Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Guide Pdf Chapter 12 Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Chemistry Solutions Chapter 12 Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids
12th Chemistry Guide Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part – I Text Book Evaluation
I. Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
The correct structure of the product tAt formed in the reaction (NEET)
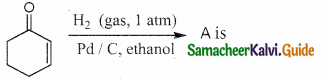
Answer:
Question 2.
The formation of cyanohydrin from acetone is an example of
a) nucleophilic substitution
b) electrophilic substitution
c) electrophilic addition
d) Nucleophilic addition
Answer:
d) Nucleophilic addition
![]()
Question 3.
Reaction of acetone with one of the following reagents involves nucleophilic
addition followed by elimination of water. The reagent is
a) Grignard reagent
b) Sn / Hcl
c) hvdrazine in presence of slightly acidic solution
d) hvdrocvanic acid
Answer:
c) hydrazine in presence of slightly acidic solution
Question 4.
In the following reaction,
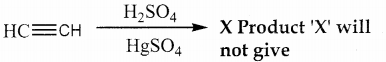
a) Tollens test
b) Victor meyer test
c) lodoform test
d) Fehiing solution test
Answer:
b) Victor meyer test
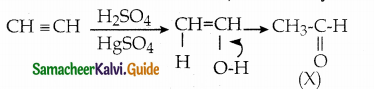
(X) reduces Tollens reagent and Fehling solution and it also answers iodoform test.
![]()
Question 5.
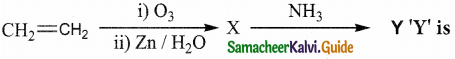
a) Formaldelyde
b) di acetone ammonia
c) hexamethvlene tetraamine
d) oxime
Answer:
c) hexamethylene tetraarnine
X – HCHO Y — (CH2)6 N4
Question 6.
Predict the product Z in the following series of reactions
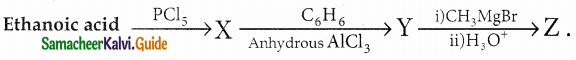
a) (CH3)2C(OH)C6H5
b) CH3CH(OH)C6H5
c) CH3CH(OH)CH2-CH3
Answer:
a) (CH3)2C(OH)C6H5
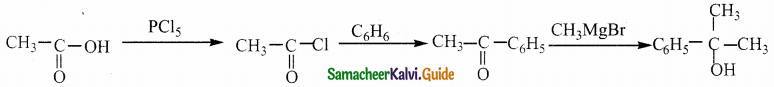
Question 7.
Assertion: 2,2 – dimethyl propanoic acid does not give HVZ reaction.
Reason: 2 – 2, dimethyl propanoic acid does not have a – hydrogen atom
a) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b) if both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c) assertion is true but reason is false
d) both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
a) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
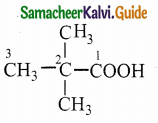
![]()
Question 8.
Which of the following represents the correct order of acidity in the given compounds
a) FCH2COOH > CH3COOH> BrCH2COOH> ClCH2COOH
b) FCH2COOH > ClCH2COOH> BrCH2COOH > CH3COOH
c) CH3COOH > C1CH2COOH > FCH2COOH> Br-CH2COOH
d) ClCH2COOH > CH3COOH > BrCH2COOH> ICH2COOH
Answer:
a) FCH2COOH > CH3COOH> BrCH2COOH> ClCH2COOH
Solution:
I effect increases the acidity. If electronegativity is high, – I effect is also high.
Question 9.
Benzoic acid ![]()
a) anilinium chloride
b) 0- nitro aniline
c) benzene diazonium chloride
d) m – nitro ben.zoic acid
Answer:
c) benzene diazonium chloride
Solution:
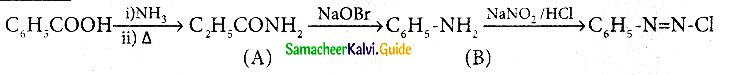
Question 10.
Ethanoic acid ![]() 2 – bromoethanoic acid. This reaction is called
2 – bromoethanoic acid. This reaction is called
a) Finkeistein reaction
b) Haloform reaction
c) Hell – Volhard – Zelinsky reaction
d) none of these
Answer:
c) Hell – Volhard – Zelinsky reaction
![]()
Question 11.
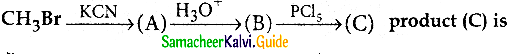
a) acetyichioride
b) chioro acetic acid
c) α- chiorocyano ethanoic acid
d) none of these
Answer:
a) acetyichioride
Solution:
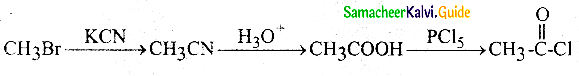
Question 12.
Which one of the following reduces Tollens reagent
a) formic acid
b) acetic acid
c) benzophenone
d) none of these
Answer:
a) formic acid
Question 13.
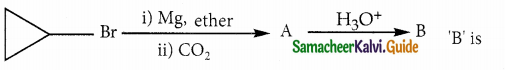
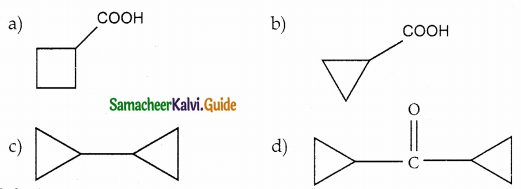
Answer:
Solution:
Question 14.
The IUPAC name of 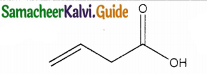
a) buy- 3- enoicacid
b) but – 1- ene-4-oicacid
c) hut – 2- ene-1-oic acid
d) but -3-ene-1-oicacicf
Answer:
a) but – 3- enoicacid
Solution:
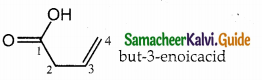
Question 15.
Identify the product formed in the reaction
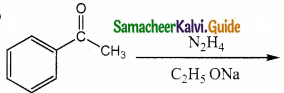
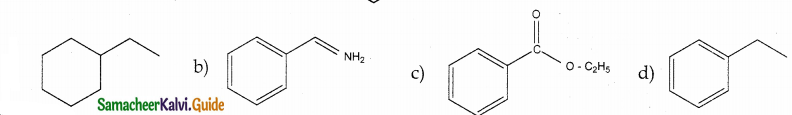 Answer:
Answer:
Solution:
group is reduced to CH2 – (Wolff – kishner reduction)
![]()
Question 16.
In which case chiral carbon is not generated by reaction with HCN
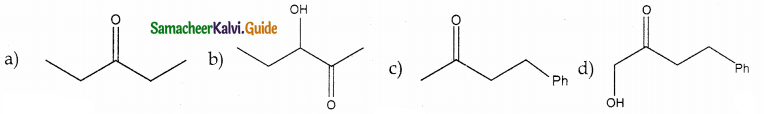
Answer:
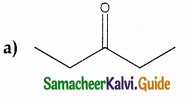
Solution:
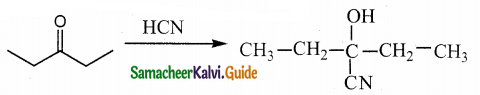
Question 17.
Assertion : p – N, N – dimethyl aminobenzaldehyde undergoes benzoin condensation
Reason : The aldehydic (-CHO) group is meta directing
a) if both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b) if both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c) assertion is true but reason is false
d) both assertion and reason are false.
Answer:
b) if both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Solution:
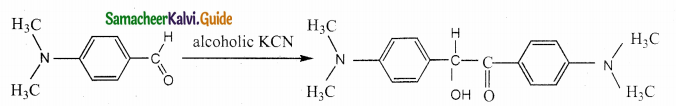
Question 18.
Which one of the following reaction is an example of disproportionation reaction
a) Aldol condensation
b) cannizaro reaction
c) Benzoin condensation
d) none of these
Answer:
b) cannizaro reaction
Solution:
Question 19.
Which one of the following undergoes reaction with 50% sodium hydroxide solution to give the corresponding alcohol and acid
a) Phenylmethanal
b) ethanal
c) ethanol
d) methanol
Answer:
a) Phenylmethanal
![]()
Question 20.
The reagent used to distinguish between acetaldehyde and benzaldehyde is
a) Tollens reagent
b) Fehling’s solution
c) 2,4 – dinitrophenyl hydrazine
d) semicarbazide
Answer:
b) Fehling’s solution
Question 21.
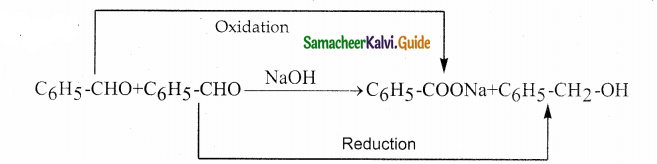
Phenyl methanal is reacted with concentrated NaOH to give two products X and Y. X reacts with metallic sodium to liberate hydrogen X and Y are
a) sodiumbenzoate and phenol
b) Sodium benzoate and phenyl methanol
c) phenyl methanol and sodium benzoate
d) none of these
Answer:
c) phenyl methanol and sodium benzoate
Solution:
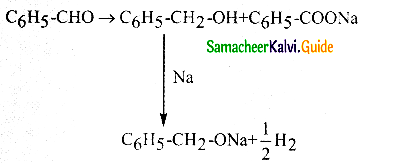
Question 22.
In which of the following reactions new carbon – carbon bond is not formed?
a) Aldol condensation
b) Friedel craft reaction
c) Kolbe’s reaction
d) Wolf kishner reduction
Answer:
d) Wolf kishner reduction
![]()
Question 23.
Alkene “A” on reaction with O3 and Zn – H2O gives propanone and ethanal in equimolar ratio. Addition of HCl to alkene “A” gives “B” as the major product. The structure of product “B” is
Answer:
Solution:
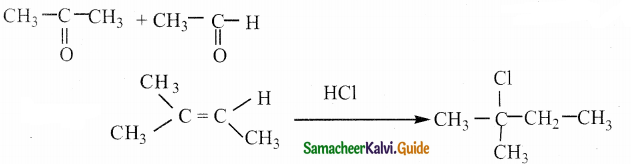
Question 24.
Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular mass. It is due to their (NEET)
a) more extensive association of carboxylic acid via van der Waals force of attraction
b) formation of carboxylate ion
c) formation of intramolecular H-bonding
d) formation of intermolecular H – bonding
Answer:
d) formation of intermolecular H – bonding
![]()
Question 25.
Of the following, which is the product formed when cyclohexanone undergoes aldol condensation followed by heating?
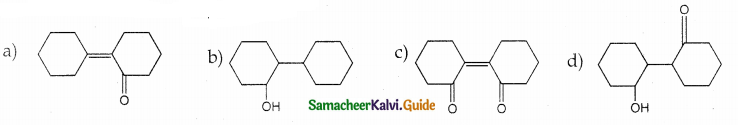
Answer:
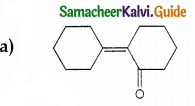
Solution:
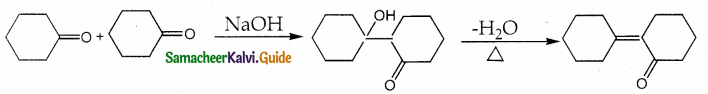
II. Short Answer
Question 1.
How is propanoic acid is prepared starting from
a) an alcohol
b) an alkylhalide
c) an alkene
Answer:
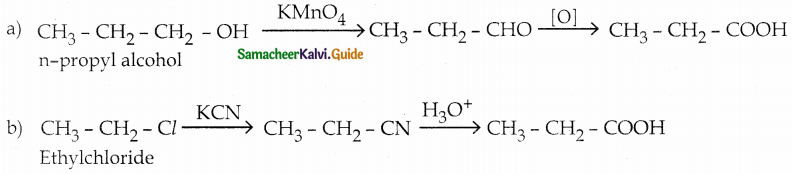
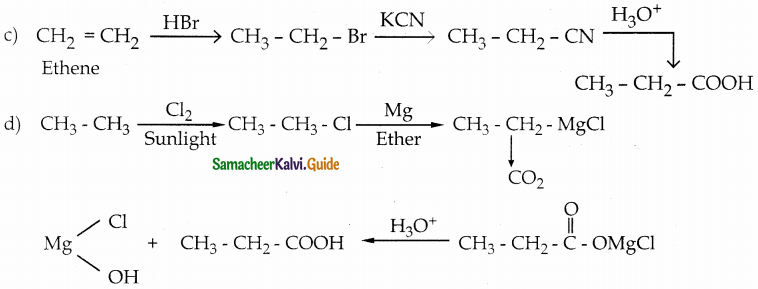
Question 2.
