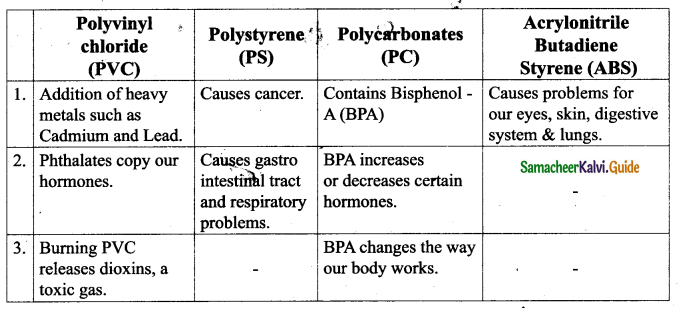
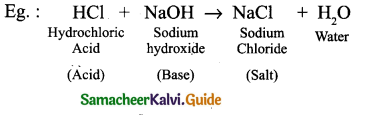
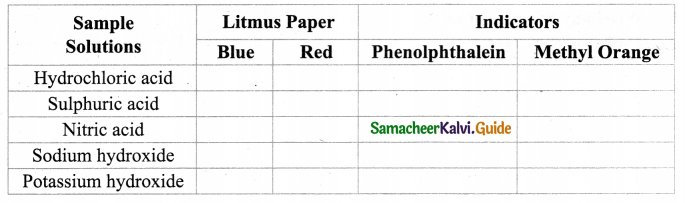
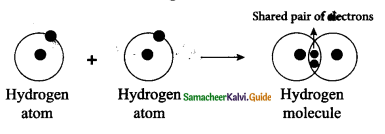
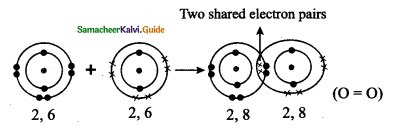
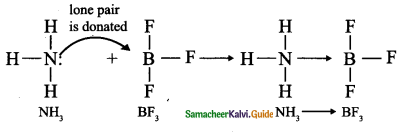
Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Guide Pdf Chapter 16 Applied Chemistry Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Solutions Chapter 16 Applied Chemistry
9th Science Guide Applied Chemistry Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer :
Question 1
One Nanometre is
(a) 107metre
(b) 10-8 metre
(c) 10-6 metre
(d) 10-9metre
Answer:
(d) 10-9 metre
Hint: 1 nanometre is also called one billionth of a metre
![]()
Question 2.
The antibiotic Penicillin is obtained from……………….
(a) plant
(b) microorganism ,
(c) animal
(d) sunlight
Answer:
(b) microorganism
Question 3.
1% solution of Iodoform is used as
(a) antipyretic
(b) antimalarial
(c) antiseptic
(d) antacid
Answer:
(c) antiseptic
Question 4.
The cathode of an electrochemical reaction involves ………………….
(a) oxidation
(b) reduction
(c) neutralisation
(d) catenation
Answer:
(b) reduction
Hint : It involves gain of electrons
![]()
Question 5.
The age of a dead animal can be determined by using an isotope of …………………
(a) carbon
(b) iodine
(c) phosphorous
(d) oxygen
Answer:
(a) carbon
Hint : C614 isotope is used
Question 6.
Which of the following does not contain natural dyes?
(a) Potato
(b) Beetroot.
(c) Carrot
(d) Turmeric
Answer:
(a) Potato
![]()
Question 7.
This type of food protect us from deficiency diseases.
(a) Carbohydrates
(b) Vitamins
(c) Proteins
(d) Fats
Answer:
(b) vitamins
Question 8.
Radiochemistry deals with
(a) oxidants
(b) batteries
(c) isotopes
(d) nanoparticles
Answer:
(e) isotopes
![]()
Question 9.
The groups responsible for the colour of an organic compound is called
(a) isotopes
(b) auxochrome
(e) chromogen
(d) chromophore
Answer:
(d) chromophore
Question 10.
Chlorinated hydrocarbons are used as
(a) fertilizers ,
(b) pesticides
(c) food colourants
(d) preservatives
Answer:
b) pesticides
![]()
II. Fill In the blanks:
1. ………….. is an electrochemical cell which converts electrical energy into chemical change
(Reaction).
