Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Guide Pdf History Term 2 Chapter 1 Vijayanagar and Bahmani Kingdoms Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Social Science Solutions History Term 2 Chapter 1 Vijayanagar and Bahmani Kingdoms
7th Social Science Guide Vijayanagar and Bahmani Kingdoms Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Who was the greatest ruler of Sangama Dynasty?
a) Bukka
b) Devaraya II
c) Harihara II
d) Krishna Devaraya
Answer:
b). Devaraya II
![]()
Question 2.
Which was the most common animal depicted on the pillars of Vijayanagara style?
a) Elephant
b) Horse
c) Cow
d) Deer
Answer:
b) Hors
Question 3.
Who was the last ruler of the Sangama Dynasty?
a) Rama Raya
b) Tirumaladeva Raya
c) Devaraya II
d) Virupaksha Raya II
Answer
d) Virupaksha Raya II
![]()
Question 4.
Who ended the Sultanate in Madurai?
a) Saluva Narasimha
b) Devaraya II
c) Kumara Kampana
d) Tirumaladeva Raya
Answer:
c) Kumara Kampana
Question 5.
Name the Bahmani King who was a linguist and a poet.
a) Ala-ud-din Hasan Shah
b) Muhammad I
c) Sultan Firoz
d) Mujahid
Answer:
c) Sultan Firoz
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks:
1. ………..was the capital of the Aravidu dynasty.
Answer:
Penukonda
2. Vijayanagar emperor’s issued a large number of gold coins called …………………….
Answer:
Varaha’s
![]()
3. Mahmud Gawan used …………………. chemists to teach the preparation and use of gunpowder.
Answer:
Persian
4. In Vijayanagara administration ……………… looked after the affairs of villages.
Answer:
Gauda
![]()
III. Match the following:
| 1. Vijayanagara | a) Ruler of Odisha |
| 2. Prataparudra | b) Astadiggajas |
| 3. KrishnaDevaraya | c) Pandurangamahatyam |
| 4. Abdur Razzaq | d) City of victory |
| 5. Tenali Ramakrishna | e) Persian emissary |
Answer:
| 1. Vijayanagara | d) City of victory |
| 2. Prataparudra | a) Ruler of Odisha |
| 3. KrishnaDevaraya | b) Astadiggajas |
| 4. Abdur Razzaq | e) Persian emissary |
| 5. Tenali Ramakrishna | c)Pandurangamahatyam |
IV.Match the statement with the reason. Tick (✓) the appropriate answer:
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : The Vijayanagar army was considered one of the feared armies in India.
Reason (R) : Vijayanagar armies used both firearms and cavalry.
a) R is not the correct explanation of A
b) R is correct explanation of A
c) A is correct and R is wrong
d) (A) and (R) are Correct
Answer:
b) R is correct explanation of A
![]()
Question 2.
Find out the wrong pair
a) Silk – China
b)Spices – Arabia
c) Precious stone – Burma
d)Madurai Vijayam – Gangadevi
Answer:
b) Spices – Arabia
Question 3.
Find the odd one out
Harihara II, Muhammad I, Krishnadeva Raya, Devaraya I.
Answer:
![]()
Question 4.
Consider the following statements and find out which is/are correct
I) Turquoise throne is one of the bejeweled royal seats of Persian kings described in Firdausi’s Shah Nama.
II) The fertile regions between the rivers Krishna and Tungabhadra and Krishna-Godavari delta were the zones of conflict among the rulers of Vijayanagar, and Bahmani.
III) Muhammad I was educated at Multan.
IV) Mahmud Gawan served with great distinction as the Prime Minister under Muhammad III.
a) i), ii) are correct
b) i), ii), iii) are correct
c) ii), iii), iv) are correct
d) iii), iv) are correct
Answer:
i), ii) are correct
![]()
V.True or False:
Question 1.
Harihara and Bukka were the founders of the Bahmani kingdom.
Answer:
False
Question 2.
Krishnadeva Raya, who reigned for 20 years, was the most illustrious ruler of the Sangama dynasty.
Answer:
False
![]()
Question 3.
Alasani Peddana was the greatest of all Astadiggajas.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
Kingship of Vijayanagar administration was hereditary, based on the principle of primogeniture.
