TN State Board 12th Computer Applications Important Questions Chapter 12 DNS (Domain Name System)
Question 1.
What are the main functions of the Domain Name system?
Answer:
Domain Name System (DNS) maintains all the directory of domain names / host names and help us to access the websites using the domain host names.
Question 2.
Write one web address and Explain it?
Answer:
www.tnschools.gov.in is a web address for TamilNadu school education department. DNS translates it into a machine friendly IP address, for example 35.173.69.207 is the IP for www.tnschools.in and directs your internet connection to the correct website.
Question 3.
Who was known as ‘God of the internet’?
Answer:
Jon Postal was an administrator of the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) until his death and he was known as ‘God of the internet’.
![]()
Question 4.
What is Absolute URL?
Answer:
Absolute URL is the complete address of a document on the Internet. Absolute URL contains all the information that are required to find the files on the internet.
Question 5.
What is Relative URL?
Answer:
Relative URL is the partial address of a document on the internet. Relative URL contains only file names with folder name.
Question 6.
Write the DNS component.
Answer:
There are three important components in the Domain Name System (DNS). They are
- Name space,
- Name server,
- zone.
![]()
Question 7.
What are the types of Name space?
Answer:
The name space can be divided by two types, they are
- flat name space,
- Hierarchical name space.
Question 8.
What is Flat name space?
- Flat name space is where the name is assigned to the IP address. They do not have any specific structure.
- In this flat name space, some meaningful names are been given to IP address for accessing.
Question 9.
What is the disadvantage of Flat name space in DNS?
Answer:
The major disadvantage of flat name space is that they cannot be used in large system. Because they need to be accessed and controlled centrally to avoid ambiguity and redundancy. But it is difficult in flat name system.
Question 10.
What is a label?
Answer:
- Label is a string which can have maximum of 63 characters.
- In other words, Labels are the names given to domains.
![]()
Question 11.
What is a Domain name?
Answer:
- Domain name is the sequence of labels.
- In domain name the sequence of labels are separated by dot (.).
Question 12.
What is ICANN?
Answer:
ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Name and Numbers) is the Non-profit organisation which assigns names and numbers for all-internet resources.
Question 13.
What is web server?
Answer:
- Web server is a program running on dedicated machine which handle the queries of www enduser.
- Server is used to host the websites and to deliver the contents of website using HTTP.
![]()
Question 14.
What is TLD?
Answer:
- TLD (Top Level Domain) which reviews the request and direct the query to name servers associated with that specific domain.
- Until the query is solved it is passed to next level domains.
Question 15.
What is the WHOIS?
Answer:
The WHOIS is a service of ICANN. It is a free, publicly available directory containing the details of registered domain names and their owners. https://whois.icann.org/en
Question 16.
Write a note on IPv4 Address.
Answer:
- IPv4 address is a 32-bit unique address given to a computer system. No two systems can have same IP address.
- There are two ways to represent the IP address, they are Binary notation and Dotted-decimal notation.
- In the binary notation the address is expressed as 32-bit binary values.
Eg: 00111001 10001001 00111000 00000111 - In dotted-decimal notation the address is written in decimal format separated by dots (.). Eg: 128.143.137.144
![]()
Question 17.
Write a short note on IPV6 address.
Answer:
- IPv6 address is a 128-bit unique address given to a computer system.
- The number of addresses that can be formed in IPv6 is 2128.
- In IPv6 address, the 128 bits are divided into eight 16-bits blocks.
- Each block is then changed into 4-digits Hexadecimal numbers separated by colon symbols.
Eg: 2001 : 0000 : 32313 : DFEI: 0063 : 0000 : 0000 : FEFB
Question 18.
Explain the URL.
Answer:
(i) URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is the address of a document on the internet.
(ii) URL is made up four parts – protocols, host name, folder name and file name.
(iii) Each part has its own specific functions.
The four parts of the URL is explain the following example.

Question 19.
Explain the Flat name space.
Answer:
- Flat name space is where the name is assigned to the IP address. They do not have any specific structure.
- In this flat name space, some meaningful names are been given to IP address for accessing.
- The major disadvantage of flat name space is that they cannot be used in large system.
- Because they need to be accessed and controlled centrally to avoid ambiguity and redundancy. But it is difficult in flat name system.
![]()
Question 20.
Explain Hierarchical name space in various parts.
Answer:
- Hierarchical name space is where the name is made up of several parts.
- The first part may represent the nature of organisation.
- The second part may represent the name of organisation.
- The third part may represent the department of the organisation and so on.
Question 21.
Write the types of name servers.
Answer:
There are three types of name servers which control the entire Domain Name
system.
- Root Name server – top level server which contains entire DNS tree, maintained by ICANN. There are 13 servers.
- Primary / Master Name server – contains a zone resource records. These records are updatable by domain name holders such as organisations.
- Secondary / slave name server – contains a copy of primary server files. This server has no authority to update but reduce the work load of master server by sharing the queries.
Question 22.
Explain the zone component in DNS.
Answer:
- The entire name space is divided into many different zones. It is the area upto which the server has access.
- Zone is defined as a group of contiguous domains and sub domains.
- If the zone has a single domain, then zone and domain are the same.
- Every zone has the server which contains a database called zone file.
Using the zone file, the DNS server replies the queries about Hosts in its zone.
![]()
Question 23.
Discuss the term Resolver in DNS?
Answer:
- The resolver is a program which is responsible for initiating the translation of a domain name into an IP address.