A Compound (A) with molecular formula C2H3N on acid hydrolysis gives(B) which reacts with thionyichioride to give compound(C). Benzene reacts with compound (C) in presence of anhydrous AlCl3 to give cornpound(D). Compound (C) on reduction with gives (E). Identify (A), (B), (C), (D) and (E) . Write the equations.
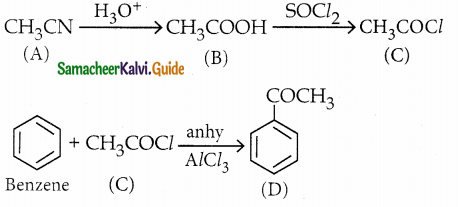
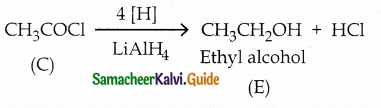
Answer:
| Compound | Name |
| A | Methylcyanide . |
| B | Acetic acid |
| C | Acetyl chloride |
| D | Acetophenone |
| E | Ethyl alcohol |
![]()
Question 3.
Identify X and Y
Answer:
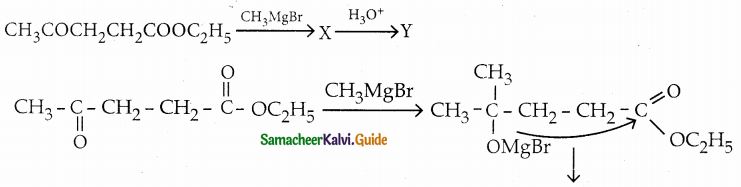
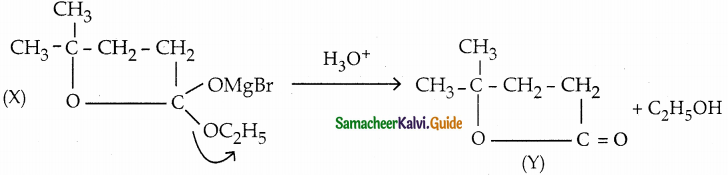
Question 4.
Identify A, B and C
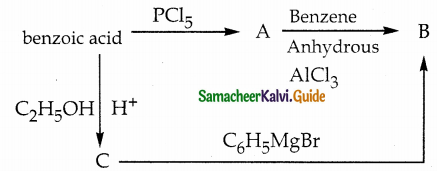 Answer:
Answer:
| Compound | Name |
| A | Benzoyl Chloride |
| B | Benzophenone |
| C | Ethylbenzoate |
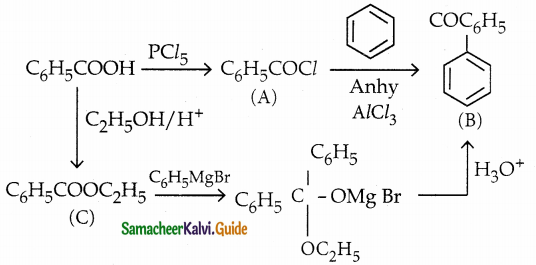
![]()
Question 5.
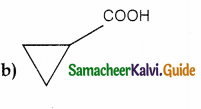
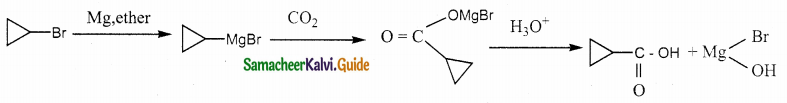
A hydrocarbon A(molecular formula C8H10) on ozonolysis gives B(C4H6O2) only. Compound C(C3H5Br) on treatment with magnesium in dry ether gives (D) which on treatment with CO2 followed by acidification gives (C). Identify A, B and C.
Solution:
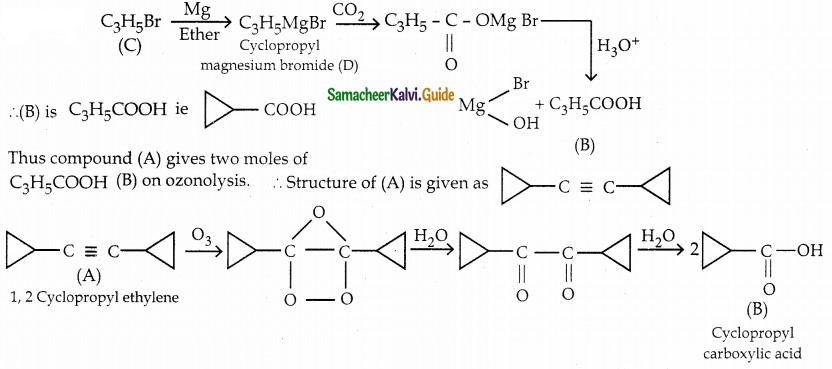
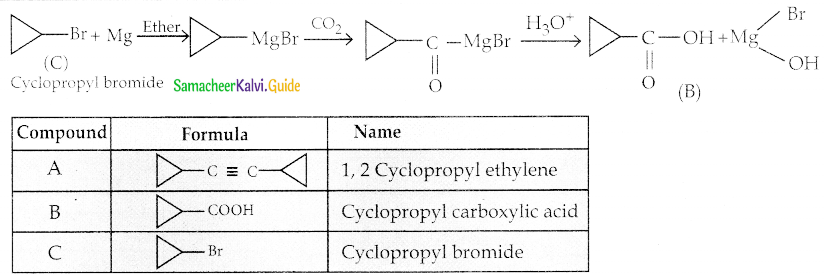
Question 6.
Identify A, B, C and D
Answer:
| Compound | Name |
| A | Acetylchloride |
| B | Acetaldehyde |
| C | 3- hydroxy butanal |
| D | Crotonaldehyde |
![]()
Question 7.
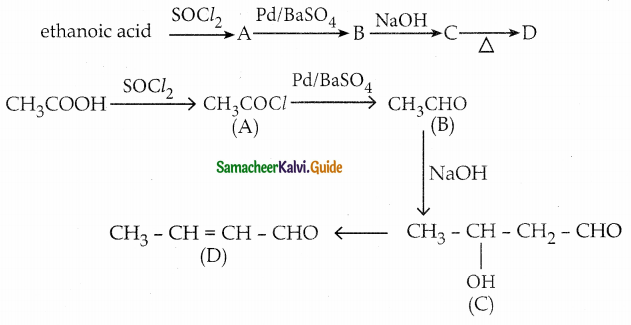
An alkene (A) on ozonolysis gives propanone and aldehyde (B), When (B) is oxidised (C) isobtained. (C) is treated with Br2/ P gives (D) which on hydrolysis gives (E). When propanone is treated with HCN followed by hydrolysis gives (E). Identify A, B, C, D and E.
Answer:
i) Compound (A) is the combination of propanone and (B)
∴ Structure of (A) is
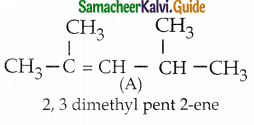
Question 8.
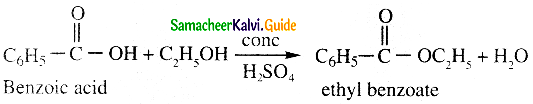
How will you convert benzaldehyde into the following compounds?
(i) benzophenone
(ii) benzoic acid
(iii) a – hydroxyphenylaceticacid
Answer:
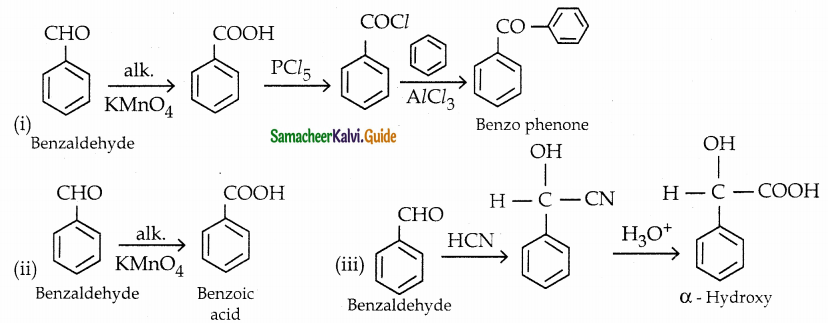
Question 9.
What is the action of HCN on
(i) propanone
(ii) 2, 4 – dichlorobenzaldehyde
(iii) ethanal
Answer:
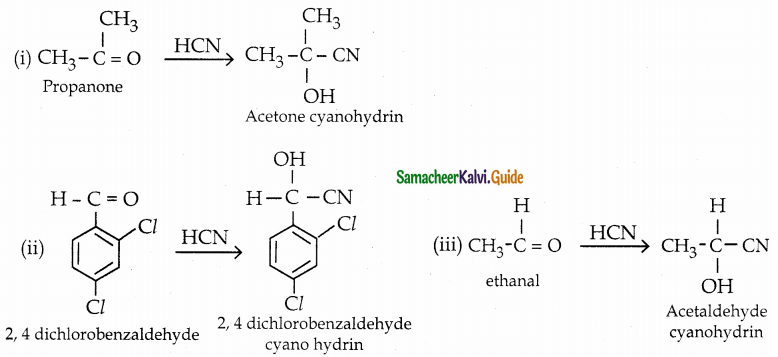
![]()
Question 10.
A carbonyl compound A having molecular formula C5H10O forms crystalline predpitate
with sodium bisulphite and gives positive Iodoform test. A does not reduce Fehiing
Solution: Identify A.
Answer:
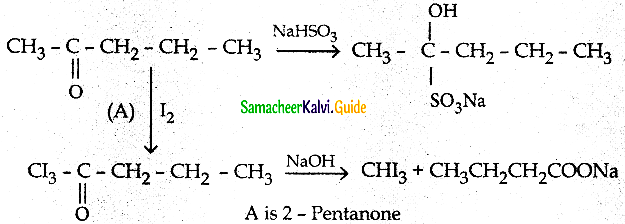
Question 11.
Write the structure of the major product of the aldol condensation of benzaldehyde with acetone
Answer:
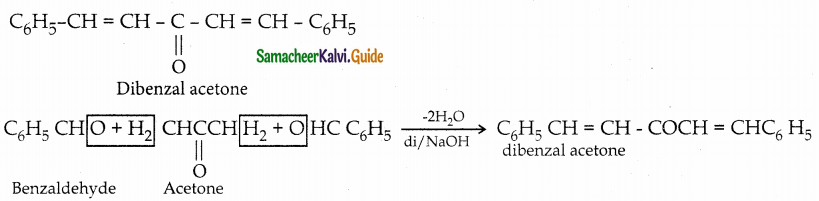
![]()
Question 12.
