Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Physics Guide Pdf Chapter 1 Nature of Physical World and Measurement Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Physics Solutions Chapter 1 Nature of Physical World and Measurement
11th Physics Guide Nature of Physical World and Measurement Book Back Questions and Answers
![]()
Part – I:
I. Multiple choice questions:
Question 1.
One of the combinations from the fundamental physical constants is \(\frac { hG }{ G }\), The unit of this expression is.
(a) Kg²
(b) m³
(c) S-1
(d) m
Answer:
(a) Kg²
Question 2.
If the error in the measurement of radius is 2%, then the error in the determination of volume of the sphere will be:
(a) 8%
(b) 2%
(c) 4%
(d) 6%
Answer:
(d) 6%
Question 3.
If the length and time period of an oscillating pendulum have errors of 1% and 3% respectively then the error in measurement of acceleration due to gravity is: [Related to AMPMT 2008]
(a) 4%
(b) 5%
(c) 6%
(d) 7%
Answer:
(d) 7%
Question 4.
The length of a body is measured as 3.15m, if the accuracy is 0.01m, then the percentage error in the measurement is:
(a) 351%
(b) 1%
(c) 0.28%
(d) 0.035%
Answer:
(c) 0.28%
![]()
Question 5.
Which of the following has the highest number of significant figure?
(a) 0.007 m²
(b) 2.64 x 1024 Kg
(c) 0.0006032 m²
(d) 6.3200 J
Answer:
(d) 6.3200 J
Question 6.
If π = 3.14, then the value of π² is:
(a) 9.8596
(b) 9.860
(c) 9.86
(d) 9.9
Answer:
(c) 9.86
Question 7.
Which of the following pairs of physical quantities have same dimension?
(a) force and power
(b) torque and energy
(c) torque and power
(d) force and torque
Answer:
(b) torque and energy
Question 8.
The dimensional formula of planck’s constant h is _____________. [AMU, Main, JEE, NEET]
(a) [ML² T-1]
(b) [ML²T-3]
(c) [MLT-1]
(d) [ML3T-3]
Answer:
(a) [ML² T-1]
Question 9.
The velocity of a particle v at an instant t is given by v = at + bt² the dimension of b is _____________
(a) [L]
(b) [LT-1]
(c) [LT-2]
(d) [LT-3]
Answer:
(d) [LT-3]
![]()
Question 10.
The dimensional formula for gravitational constant G is _____________. [Related to AIPMT 2004]
(a) [ML3T-2]
(b) [M-1L3T-2]
(c) [M-1 L-3T-2]
(d) [ML-3T2]
Answer:
(b) [M-1L3T-2]
Question 11.
The density of a material is CGS system of units Is 4 g cm-3. In a system of units in which unit of length is 10cm and unit of mass is 100g, then the value of density of material will be:
(a) 0.04
(b) 0.4
(c) 40
(d) 400
Answer:
(c) 40
Question 12.
If the force is proportional to square of velocity, then the dimension of proportionality constant is _____________. [JEE 2000]
(a) [ML T0]
(b) [ML T-1]
(c) [ML-2T]
(d) [ML-1T0]
Answer:
(d) [ML-1T0]
Question 13.
The dimension of (µ0ε0)\(\frac { -1 }{ 2 }\) is _____________. [Main AIPMT 2011]
(a) length
(b) time
(c) velocity
(d) force
Answer:
(c) velocity
Question 14.
Planck’s constant (h), speed of light in vacuum (c) and Newton’s gravitational constant (G) are takers as three fundamental constants. Which of the following combinations of these has the dimension of length? [NEET 2016 (phase II)]

Answer:
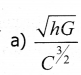
Question 15.
A length-scale (l) depends on the permittivity (c) of a dielectric material Boltzmann constant (Kb), the absolute temperature (T), the number per unit volume (n) of certain charged particles, and the charge (q) carried by each of the particles. Which of the following expression for L is dimensionally correct? [JEE (advance(d) 2016 ]
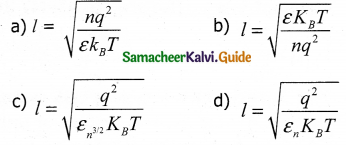
Answer:
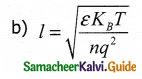
II. Short Answer Questions:
Question 1.
Briefly explain the types of physical quantities?
Answer:
Physical quantities are classified into two types. There are fundamental and derived quantities. Fundamental or base quantities are quantities which cannot be expressed in terms of any other physical quantities. These are length, mass, time, electric current, temperature, luminous intensity, and amount of substance.
Quantities that can be expressed in terms of fundamental quantities are called derived quantities. For example, area, volume, velocity, acceleration, force.
![]()
Question 2.
How will you measure the diameter of the moon using the parallax method?