- Resolver either asks server to provide information about IP address.
- It is doesn’t find any information, then it sends the request to other servers and so- on.
- Once the resolver receives the mapping it checks whether it is an error or resolution (mapping) and provides result according to that.
Question 24.
Write about IANA.
Answer:
- IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) is an affiliated authority of ICANN.
- IANA does the overall management of the DNS root, IP addressing, and other Internet protocol resource handling.
- IANA takes care of a number of key aspects of the DNS, including the root zone, and the domains.int and .arpa.
Eg: https://www.iana.org/
Question 25.
Write the basic rules of Domain names.
Answer:
- Domain can consists of Alphabets a through z and digit 0 through 9.
- Hyphens are allowed, but hyphens cannot be used as first character of a domain name.
- Spaces are not allowed.
- Special symbols such as ! $, &, _, and so on.
- Domain names have the minimum length of 2, and the maximum length of 63 characters. The entire name may be at most 253 character long.
- Domain names are not case- sensitive. (It may be upper, lower or mixing of both case letters).
![]()
Question 26.
What is name space? Explain.
Answer:
A Domain Name Space (DNS) is a name service provided by the internet for Transmission control protocol (TCP) networks or Internet Protocol (IP).
The domain names must be very unique and appropriate. The name space can be organised in two ways,
- Flat name space,
- Hierarchical name space.
(i) Flat name space:
It is where the name is assigned to the IP address. They do not have any specific structure. In this flat name space, some meaningful names are been given to IP address for accessing. The major disadvantage of flat name space is that they cannot be used in large system. To avoid this major disadvantage hierarchical name space „ is used in large.
(ii) Hierarchical name space:
It is where the name is made up of several parts. The first part may represent the nature of organisation, the second
part may represent the name of organisation, and third part may represent I the department of the organisation and so on.
The centralised authority can be given to nature and then to name of the organisation and so on. To achieve hierarchical name space, Domain Name space was designed.
Question 27.
Define the following terms, (a) Domain, (b) zone, (c) server, (d) Domain Name space, (e) Name server.
Answer:
Domain:
A domain is a single node of the Domain name space.
Zone:
A zone is a subset of the domain name space generally stored in a file.
Server:
A server can contain more than one zone files. A zone can contain more than one sub domains. .
Domain name space:
Domain name space is an entire collection domains, t sub domains and zones.
Name server:
Name server, manages the database of domain names and corresponding IP addresses.
![]()
Question 28.
List any four domain names.
Answer:
.com, .edu, .gov, .org, .net, .in
Question 29.
What is an IP address?
Answer:
IP address (Internet Protocol address;, is simply the logical address in the network layer. IP address is also used to find the host system in the whole network.
Question 30.
What are the types of IP address?
Answer:
There are two ways to represent the IP address, they are:
(i) Binary notation Eg: 00111001 10001001
(ii) Dotted-decimal notation. Eg: 128.143.137.144
![]()
Question 31.
What is an URL?
Answer:
URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is the address of a document on the . internet. URL is made up four parts – Protocols, hostname, folder name and file name. Each part has its own specific functions.
Question 32.
List out four URLs you know.
Answer:
- https://store.example.eom/topic/subtopic/descriptive-product-name#top.
- http://www.example.org/index.php
- http://www.example.com/blog
- http://cms.tn.gov.in /sites / default /files / press release / pro 70119a.jpg
Question 33.
What are the types of URL?
Answer:
Depending on the location of the document the URL is divided into two types , they are (i) Absolute URL, (ii) Relative URL.
![]()
Question 34.
What is a domain?
Answer:
A domain is a single node of the Domain Name space. Domain is a group of computers and devices on a network that are administered as a unit with common rules and procedures.
Question 35.
What is a zone?
Answer:
- Zone is defined as a group of contiguous domains and sub domains.
- If the zone has a single domain, then zone and domain are the same.
Question 36.
What is a resolver?
Answer:
The resolver is a program which is responsible for initiating the translation of a domain name into an IP address.
![]()
Question 37.
What are the categories available in domain name space?
Answer:
The domain name space can be categories in two ways, they are
- Flat name space,
- Hierarchical name space.
Question 38.
Write any four generic Top Level Domain.
Answer:
- .com – commercial organisation
- .edu – Educational Institutions
- .org – Non-profit organisation
- .net – Networking organisation
Question 39.
Write a note on DNS.
Answer:
- DNS (Domain Name System) is one of the application layer.
- To enable the use of domain names in a network, the Domain Name System (DNS) is used.
- DNS provides the domain name to IP address maping through name servers. While typing a web address, DNS translates it into a machine friendly IP address and directs your Internet connection to the correct website.
- For example 35.173.67.207 is the IP address for www.tnschools.in.
![]()
Question 40.
Differentiate IPv4 and IPv6.
Answer:
| IP v4 Address | IPv6 Address |
| IPv4 Address is a 32 bit unique address given to a computer system. | IPv6 address is a 128 bit unique address given to a computer system |
| If the network has P connections then ‘P’ addresses should be there. | The number of addresses that can be formed in IPv6 is 2128. |
| An address space is the total number of addresses that can be made by that protocol. | In IPv6 address, the 128 bits are divided into eight 16 – bits blocks. |
| It follows two ways to represent the IP address, Binary and Dotted – decimal notation. | It follows Hexadecimal number notation. |
Question 41.
Differentiate Domain name and URL.
