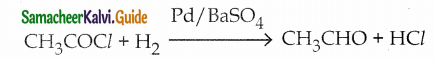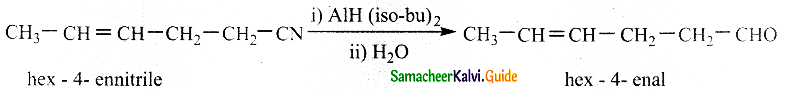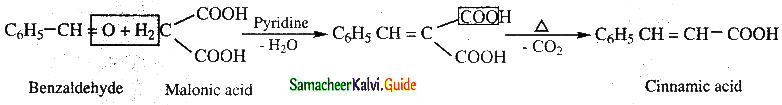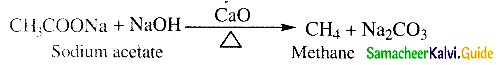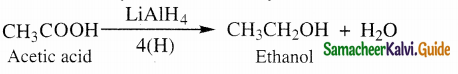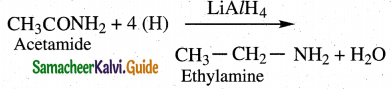Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Guide Pdf Chapter 22 The Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881 Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Solutions Chapter 22 The Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881
12th Commerce Guide The Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881 Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answers
Question 1.
Negotiable Instrument Act was passed in the year …………..
a) 1981
b) 1881
c) 1994
d) 1818
Answer:
b) 1881
Question 2.
Negotiable Instrument is freely transferable by delivery if it is a ………….. instrument.
a) Order
b) Bearer
c) both a & b
d) None of the above
Answer:
b) Bearer
![]()
Question 3.
The transferee of a Negotiable Instrument is the one ……………………
a) Who transfer the instrument
b) On whose name it is transferred
c) Who enchases it
d) None of the above
Answer:
b) On whose name it is transferred
Question 4.
The number of parties in a bill of exchange is
a) 2
b) 6
c) 3
d) 4
Answer:
c) 3
![]()
Question 5.
Section 6 of the Negotiable Instruments Act 1881 deals with
a) Promissory Note
b) Bills of exchange
c) Cheque
d) None of the above
Answer:
c) Cheque
Question 6.
……………….. cannot be a bearer instrument.
a) Cheque
b) Promissory Note
c) Bills of exchange
d) None of the above
Answer:
a) Cheque
![]()
Question 7.
When crossing restrict further negotiation
a) Not negotiable crossing
b) General Crossing
c) A/c payee crossing
d) Special crossing
Answer:
a) Not negotiable crossing
Question 8.
Which endorsement relieves the endorser from incurring liability in the event of dishonor
a) Restrictive
b) Facultative
c) Sans recourse
d) Conditional
Answer:
b) Facultative
![]()
Question 9.
A cheque will become stale after …………. months of its date
a) 3
b) 4
c) 5
d) 1
Answer:
a) 3
Question 10.
Document of title to the goods excludes
a) Lorry receipt
b) Railway receipt
c) Airway bill
d) Invoice
Answer:
d) Invoice
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by Negotiable Instrument?
Answer:
A negotiable instrument is a document which entitles a person to a certain sum of money and which is transferable from one person to another by mere delivery or by endorsement and delivery.
Question 2.
Define Bill of Exchange.
Answer:
- “A Bill of Exchange is an instrument in writing containing an unconditional order, signed by the maker, directing a certain person to pay a certain sum of money only to or to the order of a certain person or to the bearer of the instrument”.
- Negotiable Instrument Act -1881, Sec – 5.
![]()
Question 3.
List three characteristics of a Promissory Note.
Answer:
Characteristics of a Promissory Note:
- A promissory note must be in writing.
- The promise to pay must be unconditional.
- It must be signed by the maker.
Question 4.
Define Cheque.
Answer:
- A cheque is a printed instrument issued by Commercial Banks to its customers for making and receiving payments. [To withdraw self and to pay others]
- The person who draws a cheque is called – “Drawer”.
- The Bank on whom the cheque is drawn is called – “Drawee”.
- The person who receives payment on the cheque is called – “Payee”.
Question 5.
Define Endorsement.
Answer:
“When the maker or holder of a negotiable instrument signs the name, otherwise that as such maker for the purpose of negotiation, on the back or face thereof, or on a slip of paper annexed thereto.”
![]()
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the Characteristics of Negotiable Instrument.
Answer:
A negotiable instrument is transferable from one person to another without any formality, such as affixing stamp, registration, etc. When the instrument is held by the holder in due course in the process of negotiation, it is cured of all defects in the instrument with respect to ownership. Though a bill, a promissory note, or a cheque represents a debt, the transferee is entitled to sue on the instrument in his own name in case of dishonour, without giving notice to the debtor that he has become its holder.
![]()
Question 2.
Distinguish between Negotiability and Assignability. (NON)
Answer:
|
No. Basis of Difference |
Negotiability | Assignability |
|
1. Nature of title |
In case of negotiation, the transferee can get a better title than that of transfer or provided he takes the instrument for bonafide and for value. | In the case of an assignment, the assignee [Transferee] cannot get a better title than that of the assignor. [Transferor]. |
| 2. Ownership | In case it is payable to Bearer – mere delivery. In case it is payable in order – Endorsement and delivery and easy to transfer. |
The transfer of legal title takes place by means of a separate document and after complying with the necessary legal formalities. |
| 3. Notice | Notice is not necessary for the holder to claim the payment from debtors. | The assignee must give notice to the debtors. |
Question 3.
What are the characteristics of a Bill of Exchange?
Answer:
Characteristics of a Bill of Exchange:
- A bill of exchange is a document in writing.
- The document must contain an order to pay.
- The order must be unconditional.
- The instrument must be signed by the person who draws it.
- The name of the person on whom the bill is drawn must be specified in the bill itself.
![]()
Question 4.
Distinguish between Bill of Exchange and Promissory Note. (UNDI)
Answer:
|
No. Basis of Difference |
Bill of Exchange |
Promissory Note |
| 1. Undertaking | It contains an unconditional order. | It contains an unconditional undertaking. |
| 2. Number of Parties | There are three parties:
|
There are two parties:
|
| 3. Drawer of the instrument | A creditor draws a Bill on the debtor. | A debtor executes a promotion in favour of a creditor. |
| 4. Identify the parties | Both Drawer and payee can be one and the same person. | The maker himself can not be the payee because the same person cannot be both the promisor and promisee. |
Question 5.
Discuss the two different types of the crossing.
Answer:
General Crossing:
According to section 123 of the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881,
“Where a cheque bears across its face an addition of the words “and company” or any abbreviation thereof between two transverse parallel lines simply, either with or without the words “not negotiable” that addition shall be deemed a crossing and the cheque shall be deemed to be crossed generally”.
Special Crossing:
According to section 124 of the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881
“Where a cheque bears across its face an addition of the name of a banker with or without the word “not negotiable” that addition shall deem a crossing and the cheque shall be deemed to be crossed specially”.
![]()
IV. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Mention the presumptions of Negotiable Instruments.
Answer:
Presumptions of Negotiable Instrument:
- Every negotiable instrument is presumed to have been drawn and accepted for consideration.
- Every negotiable instrument bearing, a date is presumed to have been made or drawn on such a date.
- It is presumed to have been accepted within a reasonable time after the date and before its maturity.
- The transfer of a negotiable instrument is presumed to have been made before maturity.
- When a negotiable instrument has been lost, it is presumed to have been duly stamped.
- The holder of a negotiable instrument is presumed to be a holder in due course.
Question 2.
Distinguish between cheque and Bill of Exchange. (DOGS AND VP)
Answer:
|
No. Basis of Difference |
Bill of Exchange |
Cheque |
| 1. Drawn | A Bill of Exchange can be drawn on any person including Banker. | A Cheque can be drawn from a specified Banker. |
| 2. On dishonour | On dishonour there is a practice of Noting and protesting. | No such things on dishonour. |
| 3. Grace days | 3 grace days are allowed to calculate the maturity date. | Grace days are not allowed. |
| 4. Stamping | Sufficiently stamped. | Need not be stamped. |
| 5. Acceptance | Acceptance by the drawee is necessary. | Does not require any acceptance. |
| 6. Notice | Notice of dishonour is necessary. | Notice of dishonour is not necessary. |
| 7. Discounting | It can be discounted. | It cannot be discounted. |
| 8. Validity | A Bill made payable to the bearer on demand is void. | A Cheque drawn payable to the bearer on demand is valid. |
| 9. Payability | It is payable on demand | It is payable after a specified period. |
![]()
Question 3.
Discuss in detail the features of a cheque. (SAUDI PP)
Answer:
A cheque is a negotiable instrument drawn on a particular banker.
Features:
(i) Instrument in Writings:
A cheque or a bill or a promissory note must be an instrument in writing. Though the law does not prohibit a cheque from being written in pencil, bankers never accept it because of risks involved. Alternation is quite easy but detection is impossible in such cases.
(ii) Unconditional Orders:
The instrument must contain an order to pay money. It is not necessary that the word ‘order’ or its equivalent must be used to make the document a cheque. It does not cease to be a cheque just because the world ‘please’ is used before the word pay. Further, the order must be unconditional.
(iii) Drawn on a Specified Banker Only:
The cheque is always drawn on a specified banker. A cheque vitally differs from a bill in this respect as latter can be drawn on any person including a banker. The customer of a banker can draw the cheque only on the particular branch of the bank where he has an account.
(v) A Certain Sum of Money Only:
The order must be for payment of only money. If the banker is asked to deliver securities, the document cannot be called a cheque. Further, the sum of money must be certain.
(v) Payee to be Certain:
The cheque must be made payable to a certain person or to the order of a certain person or to the bearer of the instrument. The word, a person includes corporate bodies, local authorities, associations, holders of the office of an institution etc.
(vi) Signed by the Drawer:
The cheque is to be signed by the drawer. Further, it should tally with the specimen signature furnished to the bank at the time of opening the account.
![]()
Question 4.
What are the requisites for a valid endorsement? (BAD NEWS D)
Answer:
If an endorsement is to be valid, it must possess the following requisites:
- The endorsement is to be made on the face of the instrument or on its back.
- When there is no space for making further endorsements a piece of paper can be attached
- Endorsement for only a part of the amount of the instrument is invalid.
- The endorsement is complete only when delivery of the instrument is made.
- Signing in block letters does not constitute a regular endorsement.
- If the payee is an illiterate person, he can endorse it by affixing his thumb impression on the instrument.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the different kinds of endorsement.
Answer:
1. Blank or General Endorsement:
Without writing anything on the backside of the instrument, the endorser affixing his sign only.

