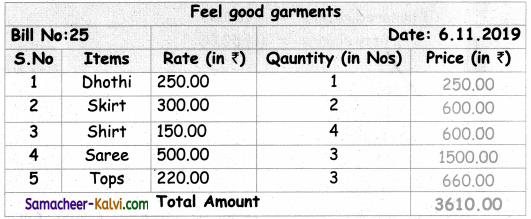
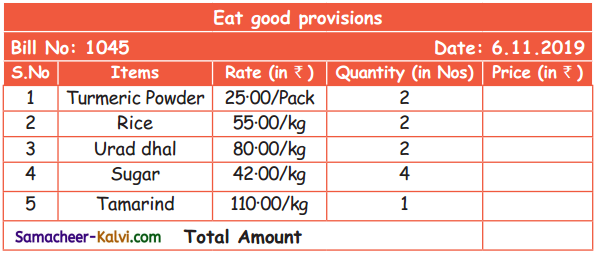
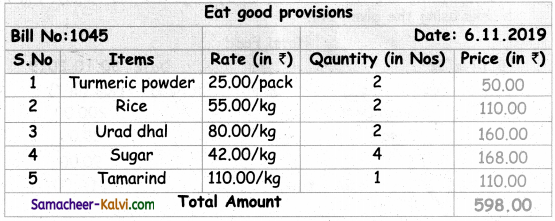
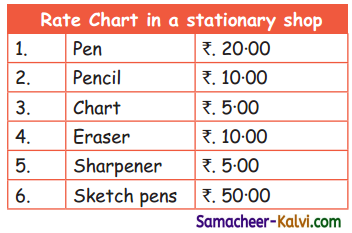
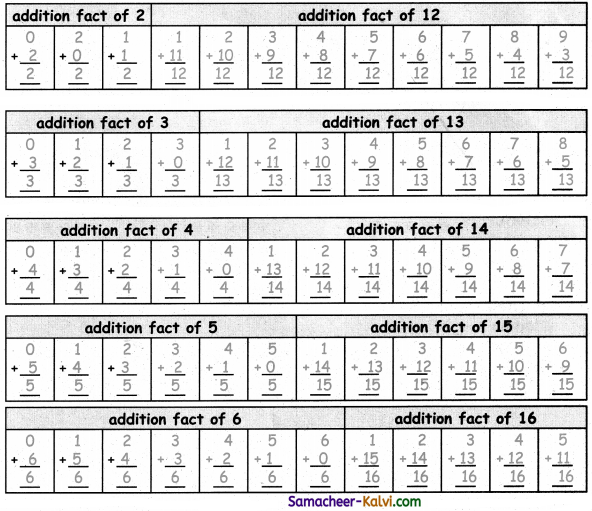
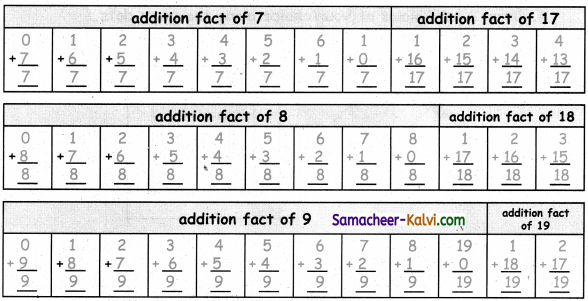
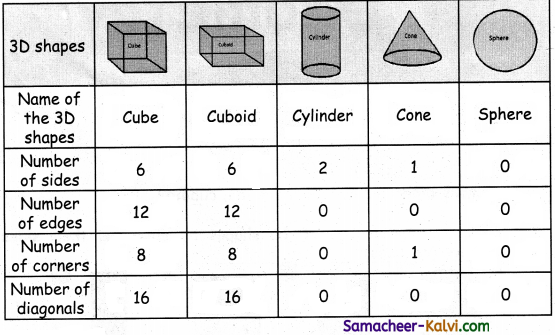
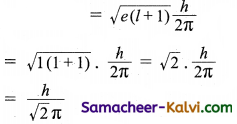TN State Board 11th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 3 Periodic Classification of Elements
Question 1.
Mendeleev predicted that elements with atomic weights 72.68 and 70 in group IV and their properties. Name the elements that were discovered later and have properties predicted by Mendeleev.
Answer:
Galium and Germanium.
Question 2.
Give Mosley’s relationship.
Answer:
There exists a linear correlation between the atomic number and frequency of X-ray emitted by an element.
√v = a (Z – b)
v = frequency of X-ray emitted by the element with atomic number Z, a, b are constants. This relationship is known as Mosley’s relationship.
![]()
Question 3.
Briefly outline anomalies of Mendeleev’s periodic table.
Answer:
(i) The position of hydrogen in the periodic table as it resembles alkali metals and halogens in their properties.
(ii) Certain elements which show similar properties have been separated in the periodic table, eg: Ba and Pb resemble each other in so many respects but they are placed in second and fourth group. Similarly Ag and Te having similar properties but separated. Ag is placed in first group and Te is placed in third group.
(iii) Elements showing marked similarities are placed in one group. For example, coinage metals (Cu, Ag, Au) have been placed with, alkali metals in the same group. Manganise has been placed in the seventh group along with halogens with which it does not show any similarity in its properties.
(iv) Certain elements with higher atomic mass were placed before the elements with lower atomic mass.
eg: Tellurium (127.6) was placed in group . VI but iodine (127) was placed in group VII. Similarly cobalt (atomic mass 59) were placed before nickel (atomic mass 58.6). The other similar pains are Ar and K (40.39), Th and Pa (232, 231).
![]()
Question 4.
Explain how will you find the atomic number . of an element from the frequency of X-rays emitted by an element.
Answer:
1. Mosley’s relationship is given as √v = a(Z – b) where v is the frequency of X-rays emitted by an element of atomic, number Z.
2. The plot of √v against Z gives a straight line. Using this relationship, we can determine the atomic number of an unknown (new) element from the frequency of X-ray emitted.
Question 5.
Briefly outline the characteristics of modem periodic table.
Answer:
(i) The modem of periodic table consists of horizontal rows called periods and vertical column called groups. There are seven periods and eight groups. The period number corresponds to the value of principal quantum number (n). The number of elements in each period is twice the atomic orbitals available in the energy level that are being filled.
Each group coptain a series of element whose atoms have the same electronic configuration. The elements in a group are separated by magic numbers of either 2 or 8 or 18 or 32. The physical properties of elements follow a systematic pattern.
(ii) The IUPAC have designated the groups from 1 to 18. Previously there were sixteen groups as VIII B consisted of three vertical columns. The groups were designated as I A, II A, III B, IV B, V B, VI B, VII B , VIII B, I B, IIB, III A, IV A, V A, VIA and VII A. The present system replaces the old system.
![]()
Question 6.