Answer:
In order to determine the diameter of the moon, initially, a distance of the moon is calculated using the parallax method. Let D be the distance of the moon from the earth. Let d be the diameter of the moon. Let ∝ be the angular size of the angular diameter of the moon (ie) the angle subtended by d at the earth.
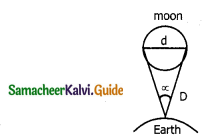
We have ∝ = d/D
d = ∝ D
The angle ∝ can be measured from the same location on the earth. When two diametrically opposite points of the moon are viewed through a telescope, the angle between the two directions gives the angular size or angular diameter. Since D is the known to size or diameter d of the moon can be determined.
Question 3.
Write the rules for determining significant figures.
Answer:
(1) All non zero digits are significant
Example: 1342 has 4 significant figures
(2) All zeros between two non-zero digits are significant
Example: 2008 has four significant figures
(3) All zeros to the right of non-zero digit but to the left of the decimal point are significant.
Example: 3070.00 has 4 significant figures.
(4) The trailing zeros are not significant, ie in the number without a decimal point. All zeros are significant if they come from the measurement.
Example: 4000 has one significant figure.
(5) If a number is less than 1, the zero (s) on the right of the decimal point but to the left of the first non-zero digit are not significant.
Example: 0.0034 has 2 significant figures.
(6) All zeros to the right of the decimal point and to the right of non zero digits are significant
Example: 40.00 has four significant figures.
(7) The number of significant figures does not depend on the system of units used.
Example: 1.53cm, 0.0150cm, 0.0000153 Km all have three significant figures.
(8) The power of 10 is irrelevant to the determination of significant figures
Example: 5.7 x 102 cm has two significant figures.
![]()
Question 4.
What are the limitations of dimensional analysis?
Answer:
(1) This method gives no information about the dimensionless constants in the formula. Like 1, 2,7i, e etc. ie they can not be determined using this analysis.
(2) This method can not decide whether the given quantity is a scalar or a vector.
(3) Using this method one cannot derive relations involving trigonometric, exponential and logarithmic functions.
(4) It cannot be applied to an equation involving more than three physical quantities.
(5) It can be used to check whether a given physical relation is dimensionally correct or not. The physical correctness can not be checked using this
For example:
s = ut + 1/3 at² is dimensionally correct were as physically not correct, as the correct equation is s = ut + 1/2at².
Question 5.
Define precision and accuracy. Explain with one example.
Answer:
The accuracy of a measurement is a measure of how close the measured value is to the true value of the quantity. The precision of measurement is the closeness of two or more measured values to each other.
The true value of a certain length is near 5.678 cm. In one experiment, using a measuring instrument of resolution 0.1 cm, the measured value is found to be 5.5 cm. In another experiment using a measuring instrument of greater resolution, say 0.01 cm, the length is found to be 5.38 cm. We find that the first measurement is more accurate as it is closer to the true value, but it has lesser precision. On the contrary, the second measurement is less accurate, but it is more precise.
![]()
III. Long Answer Questions:
Question 1.
State the principle of homogeneity and explain with an example.
Answer:
The principle of homogeneity of dimensions states that the dimensions of all the term in the physical expression should be same. This principle is used to check the correctness of the equation
For example
V2 = U2 + 2as
Writing dimensions on both sides
[LT-1]² = [LT-1]² + [LT-1]²
[L2 T2] = [L2 T2] + [L2T-2]
Here the dimensions of all the terms in the expression are same and equal to[L2T-2]
So the equation is dimensionally correct.
Question 2.
Write short notes on the following.
(a) unit
(b) rounding off
(c) dimensionless quantity
Answer:
(a) Unit:
Unit of a physical quantity is defined as an arbitrarily chosen standard of measurement of a quantity which is accepted internationally.
The units in which the fundamental quantities are measured are called fundamental or base units and the units of measurement of all other physical quantity which can be obtained by a suitable multiplication or division of powers of fundamental units are called as derived units, example area, volume.
(b) Rounding off:
While doing calculations, the result got should not has too many figures. If no case the result have more significant figures than the figures involved in the data used for calculating. The result of calculation with numbers containing more than one uncertain digits should be rounded off.
Example :
18.35 when rounded off to 3 digits 18.4
19.45 when rounded off to 3 digits 19.4
101.55 x 106 when rounded off to four digits 101.6 x 106.
(c) Dimensionless quantity:
There are two types of dimensionless quantities – (i) dimensionless variable and (ii) dimensionless constant.
- Dimensionless variables – Physical quantities which have no dimensions but have variable values are called dimensionless variables.
Examples: specific gravity, strain, refractive index, etc. - Dimensionless constants – Quantities which have constant values and also have no dimension are called dimensionless constants.