Answer:
Electrolytic cell
2. Painkiller drugs are called ………………..
Answer:
Analgesics
3. Indigo is a …………… dye.
Answer:
Vat
4. ……………and……………..are macronutrients required for plant growth.
Answer:
Nitrogen, Phosphorous, and Potassium
![]()
5. _____ is a chemical used in fingerprint analysis.
Answer:
Ninhydrin
III. Match the following:
Question1.
| Column I | Column II |
| Antipyretics | Large surface area |
| Corrosion prevention | Iodine – 131 |
| Hyperthyroidism | Fever |
| Nanoparticle | Bodybuilding |
| Proteins | Electroplating |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| Antipyretics | Fever |
| Corrosion prevention | Electroplating |
| Hyperthyroidism | Iodine – 131 |
| Nanoparticle | Large surface area |
| Proteins | Bodybuilding |
IV. Answer briefly :
Question 1.
What is Radio Carbon Dating?
Answer:
Radiocarbon dating is a method by which the age of fossil wood or animal is determined using the C-14 isotope.
Question 2.
What are called Anaesthetics? How are they classified?
Answer:
The drugs which cause loss of sensation are called Anaesthetics.
Types of Anaesthetics
General anesthetics: They are the agents, which bring about loss of all modalities of sensation, particularly pain along with ‘reversible’ loss of consciousness.
Local anesthetics: They prevent the pain sensation in localised areas without affecting the degree of consciousness.
![]()
Question 3.
What is the need for chemical fertilizers in crop fields?
Answer:
The need for chemical fertilizers In crop fields is to supply essential micro and macronutrients required for crop growth.
Question 4.
What is Forensic chemistry related to?
Answer:
Forensic chemistry applies scientific principles, techniques, and methods to the investigation of crime.
![]()
V. Answer in detail :
Question 1.
Explain the types of dyes based on their method of application.
Answer:
Dyes are classified in two ways, one, based on the method of application and others on their parent structure.
Based on the method of application:
- Acid dyes: These are acidic in nature and used for dyeing animal fibres and synthetic fibres. These can be used for protein fibre such as wool and silk. E.g. Picric acid, Naphthol yellow-s
- Basic dyes: These are basic dyes containing basic group (- NH2,- NHR, – NR2). They are used for dyeing animal fibres and plant fibres.
- Mordant dyes or Indirect dyes: These dyes have a poor affinity for cotton fabrics and hence do not dye directly. They require pretreatment of the fibre with a mordant. Mordant (latin: mordere = to bite) is a substance which can be fixed to the fibre and then can be combined with the dye to form an insoluble complex called lake. Aluminium, chromium, and iron salts are widely used as mordants. E.g. alizarin.
- Direct dyes: They have high affinity for cotton, rayon and other cellulose fibre. So they are applied directly as they fix firmly on the fabric. E.g. Congo red
- Vat dyes: It can be used only on cotton and, not on silk and wool. This dyeing is a continuous process and is carried out in a large vessel called vat. So it is called as vat dye. E.g. Indigo
Question 2.
Name various food additives and explain their functions.
Answer:
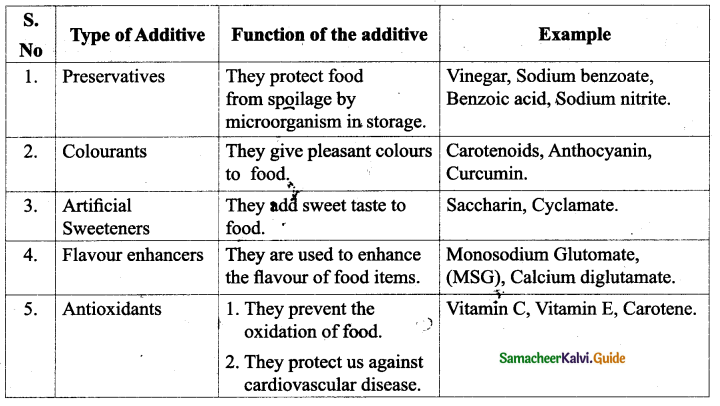
VI. Higher Order Thinking Skills :
Question 1.