The element 119 has not been discovered. What would be the IUPAC name and symbol for this element? On the basis of periodic table, predict the electronic configuration of this element.
Answer:
The root’s for 1 and 9 are un and enn respectively. Hence, the name of the element with Z = 119 is Un + Un + enn + ium = ununennium. Its symbol is uue.
The atomic number of the last number of the 7th period is 118. Thus, this element will belong to 8th period and will be the first element i.e., alkali metal (8 s).
Its electronic configuration: 2, 8, 18, 32, 32, 18, 8, 1.
Question 7.
Write the electronic configuration ofthe elements whose atomic numbers are given below:
(A) 35, (B) 18, (C) 28, (D) 38. Also predict period, group, and block to which they belong.
Answer:
(A) Atomic number 35:
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p5
A receives the last electron in 4p orbital and hence belongs to ‘p’ block and 4th period.
Group number = 10 + 7 = 17.
(B) Atomic number 18:
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
Block – ‘p’ 3rd period; (10 + 8) = 18th group.
(C) Atomic number 28:
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d8 4s2
Block – ‘s’; 4th period ; (8 + 2) = 10th group.
(D) Atomic number 38:
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 5s2
Block – ‘s’ ; 5th period ; 2nd group.
![]()
Question 8.
Write the general electronic configuration of s, p, d, and f block elements.
Answer:
‘s’ block: ns1 or 2.
‘p’ block: ns2 np1 – 6
‘d’ block: (n – 1)d1 – 10 ns1 or 2
‘f’ block: (n – 2)f1 – 14 (n – 1 )d0 or 2 ns2
Question 9.
Name the first and the last elements in the following periods (n).
(i) n = 4 (ii) n = 5 (iii) n = 6 (iv) n = 7.
Answer:
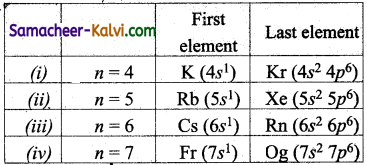
![]()
Question 10.
Mention the characteristics of ‘s’ block elements.
Answer:
(i) They have a general electronic configuration of ns1 or ns2.
(ii) They are soft metals possess low melting and boiling points. They are good conductor of electricity.
(iii) They have the largest atomic radii in their respective periods.
(iv) They have low values of ionisation enthalpy and hence highly electropositive.
(v) They are very reactive and readily form ionic compounds.
(vi) They impart (except Be, Mg) characteristic colour to the Bunsen flame.
Question 11.
Mention the characteristics of ‘p’ block elements.
Answer:
(i) Their general electronic configuration is ns2 np1 – 6.
(ii) They form generally covalent compounds but a few members show electro valency also, eg: Sn, Pb.
(iii) In a period from left to right there is a regular increase in non-metallic character. The non-metallic character decreases down the group.
(iv) Most of them are electronegative. The electronegativity increases across the period while it decreases down the group.
(v) Most of them form acidic oxides.
![]()
Question 12.
Mention the characteristics of ‘d’ block elements.
Answer:
(i) They are metals and have the general electronic configurations (n – 1)d1 – 10 ns1 or ns2.
(ii) They are less electropositive than ‘s’ block elements but more electropositive than ‘p’ block elements.
(iii) The ‘d’ block elements show variable valency.
(iv) Most of the transition elements and their compounds are good catalysts.
(v) They form both ionic and covalent compounds.
Question 13.
What are lanthanides and Actinides? [OR] Mention the characteristics of ‘f’ block elements.
Answer:
The lanthanides are the elements having the general electronic configuration 4f1 – 14 5d0 – 1, 6s2n and actinides have the general configuration 5f0 – 14, 6d0 – 2, 7s2. They are collectively known as ‘f’ block elements. These elements are metallic in nature and have high melting points. Their compounds are mostly coloured. These elements also show variable oxidation states.
Question 14.
Explain why covalent radius is always shorter than actual atomic radius.
Answer:
The formation of covalent bond involves the overlapping of atomic orbitals and it reduces the expected intemuclear distance. Therefore covalent radius is always shorter than the actual atomic radius.
![]()
Question 15.
From the inter nuclear distance between two atoms A and B (dA – B) and from their electronegativities, how will you find the covalent radius of atom A + B?
Answer:
In case of hetero nuclear diatomic molecules. The covalent radius of individual atom can also be calculated using the internuclear distance (dA – B) between two different atoms A and B. The simplest method proposed by Schomaker and Stevenson is as follows.
dA – B = rA + rB – 0.09(χA – χB)
where χA and χB are the electronegativities of A and B respectively in Pauling units.
Here χA > χA and radius is in Å.
Question 16.
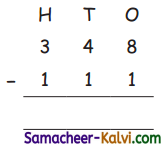
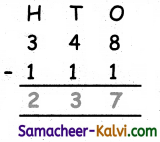
The inter nuclear distance between hydrogen and chlorine, is 1.28Å and the covalent radius of chlorine is 0.99Å. The electronegativity values of chlorine and hydrogen are 3 and 2.1 respectively. Determine the covalent radius of hydrogen atom.
Answer:
dH – Cl = rH + rCl – 0.09 (χCl – χH)
1.28 = rH +0.99 – 0.09 (3 – 2.1)
1.28 = rH + 0.99 – 0.09 (0.9)
1.28 = rH + 0.99 – 0.081
1.28 = rH + 0.909
∴ rH = 1.28 – 0.909 = 0.317 Å
![]()
Question 17.
Explain the cause for the variation of atomic radius along a period.
Answer:
Atomic radius tends to decrease in a period. Along a period, the valence electrons are added to the same shell. The simultaneous addition of protons to the nucleus, increases the nuclear charge, as well as the electrostatic attractive force between the valence electrons and the nucleus. Therefore atomic radius decreases along a period.
Question 18.
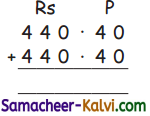
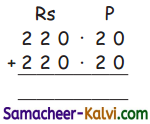
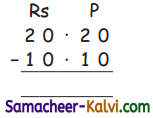
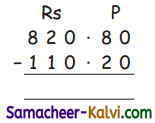
Calculate ionic radii of Na+ and F– ion in NaF crystal whose inter ionic distance is equal to 231 pm.
Answer:
d = rNa+ + rF– ……….(1)
i.e. rNa+ + rF– = 231 pm .
We know that
\(\frac{r_{\mathrm{Na}^{+}}}{r_{\mathrm{F}^{-}}}=\frac{\left(\mathrm{Z}_{\mathrm{eff}}\right)_{\mathrm{F}^{-}}}{\left(\mathrm{Z}_{\mathrm{eff}}\right)_{\mathrm{Na}^{+}}}\)
(Zeff)F– = Z – S
= 9 – 4.15 = 4.85
(Zeff)Na+ = 11 – 4.15 = 6.85
∴ \(\frac{r_{\mathrm{Na}^{+}}}{r_{\mathrm{F}^{-}}}=\frac{4.85}{6.85}\) = 0.71
⇒ rNa+ = 0.71 × rF– ……………(2)
Substituting (2) in (1)
(1) ⇒ 0.71 rF– + rF– = 231 pm
1.71 rF– = 231 pm
rF– = \(\frac{231}{1.71}\) = 135.1 pm
Substituting the value of rF– in equation (1)
rNa+ + 135.1 = 231
rNa+ = 95.9 pm
![]()
Question 19.