How are the following conversions effected
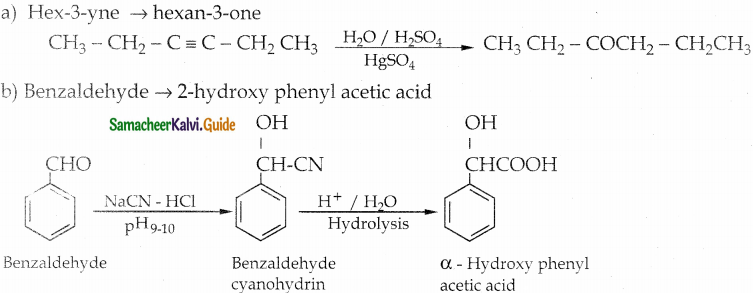
(a) propanal into butanone
(b) Hex – 3 – yne into hexan – 3 – one
(c) phenylmethanal into benzoic acid
(d) phenylmethanal into benzoin
Answer:
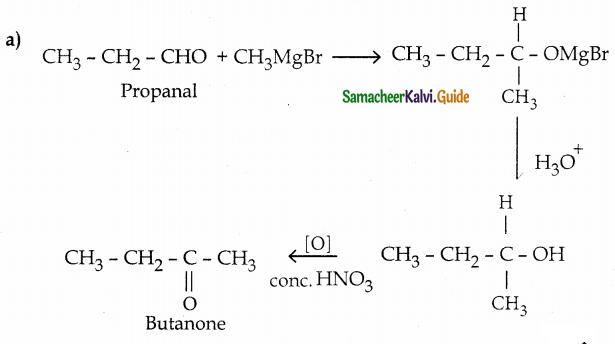
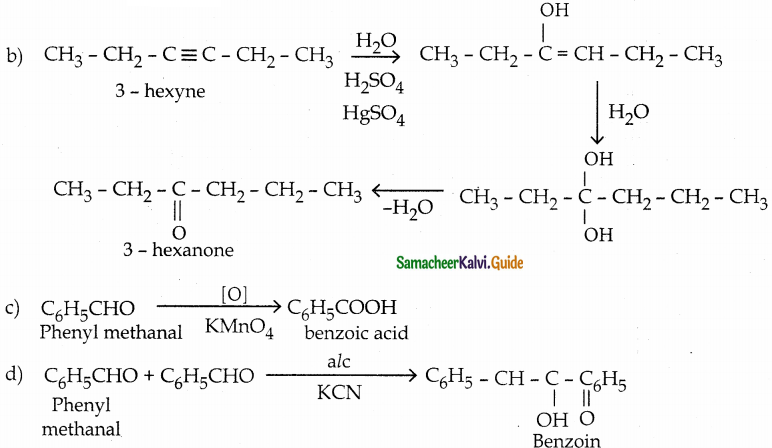
Question 13.
Complete the following reaction

Answer:
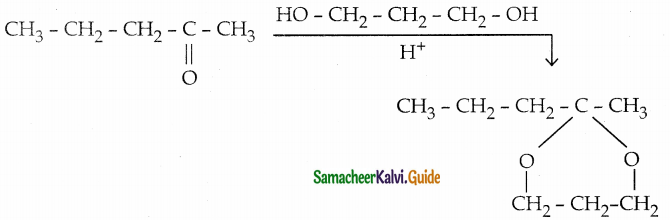
Question 14.
Identify A, B and C Benzyl bromide A C NaCN
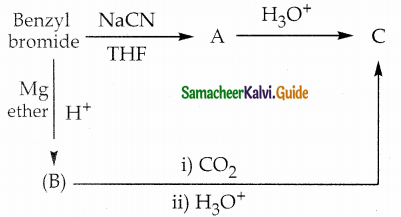
Answer:
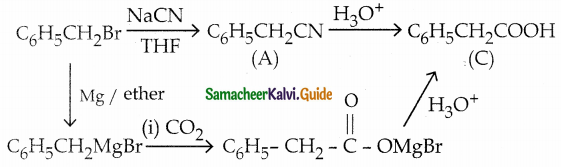
| Compound | Name | Formula |
| A | Benzyl cyanide | C6H5CH2CN |
| B | Benzyl magnesium bromide | C6H5CH2MgBr |
| C | Phenyl Acetic acid | C6H5CH2COOH |
![]()
Question 15.
Oxidation of ketones involves carbon – carbon bond clevage. Name the product (s) is / are formed on oxidising 2, 5 dimethylhexan – 2 – one using strong oxidising agent.
Answer:
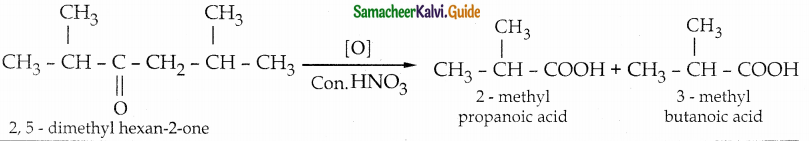
- The reaction proceeds according to Popoff’s rule.
- Popoff’s rule states that during the oxidation of an unsymmetrical ketone, the (C-CO) bonds cleaved in such a way that the keto group stays with the smaller alkyl group.
Question 16.
How will you prepare
i) Acetic anhydride from acetic acid
ii) Ethyl acetate from methyl acetate
iii) Acetamide from methylcyanide
iv) Lactic acid from ethanol
v) Acetophenone from acetylchloride
vi) Ethane from sodium acetate
vii) Benzoic acid from toluene 13
viii) Malachite green from benzaldehyde
ix) Cinnamic acid from benzaldehyde
x) Acetaldehyde from ethyne
Answer:
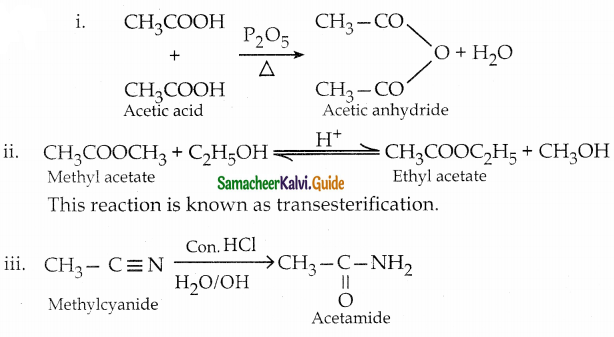
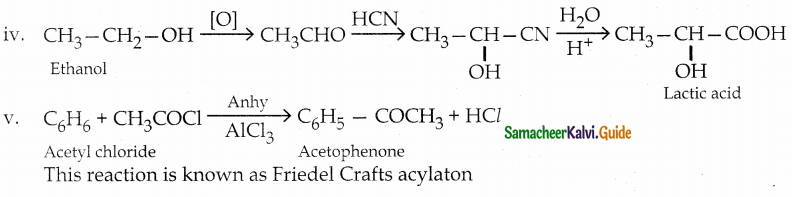
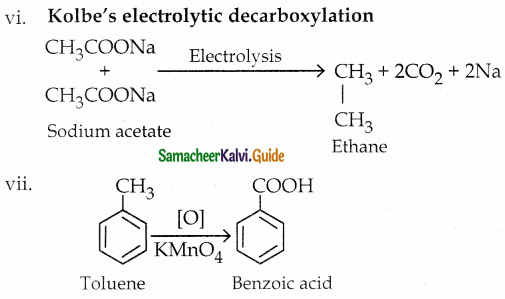
The reaction proceeds according to Popoff’s rule.
Popoff’s rule states that during the oxidation of an unsymmetrical ketone, the (C-CO) bonds cleaved in such a way that the keto group stays with the smaller alkyl group.
![]()
III. Evaluate Yourself
Question 1.
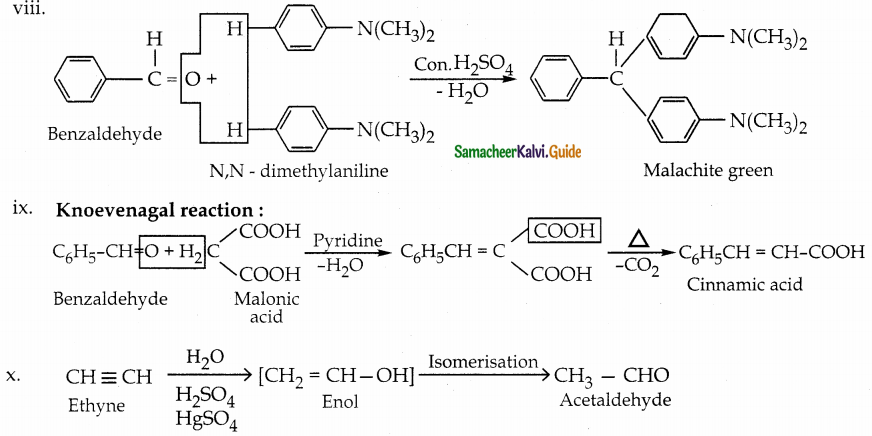
Write the IUPAC name for the following compound
Answer:
Question 2.
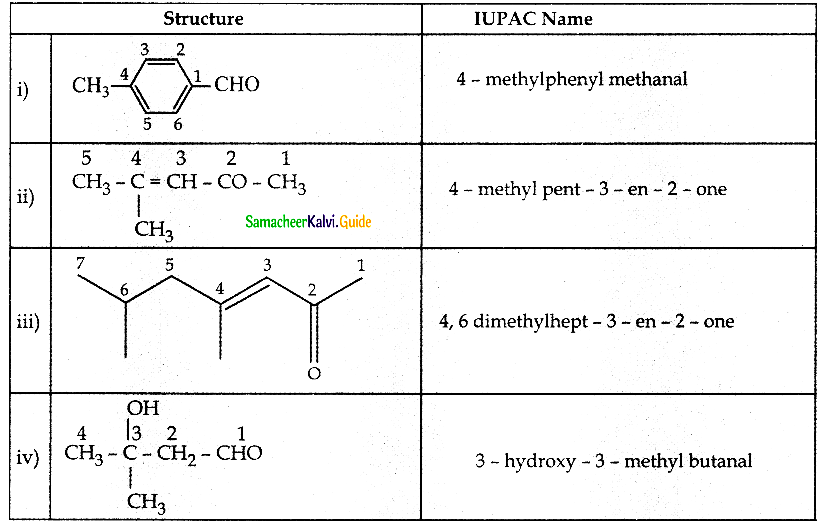
Write all possible structural isomers and position isomers for the ketone represented by the molecular formula C5H10O
Answer:
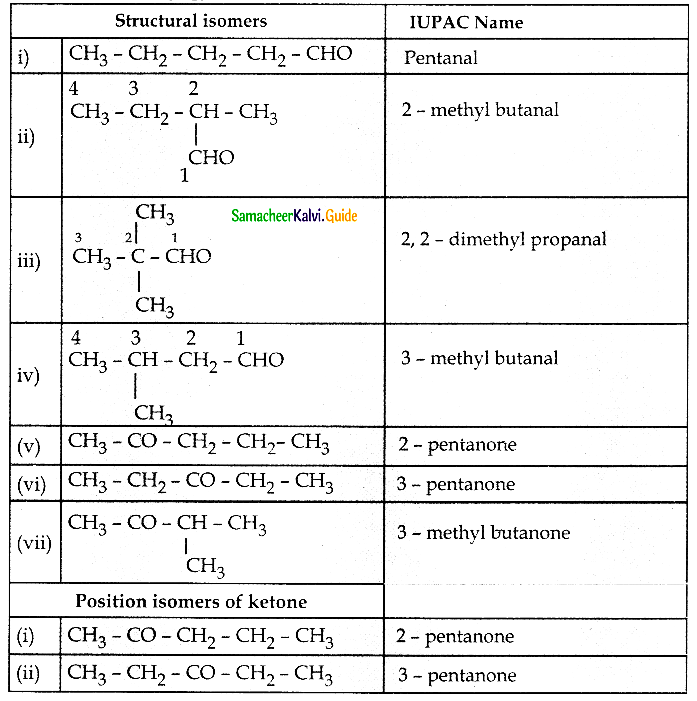
![]()
Question 3.
What happens when the following alkenes are subjected to reductive ozonolysis
1) Propene
2) 1-butene
3) Isobutylene
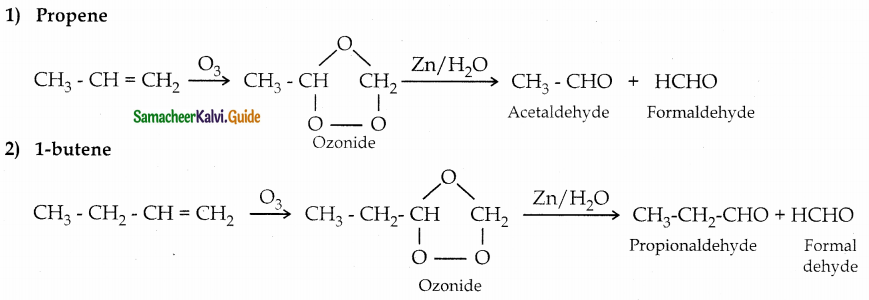
Question 4.
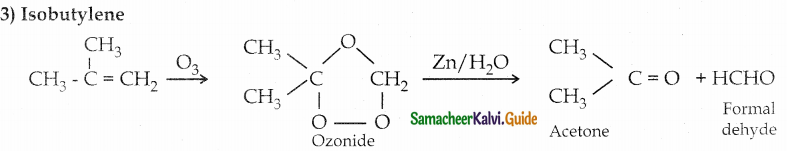
1) What happens when n-propyl benzene is oxidised using H+ / KMnO4 ?