Batteries that are used in mobile phone can be recharged. Likewise, can you recharge the batteries used in watches? justify your answer.
Answer:
The type of batteries used in watches is Primary cell. (Mercury-Oxide battery)
The type of batteries are used in mobile phone is Secondary cell. (Lithium -ion polymer battery)
The differences between primary and secondary cell are as follow:
| Primary Cell | Secondary cell |
| 1. The chemical reaction of primary cell is irreversible. | The chemical reaction is reversible. |
| 2. Hence it can not be recharged. | Hence it can be recharged. |
Question 2.
Sudha met with a fire accident. What kind of drug(s), she must take?
Answer:
Analgesics are to be administered to reduce the pain followed by antibiotics to prevent infection by microbes.
![]()
Question 3.
The soil pH of cropland is 5. What kind of fertilizers should be used in that land?
Answer:
- pH of 5 indicates the soil is Acidic.
- So alkaline fertilizers should be used.
(e.g.,) Potash fertilizers, Nitrogen fertilizers.
Intext Activities
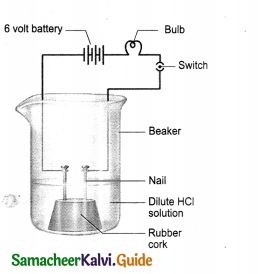
ACTIVITY – 1
With the help of your teacher, construct the galvanic cell using lemon and potato. Identify their anode, cathode and electrolyte.
Aim: To construct a galvanic cell using lemon (or) potato
Materials required :
- A large fresh juicy lemon,
- Zinc coated nail,
- Small copper coin,
- LED light,
- Connecting wires
Procedure :
- Insert the copper coin into the lemon.
- Push a zinc-coated nail into the other side of the lemon.
- The copper coin and zinc-coated nail are connected to a low voltage LED bulb.
- Now observe the results, (happenings).
Observation:
- Copper coin acts as the cathode, zinc-coated nail acts as Anode. Lemon juice acts as an electrolyte.
- We observe glow of LED light, which confirms the electricity to flow through the lemon.
Conclusion: Galvanic cell usifi^lpmon is constructed.
![]()
9th Science Guide Applied Chemistry Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
Nanoparticles are unstable when they come in contact with ………………..
(a) air
(b) Hydrogen
(c) Oxygen
(d) all the above
Answer:
(c) Oxygen
Question 2.
Which is the incorrect statement in the following?
(a) The structure of nano material is in between an atom and bulk material.
(b) Nanomaterials exist in the corresponding bulk materials.
(c) Nanomaterials have the extremely large surface area to volume ratio.
(d) SEM is used analyse the surface properties of a nanoparticle with high resolution.
Answer:
(b) Nanomaterials exist in the corresponding bulk materials
![]()
Question 3.
Which anesthetic forms a toxic carbonyl chloride?
(a) Nitrous oxide
(b) Ether
(c) Chloroform
(d) Iodoform
Answer:
(c) Chloroform
Question 4.
Paracetamol is a …………….
(a) Analgesic
(b) Antiseptic
(c) Antimalarial
(d) Antipyretic
Answer:
(c) Antipyretic
Question 5.
The antiseptic used for cleansing the wounds is ………………..
(a) Phenol
(b) Iodoform
(C) Ether
(d) Hydrogen peroxide
Answer:
(d) Hydrogen peroxide
![]()
Question 6.
Antimalarial drug obtained from Cinchona bark is ……………………
(a) Quinine
(b) Morphine.
(e) Primaquine
(d) Pyrimethamine
Answer:
(a) Quinine
Question 7.
The drug that ¡s known as “Miracle drug” is ………………….
(a) Chloroquinine
(b) Penicillin
(C) Aspirin. .
(d) Paràcetamol
Answer:
(b) Penicillin
![]()
Question 8.
In Daniel cell, saturated solution of potassium chloride (KCl) acts as ……………..
(a) Anode
(b) Cathode
(c) Salt bridge
(d) Electrolyte
Answer:
(c) Salt bridge
Question 9.