Explain why cations are smaller and anions are larger than their parent atoms?
Answer:
The ionic radius of a cation is smaller than the parent atom because the loss of one or more electrons increases the effective nuclear charge. As a result, force of attraction of the nucleus for the electron increases as a result, the electron comes closer to the nucleus.
In contrast, the ionic radii of anion is always greater than the parent atom because addition of one or more electrons decreases the effective nuclear charge. As a result, force of attraction of the nucleus for the electrons, decreases and ionic radii increase.
Question 20.
The ionisation energy of boron is less than that of beryllium. Explain.
Answer:
It is due to the fact that beryllium with completely filled 2s orbital, is more stable than partially filled valence shell electronic configuration of boron. (2s2, 2p1).
Question 21.
How does ionisation energy vary in a group?
Answer:
The ionisation energy decreases down a group. Down a group, the valence electron occupies new shells, the distance between the nucleus and the valence electron increases. So, the nuclear forces of attraction on valence electron decreases and hence ionisation energy also decreases down a group.
![]()
Question 22.
Explain the influence of shielding effect as the ionisation energy of elements.
Answer:
Down a group, the number of inner shell electron increases which in turn increases the repulsive force exerted by them on the valence electrons, i.e., the increased shielding effect caused by the inner electrons decreases the attractive force acting on the valence electron by the nucleus. Therefore the ionisation energy decreases.
Question 23.
Define‘electron affinity’.
Answer:
It is defined as the amount of energy released (required in thg case noble gases) when an electron is added to the valence shell of an isolated neutral gaseous atom in its ground state to form its anion. It is expressed in kJ mol-1.
A + e– → A– + EA
Question 24.
How does electron of affinity vary in a period? Explain the cause for variation.
Answer:
Generally electron affinity increases along a period, i.e., the amount of energy released will be more. This is due to an increase in the nuclear charge and decreases in size of atom.
![]()
Question 25.
How does electron affinity vary in a group? Explain the cause for the variation.
Answer:
Down a group, generally the electron affinity decreases. It is due to increase in atomic size and the shielding effect of inner shell electrons.
Question 26.
Oxygen an fluorine have lower electron affinity, then sulphur and chlorine in their respective groups. Explain, why?
Answer:
The sizes of oxygen and fluorine atoms are comparatively small and they have high electron density. Moreover, the extra electron added to oxygen and fluorine has to be accommodated in the 2p orbital which is relatively compact compared to the 3p orbital of sulphur and chlorine. So, oxygen and fluorine have lower electron affinity than their respective group elements sulphur and chlorine.
Question 27.
Explain Pauling method of determining electronegativity of element.
Answer:
Pauling, assigned arbitrary value of electronegativities for hydrogen and fluorine as 2.2 and 4.0 respectively. Based on this, the electronegativity values for other elements can be calculated using the following expression
(χA – χB) = 0.182 \(\sqrt{\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{AB}}-\left(\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{AA}} \times \mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{BB}}\right)^{1 / 2}}\)K Where EAB, EAA and EBB are the bond dissociation energies of AB, A2 and B2 molecules respectively.
![]()
Question 28.
Explain how electronegativity values are used to predict the nature of the bond between two atoms between A and B.
Answer:
(i) If the difference, χA – χB = 0 i.e., χA = χB the bond is purely covalent and non-polar.
eg: H2, Cl2, O2 and N2 molecules.
(ii) The difference χA – χB is small i.e., χA > χB, the bond is polar covalent.
(iii) The difference χA – χB = 1.7, the bond is 50% covalent and 50% ionic.
(iv) The difference χA – χB is very high, the bond is more ionic and less covalent. The percentage ionic character may be calculated by using the formula. % ionic character =16 (χA – χB) + 3.5 (χA – χB)2.
Question 29.
Bring out the difference between electron gain enthalpy and electro negativity.
Answer:
| Electro negativity | Electron gain enthalpy |
| It is the tendency of an atom in the combined state i.e., in a molecule to attract the shared pair of electrons. | It is the tendency of an isolated atom to attract electrons. |
| It is a relative number and cannot be determined by experiments. | It can be measured experimentally. |
| It has no units but merely a number | Its units are in eV / atom or kJ / mol or kcal / mol. |
| Electronegativity of an element is not constant and its value depends on the element to which it is covalently b onded. | It is a constant quantity for a particular element. |
| The periodicity is regular in a period but not regular in a group. | Its periodicity is not regular both in a period and group |
![]()
Question 30.
Explain the term valence or oxidation state. How does it vary in a period and in group?
Answer:
The combining capacity of an element is termed as the valency. It is linked to with the number of electrons present in the outermost energy shell of the atom. The electrons present in the outermost shell are known as valence electrons.
In the case of representative elements, the valency is generally is equal to the number of valence electrons or equal to eight – minus the number of electrons. However, transition metals show variable valency involving valence electrons and ‘tf electrons of the penultimate energy level. The common valency of transition metals are 2 or 3. The term oxidation state is now used in place of valency.
Question 31.
What do you understand by the term ‘variable oxidation state’? Which elements in a group or period exhibit variable oxidation state?
Answer:
If an element have more than are valence or oxidation state, it is said to exhibit variable oxidation state, eg: Fe exhibits oxidation state of 2 and 3 in ferrous and ferric compounds respective. Most of the elements in group 15 which have valence electron 5, show two valencies, 3 and 5. Similarly, transition and inner transition metals also show variable oxidation states.
Question 32.
Explain why noble gases are inert?
Answer:
The noble gases having completely filled electronic configuration neither accept nor lose their electron readily and hence they are chemically inert in nature.
![]()
Question 33.
The ionisation energy is directly related to metallic character. Explain the variation of metallic-character along the period and in the group.
Answer:
Metallic nature decreases in a period while non-metallic character increases. Metallic nature increases in a group while non-metallic character decreases.
Question 34.
Explain the nature of oxides formed by metals and non-metals.
Answer:
Generally metallic oxides are basic in nature
white non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature.
Na2O ⇒ basic
Cl2O7 ⇒ acidic
Question 35.
How does the basic and acidic nature of oxides vary along a period and in group?
Answer:
The basic nature of the oxide decreases in a period while acidic nature increases. In a group, basic nature of the oxide increases, while acidic nature decreases.
Question 36.
How is ionisation energy related td the metallic character? How does the basic nature of hydroxides of alkaline earth metals very down the group?