Question 2.
Full or special Endorsement:
Answer:
If the Endorser adds a direction to pay the amount mentioned, to or to the order of a specified person.

Other forms:
- Raaja in favour of Nehan.
- Nehan or order of Raaja.
- Please exchange Nehan – Raaja.
![]()
Question 3.
Conditional or Qualified Endorsement:
Answer:
The endorsee’s right to receive money is subject to the fulfilment of a particular event (condition).

Other forms:
- Pay to Preetha if she marries Yashwanth.
- Pay to Hasan on completion of the house building.
Question 4.
Restrictive Endorsement:
Answer:
When endorsement restricts or prohibits further negotiability of the instrument, by added the word “ONLY” after the endorsee’s name.

Other forms:
Raaja in favour of Nehan.
![]()
Question 5.
Sans recourse Endorsement:
Answer:
- It is an Endorsement which limits the liability of the endorser.
- The effect of this endorsement is, to render the endorser free from all liability to any subsequent holder.

Other forms:
Pay to Nehan sans recourse.
Question 6.
Sans Frais Endorsement:
Answer:
- ‘Sans Frais’ means without expense to me. [Noting charges]
- The Endorser does not want any expenses to be incurred in his account on the instrument.

Question 7.
Facultative Endorsement:
Answer:
It is an Endorsement, whereby, the Endorser waives some of his rights on the instrument.