Example: π, e, numbers, etc.
![]()
Question 3.
What do you mean by the propagation of errors? Explain the propagation of errors in addition and multiplication.
Answer:
A number of measured quantities may be involved in the final calculation of an experiment. Different types of instruments might have been used for observation.
So the errors in the final result depends on –
(i) The error in individual measurements.
(ii) On the nature of mathematical operations.
The various possibilities of the propagation or combination of errors in different arithmetical operations are called propagation of errors.
Error in addition (or) sum of two quantities:
Let ∆A and ∆B be the absolute errors in measuring two quantities A and B respectively. Then
Measured value of A = A ± AA
Measured value of B = B ± AB
Consider sum A + B = Z
The error ∆Z in Z is given by
Z + ∆Z = (A ± ∆A) + (B ± ∆B).
= (A + B ) ± (∆A + ∆B)
Z + ∆Z = Z ± (∆A + ∆B)
∆Z = ∆A + ∆B
The maximum possible error in the sum of two quantities is equal to the sum of the absolute errors in the individual quantities.
Errors in multiplication (or) product of two quantities:
Let ∆A and ∆B be the absolute errors in the two quantities A and B respectively. Consider the product Z = AB
The error ∆Z in z given by
Z ± ∆Z = (A ± ∆A) (B ± ∆B)
= (AB) ± (A ∆ B) ± (B ∆ A) ± (∆A . ∆B)
Z ± ∆ Z = Z ± (A ∆ B) (B ∆ A) + (∆A . ∆B)
LHS by Z & RHS by AB = Z.
1± \(\frac { ∆ Z }{ Z }\) = 1 ± \(\frac { ∆ B }{ B }\) ± \(\frac { ∆ A }{ A }\) ± \(\frac { ∆A.∆B }{ AB }\)
Here \(\frac { ∆A.∆B }{ AB }\) can be neglected as \(\frac { ∆A}{ A }\) & \(\frac { ∆B }{ B }\) are small
∴ The maximum fractional error in Z is
\(\frac { ∆ Z }{ Z }\) = ±\(\frac { ∆A }{ A }\) x \(\frac { ∆B }{ B }\)
∴ The maximum fractional error in the product of two quantities is equal to the sum of fractional errors is the individual quantities.
Question 4.
Explain in detail various types of errors.
Answer:
The uncertainty in a measurement is called an error.
There are 3 types of errors namely –
- Random error
- Systematic error
- Gross error.
1. Systematic errors – These are reproducible inaccuracies that are consistently in the same direction. These occur often due to problem that persists throughout the experiment. Systematic errors are further classified as
- instrumental error
- imperfection in experimental technique or procedure
- personal errors
- errors due to external causes
- least count error.
(a) Instrumental error: When an instrument is not calibrated properly at the time of manufacture instrumental errors may occur.
Example: If the measurement is made with a meter scale whose end is worn out the result obtained will have errors.
Correction – These errors can be corrected by choosing the instrument carefully.
(b) Imperfections in experimental technique or procedure: These errors arise due to limitations in the experimental arrangement.
Example: While performing experiments with a calorie meter, if there is no proper insulation, there will be radiation losses. This results in an error.
Correction – Necessary steps and corrections should be applied and followed while performing experiments.
(c) personal errors: These errors are due to individuals performing the experiments., maybe due to incorrect initial setting up of the experiment or carelessness of the individuals making the observation due to improper precautions.
(d) Errors due to external causes: The change in external conditions during experiments can cause error in measurement.
Example: Changes in temperature, humidity or pressure during measurement may affect the result of the measurement.
(e) Least count error: Least count is the smallest value that can be measured by the measuring instrument and the error due to this measurement is the least count error. The instrument’s resolution is the cause of the error. The error is half of the least value measured by the device.
Correction – Least count error can be reduced by using a high precision instrument for measurement.
(2) Random errors – Random errors may arise due to random and unpredictable variations is experimental conditions like pressure, temperature voltage supply etc., Errors may also due to persona! errors by the observer. Random errors are sometimes called “Chance errors”.
Example: While measuring the thickness of a wire using a screw gauge, different readings are taken in different trails.
Correction – By taking the arithmetic mean of all readings observed may reduce the random error and the mean value is taken as best possible true value.
(3) Gross errors – The error caused due to sheer carelessness of an observer is called gross error.
Examples: Improper setting of the instrument Making wrong observations without bothering about the sources of errors and precautions. Using wrong values in calculation Recording wrong observations
Correction – This error can be minimized only when the observer is careful and mentally alert.
![]()
Question 5.
(i) Explain the use of screw gauge and vernier calipers in measuring smaller distances:
(ii) Write a note a triangular method and radar method to measure large distances.