Answer:
Metals have low ionisation energy and highly electropositive. As the ionisation energy of the metals decreases down the group, the electro positive character of elements increases. The basic character of hydroxides of alkaline earth metals increases down the group.
| Be(OH)2 | Mg(OH)2 | Ba(OH)2 | Sr(OH)2 | Ba(OH)2 |
| amphoteric | weakly | Strongly | Strongly | Strongly |
| basic | basic | basic | basic |
![]()
Question 37.
Which of the following species will have the largest and smallest size? Mg, Mg+2, Al, Al+3
Answer:
Mg and A1 belong to the same period.
| Mg | Al | |
| Atomic Number | 12 | 13 |
Atomic size decreases from left to right across a period. Thus Mg is a larger atom than Al. Cation is smaller than the neutral atom. Mg+2 is smaller than Mg and Al+3 is smaller than Al. Thus, Al+3 ion is the smallest and Mg is the largest in size among the given species.
Question 38.
Given the formula of the species that will be isoelectronic with the following atoms or ions.
(i) Ar (ii) F– (iii) K+ (iv) S-2
Iso electronic species are those which have the same number of electrons.
(i) Ar has 18 electrons. Therefore, the species P-3, S-2, Cl–, K+, Ca+2 are isoelectronic with Ar.
(ii) F– has 10 electrons. Therefore the species, N-3,O-2, Ne, Na+, Mg+2 are isoelectronic with F–.
(iii) K+ has 18 electrons. Therefore, the species P-3, S-2, Cl–, Ar, C+2 are isoelectronic with K+.
(iv Sr+2 has 36 electrons. Therefore Br–, Kr, Rb+ etc are isoelectronic with Sr+2.
Question 39.
Account for the difference in size of Na+ (95 pm) and Mg+2 (65pm) both of which have the same noble gas configuration.
Answer:
The nuclear charge in Mg+2 is more than Na+ and therefore electrons are drawn more closely and hence size decreases.
![]()
Question 40.
Which of the following pairs of elements would you expect to have higher ionisation energy? (i) Cl or F (ii) S or Cl (iii) Na or Ne (iv) Ar or Kr.
Answer:
(i) Fluorine is expected to have higher first IE than chlorine because, it is smaller in size than chlorine and IE decreases down the group.
(ii) Chlorine is expected to have higher IE than sulphur, because it has a smaller size than sulphur. IE decreases along the period.
(iii) Neon is expected to have higher IE because it has completely filled orbitals from which removal of electron is difficult.
(iv) Argan is expected to have higher IE, because it has completely filled orbitals.
Question 41.
(i) Why chlorine has higher electron affinity than fluorine?
Answer:
The size of fluorine atom is small compared to chlorine and the electron density around the nucleus es high. This resists the addition of electron, hence the electron affinity of fluorine is less than that of chlorine atom.
(ii) Why Has nitrogen has higher Ist ionisation potential than oxygen atom?
Answer:
The electronic configuration of nitrogen and oxygen are as follows:
N = 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1 2pz1;
O = 1s2 2s1 2px2 2py1 2pz1
In, nitrogen, ‘p’ orbitals are half filled and hence possess a stable electronic configuration. It requires more energy to remove an electron. Hence IE of nitrogen is higher than that of oxygen which has a less stable electronic configuration.
(iii) Why has magnesium higher I.E. than aluminium atom?
Answer:
The electronic configuration of Mg and Al are as follows:
Mg: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 ;
Al: 1s2,2s2 2p6, 3s2 3p1.
It is more difficult to remove an electron from 3s orbital in comparison to 3p orbital because 3s electrons are closer to the nucleus. Further 3s electrons are paired and 3p is simply occupied. Hence IE of. Mg is higher than that of Al.
![]()
Question 42.
Which of the following will have the most electron gain enthalpy and which the least electronegative? P, S, Cl, F Explain your answer.
Answer:
Electron gain enthalpy becomes more negative down a period. Cl > S > P. Electron gain enthalpy becomes less negative down a group. However, adding an electron to 2p orbital leads to greater repulsion due to high electron density than adding an electron to a larger 3p orbital. Hence, chlorine is more negative electi on gain enthalpy than fluorine. Therefore, phosphorous has least electron gain enthalpy and chlorine has the most electron – gain enthalpy.
Question 43.
Show by chemical reaction, with water, that Na2O is a basic oxide and Cl2O7 is an acidic oxide.
Answer:
Na2O reacts with water and forms a base i.e, sodium hydroxide.
Na2O + H2O > 2NaOH
Cl2O7 reacts with water and forms perchloric acid.
Cl2O7 + H2O → 2HClO4
Question 44.
The first (IE1) and the second (IE2) ionisation Enthalpies of three elements, I, II and III are given below:
| I | II | III | |
| IE1 | 403 | 549 | 1142 |
| IE2 | 2640 | 1060 | 2080 |
Identify the element which is likely to be
(i) a non-metal
(ii) an alkali metal
(iii) an alkaline earth metal.
Answer:
(i) III is a non-metal because Ist and IInd ionisation enthalpies are high.
(ii) I is an alkali metal because the second ionisation enthalpy is high. In alkali metals the second electron is removed from complete octet.
(iii) II is an alkaline earth metal because these elements have two electrons in the outermost shell. First and second IE’s are in almost 1 : 2 ratio.
![]()
Question 45.
Give the IUPAC names and symbols of the following elements with atomic numbers 123, 126, 134, 148, 150.
Answer:
| Atomic number | Name | Symbol |
| 123 | Unbitrium | Ubt |
| 126 | Unbihexicum | Ubh |
| 134 | Untriquadium | Utq |
| 148 | Unquadoctium | Uqo |
| 150 | Unpentnilium | Upn |
Question 46.
What is the basic difference in approach between Mendeleev’s periodic law and modem periodic law.
Answer:
Mendeleev’s periodic law based on the properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic weights while the modem periodic law based on thp properties of elements are periodic function of atomic numbers.
Question 47.
In terms of period and group where would you locate the element with Z = 114.
Answer:
The lastmember ofthe sixth period is the element Radon with atomic number 86. Therefore, the element with atomic number 114 belongs to the seventh period. In the seventh period, 7s, 5f 6d and 6p orbitals are filled. Is, 5/and 6d orbitals filling corresponds to 26 elements i.e., and member will be with atomic number 112. It means the element in question is the second 6p element; i.e., it belongs to group 10 + 4 = 14.
![]()
Question 48.
Assign the position of the element having outer electronic configuration.
(i) ns2 np4 for n = 3.
(ii) (n – 1 )d2 ns2 for n = 4. .
(iii) (n – 2)f7 (n – 1)d1 ns2 for n = 6 in the periodic table.
Answer:
(i) The electronic configuration ofthe element is 3s2 3p4. Thus the element belongs to 3rd period and group 16.