Question 8.
Partial Endorsement:
Answer:
- It is an Endorsement that seeks to transfer only a part of the payments under the instrument.
- It is not valid.

![]()
12th Commerce Guide The Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881 Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answers
Question 1.
Number of parties to a cheque is………………..
a) 2
b) 3
c) 4
d) 6
Answer:
b) 3
Question 2.
Number of parties to a Promissory Note are …………….
a) 5
b) 3
c) 1
d) 2
Answer:
d) 2
![]()
Question 3.
A bill of exchange drawn on a specified banker is
(a) promissory note
(b) cheque
(c) hundi
(d) share
Answer:
(b) cheque
Question 4.
Section ……….. defined a Bill of Exchange.
a) 1
b) 3
c) 5
d) 7
Answer:
c) 5
![]()
Question 5.
Section …………. defined a cheque.
a) 4
b) 5
c) 6
d) 7
Answer:
c) 6
Question 6.
……………….. days will be given to Bill of Exchange as Grace Days.
a) 3
b) 4
c) 8
d) 9
Answer:
a) 3
![]()
Question 7.
A person who wants to transfer the instrument has to sign on the back is called …………..
a) Endorsee
b) Endorser
c) Indorseum
d) Indorsee
Answer:
b) Endorser
Question 8.
A piece of paper that can be attached to an instrument to sign is called ……………
a) Allonge
b) Stamp
c) Sticker
d) All of these
Answer:
a) Allonge
![]()
Question 9.
Pay to Nehan, if he got 595 marks in +2 Exam is an example for ……………. endorsement.
a) Blank
b) Full or Special
c) Condition
d) Restrictive
Answer:
c) Condition
Question 10.
Pay to Noohu or Bearer is an example for ……………… instrument
a) Bearer
b) Order
c) Inland
d) Foreign
Answer:
a) Bearer
![]()
Question 11.
Pay to Nathifa or order is an example for ………………. instrument.
a) Order
b) Bearer
c) Foreign
d) Inland
Answer:
a) Order
Question 12.
Two transverse parallel lines are not essential in …………………… crossing.
a) General
b) Special
c) Double
d) All of these
Answer:
b) Special
![]()
Question 13.
IFSC is a ………….. character code.
a) 10
b) 11
c) 12
d) 13
Answer:
b) 11
Question 14.
Pick the odd one out.
a) RTGS
b) NEFT
c) IFSC
d) MNC
Answer:
d) MNC
Question 15.
Pick the odd one out.
a) Promissory Note
b) Bills of Exchange
c) Commodity Exchange
d) Cheque
Answer:
c) Commodity Exchange
![]()
II. Match the following.
Question 1.
|
List – I |
List – II |
| i. General Endorsement | 1. Pay to Nusrath only |
| ii. Full Endorsement | 2. Pay Noman if he returns in 3 months |
| iii. Conditional Endorsement | 3. Pay Nehan |
| iv. Restrictive Endorsement | 4. Nathifa – simply signed |

Answer :
a) (i) 4, (ii) 3, (iii) 2, (iv) 1
III. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define Cheque.
Answer:
“Cheque is a bill of exchange, drawn on a specified banker and not expressed to be payable otherwise than on-demand”. – NEGOTIABLE INSTRUMENT ACT -1881, SEC – 6.
Question 2.
Define Promissory Note. [Pronote]
Answer:
“A Promissory Note is an instrument in writing, containing an unconditional promise or undertaking, signed by the maker to pay a certain sum of money only to or to the order of a certain person, or to the bearer of the instrument”. -NEGOTIABLE INSTRUMENT ACT-1881, SEC-4.
![]()
Question 3.
Give a Specimen of Cheque.
Answer:
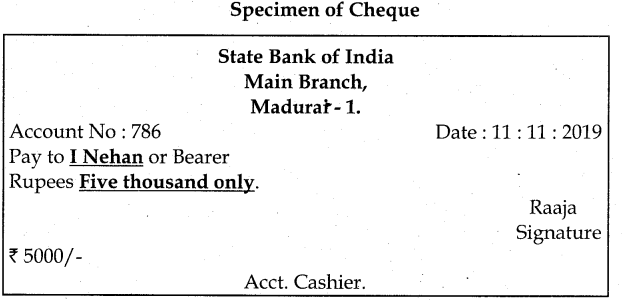
Question 4.
Draw a specimen of the Bill of Exchange.
Answer:
Specimen of a Bill of Exchange
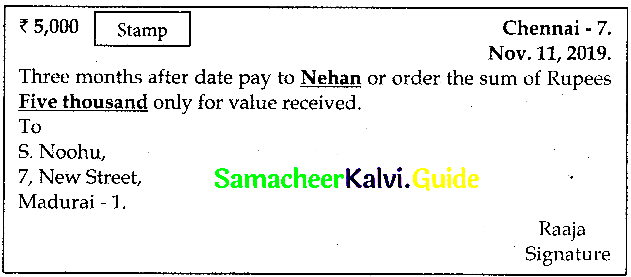
Question 5.
Show a Specimen of a Promissory Note. [Pronote]
Answer:
Specimen of a Promissory Note