Answer:
| Domain Name |
Uniform Resource Locator (URL) |
| Domain Name is the sequence of Labels are separated by dot (.). | URL is the address of a document on the Internet. |
| The domain name always read from the lower level to higher level. | URL is made up of four parts – Protocols, host name, folder name and file name. . |
| The root node always represent NULL string, all the domain name ending with dot (.). | Depending on the applications, additional information can be added to the URE. |
| Eg: Some domain name are .com, .edu, .gov, .org etc., | Eg: http://cms.tn.gov.in / sites / default / files / press – release / pro 070119.jpg |
![]()
Question 42.
What are the differences between Absolute URL and Relative URL?
Answer:
| Absolute URL |
Relative URL |
| Absolute URL is the complete address of a document on the Internet. | Relative URL is the partial address of a document on the Internet. |
| Absolute URL contains all the information that are required to find the files on the Internet. | Relative URL contains only file name or file name with folder name. |
| If any of the four parts of the URL is missing then the browser would not able to link to the specific file. | We can use this type of URL when the file is on the same server related to original document. |
| Absolute URL contains all the four necessary and fundamental parts of URL. | Relative URL contains only folder name and the file name or just the file name. |
Question 43.
Write a note on domain name.
Answer:
- Domain is the sequence of labels.
- In domain name the sequence of labels are separated by dot (.).
- The domain name is always read from the lower level to higher level i.e., from the leaf node to root node.
- Since the root node always represent NULL string, all the domain name ending with dot.
- Domain names are not case -sensitive. Domain names may also be used in other than English languages in UNICODE format.
![]()
Question 44.
Differentiate web address and URL.
Answer:
| Web Address |
Uniform Resource Locator (URL) |
| A web address more commonly defines a unique name that helps people remember a URL. | URL is the address of a document on the Internet. |
| It is usually in simpler form, such as Amazon.com | URL is the address of a particular website, audio stream or document available on the web. |
| Generally your browser will recognize the proper URL when you type in a web address. | URL consist of the Internet Protocol needed to access the item you wish to locate on the host computer. |
| Web address also known as URL, is an internet or intranet name that points to a location where a file, directory or website page is hosted. | URL is madeup four parts – protocols, host name, folder name, and file name. Each part has its own specific function. |
![]()
Question 45.
Explain briefly the components of DNS.
Answer:
There are three important components in the Domain Name System (DNS). They are
(i) Name space,
(ii) Name server,
(iii) Zone.
Name space:
The domain names must be very unique and appropriate. The names should be selected from a namespace. Hie namespace can be organised in two ways.
Flat name space:
It is where the name is assigned to the IP address. They do not have any specific structure. In this flat name space, some meaningful names are been given to IP address for accessing.
Hierarchical name space:
Hierarchical name space is where the name is made . up of several parts. The first part may represent the nature of organisation, the second part may represent the department of the organisation and so on.
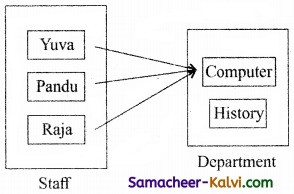
Name servers:
The information which needs to be stored in domain name space is quite large. Single system would be inefficient and insufficient to store such a huge amount as responding to requests from all over the world.
The best way to do that is to divide the entire space into many domains and subdomains.
Name server is a main part in the Domain Name system (DNS). It translate the domain names to IP addresses.
Zone:
The entire name space is divided into many different zones. It is the area up to which the server has access.
Zone is defined as a group of contiguous domains and sub domains.
If the zone has a single domain, then zone and domain are the same.
There are two conies of zone files available, master file and slave file.
![]()
Question 46.
Classify and Explain the IP address.
Answer:
Internet Protocol (IP) address is simply the logical address in the network layer.
Due to increase in the number of system in a network there is a need of more addresses which lead to two addressing methods i.e., IPv4 and IPv6.
IPv4 Address:
IPv4 address is a 32-bit unique address given to a computer system. No two systems can have same IP address.
There are two ways to represent the IP address. They are: Binary notation, Dotted-decimal notation.
In binary notation the address is expressed as 32-bit binary values.
Eg: 00111001 10001001 00111000 00000111 .
In dotted-decimal notation the address is written in decimal format separated by dots(.).
Eg: 128.143.137.144
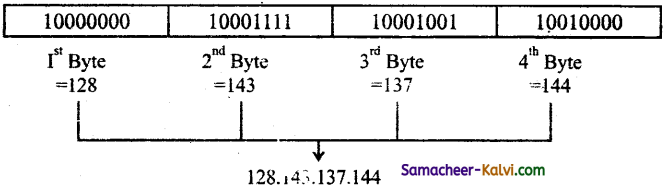
IPv6 Address:
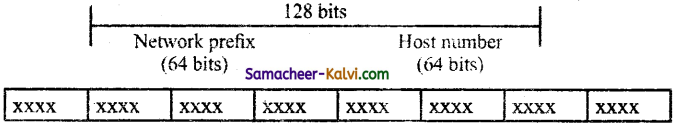
IPv6 address is a 128-bit unique address given to a computer system. The number of addresses that can be formed in IPv6 is 2<sup>128</sup>. In IPv6 address, the 128 bits are divided in to eight 16-bits blocks. Each block is then changed into 4-digit Hexadecimal numbers separated by colon symbols.
Eg: 2001 : 000 : 32313 : DFEI: 0063 : 0000 : 0000 : FEFB
![]()
Question 47.
Explain about the name server?