(ii) The electronic configuration of the element is 3d2 4s2. Thus the element belongs to 4th period and group 4.
(iii) The electronic configuration of the element is 4f7 5d1 6s2. i.e., it belongs to 6th period and group 3 (lanthanides).
Question 49.
What is the significance of the terms “isolated gaseous atom” and “ground state” while defining ionisation energy and electron affinity?
Answer:
(i) Isolated atom means a single gaseous atom free from other atoms. No energy should be utilised to separate it from other atoms. It is an ideal situation which is difficult to achieve. However, the inter atomic distances are reduced to minimum by carrying out the measurement of IE at a low pressure.
(ii) ‘Ground state’ means that the atom must be present in the most stable state, i.e., in the lowest’energy state possible for the atom.
![]()
Question 50.
Among the second period elements, the actual ionisation energies are in the order Li < B < Be < C < O < N < F < Ne Explain – Why?
(i) Be has higher IE than Boron.
(ii) Oxygen has lower IE than nitrogen and – fluorine.
Answer:
(i) The electronic configuration of Be and B are Be = 1s2 2s2; B = 1s2 2s2 2p1
In Be, the electron is removed from completely filled orbital (2s) while in boron, from 2p sub shell. 2s electrons are more strongly bond to the nuoleus than 2p electron and therefore more energy is required to remove a 2s electron than 2p electron. Consequently, Be has higher first IE than boron.
(ii) In nitrogen, all the ‘p’ orbitals are singly occupied. Thus it is a stable arrangement compared to oxygen. As a result, the removal of an electron from nitrogen requires more energy than the removal of an electron from oxygen atom. Then, nitrogen has higher IE than oxygen.
Question 51.
What are the factors due to which the ionisation energy of the main group elements tends to decrease down the group?
Answer:
(i) Atomic size:
Atomic size increases due to addition of a new energy level This decreases the force of attraction and consequently ionisation enthalpy decreases.
(ii) Screening effect:
Due to increase of inner electrons, the shielding effect increases which reduces force of attraction towards nucleus and hence IE decreases.
![]()
Question 52.
Would you expect the second electron gain enthalpy of oxygen as positive, more negative, or less negative than the first. Justify your answer.
Answer:
The second electron gain enthalpy of oxygen is positive. When an electron is added to neutral oxygen atom, a monovalent anion (O–) is formed and energy is released, i.e. first electron gain enthalpy is negative. When the electron is added to form O-2 anion, there is a lot of electrostatic repulsion as both O– anion and the electron. To overcome their repulsion energy is absorbed. Thus, the second IE of oxygen is positive.
O(g) + e → O–(g) – 141.0 kJ mol-1
O–(g) + e → O-2(g) + 780 kJ mol-1
Question 53.
The energy of an electron in the ground state of the hydrogen atom is -2.18 × 10-18 J. Calculate the ionisation energy of atomic hydrogen in J mol-1.
Answer:
IE = E∞ – En
= 0 – (-2.18 × 10-18)
= 2.18 × 10-18 J
Ionisation energy per mole = 2.18 × 10-18 × 6.023 × 1023
= 1.313 × 106 J
(2.18 × 10-18 J is IE for one electron. I.E. per mole of electron, it has to be multiplied by Avogadro Number).
![]()
Question 54.
Calculate the screening constants of alkali metals for valency electrons.
Answer:
Li (2, 1) = 2 × 0.85 = 1.7
Na (2, 8, 1) = 8 × 0.85 + 2 × 1 = 8.8
K (2, 8, 8, 1) = 8 × 0.85 + 10 × 1 = 16.8
Rb (2, 8, 18, 8, 1) = 8 × 0.85 + 28 × 1 = 34.8
CS (2, 8, 18, 18, 8, 1) = 8 × 0.85 + 46 × 1 = 52.8
Question 55.
Calculate the screening constants of members of second period for valency electrons.
Answer:
Li (2, 1) = 2 × 0.85 = 1.7
Be (2, 2) = 2 × 0.35 + 2 × 0.85 = 2.05
B(2, 3) = 2 × 0.35 + 2 × 0.85 = 2.40
C (2, 4) = 3 × 0.35 + 2 × 0.85 = 2.75
N(2, 5) = 4 × 0.35 + 2 × 0.85 = 3.10
0 (2, 6) = 5 × 0.35 + 2 × 0.85 = 3.45
F (2, 7) = 6 × 0.35 + 2 × 0.85 = 3.80
Ne (2, 8) = 7 × 0.35 + 2 × 0.85 = 4.15
![]()
Question 56.
Calculate the screening constant in Zinc for (i) 4s electron, (ii) for a 3d electron. The electronic configuration of Zinc (30) is (1s)2 (2s, 2p)8 (3s, 3p)8 (3d10) (4s)2.
Answer:
(i) σ = 1 × 0.35 + 18 × 0.85 + 10 × 1 = 25.65
(ii) σ = 9 × 0.35 + 18 × 1.0 = 21.15
Question 57.
Given the bond lengths of H2, Cl2, C – C bond in diamond, Si – C bond in carborundum and C – Cl bond in CCl4 are 0.74, 1.9, 1.54, 1.93 and 1.76 Å respectively, find the covalent radius of hydrogen., chlorine, carbon in diamond, silicon and carbon in CCl4.
Answer:
(i) Bond length dH – H) in hydrogen molecule = 0.74 Å
∴ Covalent radius of hydrogen = \(\frac{d_{\mathrm{H}-\mathrm{H}}}{2}\) = \(\frac{0.74}{2}\) = 0.37 Å
(ii) Bond length (dCl – Cl) in chlorine molecule = 1.98 Å
Covalent radius of chlorine = \(\frac{d_{\mathrm{Cl}-\mathrm{Cl}}}{2}\)
= \(\frac{1.98}{2}\) = 0.99 Å
(iii) Bond length (C – C) in diamond = 1.54 Å
∴ Covalent radius of carbon = \(\frac{1.54}{2}\) = 0.77 Å
(iv) Bond length of (dsi – C) in carborundum = 1.93 Å
dsi – C = rsi + rc
1.93 = rsi + 0.77 Refer (iii)
rsi = 1.93 – 0.77 = 1.16 Å
(v) Bond length (dC – Cl) in CCl4 = 1.76 Å ,
dC – Cl = dC – dCl
1.76 = rC + 0.99 Refer (ii)
rC = 1.76 – 0.99 = 0.77 Å
![]()
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
An element X belongs to fourth period and fifteenth group of the periodic table. Which one of the following is true regardmg the outer electronic configuration of X? It has:
(a) Partly filled ‘d’ orbitais and completely filled ‘s’ orbitais.
(b) Complete’y filled ‘s’ orbitais and completely filled ‘p’ orbitals.
(c) Completely filled ‘s’ orbitais and half filled ‘p’ orbitals.
