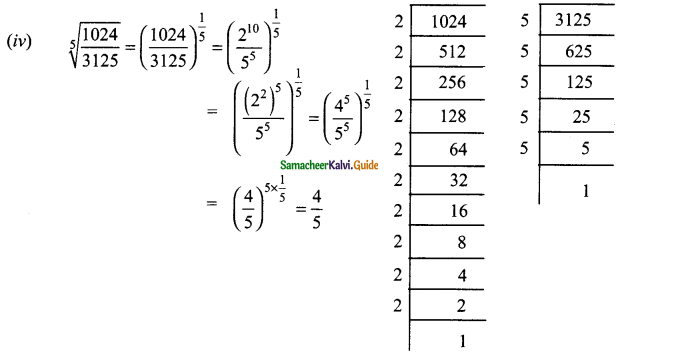
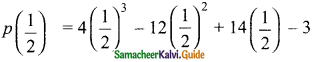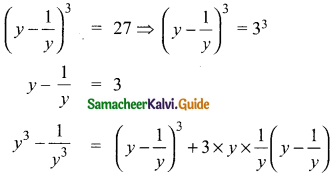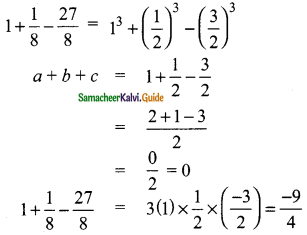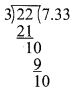Students can download Maths Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.7 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.7
Question 1.
Find the quotient and remainder of the following.
(i) 4x3 + 6x2 – 23x + 18) ÷ (x + 3)
Solution:
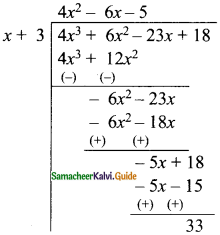
∴ The quotient = 4x2 – 6x – 5
The remainder = 33
(ii) (8y3 – 16y2 + 16y – 15) ÷ (2y – 1)
Solution:
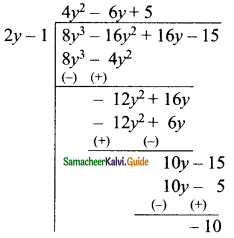
∴ The quotient = 4y2 – 6y + 5
The remainder = -10
![]()
(iii) (8x3 – 1) ÷ (2x – 1)
Solution:
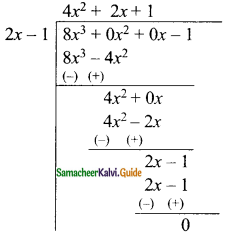
∴ The quotient = 4x2 + 2x + 1
The remainder = 0
(iv) (-18z + 14z2 + 24z3 + 18) ÷ (3z + 4)
Solution:
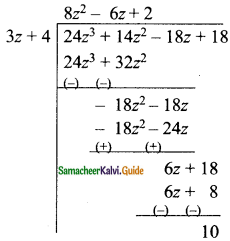
∴The quotient = 8z2 – 6z + 2
The remainder = 10
![]()
Question 2.
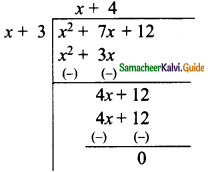
The area of a rectangle is x2 + 7x + 12. If its breadth is (x + 3) then find its length.
Solution:
Let the length of the rectangle be “l”
The breadth of the rectangle = x + 3
Area of the rectangle = length × breadth
x2 + 7x + 12 = l(x + 3)
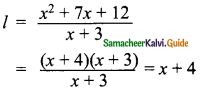
Length of the rectangle = x + 4
![]()
Question 3.
The base of a parallelogram is (5x + 4). Find its height if the area is 25x2 – 16.
Solution:
Let the height of the parallelogram be “h”.
Base of the parallelogram = 5x + 4
Area of a parallelogram = 25x2 – 16
∴ Base x Height = 25x2 – 16
(5x + 4) × h = 25x2– 16
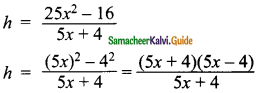
Height of the parallelogram = 5x – 4
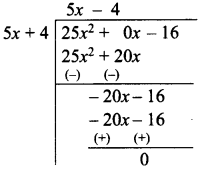
![]()
Question 4.
The sum of (x + 5) observations is (x3 + 125). Find the mean of the observations.