Answer:
True
![]()
Question 5.
There were 18 monarchs of the Bahmani dynasty.
Answer:
True
VI.Answer in one or two sentences:
Question 1.
The four dynasties of the Vijayanagara kingdom with reference to prominent rulers of each dynasty.
Answer:
Four dynasties of the Vijayanagara kingdom and its prominent rulers are:
- Sangama Dynasty – Devaraya II
- Saluva Dynasty – Saluva Narasimha
- Tuluva Dynasty – Krishnadevaraya
- Aravidu Dynasty – Tirumaladeva
Question 2.
Battle of Talikota.
Answer:
- The Sultans of Deccan kingdoms forming a league to fight against the Vijayanagar Empire.
- The battle is known as ‘Rakasa Tangadi’ or ‘Battle of Talikota’.
- They fought at Talikota in 1565 A.D. Vijayanagar was defeated.
- All the buildings, Palaces and temples were destroyed in the capital city Hampi.
![]()
Question 3.
The structure of governance in the Vijayanagar kingdom.
Answer:
- The Vijayanagar empire was divided into different mandalams, nadus, sthalas and gramas.
- Each province was administered by Mandalesvara.
- Each village had a grama sabha. Gauda, village headman, looked after the affairs of the village.
- They maintained the army consisted of the infantry, cavalry with a firearm, and elephant corps.
Question 4.
The five independent kingdoms of Deccan Sultanate.
Answer:
The five independent kingdoms of Deccan were Bidar, Bijapur, Ahmednagar, Berar and Golconda.
![]()
Question 5.
The educational reforms of Ala-ud-din Hasan Shah.
Answer:
- Hasan Shah took special care in founding a school to educate his sons.
- He opened institutions for the children of noble families in the art of soldiery.
VII. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
Discuss the career and achievements of Krishna Devaraya.
Answer:
(i) Krishnadevaraya who reigned for 20 years was the most illustrious ruler of the Tuluva dynasty.
(ii) He brought under control the independent chieftains in the Tungabhadra river basin.
(iii) The Bahmani sultan, Mahmud Shah, had been overthrown and kept in imprisonment by his minister. Krishnadevaraya freed the sultan and restored him to the throne. Prataparudra negotiated for peace and offered to marry off his daughter to him.
(iv) Accepting the offer, Krishnadevaraya returned the territory he had conquered from Prataparudra.
(v) Krishnadevaraya, with the assistance of the Portuguese gunners, could easily defeat the Sultan of Golconda and subsequently take over Raichur from the ruler of Bijapur.
A Great Builder:
(i) Krishnadevaraya built huge irrigation tanks and reservoirs for harvesting rainwater.
(ii) He built the famous temples of Krishnaswamy, Hazara Ramaswamy and Vithalaswamy in the capital city of Hampi.
(iii) He distributed the wealth he gained in wars to all major temples of South India for the purpose of constructing temple gateways (gopura), called ‘Rayagopuram,’ in his honour.
(iv) He had good friendly relationship with the Portuguese and Arabian traders, which increased the Empire’s income through customs.
Patron of Literature, Art and Architecture:
Krishnadevaraya patronised art and literature. Eight eminent luminaries in literature known as astadiggajas adorned his court.
![]()
VIII. HOTs:
Question 1.
Discuss the causes for the decline of the Vijayanagar rule. To what extent the Bahmani sultans contributed to it?
Answer:
- After Krishna Devaraya, the rulers were inefficient in the Vijayanagar empire. Making use of the situation the commanders declared independence.
- There were frequent wars between Vijayanagar and Bahmani Kingdom which made the country economically weak.
- Finally, the sultans of Deccan Kingdoms formed a league against Vijayanagar. The combined forces of the enemies defeated Vijayanagar in the Battle of Talikota in 1565 A.D.
- These sultans destroyed the buildings, palaces, temples and the capital city of Hampi.
