Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 5th English Guide Pdf Term 1 Prose Chapter 1 Earth, The Desolated Home Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Summary, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 5th English Solutions Term 1 Prose Chapter 1 Earth, The Desolated Home
5th English Guide Earth, The Desolated Home Text Book Back Questions and Answers
In-Text Question (Think):
Question 1.
What actions destroy the Earth? How will you change it?
Answer:
Human beings are responsible for deteriorating nature. The following activities destroy the Earth:
- Industrialisation : Industries release poisonous gases into the environment. Solid waste is discharged into land and water bodies, polluting the land and water.
- Emission of harmful gases: Vehicles emit a huge amount of harmful gases that pollute the air.
- Construction: Agricultural lands are used for construction.
- Deforestation: We destroy forests for urbanisation. It leads to the destruction of the natural habitat of many wild animals and birds.
- Nuclear testing: Uncontrolled release of radioactive materials cause several harmful health effects on human beings and animals. We can change it by not polluting the air, water, and land.
![]()
Let us understand:
A. Choose the correct option:
(astronomer, Earth,sol, fuels, Mars)
Question 1.
A day in Mars is called ______.
Answer:
Alien
Question 2.
______ is called the red planet..
Answer:
Mars
Question 3.
Our planet is called the ______.
Answer:
Earth
Question 4.
We get water by burning ______.
Answer:
Fuels
Question 5.
The ______ are trying to terraform Mars.
Answer:
Scientists
![]()
B. Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
The man destroyed ______.
Answer:
The Earth
Question 2.
In the Earth, we get water from ______.
Answer:
Rain
Question 3.
In Mars ______ Earth days make a year.
Answer:
687
Question 4.
You don’t need ___ and __ in the Earth.
Answer:
A space suit; an Oxygen Cylinder
Question 5.
Fruits, vegetables, and water in Mars are not __
Answer:
Real
![]()
C. Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
What is the setting of the story?
Answer:
Life on Mars is the setting of the story.
Question 2.
Name the vegetables harvested in the vegetation hab.
Answer:
Crops and Carrots are harvested in the vegetarian hub.
Question 3.
What is a sol? How many sols make a year?
Answer:
A sol is Martian solar day. 687 sols make a year.
Question 4.
How water is produced in Mars?
Answer:
Water is produced by burning fuels on Mars.
Question 5.
In this story, what happened to the earth?
Answer:
Humans had destroyed the Earth.
Question 6.
What should be done to save the earth?
Answer:
To save the Earth, we should not pollute the air, water, and land.
![]()
Let us build:
Hi friends, we will show you magic. When we combine these two words, we will get a new word with a different meaning. These words are called compound words.
இரு வார்த்தைகள் இணைந்து ஒரு புதிய வார்த்தைக் கொடுத்தால் அது Compound word எனப்படும்.
Question 1.
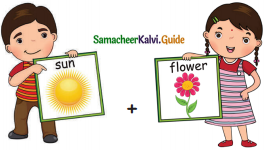 = ______
= ______
Answer:

Question 2.
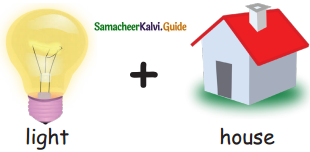 =________
=________
Answer:
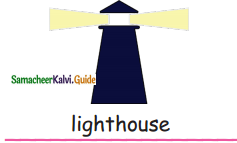
Question 3.
 = ________
= ________
Answer:

![]()
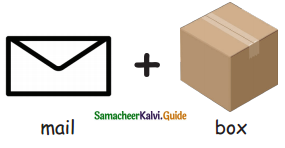
A. Write the compound words from the picture:
Question 1.
Answer:
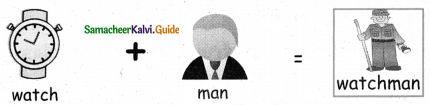
Question 2.