The process of purifying metals by electrolysis ¡s known as ……………..
(a) Electroplating
(b) Electrorefining
(e) Electromanufacturing
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Electrorefining
Question 10.
Which one among the following statements is correct?
(a) Galvanic cell converts electrical energy into chemical energy.
(b) Reduction takes place at the anode.
(c) Oxidation reaction takes place at the cathode.
(d) None of these
Answer:
(d) None of these
![]()
Question 11.
Isotopes are atoms with different number of ………………………
(a) protons
(b) neutrons
(c) electrons
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) neutrons
Question 12.
The radioisotope used for location of blood clot and circulation disorders is …………………..
(a) Na – 24
(b) I – 131
(c) Fe – 59
(d) Co – 60
Answer:
(a) Na – 24
![]()
Question 13.
The dye that can only be used on cotton is …………………….
(a) Mordant dye
(b) Vat dye
(c) Direct dye
(d) Basic dye
Answer:
(b) Vat dye
Question 14.
Which one of the following is a flavour enhancer?
(a) Sodium nitrite
(b) Sodium benzoate
(c) Cyclamate
(d) Monosodium Glutamate
Answer:
(d) Monosodium Glutamate
Question 15.
The compound that gets redUced ¡n the alcohol test is ……………………
(a) Silver nitrate
(b) Sulphuric acid
(C) Water
(d) Potassium dichromate
Answer:
(d) Potassium dichromate
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks:
1. Nanotechnology deals with materials which are smaller than …………………..
Answer:
100 nanometres
2. The metallic nanoparticles can be used as ………………….
Answer:
Very active catalysts
3. Nanoparticle substances are incorporated in fabrics to prevent …………………..
Answer:
the growth of bacteria
![]()
4. The word “drug” is derived from the French word “droque” which means a ………………..
Answer:
dry herb
5. …………… is the safest of the anesthetic drugs.
Answer:
Nitrus oxide
6. The Analgesics are also called as …………………
Answer:
Pain killer (or) Pain relievers
![]()
7. ………………. produce sleep and unconsciousness.
Answer:
Narcotics
8. Antiseptics are used internally to treat infections of the …………… and ……………..
Answer:
Intestine, Bladder
9. Malaria is a ……………… borne disease.
Answer:
vector
10. ………………. is used as an additive with other antimalarial drugs.
Answer:
Chloroquine
![]()
11. ……………. is extensively used for rheumatic fever, narrowing of the heart wall, bronchitis, and pneumonia.
Answer:
Penicillin
12. …………… is due to an imbalance in the acidity in the stomach.
Answer:
Burning sensation
13. The solution having ions is called ………………..
Answer:
Electrolyte
14. …………….. is the loss of electrons.
Answer:
Oxidation
![]()
15. The process of depositing a thin layer of one metal over another metal by the process of electrolysis is called …………………….
Answer:
Electroplating
16. When metals of a very high degree of purity are required,………………… is done.
Answer:
Electrorefining
17. The isotope used in Radiocarbon dating is …………………..
Answer:
C-14
![]()
18. The chromophore and auxochrome theory was proposed by ……………………
Answer:
Otto Witt
19. ……………… is one of the main criteria to be considered for the selection of crop (or) remediation of soil.
Answer:
Soil pH
20. Vitamin C is also powerful ……………….. that prevents food from oxidising.
Answer:
Antioxidant
21. ……………. is one of the most important evidence in crime investigation.
Answer:
Fingerprint
![]()
III. Match the following:
Question 1.
| Name of the Drug | Purpose | Example |
| 1. Antipyretics | Kills the microorganism | Chloroform |
| 2. Anaesthetics | Pain reliever | Novalgin |
| 3. Antiseptics | Reduction of fever | paracetamol |
| 4. Analgesics | Cure for malaria | Quinine |
| 5. Antimalarial | Loss of sensation | Hydrogen peroxide |
Answer:
| Name of the Drug | purpose | Example |
| 1. Antipyretics | Reduction of fever | paracetamol |
| 2. Anaesthetics | Loss of sensation | Chloroform |
| 3. Antiseptics | Kills the microorganism | Hydrogen peroxide |
| 4. Analgesics | Pain reliever | Novalgin |
| 5. Antimalarial | Cure for malaria | Quinine |
Question 2.