Answer:
(i) Name server contains the DNS database which consists of domain names and their corresponding IP addresses.
(ii) The information which needs to be stored in domain name space is quite large.
(iii) Single system would be inefficient and insufficient to store such a huge amount as responding to requests from all over the world.
(iv) The solution to this problem is to distribute the information among many computers.
(v) The best way to do that is to divide the entire space into many domains and sub domains.
(vi) Name server is a main part in the Domain Name System (DNS). It translate the domain names’to IP addresses.
(vii) There are three types of name servers which control the entire Domain Name system.
(viii) Root Name server – top level server which contains entire DNS tree, maintained by ICANN.
(ix) Primary / Master Name server – contains a zone resource records.
(x) Secondary / slave name server – contains a copy of primary server files.
This server has no authority to update.
![]()
Question 48.
What is domain name space? Explain.
Answer:
(i) Domain name space was designed to achieve hierarchical name space.
(ii) In this, the names are represented as a tree like structural with root element on the top and this tree can have a maximum of 128 levels starting from root element taking the level 0 to level 127.
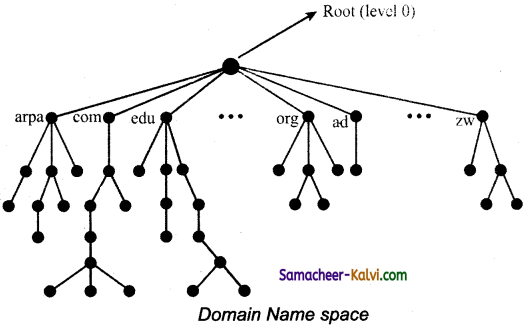
(iii) In this tree structure represent the domain name space where the root element is present at the top most level.
(iv) The next level to the root element is node. Each node in the tree has a label and a domain name.
(v) Label is a string which can have maximum of 63 characters. In other words, labels are the names given to domains.
(vi) Domain is a sub tree in domain name space tree structure. The domain can be further divided into sub domains.
(vii) Domain name is the sequence of labels.
(viii) Domain name is the sequence of labels. In domain name the sequence . of labels are separated by dot (.). The domain name is always read from the lower level to higher level.
![]()
Question 49.
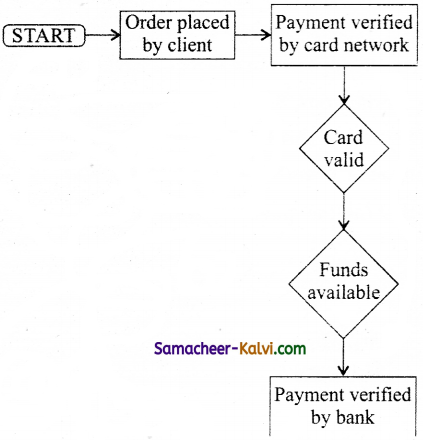
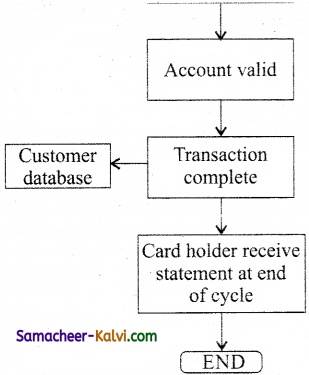
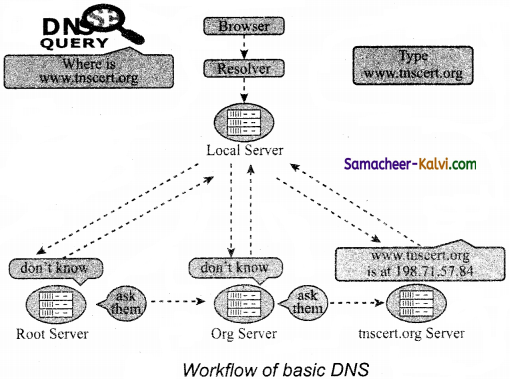
Explain how the DNS is working.
Answer:
Domain Name System (DNS) is a client / server application.
When the user enters the URL (consists of protocol, domain name, folder name, file name) in the browser, the system first checks its DNS cache for the corresponding IP address.
If the IP address is found in the cache then the information is retrieved from the cache.
If not, then the system needs to perform DNS query i.e., the system needs to query the resolver about the IP address from Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Each resolver has its own cache and if it is found in that then the query is passed to next domain server i.e., TLD (Top Level Domain) which reviews the request and direct the query to name servers associated with that specific domain. Until the query is solved it is passed to next level domains.
Finally the mapping and the record are returned to the resolver who checks whether the returned value is a record or an error. Then the resolver returns the record back to the computer browser which is then viewed by the user.
Question 50.
Find out IP address of your system.
Answer:
(i) Click start menu and type command or cmd to open command prompt.
(ii) A command prompt window will be displayed. Type ipconfig and press enter.
(iii) The IP number is listed under IPv4 Address and IPv6 Address.
Answer:
192.168.1.3
08 – 60 – 6E – D9 – 6F – D7
(iv) Find out the MAC address of the network card in the list.
Answer:
00- 14-22-01 -23 -45
(v) Find out and analyze what the other information displayed on the screen.
Answer:
- Windows IP configuration
- Ethernet adapter, Local Area connection.
- Tunnel 1 adapter, pseudo-interface.
- Tunnel 1 adapter is atap- domain.name
![]()
Question 51.
Find out IP address for the websites using command prompt.