2) How will you prepare benzoic acid using Grignard reagent.
Answer:
![]()
Question 5.
Why acid anhydrides are preferred to acyl chlorides for carrying out acylation reactions?
Answer:
Acid anhydride are preferred to acyl chloride for carrying out acylation reactions. Because
- Easily available
- Cheap
- Easy to prepare
- Easily undergo acylation without irritating odours
12th Chemistry Guide Carbonyl Compounds and Carboxylic Acids Additional Questions and Answers
Part – II – Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The aldehyde derived from vitamin B, which functions as a co-enzyme is
a) retinal
b) pyridoxal
c) cynacobalamin
d) calciferol
Answer:
b) pyridoxal
Question 2.
The IUPAC name of acrolein is
a) ethanal
b) but – 2 – enal
c) prop – 2 – enal
d) but – 1 – enal
Answer:
c) prop – 2 – enal
Question 3.
The IUPAC name of crotonaldehyde is
a) ethanal
b) but – 2 – enal
c) prop – 2 – enal
d) but – 1 enal
Answer:
b) but -2- enal
![]()
Question 4.
The IUPAC name of

a) 3-oxopentan – 5- al
b) 3 – oxopentanal
c) 1 – hydroxy – 3 – pentanone
d) 1 – ethylpropanone
Answer:
b) 3 – oxopentanal
Question 5.
The carbon atom of carbonyl group is ……………… hybridised
a) sp
b) sp2
c) sp3
d) dsp2
Answer:
b) sp2
Question 6.
2 – methyl but -2 – ene on ozonolysis gives
a) ethanal
b) propanone
c) both (a) & (b)
d) none of the above
Answer:
c) both (a) & (b)
![]()
Question 7.
Which among the following on ozonlysis give only ethanal as the product?
a) 1 – butene
b) 2- butene
c) propene
d) ethene
Answer:
b) 2- butene
Question 8.
Which among the following on ozonlysis give only methanal as the product?
a) 1 – butene
b) 2- butene
c) propene
d) ethene
Answer:
d) ethene
Question 9.
Which among the following on ozonlysis give ethanal and methanal as products?
a) 1 – butene
b) 2- butene
c) propene
d) ethene
Answer:
c) propene
![]()
Question 10.
Which among the following on ozonolysis give propanal and methanal as products
a) 1 – butene
b) 2- butene
c) propene
d) ethene
Answer:
a) 1 – butene
Question 11.
The role of barium sulphate in Rosenmund reduction is
a) catalyst
b) reducing agent
c) catalytic poison
d) promoter
Answer:
c) catalytic poison
Question 12.
Which among the following can not be prepared by Rosenmund reduction
a) HCHO
b) CH3CHO
c) C2H5CHO
d) C6H5CHO
Answer:
a) HCHO
![]()
Question 13.
The catalyst used in Stephen’s reaction is
a) Sn/HCl
b) ConcHCl/ anhy.ZnC2
c) SnCl2 HCl
d) Zn/ Hg / HCl
Answer:
c) SnCl2 HCl
Question 14.
Acetyl chloride is converted into acetone by treatment with
a) Pd/BaSO 4
b) (CH 3) 2Cd
c) SnCl 2/HCl
d) Sn/HCl
Answer:
b) (CH 3) 2Cd
Question 15.
Arrange the following compounds in decreasing order of reactivity for hydrolysis reaction.
(1) C6H5COCl
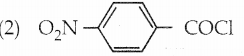
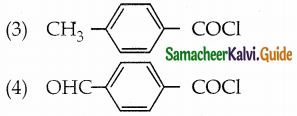
a) 2 > 4 > 1 > 3
b 2 > 4 > 1 > 1
c) 1 > 2 > 3 > 4
d) 4 > 3 > 2 > 1
Answer:
a) 2 > 4 > 1 > 3
![]()
Question 16.
The correct order of solubility in water is
a) HCHO < CH3CHO < CH3CH2CHO
b) HCHO > CH3CHO > CH3CH2CHO
c) HCHO < CH3CHO > CH3CH2CHO
d) HCHO > CH3CHO < CH3CH2CHO
Answer:
b) HCHO > CH3CHO > CH3CH2CHO
Hint: Solubility decreases with increase in the length of alkyl chain.
Question 17.
In nucleophilic addition reactions, the hybridisation of carbonyl carbon changes from
a) sp to sp2
b) sp to sp3
c) sp2 to sp3
d) sp3 to sp2
Answer:
c) sp2 to sp3
Question 18.
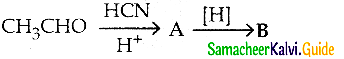
A and B are respectively
a) 2-hydroxy propanenitrile, 2-hydroxv propanoic acid
b) 2- hydroxy propane nitrile, 2- hydroxy – 1- amino propane
c) 2 – hydroxy propane nitrile, lactic acid
d) acetaldehyde cyano hydrin, lactic acid
Answer:
b) 2- hydroxy propane nitrile, 2- hydroxy -1- amino propane
![]()
Question 19.
Carbonyl compounds can be easily separated and purified by reaction with
a) HCN
b) NH2 – NH2
c) NaHSO3
d) NH2OH
Answer:
c) NaHSO3
Question 20.
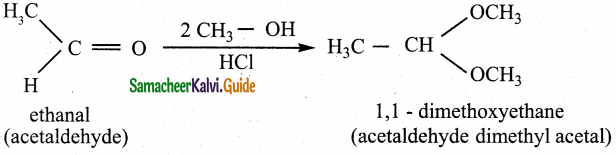
When acetaldehyde is treated with 2 equivalent of methanol in presence of HC1, the product obtained is
a) 1-methoxy ethane
b) 2-methoxy ethane
c) 1,1 – dimethoxy ethane
d) 1, 2 – dimethoxy ethane
Answer:
c) 1,1 – dimethoxy ethane
Question 21.
When hydroxyl amine is added to a carbonyl compound, the product obtained is
a) hydrazone
b) semi carbazone
c) carboxylic acid
d) oxime
Answer:
d) oxime
![]()
Question 22.
Aliphatic aldehyde which does not form an aldimine with an ethereal solution of ammonia is
a) methanal
b) ethanal
c) propanal
d) butanal
Answer:
a) methanal
Question 23.
Formaldehyde reacts with ammonia to form
a) aldimine
b) diacetone amine
c) hexamethylene tetramine
d) formaldehyde ammonia
Answer:
c) hexamethylene tetramine
Question 24.
Hexamethylene tetramine is also known as
a) Aldimine
b) Urotropine
c) Cyclonite
d) RDX
Answer:
b) Urotropine
![]()
Question 25.
Benzaldehyde reacts with ammonia to form
a) benzamide
b) hydrobenzamide
c) urotropine
d) aldimine
Answer:
b) hydrobenzamide
Question 26.
Acetone on oxidation with cone. HNO3 gives
a) formic acid
b) acetic acid
c) both (a) & (b)
d) none of the above
Answer:
c) both (a) & (b)
Question 27.
The general order of reactivity of carbonyl compounds towards nucleophilic addition reaction is
a) HCHO > RCHO > C6H5CHO > R2CO > (C6H5)2
b) HCHO > CH3CHO > C6H5CHO > CH3COCH3 > C6H5COCH3
c) C6H5COC6H5 > CH3COCH3 > C6H5CHO > CH3CHO > HCHO
d) HCHO > CH3COCH3 > C6H5 COC6H5 > CH3CHO > C6H5CHO
Answer:
b) HCHO > CH3CHO > C6H5CHO > CH3COCH3 > C6H5COCH3
![]()
Question 28.

a) Pt
b) Pd
c) Ni
d) LiAlH4
Answer:
d) LiAlH4
Question 29.
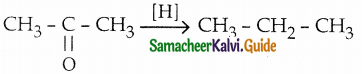 The reducing agent used in this reaction is
The reducing agent used in this reaction is
a) H2/Ni
b) Zn-Hg/HCl
c) NH2 – NH2/C2H5ONa
d) both (b) & (c)
Answer:
d) both (b) & (c)
Question 30.
The reducing agent used in clemmenson reduction is
a) H2/Ni
b) Zn-Hg/HC/
c) NH2 – NH2/ C2H5ONa
d) both (b) & (c)
Answer:
b) Zn-Hg/ HCl
![]()
Question 31.
The reducing agent used in Wolff kishner reduction is
a) H2/Ni
b) Zn-Hg/HC/
c) NH2 – NH2/ C2H5ONa
d) both (b) & (c)
Answer:
c) NH2 – NH2/ C2H5ONa
Question 32.
Acetone on reduction with magnesium amalgam and w ater gives
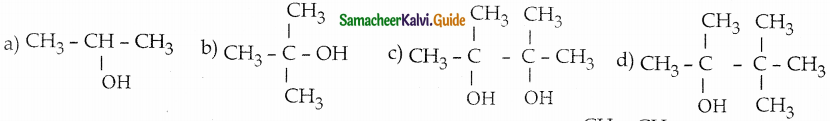
Answer:
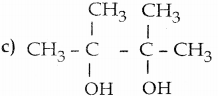
Question 33.
Which among the following will undergo haloform reaction?
a) CH3CHO
b) CH3COCH3
c) CH3COC6H5
d) all the above
Answer:
d) all the above
![]()
Question 34.
Aldehydes and ketones which contain ……………….. group undergo haloform reaction
Answer:
Question 35.
Which of the following will not undergo aldol condensation?
a) HCHO
b) C6H5CHO
c) (CH3)3CCHO
d) all the above
Answer:
d) all the above
Hint: Aldehydes with no ci-hydrogen atom will not undergo aldol condensation
Question 36.
Which among the following will undergo aldol condensation
a) HCHO
b) C6H5CHO
c) (CH3)2CHCHO
d) (CH3)3CCHO
Answer:
c) (CH3)2CHCHO
Hint: Aldehydes that contain cr-hydrogen atom will undergo aldol condensation
![]()
Question 37.
Acetaldehyde when warmed with dil NaOH followed by dehydration gives
a) 3 – hydroxv butanal
b) but – 2 – enal
c) 2 – hydroxy butanal
d) but – 3 – enal
Answer:
b) but – 2 – enal
Question 38.
When two molecules of an aldehyde or ketone having a – hydrogen atom react with dilute NaOH or KOH, the product formed is
i) α – hydroxy al4ehyde
ii) α -hydroxy ketone
iii) β – hydroxy aidehyde
iv) β – hydroxy ketone
a) (i) & (ii)
b) (i) & (iii)
c) (iii) & (iv)
d) (ii) & (iv)
Answer:
c) (iii) & (iv)
Question 39.
Aldehydes with no α-hydrogen atom when reacted with concentrated aqueous alkali undergo
a) aldol condensation
b) Claisen – schmidt condensation
c) Cannizaro reaction
d) Benzoin condensation
Answer:
c) Cannizaro reaction
![]()
Question 40.
The product obtained when formaldehyde reacts with acetaldehyde in presence of dilute NaOH is
a) 3-hvdroxy propanol
b) 3-hydroxy propanal
c) 2-hvdroxy propanol
d) 2-hydroxy propanal
Answer:
b) 3-hydroxy propanal
Question 41.
Which one of the following pairs is not correctly matched?
| Reducing agent | Name of the reaction |
| a) Zn / Hg / Con HCl | Clemension reduction |
| b) LiAlH4 | WoIf-Kishner’s reductior |
| c) Pd/ BaSO4 | Rosenmund’s reduction |
| d) SnCl2/ Con HCl | Stephen’s reduction |
Answer:
b) LiAlH4– Wolf-Kishner’s reduction
Question 42.
Which among the following will undergo Cannizaro reaction?
a) HCHO
b) C6H5CHO
c) (CH3)3CCHO
d) all the above
Answer:
d) all the above
Hint: Aldehydes with no -hydrogen atom when reacted with concentrated aqueous alkali undergo cannizaro reaction.
![]()
Question 43.
Cannizaro reaction is an example of
a) oxidation
b) reduction
c) disporportionation
d) hydrolysis
Answer:
c) disporportionation
Question 44.