Question 6.
What is Endorsement?
Answer:
- A person who wants to transfer his Negotiable Instrument has to put his signature on the backside of the instrument is called “Endorsement”.
- A person who signs on the backside of the instrument is called “Endorser”.
- A person to whom the instrument is endorsed is called “Endorsee”.
![]()
Question 7.
What is crossing and what are its types?
Answer:
- Drawing two parallel transverse lines on the left top corner of a cheque is called “Crossing”.
- Types:
- General Crossing
- Special crossing
Question 8.
Do you think that drawing following the two lines is crossing? If No, Why?
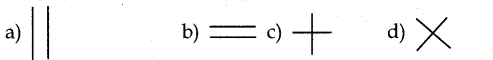
- No. the above drawing two lines are not crossing.
- Because drawing two transverse parallel lines is crossing.
![]()
IV. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is the significance of crossing?
Answer:
- A crossed cheque should not be paid across the counter.
- If a crossed cheque has been stolen and collected for the party not entitled to it, the person for whom it has been collected can be easily traced.
- Crossing ensures the safety and prevents payment into the wrong hands.
Question 2.
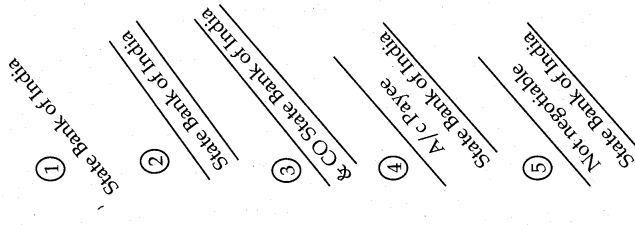
Give Specimens of General Crossing and Special Crossing.
Answer:
Specimen of General Crossing:
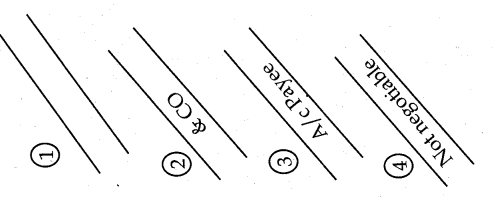
Specimen of Special Crossing :
Question 3.
Why emergency holidays are declared under the Negotiable – Instruments Act?
Answer:
- Where the maturity date of the negotiable instrument falls on a notified public holiday, it is to be paid on a preceding day.
- Where emergency holidays are declared for reasons like the Death of a leader in power, natural calamities, strike, election day etc., day should be made an emergency holiday.
- So, the negotiable instruments maturing on the emergency holiday can be paid on the next working day.
![]()
Question 4.
What is ‘MICR’ Cheque?
Answer:
- Magnetic Ink Character Recognition – MICR – code is character recognition technology used mainly by the banking industry to ease processing and clearance of cheques and other documents.
- It is found at the bottom of the cheque.
- It includes Bank code, Bank Account Number, Amount and a control indicator.
- It prevents the crime of printing counterfeit cheques or documents using technology.
- The Magnetic Ink will help to discover fake documents.
Question 5.
What is the IFSC code?
Answer:
- Indian Financial System Code – IFSC code is an – alphanumeric code which facilitates EFT in India.
- This code uniquely identifies each bank branch participating in the two main Payment and settlement systems in India.
![]()
Question 6.
When there is no space in negotiable Instrument for making further endorsement) how can it be endorsed?
Answer:
When there is no space for making further endorsements a piece of paper can be attached to the negotiable instrument for this purpose, is This piece of paper is called’Allonge’.
Question 7.
If the payee is illiterate, how can he endorse a negotiable instrument?
Answer:
- If the payee is an illiterate person, he can endorse it by affixing his thumb impression on the instrument.
- But it must be duly attested by somebody who should give his full address thereon.
![]()
V. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the various types of Negotiable Instruments.
Answer:
Bearer Instrument:
Cheque or Bill of Exchange or Promissory Note is payable to bearer is called “Bearer Instrument”.
(e.g) Pay to Nathifa or Bearer.
Order Instrument:
Cheque or Bill of Exchange or Promissory Note is payable to order is called “Order Instrument”.
(e.g) Pay to Nathifa or order
(or)
Pay to the order of Nathifa.
Ambiguous Instrument:
- The written document is not clearly mentioned whether it is Bills of Exchange or Promissory Note. It is called “Ambiguous Instrument”.
- (e.g) ‘A’ draws a Bill on ‘B’ who is a fictitious (imaginary) person and transfer it to ‘C’. Time Instrument:
- It is payable sometime in the future.
- (e.g) After three months pay to Nathifa.
Inland Instrument:
A cheque or Bill of Exchange or Promissory Note is an inland instrument subject to the following conditions.
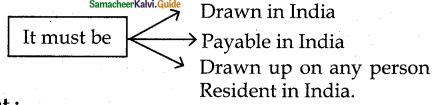
Foreign Instrument:
An instrument which is not an inland instrument is called a “Foreign Instrument”.

![]()
Question 2.
Find out the type of Instrument and the reason?
Answer:
(a) Bill drew payable to Nathifa or Bearer:
- It is Bearer Instrument.
- Reason it is payable to Nathifa or Bearer.
(b) Bill drew in London upon a merchant in Chennai and accepted and payable in Bangalore:
- It is a Foreign Instrument.
- Reason it is drawn in London.
(c) Bill drawn in Delhi upon a merchant in London and accepted and payable in London:
- It is a Foreign Instrument.
- Reason it is accepted and payable in London.
(d) Bill drawn in London on a merchant in Agra and endorsed in Delhi:
- It is a Foreign Instrument.
- It is drawn in London.
(e) A Bill was drawn by Bajaj Auto Agent on Bajaj Auto Ltd :
- It is an Inland Instrument.
- It is drawn in India.
(f) Bill drawn by Noohu on Nehan (an imaginary person) and endorsed to Nathifa:
- It is an Ambiguous Instrument.
- Reason it is drawn on a fictitious (imaginary) person.
(g) Raja gives a blank cheque to Stephen or gives an updated cheque to Stephen:
It is an Inchoate Instrument.
(h) Maran signs stamped and blank promissory Note and keep it locked in his drawer:
‘
- It is an Inchoate Instrument.
- Reason it is blank and not presented.
(i) Satheesh promise to pay Ashwin ₹ 5000 after 3 months :
- It is a Time Instrument.
- Reason it is payable after 3 months (future).
(j) Shruthika who needs funds, draws a Bill on Nusrath who accepted and discounted the bill with her banker and on due date remits the requisite amount to Nusrath :
- It is an Accommodation Instrument.
- Reason it is drawn, accepted without consideration.
(k) No document is attached to the title of goods :
It is clean Bill. Reason no document is attached to the title of goods.
![]()
Question 3.
Classify the following endorsement with reasons.
Answer:
(i) No other words except Sycd’s signature :
- It is Blank or General Endorsement.
- Reason No other words except Syed’s signature.
(ii) Pay Shahul.
(iii) Pay to Shahul or order.
(iv) Pay to Shahul or order for the account of Siva.
- It is Full or Special Endorsement.
- Reason directions to pay to or to the order of a specified person.
(v) Pay to Hameed only :
- It is Restrictive Endorsement.
- Reason it is restricted to transfer.
(vi) Pay to Justin order being the unpaid residue of the bill.
(vii) Pay to Sam or order on safe receipt of goods :
- It is conditional or Qualified Endorsement.
- Reason it is subject to fulfilment of a particular event, [condition]
(viii) Pay to Navitha Sans Recourse, (without recourse to me)
- 11 is Sans Recourse Endorsement.
- Reason – it limits the liability of the endorser.
(ix) Pay to Athivya notice of dishonour dispensed with.
- It is Faculative Endorsement.
- Reason notice of dishonour is waived.
![]()
Question 4.
Distinguish between Cheque and Promissory Note. OPS CD CD
Answer:
|
No.Basis of Difference |
Cheque |
Promissory Note |
| 1.Order | A cheque contains an order to pay the money. | A promissory Note contains an undertaking (promise) to pay the money. |
| 2.Parties | There are three parties to a cheque i) Drawerii) Draweeiii) Payee |
Only two parties. (i) Maker(ii) Payee |
| 3.Stamping | It need not be stamped. | It must be stamped. |
| 4.Crossed | A cheque can be crossed. | It cannot be crossed. |
| 5.Discounting | It cannot be discounted. | It can be discounted with a banker. |
| 6.Creditor | The Drawer of a cheque is a creditor. | The maker of a pronote is a Debtor. |
| 7.Days of Grace | No Grace days allowed. | Three grace days allowed. |