Answer:
(i) Click start menu and type command or cmd to open command prompt.
(ii) A command prompt window will be displayed. Type tracert and press enter.
Answer:
Trace the root of HOST
(iii) From the displayed window. You’ll see the IPv4 and IPv6 address,
IPv4 address:

IPv6 address:
2001 : 0DBB : AC 10 : FE01 : 0000 : 0000 : 0000 : 0000
(iv) Find out IP address for another website.
Answer:
Website – www.tn.gov.in
IP address – 218.248.161.134
10.208.48.1
Question 52.
List out websites to find out IP address of other websites For example:
https://ipinfo.info/html/ip_checker.php
Answer:
- https://www.site24x7.com / Find – IP – address – of – web-site.html
- https://www.ipvoid.com / find – website – IP/
- https://www.iplocation.net
- https://www.check-host.net / ip-info? lang-en
- https://www.ipneighbours.com
![]()
Question 53.
Use nslookup in command line and analyse what purpose it is used.
Answer:
By using NSlookup
- To find the IP address of a host.
- Find the domain name of an IP address.
- Find mail servers for a domain.
Question 54.
Buy your own domain name or create free sub-domain and connect free hosting servers.
Answer:
For example: www.goDaddy.com,www.webs.com
Use following any one website.
- www.hostinger.in / domain – name – search
- www.myhosting.com / domain – names /
- www.greengeoks.com
- www.namecheap.com / domains
- www.hostgator.com / domains.
![]()
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Which one is application layer among in the several applications?
(a) DNS
(b) URL
(c) Name space
(d) Name Server
Answer:
(a) DNS
Question 2.
Which one of the following is a web address?
(a) tnschools.txt
(b) www.tnschools.txt
(c) www.tnschools.gov.in
(d) www.tnschools.gov.doc
Answer:
(c) www.tnschools.gov.in
Question 3.
Which one of the following is the internet protocol (IP) for www.tnschools. in?
(a) 45.163.69.307
(b) 45.183.69.407
(c) 35.173.79.307
(d) 35.173.69.207
Answer:
(d) 35.173.69.207
![]()
Question 4.
Who was invented the Internet Domain Name System (DNS)?
(a) V. Mockapetris
(b) Jon Postel
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Question 5.
Who was known as God of the Internet?
(a) Jon Postel
(b) Paul V. Mockapetris
(c) William Joes
(d) John Paul
Answer:
(a) Jon Postel
Question 6.
Which address is simply the logical address in the network layer?
(a) Internet Protocol(IP)
(b) Internet Transfer Protocol (TCP)
(c) Domain Name System (DNS)
(d) IPv4 Protocol
Answer:
(a) Internet Protocol(IP)
![]()
Question 7.
Which address is a 32-bit unique address given to a computer system?
(a) IP
(b) IPv4
(c) IPv6
(d) URL
Answer:
(b) IPv4
Question 8.
Which IP address to represent the Binary notation?
(a) IP
(b) URL
(c) IPv6
(d) IPv4
Answer:
(d) IPv4
Question 9.
Which IP address to represent Dotted-decimal notation?
(a) IP
(b) URL
(c) IPv6
(d) IPv4
Answer:
(d) IPv4
![]()
Question 10.
Which address is a 128-bit unique address given to a computer system?
(a) IP
(b) IPv4
(c) IPv6
(d) URL
Answer:
(c) IPv
Question 11.
In IPv6 address, the 128 bits are divided into eight bit block.
(a) 8
(b) 12
(c) 15
(d) 16
Answer:
(d) 16
Question 12.
In IPv6 address, each block is then changed into 4-digit Hexadecimal numbers separated by symbols.
(a) ; (semi colon)
(b) : (colon)
(c) , (comma)
(d) .(full stop)
Answer:
(b) : (colon)
![]()
Question 13.
Which is the address of a document on the Internet?
(a) IP
(b) TCP
(c) URL
(d) DNS
Answer:
(c) URL
Question 14.
How many types URL divided into depending on the location of the document?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 6
Answer:
(a) 2
Question 15.
How many important components in the Domain Name System (DNS)?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 6
Answer:
(b) 3
![]()
Question 16.
Which is the complete address of a document on the internet?
(a) Absolute URL
(b) Relative URL
(c) DNS
(d) Name space
Answer:
(a) Absolute URL
Question 17.
Which contains all the information that are required to find the files on the Internet?
(a) Absolute URL
(b) Relative URL
(c) DNS
(d) Name space
Answer:
(a) Absolute URL
Question 18.
How many parts are very important in Absolute URL?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(c) 4
![]()
Question 19.
Which is the partial address of a document on the Internet?
(a) Absolute URL
(b) Relative UR L
(c) DNS
(d) Name space
Answer:
(b) Relative UR L
Question 20.
Which contains only file name or file name with folder name?
(a) Absolute URL
(b) Relative URL
(c) DNS
(d) Name space
Answer:
(b) Relative URL
Question 21.
Which type of URL is used when the file is on the same server related to original document?
(a) Absolute URL
(b) Relative URL
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Relative URL
![]()
Question 22.
The must be very unique and appropriate.
(a) Domain names
(b) URL
(c) Domain Name Space
(d) Name server
Answer:
(a) Domain names
Question 23.
How many ways in the Name space can be organised?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(a) 2
Question 24.
Which type of name space is where the name is assigned to the IP address?
(a) Flat name space
(b) Hierarchical name space
(c) Name server
(d) Zone
Answer:
(a) Flat name space
![]()
Question 25.