X. Answer Grid:
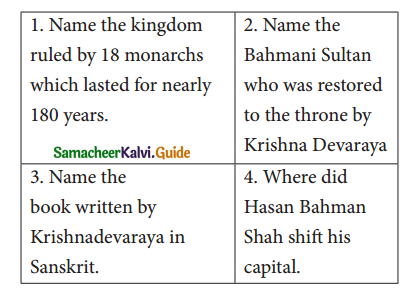
1. Name the kingdom ruled by 18 monarchs which lasted for nearly 180 years.
Answer:
Bahmani Kingdom
2. Name the Bahmani Sultan who was restored to the throne by Krishna Devaraya?
Answer:
Mahmud Shah
3. Name the book written by Krishna Devaraya in Sanskrit.
Answer:
Jambavati Kaiyanam
4. Where did Hasan Bahman Shah shift his capital.
Answer:
Gulbarga
![]()
7th Social Science Guide Vijayanagar and Bahmani Kingdoms Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct answer:
Question 1.
The repressive measures of which Muslim king led to the rise of newly independent states?
a) Balban
b) Ala – ud – din Khilji
c) Muhammed – bin – Tughlaq
d) Firoz Tuglagq
Answer:
c) Muhammed – bin – Tughlaq
![]()
Question 2.
Battle of TaliKota was fought in the year.
a) 1550
b) 1555
c) 1560
d) 1565
Answer:
d) 1565
Question 3.
The poem Madura Vijayam composed by
a) Kumara Kampana
b) Ganga Devi
c) Ibn Battuta
d) Abdur Razzaq
Answer:
b) Ganga Devi
![]()
Question 4.
The Eight Eminent Luminaries in Literature were known as
a) Ashoka Pradhan
b) Navaratnas
c) Anju Vannathar
d) Astadiggajas
Answer:
d) Astadiggajas
Question 5.
A Persian emissary who visited the court of Krishna Devaraya was
a) Wassuf
b) Marcopolo
c) IbnBattuta
d) Abdur Razzaq
Answer:
d) Abdur Razzaq
![]()
Question 6.
Who wrote a Telugu epic Amuktamalyada
a) Krishna Devaraya
b) Tenali Ramakrishna
c) Allasani Pethana
d) Tukkanna
Answer:
a) Krishna Devaraya
Question 7.
The Bahmani Kingdom was established in the year …………………………
a) 1327
b) 1337
c) 1347
d) 1350
Answer:
c) 1347
![]()
Question 8.
The territorial divisions of Bhamani Kingdom was …………………………
a) District
b) City
c) Tarafs
d) Capital
Answer:
Tarafs
Question 9.
Wasir – i – ashraf was the minister of in the Bahmani Kingdom
a) Finance
b) Deputy finance
c) Foreign affairs
d) Police affairs
Answer:
c) Foreign affairs
![]()
Question 10.
The eighth Bahmani king was……………………….
a) Mahmud bavan
b) Muhammad
c) Zahan khan
d) Sultan firoz
Answer:
d) sultan firoz
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks:
1. In South India, ……….. and ………… are the two great kingdoms.
Answer:
Vijayanagar, Bahmani
2. Vijayanagar means ………….
Answer:
the city of victory
![]()
3. ……………., head of Saivite Sringeri mutt instructed to establish the Vijayanagar kingdom.
Answer:
Vidyaranya
4. The Vijayanagar ruler who recruited Muslim fighters in their army was ……………
Answer:
Devaraya II
![]()
5. Saluva Dynasty was founded by …………………
Answer:
Saluva Narasimha
6. Tuluva Dynasty was founded by …………………
Answer:
Naras Nayaka
![]()
7. Krishna deva Raya, with the assistance of the ……………….. easily defeated the Sultan of Golconda.
Answer:
Portuguese gunners
8. Rayagopuram were built by …………….
Answer:
Krishna Devaraya
![]()
9. The notable in Krishnadevaraya Patron was ………………….
Answer:
Tenali Ramakrishna
10. Battle of Talikota also known as ……………………
Answer:
Rakasa Tangadi
![]()
11. Krishna Devaraya was succeeded by …………………….
Answer:
Achtyuda Deva Raya
12. Vijayanagar Empire collapsed in the year ……………………
Answer:
1646
![]()
13. Vijayanagar Provinces were administered by …………………
Answer:
Mandalesvara
14. The new style of temple building temple was introduced by Vijayanagar rulers is called …………………..
Answer:
Vijayanagara style
![]()
15. ………………contributed extensively to the development of the bhamani kingdom
Answer:
Mahamud Gawan
III. Match the following:
| A | B |
| 1. Bidar | a) Madura Vijayan |
| 2. Ganga Devi | b) Vijaya Nagar |
| 3. Goda Devi | c) Madrasa |
| 4. Hampi | d) Amukta malyada |
Answer:
| A | B |
| 1. Bidar | c) Madrasa |
| 2. Ganga Devi | a) Madura Vijayam |
| 3. Goda Devi | d) Amukta malyada |
| 4. Hampi | b) Vijaya Nagar |
lV. Match the statement with the reason. Tick (✓) the appropriate answer:
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : Several foreign nobles of the state to leave for their Provinces.
Reason (R) : Gawan was executed.
a) R is not the correct explanation of A
b) R is the correct explanation of A
c) A is correct and R is wrong
d) (A) and (R) are Correct
Answer:
b) R is the correct explanation of
![]()
Question 2.
Find the odd one out
a) Muhammad -1
b) Mujahid
c) Gawan
d) Shihab – ud – din Mahmud
Answer:
c) Gawan
V. State true or false:
Question 1.
Vijayanagar temple architecture belonged to the Dravidian style of Architecture
Answer:
False
![]()
Question 2.
The Capturing fertile regions between the rivers Krishna and Tungabhadra was the major cause for the wars between Vijayanagar and Bahmani Kingdom
Answer:
True
Question 3.
The Delhi Sultanate was gradually broken up into six independent Deccan Kingdoms
Answer:
False
![]()
Question 4.
Amir – i – Jumla was the finance minister of the Bahmani Kingdom.
Answer:
True
VI. Answer in one or two sentences:
Question 1.
What is Astadiggajas?
Answer:
- Astadiggajas were the eight eminent luminaries in literature adorned in the court of Krishnadevaraya
- Alasani Peddana and Tenali Ramakrishnan were the notable persons in Astadiggajas.
Question 2.
What are countries did Vijayanagar had trade contact?
Answer:
Vijayanagar traded with Persia, South Africa, Portugal, Arabia, China, Burma, South East Asia, and Sri Lanka.
![]()
Question 3.
Who were the important scholars in Vijayanagar Empire?
Answer:
Srinatha, Pothana, Jakkama, Duggana, Tenali Ramakrishna and Allasani Peddana were important scholars in the Vijayanagar Empire.
Question 4.
What is Turquoise?
Answer:
- Turquoise is a semi-precious stone sky blue in colour.
- It is one of the bejewelled royal seats of Persian kings described in Firdausi’s Shah Nama.
![]()
Question 5.
What is the Special feature of Golconda fort?
Answer:
- The Golconda Fort is located about 11 kilometers from Hyderabad.
- The fort is popular for its acoustic architecture.
- The highest point of the fort is Bala Hissar.
- There is a secret underground tunnel, which leads from the Durbar Hall to one of the palaces at the foot of the hills.
VII. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
Describe the eight ministers of the Bahmani state.
Eight ministers of the Bahmani state:
Answer:
- Vakil-us-saltana – Lieutenant of the Kingdom.
- Peshwa – He was associated with the lieutenant.
- Waziri – kull-He supervised the work of all other ministers.
- Amir-i-jumla – Minister for finance.
- Nazir – Assistant minister for finance.
- Wasir-i-ashraf – Minister of foreign affairs.
- Kotwal – Chief of police and city magistrate.
- Sadr-i-jahan – Chief justice and minister of religious affairs and endowments.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the life and achievements of Mahmud Gawan.
Answer:
Life of Mahmud Gawan:
- Mahmud Gawan was a Persian and prime minister of Muhammad HI, the sultan of Bahmani Kingdom.
- He well versed in Islamic theory, Persian, and mathematics.
- He was also a poet and a prose writer.
Achievements:
- Gawan was known for his military campaigns as well as administrative reforms.
- He used gun powder in the battle against the Vijayanagar kings in Belgaum.
- To control the provincial governors. Gawan divided the four provinces of the Sultanate into eight provinces.
- The administrative reforms introduced by Gawan improved the efficiency of the Government.