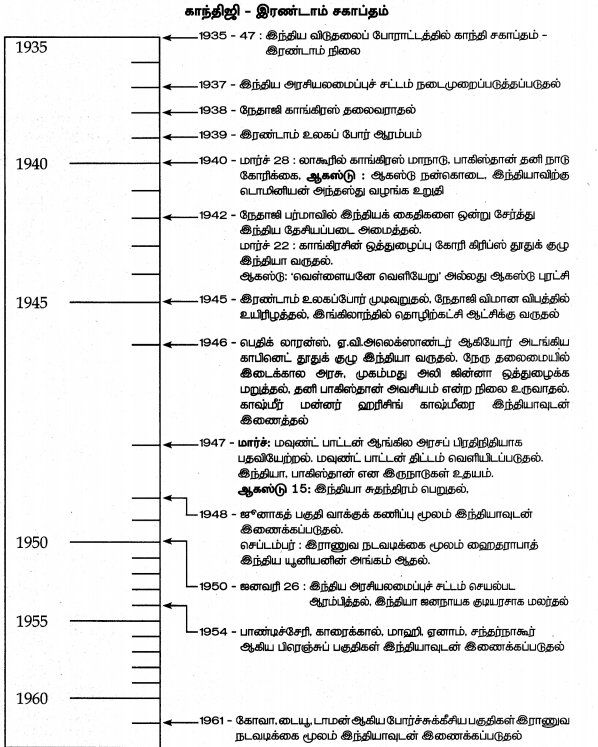
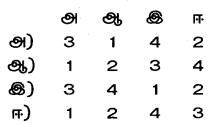
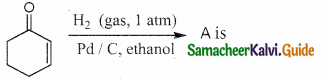
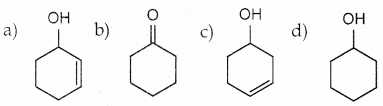
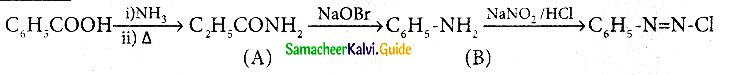
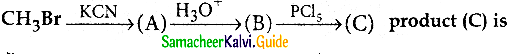
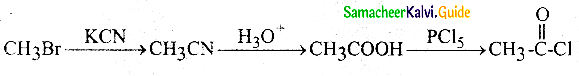
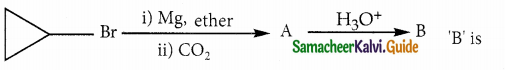
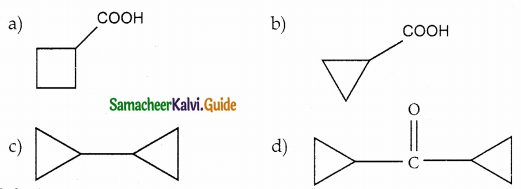
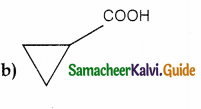
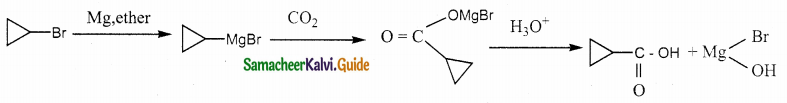
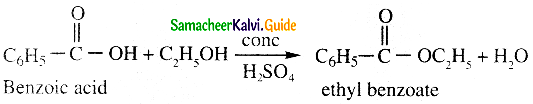
 Answer:
Answer:
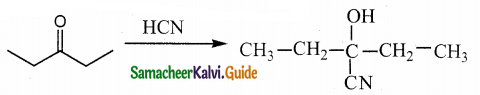
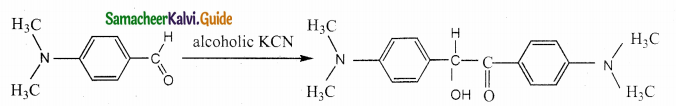
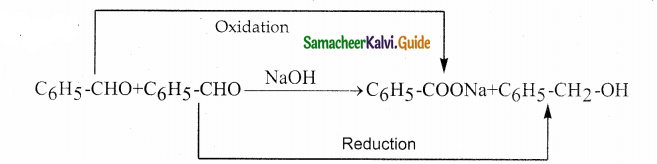
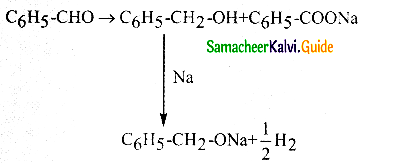