Which name space is where the name is made up of several parts?
(a) Flat name space
(b) Hierarchical name space
(c) Name server
(d) Zone
Answer:
(b) Hierarchical name space
Question 26.
Which was designed to achieve hierarchical name space?
(a) DNS
(b) Domain name space
(c) URL
(d) IP
Answer:
(b) Domain name space
Question 27.
Which is a sub tree in domain name space tree structure?
(a) Domain
(b) DNS
(c) URL
(d) IP
Answer:
(a) Domain
![]()
Question 28.
Which is always read from the lower level to higher level of node?
(a) Domain
(b) Domain Name
(c) DNS
(d) IP
Answer:
(b) Domain Name
Question 29.
Which one of the following is cannot be used as first character of a domain name?
(a) Characters
(b) Numbers
(c) Hyphens
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Hyphens
Question 30.
What is the minimum and maximum length of the Domain names characters?
(a) 2 and 63
(b) 4 and 63
(c) 2 and 65
(d) 4 and 62
Answer:
(a) 2 and 63
![]()
Question 31.
How many characters long in the domain names?
(a) 265
(b) 224
(c) 232
(d) 253
Answer:
(d) 253
Question 32.
What is the last part of a domain name?
(a) Domain name space
(b) Lower level domain
(c) Top level domain
(d) Middle level domain
Answer:
(c) Top level domain
Question 33.
Who is maintained by generic to level domains are used forgeneric purpose?
(a) IANA
(b) ICANN
(c) MSCL
(d) SUN
Answer:
(a) IANA
![]()
Question 34.
Which of the following one is not a generic domain names?
(a) .com
(b) .edu
(e) .gov
(d) .in
Answer:
(d) .in
Question 35.
How many characters are used by generic domain names?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(b) 3
Question 36.
How many characters are used by country domain?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(a) 2
![]()
Question 37.
Which of the following one is not a country domain names?
(a) .in
(b) .us
(c) .edu
(d) .uk
Answer:
(c) .edu
Question 38.
Which is store the data and provide it to clients when queried by them?
(a) Name servers
(b) Name space
(c) Label
(d) Domain name space
Answer:
(a) Name servers
Question 39.
Which are programs that run on a physical system and store all the zone data?
(a) Name space
(b) Label
(c) Name servers
(d) Domain name space
Answer:
(c) Name servers
![]()
Question 40.
Which is a main part in the domain name system?
(a) Name space
(b) label
(c) Name servers
(d) Domain name space
Answer:
(c) Name servers
Question 41.
How many types of Name servers?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(b) 3
Question 42.
Which is top level server that contains entire DNS tree, maintained ICANN?
(a) Root Name Server
(b) Primary Server
(c) Master Name Server
(d) Slave Name Server
Answer:
(a) Root Name Server
![]()
Question 43.
Which server contains a zone resource records?
(a) primary
(b) master name
(c) secondary
(d) (a) or (b)
Answer:
(d) (a) or (b)
Question 44.
Which server contains a copy of Primary server files?
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Slave Name
(d) (b) or (c)
Answer:
(d) (b) or (c)
Question 45.
Expansion of ICANN
(a) Internet corporation for Assigned Name and numbers
(b) International corporation Assigned Name and numbers
(c) International connection for Assigned Name and numbers
(d) Internet connection for Arranged Name and numbers
Answer:
(a) Internet corporation for Assigned Name and numbers
![]()
Question 46.
What is a program which is responsible for initiating the translation of a domain name into an IP address?
(a) Resolver
(b) DNS
(c) Label
(d) Name space
Answer:
(a) Resolver
Question 47.
Which is a program running on dedicated machine that handle the queries ofwww.enduser?
(a) Resolver
(b) Webserver
(c) DNS
(d) Label
Answer:
(b) Webserver
Question 48.
Which is used to host the websites and to deliver the contents of website using HTTP?
(a) Resolyer
(b) DNS
(c) Label
(d) Server
Answer:
(d) Server
![]()
Question 49.
Which is reviews the request and direct and the query to name servers associated with that specific domain?
(a) Low level domain
(b) Middle level domain
(c) Top level domain(TLD)
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(c) Top level domain(TLD)
Question 50.
The ________ is a service of ICANN.
(a) NHOIS
(b) WHOES
(c) WHOSE
(d) WHOSS
Answer:
(a) NHOIS
Question 51.
Match the following:
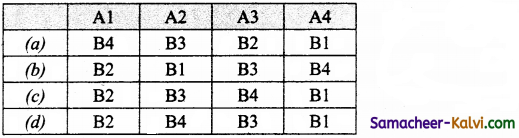
| (A) IP | (i) IP addresses |
| (B) DNS | (ii) Logical address |
| (C) IPv4 | (iii) 128 bit address |
| (D) IPv6 | (iv) 32 bit address |
(a) (A) – (iii); (B) – (iv); (C) – (ii); (D) – (i)
(b) (A) – (ii); (B) – (i); (C) – (iv); (D) – (iii)
(c) (A) – (iii); (B) – (ii); (C) – (i); (D) – (iv)
(d) (A) – (ii); (B) – (iv); (C) – (iii); (D) – (i)
Answer:
(b) (A) – (ii); (B) – (i); (C) – (iv); (D) – (iii)
![]()
Question 52.