Answer:
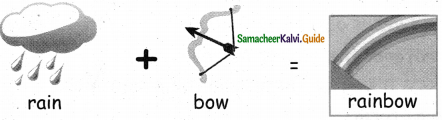
Question 3.
Answer:
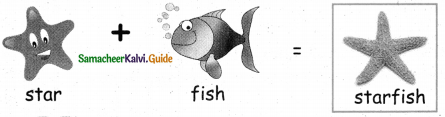
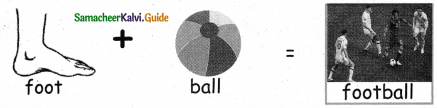
Question 4.

Answer:
![]()
B. Use the clues to complete the compound words:
Question 1.
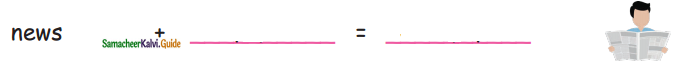
Answer:

Question 2.
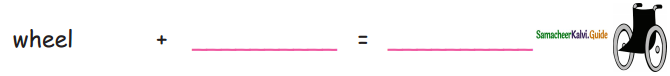
Answer:
Question 3.
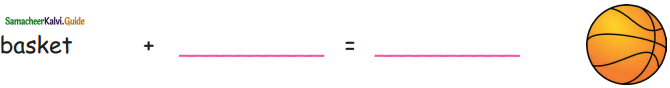
Answer:

![]()
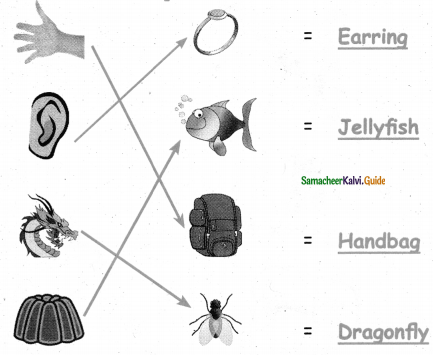
C. Match the compound words:
Question 1.

Answer:
![]()
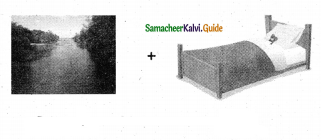
D. Draw and write your own compound words:
Question 1.
 = ______.
= ______.
Answer:

Question 2.
 = ______.
= ______.
Answer:

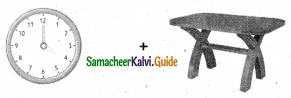
Question 3.
 = ______.
= ______.
Answer:

Question 4.
 = ______.
= ______.
Answer:

Question 5.
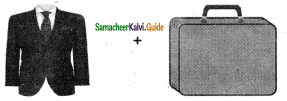 = ______.
= ______.
Answer:

![]()
E. Connect the compound words and create a new word:
Question 1.
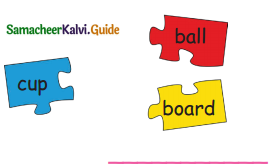
Answer:
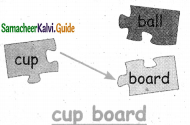
Question 2.
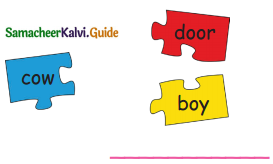
Answer:
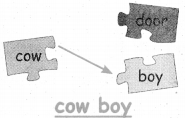
Question 3.
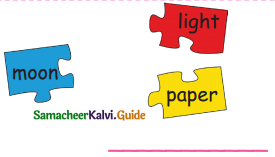
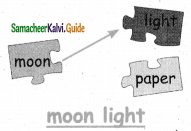
Answer:
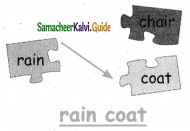
Question 4.
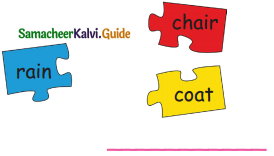
Answer:
5th English Guide Earth, The Desolated Home Additional Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write down the year in which the story was set.
Answer:
The story was set in the year 2068.
Question 2.
How many colonies did India establish on Mars?
Answer:
India established three colonies on Mars.
Question 3.
Who travelled more than 1500 km to meet Arivumathi?
Answer:
Arivumathi’s grandfather travelled more than 1500 km to meet her.
Question 4.
Where was Arivumathi sleeping?
Answer:
Arivumathi was sleeping in her capsule.
Question 5.
What is meant by dust storm?
Answer:
A dust storm is a storm in which strong winds carry a lot of dust.
![]()
Question 6.
How many sols did her grandfather take to reach her colony?
Answer:
Her grandfather took three sols to reach her colony.
Question 7.
What is the reason for the tastiness of fruits and vegetables grown in the Earth?
Answer:
The Earth had fertile soil. So the fruits and vegetables grown were tasty.
Question 8.
According to Arivu in which planet survival was very difficult?
Answer:
According to Arivu, survival was very difficult in Mars.
Question 9.
What would be the age of Arivu, if she lived on the Earth?
Answer:
Arivu would be 18 years old if she lived on the Earth.
Question 10.
Who is trying to Terraform the planet Mars?
Answer:
The scientists are trying to Terraform the planet Mars.
Question 11.
What is meant by Terraform?
Answer:
Terraform is a process by which the surface and climate would be changed to make the environment suitable to humans.
Earth, The Desolated Home Summary in English and Tamil
Let us Learn:
Earth, the Desolated Home பூமி, பாழாக்கப்பட்ட வீடு
It was the year 2068, humans had 2068 destroyed the Earth, and started colonizing the red planet Mars. India established three colonies; Arivumathi’s family lived in one such colony. On her birthday, her grandfather travelled more than 1500 km to meet her. When he reached, he saw her sleeping in her capsule.
2068 ஆம் வருடம். பூமியை (வாழ வழியற்றதாக) அழித்துவிட்ட மனிதர்கள் சிவப்பு கோளான செவ்வாய் கோளில் வாழ்விடங்களை ஏற்படுத்த தொடங்கினர். இந்தியா மூன்று காலனிகளை அமைத்திருந்தது. அத்தகைய ஒரு காலனியில் அறிவுமதியின் குடும்பமும் வசித்தது. அவளது பிறந்த நாளுக்காக 1500 கி.மீ. தொலைவிற்கும் அதிகமாக அவளது தாத்தா பயணம் செய்து அவளைக் காண வந்தார். அவர் அங்கு வந்தபோது, உருளை வடிவ படுக்கையில் அவள் உறங்கிக் கொண்டிருந்தாள்.
He said, “Wake up, Arivu.” Arivumathi was surprised, “Grandpa! When did you come? I was thinking” that you won’t be coming for my birthday.” He sighed, “Don’t you know about the dust storm of Mars? Sometimes, it even lasts for a month. But this time it did not. So I am on time. It still took me three sols to reach here. Now come on, let’s not waste time. We will go to harvest the vegetation.