Answer:
Measurement of small distances by screw gauge and vernier calipers screw gauge : The screw gauge is an instrument used for measuring accurately the dimensions of objects up to a maximum of about 50 mm. The principle of the instrument is the magnification of linear motion using the circular motion of a screw. The least count of screw gauge is 0.01 mm.
Vernier calipers: A vernier caliper is a versatile instrument for measuring the dimensions of an object namely diameter of a hole or the depth of a hole. The least count of vernier caliper is a 0.01 cm.
Measurement of larger distances: For measuring larger distance such as height of a tree, distance of a moon or a planet from earth, the triangulation method, parallax method and radar method are used.
(a) Triangulation method for the height of an accessible object:
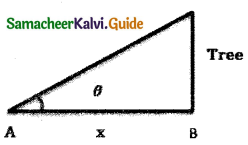
Let AB = h, be the height of a tree, to be measured. Let C be the point of observation at a distance X from B. Using a range finder placed
at C, ∠ACB = θ is measured.
∴ Considering ∆ ABC,
tan θ = \(\frac { AB }{ BC }\)
h = x tan θ
By knowing x, h can be calculated.
(b) Radar method:
RADAR is an acronym of Radio detection and ranging. A RADAR can be used to measure the distance of near planet, moon, enemy planes, moving as well as stationary targets etc. In this process, Radio signals are transmitted from the transmitter and after reflection from target, the radio signals are received by the receiver.
The time interval is recorded between the two instants i.e from time of transmission to time of reception. By knowing velocity and time, distance can be measured.
![]()
IV. Numerical Problems:
Question 1.
In a submarine equipped with sonar the time delay between the generation of a pulse and its echo after reflection form an enemy submarine is observed to be 80s. If the speed of sound in water is 1460 ms-1. What is the distance of enemy submarine?
Solution:
Time taken = 80s
Velocity of sound = V = 1460 m/s
Distance of enemy submarine d = ?
V = \(\frac{2d}{t}\)
d = \(\frac{Vt}{2}\)
= \(\frac{1460×80}{2}\)
= 1460 x 40
= 58400 m
d = 58.4k m
Question 2.
The radius of the circle is 3.12 m calculate the area of the circle with regard to significant figures.
Solution:
Given: radius: 3.12 m (Three significant figures)
Solution:
Area of the circle = πr2 = 3.14 × (3.12 m)2 = 30.566
If the result is rounded off into three significant figure, the area of the circle = 30.6 m2
![]()
Question 3.
Assuming that the frequency γ of the vibrating string may depend up on
(i) applied force (F)
(ii) Length (l)
(iii) mass per unit length (m) prove that γ ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{ l }\)\(\sqrt{\frac{F}{m}}\) using dimensional analysis.
Solution:
γ ∝ Fa lbmc
Writing dimension on both sides
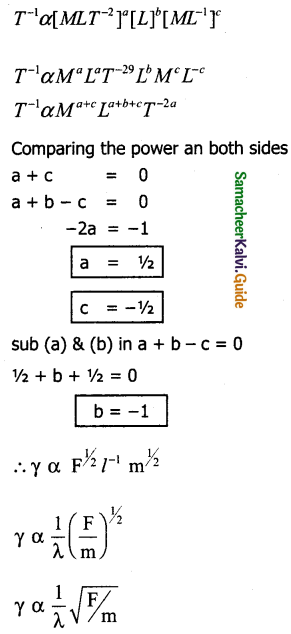
Hence Proved.
Question 4.
Jupiter is at a distance of 824.7 million Km from the earth. Its angular diameter is measured to be 35.72″ calculate the diameter of Jupiter
Solution:

Given Distance of Jupiter = 824.7 × 106 km = 8.247 × 1011 m
angular diameter = 35.72 × 4.85 × 10-6rad = 173.242 × 10-6 rad = 1.73 × 10-4 rad
∴ Diameter of Jupiter D = D × d = 1.73 × 10-4 rad × 8.247 × 1011 m
= 14.267 × 1o7 m = 1.427 × 108 m (or) 1.427 × 105 Km
Question 5.
The measurement value of length of a simple pendulum is 20 cm known with 2mm accuracy. The time for 50 oscillations was measured to be 40s with in Is resolution. Calculate the percentage accuracy in the determination of acceleration due to gravity g from the above statement.
Solution:
l = 20 x 10-2m = 20 cm
∆l = 2mm = 0.2 cm
Time for 50 oscillations = 40s
Time for 1 oscillation = T = \(\frac { 40 }{ 50 }\)
= \(\frac { 4 }{ 5 }\)s
∆T = 1s.