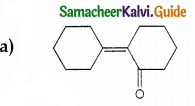
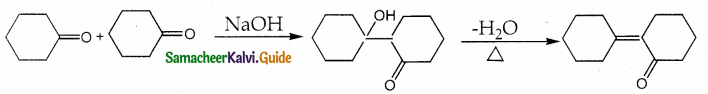
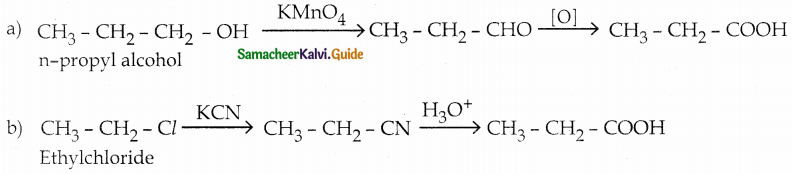
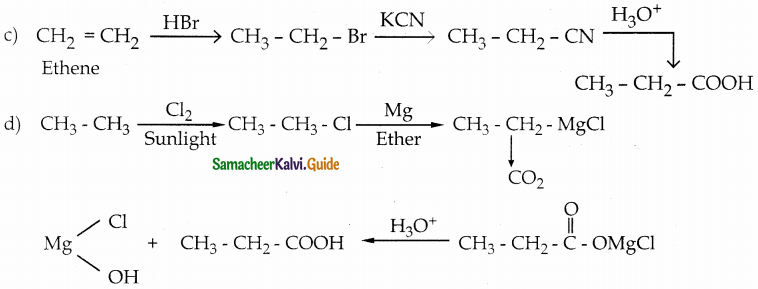
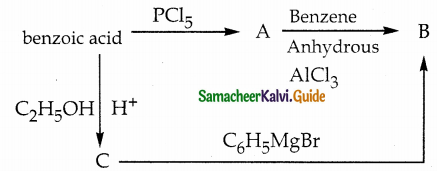 Answer:
Answer: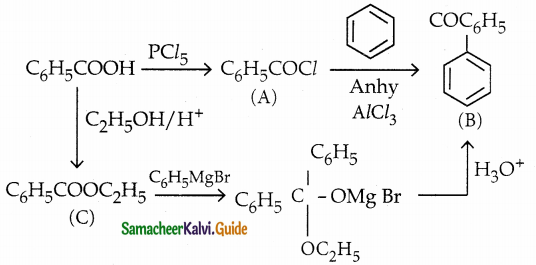
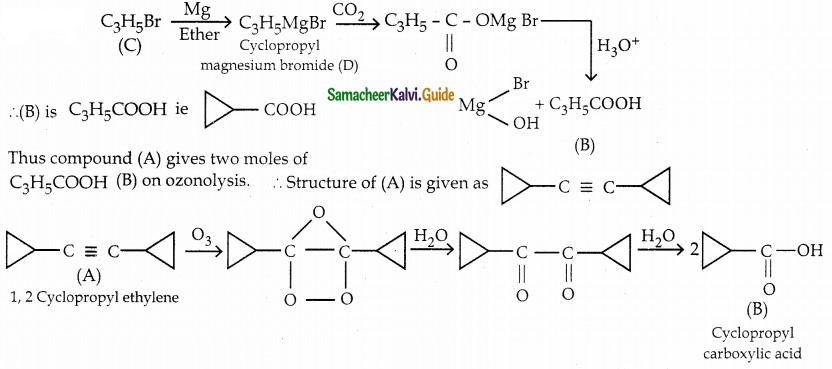
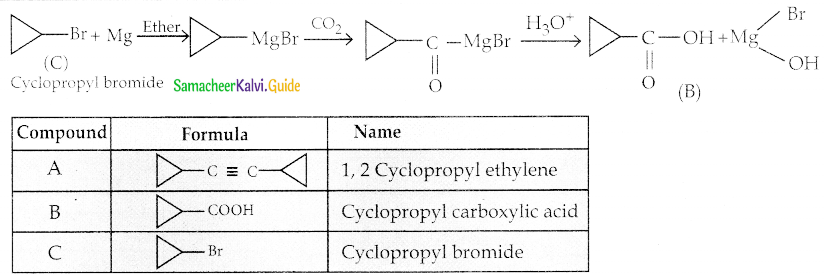
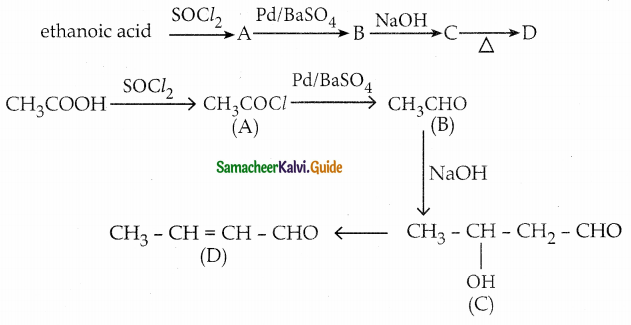
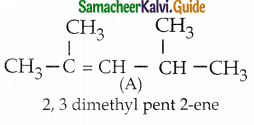
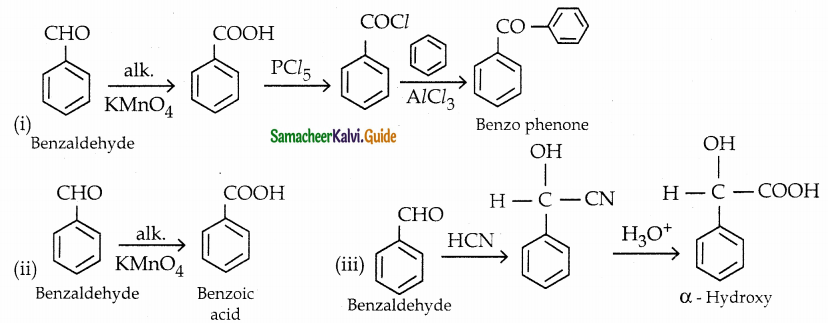
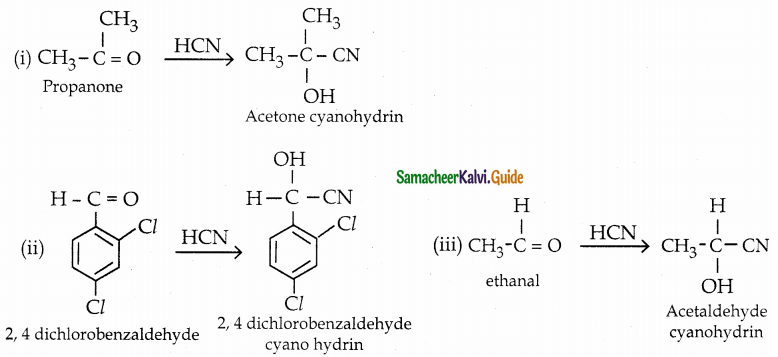
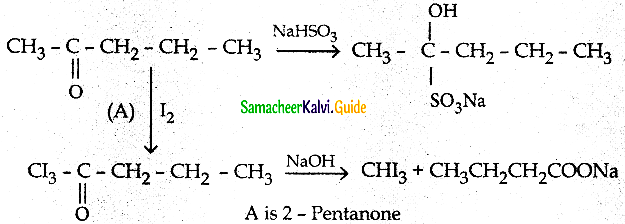
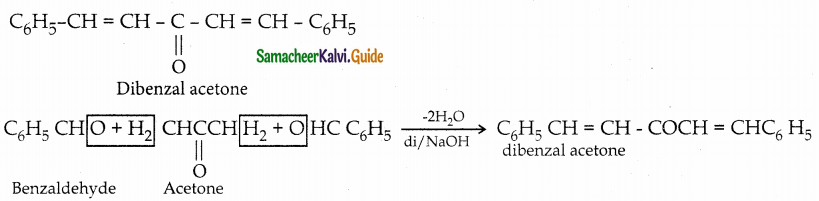
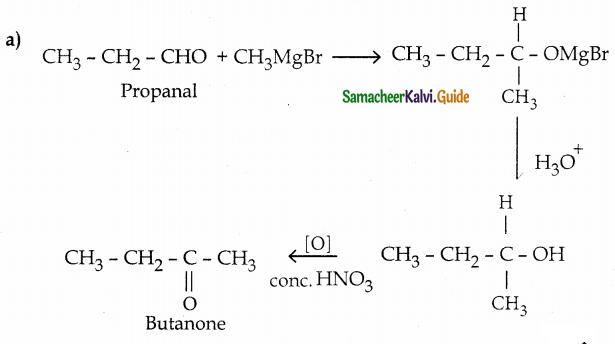
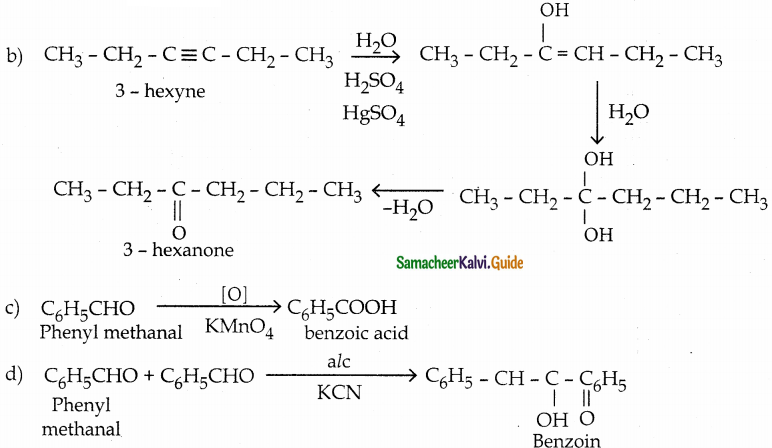