In crossed cannizaro reaction between benzaldehyde and formaldehyde, the aldehyde which gets oxidised is
a) benzaldehyde
b) formaldehyde
c) both (a) & (b)
d) none of the above
Answer:
b) formaldehyde
Question 45.
Benzaldehyde can be converted into cinnamic acid by
a) Perkin’s reaction
b) Knoevenagal reaction
c) Claisen reaction
d) both (a) & (b)
Answer:
d) both (a) & (b)
![]()
Question 46.
Aldehyde reduce Tollens reagent to
a) Ag+
b) [Ag(NH3)2]+
c) Ag
d) AgNO3
Answer:
c) Ag
Question 47.
Tollens reagent is
a) acidified AgNO3
b) ammoniacal AgNO3
c) aqueous AgNO3
d) Solid AgNO3
Answer:
b) ammoniacal AgNO3
Question 48.
When an aldehyde is treated with Fehlings solution the colour change is
a) red to blue
b) blue to red
c) colourless to pink
d) pink to colourless
Answer:
b) blue to red
![]()
Question 49.
Cyclotrimethylenetrinitramine is known as
a) urotropine
b) bakelite
c) RDX
d) formalin
Answer:
c) RDX
Question 50.
The compound used in leather tanning is
a) CH3 CHO
b) HCHO
c) CH3 COCH3
d) C6 H5 CHO
Answer:
b) HCHO
Question 51.
The IUPAC name of malonic acid is
a) Ethane dioic acid
b) Propane dioic acid
c) Butane dioc acid
d) Pentane dioic acid
Answer:
b) Propane dioic acid
![]()
Question 52.
In carboxylic acids, the carbon atom and two oxygen atoms of carboxyl group are in …………….. hybridisation respectively
a) sp3, sp2 , sp
b) sp3, sp, sp2
c) sp2, sp2, sp2
d) sp2, sp3, sp
Answer:
c) sp2, sp2, sp2
Question 53.
One sp2 hybridised orbital of carboxyl carbon overlaps with ……………. hybridised orbital of alkyl cabron in carboxylic acid.
a) sp
b) sp2
c) sp3
d) dsp2
Answer:
c) sp3
Question 54.
Ethyl Cyanide on acid hydrolysis gives
a) acetic acid
b) propionic acid
c) formic acid
d) butvric acid
Answer:
b) propionic acid
![]()
Question 55.
The acid that cannot be prepared by using Grignard reagent is
a) HCOOH
b) CH3COOH
c) C6H5COOH
d) CH3CH2COOH
Answer:
a) HCOOH
Question 56.
Methyl magnesium bromide is converted into acetic acid by reacting with
a) CH3CHO
b) HCHO
c) CO2
d) CH3COCH3
Answer:
c) CO2
Question 57.
![]() methyl propanoic acid compound A is
methyl propanoic acid compound A is
a) methyl magnesium bromide
b) isopropyl magnesium bromide
c) n-propyl magnesium bromide
d) butyl magnesium bromide
Answer:
b) iso propyl magnesium bromide
![]()
Question 58.
Which among the following is not oxidised to benzoic acid by alkaline KMnO4
a) Toluene
b) ethyl benzene
c) cumene
d) t-butyl benzene
Answer:
d) t-butyl benzene
Hint: compounds with benzylic hydrogen undergo oxidation forming benzoic acid. In t-butyl benzene there is no benzylic hydrogen, hence it does not undergo oxidation.
Question 59.
When acetic acid reacts with sodium carbonate. The brisk effervescence is due to the liberation of
a) H2
b) CO
c) CO2
d) Na2O
Answer:
c) CO2
Question 60.
Carboxylic acids turn the colour of litmus paper from
a) Yellow to orange
b) red to blue
c) blue to red
d) red to colourless
Answer:
c) blue to red
![]()
Question 61.
Acetic acid is converted into ethane by
a) LiAlH4
b) HI/Red P
c) NaBH4
d) H2/Ni
Answer:
b) HI / Red P
Question 62.
When sodium salicylate is treated with sodalime, the product obtained is
a) salicylic acid
b) benzoic acid
c) phenol
d) benzene
Answer:
c) phenol
Question 63.
Aqueous solution of sodium acetate is electrolysed to give
a) methane
b) ethane
c) ethene
d) ethyne
Answer:
b) ethane
![]()
Question 64.
The acid which reduces Tollen’s reagent is
a) HCOOH
b) CH3 COOH
c) C6 H5 COOH
d) C2H5COOH
Answer:
a) HCOOH
Question 65.
The correct order of acids with decreasing acid strength is
a) HCOOH < CH3 COOH < CH3 CH2COOH
b) HCOOH > CH3 COOH > CH3 CH2COOH
e) HCOOH < CH3 COOH > CH3 CH2COOH
d) HCOOH > CH3 COOH < CH3 CH2COOH
Answer:
b) HCOOH > CH3 COOH > CH3 CH2COOH
Question 66.
The correct order of incresing acid strength is
a) CH3COOH < ClCH2COOH < Cl2CHCOOH < CCl3COOH
b) CH3COOH < CCl3COOH < Cl2CHCOOH < ClCH2COOH
c) CCl3COOH < Cl2CHCOOH < ClCH2COOH < CH3COOH
d) ClCH2COOH > CCl3COOH < Cl2CHCOOH < CH3COOH
Answer:
a) CH3COOH < ClCH2COOH < Cl2CHCOOH < CCl3COOH
![]()
Question 66.
Which one of the following is incorrectly matched?
a) Tollen’s Reagent – AgNO3 + NH4OH
b) Fehlings solution – CuSO4 + Rochelle salt
c) Benedict’s solution – CuSO4 + Sodium Citrate + NaOH
d) Baeyer’s Reagent – Con. HCl + anhydrous ZnCl2
Answer:
d) Baeyer’s Reagent – Con. HCl + anhydrous ZnCl2
Question 68.
The correct order of acidic nature is
a) C2H5OH > H2O > C6H5OH > HCOOH
b) C6H5OH > H2O > C2H5OH > HCOOH
c) HCOOH > C6H5OH > H2O > C2H5OH
d) HCOOH > C2H5OH > C6H5OH > H2O
Answer:
c) HCOOH > C6H5OH > H2O > C2H5OH
Question 69.
The correct order of reactivity of acid derivates is
a) acid chloride < acid anhydride < ester < amide b) acid chloride > acid anhydride > ester > amide
c) acid anhydride > add chloride > amide > ester
d) acid anhydride > amide > ester > acid chloride
Answer:
b) acid chloride > acid anhydride > ester > amide
![]()
Question 70.
The IUPAC name of CH3COOC6H5 is
a) phenyl acetate
b) methyl benzoate
c) phenyl ethanoate
d) phenyl methanoate
Answer:
c) phenyl ethanoate
Question 71.
Ethanoyl chloride reacts with ethanol to form
a) methyl ethanoate
b) ethyl ethanoate
c) methyl acetate
d) ethyl propionate
Answer:
b) ethyl ethanoate
Question 72.
Which among the following does not react with acetyl chloride?
a) methyl amine
b) dimethyl amine
c) trimethyl amine
d) isobutyl amine
Answer:
c) trimethyl amine
Hint: Tertiary amine does not react with acid chloride
![]()
Question 73.
Name the product obtained when acetyl chloride is reacted with sodium acetate?
a) Methyl ethanoate
b) ethanoic anhydride
c) ethanamide
d) ethyl methanoate
Answer:
b) ethanoic anhydride
Question 74.
When ethanoic anhydride reacts with ethanol, the product obtained is
a) ethyl ethanoate
b) ethanoic acid
c) both (a) & (b)
d) none of the above
Answer:
c) both (a) & (b)
Question 75.
Ethylethanoate on reaction with ammonia gives
a) ethanamide & ethanol
b) methanamide & ethanol
c) ethanamide & methanol
d) methanamide & methanol
Answer:
a) ethanamide & ethanol
![]()
Question 76.
Amides are
a) acidic
b) basic
c) amphoteric
d) neutral
Answer:
c) amphoteric
Question 77.
Acetamide on heating with P2O5 gives
a) methyl amine
b) methyl cyanide
c) acetic acid
d) methyl amide
Answer:
b) methyl cyanide
Question 78.
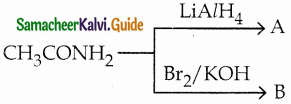
A and B are respectively
a) ethyl amine, ethanamide
b) methylamine, ethanamide
c) ethylamine, methylamine
d) methylamine, ethylamine
Answer:
c) ethylamine, methylamine
![]()
Question 79.
Which is used in medicine for treatment of gout?
a) formic acid
b) acetic acid
c) benzoic acid
d) acetyl chloride
Answer:
a) formic acid
Question 80.
Which is used in medicine as an urinary antiseptic?
a) formic acid
b) acetic acid
c) benzoic acid
d) acetyl chloride
Answer:
c) benzoic acid
![]()
II. Assertion and Reason
Question 1.
Assertion (A): The boiling point of aldehydes and ketones are much lower than those of corresponding alcohols and carboxylic acids.
Reason (R): The dipole – dipole interactions of carbonyl group is stronger than intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
a) Both A and R are correct, R explains A.
b) Both A and R are correct, R does not explain A
c) A is correct but R is wrong
d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
c) A is correct but R is wrong
Correct Reason (R): The dipole – dipole interactions of carbonyl group is weaker than intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Question 2.
Assertion (A): Aldol condensation between two different aldehydes or ketones is not very useful.
Reason (R): In crossed aldol condensation the product is usually a mixture of all possible condensation products and cannot be separated easily.
a) Both A and R are correct, R explains A.
b) Both A and R are correct, R does not explain A
c) A is correct but R is wrong
d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
a) Both A and R are correct, R explains A
![]()
Question 3.
Assertion (A) : Carboxylic acid do not give the characteristic reaction of carbonyl group.
Reason (R) : Carboxylic acid molecules are associated through intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
a) Both A and R are correct, R explains A.
b) Both A and R are correct, R does not explain A
c) A is correct but R is wrong
d) A is wrong but R is correct
Answer:
b) Both A and R are correct, R does not explain A
Correct Reason (R): Carbonyl group of carboxylic acid is involved in resonance.
III. Pick out the correct statements
Question 1.
(i) All the three sigma bonds around the carbonyl carbon lie on the same plane.
(ii) In carbonyl group, oxygen atom attracts the shared pair of electron between the carbon and oxygen towards itself and hence the bond is polar
(iii) Terminal olefins on ozonolysis give acetaldehyde as one of the product
(iv) Ethyne on hydration gives ethanal which isomerises to give an enol.
a) (i) & (ii)
b) (ii) & (iii)
c) (iii) & (iv)
d) (i) & (iv)
Answer:
a) (i) & (ii)
Correct statements :
(iii) Terminal olefins on ozonolysis give formaldehyde as one of the product.
(iv) Ethyne on hydration gives an enol which isomerises to give ethanal
![]()
Question 2.
(i) In Gattermann – Koch reaction an intermediate is formed which reacts like acetyl chloride.
(ii) Gattermann – Koch reaction is a variant of Friedel crafts acylation reaction.
(iii) Side chain chlorination of toluene gives benzyl chloride which on hydrolysis gives benzaldehyde
(iv) Friedel crafts acylation is a best method for preparing alkyl aryl ketones or diaryl ketones.
a) (i) & (ii)
b) (ii) & (iii)
c) (ii) & (iv)
d) (i) & (iv)
Answer:
c) (ii) & (iv)
Correct statements :
(i) In Gattermann – Koch reaction an intermediate is formed which reacts like formyl chloride.
(iii) Side chain chlorination of toluene gives benzal chloride which on hydrolysis gives benzaldehyde.
Question 3.
(i) Ketones restore the red colour of Schiff’s reagent.
(ii) In Fehling’s solution test aldehydes convert CU2O into Cu2+ ions.
(iii) Aldehydes reduce Tollens reagent to metallic silver.
(iv) Benedict’s solution is a mixture of CUSO4 + sodium citrate + NaOH
a) (i) & (ii)
b) (ii) & (iii)
c) (iii) & (iv)
d) (i) & (iv)
Answer:
c) (iii) & (iv)
Correct statements :
(i) Aldehydes restore the red colour of Schiff’s reagent.
