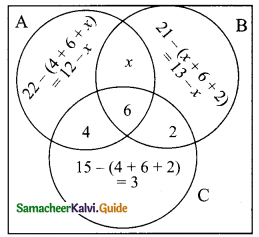
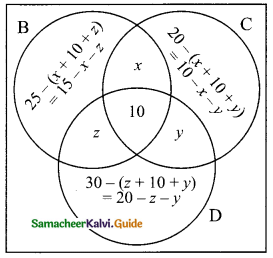
Students can download Maths Chapter 2 Real Numbers Ex 2.4 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Real Numbers Ex 2.4
Question 1.
Represent the following numbers on the number line.
(i) 5.348
Solution:
5.348 lies between 5 and 6.
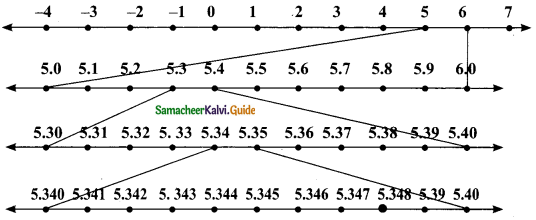
Steps of construction:
1. Divide the distance between 5 and 6 into 10 equal intervals.
2. Mark the point 5.3 which is the sixth from the left of 6 and 3 from the right of 5.
3. 5.34 lies between 5.3 and 5.4. Divide the distance into 10 equal intervals.
4. Mark the point 5.34 which is sixth from the left of 5.40
5. 5.348 lies between 5.34 and 5.35. Divide the distance into 10 equal intervals.
6. Mark a point 5.348 which is second from the left of 5.350 and seventh form the right of 5.340
![]()
(ii) 6.\(\overline {4}\) upto 3 decimal places.
Solution:
6.\(\overline {4}\) = 6.4444
6.\(\overline {4}\) = 6.444 (correct to 3 decimal places)
The number lies between 6 and 7.
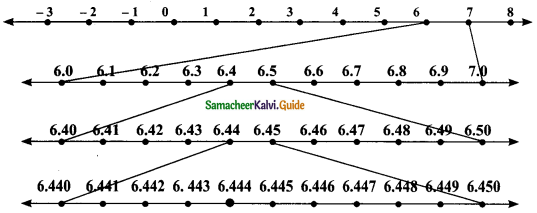
Steps of construction:
1. Divide the distance between 6 and 7 into 10 equal intervals.
2. Mark the point 6.4 which is the sixth from the left of 7 and fourth from the right of 6.
3. 6.44 lies between 6.44 and 6.45. Divide the distance into 10 equal intervals.
4. Mark the point 6.44 which is sixth from the left of 6.5 and fourth from the right of 6.40.
5. Mark the point 6.444 which is sixth from the left of 6.450 and fourth from the right of 6.440.
![]()
(ii) 4.\(\overline {73}\) upto 4 decimal places.
Solution:
4.\(\overline {73}\) = 4.737373……..
= 4.737374 (correct to 4 decimal places 4.7374 lies between 4 and 5)
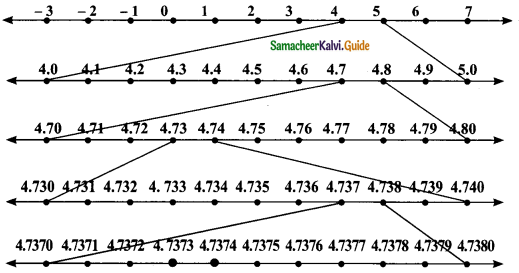
Steps of construction:
1. Divide the distance between 4 and 5 into 10 equal parts.
2. Mark the point 4.7 which is third from the left of 5 and seventh from the right of 4.
3. 4.73 lies between 4.7 and 4.8. Divide the distance into 10 equal intervals.
4. Mark the point 4.73 which is seventh from the left of 4.80 and third from the left of 4.70.
5. 4.737 lies between 4.73 and 4.74. Divide the distance into 10 equal intervals.
6. Mark the point 4.737 which is third from the left of 4.740 and seventh from the right of 4.730.
7. 4.7374 lies between 4.737 and 4.738. Divide the distance into 10 equal intervals.
8. Mark the point 4.7374 which is sixth from the left of 4.7380 and fourth from the right of 4.7370.
![]()