∆T = \(\frac { 1 }{ 50 }\)S
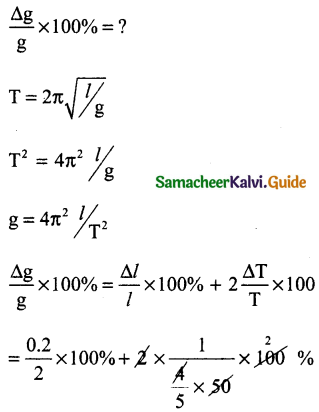
= 1% + 5%
= 6%
![]()
11th Physics Guide Nature of Physical World and Measurement Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Multiple choice questions:
Question 1.
The unit of surface tension ……
(a) MT-2
(b) Nm-2
(c) Nm
(d) Nm-1
Answer:
(d) Nm-1
Question 2.
One astronomical unit is equal to _______.
(a) 1.510 x 1012m
(b) 1.5 x 1012Km
(c) 1.5 x 1011m
(d) 1.5 x 1012Cm
Answer:
(c) 1.5 x 1011m
Question 3.
One light-year is ……
(a) 3.153 × 107 m
(b) 1.496 × 107 m
(c) 9.46 × 1012 km
(d) 3.26 × 1015 km
Answer:
(c) 9.46 × 1012 km
Question 4.
The dimensional formula for the coefficient of viscosity is _______.
(a) M0 L-1T-1
(b) M1 L1T1
(c) M1 L-1T1
(d) M2 L2T0
Answer:
(c) M1 L-1T1
Question 5.
One parsec is …..
(a) 3.153 × 107 m
(b) 3.26 × 1015 m
(c) 30.84 × 1015 m
(d) 9.46 × 1015 m
Answer:
(c) 30.84 × 1015 m
Question 6.
The dimensional formula for (ε0) permittivity of free space _______.
(a) M-1 L3 T4 A2
(b) M-1 L3 A2
(c) M-1L-3T4A2
(d) M1L3T-4A-2
Answer:
(c) M-1L-3T4A2
![]()
Question 7.
One Angstrom is ………
(a) 10-9 m
(b) 10-10m
(c) 10-12 m
(d) 10-15 m
Answer:
(b) 10-10 m
Question 8.
In the formula x = 3yz², x and y have dimensions of capacitance and magnetic induction respectively what are the dimensions of y?
(a) M3 L2 T2 Q4
(b) M3 L-2T4Q4
(c) M3 L2 T4 Q4
(d) M3L-2T4Q4
Answer:
(d) M3L-2T4Q4
Question 9.
\(\frac{1}{12}\) of the mass of carbon 12 atom is …..
(a) 1 TMC
(b) mass of neutron
(c) 1 amu
(d) mass of hydrogen
Answer:
(d) mass of hydrogen
Question 10.
The resistance of a conductor R = V/I where v = (50±2)v and I = (9 ± 0.3) A find the percentage error in R.
(a) 8.5%
(b) 3.7%
(c) 7.8%
(d) 7.3%
Answer:
(d) 7.3%
Question 11.
The study of forces acting on bodies whether at rest or in motion is …..
(a) classical mechanics
(b) quantum mechanics
(c) thermodynamics
(d) condensed matter physics
Answer:
(a) classical mechanics
![]()
Question 12.
In the measurement of pressure if maximum errors in the measurement of force and length of a square plate are 3% and 2% respectively. The maximum error is _______.
(a) 7%
(b) 8%
(c) 4%
(d) 5%
Answer:
(a) 7%
Question 13.
Which of the following is not a dimensionless physical quantity?
(a) Mechanical equivalent of heat
(b) volumetric strain
(c) atomic mass unit
(d) Avogadro’s number
Answer:
(c) atomic mass unit
Question 14.
The study of production and propagation of sound waves …..
(a) Astrophysics
(b) Acoustics
(c) Relativity
(d) Atomic physics
Answer:
(b) Acoustics
Question 15.
The physical quantities not having the same dimensions are _______.
(a) torque and work
(b) Linear momentum and planks constant
(c) stress and youngs modulus
(d) speed and (ε0μ0)-1/2
Answer:
(a) torque and work
Question 16.
Which two of the following five physical parameters have the same dimension?
(1) energy density
(2) refractive index
(3) dielectric content
(4) youngs modulus
(5) magnetic field
(a) 1 and 4
(b) 1 and 5
(c) 2 and 4
(d) 3 and 5
Answer:
(a) 1 and 4
Question 17.
The astronomers used to observe distant points of the universe by …….
(a) Electron telescope
(b) Astronomical telescope
(c) Radio telescope
(d) Radar
Answer:
(c) Radio telescope
Question 18.
The youngs modulus of a material of the wire is 12.6 x 1011 dyne/cm2. Its value is MKS system is _______.