| Column I | Column II |
| Cathodic electrolyte | Potassium chlorate (KClO3) |
| Anodic electrolyte | Potassium chloride (KCl) |
| Salt bridge | sulphate CuSO4 |
| Electro manufacturing | Zinc sulphate(ZnSO4) |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| Cathodic electrolyte | Copper sulphate CuSO4 |
| Anodic electrolyte | Zinc sulphate(ZnSO4) |
| Salt bridge | Potassium chloride (KCl) |
| Electro manufacturing | Potassium chlorate (KClO3) |
![]()
Question 3.
| Column I | Column II |
| Phosphorous-30 | Cancer |
| Iodine-131 | Pregnancy disorder |
| Cobalt-60 | Hyperthyroidism |
| Iron-59 | Blood disorder |
| Sodium-24 | Circulation disorder |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| Phosphorous-30 | Blood disorder |
| Iodine-131 | Hyperthyroidism |
| Cobalt-60 | Cancer |
| Iron-59 | Pregnancy disorder |
| Sodium-24 | Circulation disorder |
Question 4.
| Column I | Column II |
| Indirect dyes | Congo red |
| Direct dyes | Alizarin |
| Vat dyes | Methylene blue |
| Basic dyes | Picric acid |
| Acid dyes | Indigo |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| Indirect dyes | Alizarin |
| Direct dyes | Congo red |
| Vat dyes | Indigo |
| Basic dyes | Methylene blue |
| Acid dyes | Picric acid |
![]()
IV. State whether true or false. If false, correct the statement:
1. Nanoparticles are easy to synthesis, isolate, and apply.
Answer:
False,
Correct statement: Nanoparticles are difficult to synthesis, isolate, and apply.
2. When cancer occurs, cells are reproduced in a controlled manner.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: When cancer occurs, cells are reproduced in an uncontrolled manner.
3. General anaesthetics cause pain along with ‘reversible’ loss of consciousness
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: General anaesthetics relieve pain along with reversible loss of consciousness.
![]()
4. Malaria decreases body temperature.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Malaria increases the body temperature
5. High concentration of antibiotics is needed for Effective action.
Answer:
False. .
Correct statement: Low concentration of antibiotics is needed for effective action.
6. Antacids provide relief from burning sensation in the stomach.
Answer:
True,
![]()
7. In Daniel’s cell, Zinc metal acts as the cathode, and Copper metal acts as Anode.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: In Daniel’s cell, Zinc metal acts as Anode, and Copper metal acts as Cathode.
8. Radioisotopes can be easily detected and estimated quantitatively.
Answer:
True.
9. Dyes are aromatic compounds originated from plants and insects.
Answer:
True.
![]()
10. Dye should be fast to light.
Answer:
True.
11. Vinegar is used as an antioxidant.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Vinegar is used as a preservative.
12. Reduction of alcohol results in oxidation of dichromate to chromic ion.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Oxidation of alcohol results in a reduction of dichromate to chromic ion
![]()
V. Assertion and Reason type:
Mark the correct choice as:
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : Nanoparticles interact with impurities.
Reason (R) : Nanoparticles are less reactive.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is true but the reason is false
Reason (R) : Nanoparticles are highly reactive.
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : Antiseptic is a substance that prevents infections caused by disease-causing pathogens.
Reason (R) : Antiseptics either kill the microorganism or prevent their growth.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
![]()
Question 3.
Assertion (A) : After eating fruits (or) vegetables, one may feel uncomfortable due to a burning sensation.
Reason (R) : Burning sensation is due to an imbalance in the acidity of the stomach.
Answer:
(d) Assertion is false but the reason is true
Assertion (A) : After eating oily and spicy foods, one may feel uncomfortable due to a burning sensation.
Question 4.
Assertion (A) : Metals like iron are electroplated with chromium.
Reason (R) : Electroplating is done to protect chromium from rusting.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false
Reason (R) : Electroplating is done to protect iron from rusting.