(ii) In Fehling’s solution test aldehydes convert Cu2+ ions into CU2O
![]()
Question 4.
(i) Esterification reaction is reversible
(ii) Sodium borohyride reduce carboxylic acids to primary alcohols
(iii) Soda lime is a mixture of Na2O and Ca(OH)2 in the ratio 3:1 ,
(iv) When treated with HI and red phosphorous, carboxylic acid undergoes complete reduction to give
alkanes.
a) (i) & (ii)
b) (ii) & (iii)
c) (iii) & (iv)
d) (i) & (iv)
Answer:
d) (i) & (iv)
Correct statements :
(ii) Sodium borohydride does not reduce carboxylic acids to primary alcohols,
(iii) Soda lime is a mixture of NaOH and CaO in the ratio 3:1.
IV. Pick out the incorrect statements
Question 1.
(i) By Rosenmund reduction formaldehyde and ketones cannot be prepared.
(ii) If BaS04 is not used in Rosenmund reduction the product will be an alcohol.
(iii) In Stephen’s reaction alkyl cyanides are reduced to amines which on hydrolysis give corresponding aldehydes.
(iv) In Etard’s reaction chromyl chloride is used as a reducing agent.
a) (i) & (ii)
b) (ii) & (iii)
c) (iii) & (iv)
d) (i) & (iv)
Answer:
c) (iii) & (iv)
Correct statements:
(iii) In Stephen’s reaction alkyl cyanides are reduced to imines which on hydrolysis give corresponding aldehydes.
(iv) In Etard’s reaction chromyl chloride is used as an oxidising agent.
![]()
Question 2.
(i) Aldehydes and ketones have low boiling point as compared to hydrocarbons and ethers of comparable molecular mass.
(ii) There is strong molecular association in aldehydes and ketones arising out of dipole – dipole interactions.
(iii) Formaldehyde is a gas and acetaldehyde is a volatile liquid at room temperature.
(iv) Lower members of aldehydes and ketones are miscible with water because they form hydrogen bond with water
a) (i) & (ii)
b) (ii) & (iii)
c) (iii) & (iv)
d) (i) & (iv)
Answer:
a) (i) & (ii)
Correct statements:
(i) Aldehydes and ketones have high boiling point as compared to hydrocarbons and ethers of comparable molecular mass.
(iv) There is weak molecular association in aldehydes and ketones arising out of dipole – dipole interactions.
Question 3.
(i) Nitriles on hydrolysis with an acid or alkali give carboxylic acids.
(ii) The carboxylic carbon is more nucleophilic than carbonyl carbon because of the possible resonance structure.
(iii) In – COOH group, the centre carbon atom and both the oxygen atoms are in sp3 hybridisation.
(iv) Aromatic carboxylic acids can be prepared by vigourous oxidation of alkyl benzene with chromic acid
a) (i) & (ii)
b) (ii) & (iii)
c) (iii) & (iv)
d) (i) & (iv)
Answer:
b) (ii) & (iii)
Correct statements :
(ii) The carboxylic carbon is less nucleophilic than carbonyl carbon because of the possible resonance structure.
(iii) In – COOH group, the centre carbon atom and both the oxygen atoms are in sp2 hybridisation.
Question 4.
(i) Benzoic acid undergoes Friedel crafts reaction at meta position.
(ii) Carboxyl group is deactivating and aromatic carboxylic acids undergo electrophilic substitution at meta position,
(iii) Formic acid contains both aldehyde as well as an acid group.
(iv) A stronger acid will have lower Ka value but higher pKa value.
a) (i) & (ii)
b) (ii) & (iii)
c) (iii) & (iv)
d) (i) & (iv)
Answer:
d) (i) & (iv)
Correct statements :
(i) Benzoic acid does not undergo Friedel Crafts reaction.
(iv) A stronger acid will have higher Ka value but lower pKa value.
![]()
V. Match the Following
Question 1.
| Dry distillation of | Product |
| i. Calcium formate | a. Ethanal |
| ii. Calcium ethanoate | b. Benzophenone |
| iii. Calcium benzoate | c. Acetophenone |
| iv. Calcium ethanoate and calcium methanoate | d. Methanal |
| v. Calcium ethanoate and calcium benzoate | e. Propanone |
Answers:
i. – d. Methanal
ii. – e. Propanone
iii. – b. Benzophenone
iv. – a. Ethanal
v. – c. Acetophenone
![]()
Question 2.
| Reaction of Carbonyl compound with | Product |
| i. Hydroxylamine | a. Semi carbazone |
| ii. Hydrazine | b. PhemThyrazone |
| iii. Calca Phenylhydrazineium benzoate | c. Hydrazone |
| iv. Semi Carbazide | d. Oxime |
Answers:
i. – d. Oxime
ii. – c. Hydrazone
iii. – b. Phenyl hydrazone
iv. – a. Semi Carbazone
Question 3.
| Compound | Uses |
| i. Formalin | a. Hypnotic |
| ii. Urotropine | b. Perspex |
| iii. Paraldehyde | c. Hypnone |
| iv. Acetone | d. Benzhydrol |
| v. Acetophenone | e. Biological specimens |
| vi. Benzophenone | f. Urinary infection |
Answers
i. – e. Biological specimen
ii. – f. Urinary infection
iii. – a. Hypnotic
iv. – b. Perspex
v. – c. Hypnone
vi. – d. Benzhydrol
![]()
Question 4.
| Compound | Uses |
| i. Formic acid | a. Preparation of aspirin |
| ii. Benzoic acid | b. Artificial fruit essences |
| iii. Acetamide | c. Food Preservative |
| iv. Acetic anhydride | d. Preparation of Primary amines |
| v. Ethyl acetate | e. Coagulating agent for rubber latex |
Answers
i. – e. Coagulating agent for rubber latex
ii. – c. Food preservative
iii. – d. Preparation of primary amines
iv. – a. Preparation of aspirin
v. – b. Artificial fruit essences
VI. Two Marks Questions
Question 1.
Write a note on Rosenmund reduction
Answer:
- Reactant – Acid chloride
- Catalyst – Palladium
- BaSO4 stops further reduction of aldehyde into alcohol.
- Formaldehyde and Ketones cannot he prepared by this method.
- Product – Aldehyde
- Catalytic Poison – BaSO4
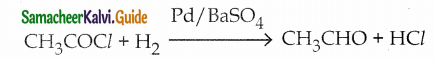
![]()
Question 2.
Write about Stephen’s reaction
Answer:
Alkyl cyanides are reduced using SnCl2 / HCl into imines which on hydrolysis gives corresponding aldehydes.
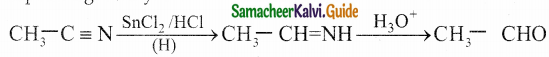
Question 3.
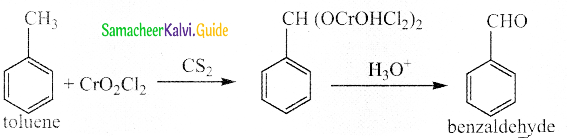
Write a note on Etard reaction
Answer:
- When toluene is oxidised by chromyl chloride benzaldehyde is obtained
- Acetic anhydride and Cr03can, also be used.
- This reaction is called Etard reaction
Question 4.
Convert hex -4- ennitrile into hex -4 – enal
Answer:
Di-isobutyl aluminium hydride (DIBAL – H) selectively reduces alkyl cyanides to form imines which on hydrolysis gives aldehydes.
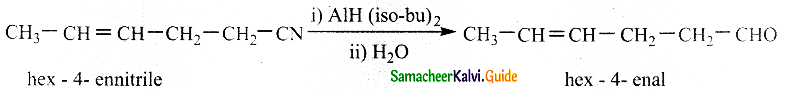
![]()
Question 5.
Write about Gattermann – Koch reaction
Answer:
- Gattermann – Koch reaction is a variant of Friedel – Crafts acvlation reaction.
- In this method, reaction of CO and HCl generate an intermediate which reacts like formyl chloride.
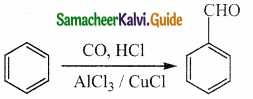
Question 6.
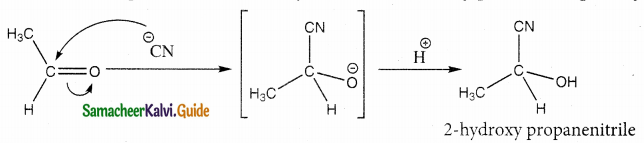
Write about the nucleophilic addition of acetaldehyde with HCN
Answer:
Attack of nucleophile CN- on carbonyl carbon followed by protonation gives cyanohydrins.
Question 7.
Illustrate Popoff’s rule
Answer:
- Oxidation of unsymmetrical ketones is governed by Popoffs rule.
- It states that during the oxidation of an unsymmetrical ketone, a (C – CO) bond is cleaved in such a
way that the keto group stays with the smaller alkvl group.

![]()
Question 8.
Write briefly about halofom reaction
Answer:
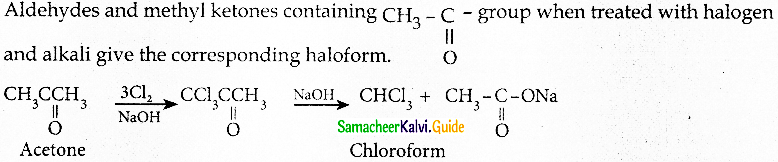
Question 9.
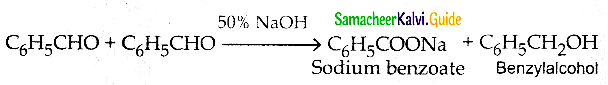
What is Cannizaro reaction?
Answer:
In the presence of concentrated aqueous or alcoholic alkali, aldehydes with no a- hydrogen atom undergo self oxidation and reduction, (dispropotination) to give a mixture of a salt of carboxylic acid and and alcohol.
Question 10.
What is Crossed Cannizaro reaction?
Answer:
- When Cannizaro reaction takes place between two different aldehydes with no a- hydrogen atom it is called crossed cannizaro reaction.
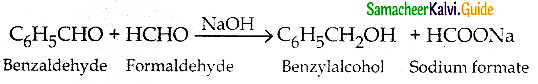
- In crossed Cannizaro reaction more reactive aldehyde is oxidised and less reactive aldehyde is reduced.
![]()
Question 11.
What is Benzoin Condensation?
Answer:
When two molecules of benzaldehyde condenses in presence of alcoholic KCN to give a hydroxy ketone benzoin, the reaction is called Benzoin condensation
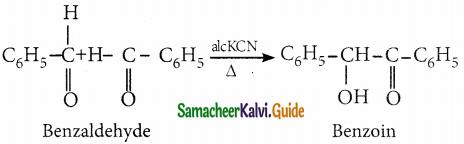
Question 12.
Write about Perkin’s reaction?
Answer:
- When an aromatic aldehyde is heated with an aliphatic acid anhydride in presence of the sodium salt of the corresponding acid, condensation takes place to form an α β – unsaturated acid.
- This reaction is known as Perkin’s reaction.
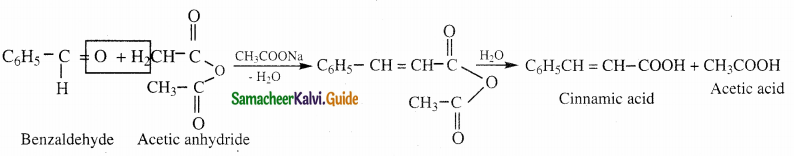
Question 13.
What is Knoevenagal reaction?
Answer:
Benzaldehyde condenses with malonic acid in presence of pyridine to form cinnamic acid. This is
known as Knoevenagal reaction.
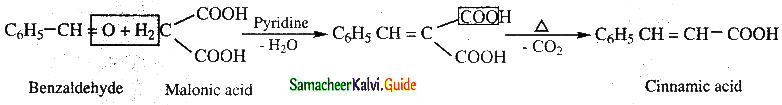
![]()
Question 14.
Mention the uses of formaldehyde
Answer:
- 40% aqueous solution of formaldehyde is known as formalin and used as a preservative for biological specimens
- Formalin has hardening effect, hence used for tanning.