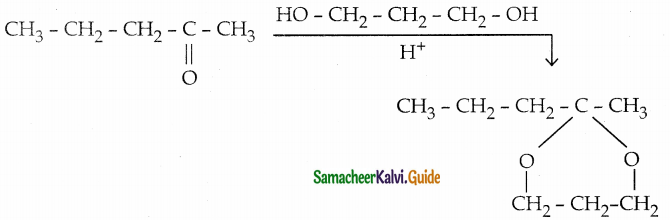
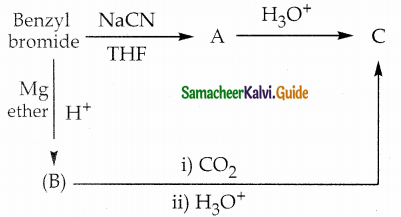
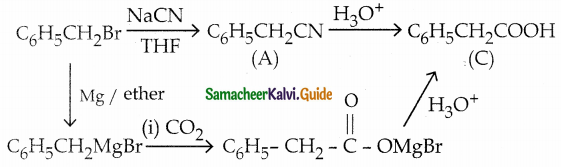
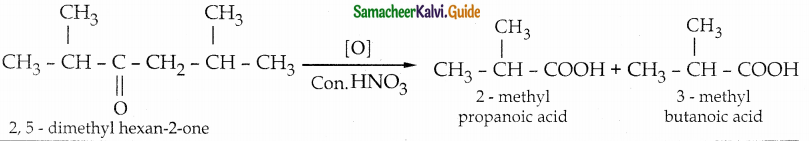
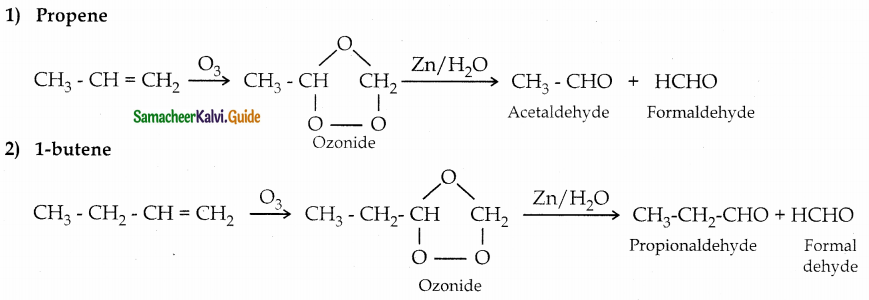
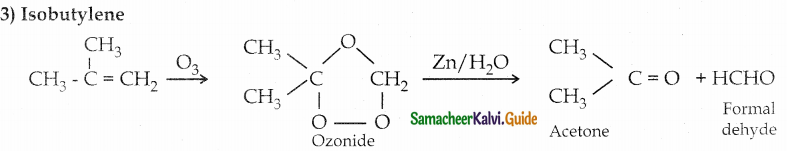