(d) Half filled ‘d’ orbitais and completely filled ‘s’ orbitals.
Answer:
(c) Completely filled ‘s’ orbitais and half filled ‘p’ orbitals.
Hint:
In the fourth period three subshells (i.e., 4s, 3d, 4p) are progressively filled in the increasing order of energy (4s < 3d < 4p). After filling up of 4s subshell with 2 electrons and 3d subshell with 10 electrons, the filling of 4p subshell begins from group 13 to 18. In the 15th, three 4p orbitals are completely filled. Thus, the outer electronic configuration of X is 4s2 4px1 4py1 4pz2. i.e., option (c) is correct.
Question 2.
Element with atomic number 56 belongs to which block?
(a) s
(b) p
(c) d
(d) f
Answer:
(a) s
![]()
Question 3.
Gadolinium belong to ‘4f’ series. Its atomic j number is 64. Which of the following I is the correct electronic configuration of gadolinium?
(a) [Xe] 4f9 5s1
(b) [Xe] 4f7 5d1 6s2
(c) [Xe] 4f6 5d2 6s2
(d) [Xe] 4f8 d2
Answer:
(b) [Xe] 4f7 5d1 6s2
Question 4.
The number of d- electrons in Fe+2 (Z = 26) is not equal to the number of electrons in which j one of the following?
(a) electron in Fe (Z = 26)
(b) p – electron in Ne (Z = 10)
(c) s – electron in Mg (Z = 12)
(d) p – electron in Cl (Z = 17)
Answer:
(d) p – electron in Cl (Z = 17)
Hint:
EC of Fe (Z = 26) = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d6 4s2
(a) EC of Fe+2 = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d6
It has 6 ‘d’ – electrons.
(b) EC of Ne (Z = 10) = 1s2 2s2 2p6
It has 6 ‘p’ – electrons.
(c) EC of Mg (Z = 12) = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2
It has 6(2 + 2 + 2) ‘s’ – electrons.
(d)EC of Cl (Z = 17) = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5
It has 11 ‘p’ – electrons.
Thus, Fe+2 has six ‘d’ electron. Hence option (d) is correct.
![]()
Question 5.
Among the elements Ca, Mg, P and Cl the order of increasing atomic radii is:
(a) Mg < Ca < Cl < P
(b) Cl < P < Mg < Ca
(c) P < Cl < Ca < Mg
(d) Ca < Mg < P < Cl
Answer:
(b) Cl < P < Mg < Ca
Hint:
Arranging the elements: Ca, Mg, P and Cl in different groups and periods in increasing order of their atomic numbers.
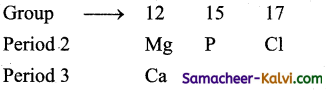
(i) Since atomic radii increase from top to bottom in a group, therefore, atomic radius of Ca is more than that of Mg i.e., Mg < Ca.
(ii) Since atomic radii decrease along a period, atomic radii Mg, P, and of Cl decrease in i the order Mg > P > Cl combining these two trends, the atomic radii increase in the order Cl < P < Mg < Ca.
Question 6.
The ionic radii (in Å) of N3, O-2 and F– are respectively:
(a) 1.71, 1.40 and 1.36
(b) 1.71, 1.36 and 1.40
(c) 1.36, 1.40 and 1.71
(d) 1.36, 1.71 and 1.40
Answer:
(a) 1.71, 1.40 and 1.36
Hint:
N-3 = (7 + 3 = 10); O-2 (8 + 2=10); F(9 + 1 = 10)
Thus these are isoelectronic ions. Among the isoelectronic ions, greater the negative charge, larger is the ionic radius. Thus ionic radii decrease in the order N-3 > O-2 > F– i.e., 1.71 > 1.40 > 1.36
![]()
Question 7.
The species Ar, K+ and Ca+2 contain the same number of electrons. In which order do their radii increase?
(a) Ca+2 < K+ < Ar
(b) K+ < Ar < Ca+2
(c) Ar < K+ < Ca+2
(d) Ca+2 < Ar < K+
Answer:
(a) Ca+2 < K+ < Ar
Hint:
Among isoelectronic species, higher the +ve charge smaller is the radius while neutral species have larger radius.
Question 8.
Among the following which one has highest cation to anion ratio?
(a) CsI
(b) CsF
(c) LiF
(d) NaF
Answer:
(b) CsF
Hint:
Amongst alkali metal cations (i.e, Cs+, Li+, Na+)Cs+ has the largest size and among halides (F–, I–) fluoride ion has the smallest size. Therefore, the ratio Cs+ to F– is the highest.
![]()
Question 9.
The ionisation potential ofNais 5.48 eV. The ionisation potential of K will be:
(a) the same as Na
(b) 4.34 eV
(c) 5.68 eV
(d) 10.88 eV
Answer:
(b) 4.34 eV
Hint:
Since ‘K’ is larger than Na, its ionisation potential is smaller than that of Na. i.e., 4.34 eV is smaller than 5.48.
Question 10.
The first ionisation potential (in eV) of Be and B respectively are:
(a) 8.29, 9.32
(b) 9.32, 8.29
(c) 9.32, 9.32
(d) 8.29, 8.29
Answer:
(b) 9.32, 8.29
Hint:
Beryllium (1s1 2s2) has higher IE than boron (1s2 2s2 2p) because the last electron in Be has to be removed from fully filled 2s orbital while in boron (1s2 2s2 2p1) the last electron is to be removed from a less tightly held up 2p electron.
![]()
Question 11.
In the following the element with the highest ionisation energy is:
(a) [Ne] 3s2 3p1
(b) [Ne] 3s2 3p2
(c) [Ne] 3s2 3p3
(d) [Ne] 3s2 3p4
Answer:
(b) [Ne] 3s2 3p2
Hint:
Due to greater stability of half filled 3p orbitals, the element with configuration (b) has the highest I.E.
Question 12.
The increasing order of the first ionisation enthalpy of the elements B, P, S and F (lowest first) is:
(a) B < P < S < F
(b) B < S < P < F
(c) F < S < P < B
(d) P < S < B < F
Ans:
(b) B < S < P < F
Hint:
B and F lie in the second period while P and S lie in the third period. Because of higher effective nuclear charge, the first IE of P and S are higher than B but lower than F. Among P and S, P has higher IE due to half filled configuration. Thus the over all order is B < S < P < F.
![]()
Question 13.
In which case, effective nuclear charge is minimum?
(a) Be
(b) Be+2
(c) Be+3
(d) all
Answer:
(a) Be
Hint:
Higher the number of electrons in the extra nuclear part (Be = 4, Be+2 = 2; Be+3 = 1) lower is the force of attraction of the nucleus on the valence electrons and hence, lower is the effective nuclear charge.
Question 14.
Which electronic configuration of an element has abnormally high difference between second and third ionisation energy?