- Formaldehyde reacts with phenol forming thermosetting plastic known as bakelite.
Question 15.
Write the uses of acetone
Answer:
- As a solvent
- Manufacture of smokeless powder (cordite).
- Nail polish remover
- In the preparation of suiphonal, a hypontic
- Manufacture of thermosetting plastic perspex.
Question 16.
Write the uses of benzaldehyde
Answer:
- As a flavouring agent
- In perfumes
- In dye intermediates
- Starting material for cinnamaldehyde, cinnamic acid benzoyl chloride etc.,
![]()
Question 17.
Mention some uses of aromatic ketones
Answer:
- Acetophenone is used in perfumery
- Acetophenone is used as a hypnotic under the name hypnone.
- Benzophenone is used in perfumery
- Benzophenone is used in the preparation of benzhydrol drop .
Question 18.
How are the following conversion effected?
Answer:
Question 19.
What is esterification?
Answer:
- When Carboxylic acids are heated with alcohols in the presence of Conc. H2SO4or dry HCl gas, esters are formed
- This is known as esterfication. .
- This reaction is reversible
![]()
Question 20.
What is decarboxylation?
Answer:
- When sodium salt of a carboxylic acid is heated with soda lime (NaOH & CaO in the ratio 3 : 1) the carboxylic acid group is removed as CO2.
- This is known as decarhoxylation.
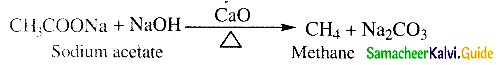
Question 21.
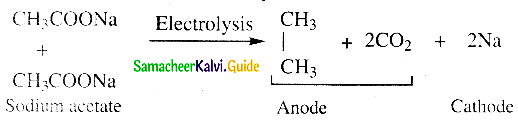
Write about Kolbe’s electrolytic decarboxylation
Answer:
- Aqueous solutions of sodium or potassium salts of carboxylic acid on electrolysis gives alkanes at anode.
- This is known as Kolbe’s electrolysis.
Question 22.
Write notes on Hell – Voihard – Zelinsky reaction (HVZ reaction)
Answer:
- Carhoxylic acids containing α – hydrogen atoms are halogenated at the α – position when treated
with chlorine or bromine in the presence of small amount of red phosphorous to form a – halo carhoxylic acids. - This is known as HVZ reaction.
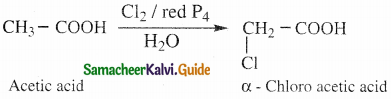
![]()
Question 23.
Mention the tests for carboxylic acids
Answer:
- Turn blue litmus to red.
- Gives brisk effervescence with sodium bi carbonate due to the evolution of CO2
- When warmed with alcohol and Conc. H2S04, gives a fruity odour due to the formation of an ester.
Question 24.
What is transesterification
Answer:
- Esters of an alcohol can react with another alcohol in the presence of a mineral acid to give the ester of second alcohol.
- This interchange of alcohol portions of the esters is termed transesterification.
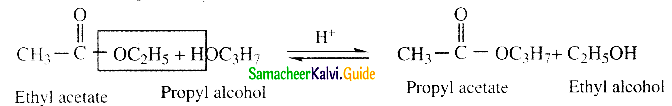
Question 25.
Write about Claisen condensation
Answer:
- Esters containing at least one a – hydrogen atom undergo self condensation in the presence of a strong base such as sodium ethoxide to form -keto ester.
- This is known as Claisen ester condensation.
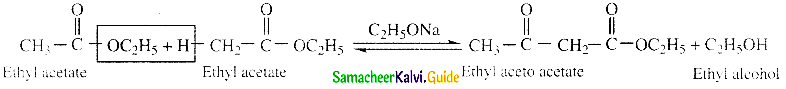
![]()
Question 26.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compounos.

(ii) CH2 = CH – CH2 – CH2OH
(iii) Neopentyl alcohol
(iv) Glycerol
Answer:
- 2-Methyl-1-phenoxv propane
- But – 3- en-1-ol
- 2,2 – dimethyl propan-1-ol
- propane – 1,2,3-triol
Question 27.
Naine the ester which has the following flavour?
1. Banana
2. Orange
3. Pineapple
4. Apricot
Answer:
1, Amyl acetate
2. Octyl acetate
3. Ethyl butyrate
4.. Amyl butyrate
![]()
VII. Three Mark Questions
Question 1.
What notes on Friedel crafts acylation and benzoylation
Answer:
- It is a best method for preparing alkyl aryl ketones or diaryl ketones.
- This reaction succeeds only with benzene and activated benzene derivatives.
i) Acylation:
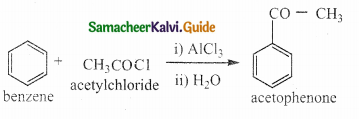
ii) Benzoylation:
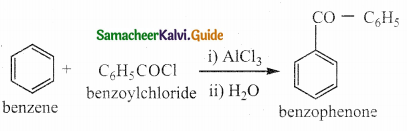
Question 2.
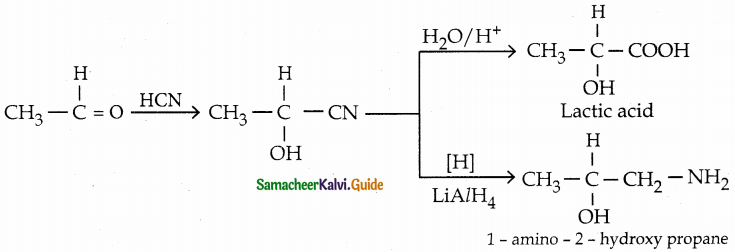
Convert acetaldehyde ito
(i) lactic acid
(ii) 1-amino-2.-hydroxy propane
Answer:
![]()
Question 3.
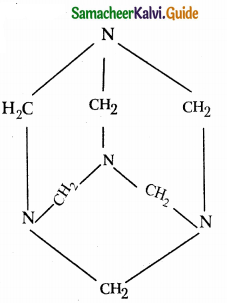
What is Urotropine? How is it prepared? Mention its uses.
Answer:
- Hexamethylene tetramine is called urotropine.
- It is prepared by reacting formaldehyde with ammonia.
- 6HCHO + 4NH3 (CH2)6N4 + 6H20
Structure :
Uses :
- Urinary anteseptic
- Nitration of urotopine under controlled condition gives an explosive RDX also called cyclonite or cyclotrimethylene trinitramine.
Question 4.
Write notes on
(i) Clemmenson reduction
(ii) Wolff – Kishner reduction
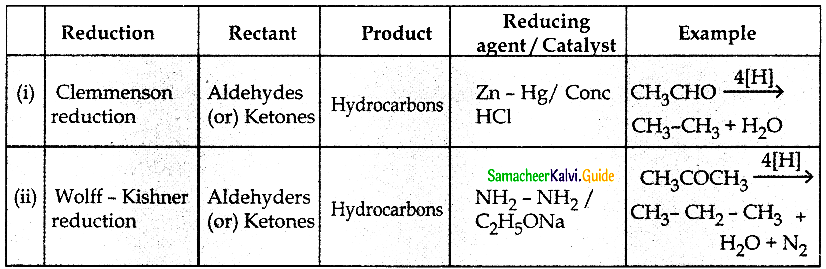
![]()
Question 5.
Explain crossed aldol condensation
Answer:
- If aldol condensation takes place between two different aldehydes or ketones or between one aldehyde and one ketone, it is known as crossed (or) mixed aldol condensation.
- This reaction is not very useful as the product is usually a mixture of all possible condensation products and cannot be separated easily.
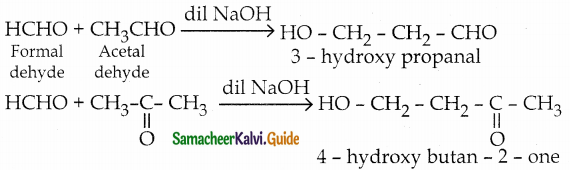
Question 6.
Write about Claisen – Schmidt condensation
Answer:
Benzaldehyde condenses with aliphatic aldehyde or methyl ketone in the presence of dil. alkali at room temperature to form unsaturated aldehyde or ketone.
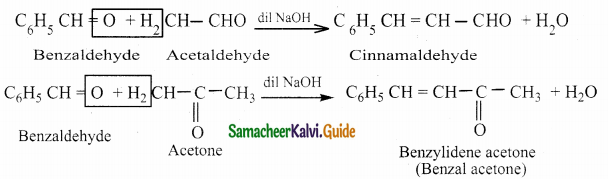
![]()
Question 7.
Write about the reduction of carboxylic acids
Answer:
(i) partial reduction to alcohols
Carboxylic acids are reduced to primary alcohols b’ LiAlH4 or hydrogen in the presence of copper
chromite as catalyst, sodium borohydride does not reduce – COOH group.
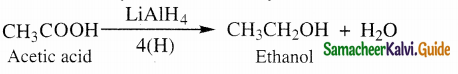
(ii) Complete reduction to alkanes
Carboxylic acids are completely reduced to alkanes with same number of carbon atoms by HI and red phosphorous.
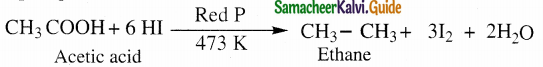
Question 8.
Explain the reducing nature of formic acid
Answer:
- Formic acid contains both an aldehyde as well as an acid group.
- Hence formic acid can be easily oxidised.
- Therfore formic acid acts as a strong reducing agent.
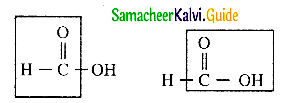
- Formic acid reduces Fehlings solution into red coloured cuprous oxide
![]()
- Formic acid reduces Tollen’s reagent to metallic silver.
![]()
![]()
Question 9.
Write briefly about the acidic nature of carboxylic acids
Answer:
- Carboxylic acids dissociate to give W ions and carboxylate ions in aqueous solution.
- Carboxylate ion is resonance stabilished.
- Hence carboxylic acids readily donate H +ions which makes them acidic
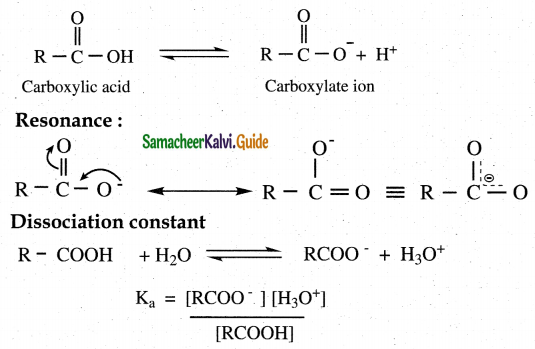
- The dissociation constant Ka is called acidity constant PKa= – log Ka
- For a stronger acid Ka value is larger but PKa value is smaller.
Question 10.
Write about the effect of substituents on the acidic natue of carboxylic acids.
Answer:
(i) Electron releasing alkyl groups decreases the acidic nature.
- Electron releasing groups (+ I groups) increase the negative charge on the carboxylate ion and destabilise it.
- Hence the loss of proton becomes difficult
- As the length of alkyl groups increases, the acidic nature decreases
∴ HCOOH > CH3COOH > CH3-CH2-COOH
(ii) Electron withdrawing groups increases the acidic nature.
- Electron withdrawing groups (-I groups) decrease the negative charge on the carboxylate ion and stabilise it.
- Hence the loss of proton becomes relatively easy.
- Acidic nature increases with increase in electronegativity of substituents
∴ F-CH2COOH > Cl-CH2COOH > Br – CH2COOH > I – CH2COOH - Acidic nature increases with increase in the number of electron withdrawing groups present in a – carbon.
∴ CCl3COOH > CHCl2COOH > CH2ClCOOH > CH3COOH
![]()
Question 11.
An organic compound C3H4 (A) on hydration with Hg2+/H2 S04 gives compound (B) which gives positive iodoform test. Compound (B) heated with NH2 – NH2 / C2 H5 ONa to give hydrocarbon (C). (B) also treated with HCHO in the presence of dil NaOH gives compound (D). Identify A, B, C and D. Write the chemical reactions involved.