Match the following:
| (A) Name space | (i) sequence of labels |
| (B) Domain Name space | (ii) Nodes |
| (C) Label | (iii) Hierarchical name space |
| (D) Domain Name | (iv) Domain names |
(a) (A) – (iii); (B) – (ii); (C) – (i); (D) – (iv)
(b) (A) – (iii); (B) – (i); (C) – (ii)- (D) – (iv)
(c) (A) – (iv); (B) – (iii); (C) – (ii); (D) – (i)
(d) (A) – (iv); (B) – (ii); (C) – (i); (D) – (iii)
Answer:
(c) (A) – (iv); (B) – (iii); (C) – (ii); (D) – (i)
Question 53.
Match the following:
| (A) .com | (i) Country domain |
| (B) .in | (ii) Zone data |
| (C) Name servers | (iii) Contiguous domains |
| (D)Zone | (iv) Generic domain name |
(a) (A) – (iv); (B) – (i); (C) – (ii); (D) – (iii)
(b) (A) – (iv); (B) – (iii); (C) – (ii); (D) – (i)
(c) (A) – (ii); (B) – (iii); (C) – (iv); (D) – (i)
(d) (A) – (ii); (B) – (i); (C)-(iv); (D) – (iii)
Answer:
(a) (A) – (iv); (B) – (i); (C) – (ii); (D) – (iii)
![]()
Question 54.
Match the following:
| (A) URL | (i) Local Name Server |
| (B) Relative URL | (ii) Four parts |
| (C) Absolute URL | (iii) Folder name |
| (D) ISP | (iv) Complete Address |
(a) (A) – (iii); (B) – (ii); (C) – (iv); (D) – (i)
(b) (A) – (iii); (B) – (i); (C) – (iv); (D) – (ii)
(c) (A) – (iv); (B) – (iii); (C) – (ii); (D) – (i)
(d) (A) – (iv); (B) – (ii); (C) – (i); (D) – (iii)
Answer:
(b) (A) – (iii); (B) – (i); (C) – (iv); (D) – (ii)
Question 55.
Match the following:
| (A) ICANN | (i) Authority of ICANN |
| (B) IANN | (ii) Service of ICANN |
| (C) TLD | (iii) Regulates an Internet |
| (D) WHOIS | (iv) Below the root domain |
(a) (A) – (iii); (B) – (iv); (C) – (ii); (D) – (i)
(b) (A) – (iii); (B) – (i); (C) – (ii); (D) – (iv)
(c) (A) – (ii); (B) – (i); (C) – (iv); (D) – (iii)
(d) (A) – (ii); (B)-(iii); (C) – (iv); (D) – (i)
Answer:
(d) (A) – (ii); (B)-(iii); (C) – (iv); (D) – (I)
![]()
Question 56.
Choose the incorrect pair.
(a) DNS – Host names
(b) IPv6 – Hexa decimal numbers
(c) IPv4 – Binary numbers
(d) http – Domain name
Answer:
(d) http – Domain name
Question 57.
Choose the incorrect pair.
(a) URL – Absolute
(b) Name space – Relative URL
(c) Domain name space – Hierarchical name space
(d) Node – lable
Answer:
(b) Name space – Relative URL
Question 58.
Choose the incorrect pair.
(a) Domain name – separate by dot
(b) Domain name – 253 character
(c) .info – country domain name
(d) Unicode – Generic domain name
Answer:
(d) Unicode – Generic domain name
![]()
Question 59.
Choose the correct pair.
(a) .au – Generic domain name
(b) ICANN – Root Name Server
(c) Zonefile – Name space
(d) Protocol – Top Level Domain
Answer:
(b) ICANN – Root Name Server
Question 60.
Choose the correct pair.
(a) Resolver – domain names
(b) Domain – Protocol
(c) TLD – IP address
(d) LANA – Naming system
Answer:
(a) Resolver – domain names
Question 61.
Choose the incorrect statement.
(a) DNS maintains all the directory of domain names / host names and help us to access the website.
(b) There are several applications in the application layer and DNS is one among them.
(c) Domain names to IP address mapping is not consistent across the network.
(d) DNS provides the domain name to IP address mapping through Name servers.
Answer:
(c) Domain names to IP address mapping is not consistent across the network.
![]()
Question 62.
Choose the incorrect statement.
(a) IPv6 address is a 128 bit unique address given to a computer system.
(b) The number of addresses that can be formed in IPv6 is 2128
(c) In IPv6 address, the 128 bits are divided into eight 16-bits blocks.
(d) Each block is then changed into 3-digit octal numbers separated by colon.
Answer:
(d) Each block is then changed into 3-digit octal numbers separated by colon.
Question 63.
Choose the incorrect statement.
(a) URL is the address of a document on the internet
(b) Absolute URL is the additional information can be added to the URL
(c) Absolute URL is the complete address of a document on the internet
(d) Relative URL is the partial address of a document on the internet.
Answer:
(b) Absolute URL is the additional information can be added to the URL
Question 64.
Choose the correct statement.
(a) In domain names, Hyphens are allowed, but hyphens cannot be used as first character.
(b) Spaces are allowed in a domain name.
(c) Domain names have the minimum length of 6 characters.
(d) Domain names are case-sensitive.
Answer:
(a) In domain names, Hyphens are allowed, but hyphens cannot be used as first character.
![]()
Question 65.
Choose the correct statements.
(a) Country domain uses 3 character country abbreviation according to country.
(b) Name servers are programs that run on a physical system and store all the zone data.
(c) Name server is a sub part in the Domain Name system
(d) Name servers does not the important task of searching the domain names.
