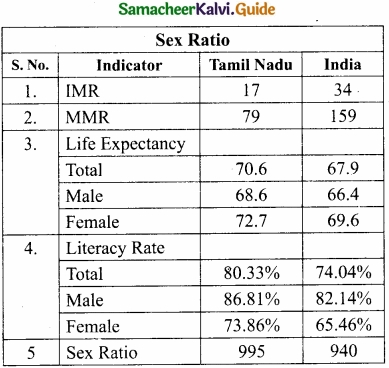
Students can Download 10th Tamil Chapter 2.2 காற்றை வா! Questions and Answers, Summary, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Tamil Solutions Chapter 2.2 காற்றை வா!
கற்பவை கற்றபின்
Question 1.
இவ்வசன கவிதையில் இடம் பெற்றுள்ள வேண்டுகோள் சொற்களும் கட்டளைச் சொற்களும் (வாசனையுடன் வா, அவித்து விடாதே…… கவிதையின் உட்பொருளை வெளிப்படுத்தத் துணை நிற்பது குறித்துப் பேசுக.
Answer:
வாசனையுடன் வா :
மகரந்தத்தூளைச் சுமந்து கொண்டு மனதை மயங்கச் செய்கின்ற இனிய வாசனையுடன் வா என்பதன் பொருளாவது இயற்கையின் தூய மணமிக்க காற்றைச் சுவாசிக்க வேண்டும் என்பதேயாகும்.
![]()
மடித்து விடாதே :
நெருப்பு எரிய சீரான காற்று அவசியம். அதிவேகக் காற்று நெருப்பைப் பரவச் செய்து மிகுந்த துன்பத்தை உருவாக்கும் மிகவும் குறைவான வேகத்தில் வீசும் காற்றானது நெருப்பு பற்றி எரிய முடியாமல் நெருப்பு அணைவதற்குக் காரணமாகிறது.
பாரதி தமது உயிரை நெருப்புக்கு ஒப்பிட்டுள்ளார். காற்றானது சக்தி குறைந்து போய் தன் உயிரை அவித்துவிடக் கூடாது எனவும் பேய் போல வீசி தமது உயிரை மடித்துவிடக் கூடாது எனவும் உட்பொருள் கொண்டு இவ்வேண்டுகோள் சொற்களைப் பயன்படுத்தியுள்ளார்.
![]()
Question 2.
திக்குகள் எட்டும் சிதறி – தக்கத்
தீம்தரிகிட தீம்தரிகிட தீம்தரிகிட தீம்தரிகிட
பக்க மலைகள் உடைந்து வெள்ளம்
பாயுது பாயுது பாயுது – தாம்தரிகிட
தக்கத் ததிங்கிட தித்தோம் – அண்டம்
சாயுது சாயுது சாயுது – பேய் கொண்டு
தக்கை யடிக்குது காற்று – தக்கத்
தாம்தரிகிட தாம்தரிகிட தாம்தரிகிட தாம்தரிகிட – பாரதியார்
இது போன்ற இயற்கையொலிகளை உணர்வுடன் வெளிப்படுத்தும் கவிதைகளைத் திரட்டி வந்து வகுப்பறையில் படித்துக் காட்டு.
Answer:

![]()
பாடநூல் வினாக்கள்
பலவுள் தெரிக
Question 1.
“உனக்குப் பாட்டுகள் பாடுகிறோம்
உனக்குப் புகழ்ச்சிகள் கூறுகிறோம்”
– பாரதியின் இவ்வடிகளில் இடம் பெற்றுள்ள நயங்கள் யாவை?
அ) உருவகம், எதுகை
ஆ) மோனை, எதுகை
இ) முரண், இயைபு
ஈ) உவமை, எதுகை
Answer:
ஆ) மோனை, எதுகை
![]()
குறுவினா
Question 1.
வசன கவிதை – குறிப்பு வரைக.
Answer:
- உரைநடையும் கவிதையும் இணைந்து யாப்புக் கட்டுகளுக்கு அப்பாற்பட்டு உருவாக்கப்படும்.
- கவிதை வடிவம் வசன கவிதை எனப்படும்.
- ஆங்கிலத்தில் Prose Poetry என்பர்.
- தமிழில் பாரதியார் இதனை அறிமுகம் செய்தார்.