Question 5.
Assertion (A) : It is possible to detect alcohol drunken drivers.
Detection is done through the electrochemical redox reaction of alcohol.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
![]()
Question 6.
Assertion (A) : Our retinal print can be forged.
Reason (R) : Our retinal print is unique.
Answer:
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true
Assertion ( A) : Our retinal print cannot be forged.
VI. Very short answer type :
Question 1.
What are the specific qualities of nanoparticles?
Answer:
- Larger surface area
- High surface energy.
- Spatial confinement
- Reduced imperfections.
Question 2.
List out the instruments used to analyse nanoparticles.
Answer:
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- Tunneling Electron Microscope (TEM).
- Atomic Force Microscope (AFM).
![]()
Question 3.
What is antipyretics?
Answer:
Antipyretics are the compounds used to reduce fever, (i.e.) lowering the body temperature to normal.
Question 4.
How are antiseptics used?
Answer:
External use: To cleanse wounds.
Internal use: To treat infections of the intestine and bladder.
Question 5.
Mention the uses of Penicillin.
Answer:
Penicillin is used for
- Rheumatic fever,
- Narrowing of the heart wall.
- Bronchitis,
- Pneumonia.
![]()
Question 6.
What are the main sources of Antibiotics?
Answer:
Main sources of Antibiotics are
- Bacteria
- Fungi and
- Actinomycetes.
Question 7.
Name any five natural antibiotics.
Answer:
- Honey
- Garlic
- Ginger
- Neem
- Turmeric.
Question 8.
What is an Electrochemical cell?
Answer:
A device that makes use of a chemical change to produce electricity (or) electricity to produce chemical change is called an Electrochemical cell.
![]()
Question 9.
What is a Daniel cell?
Answer:
Daniel cell is a type of galvanic cell in which zinc metal acts as anode and copper metal as cathode.
Question 10.
What is radioactive decay?
Answer:
- The unstable isotopes of elements lose their energy in the form of radiation to become stable.
- This phenomenon is called radioactive decay.
Question 11.
What is Vermicompost?
Answer:
Vermicompost is one of the natural fertilizers produced from domestic wastes.
![]()
Question 12.
What is a balanced diet?
Answer:
A diet that contains all the three foods such as (i) Bodybuilding foods, (ii) Energy giving foods, and (iii) Protective foods in the right proportion are called a Balanced diet.
Question 13.
Mention the use of a Biometric system.
Answer:
The biometric system compares the body prints to the specimen data stored in the system to verify the identity of a person.
VII. Answer briefly :
Question 1.
What is called as Applied Chemistry?
Answer:
Application of chemical principles and theories to various fields in order to achieve specific results or to solve real-world problems is called applied chemistry.
![]()
Question 2.
Write short notes on nanochemistry.
Answer:
- Nanochemistry is a branch of nanoscience, that deals with the chemical applications of nanomaterials in nanotechnology.
- It involves the synthesis and manipulation of materials at the atomic and molecular level.
Question 3.
Mention medical applications of Nanorobotics.
Answer:
- Nanorobotics is used in medicine and space technology.
- It plays important role in Bio-medicine in the treatment of cancer.
Question 4.
Define Drug.
Answer:
According to the World Health Organisation (WHO),
Drug is a substance or product that is used or intended to be used to modify or explore physiological systems or pathological states for the benefits of the recipient.
![]()
Question 5.
What is an Analgesics? How is it useful?
Answer:
- Analgesics are compounds which relieve all sorts of pains without the loss of consciousness.
- It is useful to treat
(a) Headaches
(b) Myalgia and
(c) arthralgia.
Question 6.
What is known is Antibiotics?
Answer:
Many microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, and molds) produce certain chemicals which inhibit the growth (or) metabolism of some other disease-causing microorganism. Such chemical compounds are known as Antibiotics.
Question 7.
Write brief notes on processes involved in cell reactions.
Answer:
An electrochemical cell involves two reactions simultaneously.
- Oxidation : Oxidation is the loss of electrons, that takes place at the anode.
Metal → Metal ion + electron(s) - Reduction: Reduction is the gain of electrons, that takes place at the cathode.