Solution:
Sum of the observation = x3 + 125
Number of observation = x + 5
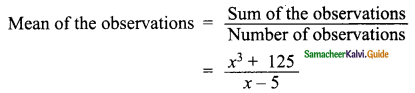
Mean = x2 – 5x + 25
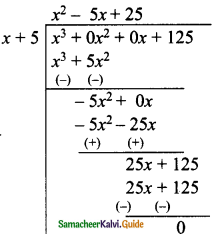
Question 5.
Find the quotient and remainder for the following using synthetic division:
(i) (x3 + x2 – 7x – 3) ÷ (x – 3)
Solution:
p(x) = x3 + x2 – 7x – 3
d(x) = x – 3 [p(x) = d(x) × q(x) + r]
x – 3 = 0
x = 3
Hence the quotient = x2 + 4x + 5
Remainder = 12
![]()
(ii) (x3 + 2x2 – x – 4) ÷ (x + 2)
Solution:
p(x) = x3 + 2x2 -x – 4
d(x) = x + 2
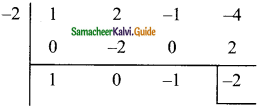
x + 2 = 0
x = -2
The quotient = x2 – 1
Remainder = -2
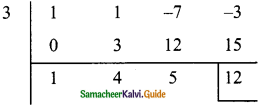
(iii) (3x3 – 2x2 + 7x – 5) ÷ (x + 3)
Solution:
p(x) = 3x3 – 2x2 + 7x – 5
d(x) = x + 3
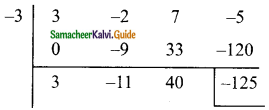
x + 3 = 0
x = -3
The quotient = 3x2 – 11x + 40
Remainder = -125
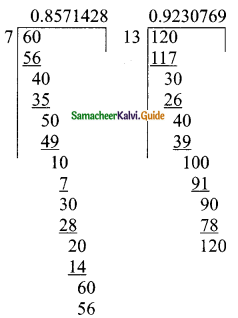
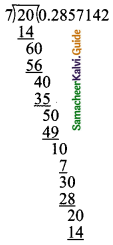
(iv) (8x4 – 2x2 + 6x + 5) ÷ (4x + 1)
Solution:
p(x) = 8x4 – 2x2 + 6x + 5
d(x) = 4x + 1
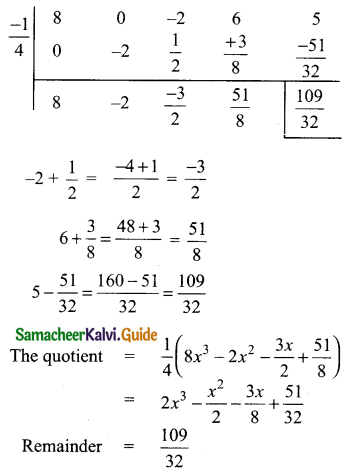
![]()
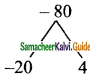
Question 6.
If the quotient obtained on dividing (8x4 – 2x2 + 6x – 7) by (2x + 1) is (4x3 + px2 -qx + 3), then find p, q and also the remainder.
Solution:
p(x) = 8x4 – 2x2 + 6x – 7
d(x) = 2x + 1
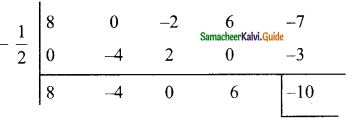
2x + 1 = 0
2x = -1
x = –\(\frac{1}{2}\)
The quotient = \(\frac{1}{2}\) [8x3 – 4x2 + 6]
= 4x3 – 2x2 + 3
= 4x3 – 2x2 + 0x + 3
The given quotient is = 4x3 + px2 – qx + 3
(compared with the given quotient)
The value of p = -2 and q = 0
Remainder = -10
![]()
Question 7.
If the quotient obtained on dividing 3x3 + 11x2 + 34x + 106 by x – 3 is 3x2 + ax + b, then find a, b and also the remainder.
Solution:
p(x) = 3x3 + 11x2 + 34x + 106
d(x) = x – 3
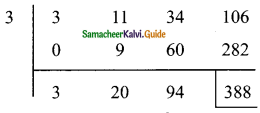
x – 3 = 0
x = 3
The quotient is = 3x2 + 20x + 94
The given quotient is = 3x2 + ax + b
Compared with the given quotient
The value of a = 20 and b = 94
The remainder = 388