சான்று :
இவ்வுலகம் இனியது, இதிலுள்ள வான் இனிமை
யுடையது காற்றும் இனிது – பாரதியார்
![]()
கூடுதல் வினாக்கள்
இலக்கணக்
குறிப்பு. – வினையெச்சங்கள்
சுமந்து, வீசி – வினையெச்சங்கள்
மிகுந்த – பெயரெச்சம்
நல்லொளி, நெடுங்காலம் – பண்புத்தொகைகள்
நல்லலயத்துடன் – குறிப்புப்பெயரச்சம்
பகுபத உறுப்பிலக்கணம்.

பலவுள் தெரிக
Question 1.
கீழ்க்காண்பனவற்றுள் பொருந்தாத இணையைக் கண்டுபிடி.
அ) மயலுறுத்து – மயங்கச்செய்
ஆ)ப்ராண – ரஸம் – உயிர்வளி
இ) லயத்துடன் – சீராக
ஈ) வாசனை மனம்
Answer:
ஈ) வாசனை – மனம்
![]()
Question 2.
பொருத்திக் காட்டுக.
i) பாஞ்சாலி சபதம் – 1. குழந்தைகளுக்கான நீதிப்பாடல்
ii) சுதேசமித்திரன் – 2. பாராட்டப்பெற்றவர்
iii) புதிய ஆத்திசூடி – 3. இதழ்
iv) சிந்துக்குத் தந்தை – 4. காவியம்
அ) 3, 4, 2, 1
ஆ) 1, 2, 3, 4
இ) 4, 3, 1, 2
ஈ) 2, 4, 1, 3
Answer:
இ) 4, 3, 1, 2
![]()
Question 3.
‘‘நீடு துயில் நீக்கப் பாடிவந்த நிலா’ என்று பாராட்டப்பட்டவர்.
அ) பாரதியார்
ஆ) பாரதிதாசன்
இ) சுரதா
ஈ) கவிமணி
Answer:
அ) பாரதியார்
Question 4.
‘சிந்துக்குத் தந்தை’ என்று பாராட்டப்பட்டவர்.
அ) பாரதியார்
ஆ) பாரதிதாசன்
இ) சுரதா
ஈ) கவிமணி
Answer:
அ) பாரதியார்
![]()
Question 5.
கேலிச் சித்திரம், கருத்துப்படம் போன்றவற்றை உருவாக்கியவர்.
அ) பாரதியார்
ஆ) பாரதிதாசன்
இ) சுரதா
ஈ) கவிமணி
Answer:
அ) பாரதியார்
Question 6.
பாட்டுக்கொரு புலவன் என்று பாராட்டப்பெறுபவர்.
அ) பாரதியார்
ஆ) பாரதிதாசன்
இ) சுரதா
ஈ) கவிமணி
Answer:
அ) பாரதியார்
Question 7.
‘காற்று’ என்னும் தலைப்பில் வசன கவிதை எழுதியவர்.
அ) பாரதியார்
ஆ) பாரதிதாசன்
இ) சுரதா
ஈ) கவிமணி
Answer:
அ) பாரதியார்
![]()
Question 8.
“காற்றே , வா மகரந்தத் தூளைச் சுமந்து கொண்டு, மனத்தை மயலுறுத்துகின்ற இனிய வாசனையுடன் வா” – என்று பாடியவர்
அ) பாரதியார்
ஆ) பாரதிதாசன்
இ) சுரதா
ஈ) கவிமணி
Answer:
அ) பாரதியார்
Question 9.
ப்ராண-ரஸம் என்ற சொல் உணர்த்தும் பொருள்
அ) சீராக
ஆ) அழகு
இ) உயிர்வளி
ஈ) உடல்உயிர்
Answer:
இ) உயிர்வளி
Question 10.
வசன கவிதையைத் தமிழில் அறிமுகப்படுத்தியவர்
அ) பாரதிதாசன்
ஆ) வல்லிக்கண்ணன்
இ) பிச்சமூர்த்தி
ஈ) பாரதியார்
Answer:
ஈ) பாரதியார்
![]()
Question 11.
‘காற்றே வா’ என்னும் கவிதையின் ஆசிரியர்
அ) பாரதியார்
ஆ) பாரதிதாசன்
இ) கண்ண தாசன்
ஈ) வாணிதாசன்
Answer:
அ) பாரதியார்
Question 12.