Metal ion + electron(s) → Metal.
![]()
Question 8.
How does a galvanic cell produce electricity?
Answer:
- At the anode, oxidation takes place which releases electrons.
- These electrons are attracted by the cathode.
- Thus electrons flowing from anode to cathode produce electricity.
Question 9.
Mention the applications of electroplating with an example.
Answer:
Applications of Electroplating :
- Electroplating is done to protect the metal from corrosion, (e.g) chrome -plating.
- Electroplating is done to beautify the surface of a metal, (e.g) Gold plating.
- Broken parts of machinery require electrodeposition of metal between broken parts.
Question 10.
List out the characteristics of Dye.
Answer:
Characteristics of Dye:
- Dye should have a suitable colour.
- Dye should be able to fix itself.
- Dye should be fast to light,
- Dye should be resistant to the action of water, dilute acids, and alkalies.
![]()
Question 11.
Define Pesticides.
Answer:
According to the World Health Organisation (WHO),
Pesticides are chemical compounds that are used to kill pests including insects, rodents, fungi, and unwanted plants (weeds).
Question 12.
How can Fingerprints be identified?
Answer:
- Fingerprints on smooth surfaces can be identified by the application of light or dark powder.
- Occult (hidden) Fingerprints are made visible by the use of Ninhydrin, which turns purple.
- Fingerprints can be made visible by high powered laser light.
Question 13.
How is alcohol consumption detected?
Answer:
- The person being tested blows through a tube, which bubbles the breath through a solution containing Sulphuric acid, Potassium dichromate, water and silver nitrate.
- Oxidation of alcohol results in the reduction of dichromate to chromatic ions with a change in color from orange to green.
![]()
Question 14.
What is Chemotherapy?
Answer:
Treatment of certain diseases by destroying the invading organism without damaging the cells of the host, by the use of certain organic compounds is known as chemotherapy. It is widely used for treating cancer.
VIII. Answer in detail :
Question 1.
Draw the cell diagram of Daniel cell. Give its reactions.
Answer:
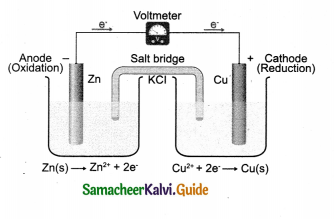
Question 2.
Daniel cell
Answer:
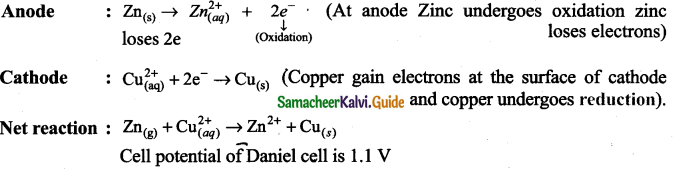
Question 3.
List the applications of Nanochemistry.
Answer:
Applications of Nanochemistry :
- The metallic nanoparticles can be used as very active catalysts.
- Chemical sensors form nanoparticles and nanowires enhance the sensitivity and sensor selectivity.
- Nanocoatings and nanocomposites are found useful in making a variety of products such as sports equipment, bicycles, and automobiles etc.
- Nanotechnology is being applied in the die production of synthetic skin and implant surgery.
- Nanomaterials that conduct electricity are being used in electronics as minute conductors to produce circuits for microchips.
- Nanomaterials are used in the preparation of cosmetics, deodorants, and sunscreen lotion. They are used to improve moisturizers, without making them too oily.
- Nanoparticle substances are incorporated in fabrics to prevent the growth of bacteria.
![]()
Question 4.
Mention the drawbacks of Nanomaterials in chemistry.
Answer:
Drawbacks of nanomaterials in chemistry :
- Nanoparticles are unstable when reacting with oxygen.
- Their exothermic combustion with oxygen can easily cause an explosion.
- Because nanoparticles are highly reactive, they inherently interact with impurities as well.
- Nanomaterials are usually considered biologically harmful and toxic.
- It is difficult to synthesis, isolate and apply them.
- There are no hard-and-fast safe disposal policies for nanomaterials.
Question 5.