(a) 12.6 x 1012 N/M2
(b) 12.6 x 1010 N/M2
(c) 12.6 x 106 N/M2
(d) 12.6 x 108 N/M2
Answer:
(a) 12.6 x 1012 N/M2
Question 19.
The dimensionless quantity _______.
(a) never has a unit
(b) always has a unit
(c) may has a unit
(d) does not exist
Answer:
(c) may has a unit
![]()
Question 20.
Which one of the following is not a fundamental quantity?
(a) length
(b) luminous intensity
(c) temperature
(d) water current
Answer:
(d) water current
Question 21.
The time dependence of a physical quantity p is givers by \(p_{0} e^{-\alpha t^{2}}\) = P, where α is a constant and t is time. The constant α is _______
(a) a dimensionless
(b) has the dimension of T2
(c) has the dimension as that of P
(d) has the dimension equal to dimensions of PT-2
Answer:
(a) a dimensionless
Question 22.
A force F is given F = at + bt² Where t is time. What are the dimensions of a & b?
(a) ML T-3 and ML2T-4
(b) MLT-3 and MLT-4
(c) MLT-1 and MLT0
(d) MLT-4and MLT-1
Answer:
(a) ML T-3 and ML2T-4
Question 23.
The triple point temperature of the water is ……
(a) -273.16 K
(b) 0K
(c) 273.16 K
(d) 100 K
Answer:
(d) 100 K
Question 24.
The force F on a sphere of radius ‘a’ moving in a medium with a velocity v is given by F = 6 π av. The dimension of η are
(a) ML-1T-2
(b) MT-1
(c) MLT-2
(d) ML-3
Answer:
(d) ML-3
![]()
Question 25.
The unit of moment of force ……
(a) Nm2
(b) Nm
(c) N
(d) NJ rad
Answer:
(b) Nm
Question 26.
If the orbital velocity of a planet is given by v = GaMbRc then _______.
(a) a = 1/3, b = 1/3, c = – 1/3
(b) a = 1/2, b =1/2, c = – 1/2
(c) a = 1/3, b = – 1/2, c = 1/2
(d) a = 1/2, b = – 1/2, c = – 1/2
Answer:
(a) a = 1/3, b = 1/3, c = – 1/3
Question 27.
The period T of a soap bubble under SHM given by T = PaDbSc where P is the pressure, d is the density of water and E is the total energy of the explosion, then the value of a, b and c are:
(a) -3/2, 1/2, 1
(b) -5/6, 1/2, 1/3
(c) 5/6, 1/2, 1/3
(d) -5/6, -1/2, 1/3
Answer:
(a) -3/2, 1/2, 1
Question 28.
One degree of arc is equal to …….
(a) 1.457 × 102 rad
(b) 1.457 × 10-2 rad
(c) 1.745 × 102 rad
(d) 1.745 × 10-2 rad
Answer:
(b) 1.457 × 10-2 rad
Question 29.
Frequency is the functions of density p length ‘l’ and tension T. The period of oscillation is proportional to _______.
(a) ρ1/2 λ² T-1/2
(b) ρ1/2 λ3/2T-1/2
(c) ρ1/2 λ3/2 T-3/4
(d) ρ1/2 λ1/2 T3/2
Answer:
(a) ρ1/2 λ² T-1/2
Question 30.
The frequency of vibration of string is given by γl = \(\frac{p}{2 \ell} \sqrt{\frac{T}{m}}\) Here l is the length, P is the number of segments in the string. T is tension is the string, the dimensional formula for ‘m’ will be.
(a) M0 L T-1
(b) M L0 T-1
(c) M L-1 T0
(d) M0 L0 T0
Answer:
(c) M L-1 T0
Question 31.
1 second of arc is equal to ………………..
(a) 0.00027°
(b) 1.745 × 10-2 rad
(c) 2.91 × 10-4 rad
(d) 4.85 × 10-6 rad
Answer:
(a) 0.00027°
![]()
Question 32.
If force (f), length (L) and time (T) are assumed to be fundamental units then the dimensional formula of the mass will be _______.
(a) FL-1T2
(b) FL-1T2
(c) FL-1 T-1
(d) FL2T2
Answer:
(a) FL-1T2
Question 33.
If pressure ‘p’ velocity v and time T are taken as fundamental physical quantities the dimensional formula for force is _______.
(a) [PV2 T2]
(b) [P-1V2T-2]
(c) [PV T2]
(d) [P-1V T2]
Answer:
(a) [PV2 T2]
Question 34.
The range of distance can be measured by using direct methods is …..
(a) 10-2 to 10-5 m
(b) 10-2 to 102 m
(c) 102 to 1(T5 m {d) 10″2 to 105 m
Answer:
(b) 10-2 to 102 m
Question 35.