காற்று எதைச் சுமந்து கொண்டு வர வேண்டுமென்று பாரதி அழைக்கிறார்?
அ) கவிதையை
ஆ) மகரந்தத்தூளை
இ) விடுதலையை
ஈ) மழையை
Answer:
ஆ) மகரந்தத்தூளை
![]()
Question 13.
பொருத்திக் காட்டுக:
i) மயலுறுத்து – 1. மயங்கச் செய்
ii) ப்ராண – ரஸம் – 2. உயிர்வளி
iii) லயத்துடன் – 3. மணம்
iv) வாசனை – 4. சீராக
அ) 1, 2, 4, 3
ஆ) 2, 3, 1, 4
இ) 3, 2, 1, 4
ஈ) 2, 1, 3, 4
Answer:
அ) 1, 2, 4, 3
Question 14.
ஆங்கிலத்தில் Prose Poetry (Free verse) என்றழைக்கப்படும் வடிவத்தைத் தமிழில் அறிமுகப்படுத்தியவர்
அ) பாரதிதாசன்
ஆ) பாரதியார்
இ) வாணிதாசன்
ஈ) கண்ண தாசன்
Answer:
ஆ) பாரதியார்
![]()
Question 15.
புதுக்கவிதை என்ற வடிவம் உருவாகக் காரணம்
அ) பாரதியின் வசன கவிதை
ஆ) ஜப்பானியரின் ஹைக்கூ
இ) வீரமாமுனிவரின் உரைநடை
ஈ) கம்பரின் கவிநயம்
Answer:
அ) பாரதியின் வசன கவிதை
Question 16.
பாரதியார் ஆசிரியராகப் பணியாற்றிய இதழ்கள்
i) இந்தியா
ii) சுதேசமித்திரன்
iii) எழுத்து
iv) கணையாழி
அ) i, ii – சரி
ஆ) முதல் மூன்றும் சரி
இ) நான்கும் சரி
ஈ) i, ii – தவறு
Answer:
அ) i, ii – சரி
![]()
Question 17.
பக்க மலைகள் உடைந்து வெள்ளம் பாயுது பாயுது பாயுது – தாம்தரிகிட என்ற இயற்கையொலிகளை உணர்வுடன் வெளிப்படுத்தும் பாடல்களைப் பாடியவர்
அ) பாரதியார்
ஆ) பாரதிதாசன்
இ) கண்ண தாசன்
ஈ) வாணிதாசன்
Answer:
அ) பாரதியார்
Question 18.
‘இனிய வாசனையுடன் வா’ என்று பாரதி அழைத்தது
அ) காற்று
ஆ) மேகம்
இ) குழந்தை
ஈ) அருவி
Answer:
அ) காற்று
![]()
Question 19.
பாரதியார் காற்றை ‘மயலுறுத்து’ அழைப்பதைக் குறிக்கும் சொற்றொடர்
அ) மணம் வீசும் காற்றாய் நீ வா
ஆ) மனதை மயங்கச் செய்யும் மணத்தோடு வா
இ) மயிலாடும் காற்றாய் நீ வா
ஈ) மகரந்தம் சுமந்து கொண்டு நீ வா
Answer:
ஆ) மனதை மயங்கச் செய்யும் மணத்தோடு வா
குறுவினா
Question 1.
பாரதியாரின் படைப்புகள் சிலவற்றைக் கூறு.
Answer:
கண்ணன் பாட்டு, குயில் பாட்டு, பாப்பா பாட்டு, பாஞ்சாலி சபதம், புதிய ஆத்திசூடி.
Question 2.
பாரதியார் எவ்வாறெல்லாம் பாராட்டப்பட்டார்?
Answer:
நீடுதுயில் நீக்கப் பாடி வந்த நிலா, சிந்துக்குத் தந்தை, பாட்டுக்கொரு புலவன், மகாகவி, கலைமகள்.
![]()
Question 3.
பாரதியாரின் பன்முகங்கள் யாவை?
Answer:
கவிஞர், கட்டுரையாளர், சிறுகதை, ஆசிரியர், இதழாசிரியர், கேலிச்சித்திரங்கள், கருத்துப்படங்களை உருவாக்குபவர்.
Question 4.