Account the role of Radioactive isotopes in Diagnosis and treatment in the Medical field?
Answer:
Radioisotopes are very useful to diagnose and treat many diseases. . Some of them are given below:
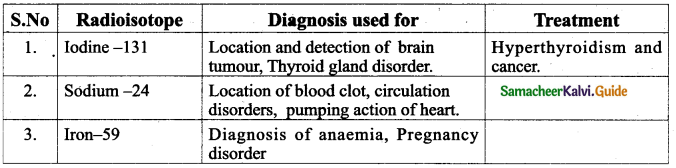
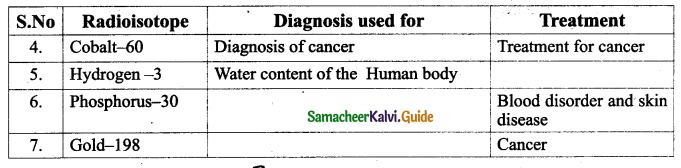
Question 6.
Give a comparative account of various drugs with their application and examples.
Answer:
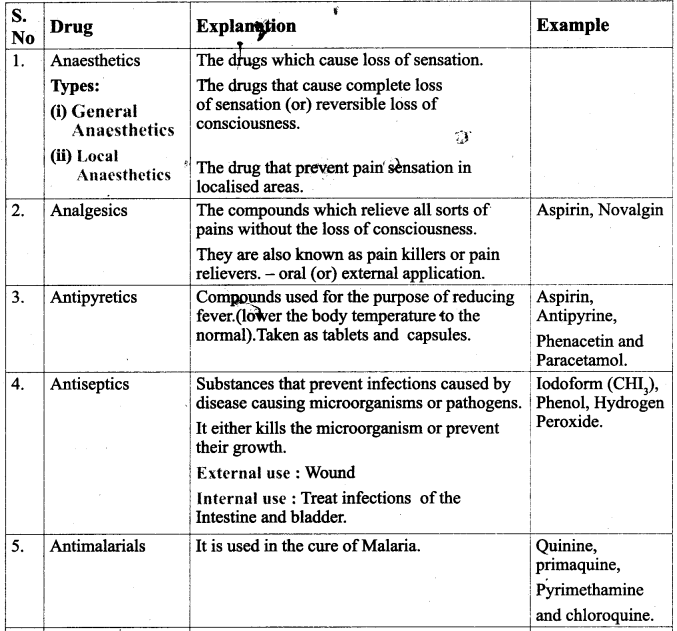

![]()
Question 7.
What are the applications of electrochemistry?
Answer:
Applications of electrochemistry :
- It has been used to discover important technical processes for the production and purification of non-ferrous metals, and for the electro- synthesis of organic compounds.
- Electrochemistry has been used to predict whether a particular reaction will occur or not.
- The detection of alcohol in drunken drivers is possible through the electrochemical redox reaction of ethanol.
- Production of metals like aluminum and titanium from their ores involves electrochemical reactions.
- Diabetes blood sugar meters measure the amount of glucose in the blood through its redox potential.
- Lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries, and fuel cells are based on electrochemical cells.
- A fuel cell is used to bring about the direct conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy.
Question 8.
Explain very briefly about various fields of Applied Chemistry.
Answer:
Various Fields of Applied Chemistry:
- Nanochemistry: It is a branch of nanoscience that deals with the chemical applications of nanomaterials in nanotechnology.
- Nanometre = 1/1,000,000,000 metre.
- Pharmaceutical chemistry: It deals with the preparation of drugs and the study of the chemical composition, nature, behaviour, structure, and influence of the drug in an organism.
- Electrochemistry: It deals with the relation between electrical energy and chemical change.
- Radiochemistry: It is the study of the chemistry of radioactive and non-radioactive isotopes.
- Dye chemistry: It is the study of dyes.
- Agricultural chemistry: It deals application of chemical and biochemical knowledge to agricultural production, the processing of raw products into foods and beverages, and environmental monitoring and remediation.
- Food chemistry: It involves the analysis, processing, packaging, and utilization of materials.
- Forensic chemistry: It applies scientific principles, techniques, and methods to the investigation of crime.