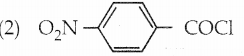
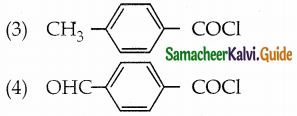
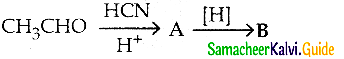

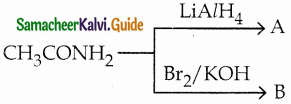
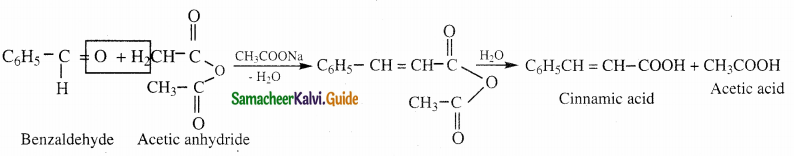
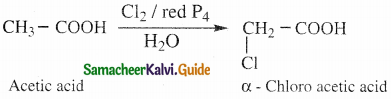
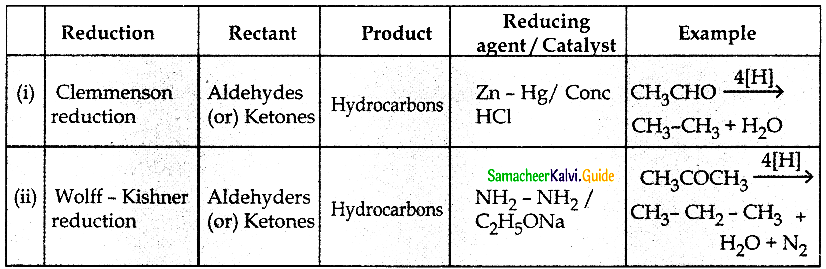
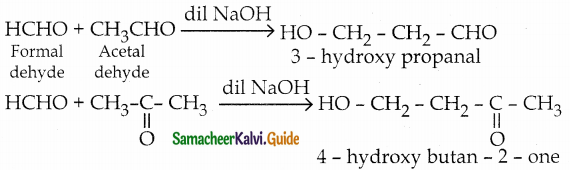
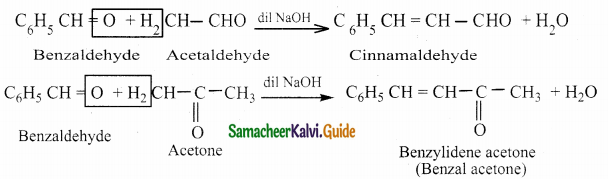
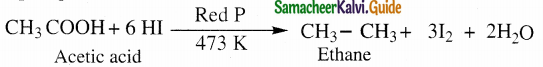
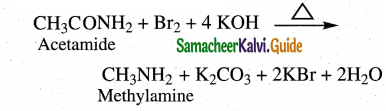
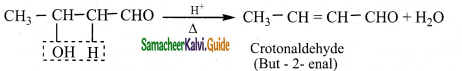
 The reducing agent used in this reaction is
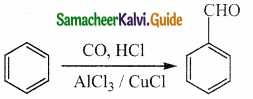
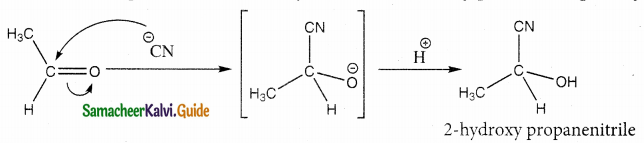
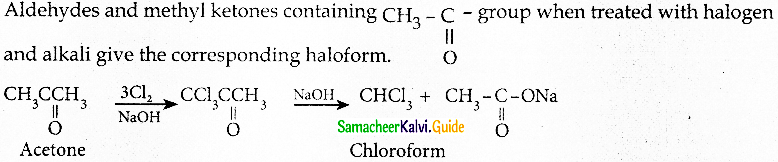
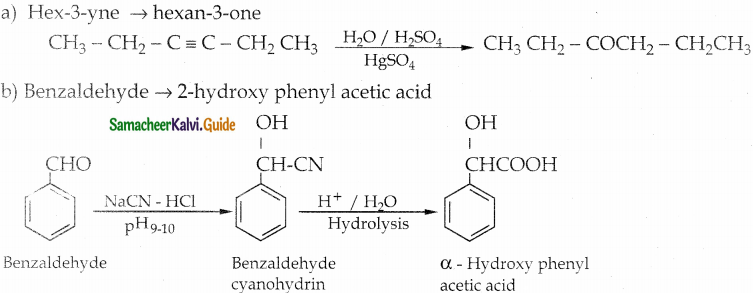
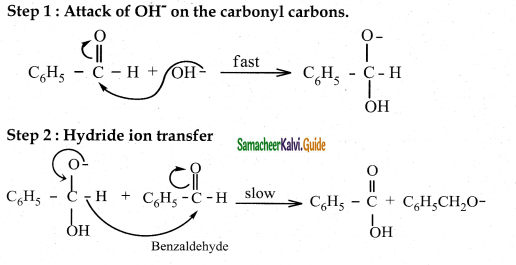
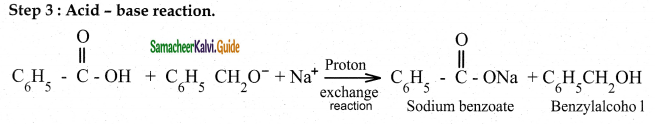
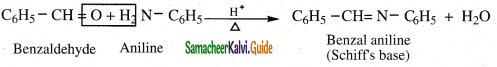
The reducing agent used in this reaction is