பாரதியார் இதழாசிரியராகப் பணியாற்றிய இதழ்களின் பெயர்களை எழுது.
Answer:
இந்தியா, சுதேசமித்திரன்.
Question 5.
‘காற்றே வா’ பாடலில் இடம் பெற்றுள்ள இயைபுச் சொற்களைக் கூறு.
Answer:
பாடுகிறோம், கூறுகிறோம், வழிபடுகின்றோம்.
![]()
Question 6.
காற்றிடம் எதனைக் கொண்டுவந்து கொடுக்குமாறு பாரதியார் வேண்டுகிறார்?
Answer:
மகரந்தத்தூளைச் சுமந்து, மனதை மயக்கும் வாசனையுடன், இலைகள் மற்றும் நீரலைகள்மீது உராய்ந்து மிகுந்த உயிர்வளியைக் கொண்டு வந்து கொடுக்குமாறு காற்றிடம் பாரதியார் வேண்டுகிறார்.
Question 7.
எப்படி வீசுமாறு காற்றைப் பாரதியார் பணிக்கிறார்?
Answer:
காற்றை மெதுவாக, நல்ல முறையில் சீராக, நீண்டகாலம் நின்று வீசிக் கொண்டிருக்குமாறு பாரதியார் பணிக்கிறார்.
Question 8.
“உனக்குப் பாட்டுகள் பாடுகின்றோம்.
உனக்குப் புகழ்ச்சிகள் கூறுகிறோம்
உன்னை வழிபடுகின்றோம்” – என்று யார் யாரிடம் கூறுகின்றார்?
Answer:
பாரதியார், காற்றிடம் கூறுகின்றார்.
![]()
சிறுவினா
Question 1.
‘காற்றே வா’ பாடலில் பாரதியார் கூறும் செய்தி யாது?
Answer:
- மகரந்தத்தூளைச் சுமந்து கொண்டு மனதை மயங்கச் செய்கின்ற வாசனையுடன் வா.
- இலைகளின் மீதும், நீரலைகளின் மீதும் உராய்ந்து வா.
- உயிர்வளியைக் கொடு. ஆனால் பேய்போல் வீசி உயிராகிய நெருப்பை அணைத்து விடாதே
- நீடித்து நின்று நன்றாக வீசு, உன் சக்தி குறைத்து எம் உயிரை அவித்து விடாதே!
- உம்மை நாம் பாடுகிறோம், புகழ்கிறோம், வழிபடுகிறோம் என்றெல்லாம் பாரதி, காற்றே வா’ என்ற பாடலில் பாடுகிறார்.

Question 2.
மகாகவி பாரதியார் குறிப்பு வகை.
Answer:
பெயர் : மகாகவி சுப்பிரமணிய பாரதியார்
பெற்றோர் : சின்னசாமி – இலக்குமி அம்மையார்
பாராட்டுகள் : ‘சிந்துக்குத் தந்தை’, ‘பாட்டுக்கொரு புலவன் பாரதி’
பணி : ஆசிரியர், இதழாசிரியர், சிறுகதை ஆசிரியர்.
படைப்புகள் : கண்ணன் பாட்டு, குயில் பாட்டு, பாப்பாப்பாட்டு, பாஞ்சாலி சபதம், புதிய ஆத்திசூடி.
பணியாற்றிய இதழ்கள் : இந்தியா, சுதேசமித்திரன்.
![]()
Question 3.
புதுக்கவிதை என்ற வடிவம் உருவாகக் காரணம் யாது?
Answer:
- உரைநடையும் கவிதையும் இணைந்து யாப்பிலக்கணத்திற்கு அப்பாற்பட்டு உருவாக்கப்படும் கவிதை வடிவம் ‘வசன கவிதை’ ஆகும்.
- ஆங்கிலத்தில் prose poetry (free verse) என்றழைக்கப்படும் இவ்வடிவம் பாரதியாரால் தமிழில் அறிமுகப்படுத்தப்பட்டது.
- உணர்ச்சி பொங்கக் கவிதை படைக்கும் இடங்களில் யாப்பு, தடையாக இருப்பதை உணர்ந்த பாரதியார் வசனகவிதை வடிவத்தைக் கையாண்டார்.
- இந்த வசன கவிதையே புதுக்கவிதை’ என்ற வடிவம் உருவாகக் காரணமாயிற்று.