The speed of light (c) gravitational constant G and planks constant h are taken as fundamental units. The dimension of time in the new system will be _______.
(a) G1/2 h1/2 C-5/2
(b) g1/2 h1/2 C1/2
(c) G1/2 h1/2 C-3/2
(d) G1/2 h1/2 C1/2
Answer:
(a) G1/2 h1/2 C-5/2
Question 36.
The rate of flow(Q) (volume of liquid flowing per unit volume through a pipe depends on radius r, Length f of pipe, pressure difference P across the ends of pipe and coefficient of viscosity of liquid η as Q α raρb ηcLdthen _______
(a) a = 4, b = 1, c = – 1, d = – 1
(b) a = 4, b = – 1, c = 1, d = – 1
(c) a = 4, b = 1, c = 1, d = – 1
(d) values of a,b,c and d cannot be determined
Answer:
(d) values of a,b,c and d cannot be determined
Question 37.
The dimensions of universal gas constant is _______
(a) ML2T-2θ-1
(b) ML2T-2θ
(c) ML3 T-1 θ-1
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) ML2T-2θ-1
Question 38.
Find odd one out.
(a) Newton
(b) metre
(c) candela
(d) Kelvin
Answer:
(a) Newton
Question 39.
Which of the following combinations have the dimensions of time? L, C, R represent inductance, capacitance, and resistance respectively.
(a) RC
(b) \(\sqrt{LC}\)
(c) L/R
(d) C/L
Answer:
(b) \(\sqrt{LC}\)
Question 40.
The dimensions of mobility are _______
(a) M-1 LA T-2
(b) ML A-1T-2
(c) MA-1T-2
(d) M-1A T2
Answer:
(d) M-1A T2
Question 41.
The smallest physical unit of time is
(a) second
(b) minute
(c) microsecond
(d) shake
Answer:
(d) shake
![]()
Question 42.
The length, breadth and thickness of strip are given by l = (10.0±0.1)cm, h=(1.00±0.01)cm t = (0.100±0.001)cm the most probable error in volume will be _______
(a) 0.03 cm3
(b) 0.111 cm3
(c) 0.012 cm3
(d) 0.12 cm3
Answer:
(a) 0.03 cm3
Question 43.
The measured mass and volume of a body are 22.42g and 4.7cm3 respectively with possible errors of 0.01 g and 0.1cm3. The maximum error in density is _______.
(a) 0.2%
(b) 2%
(c) 5%
(d) 10%
Answer:
(b) 2%
Question 44.
Half the lifetime of a free neutron is in the order of ……
(a) 10°
(b) 101 s
(c) 102 s
(d) 103 s
Answer:
(d) 103 s
Question 45.
An experiment measures quantities a, b, c and y is calculated from a formula. y = \(\frac{a b^{2}}{c^{3}}\) If the percentage errors in a,b and c are ± 1%, ± 3%, ± 2% respectively, the percentage error in calculating y is _______
(a) ± 13%
(b) ± 7%
(c) ±4%
(d) ± 1%
Answer:
(a) ± 13%
Question 46.
A student measures the distance traversed in a free fail of a body, initially at rest in a given time. He uses this data to estimate g, the acceleration due to gravity. If maximum percentage error in measurement of the distance and the time are e1 and e2 respectively the percentage error in the estimation of g is _______
(a) e2 – e1
(b) e1+ 2e2
(c) e1 + e2
(d) e1 – 2e2
Answer:
(b) e1+ 2e2
Question 47.
The heat generated in a circuit is given by Q = I²Rt. Where I is current, R is the resistance and t is the time. If an error in measuring current, resistance, and time are 2%, 1%, and 1% respectively. The maximum error in measuring heat will be _______
(a) 2%
(b) 4%
(c) 6%
(d) 8%
Answer:
(c) 6%
Question 48.
Imperfections in experimental procedure give ……………….. error.
(a) random
(b) gross
(c) systematic
(d) personal
Answer:
(c) Systematic
![]()
Question 49.
A student performs an experiment for determination of g = \(\frac{4 \pi^{2} l}{T^{2}}\) an error of ∆l. For that, he takes the time of n oscillations with the stopwatch of least count ∆T and he commits a human error of 0.1s. For which of the following data, the measurement of g will be most accurate? ∆l, ∆T, n
(a) 5m, 0.2s, 10
(b) 5mm, 0.2s, 20
(c) 5mm, 0.1s, 20
(d) 1mm, 0.1s, 50
Answer:
(d) 1mm, 0.1s, 50
Question 50.
A Screw gauge gives the following reading when used to measure the diameter of the wire.
Main scale reading = 0.
Circular scale reading = 52 divisions
Given that 1 mm on the main scale corresponds to 100 division on a circular scale. The diameter of the wire is _______.