(a) 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s1
(b) 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p1
(c) 1s2, 2s2, 2p6
(d) 1s2, 2s2 2p6, 3s2
Answer:
(d) 1s2, 2s2 2p6, 3s2
Hint: The element which has two electrons in the valence shell has the highest IE, because, the third electron has to be lost from inert gas core.
![]()
Question 15.
The following table shows the successive molar ionisation energy (kJ mol-1) of five elements A to E. Which of two elements are most likely to be in the same group of the periodic table.
Element Ionisation energy (kJ mol-1)
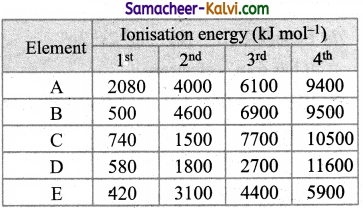
(a) C and D
(b) D and E
(c) B and D
(d) B and E
Answer:
(d) B and E
Hint:
In both elements B and E, first IE is quite low but IE2 is very large. This means after the loss of first electron, same stable configuration is attained. Therefore both these belong to the same group.
Question 16.
Electron affinity is positive when:
(a) O changes to O–
(b) O– changes to C-2
(c) O changes to O+
(d) electron affinity is always negative
Answer:
(a) O changes to O–
Hint:
Since electron affinity is negative of electron gain enthalpy, therefore electron affinity is positive when O changes to O–.
Question 17.
The first ionisation potential of Na is 5.1 eV. The value of electron gain enthalpy is:
(a) + 2.55 eV
(b) – 2.55 eV
(c) – 5.1 eV
(d) – 10.2 eV
Answer:
(c) – 5.1 eV
Hint:
Electron gain enthalpy = ~ (Ionisation enthalpy) = – (5.1) eV = – 5.1 eV
![]()
Question 18.
Which of the following represents the correct order of increasing electron gain enthalpy with ’ negative sign for the elements O, S, F and Cl?
(a) S < O < Cl < F
(b) Cl < F < O < S
(c) O < S < F < Cl
(d) F < S < O < Cl
Answer:
(c) O < S < F < Cl
Hint:
Due to greater e electronegativity of halogens, over elements of group 16, the electron gain enthalpies of halogens (F and Cl) are more negative than the corresponding elements of grou 16 (O and S). Further, due to small size of oxygen and fluorine inter electronic repulsions are more than S and Cl. Thus the electron sain enthalpy increase in the order. ,
O(- 141 kJ) < S(-200 kJ) < F(- 328 kJ) < Cl (-349 kJ)
Question 19.
The element with positive electron gain enthalpy is:
(a) hydrogen
(b) sodium
(c) oxygen
(d) neon
Answer:
(d) neon
Hint:
In inert gases, all orbitals are completely filled. Therefore they have tendency to accept an electron and hence their electron gain enthalpies are positive.
Question 20.
Which of the following species has the highest electron affinity?
(a) F–
(b) O
(c) O–
(d) Na+
Answer:
(b) O
Hint:
Energy is released when ‘O’ accepts an electron. But energy has to be spent when an electron adds to F–, O– and Na+. Hence (b) is correct.
![]()
Question 21.
The highest electron affinity is shown by:
(a) O–
(b) F–
(c) Cl2
(d) F2
Answer:
(a) O–
Hint:
The molecules, F2 and Cl2 and F– all have stable noble gas configurations. Therefore electron gain enthalpy is zero. However O has one electron less than noble gas configuration. Therefore relative gain enthalpy is highest.
Question 22.
Electronegativity of the following elements increases in the order:
(a) C, N, Si, P
(b) N, Si, C, P
(c) Si, P, C, N
(d) P, Si, N, C
Answer:
(c) Si, P, C, N
Hint:
Electronegativity increases along a period and decreases down the group. Nitrogen is more electronegative than carbon and phosphorous is less electronegative than nitrogen and more electronegative than silicon. Hence Si < P < C < N.
Question 23.
Consider the following elements: B, Al, Mg and K. The correct order of their metallic character is: (a) B > Al > Mg > K
(b) Al > Mg > B > K
(c) Mg > Al > K > B
(d) K > Mg > Al > B
Answer:
(b) Al > Mg > B > K
Hint:
Metallic character decreases along a period. Thus, K > Mg > Al. In a group, metallic character increases i.e., Al > B.
![]()
Question 24.
In which of the following options, order of arrangement does not agree with the variation of property indicated against it?
(1) Al+ < Ag+2 < Na+ < F (increasing ionic size)
(2) B < C < N < O (increasing ionisation enthalpy)
(3) I < Br < Cl < F (increasing electron gain enthalpy)
(4) Li < Na < K < Pb (increasing metallic radius)
(a) 2, 3
(b) 1, 3
(c) 3, 4
(d) 1, 4
Ans :
(a) 2, 3
Hint:
The ionic size increases as positive charge on cation decreases or the negative charge on the anion increases. Hence (1) is correct. Due to greater stability of half filled electronic configuration of N, its ionisation enthalpy is higher than ‘O’, i.e., (2) is incorrect. Due to strong inter electronic repulsions in the small sized F, the negative electron gain enthalpy is lower than that pf chlorine. Here (3) is incorrect.
The metallic character increases as the size of the metal atom increases. Hence (4) is correct. Thus the incorrect options are (2) and (3).
Question 25.
Ionic radii vary in:
(1) inversely proportional to the effective nuclear charge
(2) inversely proportional tò the square of the effective nuclear charge.
(3) direct proportion to the screening effect.
(4) direct proportion to the square of screening effect.
Choose the correct statements:
(a) 1, 2
(b) 1, 3
(c) 2, 3
(d) 2, 4
Ans :
(b) 1, 3
Hint:
Ionic radius decreases as the effective nuclear charge increases. Hence (1) is correct. Ionic radius increases as screening effect increases. Hence (3) is correct.
![]()
Question 26.
Match the entities in column I with appropriate entities in column II.
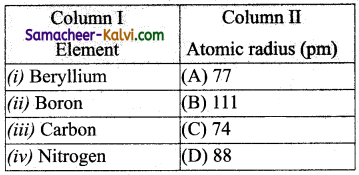
(a) (i) – (B), (ii) – (D), (iii) – (A), (iv) – (C)
(b) (i) – (D), (ii) – (A), (iii) – (C), (iv) – (B)
(c) (i) – (D), (ii) – (A), (iii) – (B), (iv) – (C)
(d) (i) – (C), (ii) – (A), (iii) – (D), (iv) – (B)
Answer:
(a) (i) – (B), (ii) – (D), (iii) – (A), (iv) – (C)
Hint:
As we move from left to right nuclear charge increases and hence atomic radius decreases.
Question 27.
Electronic configurations of same elements is given in column I and their electron gain enthalpies are given in column II. Match the electronic configurations with electrons gain enthalpy.