Answer:
(b) Name servers are programs that run on a physical system and store all the zone data.
Question 66.
Assertion (A):
There are three types of name servers which control the entire domain name system.
Reason (R):
The three types of name servers are root name server, primary / master. Name server, and secondary / slave name server.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation for A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation for A.
(c) A is true, But R is false
(d) A is false, But R is true
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation for A.
Question 67.
Assertion (A):
Every zone has the server which contains a database called . zone file.
Reason (R):
Using the zone file, the DNS server does not replies the queries about hosts in its zone.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation for A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation for A.
(c) A is true, But R is false.
(d) A is false, But R is true.
Answer:
(c) A is true, But R is false.
![]()
Question 68.
Assertion (A):
Domain Name space is an entire collection Domains, sub domains and zones.
Reason (R):
A domain is a single node of the Domain Name space.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation for A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation for A.
(c) A is true, But R is false.
(d) A is false, But R is true.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation for A.
Question 69.
Assertion (A):
Label is a string which can have maximum of 128 characters.
Reason (R):
Domain name is the sequence of labels separated by dot (•).
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation for A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation for A.
(c) A is true, But R is false.
(d) A is false, But R is true.
Answer:
(d) A is false, But R is true.
Question 70.
Assertion (A):
URL is the address of the protocol and is made up of three parts.
Reason (R):
Name servers are system software, and control the physical system.
(a) Both A and R are true.
(b) Both A and R are false.
(c) A is true, But R is false.
(d) A is false, But R is true.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are false.
![]()
Question 71.
Pick the odd one out.
(a) IP
(b) IPv4
(c) IPv6
(d) DNS
Answer:
(d) DNS
Question 72.
Pick the odd one out.
(a) client
(b) name space
(c) name server
(d) zone
Answer:
(a) client
Question 73.
Pick the odd one out.
(a) .com
(b) .edu
(c) .info
(d) .jp
Answer:
(d) .jp
![]()
Question 74.
Pick the odd one out.
(a) .au
(b) .cn
(c) .net
(d) OP
Answer:
(c) .net
Question 75.
Pick the odd one out.
(a) host name
(b) resolver
(c) folder name
(d) file name
Answer:
(b) resolver
![]()
Question 76.
Which of the following is used to maintain all the directory of domain names?
(a) Domain name system
(b) Domain name space
(c) Name space
(d) IP address
Answer:
(a) Domain name system
Question 77.
Which of the following notation is used to denote IPv4 addresses?
(a) Binary
(b) Dotted-decimal
(c) Hexadecimal
(d) (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) (a) and (b)
Question 78.
How many bits are used in the IPv6 addresses?
(a) 32
(b) 64
(c) 128
(d) 16
Answer:
(c) 128
![]()
Question 79.
Expansion of URL is:
(a) Uniform Resource Location
(b) Universal Resource Location
(c) Uniform Resource Locator
(d) Universal Resource Locator
Answer:
(c) Uniform Resource Locator
Question 80.
How many types are available in Relative URL?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(c) 4
Question 81.
Maximum characters used in the label of a node?
(a) 255
(b) 128
(c) 63
(d) 32
Answer:
(c) 63
![]()
Question 82.
In domain name, sequence of labels are separated by:
(a) ;
(b) .(dot)
(c) :
(d) NULL
Answer:
(b) .(dot)
Question 83.
Pick the odd one out from the following.
(a) node
(b) label
(c) domain
(d) server
Answer:
(a) node
Question 84.
Which of the following initiates the mapping of domain name to IP address?
(a) Zone
(b) Domain
(c) Resolver
(d) Name servers
Answer:
(c) Resolver
![]()
Question 85.
Which is the contiguous area up to which the server has access? _
(a) Zone
(b) Domain
(c) Resolver
(d) Name servers
Answer:
(a) Zone
Question 86.
ISP stands for:
(a) International Service provider
(b) Internet Service Provider
(c) Internet service Protocol
(d) Index service provider
Answer:
(b) Internet Service Provider
Question 87.
TLD stands for:
(a) Top Level Data
(b) Top Logical Domain
(c) Term Level Data
(d) Top Level Domain
Answer:
(d) Top Level Domain
![]()
Question 88.
Which of the following statements are true?
(i) Domains name is a part of URL.
(ii) URL made up of four parts
(iii)The relative URL is apart of Absolute URL
(iv) URL doesn’t contain any protocol .
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Answer:
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Question 89.
Assertion (A):
The number of addresses used in IPv6 addressing method is 128.
Reason (R):
IPv6 address is a 128 bit unique address.
(a) A is true and R is false.
(b) A is false and R is true.
(c)Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(d)Both A and R are correct and R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer:
(b) A is false and R is true.
![]()
Question 90.
Match the following:
| (A) Domain | (i) Programs that initiates translation |
| (B) Zone | (ii) Contains database of domain names |
| (C) Name server | (iii) Single node |
| (D) Resolver | (iv) Contiguous node |
(a) (A) – (i); (B) – (iv); (C) – (iii); (D) – (ii)
(b) (A) – (iii); (B) – (iv); (C) – (ii); (D) – (i)
(c) (A) – (iii); (B) – (ii); (C) – (i); (D) – (iv)
(d) (A) – (iii)-, (B) – (iv); (C) – (i); (D) – (ii)
Answer:
(b) (A) – (iii); (B) – (iv); (C) – (ii); (D) – (i)