எழுந்திரு அறிவு”, என்றபடி அவர் அவளை எழுப்பினார். அறிவுமதி ஆச்சரியமடைந்தாள். “தாத்தா, எப்போது வந்தீர்கள்? என் பிறந்த நாளுக்கு நீங்கள் வரமாட்டீர்கள் என்று நான் நினைத்துக் கொண்டிருந்தேன்”, என்றாள் அவள். அவர் பெருமூச்சு விட்டார். “செவ்வாய் கோளில் உள்ள புழுதிப் புயல் பற்றி உனக்குத் தெரியாதா? சில சமயம் அது ஒரு மாதம் வரையிலும் கூட நீடிக்கும். ஆனால் இந்த முறை அப்படியல்ல. ஆகவே நான் சரியான hab for vegetables.”. நேரத்திற்கு வந்து விட்டேன். இங்கு வர எனக்கு மூன்று நாட்கள் ஆகிவிட்டன. சரி, வா. நேரத்தை வீணாக்க வேண்டாம், நாம் காய்கறி தோட்டத்திற்குச் சென்று காய்கறிகளை அறுவடை செய்வோம்” என்றார் அவர்.
![]()
In the hab, he said, “Hmm, these carrots are not tasty anymore, like the ones I ate in my childhood.” She asked, “Why do you say so, Grandpa?” Grandfather explained, “The vegetables we grow here do not taste like the ones on the Earth. I really wish you had tasted the carrots from the Earth.” Arivu asked eagerly, “How did they grow the crops and vegetables on The Earth?”
காய்கறி தோட்டத்திற்கு வந்த அவர், “நான் குழந்தைப் பருவத்தில் சாப்பிட்டது போல, இந்த கேரட்கள் சுவையாக இல்லை” என்றார். “ஏன் அப்படிச் சொல்கிறீர்கள்,” என்று கேட்டாள் அவள். “இங்கு நாம் வளர்க்கும் காய்கறிகள், பூமியில் பூமியில் இருந்தது போல சுவையாக இல்லை. பூமியில் விளைந்த கேரட்களை நீ சாப்பிட்டுப் பார்த்திருக்க வேண்டும் என விரும்பினேன்,” என்றார் அவர். “பூமியில் பயிர்களையும், காய்கறிகளையும் அவர்கள் எவ்வாறு வளர்த்தார்கள்?”, என அறிவு ஆர்வத்துடன் கேட்டாள்.
Now, the grandfather was sad, like he is missing the Earth. He said, “The Earth had fertile soil, so the fruits and vegetables grown were healthy and tasty.” She asked, “But, I learnt that humans used chemical fertilizers, and polluted the soil. Here, we get unpolluted food and water. Is that correct?”
பூமியில் தான் வாழ முடியாததற்கு தாத்தா இப்போது வருத்தப்பட்டார். “பூமியில் வளமான மண் இருந்தது. ஆகவே அதில் விளைந்த பழங்களும், காய்கறிகளும் சுவையாகவும், ஆரோக்யம் தருவதாகவும் இருந்தன ,” என்றார் அவர். “ஆனால், மனிதர்கள் இரசாயன உரங்களைப் பயன்படுத்தி நிலத்தை மாசுபடுத்தியதாக நான் அறிந்தேன். இங்கே மாசுபடாத உணவும் தண்ணீ ரும் நமக்கு கிடைக்கிறது. சரிதானே?”, என்றாள் அறிவுமதி.
Grandfather laughed, “Already, I told you. These fruits, vegetables, and water are not the same as in the Earth. They are not real.” Arivu exclaimed, “Even the water?” He said “Of course! In Mars, we get water from burning fuels. On the Earth, we used to get water from rain, it was natural, and it was free!” She said “Grandpa, enough of your stories about the Earth. I know that life there was easy but, here survival is very difficult.” He replied, “Yes my dear, adapting to Mars is difficult. Today, we are fighting for things which we got easily.”
![]()