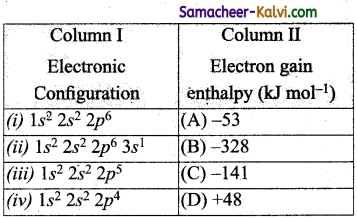
(a) (i) – (D), (ii) – (A), (iii) – (B), (iv) – (C)
(b) (i) – (A), (ii) – (B), (iii) – (D), (iv) – (C)
(c) (i) – (B), (ii) – (D), (iii) – (A), (iv) – (C)
(d) (i) – (C), (ii) – (B), (iii) – (A), (iv) – (D)
Ans :
(a) (i) – (D), (ii) – (A), (iii) – (B), (iv) – (C)
Hint:
(i) The electronic configuration corresponds to noble gas. Noble gases have positive value of electron gain enthalpy i.e 48 kJ mo-1.
(ii) The electronic configuration corresponds to alkali metal. Alkali metals have small negative electron gain enthalpy, i.e., -53 kJ mol-1
(iii) The electronic configuration corresponds to a halogen. Halogens have high negative electron gain enthalpy i.e., -328 kJ mol-1.
(iv) The electronic configuration corresponds to group 6 (i.e., oxygen). Group 6 elements have ion electron gain enthalpy than group 7 element, i.e., -141 kJ mol-1.
![]()
Question 28.
In the following questions, one of the option is totally different from the rest of the options. Identify the options.
(a) oxygen
(b) sulphur
(c) polonium
(d) astatine
Ans :
(d) astatine
Hint:
Astatine is a 7th group element while others are 6th group elements.
Question 29.
Which pair of elements with atomic numbers represent ‘s’ block elements.
(a) 7, 15
(b) 5, 12
(c) 9, 18
(d) 4, 14
Answer:
(d) 4, 14
Question 30.
One of the following have different number of electrons in its atom. Identify that atom.
(a) N+
(b) O-2
(c) F–
(d) Cl–
Answer:
(d) Cl–
Hint:
Cl– have 18 electrons while all others are isoelectronic with total of 10 electrons each.
![]()
Question 31.
Eka- aluminium and Eka- silicon are known as:
(a) Gallium and germanium
(b) Aluminium and silicon
(c) Iron and sulphur
(d) Carbon and silicon
Answer:
(a) Gallium and germanium
Question 32.
Choose the isoelectronic species from arrange the following:
Atomic number of Cs = 55, Br = 35.
(a) Cs+ and Br–
(b) Ca+2, Mg+2
(c) N-3, F–
(d) Al+3,Cl–
Answer:
(c) N-3, F–
Question 33.
In which of the following, the atomic radius of the first element is lesser than the second?
(a) B and C
(b) Al and Si
(c) Na and Mg
(d S and P
Answer:
(a) B and C
Hint:
Atomic radius decreases along the period. The order of elements in (d) is P and S. Hence sulphur has a lesser atomic radius than P.
![]()
Question 34.
Assertion :
Helium and beryllium have similar outer electronic configuration of the type ns2.
Reason :
Both are chemically inert.
(a) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) if assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) if both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
(c) if assertion is true, but reason is false.
Question 35.
Assertion:
The element with electronic configuration [Xe]54 4/1 5d1 6s2 is a block element.
Reason :
The last electron enters the ‘cf orbital.
(a) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) if assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) if both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
(d) if both assertion and reason are false.
Question 36.
Assertion:
When atoms of the first transition series ionise, the ‘4s’ electrons are ionised before the ‘3d’ electrons.
Reason :
The energy of ‘3d’ electrons is lower than that of ‘4s’ electrons.
(a) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) if assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) if both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
(a) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
![]()
Question 37.
Assertion:
Na+ and Al+3 are isoelectronic but the magnitude of the ionic radius of Al+3 is less than that of Na+.
Reason :
The magnitude of effective nuclear charge of the outer shell of electrons of Al+3 is greater than that of Na+
(a) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct- explanation of the assertion.
(b) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) if assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) if both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
(a) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct- explanation of the assertion.
Question 38.
Assertion:
The ionisation of ‘s’ electron requires more energy than ionisation of ‘p’ electrons of the same shell.
Reason :
‘s’ electrons are closer to the nucleus than ‘p’ electrons and have more strongly bond to the nucleus.
(a) if both assertion and reason are tree and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) if assertion is true, but reason is false.
(d) if both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
(a) if both assertion and reason are tree and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 39.
Identify the wrong statement in the following:
(a) Amongst isoelectronic species, smaller the positive charge on the cation, smaller is the ionic radius.
(b) Amongst isoelectronic species, greater the negative change on the anion, larger is the ionic radius.
(c) Atomic radius of elements increase, as one moves down the first group of the periodic table.
(d) Atomic radius of the elements decreases as one moves across from left to right in the 2nd period of the periodic table.
Answer:
(a) Amongst isoelectronic species, smaller the positive charge on the cation, smaller is the ionic radius.
Hint:
Amongst isoelectronic species, smaller the positive charge, smaller is the ionic radius is the wrong statement. Actually it should be smaller the positive charge, bigger is the ionic radius.
![]()
Question 40.
The incorrect statement among the following
(a) The first ionisation potential of Al is less than the first ionisation potential of Mg.
(b) The second ionisation potential of Mg is greater than the second ionisation potential of Na.
(c) The first ionisation potential of Na is less than the first ionisation potential of Mg.
(d) The first ionisation potential of Mg is greater than the third ionisation potential of Al.
Answer:
(b) The second ionisation potential of Mg is greater than the second ionisation potential of Na.
Hint:
∆H2 of Na is higher than that of Mg because, in case of Na, the second electron has to be removed from the noble gas core, while in the case of Mg, the removal of second electron gives the noble gas core.
Question 41.
Consider the following ionisation steps.
M(g) → M+ (g) + e ∆H = 100 eV
M(g) → M+2 (g) + 2e ∆H = 250 eV
Select the correct statement:
(a) ∆H1 of M(g) is 150 eV
(b) ∆H1 of M+(g) is 150 eV
(c) ∆H2 of M(g) is 150 eV
(d) ∆H2 of M(g) is 150 eV
Answer:
(d) ∆H2 of M(g) is 150 eV.
![]()
Question 42.
Following statements regarding periodic trends of chemical reactivity of the alkali metals and the halogens are given. Which of these statement gives the correct picture?
(a) Chemical reactivity increases with increase in atomic number down the group in both alkali metals and halogens.
(b) In alkali metals, the reactivity increases, but in halogens, it decreases with increase in atomic number down the group.
(c) The reactivity decreases in alkali metals but increases in the halogens with increase in atomic number.
(d) In both alkali metals and the halogens, the chemical reactivity decreases with increase in atomic number down the group.
Answer:
(b) In alkali metals, the reactivity increases, but in halogens, it decreases with increase in atomic number down the group.