(a) 0.52 cm
(b) 0.052 cm
(c) 0.0026 cm
(d) 0.005 cm
Answer:
(b) 0.052 cm
Question 51.
The error caused due to the sheer carelessness of an observer is called as ……………. error.
(a) Systematise
(b) Gross
(c) Random
(d) Personal
Answer:
(b) Gross
Question 52.
The force (F) velocity(v) and time “T” are taken as fundamental units then the divisions of mass are _______.
(a) [FVT2]
(b) [FV-1T-1]
(c) [FV T-1]
(d) [FV-1T]
Answer:
(d) [FV-1T]
Question 53.
Attempting to explain diverse physical phenomenon with few concepts and law is _______.
(a) unification (or) reductionism
(b) neither unification nor reductionism
(c) unification
(d) reductionism
Answer:
(c) unification
Question 54.
An attempt to explain a microscopic system in terms of its microscopic constituents _______.
(a) unification
(b) reductionism
(c) neither unification or reductionism
(d) neither unification nor reductionism
Answer:
(b) reductionism
Question 55.
The study of nature of particles is _______ a branch of physics.
(a) nuclear physics
(b) quantum mechanics
(c) condensed another physics
(d) high energy physics
Answer:
(d) high energy physics
Question 56.
The ratio of the mean absolute error to the mean value is called …………….
(a) absolute error
(b) random error
(c) relative error
(d) percentage error
Answer:
(c) Relative error
![]()
Question 57.
1″ is equal to _______ radian.
(a) 1.745 x 10-2 rad
(b) 1.78 x 10-3 rad
(c) 2.91 x 10-4 rad
(d) 4.847 x 10-6 rad
Answer:
(d) 4.847 x 10-6 rad
Question 58.
From a point on the ground, the top of a tree is seen to have an angle of elevation of 60°. The distance between the tree and a point is 50 m. The height of the tree is _______.
(a) 86.6 m
(b) 90.6 m
(c) 92.8 m
(d) 80.6 m
Answer:
(a) 86.6 m
Question 59.
The maximum possible error in the sum of two quantities is equal to …….
(a) Z = A + B
(b) ∆Z = ∆A + ∆B
(c) ∆Z = ∆A/∆B
(d) ∆Z = ∆A – ∆B
Answer:
(b) ∆Z = ∆A + ∆B
Question 60.
Number of a significant digit in 0.030400
(a) 6
(b) 5
(c) 4
(d) 3
Answer:
(b) 5
![]()
II. Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
A new unit of length is chosen such that the speed of light in a vacuum is unity. What is the distance between the sun and the earth in terms of the new unit if light takes 8 min and 20 s to cover this distance?
Answer:
Speed of light in vacuum, c = 1 new unit of length s-1
t = 8 min. 20 sec, = 500 s
x = ct= 1 new unit of length s-1 × 500s
x = 500 new unit of length
![]()
Conceptual Questions:
Question 1.
Why it is convenient to express the distance of stars in terms of light-year (or) parsec rather than in Km?
Solution:
One light-year = 9.46 x 1015 m = 9.46 x 1012 Km. As the distance of stars is extraordinarily large, so it is convenient to express them in light-year rather than in meters or in kilometers.
Question 2.
Show that a screw gauge of pitch 1 mm and 100 divisions is more precise than a vernier caliper with 20 divisions on the sliding scale.
Solution:
The device that has a minimum least count is said to be more precise.
In case of screw gauge: Least count
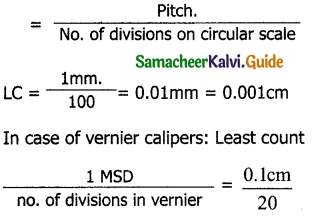
= 0.05 mm
Out of this screw, gauges is having the minimum least count. So screw gauge is more precise.
Question 3.
What is the difference between mN, Nm, and nm?
Answer:
mN means milli newton, 1 mN = 10-3 N, Nm means Newton meter, nm means nanometer.
Question 4.
Having all units in atomic standards is more useful. Explain.
Answer:
It became necessary to redefine all units in atomic standards because the prototype offers the following difficulties.
- It is difficult to preserve prototype models.
- It is difficult to produce replicas of prototypes for their use in different countries.
- The techniques used for producing replicas are not of very high accuracy.
- Atomic standard units can be reproduced anywhere and at any time.
- It is variant in time and space.
- It is unaffected by environmental conditions like temperature, pressure, etc.
- It has an accuracy of 1 part in 109.
Question 5.
Why dimensional methods are applicable only up to three quantities?
Answer:
The dimensional analysis is not applicable on more than 3 physical quantities because the equating powers of M, L & T, we get three unknowns. Similar constraints are present for electrical or other non-mechanical quantities also