Answer:
An organic compound C3H4 (A) is Propyne on hydration to give Compound (B) is Acetone it is undergoes positive iodoform test.
Hydration of alkynes, other than acetylene gives ketones.
Compound (A)
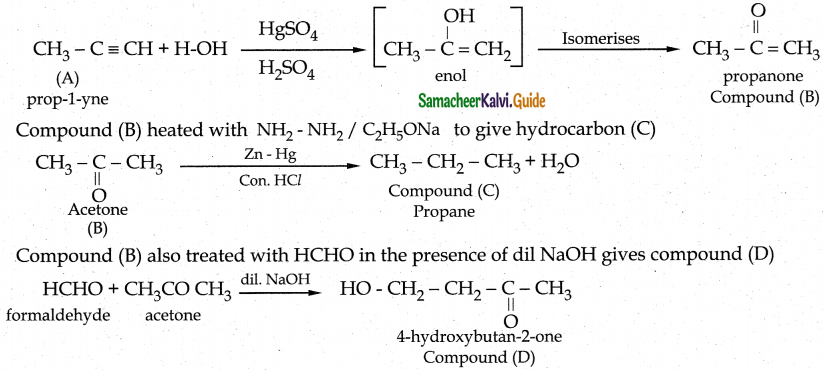
| Compound | Name |
| A | Prop-1-yne |
| B | Acetone |
| C | Propane |
| D | 4-Hydroxy butan-2-one |
![]()
Question 12.
Convert acetamide into
(i) methyl amine
(ii) ethyl amine
Answer:
i) Hoffmans degradation
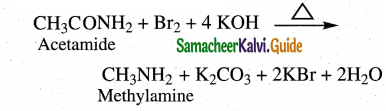
Amides undergo Hoffman’s degradation to give amines with one carbon less than the parent amide.
ii) Reduction
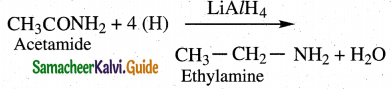
Amides undergo reduction with LiAlH4 or Na/alcohol to form amines with same number
of carbon as parent amide.
Question 13.
How will you prepare acetyichioride from CH3COOH
Answer:
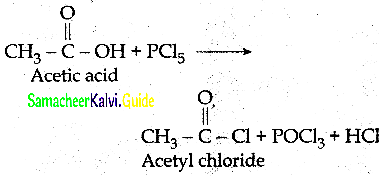
VIII. Five Mark Questions
Question 1.
Write the mechanism of addition of alcohol to acetaldehyde Addition of alcohol
Answer:
When aldehydes / ketones is treated with 2 equivalents of an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst acetals are formed.
For example
When acetaldehyde is treated with 2 equivalent of methanol in presence of HCl, 1,1, – dimethoxy ethane is obtained.
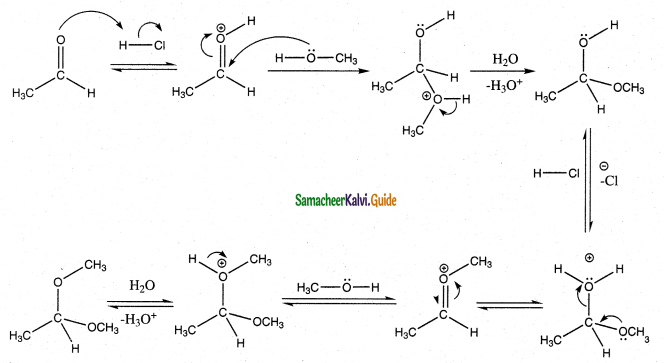
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the addition of ammonia derivatives to carbonyl compounds
Answer:
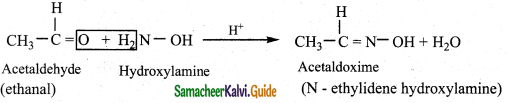
i) Reaction with hydroxyl amine
Aldehyde and ketones react with hydroxylamine to form oxime.
Example:
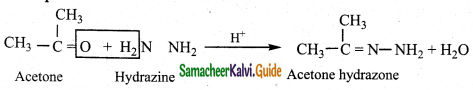
ii) Reaction with hydrazine
Aldehydes and ketones react with hydrazine to form hydrazone.
Example:
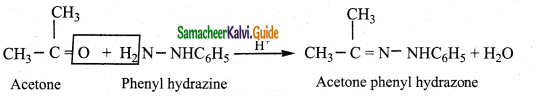
iii) Reaction with phenyl hydrazine
Aldehydes and ketones react with phenyl hydrazine to form phenyl hydrazone
Question 3.
What is the action of ammonia on
(Iacetaldehyde (ii) acetone (iii) Benzaldehyde
Answer:
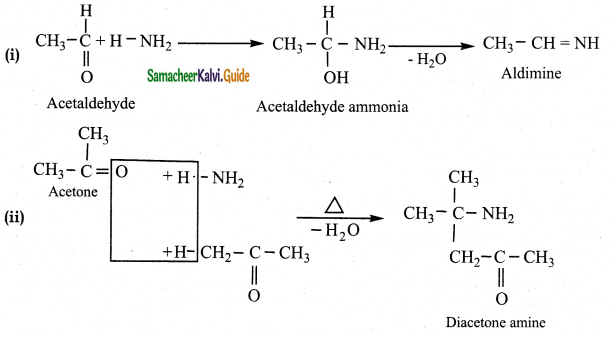
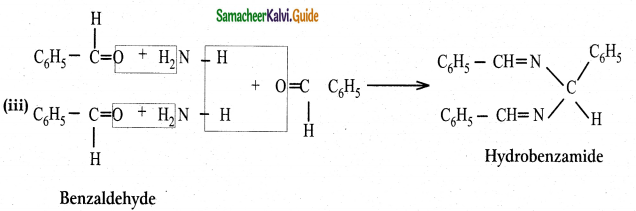
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the mechanism of aldol condensation
Answer:
In presence of dilute NaOH or KOH, two molecules of an aldehyde or ketone having α- hydrogen atoms add together to give β- hydroxy aldehyde (aldol) or β- hydroxy ketone (ketol)
This is known as aldol condensation
Aldol or ketol readily loses water to form α, β – unsaturated aldehyde or ketone.
Mechanism
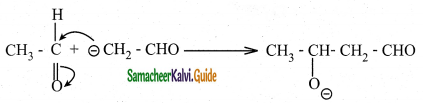
The mechanism of aldol condensation of acetaldehyde takes place in three steps.
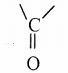
Step 1:
The carbanion is formed as the α – hydrogen atom is removed as a proton by the base.

Step 2:
The carbanion attacks the carbonyl carbon of another unionized aldehyde to form an alkoxide ion.
Step 3 :
The alkoxide ion formed is protonated by water to form aldol.
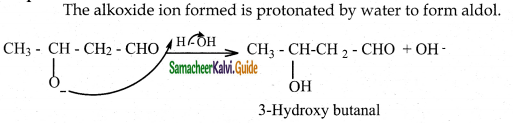
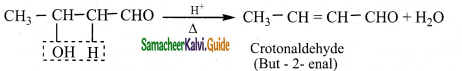
The aldol rapidly undergoes dehydration on heating with acid to form O – R unsaturated aldehyde.
Question 5.
Explain the mechanism of cannizaro reaction
Answer:
- Reactant – Two molecules of aldehyde with no o – hydrogen atom.
- Reagent – Concentrated aqueous or alcoholic alkali
- Reaction – Self oxidation and reduction (disproportionation)
- Products – Salt of carboxylic acid and an alcohol
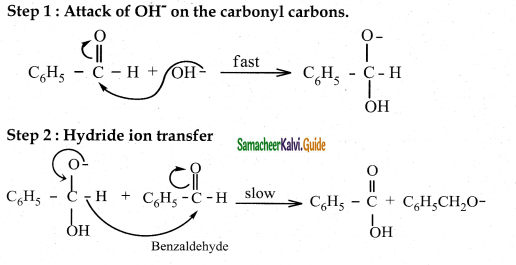
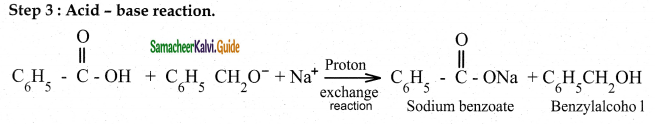
Cannizaro reaction is a characteristic of aldehyde having no a hydrogen.
![]()
Question 6.
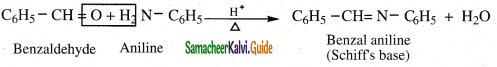
Convert benzaldehyde into
(i) Schiff’s base,
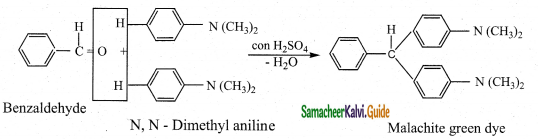
(ii) Malachite green dye
Answer:
i) Benzaldehyde reacts with primary amines (aliphatic or aromatic) in presence of an acid to form schiff’s base.
ii) Benzaldehyde condenses with tertiary aromatic amines like N, N – dimethyl aniline in the presence of strong acids to form triphenyl methane dye.
Question 7.
How can you identify aldehydes
Answer:
i) Tollens reagent test:
- Tollens reagent is ammonical silver nitrate.
- When an aldehyde is warmed with Tollens reagent, a bright silver mirror is produced due to the formation of silver metal.
- This is also known as silver mirror test.
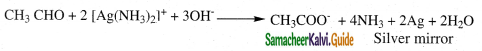
ii) Fehlings Solution test:
- Fehlings Solution A – aqueous copper sulphate
- Fehlings Solution B – alkaline solution of sodium potassium tartarate (Rochelle salt)
- When an aldehyde is warmed with a mixture of Fehlings A & B solutions deep blue colour solution is changed to red precipitate of cuprous oxide.
![]()
iii) Benedict’s solution test:
- Benedict’s solution is a mixture of CUSO4+ sodium citrate + NaOH.
- An aldehyde reduces Cu2+ ion into red precipitate of cuprous oxide.
![]()
iv)
- Schiff’s reagent is Rosaniline hydrochloride dissolved in water and its red colour is decolourised by passing SO2.
- Aldehydes restore the red colour of Schiff’s reagent.
![]()
Question 8.
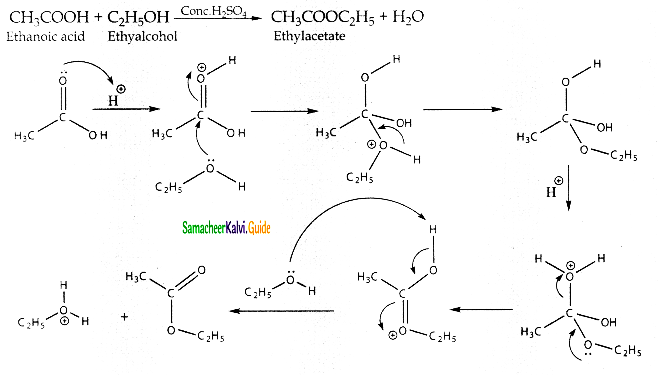
What happens when ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol in the presence of con.H2SO4. Give its complete mechanism,
Answer:
Question 9.
An Organic compound (A) C2H4O reduce Tollen’s and Fehling’s solution. (A) react with methanol and HCl to give compound (B) C4H10O2 (A) on reaction with Methanal in the presence of dilute NaOH to give compound (C) C3H6O2. Identify compounds A, B, C with necessary reactions.
Answer:
Compound (A) is Acetaldehyde (CH3-CHO)
When acetaldehyde is treated with 2 equivalent of methanol in presence of HCl, 1,1-dimethoxy ethane is obtained.
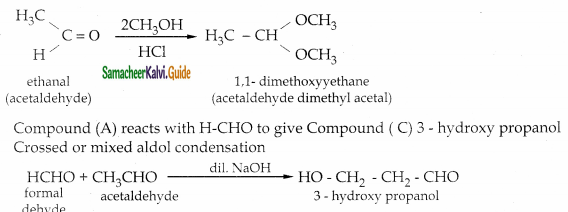
| Compound | Name |
| A | CH3-CHO |
| B | CH3 – CH(OCH3)2 |
| C | HO-CH2 -CH2-CHO |