தாத்தா சிரித்தபடி, “ஏற்கனவே நான் உனக்குச் சொன்னேன், இந்த பழங்கள், காய்கறிகள் மற்றும் நீர் ஆகியன பூமியில் இருந்தது போல இல்லை. இவை இயற்கையானதல்ல, என்றார். அறிவு வியந்தபடி, “தண்ணீ ர் கூடவா?”, என்று கேட்டாள். அவர் சொன்னார், “ஆம்! செவ்வாயில் எரிபொருள்களை எரிப்பதால் நமக்கு தண்ணீர் கிடைக்கிறது. பூமியிலோ, இயற்கையாகப் பெய்யும் மழையால் நாம் நீர் பெற்றோம், அதுவும் இலவசமாக. “தாத்தா, பூமியைப் பற்றிய உங்கள் கதைகள் போதும். அங்கு வாழ்க்கை எளிதாக இருந்ததென எனக்குத் தெரியும். ஆனால் இங்கு வாழ்வது மிகவும் சிரமம்,” என்றாள் அவள். “ஆம், என் செல்லம்! செவ்வாய் கோளுக்கு ஏற்றபடி நாம் மாறுவது சிரமம்தான். முன்பு சுலபமாக நமக்கு கிடைத்தவைகளுக்கொல்லாம் இப்போது நாம் சண்டையிட்டுக் கொண்டிருக்கிறோம்,” என்று அவர் பதிலளித்தார்.
He continued, “In the Earth, you did not need a spacesuit or an oxygen cylinder. Also, the years are longer here.” Arivu said, “Yes, grandpa. In Mars, 687 days make a year.” He smiled, “Ha! Ha! Yes, you would be 18 years old on the Earth now.”
“விண்வெளி ஆடையோ, ஆக்ஸிஜன் சிலிண்டரோ பூமியில் உனக்கு தேவைப்படாது. என்று தாத்தா கூறினார். “ஆம், தாத்தா, செவ்வாயில் ஓர் ஆண்டுக்கு 687 நாட்கள்,” 18என்றாள் அறிவு. தாத்தா புன்னகைத்தபடி, “ஆம், பூமியில் உன் வயது இப்போது 18 ஆக இருந்திருக்கும்,” என்றார்.
Grandpa thought to himself, “We destroyed our home. The home that nature had offered us. Now, we are trying to make this our home.”
தாத்தா தன் மனதிற்குள் நினைத்துக் கொண்டார், “நாம் நமது வீட்டை அழித்து விட்டோம். அது இயற்கை நமக்கு அளித்த வீடு. இப்போது, இதனை நமது வீடாக மாற்ற முயற்சிக்கிறோம்.
Arivu looked at him and said, “Don’t, worry grandpa, the scientists are “trying to Terraform the Mars.” He said, “True, but nothing can be the Earth. Earth is our home. Ah, let us leave this for now. Today we should celebrate.”
நாம் வாழ்வதற்கு வசதியாக இருக்கும்படி விஞ்ஞானிகள் – மாற்ற முயற்சி செய்து கொண்டிருக்கிறார்கள்,” என்றாள். விட்டுவிடுவோம். இன்று நாம் கொண்டாட வேண்டும்,” என்றார் அவர்.
Earth, The Desolated Home Space Glossary
Adapting – Modify, readjust (வாழ்வதற்கு ஏற்றவாறு தன்னை மாற்றிக் கொள்ளுதல்)
Capsule – A small cylinder-shaped bed (உருளை வடிவ படுக்கை )
Celebrate – Rejoice (கொண்டாடு)
Crops – cultivated plants (பயிர்கள்)
Destroyed – Ruined, spoiled (அழித்த ல்)
Eagerly – Excitedly (ஆர்வத்துடன்)
Established – Set up (அமைத்தல்)
Exclaimed – Cry out suddenly with surprise (வியப்புடன் சத்தமிடுதல்)
Fertile – Productive (செழிப்பான / வளமான)
Fuels – An energy source for engines, power plants, or reactors (எரிபொருட்கள்)
Grow – Develop, rise (வளர்த்த ல்)
Hab – Habitat, human settlement (தங்குமிடம்)
Harvest – Reap (அறுவடை)
Last – Continue (நீடித்தல் / தொடருதல்)
Offered – Provided (வழங்குதல்)
Polluted – Contaminated (மாசுபடுத்துதல்)
Sad – Unhappy (வருத்தம்)
Scientist – An expert in science (விஞ்ஞானி)
Sighed – To exhale audibly in a long deep breath, as in weariness or relief (பெருமூச்சு விடுதல்)
Soil – Land (மண் / நிலம்)
Sol – Martian solar Day, A Martian day (செவ்வாய் கோளில் ஒரு நாள் ஒரு நாள்)
Started – Began (ஆரம்பித்தல்)
Storm – Tempest (புயல்)
Surprised – Amazed (வியப்படைதல்)
Survival – To remain alive (உயிர் வாழ்வது)
Terraform – A process by which the surface and climate would be changed to make the environment suitable to humans
(வாழ்வதற்கு ஏற்றபடி மாற்றியமைக்கும் முறை)
Travelled – To go from place to place (பயணித்த ல்)
Unpolluted – Clean (மாசுபடாத, சுத்தமான)